Abstract
Five layers of detrital amphiboles in the CJ08-008 sediment core from the northwest Indian Ocean have been found. To analyze their genetic types and provenance, an electron probe microanalysis of 300 amphibole grains from the core was conducted to calculate the numerical and characteristic values of cations in the crystal structure. The results showed that amphiboles with high Si, Ca, and Mg contents and low Na and K contents exhibit a low degree of weathering and that amphiboles mainly comprise tschermakite (46.43~70.69%), followed by magnesiohornblende, in the calcic amphibole subgroup. The types of sources for these amphiboles are mainly different types of metamorphic and magmatic rock. A large proportion of the detrital amphiboles (>60%) are derived from metamorphic rocks, followed by intermediate acid-intrusive rocks. The genetic analysis of amphiboles showed that most of the medium acid-intrusive amphiboles belong to the crust–mantle type, followed by the mantle type. Most of the amphiboles of metamorphic origin are of the low-pressure type. The amphiboles in the CJ08-008 sediment core exhibit characteristics different from those brought by monsoons from surrounding land masses. The variations in the amphiboles indicate different sources, which may have different origins; these origins could include the Carlsberg Ridge, the Owen Fault Zone, or older submarine sediment sequences eroded by turbidity currents.
1. Introduction
The northwest Indian Ocean is a monsoon region that receives a substantial quantity of dust from Asia and Africa. This dust has led to the formation of significant sedimentary systems along the Asian–African continental margin [1]. The area surrounding this region is characterized by medium-sized rivers and sandy regions, resulting in the formation of different sedimentary systems due to the input of eroded materials into the ocean. Numerous studies have indicated that the terrigenous material in the adjacent basins of the ridge is mainly transported by monsoonal activity over the Indian Ocean [2,3,4,5]. The Carlsberg Ridge (CR), located in the northwest Indian Ocean, is an important geomorphic unit where products from the weathered and hydrothermal parts of the CR are transported into the ocean basin, and these products are preserved in sediment [6,7,8]. Cronan [9] found that three sediment cores, DSDP234, DSDP235, and DSDP236, obtained from the southwestern side of the CR, contained 0–2% heavy minerals, which suggests that volcanic activity may influence the composition of sediments in this area. Recent explorations by the manned submersible “Jiaolong” during the 28th and 38th Chinese Oceanographic Expeditions discovered various biological and unique geological structures at the bottom of the ridge, including multiple active hydrothermal vents, such as “Wocan-1” and “Wocan-2”. An analysis of the sulfide-containing sediments collected from some sites confirmed that there is weak hydrothermal activity in the CR, meaning that its influence on the distribution of materials on both sides of the ridge is limited [10,11]. Therefore, some researchers have used sediment minerals to characterize the various geological processes along the ocean ridge, thus providing a good method for studying sediment sources in the northwest Indian Ocean region. In this study, a sediment core from the northwest Indian Ocean, CJ08-008, was selected as a source for our research. Although mainly composed of foraminifera, microscopic examination of the core revealed five layers of amphiboles with a particle size greater than 0.063 mm, and these were accompanied by minor minerals such as garnet, barite, and kyanite. The source of amphiboles, whether from CR or the surrounding land mass and other sediments, aroused our interest.
Previous studies on detrital minerals have mainly focused on mineral types and assemblages, providing general information about the origins and depositional environments [12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. However, these methods have been unable to clearly determine the affinity of minerals [19]. Single-grain detrital minerals can minimize the interference of source rock types, alteration processes and degrees, and transport and deposition in provenance analyses. The crystal chemistry characteristics of individual minerals can effectively differentiate sediment sources. Therefore, they have become a powerful tool for analyzing the provenance of marine sediments and have yielded significant results. Amphibole, a common heavy mineral, has been successfully used to determine the properties and locations of sediment provenance, as well as investigate sediment transport processes, mechanisms, and contributions from different sources [20]. Previous studies have primarily focused on identifying the visible optical and morphological characteristics of different types of amphiboles. However, it is important to note that amphiboles with similar optical features may possess different crystal chemistry characteristics that can indicate variations in the parent rock types and sedimentary environment [21,22,23]. By examining the crystal structure, molecular formula, and relevant crystal chemistry characteristics of individual amphibole grains, it is possible to differentiate amphibole species and determine the parent rock types and depositional environments. This information serves as a basis for provenance analysis [24,25,26,27,28,29]. The Mg–(Na + K + Ca)–(Fe2+ + Fe3+) ternary diagram is a useful tool for distinguishing the genetic types of amphiboles [23]. As the provenance method transitions from qualitative to quantitative analysis, it has become increasingly popular to use these techniques to quantitatively analyze the sources of detrital minerals in deep-sea sediments across different periods.
