Abstract
The effects of the interaction between sandy, mobile, low-relief (sorted) bedforms and two sewage outfalls were investigated along the south shore of Long Island, NY. Sand bedforms at scales from ripples to ridges are common on continental shelves. In dynamic environments, these features can migrate 10s to 100s of meters per year, especially during storms. Beyond engineering considerations, little is known of the interaction between these mobile features and anthropogenic structures. Modification of bedform topography and sediment grain-size distribution can be expected to alter the species composition, abundance, and diversity of the benthic community. At the study site, the interaction increased the scour of modern fine- to medium-grained sediments extending out to a kilometer and uncovered coarser-grained late Pleistocene sediments. This alteration of the seafloor in turn resulted in changes in composition, higher abundance, and lower diversity in the species assemblage found in the impacted area. The most advantaged species was Pseudunciola obliquua, a sightless, tube-building, surface deposit-feeding amphipod that is known to prefer a dynamic coarse sand habitat. Overall, the ecological effects of artificial structures on a wave-dominated seabed with sorted bedforms have not been adequately assessed. In particular, and of great importance, is the pending large-scale development of wind farms off the East Coast of the U.S.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Increasingly, coastal states are exercising sovereign rights over marine space on the continental shelf to meet the already high demand for artificial reefs, offshore oil rigs, aquaculture facilities, sewage outfalls, renewable energy devices for raw materials, energy production from renewable sources, oil and gas exploitation, maritime shipping and fishing activities, ecosystem and biodiversity conservation, as well as tourism, and underwater cultural heritage. The shelf, however, is a dynamic environment. Mobil features, like sand ridges, are bathymetric features vital for commercial and recreational fishing areas []. Habitats shift, however, both naturally and in response to human activity. Fixed offshore infrastructure can affect, and are affected by, sedimentary processes on the sea floor. Normal shelf sediment transport in a region, like the migration of bedforms and ridges, can bury or expose seabed infrastructure. In addition, fixed offshore structures will change the flow of bottom water and hence sediment transport patterns in and around the structure [,]. Resultant changes to both the sea floor composition and morphology (bedforms and ridges) will impact both the submerged structure’s stability and, perhaps, functioning as well as induce changes to the benthic habitat and local ecology (e.g., []).
In this study, the interaction of the sea floor with two ocean outfalls on the South Shore of Long Island (Figure 1) was examined. We show that the presence of the physical structures modified the natural, sand transport leading to variations in habitat consequently affecting the benthic community structure. The presence of the infrastructure impacted the sea floor for at least one kilometer from the structures. Findings from this study provide insight into plausible local ecological consequences on benthic infaunal communities that may result from artificial marine structures, such as wind farm structures, operated over long temporal scales.
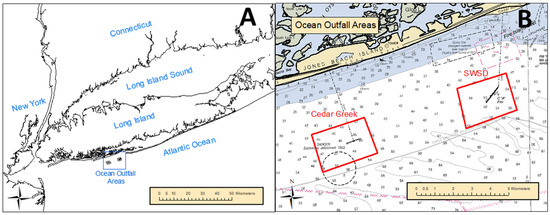
Figure 1.
Location map south of Long Island, NY, USA (A) and ocean outfalls study areas (B).
1.2. Review
Although anthropogenic marine structures are deployed across both hard and soft bottom substrates (e.g., [,,]) the majority of marine man-made structures are primarily deployed on soft-sediment habitats, because these habitats are one of the most ubiquitous comprising over 70% of all marine habitats on the continental shelves [,]. Soft-sediment communities serve crucial roles in ecological functioning. For example, they can regulate nutrient cycling via bioturbation, engineer habitats for themselves and other species, and facilitate energy transfer to upper trophic levels in local food webs [,,].
Changes in grain size, micro- and macro-topography, and other hydrographic conditions can strongly influence the composition of benthic assemblages (e.g., []). For example, Barros et al. [] determined that sand ripples generated by an artificial reef resulted in greater abundances of benthic macrofauna in troughs relative to crests in sand-ripple beds. Similarly, Ramey et al. [], off coastal New Jersey, found more variability in benthic infauna between troughs and crests of sand ripples less than one meter apart than similar features between two meters and four kilometers apart. Differences in grain size within and outside rippled scour depressions, with a relief of 0.3 to 0.5 m, within Monterey Bay, CA, for example, altered fish and invertebrate density and species richness []. At a larger spatial scale, Vasslides and Able [] identified distinct differences in abundance, richness, and composition of demersal fish assemblages associated with sampling location relative to shoreface sand ridges.
Sorted bedforms are generally low-relief, sandy bedforms with a range of features from ripples to sand waves that provide distinct habitats in response to waves and currents []. They are an important source of seafloor patchiness [] and common features on continental shelves [,] found worldwide including New York and New Jersey [,], North Carolina [], California [], Norway [], the Mediterranean [], and New Zealand []. Although engineering assessments of the movement of sorted bedforms have been done (e.g., [,]), there is little information about how they might interact with structures. Knowledge regarding the modification of benthic geomorphology and sediment composition from hydrological changes caused by submerged offshore marine structures often is limited to near field effects (~10 m) surrounding the structures, although the area of water-column impacts is generally assumed to encompass the tidal excursion []. Sediment scouring is one major consequence of submerged artificial structures that is relatively understudied but can cause drastic changes to seafloor bathymetry []. For example, the vertical oriented monopile structures of wind turbines can generate severe sediment scouring that is a product of subtidal currents increasing in local speed and further eroding the nearby sediment up to a depth of as much as twice the monopile diameter [,,].
