Abstract
In recent years, the global tuna fishing and aquaculture industry has encountered significant challenges in balancing operational efficiency with sustainable resource management. This study introduces an innovative approach utilizing an advanced computer vision model, PA-YOLOv8, specifically adapted for drones, to enhance the monitoring and management of tuna populations. PA-YOLOv8 leverages the capabilities of YOLOv8, a state-of-the-art object detection system known for its precision and speed, tailored to address the unique demands of aerial surveillance in marine environments. Through comprehensive modifications including downsampling techniques, feature fusion enhancements, and the integration of the Global Attention Module (GAM), the model significantly improves the detection accuracy of small and juvenile tuna within complex aquatic landscapes. Experimental results using the Tuna dataset from Roboflow demonstrate marked improvements in detection metrics such as precision, recall, and mean average precision (mAP), affirming the model’s effectiveness. This study underscores the potential of integrating cutting-edge technologies like UAVs and computer vision in promoting sustainable practices in the aquaculture sector, setting a new standard for technological applications in environmental and resource management. The advancements presented here provide a scalable and efficient solution for real-time monitoring, contributing to the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems.
1. Introduction
In the recent years, the global industry engaged in the capture and cultivation of tuna has witnessed a series of transformative shifts that have not only marked significant strides in the modus operandi of its operations but also ushered in an era where it grapples with unprecedented challenges in the realm of sustainable resource stewardship. This period of change is characterized by a burgeoning global demand for seafood products, a surge fueled by both population growth and an increasing awareness of seafood’s nutritional benefits. This demand, in concert with the critical necessity to conserve the biodiversity of our oceans, has catalyzed the industry to embark on a quest for innovative methodologies aimed at bolstering operational efficiency and ensuring environmental sustainability. Within the context of these evolving dynamics, the strategic incorporation of avant-garde technological solutions, most notably computer vision technologies and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), has emerged as a cornerstone initiative poised to revolutionize the practices of monitoring and conservation within this sector. The research proposition titled, our study epitomizes an enthusiastic endeavor to harness the most cutting-edge advancements in computer vision technology. This is with the aim of refining the techniques employed for aerial surveillance, specifically honing in on the optimization of processes related to the monitoring of tuna populations.
The impetus behind the integration of computer vision models, especially those that are endowed with the capabilities inherent in YOLOv8, into the frameworks governing aquaculture operations is deeply rooted in their documented success in achieving high-precision object detection across a myriad of settings. YOLOv8 stands as a near-latest iteration preceding YOLOv9 but distinguishes itself as the more stable version that has seen wide applications in both academic research and real-world scenarios. While YOLOv9 continues to undergo modifications within the “You Only Look Once” series [1,2,3,4], YOLOv8 is a highly effective real-time object detection technology, known for its precise and fast performance. Nevertheless, the application of such sophisticated models to the fisheries and aquaculture industry presents a unique set of challenges. This is particularly true in the context of detecting small-scale entities like tuna within the expansive and complex marine environments that are captured by drone-mounted cameras. It necessitates a process of adaptation and optimization of these models, exemplified by the development of the PA-YOLOv8 model, to navigate the specific hurdles posed by drone-based surveillance of the marine ecosystem.
To surmount these challenges and significantly augment the efficiency of the model within the unique context of the aquaculture industry, a holistic suite of technical enhancements has been carefully curated and implemented. These advancements span the introduction of an innovative downsampling technique designed [5,6,7,8] to preserve pivotal image features, a thorough optimization of the model’s structural backbone and neck to facilitate superior feature processing capabilities, and the recalibration of loss functions [9,10,11] to more accurately reflect the distinctive attributes of images captured by drones. Furthermore, the establishment of branches capable of high-resolution detection enables the precise identification of minuscule objects. Concurrently, the elimination of superfluous prediction layers streamlines the model, tailoring it more effectively to the identification of smaller marine species. The integration of state-of-the-art techniques such as the Global Attention Module (GAM) [12,13,14] and Speed-up Convolution (SPD-Conv) [15,16,17,18] further fortifies the model’s capacity for learning and stabilization, guaranteeing an exceptional performance standard in the detection and analysis of information pertaining to small or distant marine entities.
The deliberate selection of these technological innovations for the PA-YOLOv8 model underscores not only their potency in enhancing the accuracy and speed of object detection but also their versatility in aligning with the overarching objectives of sustainable marine resource management. Through the introduction of these pioneering improvements, the research in question endeavors to forge new frontiers in the application of cutting-edge computer vision technology and drone capabilities to tackle the urgent challenges confronting the tuna fishing and aquaculture sector. This initiative seeks to contribute fundamentally to the conservation of marine ecosystems and the promotion of sustainable practices within the aquaculture industry. It aims to meld technological innovation with environmental stewardship and sustainability in industrial operations, thereby setting a novel precedent for the integration of technology into strategies for environmental and resource management. This study signifies a contribution toward actualizing the full potential of computer vision technology and UAVs [19,20,21] in enhancing the practices of monitoring, managing, and conserving resources in the swiftly evolving domain of aquaculture, thereby establishing a new benchmark for the confluence of technology and strategic environmental and resource management.