In this study, we analyzed the types of source rock and traced them back to the rock types to identify their provenance. Using this approach, we conducted an electron probe element analysis on the amphiboles in the CJ08-008 sediment core and distinguished their types and genesis, thus providing important information for the identification of provenance.
2. Study Area
The study area is located between the Gulf of Aden and the Arabian Sea, which are connected to the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, respectively. The surrounding area consists of the Somali Plate, Arabian Plate, and Indian Plate. The Somali Plate and Arabian Plate mainly consist of sedimentary rocks from the Cenozoic and Mesozoic periods, with some much older metamorphic rocks. The Indian Plate is primarily composed of igneous rocks, followed by sedimentary and metamorphic rocks dating back to the Archaean period. The CR and the ocean basin are mainly basalt bases or gabbro bases, overlaid with semi-oceanic and oceanic sediments. Moreover, the study area has experienced frequent hydrothermal activity, which may be related to tectonic structures and sedimentary environments [30,31].
Our study core was obtained from the western part of the Arabian Basin, which has varying geological structures and topographies. The western region is influenced by the Carlsberg Ridge and Owen Fracture Zone, resulting in complex topography. The Carlsberg Ridge has water depths ranging from 2000 to 4000 m, with some areas shallower than 2000 m. In contrast, the Owen Fracture Zone has greater water depths, often exceeding 4000 m and even reaching depths greater than 5000 m. The survey area is relatively flat, with water depths ranging from 4000 to 5000 m [31].
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Material
The CJ08-008 sediment core was acquired at a water depth of 4374 m and obtained using a gravity corer with a length of 108 cm. The sediment at the site primarily comprises clay calcareous ooze (Figure 1).
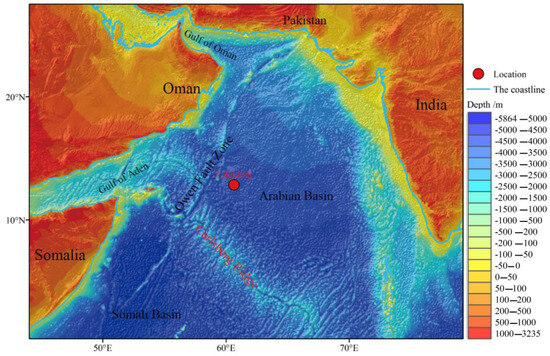
Figure 1.
Topographic map of the study area and sample station (topographic data are from GEBCO—The General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans).
3.2. Methods
First, the cylindrical core sample was divided into 2 cm intervals, and approximately 15 g of the original sample was collected from each layer. Wet sieving was performed using sieves with a mesh size of 0.063 mm. The sieved sediment was dried, weighed, and then separated using bromoform (CHBr3, d420 = 2.889 g/cm3) as a heavy liquid. The mineral separation process was performed at room temperature (20 °C ± 1 °C). The samples were stirred every 15 min for a total of three times. After an 8 h settling period, the light and heavy minerals were separated, washed, dried, and weighed, resulting in the final light and heavy detrital mineral samples.
Owing to the great abundance of foraminifera in the sediment, the content of detrital minerals was extremely low. To identify and classify the heavy minerals, they were carefully examined on glass slides using a binocular microscope. The minerals were analyzed based on their color, morphology, streak, magnetism, and surface characteristics. Amphiboles were found in five layers at depths of 46, 94, 102, 104, and 108 cm, and samples were selected from each layer. The number of amphiboles selected per layer ranged from 60 to 100 (Figure 2). Thin sections of the amphiboles in each layer were prepared and analyzed using an electron probe (Figure 2).
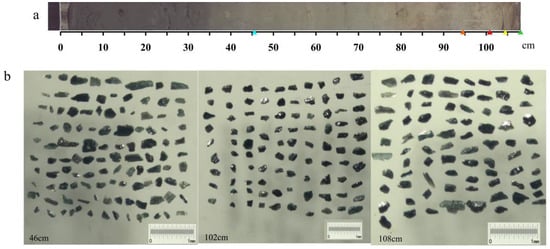
Figure 2.
Image of the core CJ08-008. (a) The triangular symbols indicate the presence of amphiboles at depths of 46, 94, 102, 104, and 108 cm. (b) Microscopic images of the amphiboles from the layers at 46, 102, and 108 cm depths.
Micro-area quantitative composition analysis was conducted at the Marine and Coastal Geology Laboratory of the Third Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources. The analysis was performed using a JEOL JXA-8100 electron probe equipped with four spectrometers. Prior to analysis, the samples were coated using a 20 nm carbon film. The conditions for amphibole mineral analysis were as follows: an acceleration voltage of 15 kV, a beam current of 10 nA, and a beam diameter of 3 μm. Standard samples used in the analysis included jadeite (Na), olivine (Mg), albite (Al, Si), orthoclase (K), diopside (Ca), rutile (Ti), rhodonite (Mn), and hematite (Fe). Sixty random measurements were performed to ensure statistical accuracy, and the Fe content was calculated by following the method proposed by Zheng [32].