Another consequence found on wave-dominated coasts [] with considerable erosion, transport, and deposition is the interruption of longshore movement of sorted bedforms and shoreface-attached sand ridges. Tidal currents, storm-driven currents, surface waves and internal waves all provide a stress on the sea floor that can move sediment (e.g., []). Bottom currents on the Long Island continental shelf have been observed to exceed the critical erosion velocity of fine sand-size particles intermittently during all seasons especially during sustained winter storms []. Numerical models of circulation and sediment transport have been used on the shelf to predict that winds from the northeast might generate currents strong enough to transport sediment in water depths between 20 m and 50 m [,]. Low-relief sand ridges or sand waves are known to migrate on the Long Island continental shelf most likely mobilized by currents during storms [,]. These common linear features migrate naturally up to tens of meters per year under normal conditions [,] but have been documented to move by as much as 450 m during periods of major storms []. Scour around structures tends to create near-field effects (~10 m) (e.g., [,,,,]). Changes in bedform mobility due to offshore infrastructure also can impact the benthic sediment a few hundred meters from the structures [] but the impacts of the latter on benthic habitats and local ecology are not well known. The manuscript documents far-field changes in the mobile seafloor on the inner Continental Shelf due to offshore infrastructure and identifies associated changes in the benthic habitat and community structure.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Areas
Two major ocean outfalls occur along the South Shore of NY (Figure 1): Cedar Creek and Southwest Sewer District (SWSD). About 223,000 cubic meters per day of treated wastewater is discharged at Cedar Creek at a depth of 15 m, about 4 km south of Tobay Beach, NY (40.5662, −73.4457). The diffuser array has 120 diffuser structures with diameters of about 1.5 m that rise about 2.5 m above the sea floor. A centrally located junction is about two meters square and rises about 2 m above the seafloor. The outfall of the SWSD discharges about 102,000 cubic meters per day of treated wastewater, 7.8 km east of the Cedar Creek outfall in 15 m of water, 4.3 km offshore (40.5855, −73.3607). The ocean currents around these sites are dominated by a semidiurnal tide superimposed on a net westward drift. The mean tidal range is approximately 0.8 m. Tidal excursions are approximately 1.5 to 2.1 km []. Significant wave heights are typically less than one meter but can reach over five meters in the extreme []. Upwelling driven by the response to alongshore winds provides an onshore flow at depth. The diffusers seemed to have worked properly, and any elevated concentrations of nutrients were found to have been dissipated within tens of meters []. The effluent had no measurable impact on the plankton community and the wastewater nutrient concentrations at the surface were minimal [].
A 2014 NOAA side-scan sonar survey [] documented variability due to changes in sediment type, and the occurrence of many large sedimentary features. Sorted bedforms and shoreface-attached sand ridges are particularly common on the Long Island shelf []. They may be several kilometers long and have been found as far as 20 km offshore []. The sea floor near the outfalls consisted of sorted bedforms with a relief of less than one meter. Although of low relief, these features were identified by changes in the acoustic backscatter, which have also been used successfully to delineate benthic infaunal habitats []. Backscatter contrast in these features was created by a veneer of lower backscatter, modern, fine-to-medium-grained sediments over coarser-grained Pleistocene gravel [] the latter of which produced a higher backscatter when exposed. The sea floor near the SWSD outfall had been found earlier to have been substantially disturbed by fishing activity [], but little fine-grained sediment was found to have accumulated and no benthic and planktonic impacts were documented.
2.2. Multibeam Sonar Survey
Multibeam sonar surveys were carried out in 2018 using a dual-head multibeam echo sounder (EM3000D, Kongsberg Maritime, Kongsberg, Norway) operating at the nominal sonar frequency of 300 kHz. Sound velocities and vessel heave, pitch, roll and heading were recorded concurrently for the correction of raw bathymetric data. Full bathymetric and backscatter coverage over 4.8 km2 was centered on each of the outfalls. Navigation and vertical elevation were determined by real-time kinematic (RTK) GPS. The RTK elevations were referenced to Vertical Datum of 1988 (NAVD88) calculated by using the ellipsoidal heights, and the geoid elevation (geoid 12a) was determined using online software provided by the National Geodetic Survey (http://ngs.noaa.gov (accessed on 30 May 2018)). The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) water-level observations collected at Sandy Hook, New Jersey, about 30 km WSW of the survey area, were used to confirm the tidal correction. Data processing was conducted using SwathEd software (Ocean Mapping Group, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, NB, Canada). The final bathymetry grids and backscatter mosaics were formed at horizontal resolutions of between 0.5 and 2.0 m as the footprint of the multibeam insonified area increased with water depth. Acoustic backscatter was taken as a proxy for bottom type. Lighter areas with high backscatter were interpreted as more coarse-grained than darker areas with low backscatter, although the presence of surficial material such as shells, sediment texture, and fine scale topography also affect backscatter. Bands of differing reflectivity trending NW–SE, as were found in this study, are a normal pattern along the South Shore of Long Island.
2.3. Sediment and Faunal Sampling
As will be shown later in the results, the sonar backscatter data suggested that the diffusers differentially disrupted sand waves and bottom type to the south. Sampling stations therefore were located north and south of the line oriented on the outfalls that bisected observed bottom type provinces. Benthic sediments were collected with a 0.04 m2 Modified van Veen grab sampler. To characterize sediment and fauna characteristics, sampling transects were oriented approximately northwest–southeast to follow sorted bedforms that were visually identified in the backscatter results. Five transects were allocated to each study area, with three outfall transects following a sorted bedform backscatter province that intersected the outfall and two control transects oriented along bedform provinces located to the west of the outfall. Transects were designated as A-J in a west-to-east direction. Six benthic grab samples were collected within each of the transects (e.g., A1–A6) with three samples to the north and three to the south of the line oriented in the direction of the outfalls that bisected each study area. As will be shown in the results, this north–south orientation split the sand-wave provinces associated with the outfall transects into undisturbed and disturbed subareas, consistent with a southwestward movement of the bedforms indicated by Schwab et al. []. Along a transect, sample locations were approximately 250 m apart, at least 100 m from a sorted bedform province boundary, and at least 150 m from the outfall diffuser. Flanagan et al. [] found no evidence of spatial autocorrelation in benthic community structure remained at distances of 250 m after accounting for the effect of bottom backscatter province. These sampling stations were, therefore, assumed to be independent in later statistical analysis of the data.
