Abstract
The ecological succession has been widely studied by means of biofouling assemblages among different substrates, and mainly targeted in early stages on artificial ones. The present study focuses on biofouling that colonizes carbonated structures, a material similar to the natural substrate produced by the electrolysis of seawater, which is relatively very little studied. We have observed the colonization of sessile macrofouling of the port of Alicante (SE Spain, Western Mediterranean) on two types of substrates (electrolytic carbonated and steel) over 12 months of succession. The assemblages of both substrates have been analyzed by means of diversity indexes and multivariate analysis (PERMANOVA and SIMPER) in order to see the differences over time. The carbonated substrate has presented a community with higher values of biological diversity, structure and complexity, although the differences in species composition between substrates are not evident during all immersion periods. Thus, these results seem to indicate that, even after 12 months of immersion, communities are still in a dynamic successional stage.
1. Introduction
The ecological succession is a process in which a serial substitution of species takes place, with the consequent structural and functional changes in the community, after the appearance of (new) free space [1]. Regarding this, the biofouling community has been widely studied in order to understand how the primary and secondary succession processes work in the marine environment, principally in the intertidal zone [2,3,4]. However, during the last years, the studies are being focused in the subtidal zone [5,6,7]. Being aware of how the succession works is important for the correct management of marine ecosystems, not only to develop artificial reefs, but also to control the recruited organisms on the artificial submerged structures in the marine environment [5,8,9,10].
Many studies have been carried out about the initial stages of colonization, and it has been shown that the sequence of early colonizers will have an effect on the biodiversity and structuration of the developed fouling communities [5,11,12,13,14]. This early colonization will depend on propagule availability and environmental conditions, as most of the macrofouling organisms are driven by seasonality [1,6,15]. Another factor which influences the colonization and succession process is the substrate material. This affects directly to the species preference [16,17,18], generating differences in the biofouling assemblages in the early stages of colonization and maintaining them over time [6,8,19,20]. In fact, many studies have been carried out comparing biofouling communities between different substrates (natural and artificial), and they showed that the communities differ in terms of species composition, structure, diversity and biotic interactions [5,21,22,23], generating even different biofouling communities within the same habitat and environmental conditions (e.g., [1,8,11,24,25]). Moreover, it has been seen that several natural materials, like sandstone, or even concrete (which can be considered as an artificial stone) may present higher biodiversity than other materials like steel [19,23,26], as they are more similar to natural rock [17,27]. In this regard, the succession process in the biofouling is affected by the time and the early colonizers, so that the events occurring during the process, principally in the early stages, will affect the final result, leading to different successional biofouling communities which will finish at different endpoints [6,28]. Nevertheless, some authors (e.g., [14,29,30]) have recorded that those different endpoints tend to converge and homogenize to the same local community. In fact, regarding the experiments performed with different substrates in the same habitat and environmental conditions, the same controversy appeared, as some authors found that communities converge [8] and others do not [19].
The substrate may cause differences within biofouling assemblages, so the type of material to choose is a relevant factor when it comes to building artificial reefs [19]. Most artificial reefs are made of artificial materials like concrete, steel, fiberglass and PVC [31], but only a few are built of natural rock, which has a higher initial recruitment than other artificial materials [16,17,27]. In fact, new concrete compositions are being developed to improve this artificial substrate’s ecological properties [17,32,33]. Hence, there is a need to find materials with similar characteristics to natural rock in order to use them as material for artificial reefs or other marine structures. One of these materials is electrolytic carbonated substrate. This substrate is the consequence of the application of electrolysis to metallic materials immersed in sea water, for instance when preventing the corrosion of marine metallic structures by cathodic protection [34]. Along the process, a carbonated layer, made of CaCO3 and Mg(OH)2, precipitates around the cathode [35,36,37]. This layer is generated from the salts dissolved in the surrounding marine water, which allows this layer to be like natural carbonated rocks [31]. The potential of this material for the construction of artificial reefs was shown by Hilbertz [36], but scarce studies were performed. In fact, most of them have been carried out in tropical areas for the restoration of coral reefs [38,39,40,41] and they do not observe the colonization of other species, but corals.