2. Research Materials and Methodological Approach
2.1. Justification for Selecting YOLOv8 as the Foundation for the Research on Deploying a Computer Vision Model Suitable for Drones in the Tuna Fishing and Aquaculture Industry
In the domain of real-time object detection, the YOLO (You Only Look Once) algorithm stands as a paradigm of innovation and efficiency, having garnered widespread acclaim and acceptance for its pioneering capabilities. The algorithm’s popularity is rooted in its lightweight network architecture, efficacious feature fusion methodologies, and notably more accurate detection outcomes. Among its iterations, YOLOv5 and YOLOv7 have become standout versions, utilizing deep learning to enable efficient and real-time object detection. Notably, YOLOv5 marked a significant advancement over earlier versions. YOLOv5, in particular, represented a leap forward from its predecessor, YOLOv4, by adopting the Cross Stage Partial (CSP) network structure, which enhanced computational efficiency by minimizing redundant calculations. Despite its advancements, YOLOv5 encountered limitations in detecting small and densely clustered objects and faced challenges in complex scenarios such as occlusions and pose changes.
YOLOv7 introduced a novel training strategy, the Trainable Bag of Freebies (TBoF), which encompassed a series of trainable enhancements like data augmentation and MixUp, significantly boosting the accuracy and generalization capability of object detectors. However, it was constrained by its dependency on training data, model structure, and hyperparameters, leading to performance inconsistencies in certain conditions. Moreover, its demand for increased computational resources and extended training periods to attain optimal performance was a notable drawback.
Enter YOLOv8, unveiled in 2023, which aspired to amalgamate the strengths of numerous real-time object detectors. It preserved the CSP concept from YOLOv5 and integrated feature fusion techniques (PAN FPN) and the SPPF module, culminating in a suite of enhancements. These included the introduction of state-of-the-art models for various resolutions of object detection and instance segmentation, models scalable based on a coefficient similar to that in YOLOv5, and a novel C2f module inspired by the ELAN structure found in YOLOv7. Furthermore, YOLOv8 innovated on the detection head by segregating classification and detection functions, employed Binary Cross-Entropy (BCE) for classification loss, and introduced a sophisticated form of regression loss (CIOU loss + DFL and VFL) to enhance detection accuracy.
YOLOv8 builds on the achievements of its predecessors, incorporating new attributes and enhancements to boost both performance and adaptability, delivering leading-edge results and impressive speeds. This version introduces five different model sizes: nano, small, medium, large, and very large. The nano model, which has just 3.2 million parameters, is ideally suited for mobile device deployment using only CPU resources. For the purpose of UAV detection, this study utilizes the YOLOv8s model, which enhances and expands the nano model’s architecture. YOLOv8 is structured into three primary components: the backbone, neck, and head, which are responsible for feature extraction, the fusion of multiple features, and generating the prediction output, respectively. The architecture of the YOLOv8 network is depicted in Figure 1.
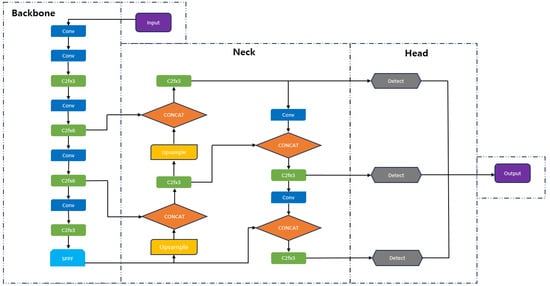
Figure 1.
Structure diagram of YOLOv8.
A pivotal feature of YOLOv8 is its extensibility and compatibility with prior YOLO versions, facilitating comparative performance analyses. This attribute, coupled with its advancements in accuracy and the introduction of anchor-free dynamics and the dynamic Task-Aligned Assigner for precision in anchor matching, positions YOLOv8 as the most accurate detector to date. The algorithm’s adaptability and the enhancements in computational and detection efficiency render it an ideal foundation for the research project aimed at deploying a computer vision model based on YOLOv8 suitable for drone utilization in the tuna fishing and aquaculture industry.
The feature extraction network in YOLOv8 is designed to pull individual-scale features from images processed by the SPPF and C2f modules. The C2f module, a streamlined version of the original C3 module, incorporates a convolutional layer to lighten the model while integrating the ELAN structure’s advantages from YOLOv7. This enhancement broadens the gradient flow information by using bottleneck modules in the gradient branch. The SPPF module reduces the number of layers from the standard SPP (spatial pyramid pooling), cutting down on unnecessary operations and speeding up feature fusion.
The network’s multi-scale fusion module blends elements from both the FPN (feature pyramid network) and PAN (path aggregation network) to merge two-dimensional features from both low and high levels. This fusion bolsters smaller receptive field features at lower levels and boosts target detection across various sizes. In the detection phase, the network pinpoints target locations, categories, confidence scores, and other relevant data. YOLOv8’s head shifts from an anchor-based system to an anchor-free framework, eliminating IOU matching and one-sided scaling, employing a task aligner to differentiate between positive and negative samples. It executes multi-scale predictions using downsampled features from scales of 8, 16, and 32 to finely tune predictions across small, medium, and large targets. Figure 2 illustrates these detailed modules within the YOLOv8 network.