Sixty bottom samples for fauna and sediments were collected between 14 and 17 August 2018, with 30 at each study area. Subsamples of sediments for grain size were taken from each grab sample, and the remaining sediment was washed through a 0.5 mm sieve for fauna analysis. All material left on the sieve was preserved in 10% buffered formalin and stained with rose bengal. Faunal samples were rewashed in the lab and transferred to 70% ethanol before sorting and identification. Individual organisms were identified to species level whenever possible and the total for each taxon enumerated. Unless otherwise noted, all abundances are expressed as the number of individuals per sample (i.e., per 0.04 m2). A total of 43,965 animals representing 88 taxa were collected.
Sediment grain size analysis, following methodology in Folk [], was used to estimate percent composition by weight of major size fractions (gravel, sand, silt-clay). Sediment subsamples were initially partitioned into three size fractions by adding 50 mL of a 1% Calgon solution to the sample, mixed to disaggregate the particles in the sample, and wet sieved with distilled water through a combination of 2 mm and 63-micron sieves. The fraction greater than 2 mm (gravel) and the 2 mm to 63-micron (sand) fractions were placed in a drying oven at 60 °C for at least 48 h to obtain dry weights. Because sand dominated the samples, the sand fraction was further analyzed in a two-meter-long, temperature-controlled settling column to obtain a more detailed grain size distribution. Phi sizes between about 4 Phi to −10 Phi were determined over a 30-min test to a resolution of 0.001 Phi to calculate the mean, median, and skewness. Water containing a mud fraction less than 63 microns (silt-clay) was brought up to 1000 mL total volume by adding distilled water in a graduated cylinder, mixed thoroughly, and subsampled with a 20 mL pipette at a depth of 20 cm, 20 s after mixing to obtain an estimate of silt-clay. Pipette samples were placed in a drying oven at 60 °C for at least 48 h to obtain dry weight estimates. Silt-clay weight estimates included a correction for the amount of Calgon introduced to the samples.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Faunal data at each sampling station were summarized by calculating community structure metrics that included abundance (total number of individuals per grab sample), species richness S (number of taxa per grab sample), Shannon diversity ( where pi is the proportion of individuals of each species, equitability (), and Simpsons index of diversity for large samples (D . Equitability ranges from 0 to 1 and measures how evenly individuals are distributed among the S species present. Simpson’s index of diversity also ranges from 0 to 1.
Examining differences in abundance of individual taxa between groups of sampling stations was performed using a group-equalized point biserial correlation coefficient () which corrects the correlation coefficient for the unequal number of observations in the groups [,]. This method was used to identify those individual taxa that were “indicator species” for specific groups. A Bonferroni correction was used to set the significance level of the correlations at where and is the number of taxa (88). Abundance data were Hellinger transformed prior to this analysis, as noted below.
Grab sample data were analyzed by redundancy analysis (RDA), a multivariate direct gradient technique that explicitly incorporates environmental variables in the analysis of the faunal data. RDA, first suggested by Rao [], is a technique that combines ordination of sample sites based on species abundance data with regression on the environmental data in order to examine the relationship between community structure and environmental variables []. By examining the environmental and biological data simultaneously, this analysis depicts the trends in the species data that are related to the selected environmental data. RDA is based on Euclidean distance, which is not the most appropriate resemblance measure for species data, since it incorrectly interprets shared species absences between samples as similarities. In order to circumvent this shortcoming, abundance data were Hellinger transformed by taking the square root of relative abundances of each species in a sample []. This transformation focuses the analysis on compositional differences, reduces the influence of the most abundant species, and combined with Euclidean distance, has been shown to produce good representations of ecological data []. RDA analyses were conducted in Canoco 4.5 (Microcomputer Power, Ithaca, NY, USA).
To quantify the effect of the outfall diffusers on benthic community structure, multivariate nonparametric analysis of variance was carried out on the Hellinger transformed species data within the RDA. Two categorical factors were defined. Sorted bedform transects were designated as control or impacted outfall based on their location relative to the diffusers. Since the sonar backscatter data suggested that the diffusers differentially disrupted sand waves and bottom type to the south, the second categorical factor distinguished whether a sampling station was located north or south of the line oriented on the outfalls that bisected the study areas. Sampling stations along a transect were, therefore, designated as north (e.g., A1, A2, A3) or south (e.g., A4, A5, A6). The only exception to this north–south designation was for stations I4-6; these stations were included as south to balance the experimental design. Data were analyzed as a hierarchical split-plot experiment. Sorted bedform provinces were whole-plots and sampling stations within provinces were split-plots. The interaction between the two categorical factors was examined first by explicitly defining each interaction term as an explanatory variable (N*Control, S*Control, N*Outfall, S*Outfall). As with any analysis of variance, an F-ratio statistic was calculated that expresses how strongly the species assemblage data are explained by the explanatory variables []. The size of this F statistic was assessed by permutation test. Sorted bedform provinces and sampling stations within provinces were permuted 1000 times, with provinces freely exchanged between control and impacted and with stations freely exchanged between north and south but always remaining within their province. If an interaction model was not justified from this analysis, the effect of each categorical factor would then be considered separately in an additive model.
3. Results
3.1. Multibeam Sonar Backscatter
Here, sand waves are large features that created multibeam backscatter patterns oriented approximately northwest–southeast (Figure 2A,B). The presence of the outfall seemed to have disrupted the natural migration of sand waves in the area modifying the sediment composition, resulting in backscatter differences to the north and south of the diffuser. Visual examination of the multibeam backscatter patterns suggested the presence of about 19 sharply edged provinces with differing bottom type (Figure 3A,B). Ten of the sand wave provinces were targeted for bottom sampling (Figure 4A,B).
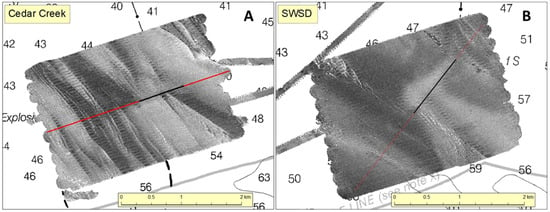
Figure 2.
