A Comparative Study on Acoustic Characteristics of Methane and Tetrahydrofuran Hydrate-Bearing Sediments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
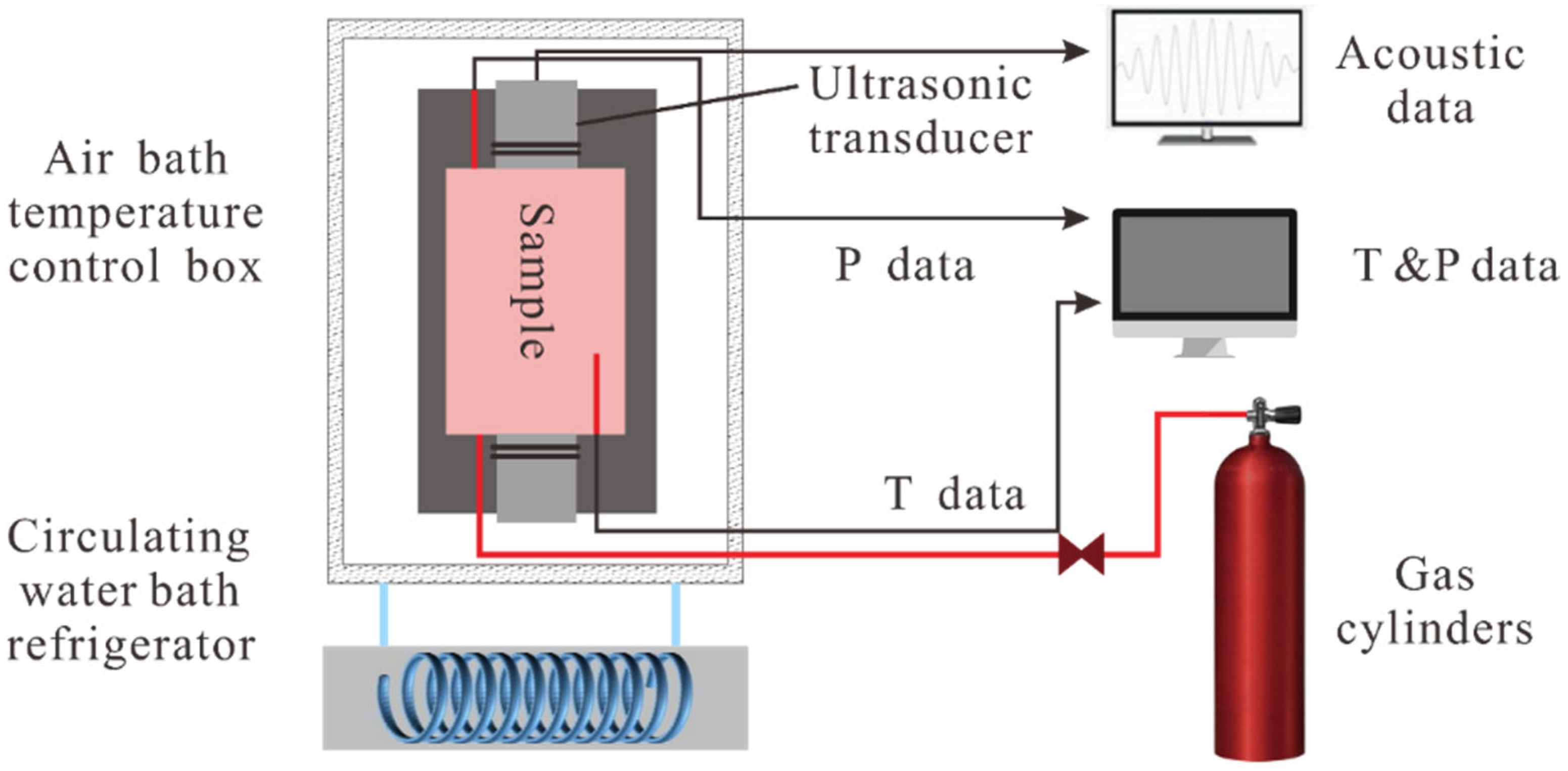
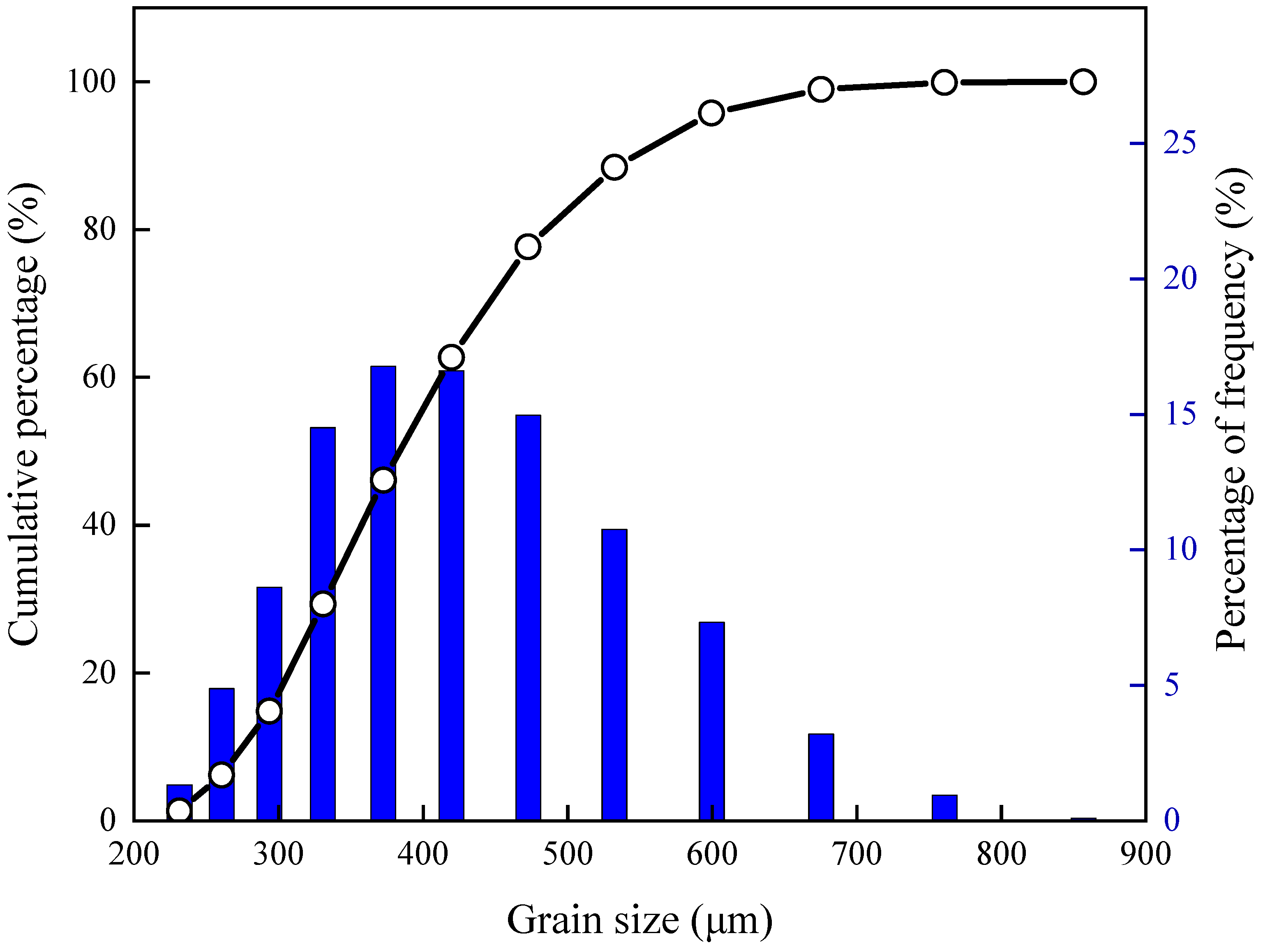
2.1. Experimental Device and Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Experimental Procedure
- (1)
- Sample preparation. First, the methane hydrate was prepared according to the pre-determined ratio, and 0.03% SDS solution was fully mixed with the dried sediment, pressed, and then added to the reactor to secure the lower vessel cover.
- (2)
- Reactor installation. After adding the specimen, the upper vessel lid was tightened and the gas cylinder, pressure regulation system, and temperature control system were connected.
- (3)
- Leak detection and vessel cleansing. Slightly overpressured methane gas was injected into the vessel and left to stand for some time while the temperature stabilized. We compared the pressure valve data before and after, and if no change was observed, we determined that no air leakage occurred. The pressure was then discharged, and the vessel was inflated and deflated several times, utilizing high-pressure methane gas to cleanse the interior.
- (4)
- Pressurization. Methane gas was slowly added to the reactor until the internal pressure reached approximately 8.3 MPa. This state was maintained until the temperature stabilized, ensuring that the methane gas fully infiltrated the sediment.
- (5)
- The circulating water bath refrigerator and the air bath temperature control box were switched on to set the temperature to 1 °C. The temperature, pressure, and ultrasonic data acquisition software programs were started to initiate data collection.
- (6)
- THF hydrate can be synthesized simply by controlling the temperature. Since THF is volatile, the sediment and THF solution were added in layers to ensure a solution that was sufficiently mixed with the sediment, and the sediments were cleaned and dried at the end of each experiment.
3. Results
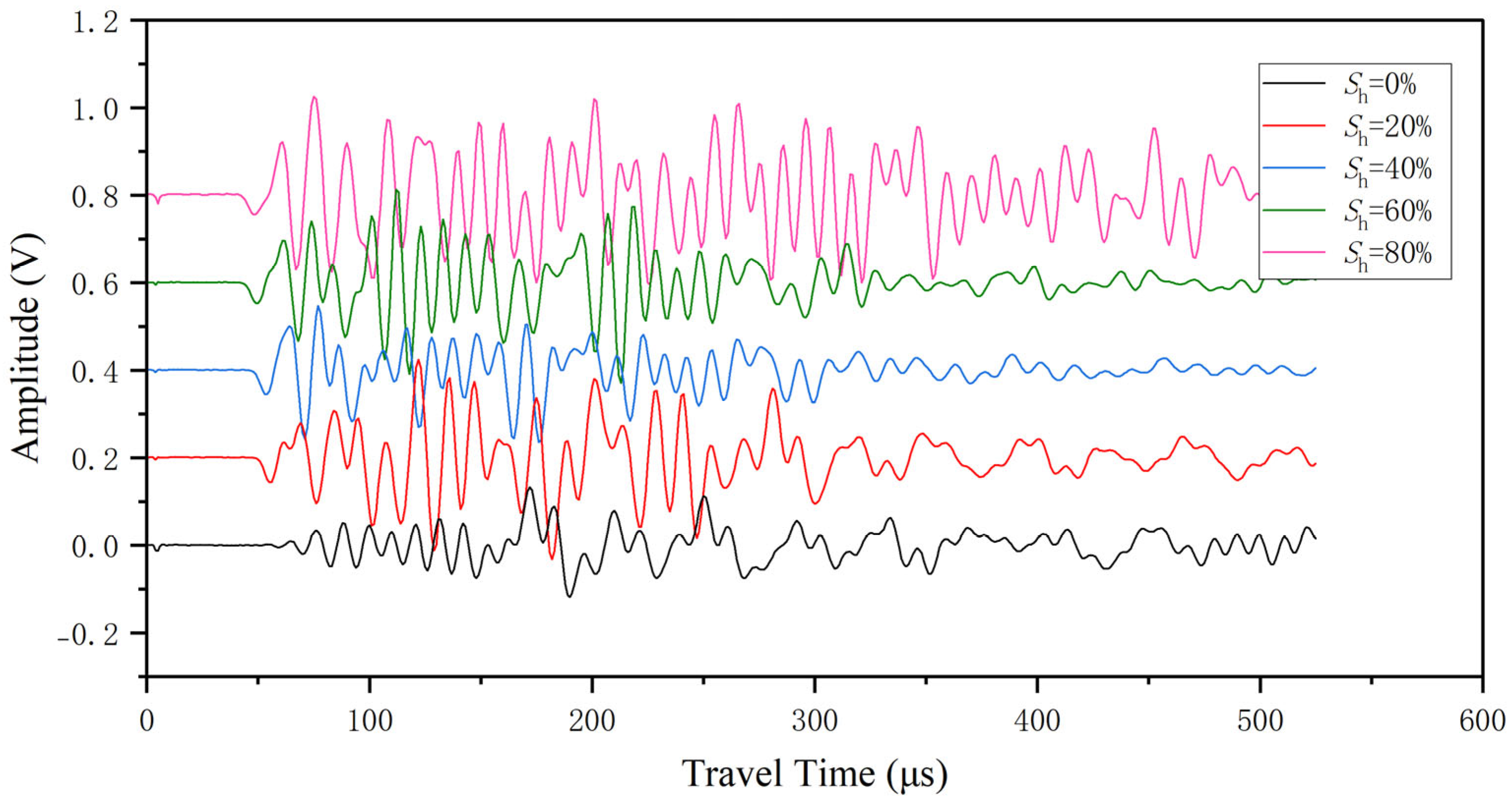
3.1. Wave Velocity of Methane Hydrate-Bearing Sediments
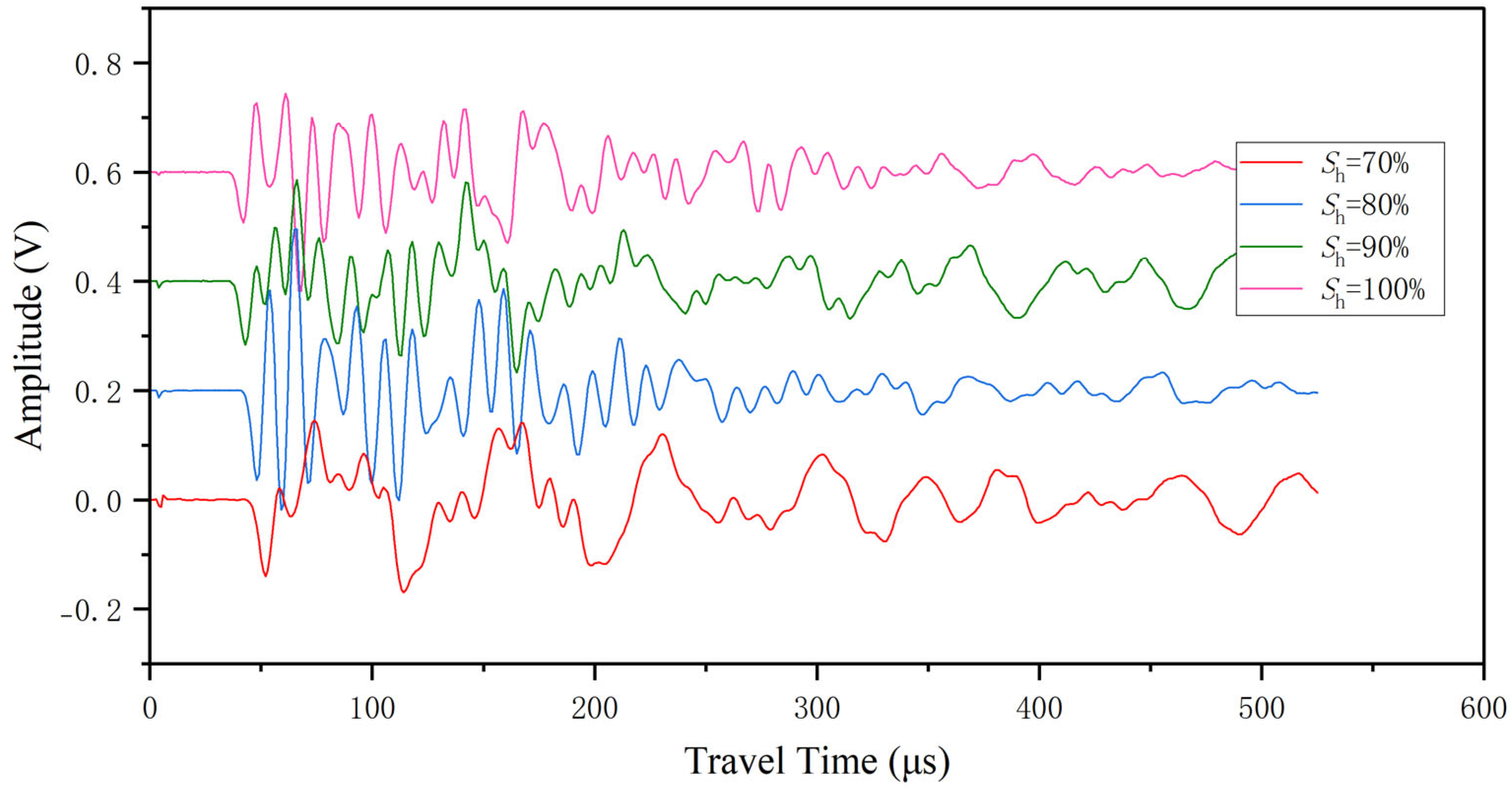
3.2. Wave Velocity of THF Hydrate-Bearing Sediments
4. Discussion
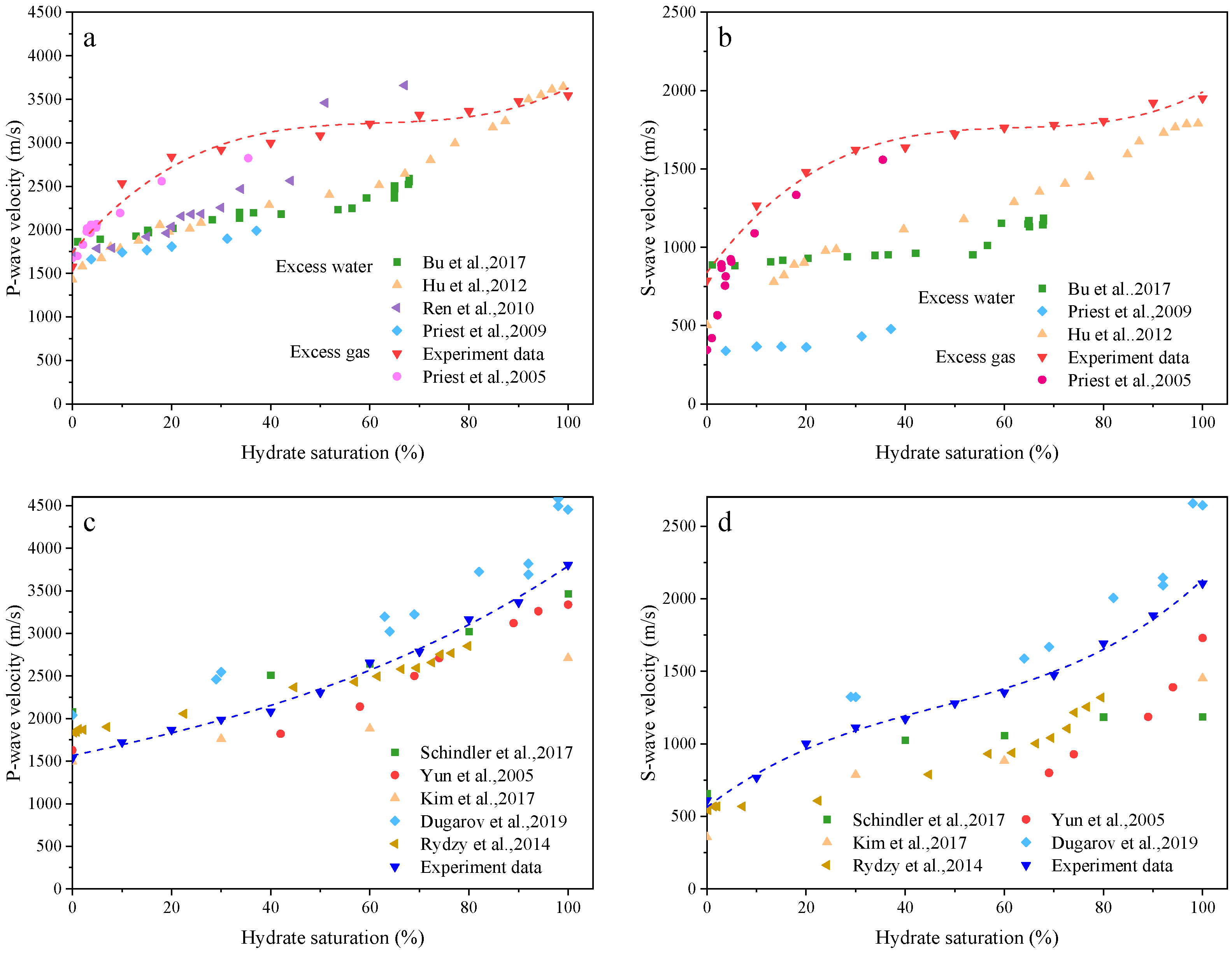
4.1. Velocity Changes with Hydrate Saturation
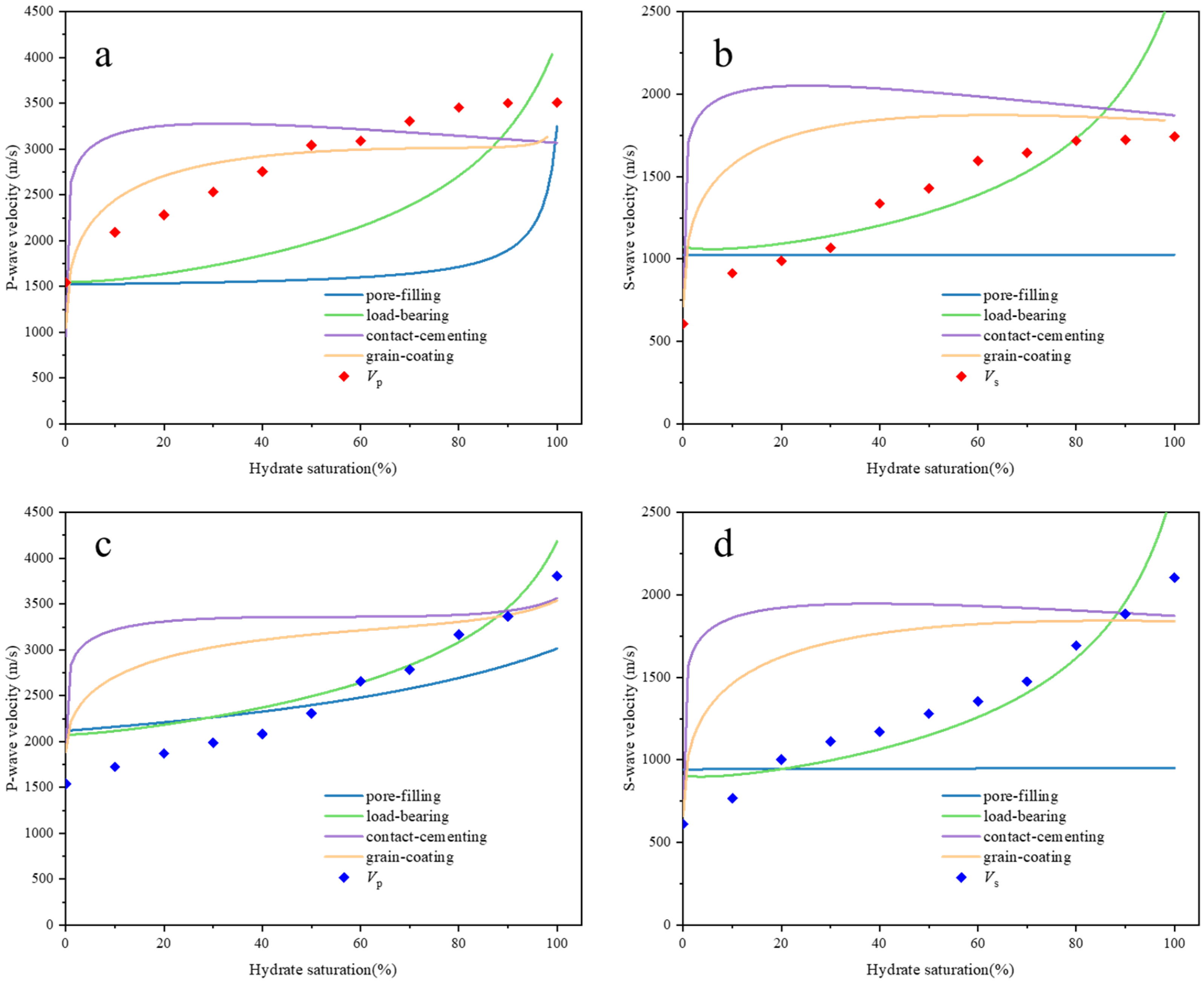
4.2. Validation of Velocity Models
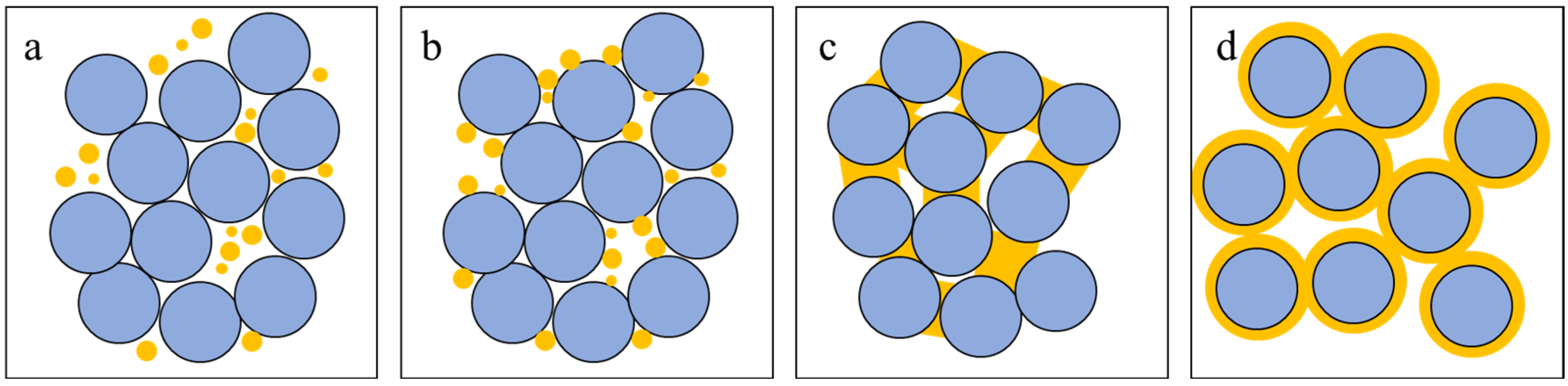
4.3. Acoustic Response Differences of Two Types of Hydrate-Bearing Sediments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Effective Medium Theory