Thus, the aim of this work is to observe the colonization of sessile macrofouling of the port of Alicante on two types of substrates (electrolytic carbonated and steel) over 12 months of succession. We hypothesized that the colonization and succession would be more effective in the electrolytic carbonated one as it is more like natural environment/rock. In a previous work [42], the colonization (after 3 months of immersion) of the different substrates was studied, being significantly higher in the carbonated structures. In addition, it is aimed to determine the structure of sessile community over the succession process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
This study was located in Alicante’s harbor (SE Spain), concretely in dock No. 9 (38°20′09.23″ N–00°29′05.81″ W). The experimental work was carried out between 15 October 2019 and 13 October 2020. The dock is located in the outer quay (Figure 1) and has a sandy–muddy seafloor with a maximum depth of 10 m. The mean surface seawater temperature varies according to the season, having a range of 14.1 to 28.3 °C, as well as salinity with a range of 37.8 to 37.3 PSU (according to https://www.puertos.es/es-es, accessed: 17 February 2024).
Figure 1.
Alicante’s harbor location and ninth dock position (white circle). Images adapted from Google Earth via QGIS 3.16.7.
2.2. Sampling
To study the colonization and succession of biofouling, 24 square steel meshes of 15 × 15 cm were used, 12 of which were previously subjected to an electrolytic process as in [36], until a 0.5 mm carbonated layer was deposited around them. In this way, 12 bare steel meshes acted as the control treatment. The meshes were arranged in three horizontal profiles of eight meshes each, four of each type, and they were placed alternately within the profile. The three profiles (all 24 meshes) were anchored at 2 m depth on 15 October 2019 with the help of three small cranes. Note that each profile was separated by 1.5 m. In order to see the colonization process, every 3 months, two meshes (carbonated and bare steel) were manually collected from each profile (a total of six meshes: three carbonated and three bare steel). These collections were made in January, March, June and October. In this way, samples were taken after 3, 6, 9 and 12 months of immersion (hereafter immersed time). The meshes were fixed with 10% formalin–seawater for at least 48 h. Then, the organisms were scraped and identified to the lowest taxon possible (based on World Register of Marine Species: https://www.marinespecies.org accessed: 15 December 2023). Only sessile macrofouling taxa were used in this work.
2.3. Data Treatment
In order to assess the effect of the substrate and the immersed time in the colonization process of sessile biofouling assemblages, both univariate and multivariate analyses were performed. In both cases, a two-way linear model was used, with substrate and immersed time as fixed and orthogonal factors, with two (carbonated vs. control) and four levels (3 vs. 6 vs. 9 vs. 12 months), respectively. It is important to highlight that the third replicate of the carbonated treatment for the last immersed period (12 months) was lost, so the mean value of the other two meshes was used as value for that replicate.
The effect of substrate and immersed time in the diversity of the community was assessed with two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) over the different diversity indexes calculated: species richness (S), Shannon–Wiener index (H′, 2 base), Pielou’s evenness (J′) and abundance (N) organisms/cm2 (for solitary organisms, each organism was counted, whereas for colonial organisms, each colony was treated as a single organism). In the cases that significant differences were found a Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc test was performed.
For the purpose of assessing the effect of substrate and immersed time on the colonization and succession process of biofouling assemblages, a two-way permutational multivariate ANOVA (PERMANOVA) [43] was conducted and a non-metric multidimensional scaling (nMDS) to visualize the results by using Bray–Curtis dissimilarity [44]. Note that, prior to the analysis, the data set was transformed with the fourth root, in order to reduce the weight of most abundant species. Moreover, a Similarity percentage (SIMPER) analysis was performed to detect which species contribute more to the differences and which are the characteristic ones of each substrate and period, and a permutational analysis of dispersion (PERMDISP) to test whether these differences were caused by the factor or the dispersion of the data [45]. Furthermore, a univariate PERMANOVA was performed for each species/taxon determined by SIMPER, in order to detect whether each one’s abundance was significantly different between substrates. For that purpose, Euclidean distance was used when performing PERMANOVA analysis to avoid the assumption of normality of data [43]. PERMANOVA, nMDS, SIMPER and diversity index calculation were conducted in PRIMER v.6+PERMANOVA software [45], whereas the different ANOVA were conducted in R 4.1.2 [46].
3. Results
3.1. Taxonomic Study
We identified 61 different taxa during this study, most of them (53) to species level (see Supplementary Table S1). Among them, 58 (95.1%) have been recruited in the carbonated treatment and 43 (70.5%) in the control one, which means that 18 taxa were exclusive to the carbonated substrate and 3 to the control. In addition, focusing on the different submersion periods per substrate (carbonated vs. control), 29 vs. 14 taxa appeared after 3 months, 32 vs. 19 after 6 months, 43 vs. 29 after 9 months and 23 vs. 21 after 12 months. Among them, nine taxa appeared over the four periods, three are exclusive for the first immersion period, one for the second, eight for the third and six for the last one.