Sonar backscatter maps covering an area of about 3.0 × 1.6 km around (A) the Cedar Creek outfall and (B) the SWSD outfall. The outfall diffuser is represented as a black line. Acoustic backscatter was taken as a proxy for bottom type or habitat. High backscatter (light grey) usually corresponds to coarser sediments and/or coarser-scale morphology relative to low backscatter areas (dark greys).
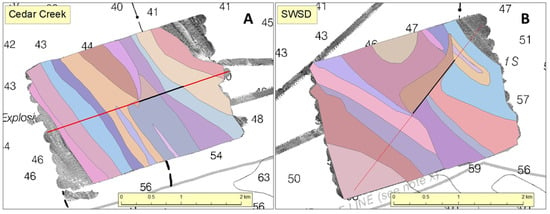
Figure 3.
Sand wave provinces around (A) the Cedar Creek outfall and (B) the SWSD outfall. The outfall diffuser is represented as a black line. The red line bisects the study area into north and south regions and is oriented in the same direction as the outfall. Colors delineate the extent of provinces. The colors were arbitrarily chosen and do not represent similar conditions between outfall areas.
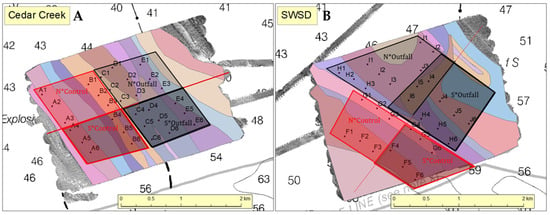
Figure 4.
Sampling transects (A–J), sampling locations along a transect (1–6), and the split-plot factor design used in the RDA analysis to test the impact of the diffusers on benthic fauna community structure.
3.2. Sediment and Faunal Sampling
Grain sizes ranged from 0.02 mm (2.15 phi) to 0.3 mm (1.65 phi), and only 8% of the samples had a fine-grained, silt-clay (i.e., less than 0.00625 mm or 4 phi) fraction greater than 3%, and none greater than 6.3%. Grain size data are tabulated in the Supplementary Materials. Coarser sediment was found in an impacted zone near the outfall, while finer sediment tended to be found further to the west. Although the sea floor was comprised primarily of sand, other observations in the area showed that there was a large settling flux of suspended particulates to the sea floor. During this study, any open enclosures on instruments deployed on the sea floor tended to trap and retain fine-grained sediment. Only a small fraction of this fine sediment was incorporated into the bottom sediment by bioturbation, but even low-relief bedforms can trap some particulates in the sediment enhancing the backscatter discrimination of the sorted bedforms and leaving a bimodal distribution of grain sizes.
A total of 43,965 animals representing 88 taxa were collected in the 60 samples. The average abundance in the 60 samples was 733 ± 531 (sd) individuals per sample (18,320 ± 13,274 per m2) and the average species richness was 25 ± 4 (sd) taxa per sample. Of the 88 taxa, 45% were polychaetes, 17% were mollusks, 31% were crustaceans, and the remainder (7%) was distributed among six other groups (Actiniaria, Echinodermata, Holothuroidea, Nemertinea, Oligochaeta, Turbellaria). Numerical dominants included the amphipod Pseudunciola obliquua (average abundance = 491 individuals per sample), the polychaete Polygordius spp (60 per sample), the amphipod Ampelisca spp (25 per sample), the polychaete Prionospio pygmaeus (23 per sample), the amphipod Protohaustorius wigleyi (20 per sample), the amphipod Acanthohaustorius millsi (18 per sample), the amphipod Rhepoxynuis epistomus (16 per sample), oligochaetes (12 per sample), the polychaete Caulleriella venefica (10 per sample), and the bivalve Spisula solidissima (5 per sample). These 10 taxa represented about 93% of the total number of individuals collected, and no other taxon had an average abundance greater than 5 per sample. Faunal data are tabulated in the Supplementary Materials.
3.3. Statistical Analysis
The RDA ordination triplot in Figure 5 displays the relationship between benthic faunal community structure and the categorical explanatory variables (Control/Outfall and N/S). In this ordination diagram, points represent the community structure at each sampling station; those that plot close to one another have similar species composition while points far apart are dissimilar. The larger red triangles represent the categorical explanatory variables and are located at the centroid of the stations belonging to that categorical variable (e.g., the red triangle labeled N*Control is the centroid of the samples in the designated regions indicated in Figure 4). The black arrows represent the direction of the steepest increase for selected species whose variances are well explained by the RDA analysis. The origin is the mean Hellinger transformed abundance of the species and decreasing values extend through the origin in the direction opposite the head of the arrow. Station points can be orthogonally projected onto the arrow of a species (i.e., the direction of the projected point is perpendicular to the arrow); this projection approximately orders the samples from the largest to the smallest value for that species.
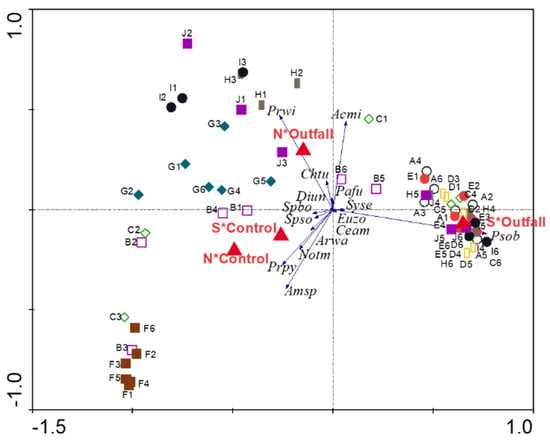
Figure 5.
RDA ordination triplot for the benthic fauna. Species codes are tabulated in the Supplementary Materials. Different sample symbols were assigned to each transect.