References
- Chong, Z.R.; Yang, S.H.B.; Babu, P.; Linga, P.; Li, X.-S. Review of Natural Gas Hydrates as an Energy Resource: Prospects and Challenges. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 1633–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makogon, Y.F.; Holditch, S.A.; Makogon, T.Y. Natural Gas-Hydrates—A Potential Energy Source for the 21st Century. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2007, 56, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, R. Is Gas Hydrate Energy Within Reach? Science 2009, 325, 957–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collett, T.; Bahk, J.-J.; Baker, R.; Boswell, R.; Divins, D.; Frye, M.; Goldberg, D.; Husebø, J.; Koh, C.; Malone, M.; et al. Methane Hydrates in Nature—Current Knowledge and Challenges. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geophysical Characterization of Gas Hydrates; Riedel, M.; Willoughby, E.C.; Chopra, S. (Eds.) Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-56080-218-1. [Google Scholar]
- Waite, W.F.; Santamarina, J.C.; Cortes, D.D.; Dugan, B.; Espinoza, D.N.; Germaine, J.; Jang, J.; Jung, J.W.; Kneafsey, T.J.; Shin, H.; et al. Physical Properties of Hydrate-Bearing Sediments. Rev. Geophys. 2009, 47, RG4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, F.; Yan, C.; Sun, H.; Li, Q.; Song, B. Experimental Study on Dynamic Acoustic Characteristics of Natural Gas Hydrate Sediments at Different Depths. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 26877–26889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Hu, G.; Liu, C.; Dong, J.; Xing, T.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Meng, Q. Effect of Methane Gas on Acoustic Characteristics of Hydrate-Bearing Sediment-Model Analysis and Experimental Verification. J. Ocean Univ. China 2021, 20, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.-W.; Ye, Y.-G.; Zhang, J.; Diao, S.-B.; Liu, C.-L. Acoustic Properties of Hydrate-Bearing Unconsolidated Sediments Measured by the Bender Element Technique. Chin. J. Geophys. 2012, 55, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, J.A.; Best, A.I.; Clayton, C.R.I. A Laboratory Investigation into the Seismic Velocities of Methane Gas Hydrate-Bearing Sand: Seismic Velocity of hydrate-bearing Sand. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2005, 110, B04102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ning, F.; Hu, G.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Peng, L.; Wang, D.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z. Characterization of Seismic Wave Velocity and Attenuation and Interpretation of Tetrahydrofuran Hydrate-Bearing Sand Using Resonant Column Testing. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 122, 104620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, N.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Bu, Q.; Hu, G. Influences of Stress State on Compressional Wave Velocity of Sandy Hydrate-Bearing Sediment: Experiments and Modeling. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 234, 212683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Hu, G.; Liu, C.; Xing, T.; Li, C.; Meng, Q. Acoustic Characteristics and Micro-Distribution Prediction during Hydrate Dissociation in Sediments from the South China Sea. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 65, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, G.; Bu, Q.; Liu, C.; Dong, L.; Wan, Y.; Mao, P.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z. Elastic Wave Velocities of Hydrate-Bearing Sands Containing Methane Gas Bubbles: Insights from CT-Acoustic Observation and Theoretical Analysis. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 88, 103844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Madhusudhan, B.N.; Marín-Moreno, H.; North, L.J.; Ahmed, S.; Falcon-Suarez, I.H.; Minshull, T.A.; Best, A.I. Laboratory Insights Into the Effect of Sediment-Hosted Methane Hydrate Morphology on Elastic Wave Velocity From Time-Lapse 4-D Synchrotron X-Ray Computed Tomography. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2018, 19, 4502–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæther, M.M.; Almenningen, S.; Ersland, G.; Lunde, P. Compressional Wave Phase Velocity Measurements during Hydrate Growth in Partially and Fully Water Saturated Sandstone. Fuel 2022, 324, 124522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, G.; Bu, Q.; Wu, N.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Li, C.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, W.; et al. Elastic Wave Velocity of Marine Sediments with Free Gas: Insights from CT-Acoustic Observation and Theoretical Analysis. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 150, 106169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Xing, T.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Kang, J.; Meng, Q.; Hu, G. Effect of Hydrate Microscopic Distribution on Acoustic Characteristics during Hydrate Dissociation: An Insight from Combined Acoustic-CT Detection Study. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Q. Acoustic Response of Gas Hydrate Formation in Sediments from South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Best, A.I. The Influence of Gas Hydrate Morphology on Reservoir Permeability and Geophysical Shear Wave Remote Sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2021JB022206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y. Microstructural Characteristics of Natural Gas Hydrates Hosted in Various Sand Sediments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 22632–22641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, J.A.; Rees, E.V.L.; Clayton, C.R.I. Influence of Gas Hydrate Morphology on the Seismic Velocities of Sands. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2009, 114, 2009JB006284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultaniya, A.K.; Priest, J.A.; Clayton, C.R.I. Measurements of the Changing Wave Velocities of Sand during the Formation and Dissociation of Disseminated Methane Hydrate. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Moreno, H.; Sahoo, S.K.; Best, A.I. Theoretical Modeling Insights into Elastic Wave Attenuation Mechanisms in Marine Sediments with Pore-filling Methane Hydrate. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 1835–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Meng, Q.; Dong, J.; Li, C.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Kang, J.; Hu, G. Integration of Pore-Scale Visualization and an Ultrasonic Test System of Methane Hydrate-Bearing Sediments. Energies 2022, 15, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Jia, R.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.; Li, X. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Pore-Filling and Fracture-Filling Clayey Silt Hydrate-Bearing Sediments. Energy 2023, 284, 129354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Park, T.; Jarvis, K.; Pan, L.; Tepecik, I.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, Z.; Choi, J.-H.; Gai, X.; Galindo-Torres, S.A.; et al. Pore-Scale Observations of Natural Hydrate-Bearing Sediments via Pressure Core Sub-Coring and Micro-CT Scanning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Mu, H. A Review of Micro Computed Tomography Studies on the Gas Hydrate Pore Habits and Seepage Properties in Hydrate Bearing Sediments. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 83, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Tang, H.; Wu, P.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Li, Y. Acoustic Characteristics on Clayey-Silty Sediments of the South China Sea during Methane Hydrate Formation and Dissociation. Energy 2023, 282, 128978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeq, D.; Alef, K.; Iglauer, S.; Lebedev, M.; Barifcani, A. Compressional Wave Velocity of Hydrate-Bearing Bentheimer Sediments with Varying Pore Fillings. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 23193–23200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.S. Compressional and Shear Wave Velocities in Uncemented Sediment Containing Gas Hydrate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L10609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Acoustic Velocity and Electrical Resistance of Hydrate Bearing Sediments. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 70, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugarov, G.A.; Duchkov, A.A.; Duchkov, A.D.; Drobchik, A.N. Laboratory Validation of Effective Acoustic Velocity Models for Samples Bearing Hydrates of Different Type. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 63, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchkov, A.D.; Dugarov, G.A.; Duchkov, A.A.; Drobchik, A.A. Laboratory Investigations into the Velocities and Attenuation of Ultrasonic Waves in Sand Samples Containing Water/Ice and Methane and Tetrahydrofuran Hydrates. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2019, 60, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Kim, J.; Lei, L.; Ning, F.; Dai, S. Tetrahydrofuran Hydrate in Clayey Sediments—Laboratory Formation, Morphology, and Wave Characterization. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 3307–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Peyvandi, K.; Varaminian, F.; Mokarian, Z. Investigation of THF Hydrate Formation Kinetics: Experimental Measurements of Volume Changes. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Dong, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, P.; Yang, L. Effect of a Weak Electric Field on THF Hydrate Formation: Induction Time and Morphology. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 194, 107486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, S.; Pahlavanzadeh, H.; Manteghian, M. Experimental Study and Kinetic Modeling on THF Hydrate Formation under a Static Electric Field. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 95, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J. Investigation of the Induction Time for THF Hydrate Formation in Porous Media. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 24, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, B.; Schicks, J.M.; Luzi-Helbing, M.; Naumann, R.; Herbst, M. The Difference between Aspired and Acquired Hydrate Volumes–A Laboratory Study of THF Hydrate Formation in Dependence on Initial THF:H2O Ratios. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 117, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yun, T.S.; Santamarina, J.C.; Ruppel, C. Observations Related to Tetrahydrofuran and Methane Hydrates for Laboratory Studies of Hydrate-Bearing Sediments: Study of hydrate-bearing sediments. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2007, 8, Q06003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, Y.; Jin, Y.; Yoneda, J.; Kida, M.; Egawa, K.; Ito, T.; Suzuki, K.; Nagao, J. Effect of Methane Hydrate Morphology on Compressional Wave Velocity of Sandy Sediments: Analysis of Pressure Cores Obtained in the Eastern Nankai Trough. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 66, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Liao, H.; Lin, D.; Bu, Q.; Liu, Z. Mechanical Properties of the Clayey-Silty Sediment-Natural Gas Hydrate Mixed System. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2021, 8, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Cheng, Y.; Li, M.; Han, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Teng, F.; Ding, J. Mechanical Experiments and Constitutive Model of Natural Gas Hydrate Reservoirs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19810–19818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Li, X.-S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.-W.; Chen, Z.-Y. Effects of Gas Occurrence Pattern on Distribution and Morphology Characteristics of Gas Hydrates in Porous Media. Energy 2021, 226, 120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, W.F.; Winters, W.J.; Mason, D.H. Methane Hydrate Formation in Partially Water-Saturated Ottawa Sand. Am. Mineral. 2004, 89, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.T.; Hu, G.W.; Ye, Y.G.; Liu, C.L.; Li, C.F.; Best, A.I.; Wang, J.S. The Elastic Wave Velocity Response of Methane Gas Hydrate Formation in Vertical Gas Migration Systems. J. Geophys. Eng. 2017, 14, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, M.; Batzle, M.L.; Prasad, M. Micro X-Ray Computed Tomography Imaging and Ultrasonic Velocity Measurements in Tetrahydrofuran-hydrate-bearing Sediments. Geophys. Prospect. 2017, 65, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Seol, Y.; Dai, S. Waves in THF hydrate-bearing sand. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, (ICGH2017), Denver, CO, USA, 25–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rydzy, M.B. The Effect of Hydrate Formation on the Elastic Properties of Unconsolidated Sediment; Colorado School of Mines: Golden, CO, USA, 2014; ISBN 1-303-69766-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dvorkin, J.; Nur, A. Elasticity of High-porosity Sandstones: Theory for Two North Sea Data Sets. Geophysics 1996, 61, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgerud, M.B.; Dvorkin, J.; Nur, A.; Sakai, A.; Collett, T. Elastic-Wave Velocity in Marine Sediments with Gas Hydrates: Effective Medium Modeling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2021–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, C. Seismic Characterization of Methane Hydrate Structures; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, R.; Ojha, M.; Kumar, P. Review of Rock Physics Theories for Quantifying Gas Hydrate and Associated Uncertainties. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2023, 256, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Han, D.; Wang, Y. A Review of Rock Physical Models for Elastic Properties Characterization of Gas Hydrate Bearing Sediments. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 218, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, S.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, J. A Unified Contact Cementation Theory for Gas Hydrate Morphology Detection and Saturation Estimation from Elastic-Wave Velocities. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 113, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, T.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Li, A. Morphology Identification of Gas Hydrate Based on a Machine Learning Method and Its Applications on Saturation Estimation. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 234, 1307–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, A.I.; Priest, J.A.; Clayton, C.R.I.; Rees, E.V.L. The Effect of Methane Hydrate Morphology and Water Saturation on Seismic Wave Attenuation in Sand under Shallow Sub-Seafloor Conditions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 368, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavko, G.; Mukerji, T.; Dvorkin, J. The Rock Physics Handbook, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-108-33301-6. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, G.R.; Arif, M.; Isah, A.; Ali, M.; Mahmoud, M.; Hoteit, H.; Keshavarz, A.; Iglauer, S. Gas Hydrate Characterization in Sediments via X-Ray Microcomputed Tomography. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 234, 104233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouachi, M.; Falenty, A.; Sell, K.; Enzmann, F.; Kersten, M.; Haberthür, D.; Kuhs, W.F. Microstructural Evolution of Gas Hydrates in Sedimentary Matrices Observed with Synchrotron X-Ray Computed Tomographic Microscopy: MICROSTRUCTRE OF GAS HYDRATES. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2015, 16, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xu, N.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Review of Morphology Studies on Gas Hydrate Formation for Hydrate-Based Technology. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 8148–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, F. Elastic waves through a packing of spheres. Geophysics 1951, 16, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindlin, R.D. Compliance of Elastic Bodies in Contact. J. Appl. Mech. 1949, 16, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorkin, J.; Nur, A.; Yin, H. Effective Properties of Cemented Granular Materials. Mech. Mater. 1994, 18, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
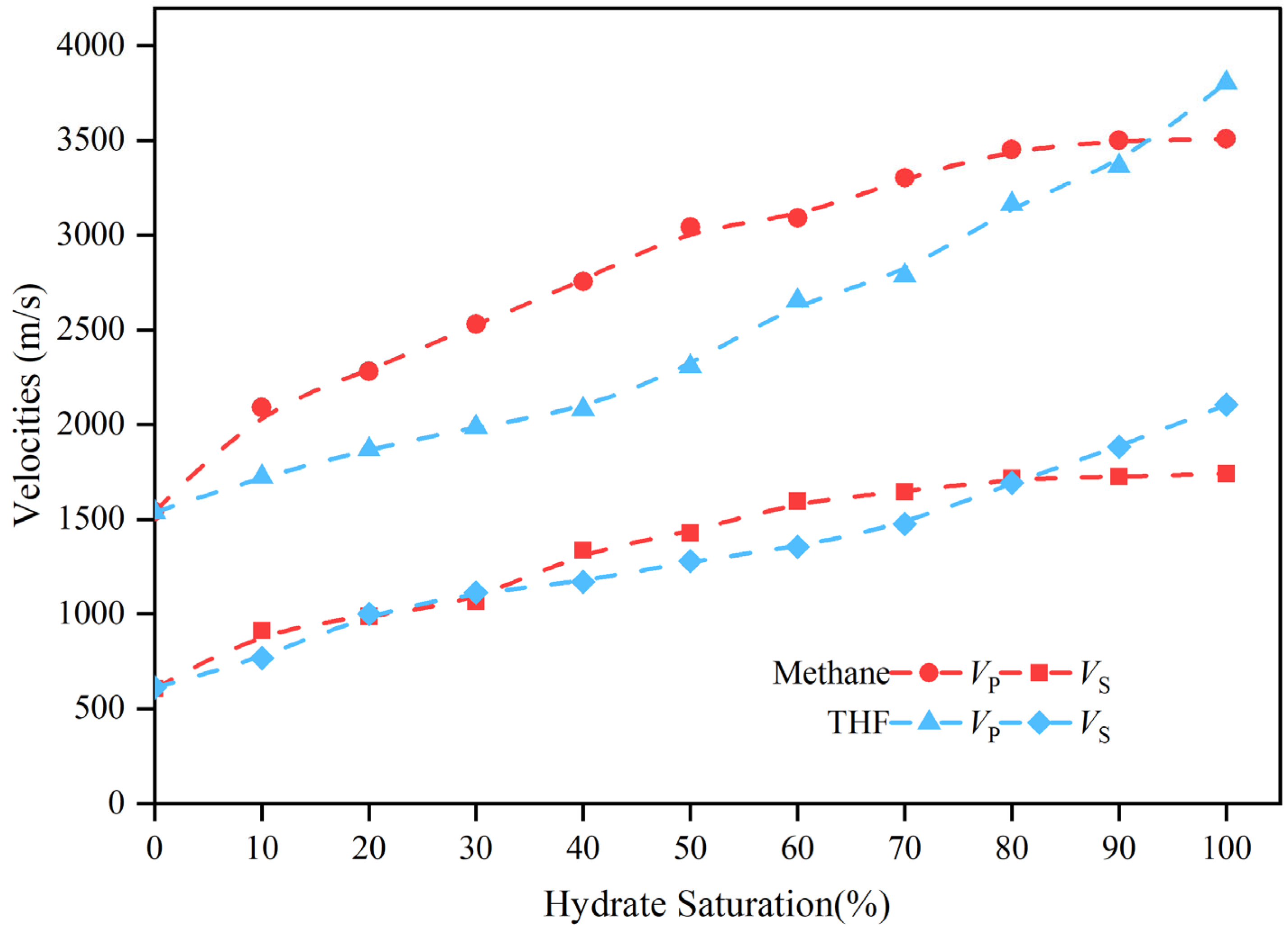
| Hydrate Saturation (%) | Methane Hydrate Samples | THF Hydrate Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vp (m/s) | Vs (m/s) | Vp (m/s) | Vs (m/s) | |
| 0 | 1540.1 | 606.3 | 1537.8 | 610.1 |
| 10 | 2089.8 | 913.0 | 1723.6 | 767.2 |
| 20 | 2281.7 | 988.2 | 1869.7 | 1002.0 |
| 30 | 2529.1 | 1066.2 | 1988.4 | 1112.4 |
| 40 | 2755.7 | 1336.5 | 2081.3 | 1170.4 |
| 50 | 3041.5 | 1428.1 | 2306.0 | 1280.0 |
| 60 | 3090.0 | 1596.3 | 2655.4 | 1354.1 |
| 70 | 3303.5 | 1644.6 | 2785.7 | 1474.2 |
| 80 | 3452.1 | 1716.6 | 3163.8 | 1691.6 |
| 90 | 3500.7 | 1723.8 | 3364.6 | 1884.1 |
| 100 | 3508.0 | 1741.7 | 3805.4 | 2105.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Bu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Meng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, G. A Comparative Study on Acoustic Characteristics of Methane and Tetrahydrofuran Hydrate-Bearing Sediments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122239
Zhao W, Bu Q, Wang Z, Liu T, Meng Q, Zhao Y, Hu G. A Comparative Study on Acoustic Characteristics of Methane and Tetrahydrofuran Hydrate-Bearing Sediments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122239
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wengao, Qingtao Bu, Zihao Wang, Tong Liu, Qingguo Meng, Yapeng Zhao, and Gaowei Hu. 2024. "A Comparative Study on Acoustic Characteristics of Methane and Tetrahydrofuran Hydrate-Bearing Sediments" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122239
APA StyleZhao, W., Bu, Q., Wang, Z., Liu, T., Meng, Q., Zhao, Y., & Hu, G. (2024). A Comparative Study on Acoustic Characteristics of Methane and Tetrahydrofuran Hydrate-Bearing Sediments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122239