Looking each species in the different periods and substrates, it was found that, among the species which appear over all the immersed times, Balanus trigonus, Turbicellepora magnicostata and Bougainvillia muscus only meet that statement in carbonated substrate, as they are not always present in the control one. Moreover, there are species which appear in both substrates, but they need more time to be recruited in the control treatment. These species are Crisia eburnea, Scrupocellaria scruposa, Spirobranchus triqueter, Hydroides dirampha, Parasabella langerhansi, Leuckartiara octona, Styela plicata, S. canopus, Gregariella petagnae, Anomia ephippium and Leucetta solida.
Referring to the different taxa, Bryozoa has been the most diverse taxa (18 spp.) over the study and Hydrozoa the most abundant (mainly by three species, namely Obelia dichotoma, Bougainvillia muscus and Eudendrium sp.). It must be highlighted, also, that the species Hydroides elegans was the most abundant species (after O. dichotoma) during the study. Analyzing the taxa by treatments (Figure 2), there is a high abundance of Hydrozoa in both substrates during the first two periods of immersion, but in the third one (after 9 months), the abundances of the different taxa are very similar to each other in the case of carbonated treatment, while this is not happening in the control one. In fact, during that period of immersion, the highest species richness for all the taxa in both treatments were recorded. However, after 12 months of immersion, there was again a domination of Hydrozoa, in terms of abundance, and Bryozoa, in terms of richness, as in the beginning of the experiment.
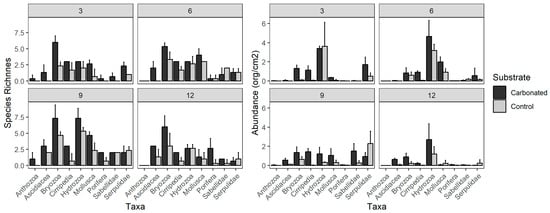
Figure 2.
Graphical representation of species richness and abundance (number of organisms per cm2) for each taxon in the two substrates over the four periods of immersion: (3) October 2019; (6) January 2020; (9) March 2020; (12) June 2020. Bars: standard error. Org equals to organism.
3.2. Biofouling Assemblages
Regarding the effect of substrate and immersed time in the composition of biofouling assemblages, differences were found for both factors and their interaction (Table 1). The biofouling composition was different among substrates after 3 and 9 months of immersion, but not after 6 and 12 months, although there were marginally significant points (Table 1). These results were clearly seen within the nMDS, where different substrates were far from each other in all immersion periods, except for those immersed for 6 months, where points were very close to each other, with a high similarity (60% between them) (Figure 3). Moreover, the SIMPER analysis showed that the dissimilarities among substrates were reduced from the first to second period, but they increased in the following periods, reaching a maximum in the last period (51.91%, 38.72%, 46.2% and 62.5%, respectively). It must be highlighted that the higher dispersion was found in the control (steel) treatment (PERMDISP < 0.05), clearly seen after 12 months, when the similarity within samples was nearly 30%. However, in the carbonated treatment the similarity was always over 70%, except for the samples immersed for 6 months (65.84%).

Table 1.
PERMANOVA results for the abundance of macrofouling assemblages for the different substrates and immersed times. Note: * = p-Value < 0.05, *** = p-Value < 0.001.
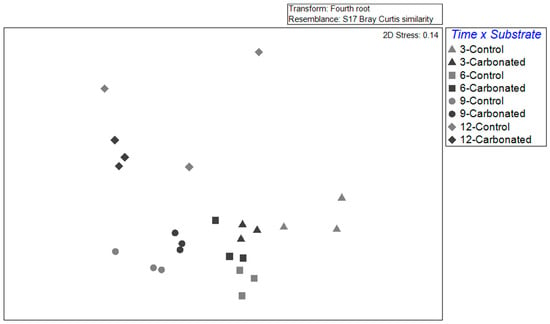
Figure 3.
A non-metric multidimensional scaling (nMDS) based on Bray–Curtis similarity of biofouling assemblages for each immersion length and substrate type.
