Numerical Study on Wave Dissipation and Mooring Force of a Horizontal Multi-Cylinder Floating Breakwater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Establishment and Verification of Numerical Model
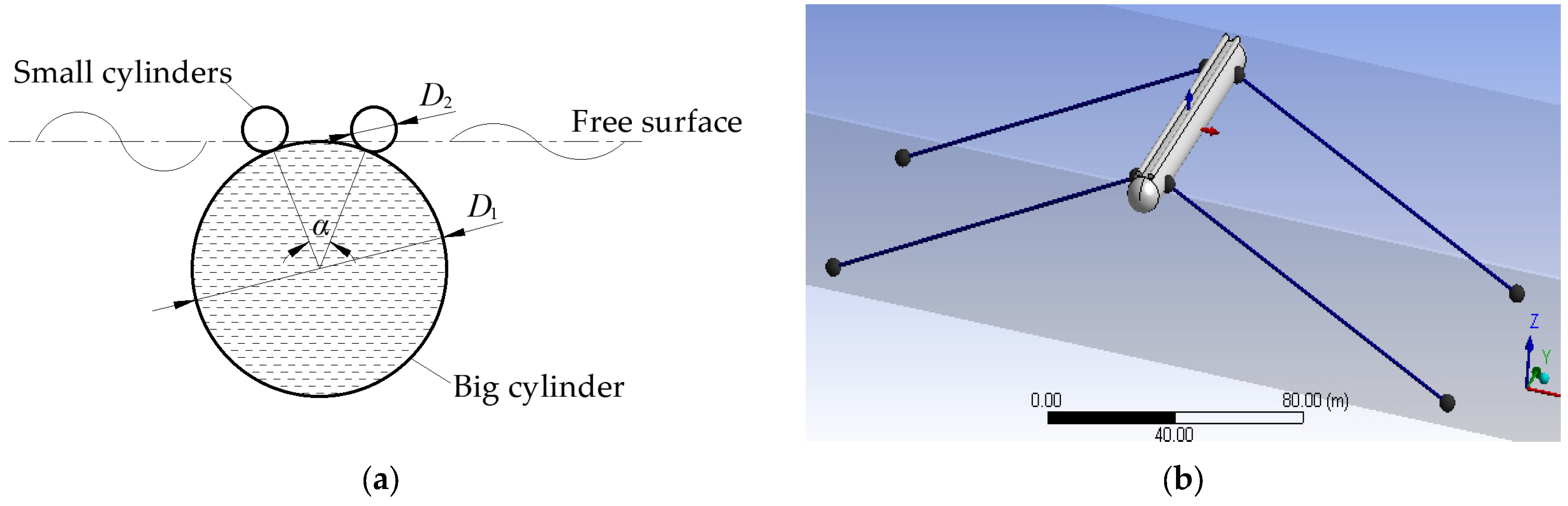
2.1. Establishment of Numerical Model
- (i)
- At the seabed (z = −d),
- (ii)
- For the free surface (z = 0),
- (iii)
- For the immersed surface of the object,
2.2. Verifications of Numerical Model
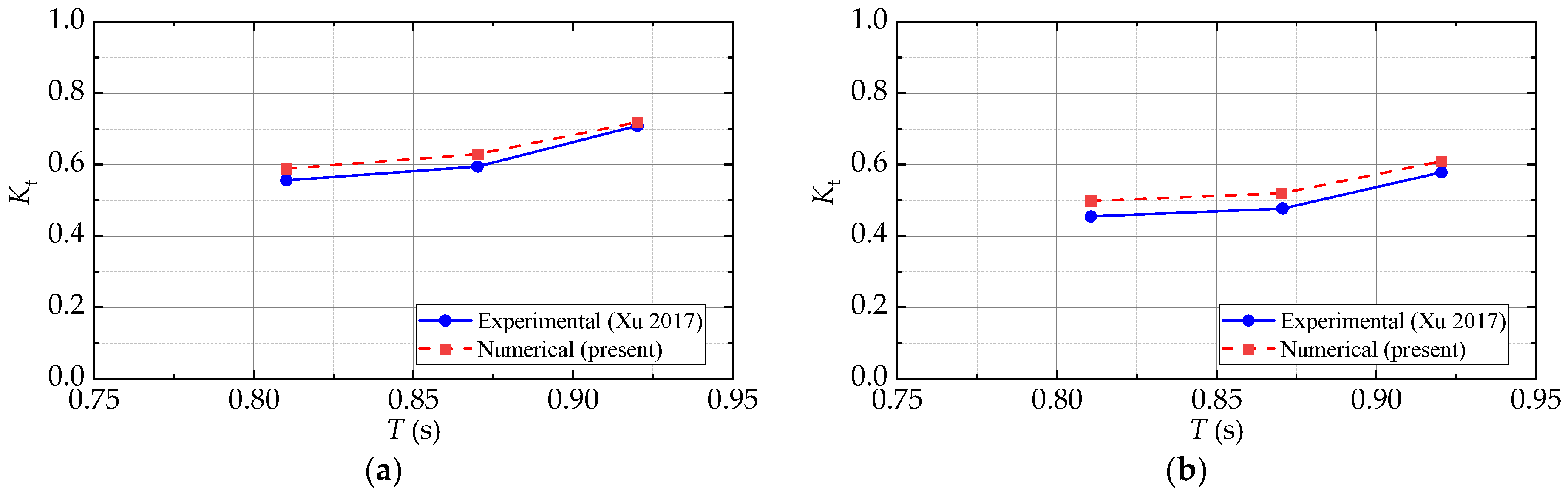
2.2.1. Modeling of Double-Box Floating Breakwater
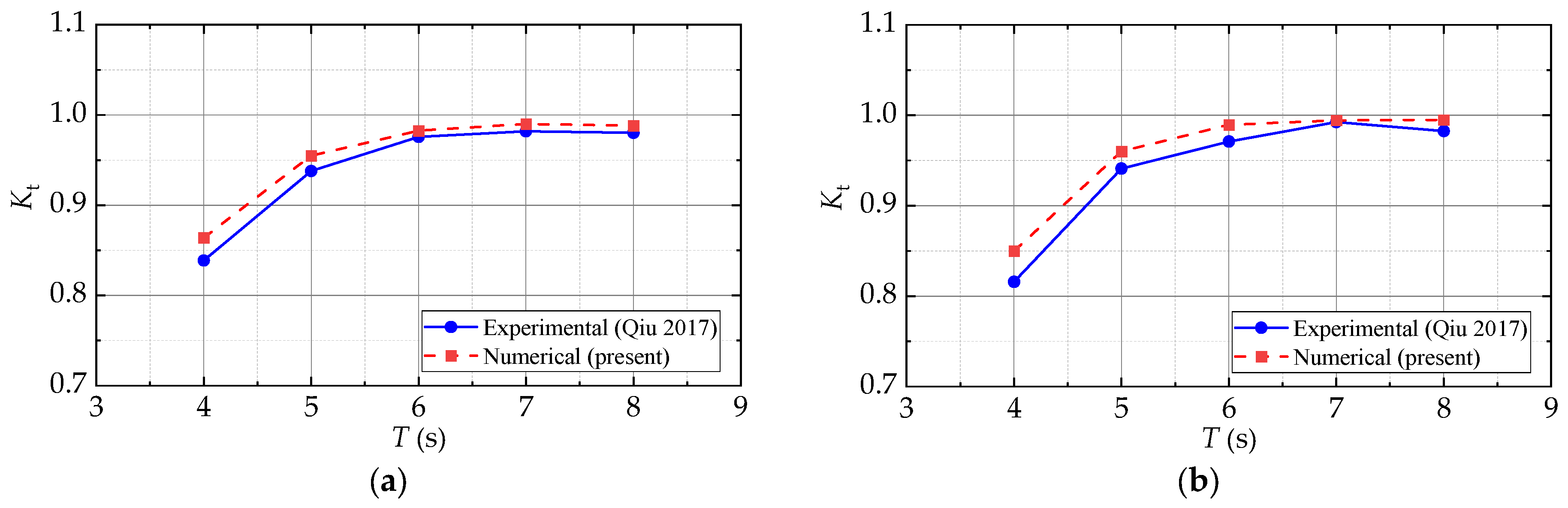
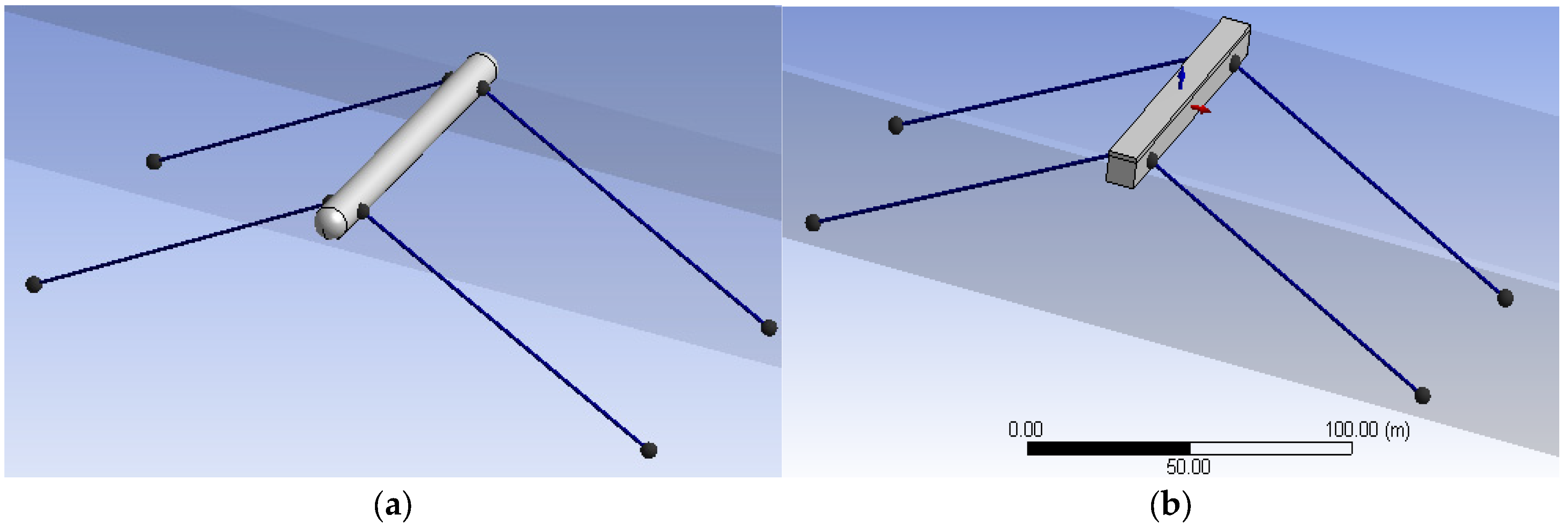
2.2.2. Modeling of Multi-Cylinder Floating Breakwater
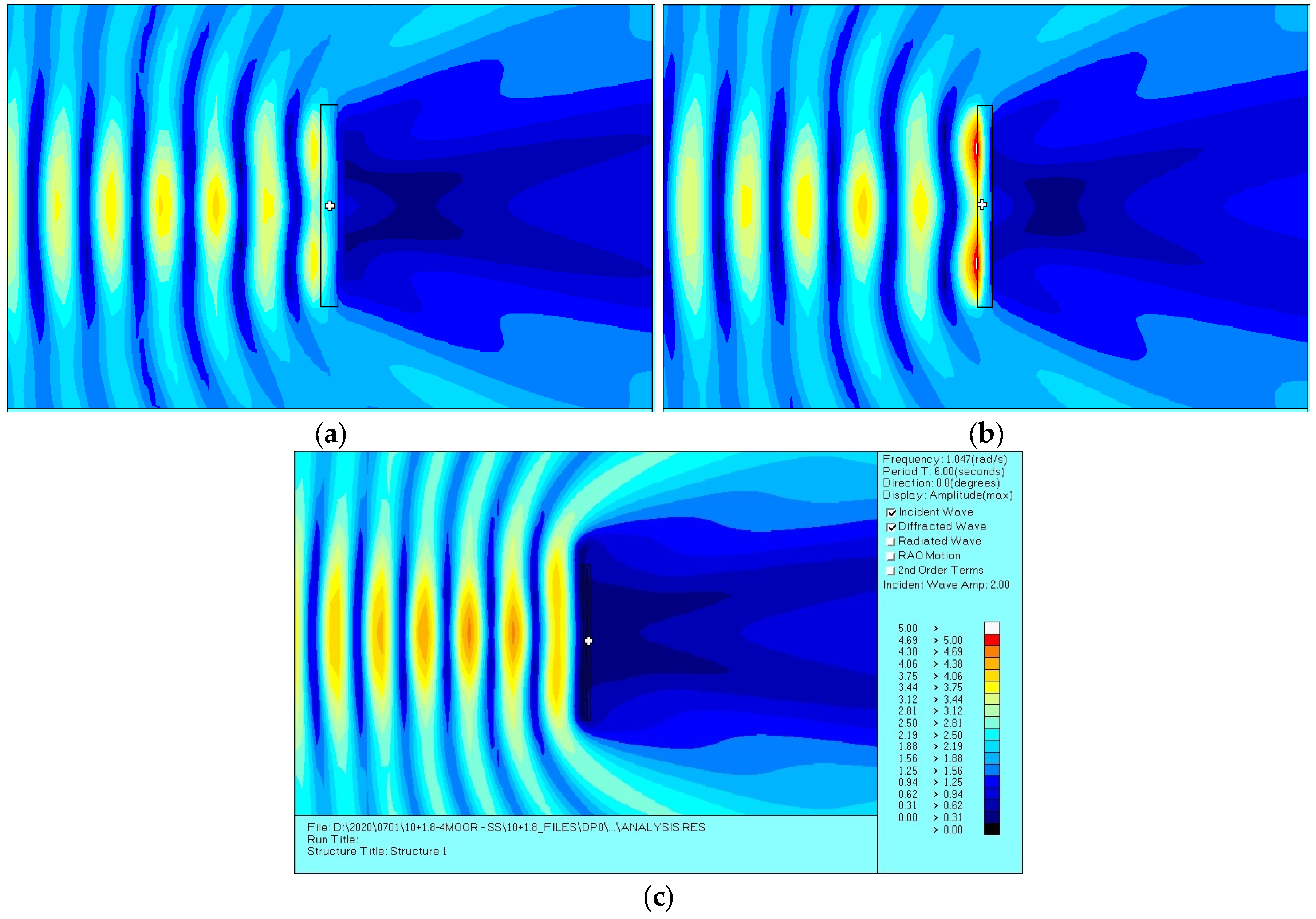
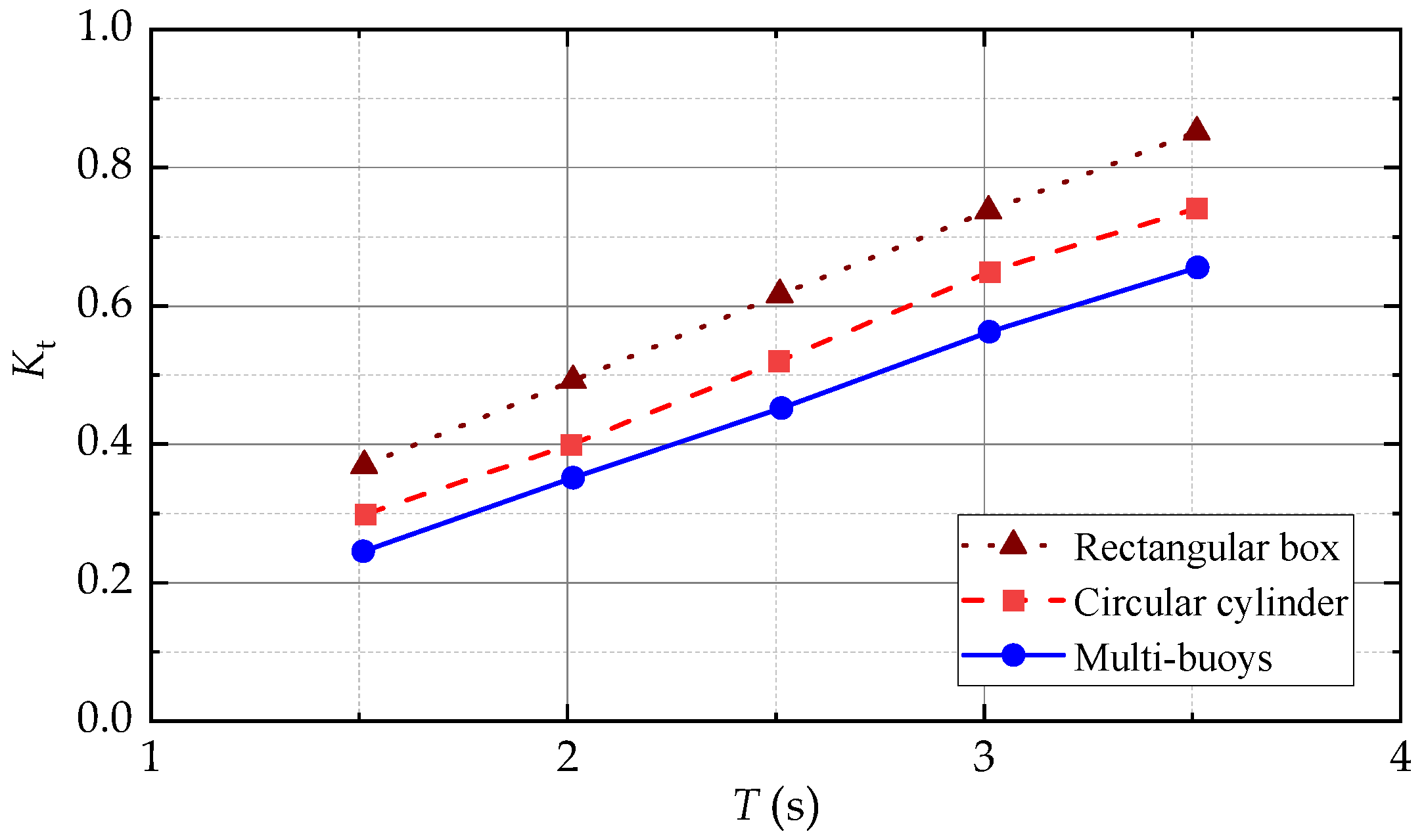
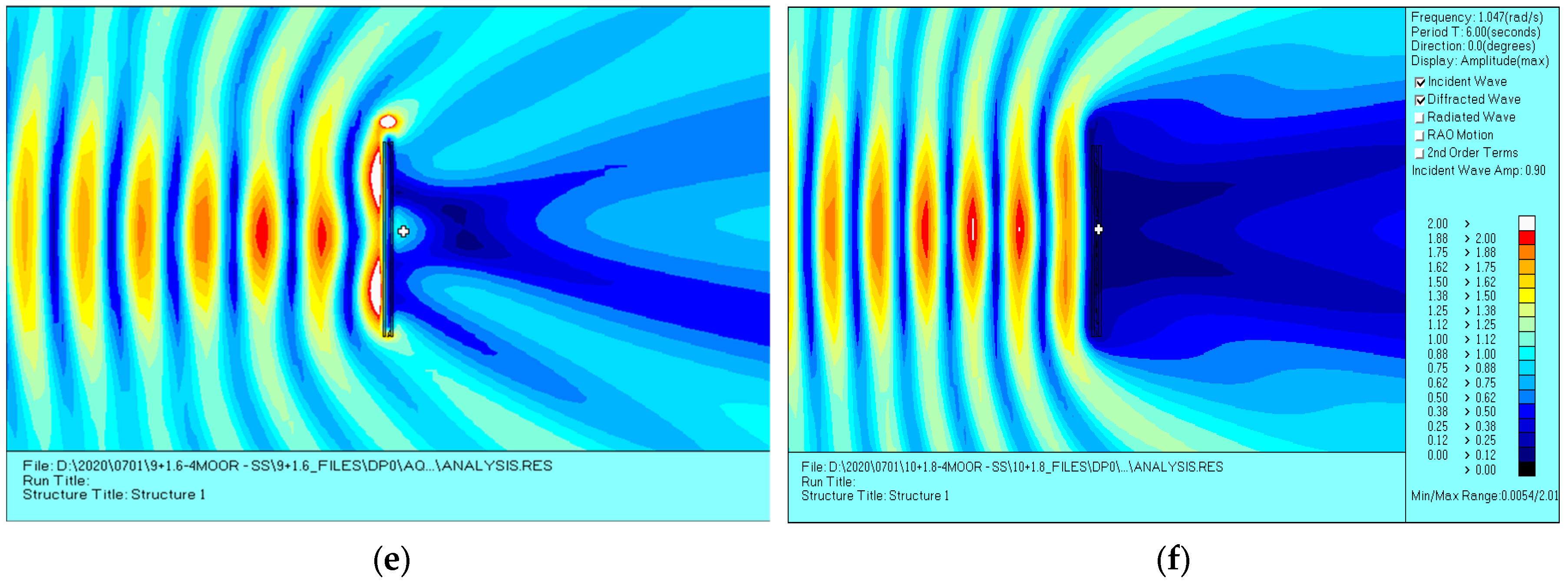
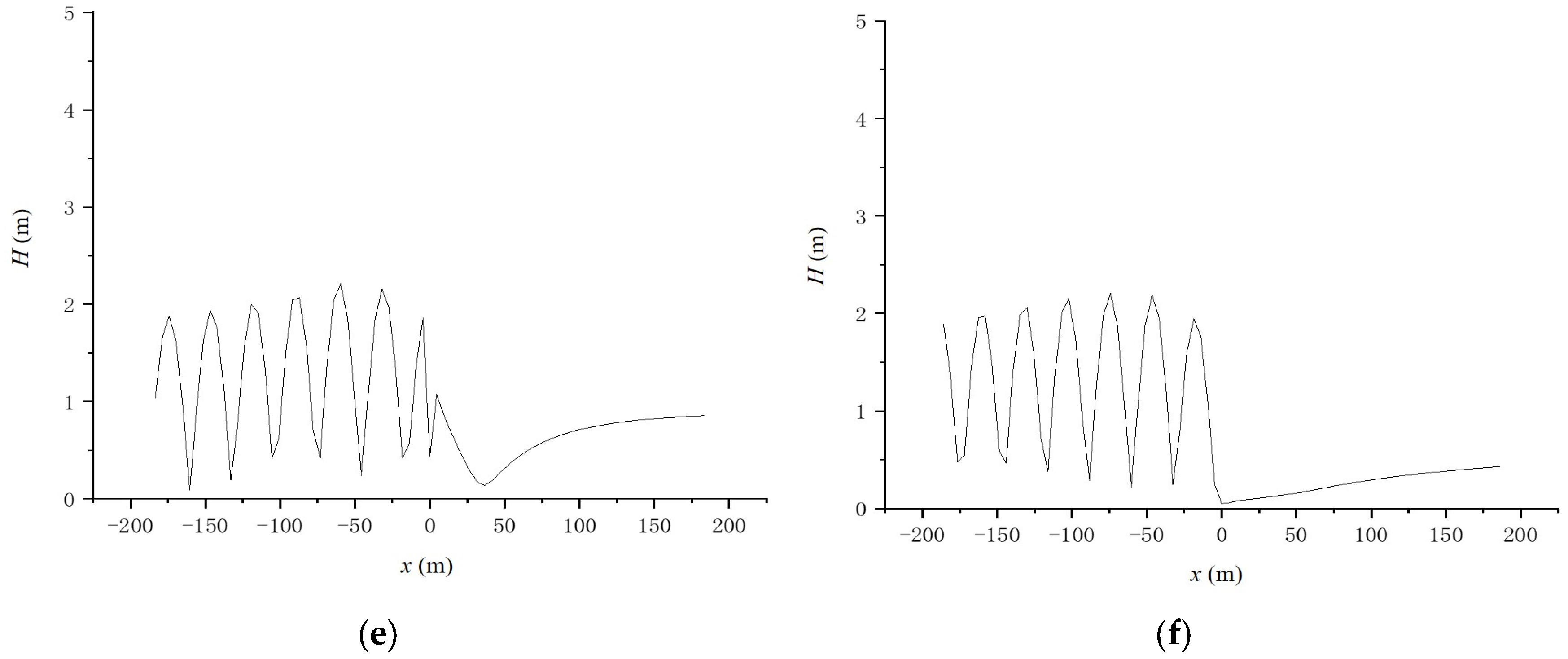
3. Comparisons among Floating Breakwaters with Different Cross-Sections
4. Analysis of Wave Dissipation Capacity of Multi-Cylinder Floating Breakwater
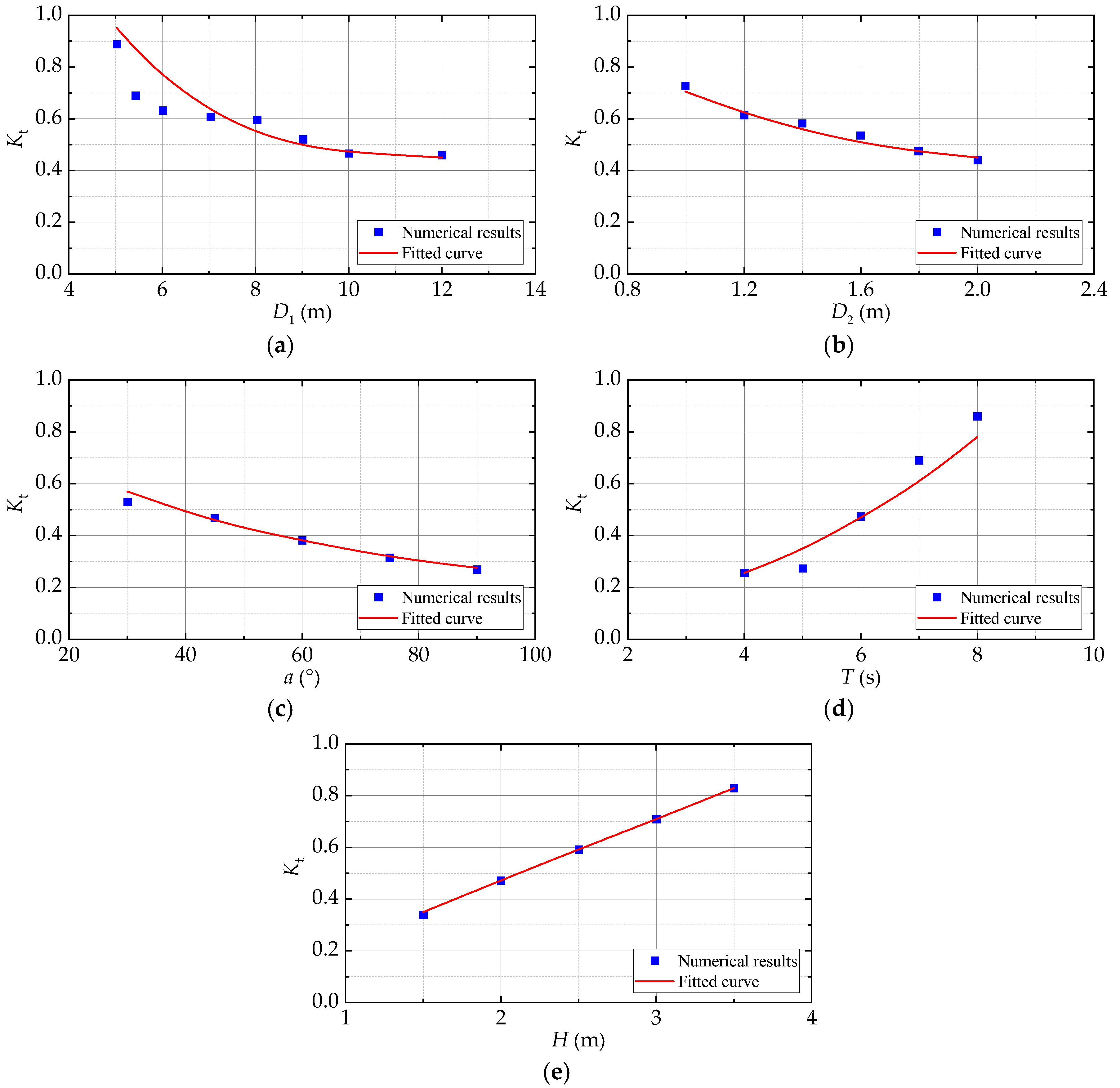
4.1. Effects of Influential Factors on Wave Transmission Coefficient
4.1.1. Effect of Large Cylinder Diameter
4.1.2. Effect of Small Cylinder Diameter
4.1.3. Effect of the Angular Position of Small Cylinder
4.1.4. Effect of Incident Wave Period
4.1.5. Effect of Incident Wave Height