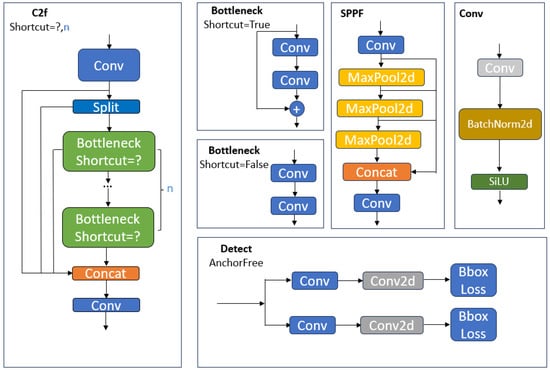
Figure 2.
Detail structure diagram of YOLOv8.
Target detection from UAV perspectives presents multifaceted challenges, underscored by the need for high accuracy and computational efficiency in small object detection. Innovations such as UFPMP-Net and HRDNet, among others, have made strides in UAV image detection by optimizing feature engineering and employing feature fusion techniques. However, these advanced target detection methods often necessitate substantial memory and computing resources, making them less feasible for deployment on low-power image processors typical of edge devices. YOLOv8, through its iterations and enhancements in network architecture, including the backbone, neck, and head components, has significantly reduced these limitations, offering a promising avenue for research and practical application in UAV-based monitoring systems for the aquaculture sector. This study aims to leverage YOLOv8’s robust framework and its proven efficacy in object detection to develop a model that is not only highly accurate and fast but also scalable and efficient for deployment in the challenging environment of tuna fishing and aquaculture, thereby providing a new paradigm in the application of UAV technology for sustainable fishery management.
2.2. Developing a YOLOv8 Network Structure Suitable for Drones Used in Oceanic Tuna Fishing and Farming
2.2.1. Enhancing Small Object Detection in YOLOv8 Using Advanced Downsampling and Feature Fusion Techniques
While YOLOv8 has achieved significant accomplishments, the model still faces some limitations in identifying small objects in complex scenes. Analysis indicates two main reasons for the inaccurate detection of small objects. During the feature extraction process, the neural network is often distracted by larger objects, resulting in insufficient data collection on smaller objects, which leads to their neglect throughout the learning process, affecting detection effectiveness. Smaller objects are easily obscured by other objects, making it difficult to distinguish and locate them in images.
To tackle these challenges, the research introduces a novel detection algorithm designed to enhance the detection of small objects while maintaining the performance for detecting objects of standard size. Initially, the study recommends the MDC module for the downsampling function. This module employs depthwise separable convolution, Maxpool, and a 3 × 3 convolution with a stride of 2 for concatenation, effectively compensating for information losses during downsampling and better preserving contextual details during feature extraction. Additionally, the feature fusion technique has been refined to more effectively merge shallow and deep data layers, ensuring a more thorough retention of information through the feature extraction phase. This enhancement helps overcome issues related to non-detection due to poor target positioning and the confusion that can arise with larger targets. Lastly, the DC module, consisting of depthwise separable convolution followed by a 3 × 3 convolution, is repetitively stacked and integrated to form a new network architecture. This module replaces the C2f module prior to the detection head, deepening the overall network structure and achieving greater resolution without a significant increase in computational demands. This strategy not only secures more contextual information but also significantly mitigates the problems of low detection accuracy due to overlapping objects. The specific structures are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
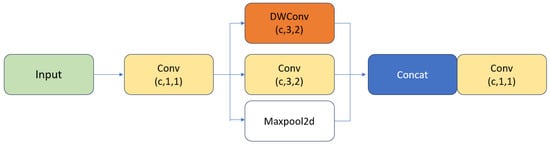
Figure 3.
Downsampling method.
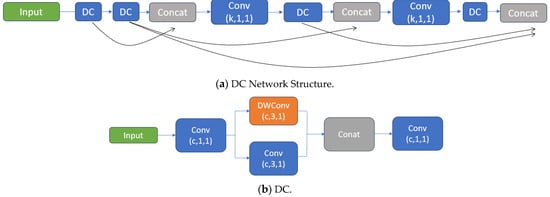
Figure 4.
Detailed components of the YOLOv8 network architecture. (a) This paper introduces a new network structure that incorporates the principles of DenseNet and VOVNet. This structure innovatively substitutes the traditional convolution layers with a parallel arrangement of standard and depthwise separable convolutions. (b) The basic building block of the network consists of a combination of standard and depthwise separable convolutions, optimizing both efficiency and computational load.
2.2.2. Optimizing YOLOv8 for Enhanced Detection of Micro-Sized UAV Targets
The original YOLOv8 model utilizes a deep residual network for extracting target features and employs a Pyramidal Attention Network (PAN) for multi-scale prediction. This architecture is designed to handle a broad range of object sizes effectively. However, the model still performs three downsampling iterations during the feature extraction phase to generate the maximum feature map. While this technique aims to consolidate and enhance the detectable features across various scales, it inadvertently results in a significant loss of detailed feature information. This loss is particularly problematic when attempting to detect very small targets such as micro-sized Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), where preserving high-resolution details is crucial for successful detection.