In addition, the SIMPER analysis showed that the number of species which contributed significantly to the dissimilarity between substrates on each period varied as immersed time went on (nine, five, eleven and seven species, respectively, being always more abundant on the carbonated treatment). Thus, the characterizing species changed over the immersed times: reducing from the first to second period, increasing in the third and decreased again in the last one, highlighting a trend every 6 months. This change in species composition showed also that filter-feeders (ascidians) became typical species as the succession process continued, especially after 12 months. Among the species, Filicrisia geniculata and Perforatus perforatus stood out, as they were typical of the carbonated treatment, and they contributed to the dissimilarity among substrates in the four periods, with a mean contribution of 5.4% in each one. Moreover, another species to highlight is Balanus trigonus, which was also a typical species in the carbonated treatment and had the highest contribution to the dissimilarity in all the periods except for the last one. On the other hand, there were the following species, which characterized the biofouling assemblages of the carbonated treatment on each period: (i) Schizoporella errata, Mytilus galloprovincialis, Spirobranchus triqueter, Turbicellepora magnicostata and Hydroides elegans (3 months); (ii) Obelia dichotoma (6 months); (iii) Bougainvillia muscus, Watersipora subtorquata and Sycon elegans (9 months); and (iv) Styela canopus and Botrylloides cf. niger (12 months). This goes along with the results seen in Section 3.1, as the characterizing species of the biofouling assemblages were the ones which appeared over all the periods of immersion, and they had their greatest differences in terms of abundance between substrates in those periods. In addition, for the cases of S. elegans and B. cf. niger, they only appeared in those periods.
3.3. Biofouling Diversity
Referring to biodiversity, all indexes and abundance were statistically higher in the carbonated substrate (Table 2 and Figure 4). In addition, a temporal trend can be seen, where the species richness and Shannon–Wiener index were higher after 9 months of immersion than in any other period, whereas the abundance was kept similar during the first three periods, before decreasing in the last. Pielou’s evenness was not affected by the immersion length.

Table 2.
ANOVA results for each diversity index and abundance of biofouling community for both substrate and immersed times. Note: * = p-Value < 0.05, ** = p-Value < 0.01, *** = p-Value < 0.001.
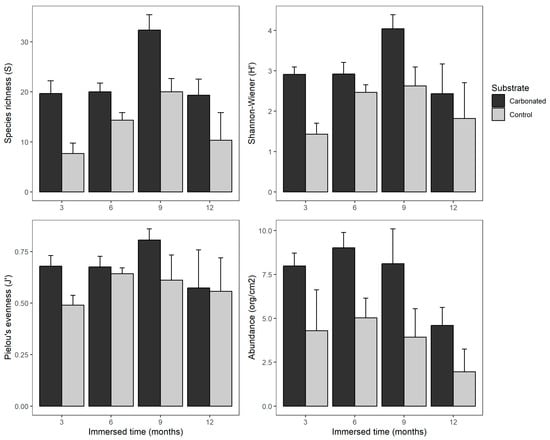
Figure 4.
Bar graph for the different diversity indexes measured and abundance (number of organisms per cm2) for each substrate and immersion length (months). Bars: standard error.
4. Discussion
The substrate caused differences in the biofouling assemblages during the early colonization stage and during the succession process. This is supported by several studies in which the assemblages differed between substrates as succession develops [17,19]. However, in this work, there are periods in which the differences are not clear, suggesting that the biofouling community still remains in a dynamic state, and it did not reach final succession stage, as it did in [6], after being immersed for one year in the Central Mediterranean. In fact, a clear seasonal pattern was observed, in which, every 6 months, the biofouling assemblages tended to converge and then diverge again (only tested for first 6 months, as the study finished after 12 months). These periods corresponded to winter and summer, when recruitment rates were lower and higher, respectively [1,6,14,15]. Nevertheless, both periods have been characterized by a dominance of hydrozoans (Obelia dichotoma and Bougainvillia muscus after 6 months and Eudendrium sp. after 12). Hydrozoans are erect, stolonal and fast-growing species, which gives them the ability to colonize the empty space easily and grow over other species. In fact, this suggests they can exploit the least suitable seasons to colonize better than other species, and, during winter, they can use the space left behind by algae as there is less available light [47]. Furthermore, once the unfavorable winter months left, the diversity of both substrates increased and the differences in biofouling composition appeared again. One reason to explain this is the arborescent three-dimensional growth of hydrozoans, which increases the complexity and colonization of both vagile and sessile species for the next periods. Indeed, it has been proven that they can easily recruit mytilids and some solitary ascidians; among others, this occurred in [47,48,49,50,51] as it happened in this work: the appearance of Mytilus galloprovincialis after 6 months and Styelidae juveniles after 9.
