A Data-Driven Approach to Identify Major Air Pollutants in Shanghai Port Area and Their Contributing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Site and Data Description
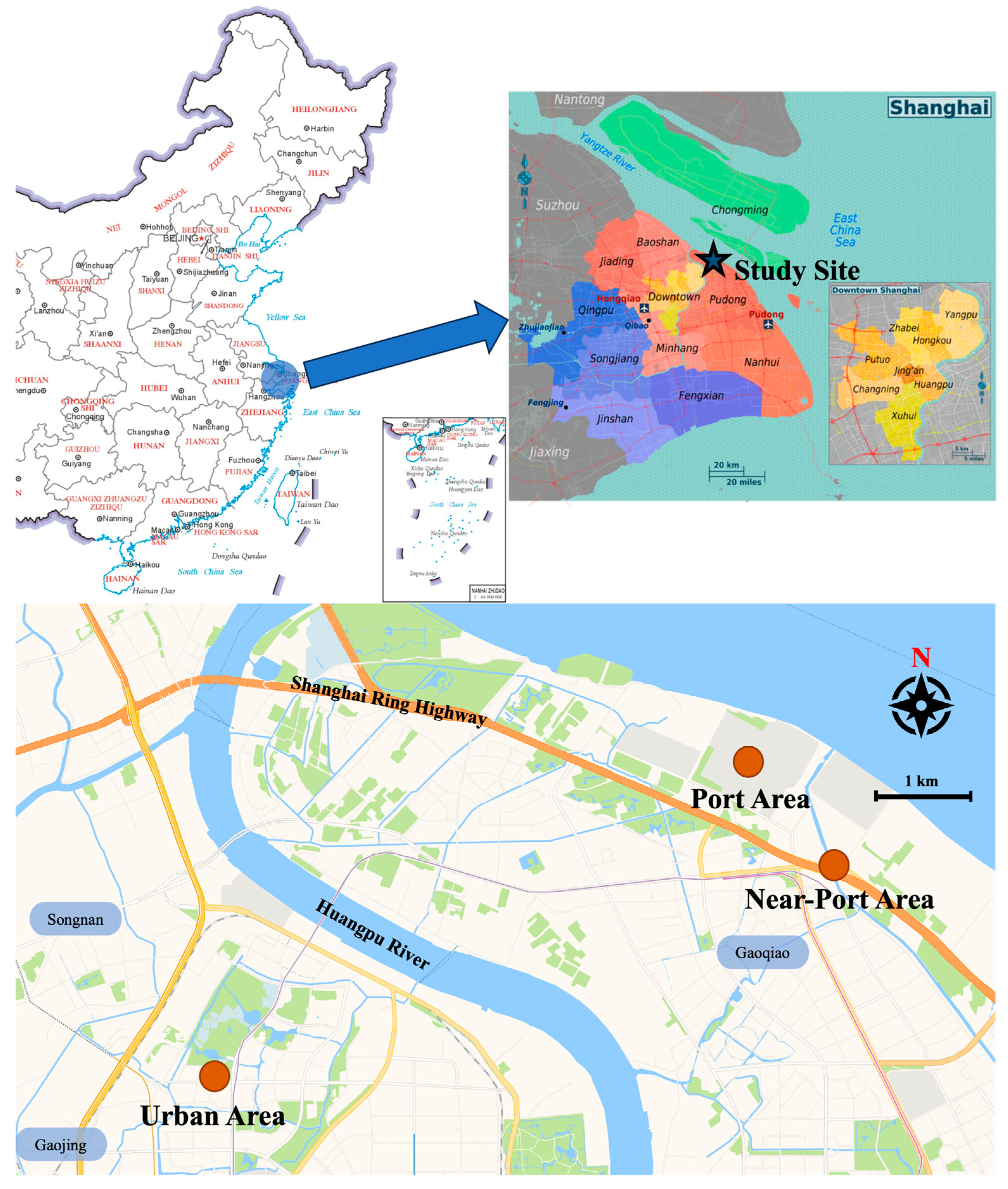