To address these challenges, this study proposes several targeted improvements to the YOLOv8 model, aiming to optimize it for the detection of micro-sized UAV targets, which are often critical in surveillance and monitoring applications. These enhancements are designed to refine the model’s ability to process and analyze small-scale features without overwhelming computational demands. The specific enhancements made in this revised model are detailed below.
Introduction of a High-Resolution Detection Branch: A significant modification in our approach involves the integration of a high-resolution detection branch within the detection head of the model. This new branch specifically focuses on processing smaller feature maps (160 × 160 pixels), which undergo fewer downsampling operations compared to the standard model. By reducing the number of downsampling steps, this branch retains a greater level of detail, which is essential for identifying small objects. This adaptation is particularly beneficial for detecting tuna, which may be represented by only a small number of pixels in larger images. Displayed in Figure 5, this scheme involves the introduction of a high-resolution detection branch that focuses on smaller feature maps to enhance the detection of tiny UAV targets. This branch reduces the number of downsampling steps to preserve more detailed information, crucial for detecting micro-sized objects.
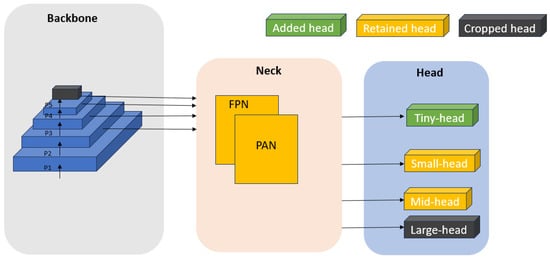
Figure 5.
Improvement scheme at the head.
Optimization of Multi-Scale Feature Extraction Module: Recognizing the limitations of traditional convolution operations in handling features of small objects, we have replaced the standard convolution layers in the feature extraction module with Space-to-Depth Convolution (SPD-Conv) layers. SPD-Conv layers use a combination of space-to-depth layer operations and non-stride convolutions to better capture the intricacies of various object sizes and complexities. This method is especially advantageous for tasks involving low-resolution images or small detection objects, where every pixel contains crucial information. The SPD-Conv effectively increases the model’s sensitivity to finer details, thus improving its performance in detecting tiny UAV targets. Illustrated in Figure 6, the SPD-Conv structure utilizes a combination of space-to-depth layers and non-stride convolutions. This novel architectural feature aims to improve the feature extraction process, particularly beneficial for handling low-resolution images or small objects effectively by preserving more relevant feature details.
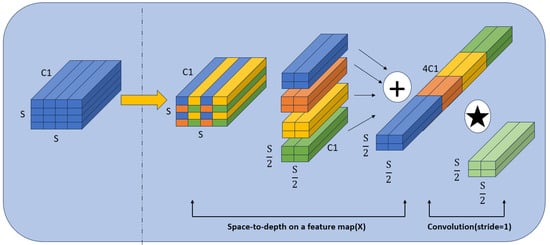
Figure 6.
Structure of SPD-Conv.
Integration of GAM Attention Mechanism: To further refine the model’s capability to focus on and retain important features across varying scales, the GAM attention mechanism has been introduced into the feature fusion module. The GAM mechanism utilizes principles from the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) and focuses sequentially on channel and spatial features within the network. By doing so, it significantly enhances the network’s ability to concentrate on areas of the feature map that are most likely to contain relevant information, thus optimizing the detection process. This attention mechanism is particularly effective in scenarios where targets have few distinguishing features and are easily lost amidst background noise. Shown in Figure 7, the GAM attention mechanism is integrated into the feature fusion module to enhance the model’s capacity for maintaining and emphasizing critical feature information across various scales. This module uses attention mechanisms to focus on significant features within the data, which helps in improving the overall detection capabilities of the network, especially in complex detection scenarios involving small or subtle targets.
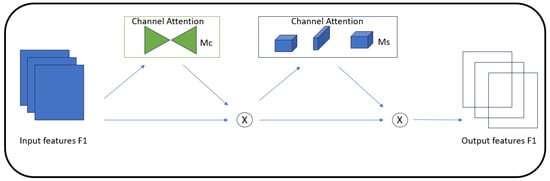
Figure 7.
The GAM attention module.
Given the mapping of input attribute , intermediate state and output are defined as follows:
In the recent revision of YOLOv8, the loss function has undergone significant modifications due to the adoption of the anchor-free design, differing notably from the YOLOv5 series. The optimization of the loss function in YOLOv8 is now split into two primary components: classification and regression. The classification loss continues to employ the Binary Cross Entropy Loss (BCEL), while the regression part incorporates the Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) and the Bounding Box Regression Loss (BBRL). The comprehensive loss function is formulated as follows:
The classification loss, essentially a cross entropy loss, is given by the following:
Here, “class” represents the number of categories, “weight[class]” denotes the weights assigned to each class, and is the probability value after sigmoid activation.
The Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) optimizes the focal loss function by transitioning the discrete classification results into continuous outcomes through integration. It is expressed as the following:
In this equation, and denote values flanking the consecutive labels , satisfying , and is calculated as with implemented via a softmax layer.