The samples used for the dating analysis were processed using micropaleontology methods. Clean and undissolved planktonic foraminifera species Globorotalia menardii with a size of 63–125 μm were selected from the 20 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm, and 80 cm layers and sent to Beta Laboratory in the United States for testing.
The age of the test was determined at Beta Laboratory using the calibration calendar age (Table 1). Calibration with the MARINE20 database was performed using BetaCal 4.20 software and the HPD (high probability density) range method.

Table 1.
Dating results.
The dating results only record values after 41.19 ka because foraminifera below 82 cm were generally fragmented and, therefore, did not meet the testing requirements. Beta Laboratory did not test this layer. The age framework of the CJ08-008 sediment core was reconstructed using linear interpolation and extrapolation methods. The sedimentation rate shown in Table 1 is similar to that determined for the surrounding sea basin [1].
4. Results
4.1. Amphiboles’ Mineral Features
In the CJ08-008 sediment core, five layers containing amphiboles were identified. The amphiboles appeared columnar under the microscope, with long and short columns together with small granules. The colors were principally light and dark green. Extending along the C axis, they were subangular, subcircular, angular, bore no scratches, and showed no sign of weathering (Figure 2).
4.2. Chemical Characteristics of Amphibole Grains
The chemical characteristics of the amphibole grains were analyzed using electron probes. A total of 300 data points were collected from sixty individual mineral grains taken from the five layers. The average composition of the amphiboles in each layer is presented in Table 2. The highest average content was found for SiO2, exceeding 43% and reaching a maximum value of 45.74%. The next most abundant elements were Al2O3, CaO, and MgO, all exceeding 10% in content. The average content of TiO2 was relatively low, below 1%. The variation in the Na2O content was minimal, not exceeding 1.5%. The content of K2O was even lower, ranging from 0.47% to 0.75%.
The calculation of the amphibole content was based on 23 oxygen atoms, and the distribution of Fe3+ and Fe2+ in total iron was calculated by following the method proposed by Schumacher [33]. The weight percent of elemental oxides was converted into the number of cations in atoms per formula unit (apfu) by following the instructions in the appendices of Deer [21].

Table 2.
Percentage oxide content and cation values based on 23 oxygen atoms obtained from probe tests of different layers.
Table 2.
Percentage oxide content and cation values based on 23 oxygen atoms obtained from probe tests of different layers.
| Layer Number | CJ08-008-46 | CJ08-008-94 | CJ08-008-102 | CJ08-008-104 | CJ08-008-108 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage (%) | |||||
| SiO2 | 44.69 | 45.74 | 44.00 | 43.78 | 44.74 |
| TiO2 | 0.76 | 0.65 | 0.83 | 1.19 | 0.89 |
| Al2O3 | 11.65 | 11.14 | 11.85 | 12.33 | 11.40 |
| TFeO | 15.43 | 13.13 | 15.62 | 15.39 | 15.86 |
| MnO | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| MgO | 10.77 | 12.60 | 10.65 | 10.65 | 10.77 |
| CaO | 11.04 | 11.31 | 11.29 | 11.15 | 11.09 |
| Na2O | 1.39 | 1.48 | 1.47 | 1.50 | 1.43 |
| K2O | 0.67 | 0.47 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.73 |
| Total | 97.37 | 96.83 | 96.81 | 97.06 | 97.27 |
| Layer number | CJ08-008-46 | CJ08-008-94 | CJ08-008-102 | CJ08-008-104 | CJ08-008-108 |
| Number of cations | Cation values based on 23 oxygen atoms | ||||
| Na | 0.41 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.41 |
| K | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.15 |
| Mg | 2.34 | 2.65 | 2.31 | 2.32 | 2.30 |
| Ca | 1.76 | 1.74 | 1.76 | 1.76 | 1.75 |
| Fe2+ | 1.06 | 0.69 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 1.12 |
| Fe3+ | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.85 |
| Mn | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Ti | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| ⅥAl | 1.43 | 1.47 | 1.55 | 1.57 | 1.47 |
| ⅣAl | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.57 | 0.50 |
| Si | 6.57 | 6.53 | 6.45 | 6.43 | 6.53 |
| The pressure value (kbar) | CJ08-008-46 | CJ08-008-94 | CJ08-008-102 | CJ08-008-104 | CJ08-008-108 |
| P | 4.83 ± 0.5 | 5.04 ± 0.5 | 5.33 ± 0.5 | 5.59 ± 0.5 | 4.87 ± 0.5 |
| 4.33–5.33 | 4.54–5.54 | 4.83–5.83 | 5.09–6.09 | 4.37–5.37 | |
The pressure value P is calculated using the formula proposed by Johnson and Rutherford [34].