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Data Description
2.3. Data Preprocessing
3. Methodology
3.1. Random Forest
3.2. Orthogonal Experimental Design
4. Results and Analysis
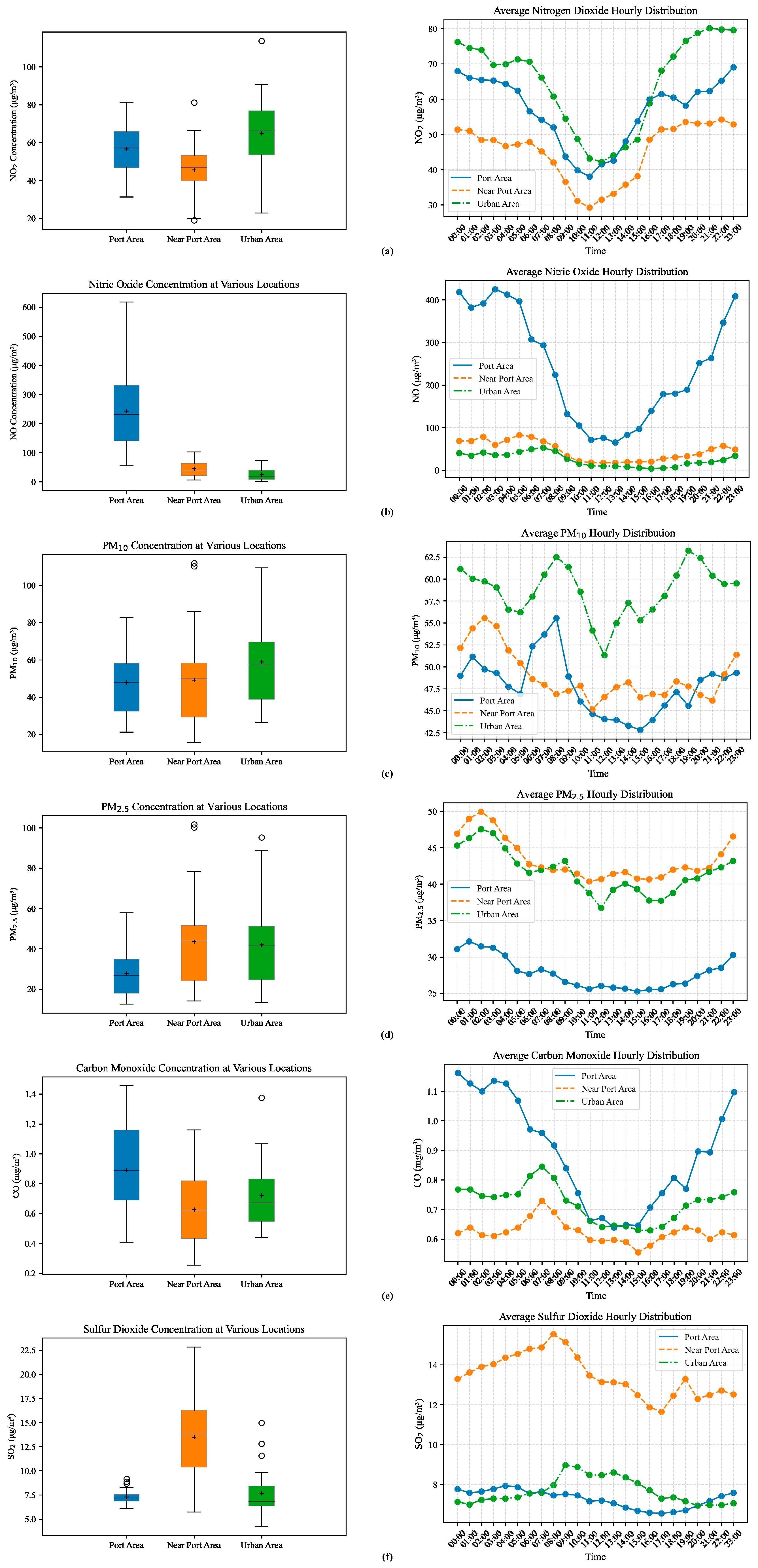
4.1. Major Pollutants in the Port Area
4.1.1. NO and CO