The regression loss diverges from the commonly used CIoU loss in YOLOv8 to employ the Wise-IoU loss function, which incorporates a dynamic non-monotonic focusing mechanism. This adaptation is particularly useful when dealing with low-quality labels in training data, as it utilizes the “outlier” factor to modulate the impact of geometric discrepancies (like distance and aspect ratio) on the model, thus preventing excessive penalties. When the predicted bounding box aligns closely with the actual target box, the loss function promotes improved model generalization with less need for extensive training by reducing the focus on geometric differences. The formula for Bounding Box Regression Loss (BBRL) utilizing Wise-IoU v3, which incorporates a dual-layer attention mechanism and a dynamic non-monotonic Feature Matching (FM) mechanism, is specified as follows:
In this expression, the extent of deviation in the predicted box is indicated, where a lower degree suggests better quality of the anchor box. This factor helps to adjust the focal number non-monotonically, allocating smaller gradient enhancements to prediction boxes with substantial outliers, effectively reducing the adverse gradients from low-quality training samples. Figure 8 shows schematic diagram of the Wise-IoU solution.
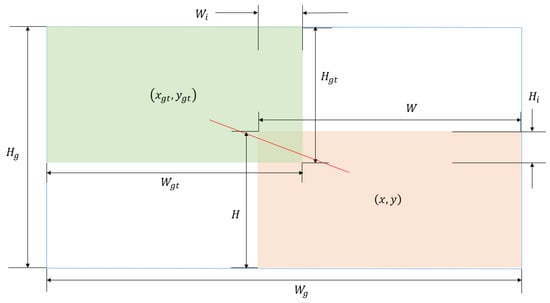
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the Wise-IoU solution.
The proposed improvements to the YOLOv8 model are aimed at significantly enhancing its performance for micro-target detection tasks. By reducing feature loss during processing, enhancing the resolution at which small objects can be detected, and improving feature attention and retention, the model becomes more adept at identifying and classifying small-scale UAVs. This optimized model configuration, depicted in the improved network architecture shown in Figure 9, ensures a balance between maintaining high detection accuracy and managing computational efficiency, making it highly suitable for real-world applications where speed and accuracy are paramount.
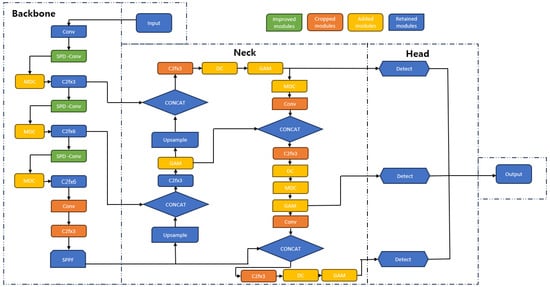
Figure 9.
Improved YOLOv8 network structure diagram.
3. Preparation of Experiments and Outcome Analysis
In this study, the authors employ the publicly available Tuna dataset from Roboflow to assess the effectiveness of the model. The discussion includes details about the dataset, the network configuration and training procedures, evaluation metrics, an ablation study, comparative analyses, and tests using a proprietary dataset. The dataset comprises 3200 images. Prior to training, these images and their corresponding labels are segmented into training, validation, and test sets using an 8:1:1 ratio. Considering the available hardware and multiple experimental trials, the authors have chosen to set the batch size at 4 (to achieve learning efficiency, we have reduced the batch size to a smaller one to avoid memory jumps that cause errors in learning) and the number of epochs at 200.
3.1. Test Platform Setup
The experimental setup described in this paper utilizes a Windows 10 operating system, supported by hardware that includes 64 GB of RAM, an NVIDIA GTX3050 GPU, and an Intel i7-13700KF CPU running at 3.40 GHz. The software environment is based on torch version 1.12.1 with cu118, and the development is conducted using Pycharm Community 2024.1.1.
The dataset used for this study is a compilation of datasets named Thunnus_albacares, Thunnus_albacares 2, Thunnus_albacares 3, Thunnus_albacares 4, and Thunnus_albacares 5 from the open source Roboflow. This dataset includes images of yellowfin tuna from various angles, locations, sizes, and environments. This diversity in the data enriches the learning model proposed, and combining multiple datasets helps avoid errors and omissions in the learning process. Figure 10 shows some representative images from the dataset used in this study.
Figure 10.
Some representative images from the dataset used in this study.
3.2. Assessment Metrics
The evaluation metrics employed include mean average precision (), average precision (), precision (), and recall (). The formulas for precision () and recall () are illustrated in Equations (7) and (8), respectively:
where stands for the number of correctly predicted bounding boxes, indicates the number of incorrect positive detections, and represents the number of targets that were missed. Average precision () measures the average accuracy of the model, while mean average precision () calculates the mean of these values across different categories, with “” representing the total number of categories. The formulas for calculating and are provided in Equations (9) and (10), respectively.
3.3. Results Analysis
To assess the detection efficacy of the enhanced technique for small targets at various stages, the authors performed stage-specific ablation studies using the Tuna dataset from Roboflow, comparing the results with those from YOLOv8s. This dataset encompasses a diverse range of conditions, having been compiled under varying landscape, weather, and lighting situations, which includes numerous small-size targets in challenging environments. Additionally, the dataset furnishes details such as scene visibility, object classification, and occlusion levels. Due to its comprehensive and authoritative nature, the Tuna dataset is perfectly suited for the controlled experiments conducted in this study.