There is no doubt that the presence of propagules in the environment determines the appearance and abundance of certain species relative to others [14,52], and it was observed that species were substituted during the succession process. In fact, this propagule availability in the environment has a seasonality which allows or facilitates the recruitment of some species over others [14,53], leading to different biofouling communities depending on the time of immersion, as reported in Lezzi and Giangrande [6]. However, some species were characteristic of carbonated treatment, appearing in all or almost every period on it (B. trigonus, F. geniculata y P. perforatus) which means that their propagules were abundant in the study area, and they can act as pioneer species and persist on that substrate over time. In fact, these species have a calcareous skeleton, and [54,55] and [26] showed that cathodically protected structures and calcareous substrates have a higher recruitment of barnacles, agreeing with this finding.
On the other hand, a substitution of species was observed as the succession went ahead, where active filter-feeders (mainly ascidians) became more important, particularly at the end of the experiment. The dominant ascidians were the typical ones of port environments and during the summer months [51,56]. In the case of ascidians, it has been reported that their larvae prefer rough surfaces to settle [21,57] explaining why they are more abundant on the carbonated substrate. Moreover, during this species substitution process, there are species, such as Crisia denticulata, Savignyella lafontii, Botrylloides cf. niger, Ostrea stentina, S. ciliatum and Sycon sp., which appeared only after 12 months. This finding is explained by the seasonality of the species (as in the case of B. cf. niger, which is a typical species of warm periods) or by the need of a developed pioneer community to settle, as in the case of Sycon spp., which need a developed algal community [58]. In addition, a lag in the recruitment of certain species (Scrupocellaria scruposa, Spirobranchus triqueter, Hydroides dirampha, Parasabella langerhansi, Leuckartiara octona, Styela plicata and S. canopus) can be observed between both substrates. These species took at least one trimester longer to be recruited in the control treatment, which reinforces the fact that the carbonated substrate has higher recruitment and diversity rates. This may be due to the fact that the pioneer community developed more rapidly in the carbonated substrate, not only because of its greater capacity for initial recruitment [42], but also because of the greater abundances of hard-shelled organisms, such as balanids and mytilids, and hard-bodied organisms like solitary ascidians, among others. These organisms are able to generate more space to be colonized by other organisms, thus increasing the capacity for recruitment of new species over time. Furthermore, as recruitment is also dependent on the presence of propagules in the environment, the gap in the recruitment among both substrates could be explained by the enhancement of propagules from the species that developed in the carbonated treatment, which were easier recruited in the carbonated meshes.
The higher biological diversity values were obtained in the carbonated treatment, being significantly higher after 3, 6 and 9 months, and decreasing in the last period. These findings are consistent with other studies [19,23,26] that found higher biological diversity values in natural rock and concrete substrates that were similar to electrolytic carbonated substrates. Moreover, the results are comparable to studies conducted by Neves et al. [59] and Albano and Obenat [23], in which calcareous substrates, such as concrete, had a higher abundance of organisms than other substrate types because their surfaces are similar to natural rocks. The differences found among substrates are consistent over time from the beginning of colonization, indicating that the carbonated substrate is capable of generating a more structured and developed fouling community in less time than steel. Nevertheless, a drop in the diversity and abundance of organisms has been observed after 12 months of immersion, matching with a certain homogenization of the assemblages, possibly due to greater competition among species due to substrate limitation [5,60]. It was in this period when the higher dissimilarities between substrates were found and a dominance of Eudendrium sp. was detected in both substrates. The remaining dominant species differed according to the substrate, with arborescent bryozoans and ascidians (mostly solitary) predominant in the carbonated one and hydrozoans and serpulids (H. elegans) in the control. The dominance of these fast-growing and high space colonizer fouling species [61] may explain the decreasing of indexes and the convergency, rather than statistical differences, of assemblages in this period. However, it was expected that the diversity and the abundance of organisms will continue increasing, due to a major propagule supply enhanced by the warming of seawater [1,6,14,62,63]. Nevertheless, the effect of higher temperatures during the last period of sampling (the meshes submerged for 12 months) could also explain the decreasing of abundance of fouling species as some species cannot cope with them, mainly the ones dominant during the cold months.
As has been explained, the dissimilarities within the biofouling assemblages in the substrates were high and there was not a clear homogenization of communities among both substrates after 12 months of immersion, as there was when the dissimilarities were higher. Hence, it indicates that the communities did not reach an endpoint. So, a longer-term study is required, as conducted in other works (e.g., [8,19]) to elucidate where the communities reach and how the succession process develops on both substrates. In fact, it could be hypothesized that, as carbonated treatment has more dead and alive hard-bodied species, once the warm period has ceased, the largest space availability of that substrate will be easily and rapidly colonized by species. In addition, considering the seasons, a complementary work is suggested by the authors in order to see the effect of immersion time (season) on both early colonization and succession over the two substrates, as was carried out in [6,14,15], and to determine the seasonal peaks of the species from Alicante’s harbor.
