Noise Reduction of Velocity Measured by Frequency-Supervised Combined Doppler Sonar Using an Adaptive Sliding Window and Kalman Filter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Conventional Doppler Sonar (CNDS)
2.2. Coherent Doppler Sonar (CHDS)
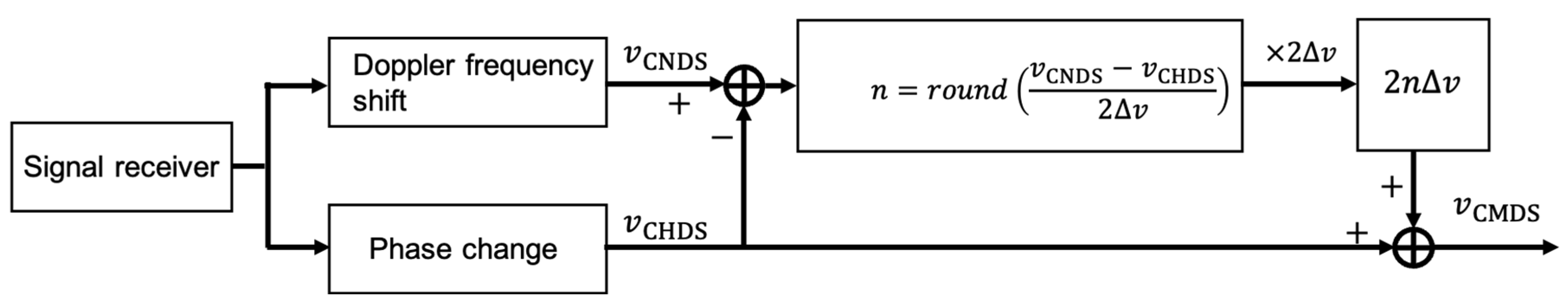
2.3. Combined Doppler Sonar (CMDS)
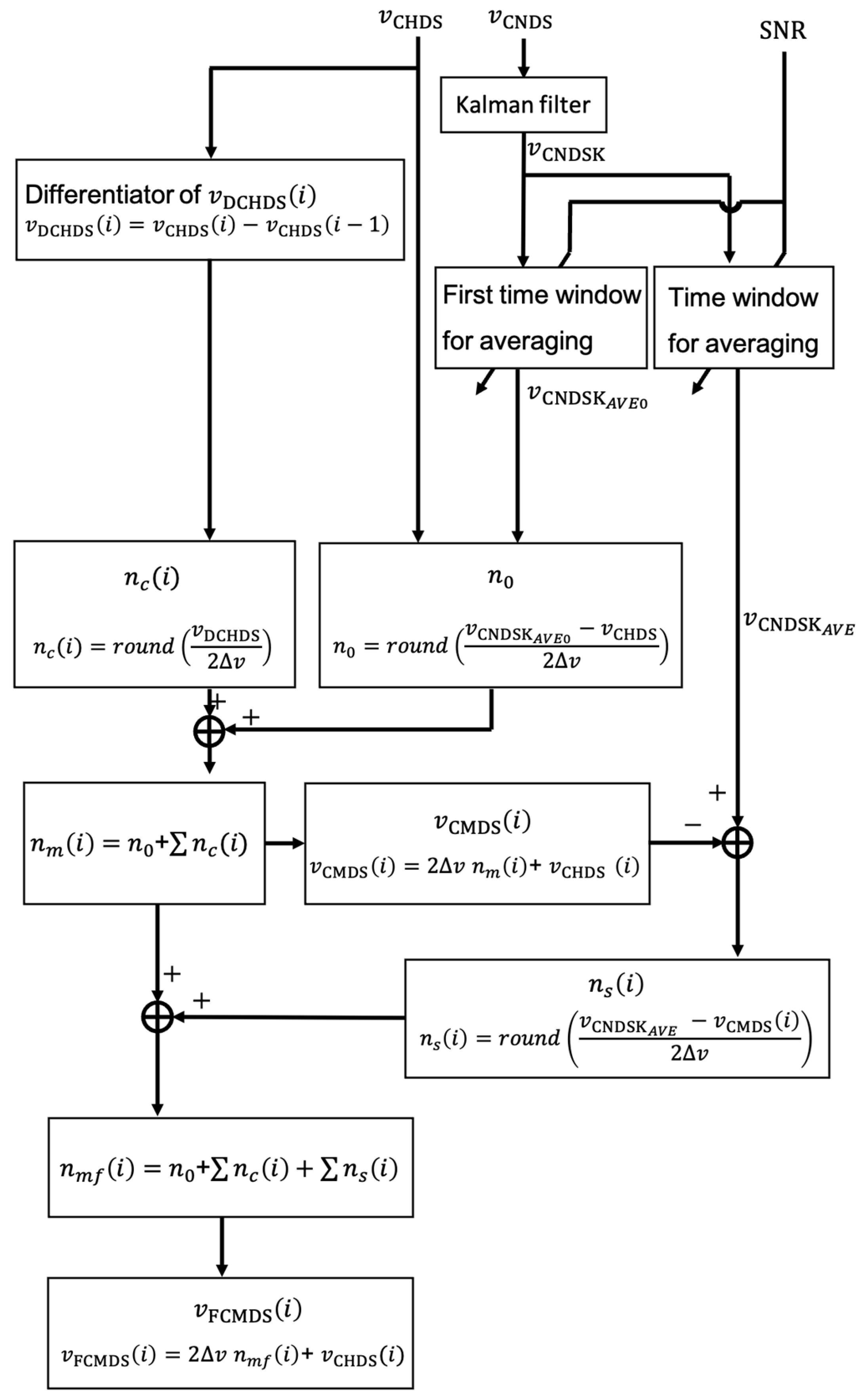
2.4. Combined Doppler Sonar Using Kalman Filter and Linear Prediction (CMDS_KL)

2.5. Frequency-Supervised Combined Doppler Sonar Using an Adaptive Sliding Window and Kalman Filter (CMDS_FK)
3. Error Analysis
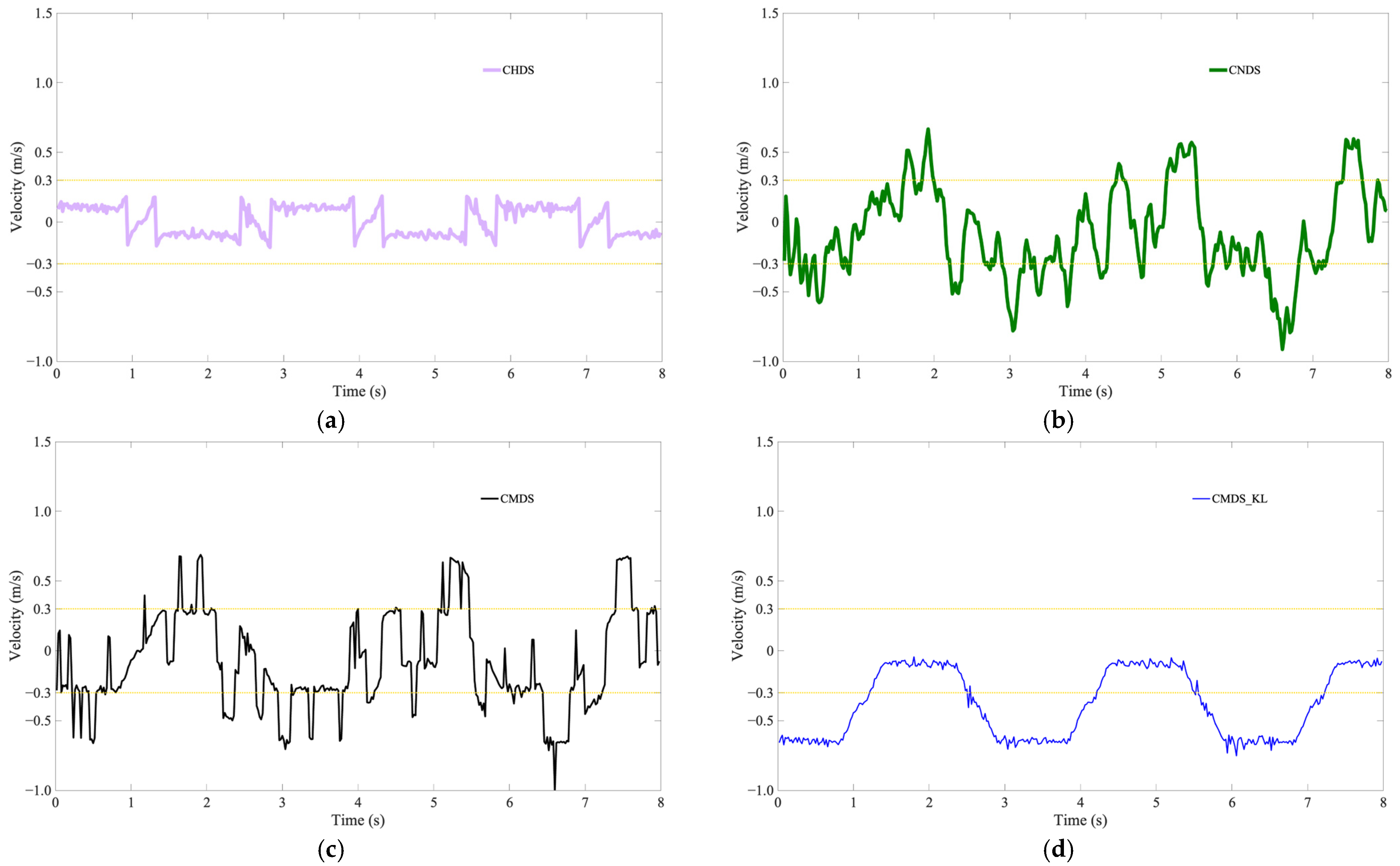
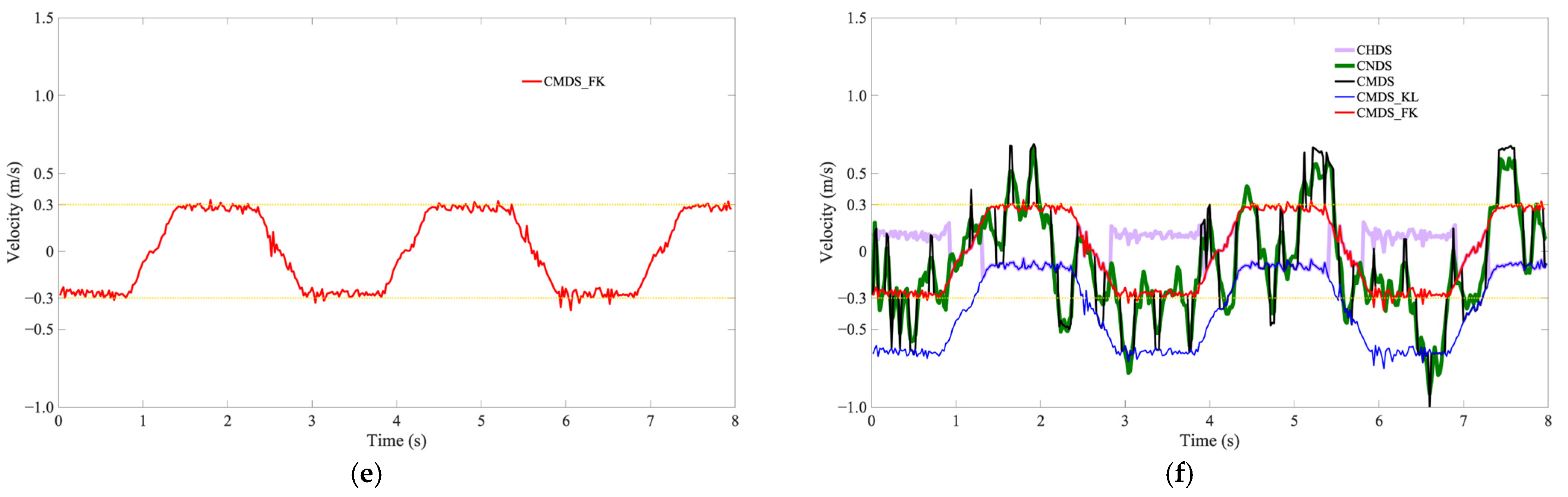
4. Experiments
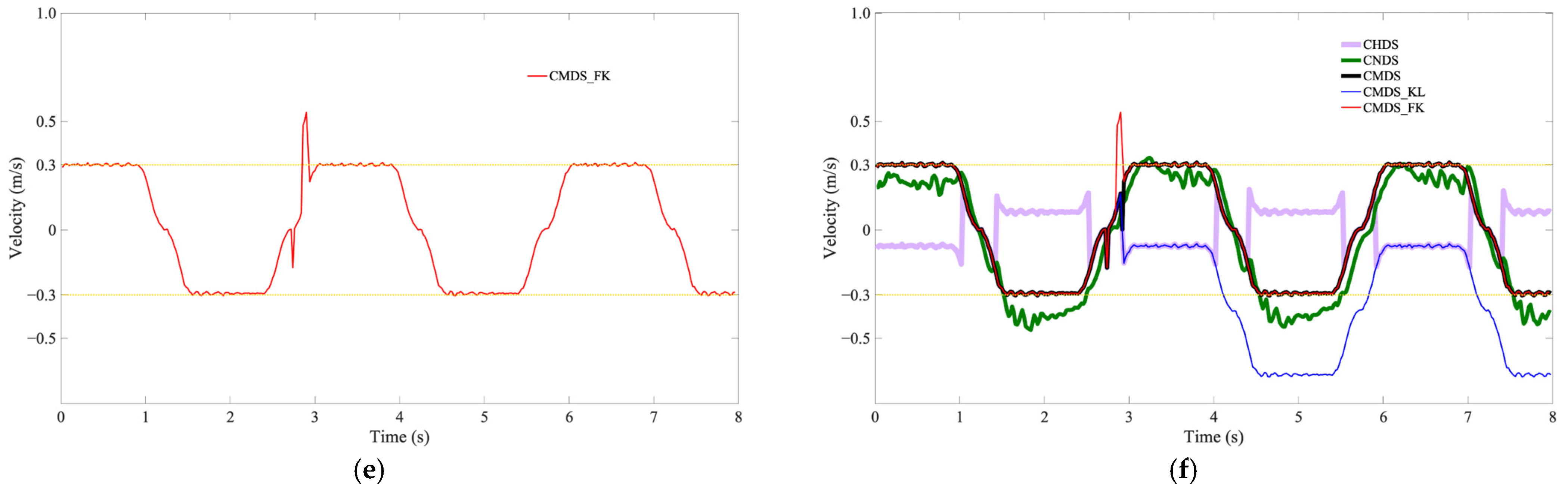
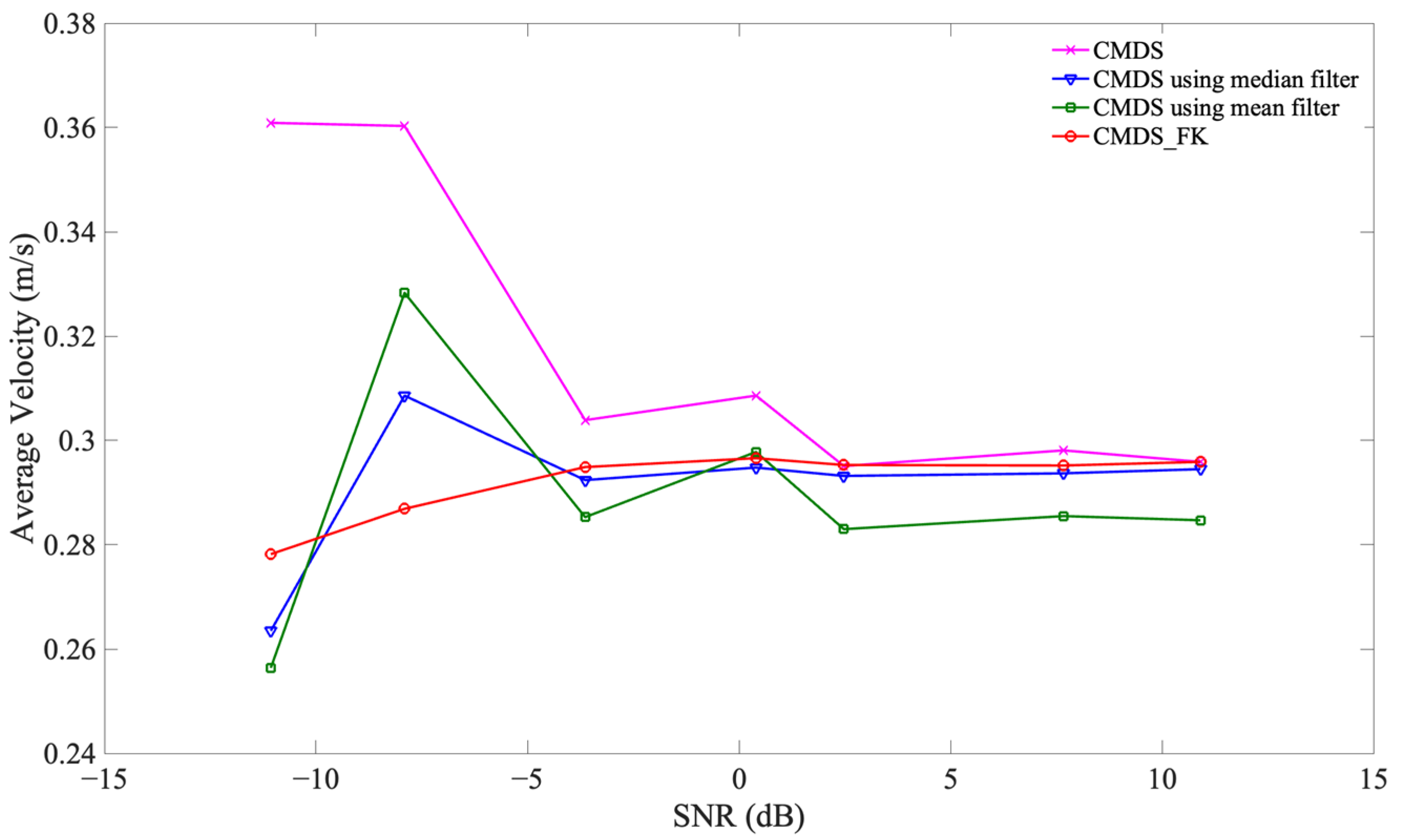
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doisy, Y. Theoretical Accuracy of Doppler Navigation Sonars and Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrmann, A.; Hackett, B.; Roed, L.P. High resolution measurements of turbulence, velocity and stress using a pulse-to-pulse coherent sonar. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 1990, 7, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veron, F.; Melville, W.K. Pulse-to-pulse coherent Doppler measurements of waves and turbulence. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 1999, 16, 1580–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhermitte, R.; Serafin, R. Pulse-to-pulse coherent Doppler sonar signal processing techniques. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 1984, 1, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedel, L. Modeling pulse-to-pulse coherent Doppler sonar. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2008, 25, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleman, I.; Beekhuis, H. Analysis and correction of dual PRF velocity data. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2003, 20, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, P.; May, P.T. Correction of dual PRF velocity errors for operational Doppler weather radars. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2003, 20, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, A.E.; Zedel, L.; Craig, R.; Paul, W. Multi-frequency, pulse-to-pulse coherent Doppler sonar profiler. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE/OES/CMTC Working Conference on Current Measurement Technology, Charleston, SC, USA, 17–19 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zedel, L.; Hay, A.E. Resolving velocity ambiguity in multifrequency, pulse-to-pulse coherent Doppler sonar. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2010, 35, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Kouguchi, N. Combined Method of Conventional and Coherent Doppler Sonar to Avoid Velocity Ambiguity. J. Mar. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 41, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Kouguchi, N. Measurement Error Analysis of Combined Doppler Sonar Using Adaptive Algorithm. J. Mar. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 42, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.P.; Godsill, S.J.; Mandic, D.P. Filtering Structures for α-Stable Systems. IEEE Contr. Syst. Lett. 2023, 7, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, R.; Yi, Y.; Bermak, A. Investigation of filtering algorithm for noise reduction in displacement sensing signal. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 7808–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Kouguchi, N.; Li, Y. Velocity Measurement of Coherent Doppler Sonar Assisted by Frequency Shift, Kalman Filter and Linear Prediction. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokloff, N.A. Matrix algorithm for Doppler sonar navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE OCEANS’94, Brest, France, 13–16 September 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Taudien, J.Y.; Bilen, S.G. Quantifying Long-Term Accuracy of Sonar Doppler Velocity Logs. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 43, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurther, D.; Lemmin, U.A. A correction method for turbulence measurements with a 3D acoustic Doppler velocity profiler. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2001, 18, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, J.; Zedel, L.; Hay, A.E. On the Distribution of Velocity Measurements from Pulse-to-Pulse Coherent Doppler Sonar. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2012, 37, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, K.; Kensaku, F.; Yoshio, I.; Yutaka, F. A noise reduction method based on linear prediction analysis. Electr. Commun. Jpn. 2003, 86, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. Trans. ASME J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Fang, H.; Yan, M. Kalman filter-based adaptive control for networked systems with unknown parameters and randomly missing outputs. Int. J. Robust Nonlin. 2010, 19, 1976–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Hofmann, W.; Werner, R. Improving operational performance of active magnetic bearings using Kalman filter and state feedback control. IEEE T. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 821–829. [Google Scholar]
- Lefferts, E.J.; Markley, F.L.; Shuster, M.D. Kalman filtering for spacecraft attitude estimation. J. Guid. Control Dynam. 1982, 5, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kishore, T.; Deergha Rao, K. Efficient median filter for restoration of image and video sequences corrupted by impulsive noise. IETE J. Res. 2010, 56, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, G.; Chauhan, S.; Sehri, M.; Zimroz, R.; Dumond, P.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, M.K. A roadmap to fault diagnosis of industrial machines via machine learning: Abrief review. Measurement 2025, 242, 116216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Pulse Envelop | Square |
| Length of Pulse | 0.6 ms |
| Size of Water Tank | 150 cm × 70 cm × 70 cm |
| Accuracy of Moving Machine | 1 mm/s |
| Carrier Frequency of Pulse | 200 kHz |
| Pulse Repetition Frequency | 50 Hz |
| Stable Moving Velocity of Transducer | 0.300 m/s |
| Depth of the Hydrophone and the Transducer | 0.20 m |
| Temperature | 10.8 °C |
| Sound Speed | 1450 m/s |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| State Transition Matrix | |
| Control Input Matrix | |
| Measurement Matrix | |
| Covariance of Observation Noise | |
| Covariance of Process Noise | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Chen, P.; Li, Y. Noise Reduction of Velocity Measured by Frequency-Supervised Combined Doppler Sonar Using an Adaptive Sliding Window and Kalman Filter. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122320
Liu P, Liu B, Zhu X, Chen P, Li Y. Noise Reduction of Velocity Measured by Frequency-Supervised Combined Doppler Sonar Using an Adaptive Sliding Window and Kalman Filter. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122320
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Peng, Bingxin Liu, Xueyuan Zhu, Peng Chen, and Ying Li. 2024. "Noise Reduction of Velocity Measured by Frequency-Supervised Combined Doppler Sonar Using an Adaptive Sliding Window and Kalman Filter" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122320
APA StyleLiu, P., Liu, B., Zhu, X., Chen, P., & Li, Y. (2024). Noise Reduction of Velocity Measured by Frequency-Supervised Combined Doppler Sonar Using an Adaptive Sliding Window and Kalman Filter. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122320