To evaluate the performance enhancements of each component, several models were defined: Baseline Model 1 (YOLOv8s), Improved Model 2 (with enhanced downsampling), Improved Model 3 (enhanced downsampling plus a tiny head and removed large head), Improved Model 4 (including downsampling, a tiny head, removed large head, and enhanced SPD-Conv), Improved Model 5 (featuring downsampling, a tiny head, removed large head, enhanced SPD-Conv, and added GAM), and Improved Model 6 (incorporating downsampling, a tiny head, removed large head, enhanced SPD-Conv, added GAM, and a revised loss function). The authors quantitatively analyzed changes in evaluation metrics across these six models, highlighting the optimal results for each metric. To ensure the validity of the experiment, mAP0.5 and mAP0.5:0.9 were used as the evaluation indices. The experimental results are detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Variations in outcomes from ablation studies. Bold represents the indicators with the best results in the experiment.
Referring to Table 1, the following can be observed.
The refinement of the downsampling technique along with the integration of a tiny detection head resulted in improvements of 0.5%, 5.5%, 11.1%, and 7.08% in precision (P), recall (R), mean average precision (mAP0.5), and mAP0.5:0.95, respectively. These enhancements indicate that optimizing the high-resolution detection head substantially enhances the detection capabilities for smaller targets. Additionally, the reduction in the large target detection layer significantly lowered the parameter count by 74.81%.
The results for Improved Models 3, 4, 5, and 6 illustrate that upgrading the SPD-Conv module notably enhances the recall (R) of the model. This suggests that refining the convolution module to SPD-Conv within the backbone network better preserves features of small targets and decreases the chances of their non-detection. Furthermore, the incorporation of the GAM has positively influenced the precision (P) of the model, suggesting that adding the GAM in the neck enhances feature fusion within the network and lowers the incidence of false positives. The addition of both SPD-Conv and GAM led to enhancements in P, R, and mAP, though it slightly increased the number of parameters and the model size.
When comparing the results of the enhanced model 6 (our proposed model) with model 1 (the baseline model), it is evident that fully implementing the suggested enhancements resulted in an increase in inference time. The improved model reached a frame rate of 221 frames per second, which, although lower than the 285 frames per second of the baseline model, still meets the real-time requirements for practical deployment. Moreover, the proposed model significantly bettered the metrics of precision (P), recall (R), mean average precision (mAP), and reduced the number of parameters.
Figure 11 shows size and distribution of the self-built Tuna dataset for drones.
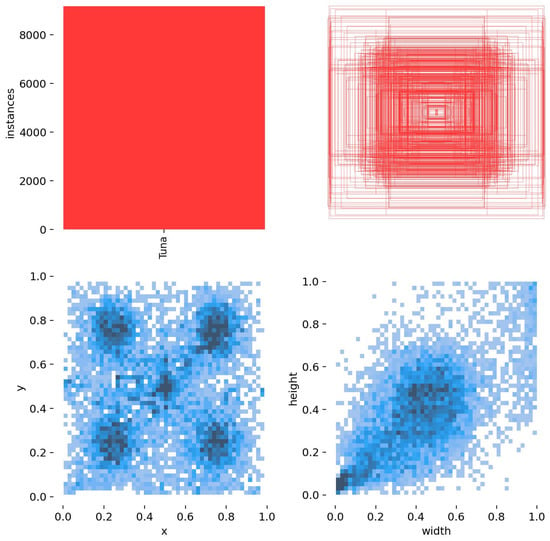
Figure 11.
Size and distribution of self-built Tuna dataset for drones.
It can be easily observed that the dataset is evenly distributed with various sizes, enabling the drone to track objects at varying distances. This brings efficiency to its practical applications.
After adjusting the dataset into an 8:2 split and conducting a comparison between the proposed controller and the baseline yolov8s, the results show that the proposed model is more suitable for drones used in the tuna fishing and harvesting industry due to its higher efficiency, accuracy, and more stable parameters when applied in this case. The study lays the groundwork for developing practical models to be applied in smart tuna farms and efficient tuna fishing, contributing to enhanced performance and reducing the effort required by fishermen. The results are presented in Figure 12 and Figure 13.
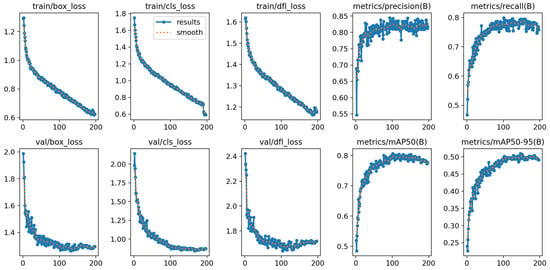
Figure 12.
Results of YOLOv8s.
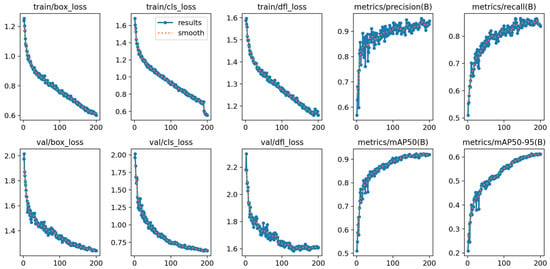
Figure 13.