Permutation tests indicated that the interaction between N/S and Control/Outfall was significant for both the first canonical axis (F-ratio = 13.55, p = 0.011) and for all canonical axes combined (F-ratio = 5.92, p = 0.001). The four categorical interaction variables (N*Control, S*Control, N*Outfall, S*Outfall) explained 24.1% of the total variability in community structure. The N*Control and S*Control centroids plotted close together in the ordination diagram indicating that their community structure was the most similar of the four station groups. In contrast, N*Outfall and S*Outfall had distinctly separated centroids, indicating distinct differences in community structure north and south of the outfalls. The S*Outfall centroid was also distinctly separated from the control centroids along the first canonical axes. It should be noted that heterogeneity of variances probably also contributed to the significant permutation test outcome. Control province points (e.g., F1–F6) were more tightly grouped together while impacted province points (e.g., I1–I6) were more scattered in the ordination diagram.
The observed gradient in benthic faunal community structure can be attributed at least in part to variation in sediment grain size within the study areas. In Figure 6, a contour plot, generated from a local polynomial regression with locally estimated scatterplot smoothing (loess) between mean grain size in phi units and sample scores, was overlaid on the ordination diagram. The coarsest sediments were associated with South*Outfall stations, although some North*Outfall stations in provinces D and E, and those of province A, are also associated with low phi size values.
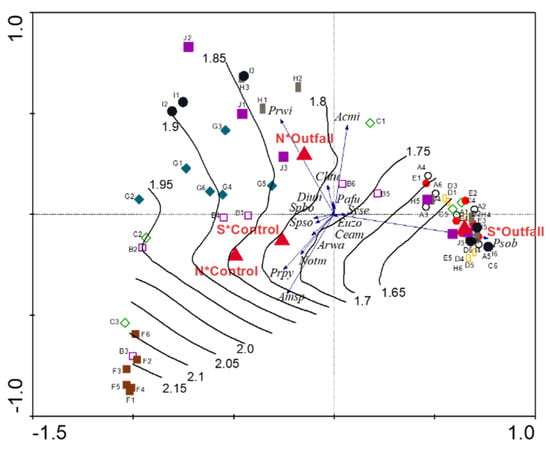
Figure 6.
A contour-based attribute plot of mean grain size in phi units overlaid on the RDA ordination triplot for the benthic fauna. The contour plot was generated from a locally weighted polynomial regression (loess) between mean grain size and sample scores. Species codes are tabulated in the Supplementary Materials.
Point-biserial correlation analysis of Hellinger transformed abundance on individual taxa indicated that 16 of 88 taxa were associated with one of the four geographic regions (Table 1) at the p < 0.05 level. Four taxa (Acanthohaustorius millsi, Pseudunciola obliquua, Euclymene (f. Clymenella) zonalis, and Syllides setosa) were significant at a family error rate of 0.05. A. millsi was positively associated with N*Outfall stations. It is an infaunal, mobile, surface deposit-feeding amphipod. Three species were associated with the S*Outfall region and presumably positively affected by the sediment changes associated with the outfall. These three species had the greatest point biserial correlations, suggesting the strongest association with a spatial region. P. obliquua is a sightless, tube-building, surface deposit-feeding amphipod. Its preferred substrate is medium to coarse sand [] and is a dominant species on dynamic sandy bottoms []. It has an annual life history and would have been ovigerous during the sampling period. E. zonalis and S. setosa are both polychaetes. E. zonalis is a head-down, tube-building, subsurface deposit feeder, while S. setosa is an epifaunal, motile, carnivore.

Table 1.
Species with a significant association with one of the four spatial regions. rpb = point biserial correlation coefficient. p-value = significance level. Only taxa with p < 0.05 are listed. Bonferroni correction for n = 88 species requires p-values to be 0.05/88 < 0.00057 to be significant at a family error rate of 0.05. These species are shown in bold font.
The maximum or minimum of most community structure metrics occurred at S*Outfall stations. Abundance was highest at S*Outfall stations and declined along the first ordination axis in the direction of N*Outfall, S*Control, and N*Control stations (Figure 7A). Shannon diversity (Figure 7B), evenness (Figure 7C), and Simpson’s index (not plotted) increased along the first ordination axis in the direction of N*Outfall, S*Control, and N*Control stations. Species richness (Figure 7D) was more complicated and did not show an obvious relationship to the S*Outfall stations.
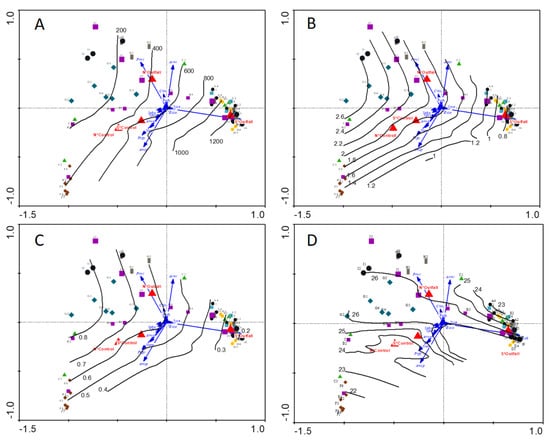
Figure 7.
Contour-based attribute plots of abundance (A), Shannon diversity (B), evenness (C), and species richness (D) overlaid on the Figure 5 RDA ordination triplot for the benthic fauna. The contour plots were generated from a locally weighted polynomial regression (loess) between the metric and sample scores. Species codes are tabulated in the Supplementary Materials.
4. Discussion
In this study, effects on the shelf sediment composition and morphology and the infaunal assemblage out to a distance of one kilometer were observed as a result of the interaction between mobile sorted bedforms and outfall structures. The outfall structures disrupted the natural migration of sand bedforms in the area modifying the sediment composition. Although the sea floor is comprised of sand, there is a large flux of suspended particulates on the sea floor. Anecdotally, any open enclosures on the instruments (e.g., ADCP) deployed for this study tended to trap and retain copious amounts of mud, but only a small fraction was permanently incorporated into the bottom sediment. Such a process may also have incorporated wastewater with elevated nutrients into the surficial sediment, although, as mentioned earlier, the diffusers seemed to have worked properly and any elevated concentrations of nutrients were found to have been dissipated within tens of meters [], so we believe this would be insignificant in impacting the benthic community.