5. Discussion
5.1. Amphibole Classification
This study adopted the official amphibole classification and nomenclature approved by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA), as outlined by Hawthorne [27] and implemented in the computer program of Oberti [35]. To make the notation simpler, we write the sum of the small divalent cations at B as BΣM2+ = BMg + BFe2+ + BMn2+ and the sum of the B cations as ΣB = BLi + BNa + BΣM2+ + BCa.
The first four subgroups comprise the most common rock-forming amphiboles.
(1) Magnesium–iron–manganese amphiboles: B(Ca + ΣM2+)/ΣB ≥ 0.75, and BΣM2+/ΣB > BCa/ΣB;
(2) Calcium amphiboles: B(Ca + ΣM2+)/ΣB ≥ 0.75 and BCa/ΣB ≥ BΣM2+/ΣB;
(3) Sodium–calcium amphiboles: 0.75 > B(Ca + ΣM2+)/ΣB > 0.25, BCa/ΣB ≥ BΣM2+/ΣB, 0.75 > B(Na + Li)/ΣB > 0.25, and BNa/ΣB ≥ BLi/ΣB;
(4) Sodium amphiboles: B(Na + Li)/ΣB ≥ 0.75 and BNa/ΣB ≥ BLi/ΣB.
Based on the nomenclature and the data presented in Table 2, the calculation reveals that the amphiboles from the CJ08-008 sediment core’s five layers belong to the calcic amphibole subgroup. This classification is confirmed by the analysis of nearly 300 sets of data.
The classification diagrams presented below involve the A and C cations. We express the aggregate charges as A+ = A(Na + K + 2 Ca) and C+ = C(Al + Fe3+ + 2 Ti4+), where the cations are expressed in atoms per formula unit (apfu). By plotting all the samples on these classification figures, where C(Al + Fe3+ + 2 Ti4+) apfu is the abscissa and A(Na + K + 2 Ca) apfu is the vertical coordinate, we completed the subdivision of the amphiboles according to the calcic amphibole division rule [27,34,36]. Finally, we determined the name of the single amphibole mineral (Figure 3).
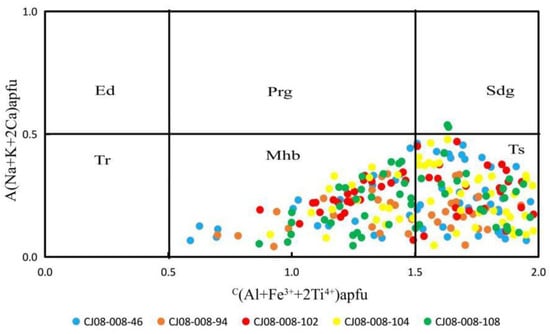
Figure 3.
Classification of sedimentary amphiboles in the northeast Indian Ocean (the classification method refers to Hawthorne [27]). Abbreviations for mineral names: Ed = edenite; Prg = pargasite; Sdg = sadanagaite; Tr = tremolite; Mhb = magnesiohornblende; Ts = tschermakite.
According to the classification of the amphiboles in the samples from the CJ08-008 sediment core (Table 3), tschermakite (Ts) has the highest content (>60%), followed by magnesiohornblende (Mhb) (>29%); sadanagaite (Sdg) is only present in the 108 cm layer at a proportion of 3.57%. Ts has the highest proportion in the CJ08-008-104 samples (70.69%), followed by CJ08-008-46 (68.42%), CJ08-008-94 (62.00%), and CJ08-008-102 (60.71%), with the lowest content in CJ08-008-108 (46.43%). The highest proportion of Mhb occurs in the CJ08-008-108 sample (50.00%), followed by CJ08-008-102 (39.29%), CJ08-008-94 (38.00%), and CJ08-008-46 (31.58%), with the lowest content in CJ08-008-104 (29.31%).

Table 3.
The number and percentage of different types of amphiboles in different layers of core CJ08-008 (%).
Comparing these results, it is evident that Ts is the dominant amphibole in CJ08-008-46, CJ08-008-94, CJ08-008-102, and CJ08-008-104; Mhb is dominant in CJ08-008-108, with some Sdg present as well. These variations are attributed to different origins. Considering their ages, it can be inferred that there are differences in the sediment supply at 18.76, 35.91, 38.92, 39.68, and 41.19 ka.
The average pressure of amphibole formation at each corresponding layer was calculated using the experimental formula proposed by Johnson and Rutherford [37]: P (±0.5 kbar) = −3.46 + 4.23 AlT. The highest value is 5.09–6.09 kbar recorded for the 104 cm layer amphiboles, and the lowest value ranges from 4.33 to 5.33 kbar, determined for the 46 cm layer.