Results of proposed model.
Based on Figure 12 and Figure 13, and a comparison of the effectiveness between the YOLOv8s model and the proposed model in the context of object detection from images captured by UAVs, the main evaluation metrics include box loss, classification loss, precision, recall, and mean average precision (mAP).
Analysis of results from the training and validation sets shows that the proposed model has several distinct advantages over the YOLOv8s model. Specifically, in terms of box loss and classification loss on the validation set, the proposed model shows lower metrics, indicating a more accurate ability to detect and classify objects in images. Although the YOLOv8s model also records impressive loss reductions, the metrics on the validation set remain higher compared to those of the proposed model.
In terms of precision and recall, the proposed model significantly outperforms with a stable precision above 0.9 and a recall above 0.8, whereas YOLOv8s achieves a precision below 0.85 and a recall around 0.75. This demonstrates that the proposed model is better at distinguishing true positives and minimizing false positives than YOLOv8s.
Finally, a comparison of the mAP shows that while both models perform well, the proposed model has a mAP50 above 0.9 compared to YOLOv8s’s below 0.8; additionally, the proposed model has a mAP95 that is 0.1 higher than YOLOv8s, specifically above 0.6 compared to below 0.5, respectively. This indicates a better ability to detect smaller or more challenging objects. These results solidify the position of the proposed model as a truly effective solution for handling complex and diverse real-world application scenarios. Continued research and improvements to the proposed model will be necessary to enhance its competitive ability and effectiveness in practical applications.
Figure 14 shows results of detecting yellowfin tuna from a drone’s perspective. Despite variations in the environment, the detection is clear and accurate.

Figure 14.
Results of detecting yellowfin tuna from a drone’s perspective.
The integration of the PA-YOLOv8 model, designed specifically for UAVs in the tuna fishing and aquaculture industry, represents a significant stride towards addressing the dual challenges of operational efficiency and sustainability in marine resource management. Our findings underscore the pivotal role of advanced computer vision technologies, such as the YOLOv8, which has demonstrated exceptional capability in the high-precision detection of marine life, particularly tuna, from aerial perspectives. The specific adaptations and enhancements made to the YOLOv8 model—namely, the introduction of downsampling methods, feature fusion techniques, and the novel Global Attention Module (GAM)—have collectively enabled a marked improvement in the model’s ability to discern small-scale marine species within complex oceanic environments.
4. Discussion
One of the critical findings from this research is the model’s enhanced capability to detect small objects, which is crucial for monitoring juvenile tuna and ensuring the sustainability of tuna populations. The optimizations in downsampling and feature fusion have been particularly effective in mitigating the loss of detail that typically occurs with standard detection models, thereby significantly improving detection accuracy and reliability.
Furthermore, the experimental results obtained using the Tuna dataset from Roboflow have provided compelling evidence of the model’s robustness and efficacy. The improved detection rates, as demonstrated by higher precision (P), recall (R), and mean average precision (mAP) across several model iterations, highlight the potential of this technology to revolutionize the way authors monitor and manage marine resources. The systematic ablation studies conducted underscore the incremental benefits of each technological enhancement, validating our methodology and approach.
5. Conclusions
The research paper presented aims to address specific gaps within the realm of object detection applied to the fishing industry, particularly using UAVs for monitoring tuna populations. The study introduces the PA-YOLOv8, an advanced computer vision model tailored for drones, which significantly enhances object detection capabilities in aquatic environments. This model incorporates strategic modifications such as downsampling techniques, feature fusion enhancements, and the integration of the Global Attention Module (GAM). These innovations result in marked improvements in the detection accuracy of small and juvenile tuna, which is crucial for sustainable fishing practices.
The novelty and contribution of PA-YOLOv8 lie in its ability to accurately detect small-scale marine life within complex oceanic scenes, an essential feature for ecological monitoring and resource management. By implementing these enhancements, the model addresses critical challenges in current detection methods, which often struggle with small object recognition in expansive marine environments captured by drone-mounted cameras. The research thus fills a significant gap by improving both the technological aspect of object detection and contributing to the sustainable management of marine resources. This aligns with the broader goal of integrating cutting-edge technologies to support sustainable practices in the aquaculture sector, thereby advancing the state of the art in environmental conservation efforts. By integrating advanced computer vision technologies tailored specifically for drone use, the PA-YOLOv8 model represents a significant step forward in enhancing the monitoring and management of tuna populations. This model has demonstrated a marked improvement in detecting small and juvenile tuna, which is crucial for assessing stock levels and implementing sustainable fishing practices.
With its precise detection capabilities, the proposed solution addresses several critical challenges in the tuna fishing industry. Firstly, it enables more accurate population assessments, which are essential for setting quotas and preventing overfishing. Secondly, the ability to monitor tuna in real-time offers fisheries the opportunity to adjust their strategies promptly, thereby improving catch efficiency while reducing the bycatch of non-target species. This dual benefit of enhancing both sustainability and profitability highlights the transformative potential of PA-YOLOv8 in commercial fishing operations.