In the case of the outfall diffusers, the presence of the physical structures modifies the natural sediment transport leading to variations in substrate consequently manifest in the benthic community structure. Benthic samples showed evidence of a sediment impact with generally coarser sediments dominating around and south of the outfalls, primarily due to scour and winnowing of finer-grained sediments. These differences in grain size and changes in other hydrodynamic conditions altered the benthic community structure with increased abundance, lower diversity and evenness, and changes in species composition associated with the impacted area of the outfalls. This impact seems to extend for at least one kilometer from the structures, comparable to the tidal excursion. Coarser sediments dominated around and south of the outfalls due to scour and winnowing of finer-grained sediments. The differences in grain size and changes in other hydrodynamic conditions altered the benthic community structure with increased abundance, lower diversity and evenness, and changes in species composition associated with the impacted area of the outfalls.
Faunal differences documented in this study were dominated by changes in the abundance of the amphipod Pseudunciola obliquua. This species is found in medium to coarse sand [] and dynamic sandy bottoms []. While not much is known about the ecology of P. obliquua, a functionally similar, tubiculous amphipod species common in the New York Bight, Ampelisca abdita, is an extremely important food source for winter flounder, scup, spot, weakfish, and silver hake, cunner, Northern puffer, and Atlantic croaker [,,]. A similar trophic role as food for demersal fish might be expected for P. obliquua. Of the four species significantly associated at a family error rate of 0.05 with a spatial region, three of them were associated with the S*Outfall. These three S*Outfall species were advantaged in some way in the generally coarser sediments. Hallenbeck et al. [] found lower faunal abundances and species richness in the coarser sediments of rippled scour depressions relative to the finer-grained sediments outside and attributed the differences to a well-established negative relationship between grain size and species abundance and diversity. In contrast to the “relatively depauperate” coarse sediment habitat they observed, we found higher abundances and no strong relationship between grain size and species richness. This is possibly due to an ambient, high flux of fine-grained sediment being transported in our study area and/or some input from the STP outfall, although the disparate life history characteristics of the three species advantaged in the S*Outfall regions suggest a complicated relationship to physical environmental characteristics. Although the abundance and species richness patterns we found disagree with Hallenbeck et al. [], the overall lower diversity and evenness we observed was consistent with their study conducted in California State waters.
Sorted bedforms and possibly shore-attached ridges are widespread and move at rates of 10s to 100s m yr−1, especially during storms (e.g., []). Infrastructure on the seafloor produces a chronic, permanent impact on sediment composition and morphology and a subsequent impact on benthic species composition, abundance, and diversity. Visual observations (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4) indicated that the sorted bedforms in the N*Control and S*Control were reforming into continuous features to the west of the outfalls. Features thus maintained could persist for biologically relevant periods of time before being “reset” by the next sufficiently extreme event or possibly migrating through the area. Thus, the extent to which structures modify the seafloor as well as the lifetimes of these modifications needs to be evaluated. The ecological effects of artificial structures on the seabed have not been adequately assessed. In particular, and of great importance, is the pending large-scale development of wind farms off the East Coast of the U.S.
5. Conclusions
The inner shelf is a dynamic environment. In the presence of mobile shelf sands, fixed infrastructure can be buried or exposed by naturally migrating bedforms by up to a meter or more. Exposed points of fixed infrastructure can alter and maintain changes in substrate composition and morphology asymmetrically to a distance exceeding one kilometer, both in the direction of bedform migration and perpendicular to the migration pathway. Changes in habitat substrate composition alone can in turn be reflected in benthic abundance, diversity, species richness, and evenness. Habitat alterations from multiple structures with spacings of less than a kilometer should be expected to interact and overlap to cover the field of installation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jmse12122142/s1, Table S1. Grain-size Data. Table S2. Benthic fauna species list, average abundance, frequency of occurrence, and percent frequency of occurrence.
Author Contributions
All authors participated in conceptual design. R.M.C. and J.B. prepared the biological methods; H.J.B. carried out the sedimentological methods; R.D.F. conducted the multibeam methods. These authors verified the various relevant data. All authors participated in the formal analysis and investigation. R.M.C. and H.J.B. prepared the original draft and coordinated review and editing. Project Administration: H.J.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Division of Marine Resources, Memorandum of Understanding AM11315, Task #14.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the authors and contained in a report to the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation.