5.2. Formation of Amphibole Grains
The chemical characteristics of amphibole grains vary depending on their origin and are influenced by factors such as mineral composition, structure, and geological processes. The composition of amphiboles is determined by the parent rock and shows clear inheritance. These differences are mainly due to variations in the parent rock, temperature, pressure, and the properties of hydrothermal fluids, which result in isomorphic substitutions at different locations. To determine the origins of these amphiboles, the relative variations in the number of cations at each structural site in the unit cell can be used as indicators. Therefore, cations with high content and significant differences, or specific combinations of cations that reflect the origin’s characteristics, can be selected as end-member components for crystal chemistry-genetic diagrams [19,22,38,39].
These studies have shown that the Ti content in amphiboles is sensitive to temperature changes, with higher temperatures leading to a larger Ti content. Furthermore, the Si content is influenced by the type of magma and metamorphic source rock. Therefore, the combination of Si and Ti can accurately indicate the genetic type of amphiboles [16,29,40,41]. The distribution of amphiboles in the CJ08-008 core was analyzed using the Si–Ti correlation diagram based on the classification proposed by Chen [16]. The results indicate that most of the amphiboles were derived from metamorphic rocks, followed by medium acid-intrusive rocks and retrogressive metamorphic rocks. A few of the amphiboles were derived from ultrabasic–basic rocks (Figure 4).
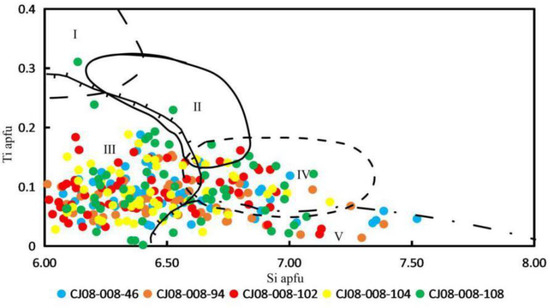
Figure 4.
Si-Ti variation map of amphiboles of different layers in CJ08-008 and genetic types (the classification method refers to Chen [16]). I = magmatic amphiboles in volcanic rocks; II = magmatic amphiboles in ultrabasic–basic rocks; III = amphiboles in metamorphic rocks; IV = amphiboles of magmatic genesis in medium acid-intrusive rocks; V = amphiboles of retrogressive metamorphic or metasomatic genesis.
We categorized the amphibole data from these five layers into three genetic types: metamorphic rocks, magmatic genesis in medium acid-intrusive rocks, and retrogressive metamorphic rocks. The results are described below (Table 4).

Table 4.
Percentage of amphibole genesis types in different layers.
(1) Metamorphic genesis: The highest proportion of metamorphic amphiboles was found in the 104 cm layer (76.67%), followed by the 102 cm layer (71.67%). The lowest proportion was observed in the 108 cm layer (60.38%).
(2) Magmatic genesis in medium acid-intrusive rocks: The highest proportion of amphiboles with this genesis was found in the 108 cm layer (30.19%), while the lowest content was in the 94 cm layer (13.73%).
(3) Retrogressive metamorphic rocks: The highest proportion of amphiboles with this genesis was found in the 94 cm layer (17.65%), and the lowest proportion was in the 104 cm layer (5.00%).
5.2.1. Genesis of Magmatic Amphibole
To analyze the magma source in detail, we plotted the amphiboles with a magmatic genesis in medium acid-intrusive rocks on a Ca–Fe2++Fe3+–Mg ternary diagram (Figure 5). The results showed that most of the medium acid-intrusive amphiboles belong to a crust–mantle type that accounted for 60%, followed by a mantle type that accounted for 40%.
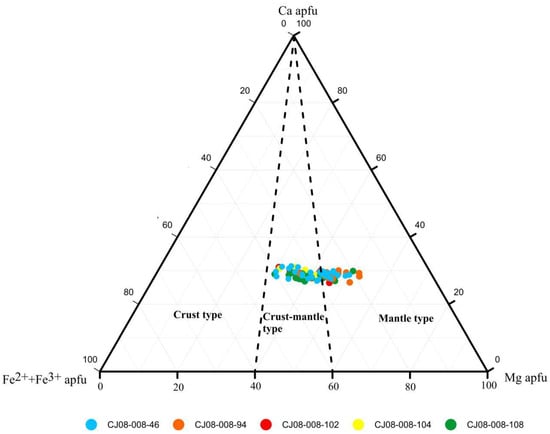
Figure 5.
Provenance of amphibole magma (the classification method refers to Chen et al., 1988 [22]).