Based on the above, the carbonated substrate presented a community with higher values of biological diversity, structure and complexity, although the differences in species composition between substrates were not evident during all immersion periods, which seems to indicate that, even after 12 months, the communities were still in a dynamic successional stage.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jmse12030443/s1. Table S1: average abundance (X + SE) of the observed taxons (organisms/cm2) by moth and substrata: (C) carbonated; (S) steel. Table S2: SIMPER results for the abundance of biofouling assemblages (fourth root transformed data). Note: * = p-Value < 0.05, ** = p-Value < 0.01, *** = p-Value < 0.001.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.-Á.C. and A.A.R.-E.; methodology, A.C.-R., C.A., M.-Á.C., P.G., V.M. and A.A.R.-E.; formal analysis, A.C.-R.; investigation, A.C.-R., C.A., M.-Á.C., P.G., V.M. and A.A.R.-E.; writing—original draft preparation, A.C.-R.; writing—review and editing, C.A., M.-Á.C., P.G., V.M. and A.A.R.-E.; supervision, M.-Á.C. and A.A.R.-E.; project administration, A.A.R.-E.; funding acquisition, A.A.R.-E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research forms part of the ThinkInAzul program and was funded by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación with funding from European Union NextGenerationEU (PRTR-C17.I1) and by Generalitat Valenciana (THINKINAZUL/2021/014).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Port Authority of Alicante for their support and to facilitate the work in the port.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Jenkins, S.R.; Martins, G.M. Succession on Hard Substrata. In Biofouling; Simone, D., Jeremy, C.T., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J.; Underwood, A.J. Effects of Substratum on the Recruitment and Development of an Intertidal Estuarine Fouling Assemblage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1994, 184, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.M.; Swearingen, D.C. Effects of Seasonality, Length of Immersion, Locality and Predation on an Intertidal Fouling Assemblage in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1998, 225, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraitis, P.S.; Dudgeon, S.R. Experimental Evidence for the Origin of Alternative Communities on Rocky Intertidal Shores. Oikos 1999, 84, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-J.; Shao, K.-T. The Development of Subtidal Fouling Assemblages on Artificial Structures in Keelung Harbor, Northern Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2002, 41, 170–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lezzi, M.; Giangrande, A. Seasonal and Bathymetric Effects on Macrofouling Invertebrates’ Primary Succession in a Mediterraenan Non-Indigenous Species Hotspot Area. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 572–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, T.; Hassenrück, C.; Al Fahdi, D.; Jose, L.; Al Senafi, F.; Mahmoud, H.; Abed, R.M.M. Monthly Succession of Biofouling Communities and Corresponding Inter-Taxa Associations in the North- and South-West of the Arabian Gulf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 787879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulleri, F. Role of Recruitment in Causing Differences between Intertidal Assemblages on Seawalls and Rocky Shores. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 287, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierri, C.; Longo, C.; Giangrande, A. Variability of Fouling Communities in the Mar Piccolo of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Mediterranean Sea). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2010, 90, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megina, C.; González-Duarte, M.M.; López-González, P.J.; Piraino, S. Harbours as Marine Habitats: Hydroid Assemblages on Sea-Walls Compared with Natural Habitats. Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J.P.; Karlson, R.H. Development and Stability of the Fouling Community at Beaufort, North Carolina. Ecol. Monogr. 1977, 47, 425–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L. Predicting Direct and Indirect Interactions during Succession in a Mid-Littoral Rocky Shore Assemblage. Ecol. Monogr. 2000, 70, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wu, R.S.S. Seasonal Effects on Recolonization of Macrobenthos in Defaunated Sediment: A Series of Field Experiments. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 351, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, M.; Krueger, I.; Dumont, C.P.; Lenz, M.; Thiel, M. Does Primary Colonization or Community Structure Determine the Succession of Fouling Communities? J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 395, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezzi, M.; Del Pasqua, M.; Pierri, C.; Giangrande, A. Seasonal Non-Indigenous Species Succession in a Marine Macrofouling Invertebrate Community. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 937–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz-Pinto, F.; Torrontegi, O.; Prestes, A.C.L.; Álvaro, N.V.; Neto, A.I.; Martins, G.M. Invasion Success and Development of Benthic Assemblages: Effect of Timing, Duration of Submersion and Substrate Type. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 94, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sempere-Valverde, J.; Ostalé-Valriberas, E.; Farfán, G.M.; Espinosa, F. Substratum Type Affects Recruitment and Development of Marine Assemblages over Artificial Substrata: A Case Study in the Alboran Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 204, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, L.B.; White, F.J.; Schofield, M.; Hanley, M.E.; Burrows, M.T.; Thompson, R.C.; Skov, M.W.; Evans, A.J.; Moore, P.J.; Hawkins, S.J. Facing the Future: The Importance of Substratum Features for Ecological Engineering of Artificial Habitats in the Rocky Intertidal. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 67, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J. Epifaunal Colonization of the Loch Linnhe Artificial Reef: Influence of Substratum on Epifaunal Assemblage Structure. Biofouling 2005, 21, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainburg, L.A.; Trassens, M.E.; Bastida, J.; Farenga, M.O.; Isla, F.I.; Bastida, R.O. Nearshore Benthic Communities and Bioengineers from the Macrotidal San Jorge Gulf: Patagonia, Argentina. Thalass. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 28, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chase, A.L.; Dijkstra, J.A.; Harris, L.G. The Influence of Substrate Material on Ascidian Larval Settlement. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megina, C.; González-Duarte, M.M.; López-González, P.J. Biofouling the Journal of Bioadhesion and Biofilm Research Benthic Assemblages, Biodiversity and Invasiveness in Marinas and Commercial Harbours: An Investigation Using a Bioindicator Group. Biofouling 2016, 32, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, M.J.; Obenat, S.M. Fouling Assemblages of Native, Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species on Artificial Structures, Depths and Temporal Variation. J. Sea Res. 2019, 144, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulleri, F.; Chapman, M.G.; Underwood, A.J. Intertidal Assemblages on Seawalls and Vertical Rocky Shores in Sydney Harbour, Australia. Austral. Ecol. 2005, 30, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meester, L.; Vanoverbeke, J.; Kilsdonk, L.J.; Urban, M.C. Evolving Perspectives on Monopolization and Priority Effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushiama, S.; Smith, J.A.; Suthers, I.M.; Lowry, M.; Johnston, E.L. The Effects of Substratum Material and Surface Orientation on the Developing Epibenthic Community on a Designed Artificial Reef. Biofouling 2016, 32, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuhmacher, H.; Schillak, L. Integrated Electrochemical and Biogenic Deposition of Hard Material—A Nature-like Colonization Substrate. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 672–679. [Google Scholar]
- Beisner, B.E.; Haydon, D.T.; Cuddington, K. Alternative Stable States in Ecology. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 343–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.; Edwards, M.; Firth, L.; Johnson, M. Successional Changes of Epibiont Fouling Communities of the Cultivated Kelp Alaria Esculenta: Predictability and Influences. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2017, 9, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaza, A.K.; Williams, J.P. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of the Overwater Structure Fouling Community in Southern California. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 1771–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siboni, N.; Martinez, S.; Abelson, A.; Sivan, A.; Kushmaro, A. Conditioning Film and Initial Biofilm Formation on Electrochemical CaCO3 Deposition on a Metallic Net in the Marine Environment. Biofouling 2009, 25, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, R.S.; Archibald, N.; Comber, S.; Knights, A.M.; Thompson, R.C.; Firth, L.B. Partial Replacement of Cement for Waste Aggregates in Concrete Coastal and Marine Infrastructure: A Foundation for Ecological Enhancement? Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkol-Finkel, S.; Hadary, T.; Rella, A.; Shirazi, R.; Sella, I. Seascape Architecture—Incorporating Ecological Considerations in Design of Coastal and Marine Infrastructure. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.C. Anticorrosive and Antifouling Coating and Method of Application. U.S. Patent No. 2,200,469, 14 May 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Eickhoff, A.J.; Shaw, W.E. Principles of Protecting Metals with Organic Coatings. Corrosion 1948, 4, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbertz, W.H. Electrodeposition of Minerals in Sea Water: Experiments and Applications. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1979, 4, 94–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartt, W.H.; Culberson, C.H.; Smith, S.W. Calcareous Deposits on Metal Surfaces in Seawater—A Critical Review. Corrosion 1984, 40, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakti, L.A.A.; Virgota, A.; Damayanti, L.P.A.; Radiman, T.H.U.; Retnowulan, A.; Sabil, A.; Robbe, D. Biorock Reef Restoration in Gili Trawangan, North Lombok, Indonesia. In Innovative Methods of Marine Ecosystem Restoration; Goreau, T.J., Trench, R.