Acknowledgments
We were fortunate to have the support of the staff of the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation’s Division of Marine Resources, especially Assistant Director Dawn McReynolds, and Ocean Coordinators Casey Personius and Sherryll Jones.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Vasslides, J.; Able, K. Importance of shoreface sand ridges as habitat for fishes off the northeast coast of the United States. Fish. Bull. 2008, 106, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yamini, O.A.; Mousavi, S.H.; Kavianpour, M.R.; Movahedi, A. Numerical modeling of sediment scouring phenomenon around offshore wind turbine pile in marine environment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, M.; Long, M.; Doherty, P. Geological and geotechnical constraints in the Irish Sea for offshore renewable energy. J. Maps 2020, 16, 1758811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, D.A.; Deschutter, Y.; Vincx, M.; Vanaverbeke, J. Enrichment and shifts in macrobenthic assemblages in an offshore wind farm area in the Belgian part of the North Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 95, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulleri, F. Role of recruitment in causing differences between intertidal assemblages on seawalls and rocky shores. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 287, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafforn, K.A.; Glasby, T.M.; Airoldi, L.; Rivero, N.K.; Mayer-Pinto, M.; Johnston, E.L. Marine urbanization: An ecological framework for designing multifunctional artificial structures. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heery, E.C.; Bishop, M.J.; Critchley, L.P.; Bugnot, A.B.; Airoldi, L.; Mayer-Pinto, M.; Sheehan, E.V.; Coleman, R.A.; Loke, L.H.; Johnston, E.L.; et al. Identifying the consequences of ocean sprawl for sedimentary habitats. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 492, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrush, S.F.; Dayton, P.K. Disturbance to marine benthic habitats by trawling and dredging: Implications for marine biodiversity. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 449–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, J.E.; Grabowski, J.H. Soft-sediment communities. In Marine Community Ecology and Conservation; Bertness, M.D., Bruno, J.F., Silliman, B.R., Stachowicz, J.J., Eds.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 227–249. [Google Scholar]
- Raffaelli, D.; Bell, E.; Weithoff, G.; Matsumoto, A.; Cruz-Motta, J.J.; Kershaw, P.; Parker, R.; Parry, D.; Jones, M. The ups and downs of benthic ecology: Considerations of scale, heterogeneity and surveillance for benthic-pelagic coupling. J. Exp. Mar. BioL. Ecol. 2003, 285, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.S.; González, M.T.; Bremner, J.; Oliva, M.; Heilmayer, O.; Laudien, J.; Riascos, J.M. Functional diversity of marine macrobenthic communities from sublittoral soft-sediment habitats off northern Chile. Helgoland Mar. Res. 2011, 65, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.R.; Kadin, M.; Nascimento, F.J.; Tamelander, T.; Törnroos, A.; Bonaglia, S.; Bonsdorff, E.; Brüchert, V.; Gårdmark, A.; Järnström, M.; et al. The importance of benthic-pelagic coupling for marine ecosystem functioning in a changing world. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 2179–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.S.; Elliot, M. Ecology of Marine Sediments: From Science to Management, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; 225p. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, F.; Underwood, A.J.; Archambault, P. The influence of troughs and crests of ripple marks on the structure of subtidal benthic assemblages around rocky reefs. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, P.A.; Grassle, J.P.; Grassle, J.F.; Petrecca, R.F. Small-scale, patchy distributions of infauna in hydrodynamically mobile continental shelf sands: Do ripple crests and troughs support different communities? Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 2222–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallenbeck, T.R.; Kvitek, R.G.; Lindholm, J. Rippled scour depressions add ecologically significant heterogeneity to soft-bottom habitats on the continental shelf. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 468, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Coco, G.; Murray, A.B.; Green, M.O. Sorted bed forms as self-organized patterns: 1. Model development. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F03015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.B.; Thieler, E.R. A new hypothesis and exploratory model for the formation of large-scale inner-shelf sediment sorting and “rippled scour depressions”. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchione, D.A.; Grant, W.D.; Tate, G.B. Rippled scour depressions on the inner continental shelf off central California. J. Sed. Petrol. 1984, 54, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, W.C.; Thieler, E.R.; Allen, J.R.; Foster, D.S.; Swift, B.A.; Denny, J.F. Influence of inner-continental shelf geologic framework on the evolution and behavior of the barrier-island system between Fire Island inlet and Shinnecock inlet, Long Island, New York. J. Coast. Res. 2000, 16, 408–422. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, W.C.; Denny, J.F.; Butman, B.; Danforth, W.W.; Foster, D.S.; Swift, B.A.; Lotto, L.L.; Allison, M.A.; Thieler, E.R. Seafloor Characterization Offshore of the New York—New Jersey Metropolitan Area Using Side-Scan Sonar; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 00-295; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2000; 16p.
- Gutierrez, B.T.; Voulgais, G.; Thieler, E.R. Exploring the persistence of sorted bedforms on the inner continental shelf of Wrightsville Beach, North Carolina. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellac, V.K.; Boe, R.; Rise, L.; Siagstad, D.; Longva, O.; Dolan, M. Rippled scour depressions on the continental shelf bank slopes off Nordlan and Troms, Northern Norway. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, G.; Budillon, F.; Conforti, A.; Di Bitetto, M.; Di Martino, G.; Innangi, S.; Simeone, S.; Tonielli, R. Sorted bedforms over transgressive deposits along the continental shelf of western Sardinia (Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Geol. 2015, 359, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, K.P.; Healy, T.R. Formation of ripple bands in a wave-convergence zone. J. Sed. Petrol. 1988, 58, 195–207. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth, A.A.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H.; de Vriend, H.J. Modelling sand wave migration in shallow shelf seas. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 2795–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenders, S.; Damveld, J.H.; Schouten, J.; Hoekstra, R.; Roetert, T.J.; Borsje, B.W. Numerical modeling of the migration direction of tidal sand waves over sand banks. Coast. Eng. 2021, 163, 103790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Papanicolaou, A. Sediment Threshold under Stream Flow: A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Civil Eng. 2008, 12, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, R.J.; Harris, J.M.; Sutherland, J.; Rees, J. The nature of scour development and scour protection at offshore windfarm foundations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Boon, J.H.; Sutherland, J.; Whitehouse, R.; Soulsby, R.; Stam, C.J.M.; Verhoeven, K.; Høgedal, M.; Hald, T. Scour behaviour and scour protection for monopile foundations of offshore wind turbines. In Proceedings of the European Wind Energy Conference, EWEC, London, UK, 22–25 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Neill, S.P.; Litt, E.J.; Couch, S.J.; Davies, A.G. The impact of tidal stream turbines on large-scale sediment dynamics. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Arnott, R. Wave-Dominated Coasts. In Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science; Wolanski, E., McLusky, D.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 73–116. [Google Scholar]
- Butman, B.; Alexander, P.S.; Scottic, A.; Beardley, R.C.; Anderson, S.P. Large internal waves in Massachusetts Bay transport sediment offshore. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 2029–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, J.W.; Swift, D.J.P.; Gadd, P.E.; Stubblefield, W.L.; Case, F.N.; Brashhear, H.R.; Haff, K.W. Fair weather and storm sand transport on the Long Island, New York, inner shelf. Sedimentology 1978, 25, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.K.; Signell, R.P. Circulation and sediment transport in the vicinity of the Hudson Shelf Valley. In Estuarine and Coastal Modeling: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 3–5 November 1999; Spaulding, M.A., Ed.; The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 1999; pp. 380–394. [Google Scholar]
- Butman, B.; Alexander, P.S.; Harris, C.K.; Lightsom, F.S.; Martini, M.A.; ten Brink, M.B.; Traykovski, P.A. Oceanographic Observations in the Hudson Shelf Valley, December 1999–April 2000: Data Report; U.S. Geological Survey Open File Report 02-217; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003.