Furthermore, by reducing the labor and time typically required for manual monitoring and by providing more reliable data, the PA-YOLOv8 model could lead to better resource management and a healthier marine ecosystem. As this technology continues to evolve, it may become a cornerstone tool in the global effort to ensure the long-term sustainability of tuna stocks and, by extension, the marine environments they inhabit.
The research undertaken has set a new benchmark in the application of UAV and computer vision technology for sustainable fishery management. The PA-YOLOv8 model not only meets the high demands of real-time processing and accuracy but also aligns with the broader goals of environmental stewardship. By significantly enhancing the detection capabilities for small and juvenile tuna, the model contributes to the conservation efforts essential for maintaining healthy tuna populations, which are critical to the ecological balance of marine ecosystems.
Moreover, the scalability and efficiency of the PA-YOLOv8 model make it a viable solution for widespread adoption within the industry. Its performance in test results suggests that it can be effectively deployed across different regions and conditions, providing a reliable tool for enhancing the sustainability practices of tuna fishing and aquaculture operations globally.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates the profound impact of integrating cutting-edge technologies in addressing the complex challenges of modern aquaculture and fisheries. The advancements in computer vision and UAV technology exemplified by the PA-YOLOv8 model offer promising pathways for enhancing resource management, ensuring sustainable fishing practices, and ultimately supporting the global initiative towards more sustainable oceans. Future research should continue to refine these models, explore their applications in other contexts, and evaluate their long-term impacts on marine conservation efforts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.-A.P.; methodology, D.-A.P. and S.-H.H.; software, D.-A.P.; formal analysis, D.-A.P. and S.-H.H.; resources, D.-A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, D.-A.P.; writing—review and editing, S.-H.H.; supervision, S.-H.H.; project administration, S.-H.H.; funding acquisition, S.-H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the research grant of the Gyeongsang National University in 2024.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data and equipment are available at Hydraulic Pneumatic and Marine System Laboratory in Gyeongsang Nation University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Chaurasia, A.; Borovec, J.; NanoCode012; TaoXie; Kwon, Y.; Michael, K.; Liu, C.; Fang, J.; et al. Ultralytics/yolov5: v6.0—Robustness & Reproducibility Update; Version v6.0; Zenodo: Genève, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Cabello, M.A.; Garcia-Gonzalez, J.; Luque-Baena, R.M.; López-Rubio, E. The effect of downsampling–upsampling strategy on foreground detection algorithms. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 4935–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foged, L.J.; Saccardi, F.; Mioc, F.; Iversen, P.O. Spherical near field offset measurements using downsampled acquisition and advanced NF/FF transformation algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Davos, Switzerland, 10–15 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Elhadad, A.; Jamjoom, M.; Abulkasim, H. Reduction of NIFTI files storage and compression to facilitate telemedicine services based on quantization hiding of downsampling approach. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrabaszcz, P.; Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. A downsampled variant of imagenet as an alternative to the cifar datasets. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.08819. [Google Scholar]
- Sekharamantry, P.K.; Melgani, F.; Malacarne, J. Deep learning-based apple detection with attention module and improved loss function in YOLO. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Fu, X.; Yu, T.; Guo, Y.; Wang, R. DC-SPP-YOLO: Dense connection and spatial pyramid pooling based YOLO for object detection. Inf. Sci. 2020, 522, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Ma, Y.; Yahya, M.; Ahmad, B.; Nazir, S.; Haq, A.U. Object detection through modified YOLO neural network. Sci. Program. 2020, 2020, 8403262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Ge, Y.; Duan, S. GAU-Net: U-Net based on global attention mechanism for brain tumor segmentation. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1861, No. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y. GAM: Gradient attention module of optimization for point clouds analysis. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Hoffmann, N. Global attention mechanism: Retain information to enhance channel-spatial interactions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.05561. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Zhu, K.; You, S. YOLO-SSFS: A Method Combining SPD-Conv/STDL/IM-FPN/SIoU for Outdoor Small Target Vehicle Detection. Electronics 2023, 12, 3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Fang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Tang, Z.; Han, Y.; Ma, Z. YOLOv6-ESG: A lightweight seafood detection method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.; Singh, P.; Gupta, K.; Jain, A.K.; Jain, A.; Jain, A. UAV Based YOLOV-8 Optimization Technique to Detect the Small Size and High Speed Drone in Different Light Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Disruptive Technologies (ICDT), Greater Noida, India, 15–16 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kaff, A.; Martin, D.; Garcia, F.; de la Escalera, A.; Armingol, J.M. Survey of computer vision algorithms and applications for unmanned aerial vehicles. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 92, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoy, P.; Correa, J.F.; Mondragón, I.; Martínez, C.; Olivares, M.; Mejías, L.; Artieda, J. Computer vision onboard UAVs for civilian tasks. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2009, 54, 105–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, L.D.; Loyaga, E.S.; Cruz, P.J.; Lema, H.P.; Abad, J.; Valencia, E.A. Low-Cost Computer-Vision-Based Embedded Systems for UAVs. Robotics 2023, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakaletsis, E.; Symeonidis, C.; Tzelepi, M.; Mademlis, I.; Tefas, A.; Nikolaidis, N.; Pitas, I. Computer vision for autonomous UAV flight safety: An overview and a vision-based safe landing pipeline example. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).