4.1.2. NO2
4.1.3. SO2
4.1.4. PM10 and PM2.5
4.2. Source Contribution Analysis
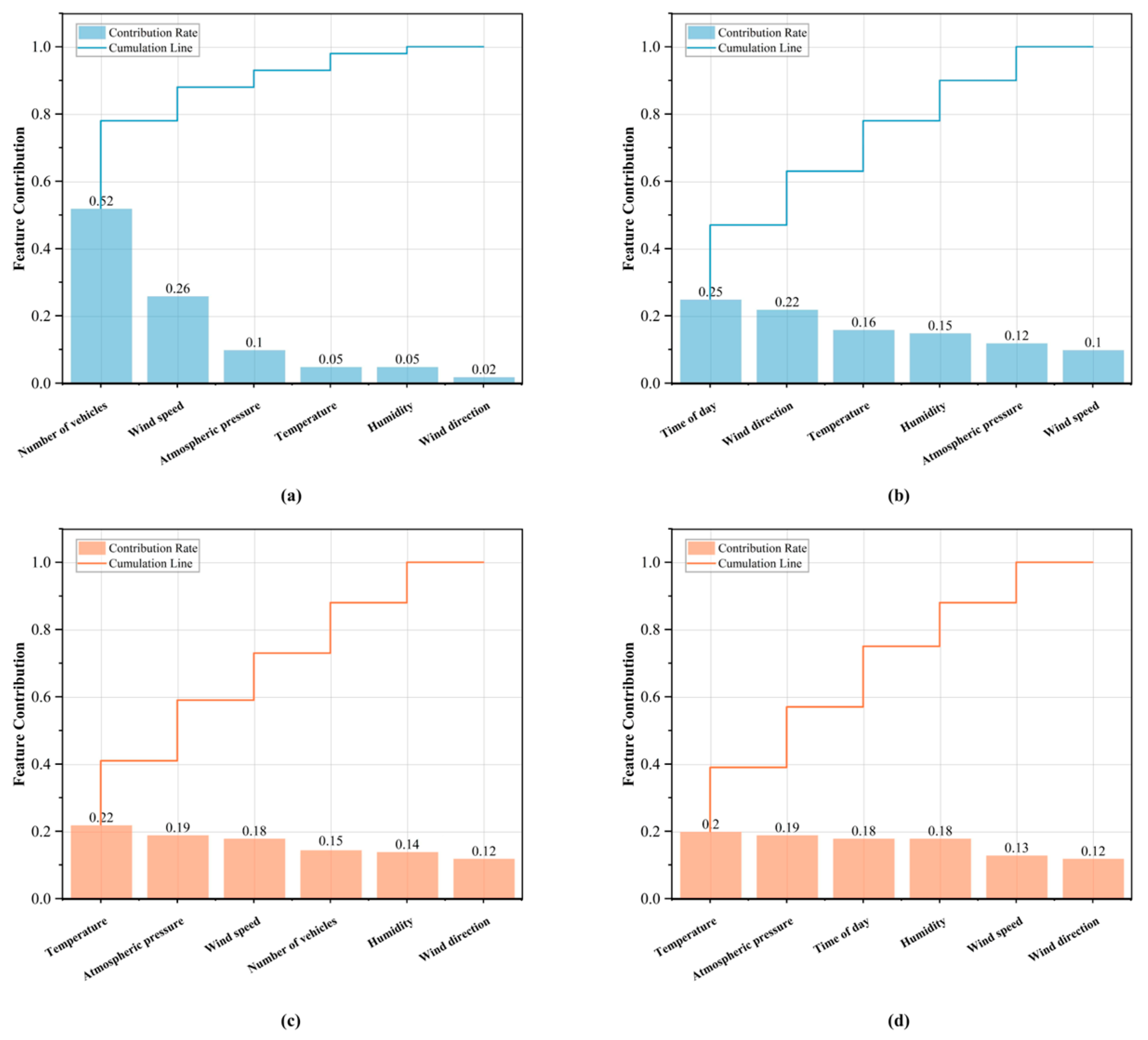
4.3. Impact Analysis of Important Factors
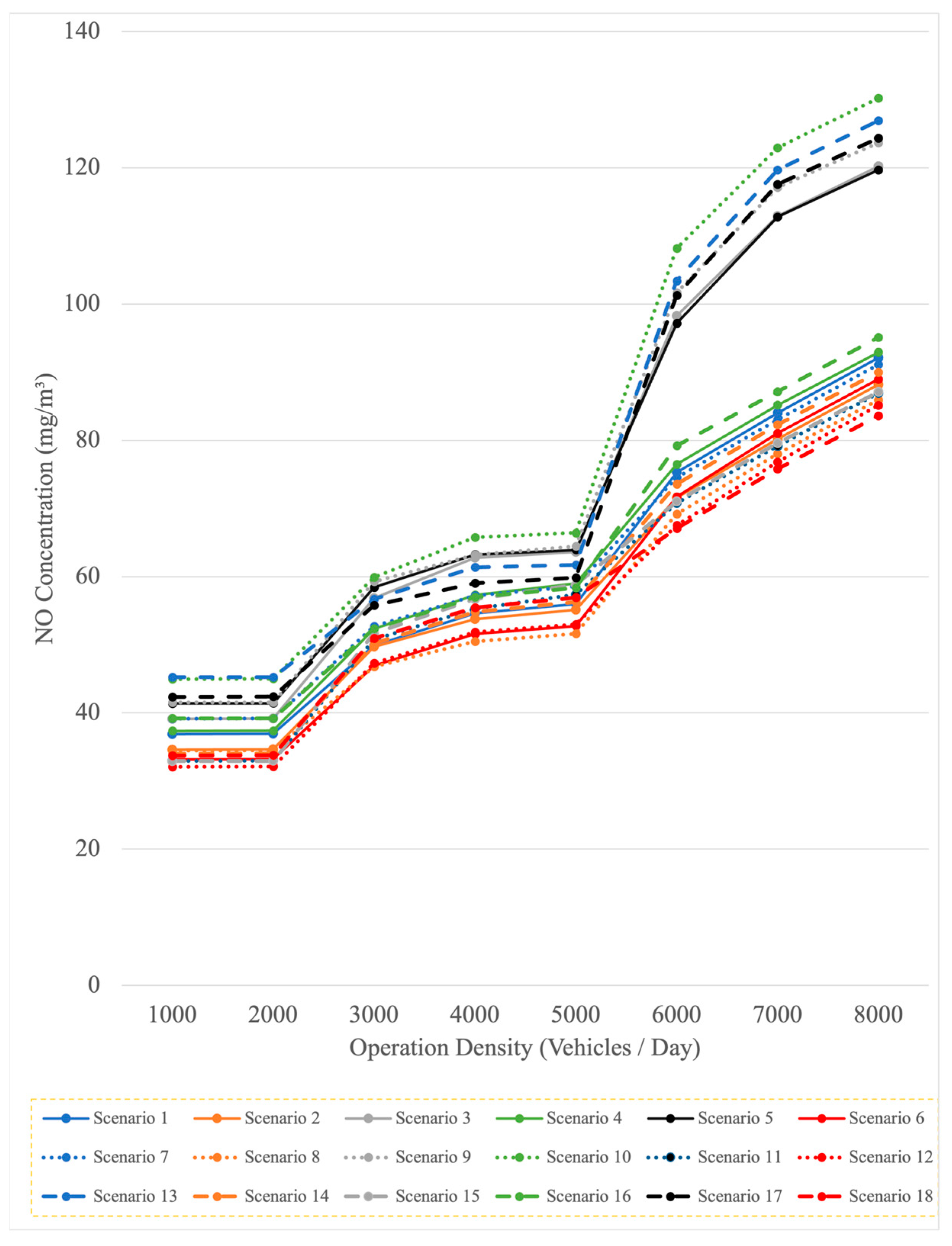
4.3.1. Number of Vehicles
- Temperature: high (15 °C), medium (10 °C), low (5 °C);
- Air Pressure: high (1030 hPa), medium (1020 hPa), low (1010 hPa);
- Humidity: high (85%), medium (75%), low (70%);
- Wind Speed: high (3 km/h), medium (2 km/h), low (1 km/h);
- Wind Direction: SE, S, N.