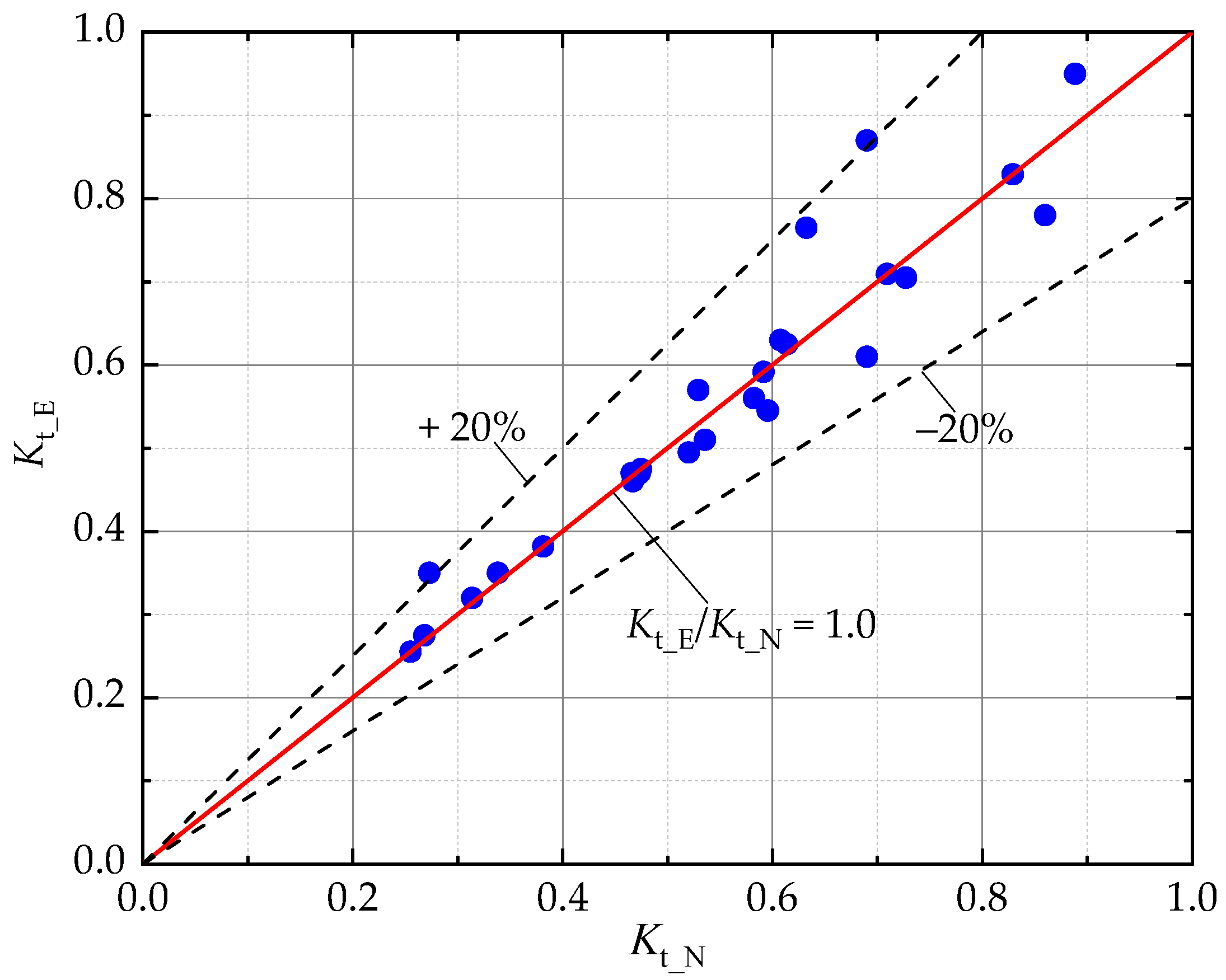
4.2. Empirical Formula
5. Analysis of Total Mooring Force of Multi-Cylinder Floating Breakwater
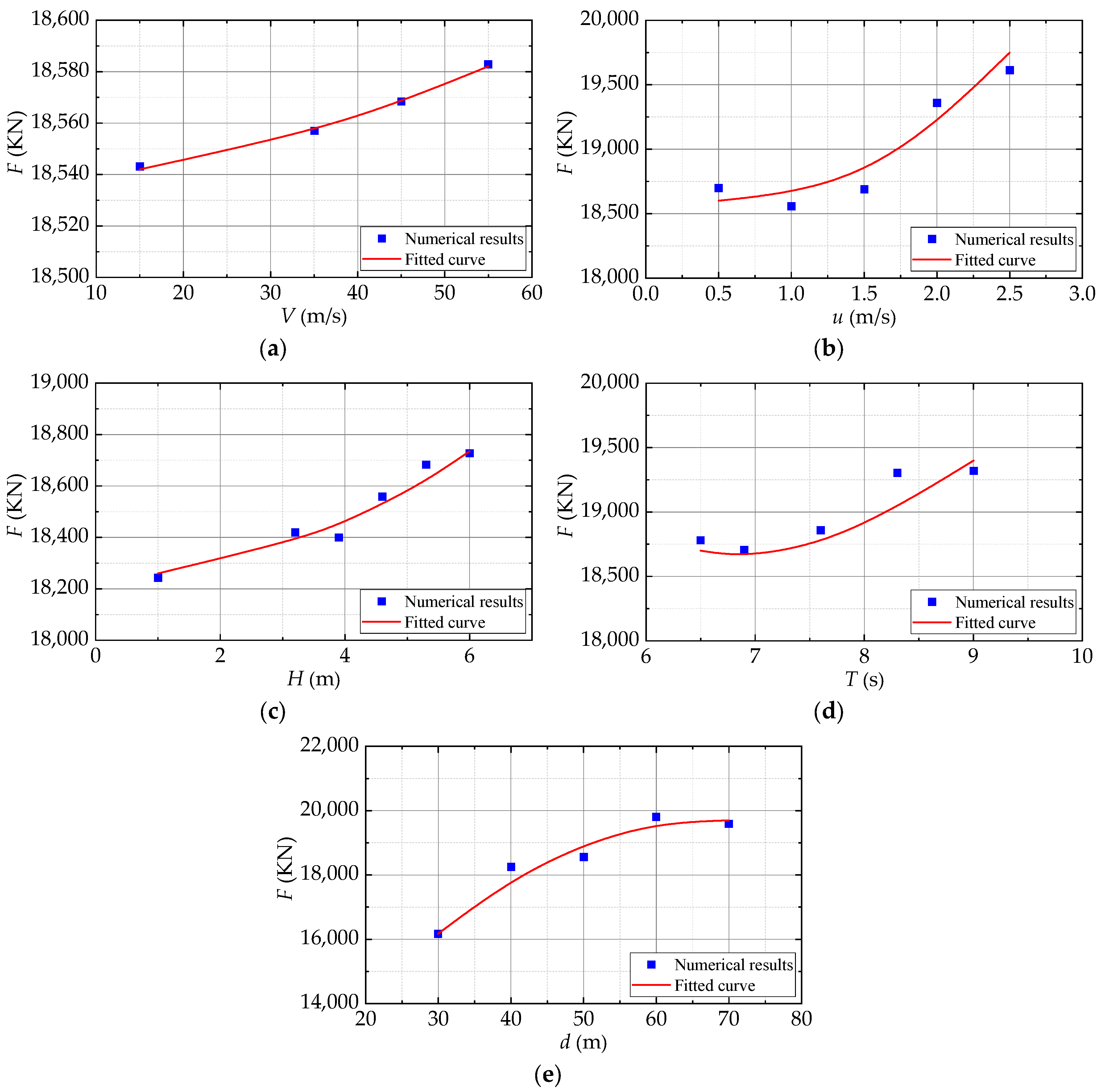
5.1. Effects of Influential Parameters of Mooring Chain Force
5.1.1. Effect of Wind Speed
5.1.2. Effect of Current Velocity
5.1.3. Effect of Incident Wave Height
5.1.4. Effect of Incident Wave Period
5.1.5. Effect of Water Depth
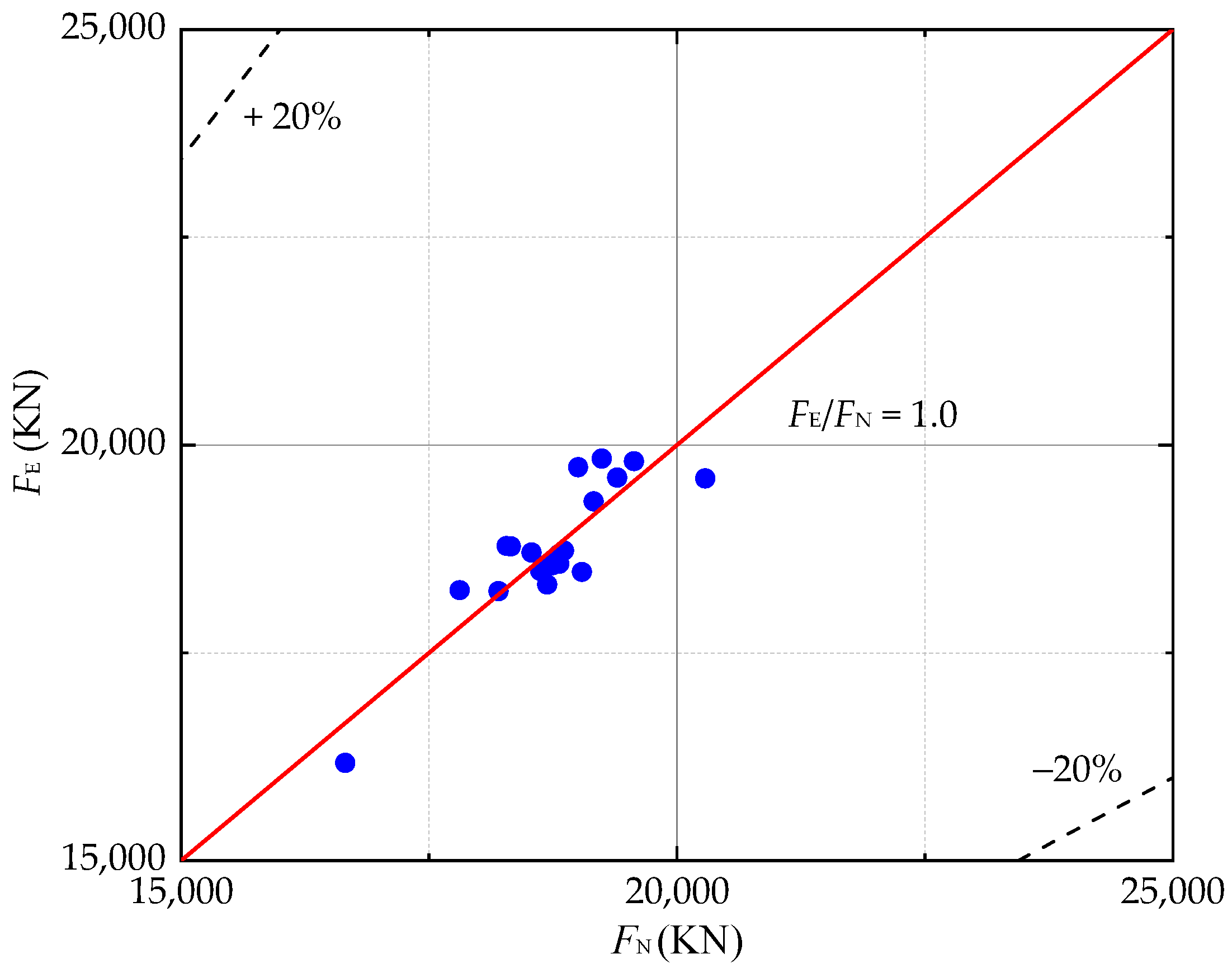
5.2. Empirical Formula
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Teng, B. Wave Action on Maritime Structures, 2nd ed.; Oceanic Express: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Wang, C.M.; Utsunomiya, T.; Duan, W. Review of recent research and developments on floating breakwaters. Ocean Eng. 2018, 158, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, E.; Ferreras, J.; Sanchez-Tembleque, F. Experimental study on wave transmission coefficient, mooring lines and module connector forces with different designs of floating breakwaters. Ocean Eng. 2011, 38, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; He, F.; Zhang, W. A floating box-type breakwater with slotted barriers. J. Hydraul. Res. 2014, 52, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukogeorgaki, E.; Niki, E.; Lentsiou, M.; Aksel, M.; Yagci, O. Experimental investigation of the hydroelastic