Furthermore, Xie and Zhang [42] found that the M value (Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)) of amphiboles can be used as an indicator to distinguish the genesis of the source rock. For example, M > 0.7 indicates a mantle type; M = 0.5–0.7 indicates a mixed crust–mantle type; and M < 0.5 indicates a crust type. We calculated and divided the M value of the amphiboles with a magmatic genesis in the CJ08-008 samples (Figure 6). The results show that in layers 106 cm and 108 cm, the amphiboles were mainly composed of crust–mantle mixing, whereas in layer 94 cm, the amphiboles were mainly derived from mantle sources. This is consistent with the genetic explanation provided in Figure 6. In layers 46 cm and 102 cm, the magma source was mainly mantle, followed by crust–mantle mixing, which differs slightly from the projection result shown in Figure 5. We believe that the result in Figure 5 is controlled by the total Fe. Additionally, in Figure 6, the factors affecting the M value are influenced by Fe2+. Moreover, the difference between the two results is not significant, and we believe that both sources (crust–mantle and mantle) are reasonable for the amphibole magma sources found in medium acid-intrusive rocks.
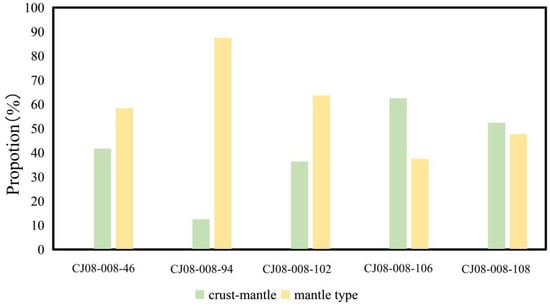
Figure 6.
M value statistics of five different layers of amphiboles in magmatic rocks in the northeast Indian Ocean (the classification method refers to Xie and Zhang [43]).
5.2.2. Genesis of Metamorphic Amphiboles
During metamorphism, a high IVAl content in amphiboles indicates a significant substitution of IVAl for Si, resulting from high temperatures [37,40]. Additionally, a high IVAl content suggests that the rocks were formed under high pressure. When the ratio of the IVAl content to the VIAl content is 2, the corresponding pressure is 500 mPa. As the pressure increases, the ratio decreases. In the CJ08-008 samples, both the IVAl content and the IVAl content in the amphiboles are greater than 2 and close to 3, indicating that the pressure was close to 500 mPa during the formation of the amphiboles that occurred in the five sediment layers. Figure 7 illustrates the relationship between the IVAl and Si content of the amphiboles and the regional metamorphic pressure. Generally, there is a clear linear relationship between the IVAl and Si content of amphiboles and the regional metamorphic pressure. In the figure, it can be observed that the metamorphic amphiboles in the CJ08-008 samples mostly have a low-pressure metamorphic origin, with pressures below 500 mPa.
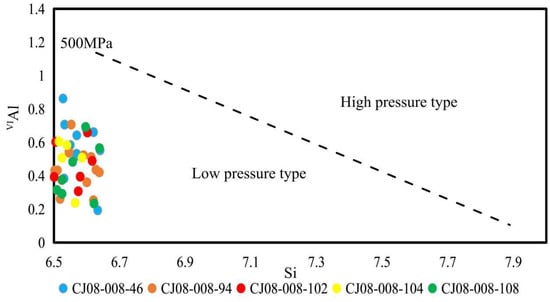
Figure 7.
Diagram of metamorphic amphiboles VIAl-Si in the northeast Indian Ocean (the classification method refers to [37,40].
5.3. Intragranular Environment of Amphiboles
Concerning the intragranular environment of amphiboles during their formation, the occupancy of the A site in the chemical formula indicates the reducing or oxidizing state. A value of 1.0 (indicating full occupancy by potassium and sodium) reflects the strongest reducing state. Conversely, a value of 0 (indicating that all potassium and sodium enter the B site) reflects the strongest oxidizing state [44,45]. The number of A site cations in the magnesio-calcic amphiboles and magnesio-ferro amphiboles obtained from sedimentary rocks in the northwest Indian Ocean is below 0.24, indicating a relatively high degree of oxidation.