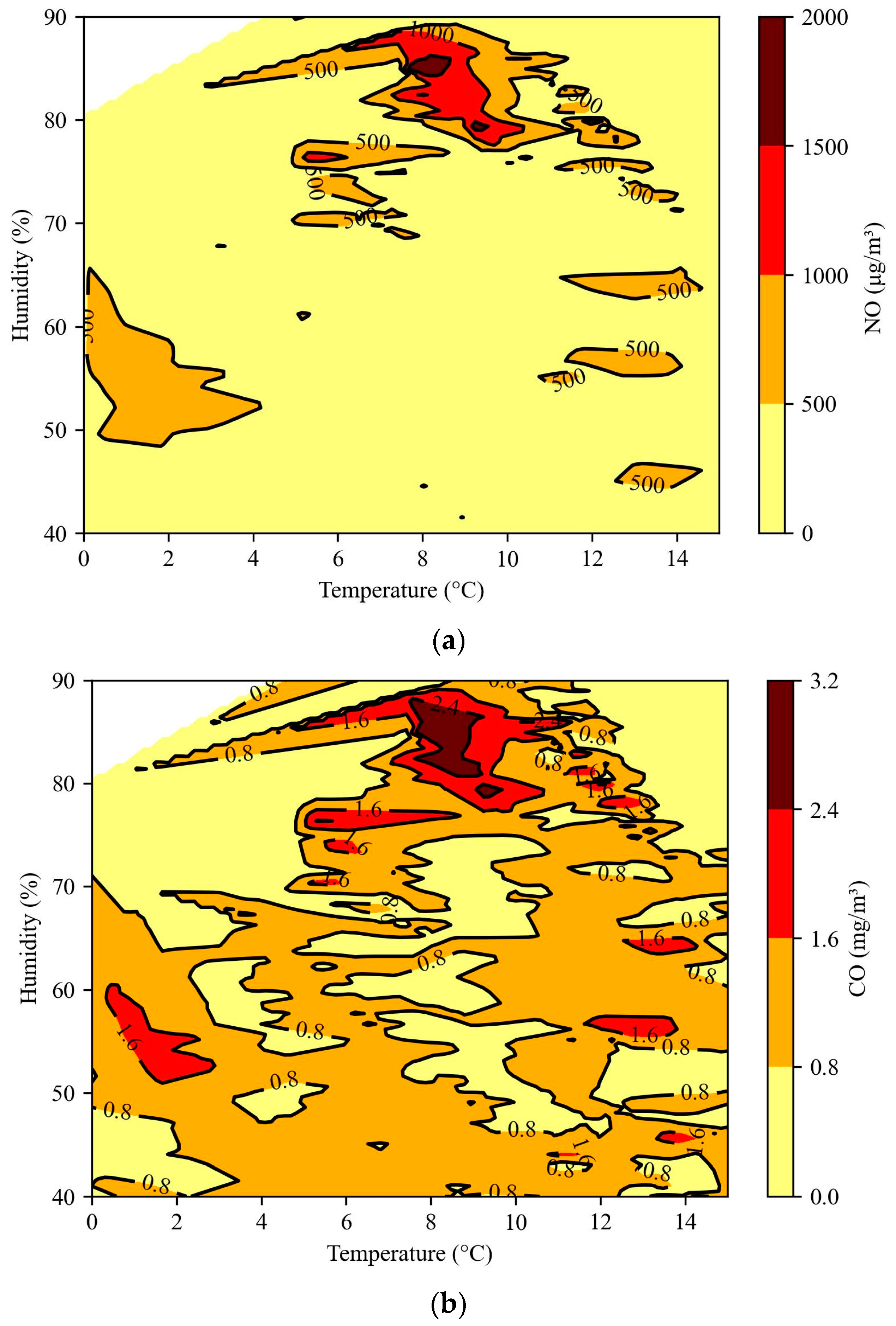
4.3.2. Temperature and Humidity
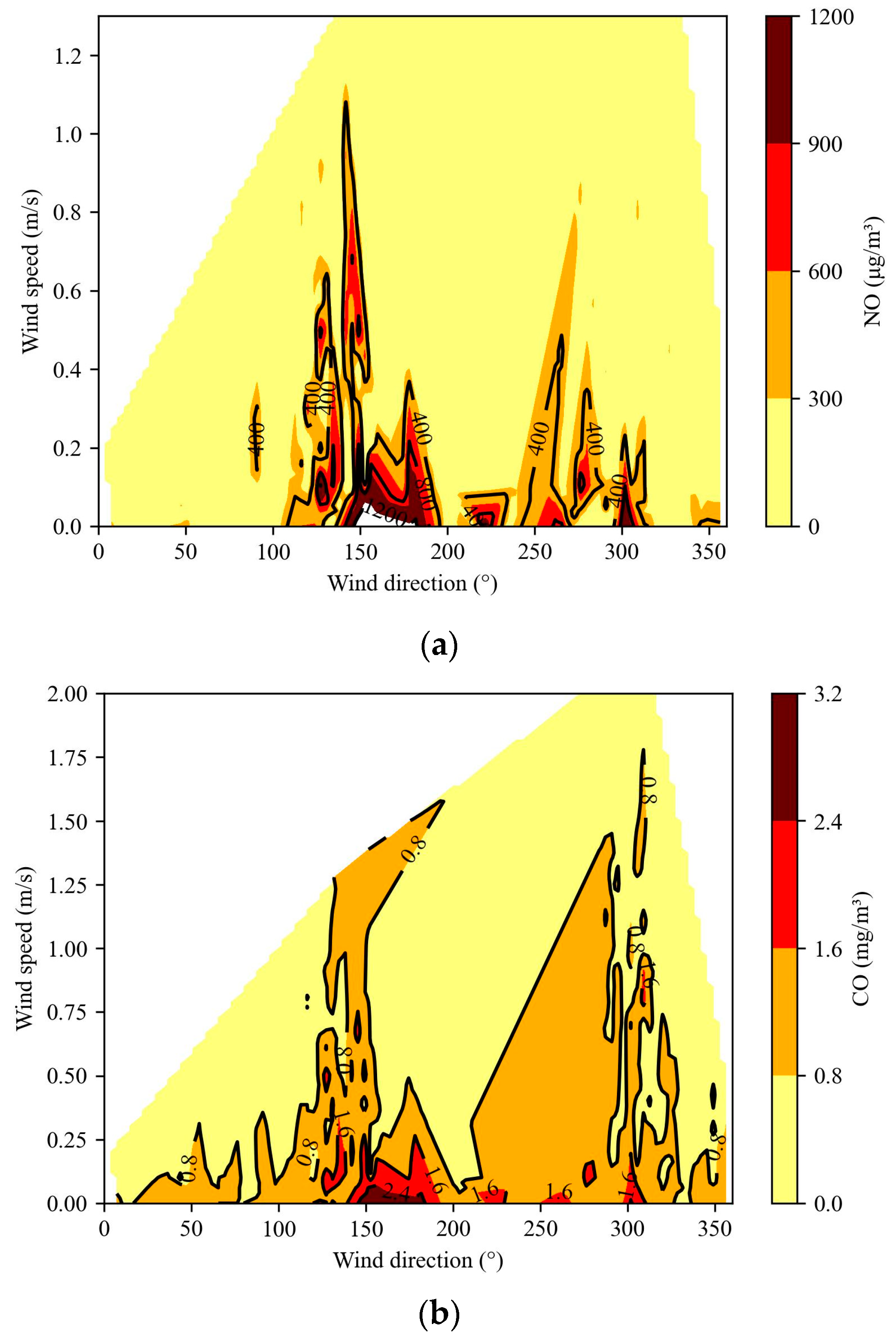
4.3.3. Wind Speed and Wind Direction
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Barberi, S.; Sambito, M.; Neduzha, L.; Severino, A. Pollutant Emissions in Ports: A Comprehensive Review. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.; Solomon, G. Pollution prevention at ports: Clearing the air. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2004, 24, 749–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Jiao, Y.; Jia, R.; Liang, Y. Review on the Research Status of Air Pollutant Emission in Port Area in the Development of Green Port. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. Nat. Sci. 2021, 40, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Brown, R.; Yang, L.; Morawska, L.; Ristovski, Z.; Fu, Q.; Huang, C. Shipping emissions and their impacts on air quality in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Geng, P. A Review of Air Pollution Monitoring Technology for Ports. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-M.; Shofer, S.; Gokhale, J.; Kuschner, W.G. Outdoor air pollution: Overview and historical perspective. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 333, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelishadi, R.; Poursafa, P. Air pollution and non-respiratory health hazards for children. Arch. Med. Sci. 2010, 6, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.D.; Lu, D.N.; Zhao, H.M.; Peng, Z.R. Characterizing CO2 and NOx emission of vehicles crossing toll stations in highway. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 126, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengberg, A.; IEEE. Versatile use of Port and Harbor MetOcean Systems for safety, environmental monitoring, science and recreation. In Proceedings of the Oceans ‘04 MTS/IEEE Techno-Ocean ‘04 Conference, Kobe, Japan, 9–12 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Smailys, V.; Strazdauskiene, R.; Bereisiene, K. Evaluation of a possibility to identify port pollutants trace in Klaipeda City air pollution monitoring stations. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2009, 50, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Jeong, M.-H.; Jeon, S.-B.; Khan, M.S. Time-Series Analysis of Ship Movements Using Community Detection and Functional Data Analysis across the East Coast of the Republic of Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2023, 39, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, F.; Fan, Y. Research on ecological evaluation of Shanghai port logistics based on emergy ecological footprint models. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Qin, D.; Sun, M.; Yi, Z.; Ma, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C. Method for Tracing Source of Air Pollution Discharge in Rubbish Incineration Power Plant Using Electronic Device. Patent Application No CN202210607574.X, 30 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Ying, D.; Li, Y.; Sheng, Y.; He, T.; Shi, P.; Liu, M.; Zhao, L. Method for establishing soil contaminant discharge inventory: An arsenic-contaminated site case study. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, W. Source appointment of PM2.5 in Qingdao Port, East of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezeh, G.C.; Abiye, O.E.; Obioh, I.B. Elemental analyses and source apportionment of PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 aerosols from Nigerian urban cities. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2017, 3, 1323376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, Q.; Ho, T. Source apportionment simulations of ground-level ozone in Southeast Texas employing OSAT/APCA in CAMx. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 253, 118370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsudin, M.S.; Azid, A.; Razik, M.A.; Zaudi, M.A.; Shaharudin, S.M. Source of apportionment of Air Quality Parameters at Federal Port of Malaysia with Emphasis on Ship Emission. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 810, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celic, J.; Cuculic, A.; Valcic, M. Remote Sensing for Ship Emissions Monitoring in Adriatic Ports: An Approach. In Proceedings of the 54th ELMAR International Symposium, Zadar, Croatia, 12–14 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Zhang, C.; Lai, L.; Liao, Q.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, J. Motor Car Exhaust Gas Remote Sensing Monitoring System. Patent Application No CN201911046102.6, 31 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Steffens, J.; Kimbrough, S.; Baldauf, R.; Isakov, V.; Brown, R.; Powell, A.; Deshmukh, P. Near-port air quality assessment utilizing a mobile measurement approach. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammin, P.; Sarhani, M.; Heilig, L.; Voß, S. Applications of Real-Time Data to Reduce Air Emissions in Maritime Ports. In Design, User Experience, and Usability. Case Studies in Public and Personal Interactive Systems; Lecture Notes in Computer, Science; Marcus, A., Rosenzweig, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 31–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoursamaei, M.; Moradi, M.; Gonzalez-Ramirez, R.G.; Lalla-Ruiz, E. Machine Learning for Promoting Environmental Sustainability in Ports. J. Adv. Transp. 2023, 2023, 2144733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Guo, J.D.; Xin, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W. Port sustainability through integration: A port capacity and profit-sharing joint optimization approach. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2023, 245, 106867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Q.; Liang, C.J.; Hu, X.Y.; Li, Y. Planning connections between underground logistics system and container ports. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 139, 106199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbatov, Y.; Georgiev, P.; Fuchedzhieva, I. Extreme Value Analysis of NOx Air Pollution in the Winter Seaport of Varna. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Chen, J.H.; Gao, X.J.; Zhang, R. Spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors of Air pollutants over port cities of the Yangtze River Delta. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2023, 16, 1587–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, R.T.; Chen, R.D.; Lai, K.K. Missing Data Preprocessing in Credit Classification: One-Hot Encoding or Imputation? Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2022, 58, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shehari, T.; Alsowail, R.A. An Insider Data Leakage Detection Using One-Hot Encoding, Synthetic Minority Oversampling and Machine Learning Techniques. Entropy 2021, 23, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talekar, B.; Agrawal, S. A Detailed Review on Decision Tree and Random Forest. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2020, 13, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Dai, Q.; Fan, W.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Feng, Y. Impacts of meteorology and precursor emission change on O-3 variation in Tianjin, China from 2015 to 2021. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, S.K.; Carslaw, D.C. Using meteorological normalisation to detect interventions in air quality time series. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan R, P. Using random forest to model the domain applicability of another random forest model. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 2837–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybarczyk, Y.; Zalakeviciute, R. Machine Learning Approaches for Outdoor Air Quality Modelling: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, J.L.; Miller, M.E.; Tooze, J.; Ip, E. A comparison of random forest variable selection methods for classification prediction modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 134, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.W.; Yin, H.T. The Visualization of E-commerce High-dimensional Data Based on Random Forest. Agro Food Ind. Hi-Tech 2017, 28, 987–991. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, V.; Sharma, J.; Singhal, K.; Phophalia, A. Exponentially Weighted Random Forest. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (PReMI), Tezpur Univ, Tezpur, India, 17–20 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J. Ladle Furnace Temperature Prediction Model Based on Large-scale Data with Random Forest. IEEE-CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2017, 4, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geramita, A.V.; Geramita, J.M.; Wallis, J.S. Orthogonal desingns. Linear Multilinear Algebra 1976, 3, 281–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seberry, J. Orthogonal Designs, in Orthogonal Designs: Hadamard Matrices, Quadratic Forms and Algebras; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Cai, Z.; Jiang, L. Enhancing the performance of differential evolution using orthogonal design method. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 206, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.X.; He, X. Improvement of emission characteristics and thermal efficiency in diesel engines by fueling gasoline/diesel/PODEn blends. Energy 2016, 97, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, S.; Míguez, J.L.; Porteiro, J.; López-González, L.M.; Granada, E.; Morán, J.C.; Paz, C. Exhaust emissions from diesel, LPG, and gasoline low-power engines. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2008, 30, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, M.J.; Gkantonas, S.; El Helou, I.; Pathania, R.; Mastorakos, E.; Boies, A.M. Measurements and modelling of the three-dimensional near-field dispersion of particulate matter emitted from passenger ships in a port environment. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 290, 119384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternina-Arboleda, C.D.; Agudelo-Castaneda, D.; Voss, S.; Das, S. Towards Cleaner Ports: Predictive Modeling of Sulfur Dioxide Shipping Emissions in Maritime Facilities Using Machine Learning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Deng, S.L.; Gao, Y.; Qu, L.; Li, M.C.; Chen, D. Characterization of air pollution in urban areas of Yangtze River Delta, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Zhan, H.G.; Ni, P.T.; Cai, S.Q. A model study of the effects of river discharges and winds on hypoxia in summer in the Pearl River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Foy, B.; Heo, J.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Schauer, J.J. Source attribution of air pollution using a generalized additive model and particle trajectory clusters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Mfum, S.; Hudson, M.D.; Osborne, P.E.; Roberts, T.J.; Zapata-Restrepo, L.M.; Williams, I.D. Atmospheric Pollution in Port Cities. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pollutant | Time Span | R-Square |
|---|---|---|
| NO | Month | 0.64 |
| Day | 0.77 | |
| CO | Month | 0.81 |
| Day | 0.79 |
| Scenarios | Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Air Pressure | Humidity | Wind Speed | Wind Direction | |
| 1 | High | High | High | High | SE |
| 2 | High | Medium | Medium | Medium | S |
| 3 | High | Low | Low | Low | N |
| 4 | Medium | High | High | Medium | S |
| 5 | Medium | Medium | Medium | Low | N |
| 6 | Medium | Low | Low | High | SE |
| 7 | Low | High | Medium | High | N |
| 8 | Low | Medium | Low | Medium | SE |
| 9 | Low | Low | High | Low | S |
| 10 | High | High | Low | Low | S |
| 11 | High | Medium | High | High | N |
| 12 | High | Low | Medium | Medium | SE |
| 13 | Medium | High | Medium | Low | SE |
| 14 | Medium | Medium | Low | High | S |
| 15 | Medium | Low | High | Medium | N |
| 16 | Low | High | Low | Medium | N |
| 17 | Low | Medium | High | Low | SE |
| 18 | Low | Low | Medium | High | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.-Z.; Peng, Z.-R.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Pan, J.; He, H. A Data-Driven Approach to Identify Major Air Pollutants in Shanghai Port Area and Their Contributing Factors. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12020288
Li X-Z, Peng Z-R, Fu Q, Wang Q, Pan J, He H. A Data-Driven Approach to Identify Major Air Pollutants in Shanghai Port Area and Their Contributing Factors. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(2):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12020288
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xing-Zhou, Zhong-Ren Peng, Qingyan Fu, Qian Wang, Jun Pan, and Hongdi He. 2024. "A Data-Driven Approach to Identify Major Air Pollutants in Shanghai Port Area and Their Contributing Factors" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 2: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12020288
APA StyleLi, X.-Z., Peng, Z.-R., Fu, Q., Wang, Q., Pan, J., & He, H. (2024). A Data-Driven Approach to Identify Major Air Pollutants in Shanghai Port Area and Their Contributing Factors. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(2), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12020288