- Trowbridge, J.H. A mechanism for the formation and maintenance of shore-oblique sand ridges on storm-dominated shelves. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 16071–16086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, D.; Falques, A.; DeSwart, H.E.; Walgreen, M. Modeling the formation of shore-face connected sand ridges on storm-dominated inner shelves. J. Fluid Mech. 2001, 441, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Goff, J.A.; Flood, R.D.; Christensen, B.; Austin, J.A. Sorted bedforms off western Long Island, New York, USA: Asymmetrical morphology and twelve-year migration record. Sedimentology 2018, 65, 2202–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrini, V.L.; Flood, R.D. A comparison of rippled scour depressions identified with multibeam sonar: Evidence of sediment transport in inner shelf environments. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 1979–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, W.C.; Baldwin, W.E.; Warner, J.C.; List, J.H.; Denny, J.F.; Liste, M.; Safak, I. Change in morphology and modern sediment thickness on the inner continental shelf offshore of Fire Island, New York between 2011 and 2014: Analysis of hurricane impact. Mar. Geol. 2017, 391, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.; VanBlaricom, G.R.; Dayton, P.K. Man-made structures on marine sediments: Effects on adjacent benthic communities. Mar. Biol. 1982, 70, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, R.F.; Anderson, T.W. Influence of an artificial reef on the surrounding infaunal community. Mar. Biol. 1990, 107, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, F.; Underwood, A.J.; Lindegarth, M. The influence of rocky reefs on structure of benthic macrofauna in nearby soft-sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 52, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannheim, J.; Bergstrom, L.; Birchenough, S.N.R.; Brzana, R.; Boon, A.R.; Coolen, J.W.P.; Dauvin, J.-C.; De Mesel, I.; Derweduwen, J.; Gill, A.B.; et al. Benthic effects of offshore renewables: Identification of knowledge gaps and urgently needed research. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2020, 77, 1092–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemery, L.G. Changes in Benthic and Pelagic Habitats Caused by Marine Renewable Energy Devices. In Ocean Energy Systems-Environmental 2020 State of the Science Report: Environmental Effects of Marine Renewable Energy Development Around the World; Copping, A.E., Hemery, L.G., Eds.; Ocean Energy Systems (OES): Lisbon, Portugal, 2020; pp. 104–125. [Google Scholar]
- Games, K.P.; Gordon, D.I. Study of sand wave migration over five years as observed in two windfarm development areas, and the implications for building on moving substrates in the North Sea. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 2014, 05, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokuniewicz, H.J.; Cerrato, R.M.; Flagg, C.; Flood, R.; Huang, Y.; Lonsdale, D.; Schweitzer, K.; Swanson, R.; Willig, K.; Wilson, R. Impacts of Ocean Sewage Treatment Plant Outfalls; Draft Final Report, NYSDEC/SoMAS; 2020; 72p. Available online: https://extapps.dec.ny.gov/docs/fish_marine_pdf/dmrsomasoutfalls.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- Schweitzer, K. The Seasonal and Spatial Effects of a Sewage Outfall on the Planktonic Community Composition and Abundance. Master’s Thesis, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY, USA, 2019; 92p. [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan, A.M.; Flood, R.D.; Maher, N.P.; Cerrato, R.M. Quantitatively characterizing benthic community-habitat relationships in soft-sediment, nearshore environments to yield useful results for management. J. Environ. Manang. 2019, 249, 109361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.A.; Weltner, R.; Aluck, R.; Bissett, D. State of seafloor and sewage outfall pipes offshore Jones Beach, NY. In Vivo: The Publication of the Metropolitan Association of College and University Biologists. In Proceedings of the 43rd annual MACUB Conference, Malloy College, Rockville Center, NY, USA, 23 October 2010; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan, A.M.; Flood, R.D.; Frisk, M.G.; Garza, C.D.; Lopez, G.R.; Maher, N.P.; Cerrato, R.M. The relationship between observational scale and explained variance in benthic communities. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folk, R.L. Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks; Hemphill Pub. Co.: Austin, TX, USA, 1974; 64p. [Google Scholar]
- De Cáceres, M.; Legendre, P. Associations between species and groups of sites: Indices and statistical inference. Ecology 2009, 90, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tichý, L.; Chytrý, M. Statistical determination of diagnostic species for site groups of unequal size. J. Veg. Sci. 2006, 17, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.R. The use and interpretation of principal components analysis in applied research. Sankhyā Ser. A 1964, 26, 329–358. [Google Scholar]
- Jongman, R.H.G.; ter Braak, C.J.F.; Van Tongeren, O.F.R. 1995. Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; 299p. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E.D. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002; 500p. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, R.J.; Cutter, G.R., Jr.; Hobbs, C.H. Potential impacts of sand mining offshore of Maryland and Delaware: Part 2—Biological considerations. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 20, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.A.; Woodhead, P.M.J. The life history and sexual biology of Pseudunciola obliquua (Crustacea: Amphipoda) in the New York Bight. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1984, 18, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, D.R.; Tancredi, J.T. Secondary production of the amphipod Ampelisca abdita Mills and its importance in the diet of juvenile winter flounder (Pleuronectes americanus) in Jamaica Bay, New York. Estuar. Coasts 1992, 15, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steimle, F.W.; Pikanowski, R.A.; Macmillan, D.G.; Zetlin, C.A.; Wilk, S.J. Demersal Fish and American Lobster Diets in the Lower Hudson—Raritan Estuary; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-NE-161; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2000; 106p.
- Cerrato, R.M. Long-term and large-scale patterns in the benthic communities of the Lower Bay Complex. In The Hudson River Ecosystem; Levinton, J.S., Waldman, J.R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 242–465. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).