and the structural response of a moored pontoon-type modular floating breakwater with flexible connectors. Coast. Eng. 2017, 121, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, M.; Gao, Z.; Xu, T.; Guo, W.; Ji, X.; Yuan, C. Experimental investigation on hydrodynamic effectiveness of a water ballast type floating breakwater. Ocean Eng. 2018, 167, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X. Experimental study on wave attenuation performance of a new type of floating breakwater with twin pontoons and multi porous vertical plates. China Ocean Eng. 2022, 36, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Domenico, D.M. Comparison of hydrodynamic performances between single pontoon and double pontoon floating breakwaters through the SPH method. China Ocean Eng. 2022, 36, 894–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, N. Flow mechanism of impulsive wave forces and improvement on hydrodynamic performance of a comb-type breakwater. Coastal Eng. 2018, 133, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Zang, Z.P.; Zhang, J.F. Experimental study on the hydrodynamic characteristics of a fixed comb-type floating breakwater. Water 2023, 15, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Teng, B.; Guan, C.; Lin, D. Experiments on wave transmission coefficients of floating breakwaters. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Z. Hydrodynamic performance of a T-shaped floating breakwater. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 82, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruol, P.; Martinelli, L.; Pezzutto, P. Formula to predict transmission for π-type floating breakwaters. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2012, 139, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, S.; Duan, W. A new L type floating breakwater derived from vortex dissipation simulation. Ocean Eng. 2018, 164, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, E.D.; Bingham, H.B.; Skou Friis, A.P.; Larsen, A.K.; Jensen, K.L. An experimental and numerical study of floating breakwaters. Coastal Eng. 2018, 137, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, P.; Duan, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, B. Experimental study on the dissipation characteristics of curtain-type flexible floating breakwater. J. Coastal Res. 2015, 73, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhao, D.; Wang, M. Study on wave dissipation characteristics of flexible floating breakwater. Yangtze River 2017, 48, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- López, A.; Ferreras, J.; Peña, E. Structural performance of a floating breakwater for different mooring line typologies. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2013, 140, 04014007. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, A. Experimental study on hydrodynamic characteristics of the box-type floating breakwater with different mooring configurations. Ocean Eng. 2022, 254, 111296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeren, Y.; Wren, D.G.; Altinakar, M.; Work, P.A. Experimental investigation of cylindrical floating breakwater performance with various mooring configurations. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2011, 137, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, Q.; Wang, G. Fully coupled dynamic analysis of a FPSO and its MWA system with mooring lines and risers. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 58, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; He, M.; Li, Y.; Dong, P. Application of smoothed particle hydrodynamics for modeling the wave-moored floating breakwater interaction. Appl. Ocean Res. 2017, 67, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc. AQWA Reference Manual; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Shao, X. Numerical Study on Wave Dissipation Performance of OWC-Perforated Floating Breakwater under Irregular Waves. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Chen, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, L.; Zhao, W. A constant parameter time domain model for dynamic modelling of multi-body system with strong hydrodynamic interactions. Ocean Eng. 2023, 268, 113376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, F. Experimental Study on Wave Dissipation Characteristic of a Double-box Floating Breakwater with Regulating Function. Port Eng. Technol. 2017, 54, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeno, M.; Shimoda, N.; Iwata, K. A new type of breakwater utilizing air compressibility. In Proceedings of the 21st Coastal Engineering Conference, ASCE, Torremolinos, Spain, 20–25 June 1988; pp. 2326–2339. [Google Scholar]
- Murali, K.; Mani, J.S. Performance of cage floating breakwater. J. Waterw. Port. Coast. Ocean Eng. 1997, 123, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzaki, K.I.; Ikehata, Y.; Matsunaga, N. Performance of the wave energy dissipation of a floating breakwater with truss structures and the quantification of transmission coefficients. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, J.S. Design of Y-frame floating breakwater. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2014, 117, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.C.; Ma, Q.W.; Duan, W.Y.; Ma, S. Numerical prediction and experimental measurement on truss spar motion and mooring tension in regular waves. J. Ship Mech. 2016, 20, 288–305. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; You, Z.; Bai, X.; Liu, Z.; Geng, J.; Johanning, L. Experimental and numerical analysis on the mooring tensions of the coupled tunnel-barge system in waves. Ocean Eng. 2021, 235, 109417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Floating Breakwater Type | Reference | d/L | H/L | B/L | Kt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two pontoon types | Ikeno et al. (1988) [27] | 0.33 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.68 |
| Single-box type | Ikeno et al. (1988) [27] | 0.33 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.88 |
| Y-frame without pipe | Mani (2014) [30] | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.92 |
| Y-frame with pipe | Mani (2014) [30] | 0.46 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.46 |
| Cage type | Murali & Mani (1997) [28] | 0.46 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.50 |
| Box type with steel truss | Uzaki et al. (2011) [29] | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.91 |
| Porous breakwater | Ji et al. (2016) [21] | 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.86 |
| Mesh cage breakwater | Ji et al. (2016) [21] | 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.88 |
| Single-box type | Present study | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.86 |
| Multi-buoy type | Present study | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Qiao, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, T. Numerical Study on Wave Dissipation and Mooring Force of a Horizontal Multi-Cylinder Floating Breakwater. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030449
Zang Z, Fang Z, Qiao K, Zhao L, Zhou T. Numerical Study on Wave Dissipation and Mooring Force of a Horizontal Multi-Cylinder Floating Breakwater. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(3):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030449
Chicago/Turabian StyleZang, Zhipeng, Zhuo Fang, Kuan Qiao, Limeng Zhao, and Tongming Zhou. 2024. "Numerical Study on Wave Dissipation and Mooring Force of a Horizontal Multi-Cylinder Floating Breakwater" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 3: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030449
APA StyleZang, Z., Fang, Z., Qiao, K., Zhao, L., & Zhou, T. (2024). Numerical Study on Wave Dissipation and Mooring Force of a Horizontal Multi-Cylinder Floating Breakwater. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(3), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030449