5.4. Source of Amphiboles
The sediments in the northwest Indian Ocean mainly consist of biogenic and terrigenous sources and the products of ridge processes. Terrigenous input is mainly influenced by monsoonal and oceanic currents, which are driven by the monsoon. During winter, ocean currents flow counterclockwise and are referred to as the southeast monsoon current, whereas in summer, they flow clockwise and are known as the northeast monsoon current. The differing directions of these ocean currents contribute to a complex array of debris they transport [1,7,45]. The study area is surrounded by the Arabian Sea, which connects to the Red Sea; in addition, the Arabian Sea connects to the Persian Gulf through the Gulf of Oman. Ocean currents in these regions transport terrigenous minerals from nearby landmasses, including the Somali Plate, Arabian Plate, and Indian Plate. Additionally, erosion minerals from the CR can be transported by ocean currents and deposited in the sedimentary basin [6,9,10], as the core was obtained at a distance of 480 km from the CR and 210 km from the Owen Fracture Zone (OFZ). Because the OFZ is much closer to the core site and is tectonically active, causing numerous earthquakes, landslides, and active faults, it may be another source of recent sediment in the basin. In Figure 8, it is clear that the detrital minerals in the northwest Indian Ocean may contain various types of magmatic and metamorphic rock minerals. Owing to the wide range of sediment sources in the ocean basin, different types of minerals mix together during deposition. Previous research and experience have shown that minerals transported by monsoons are characterized by distant source transport and mainly consist of clay minerals, volcanic ash, and mica minerals, whose transport abrasion can be observed microscopically on the surface of the sediment minerals. In terms of morphology, the minerals are rounded and reveal a relatively high degree of weathering, and the characteristics of monsoon sedimentation are periodic [46,47,48]. In the core we examined, only five layers of sediment containing amphiboles were identified, and the characteristics of the amphiboles in these five layers did not show periodicity. Sediment, if transported by the monsoon, would have cyclical characteristics, so the possibility of the amphiboles in CJ08-008 having been transported by a monsoon is very small. The land blocks surrounding the northwest Indian Ocean are composed of large areas of sedimentary rocks and a small number of intrusive rocks, which provide a source for amphiboles. However, amphiboles transported from surrounding land blocks would have a high degree of roundness after being carried long distances, with abraded mineral surfaces and a high degree of weathering.
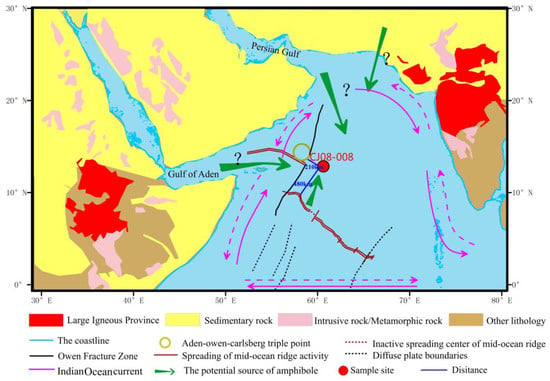
Figure 8.
Continental block lithology surrounding the northwest Indian Ocean and its provenance around the station (continental block lithology information refers to the CGMW (Commission for the Geological Map of the World), Indian Ocean current refers to [45]. The rose-red-dashed line stands for the southeast monsoon current, and the rose-red-solid line stands for the northeast monsoon current).
Kettanah [6] analyzed the geochemical characteristics of amphiboles in northern Iraq, showing that amphibolite pods and diorite dikes are of igneous fore-arc origin, formed from calc-alkaline and/or tholeiitic magma within an active continental margin setting. Hadiseh [49] studied the amphibolites found in the Sanandaj–Sirjan zone of Iran, revealing that the protoliths of the studied amphibolites were affected by crustal components. The chemical composition of these amphiboles differs from that of the CJ08-008 amphiboles. In the scatter diagram of the amphibole genetic variation (Figure 4), it can be seen that most of the amphiboles are sourced from metamorphic rocks, followed by medium acid-intrusive magmatic rocks and retrogressive metamorphic or metasomatic rocks. Furthermore, only a few amphiboles from the core show a source affinity to ultrabasic–basic rocks.
The CR occurs on a slow expansion ridge, and the magmatic activity along the ridge is not as intense as that on the Atlantic Ridge [9]. The basic rocks formed by the CR are metamorphosed, and the slow expansion of the CR causes the differentiation of the regional crystallization of basaltic magma, which can produce metamorphic and intermediate acidic rocks. Similarly, the OFZ also has magmatic activity, which has produced metamorphic and intermediate acidic rocks. After exposure to the sea floor or land, long-term submarine or subaerial weathering and metamorphic, magmatic, or hydrothermal processes produce debris minerals. When transported by ocean currents, minerals with higher specific gravity are locally enriched, while minerals with lower specific gravity are carried further away. Previous studies have also found that amphiboles are present in the subduction zones of other oceanic basins [50,51], while granite and dacite have been found in the oceanic crust [52,53,54,55] and mafic–hydrothermal debris have been found in the axial sediments of the CR [9]. These research reports further confirm the possibility that the amphiboles in the CJ08-008 sediment core originated from the CR or OFZ.
In addition, amphibole particles that were relatively large, angular, and fresh were found during our microscopic observation. Considering the location of the major landforms, the station is located in the basin near the CR and OFZ, which can directly receive the volcanic products from these regions. In addition, the distance that heavy minerals are transported under ocean currents must be close. Thus, we speculate that the amphiboles from the CJ08-008 sediment core were transported from a nearby source, such as the CR or OFZ.