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Fitri, D.; Rachman, M.A. Gorgonian Soft Corals Have Higher Growth and Survival in Electrical Fields. In Innovative Methods of Marine Ecosystem Restoration; Goreau, T.J., Trench, R.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Goreau, T.J. Marine Electrolysis for Building Materials and Environmental Restoration. In Electrolysis; Linkov, V., Kleperis, J., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Goreau, T.J.; Hilbertz, W. Reef Restoration Using Seawater Electrolysis in Jamaica. In Innovative Methods of Marine Ecosystem Restoration; Goreau, T.J., Trench, R.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Rodríguez, A.; Antón, C.; Climent, M.Á.; Garcés, P.; Montiel, V.; Ramos-Esplá, A.A. Early Colonization of Sessile Megabenthos on Electrolytic Carbonated Structures (Alicante’s Harbor, Western Mediterranean). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.; Gorley, R.; Somerfield, P.; Warwick, R. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 3rd ed.; Primer-E Ltd.: Albany, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; Primer-E: Albany, New Zealand, 2008; pp. 1–224. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Boero, F. The Ecology of Marine Hydroids and Effects of Environmental Factors: A Review. Mar. Ecol. 1984, 5, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, T.A.; Hurd, L.E. Development in an Estuarine Fouling Community: The Influence of Early Colonists on Later Arrivals. Oecologia 1980, 46, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, T.A. Structural Aspects of Sessile Invertebrates as Organizing Forces in an Estuarine Fouling Community. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1981, 53, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.; Sherman, H.; Harris, L.G. The Role of Colonial Ascidians in Altering Biodiversity in Marine Fouling Communities. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 342, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldred, N.; Clare, A.S. Mini-Review: Impact and Dynamics of Surface Fouling by Solitary and Compound Ascidians. Biofouling 2014, 30, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Romero, C.; de la Cruz, M.; Escribano-Ávila, G.; García-Fernández, A.; Iriondo, J.M. What Causes Conspecific Plant Aggregation? Disentangling the Role of Dispersal, Habitat Heterogeneity and Plant–Plant Interactions. Oikos 2016, 125, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimanski, K.B.; Goldstien, S.J.; Hopkins, G.A.; Atalah, J.; Floerl, O. Life History Stage and Vessel Voyage Profile Can Influence Shipping-Mediated Propagule Pressure of Non-Indigenous Biofouling Species. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eashwar, M.; Ananth, V.; Paulraj, S.; Subramanian, G. Biofouling Studies Relating to Cathodic Protection of Some Metals in Seawater. Bull. Electrochem. 1985, 1, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Eashwar, M.; Subramanian, G.; Chandrasekaran, P.; Manickam, S.T.; Maruthamuthu, S.; Balakrishnan, K. The Interrelation of Cathodic Protection and Marine Macrofouling. Biofouling 1995, 8, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Esplá, A.A. Ascidias Litorales del Mediterráneo Ibérico: Faunística, Ecología y Biogeografía. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.; Ubagan, M.D.; Shin, S.; Kim, D.G. Comparison of Recruitment Patterns of Sessile Marine Invertebrates According to Substrate Characteristics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brümmer, F.; Nickel, M.; Sidri, M. Porifera (Esponjas). In El Mar Mediterráneo II/1: Guía Sistemática y de Identificación; Hofrichter, R., Ed.; Ediciones Omega, S.A.: Barcelona, Spain, 2005; pp. 302–383. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, C.S.; Rocha, R.M.; Pitombo, F.B.; Roper, J.J. Use of Artificial Substrata by Introduced and Cryptogenic Marine Species in Paranaguá Bay, Southern Brazil. Biofouling 2007, 23, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.A.; Dias, G.M.; Flores, A.A.V. Adding Early-Stage Engineering Species Affects Advanced-Stage Organization of Shallow-Water Fouling Assemblages. Hydrobiologia 2018, 818, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oricchio, F.T.; Marques, A.C.; Hajdu, E.; Pitombo, F.B.; Azevedo, F.; Passos, F.D.; Vieira, L.M.; Stampar, S.N.; Rocha, R.M.; Dias, G.M. Exotic Species Dominate Marinas between the Two Most Populated Regions in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklinski, P.; Berge, J.; McFadden, L.; Dmoch, K.; Zajaczkowski, M.; Nygård, H.; Piwosz, K.; Tatarek, A. Seasonality of Occurrence and Recruitment of Arctic Marine Benthic Invertebrate Larvae in Relation to Environmental Variables. Polar Biol. 2013, 36, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, J.P. Temperature, Space Availability, and Species Assemblages Impact Competition in Global Fouling Communities. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).