Based on the dating results, we created a diagram (Figure 9) showing the parent rock properties and amphiboles in the five layers. Amphiboles with a metamorphic genesis are the most abundant mineral in all the layers, followed by amphiboles with a magmatic genesis in medium acid-intrusive rocks; however, their compositions vary according to depositional period. For example, amphiboles with a metamorphic genesis are in the highest proportion at the 104 cm layer, while medium acid-intrusive rock amphiboles with a magmatic genesis are in the highest proportion at the 108 cm layer. The conditions under which the amphiboles in the five layers were formed are, primarily, the crust–mantle type, followed by the mantle type and the crustal type; these represent significantly different temperature and pressure conditions (Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). The mantle type represents the highest temperature–pressure conditions, followed by the crust–mantle type; the crustal type represents the lowest temperature–pressure conditions. The amphiboles from the 46, 102, 104, and 108 cm layers indicate a magmatic genesis—a crust–mantle-type source—and were formed under relatively low temperature–pressure conditions, while the mantle-type amphiboles from the 96 cm layer were formed under high-temperature and low-pressure conditions. The variations in the amphiboles indicate different sources, suggesting different origins.
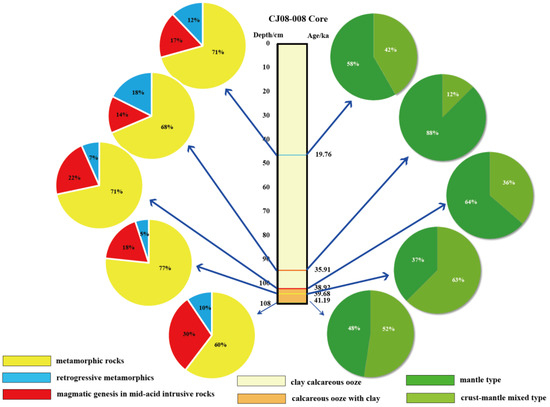
Figure 9.
The amphibole magma source ratio and genesis ratio of amphiboles in the five layers; the percentage was calculated based on the quantity of amphibole analyzed via electron probe analysis of the CJ08-008 core.
The source of these amphiboles remains underdetermined, as they could originate from the CR, OFZ, or older submarine sediment sequences eroded by local turbidity currents.
6. Conclusions
The amphiboles in the sediment belong to the calcic amphibole subgroup, with the majority of amphiboles being either tschermakite or magnesiohornblende. We calculated the average pressure during the formation of the amphiboles; the highest pressure, ranging from 5.09 to 6.09 kbar, was observed for the amphiboles in the 104 cm layer, while the lowest pressure, ranging from 4.33 to 5.33 kbar, was observed for the amphiboles in the 46 cm layer.
The amphiboles in the northeast Indian Ocean sediments originated mostly from metamorphic rocks, with a smaller proportion derived from magmatic and medium acid-intrusive rocks. Amphiboles with a magmatic genesis mainly represent the crust–mantle type, followed by the mantle type. The amphibole minerals in the CJ08-008 sediment core could originate from the CR, OWR, or older sediments exposed to tectonic activity.
Given that amphiboles are found in a few geological layers, an increased number of samples will enhance our ability to investigate the source of amphiboles. Studying adjacent cores will be our future research. Moreover, an extensive examination of diverse geological tectonic units within the marine environment throughout the history of tectonic activities will be crucial for our future research and investigations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.W., Y.L. and B.J.; methodology, F.W., D.L., B.J. and M.W.; software, F.W. and Z.L.; validation, Y.L. and B.J.; formal analysis, F.W., Y.L. and P.S.; investigation, Y.L., D.L., J.C. and L.W.; resources, Y.L. and J.C.; data curation, D.L. and B.J.; writing—original draft preparation, F.W., Y.L., B.J., M.W. and M.C.; writing—review and editing, F.W., Y.L., B.J. and M.C.; visualization, P.S.; supervision, F.W., Y.L. and B.J.; project administration, Y.L. ; funding acquisition, Y.L. and J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Programme on Global Change and Air-Sea Interaction (Grant Nos. GASI-04-HYDZ-02, GASI-01-WIND-CJ08, and GASI-01-WIND-CJ09), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China (Grant No.2022J05228).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wiem, F.; Franck, B.; Anne-Marie, L. Past productivity variations and organic carbon burial in the gulf of aden since the last glacial maximum. Quaternaire 2016, 27, 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sirocko, F.; Sarnthein, M. Wind-borne deposits in the northwestern Indian ocean: Record of holocene sediments versus modern satellite data. Paleoclimatol. Paleometeorol. Mod. Past Patterns Glob. Atmos. Transp. 1989, 282, 401–433. [Google Scholar]
- Rampen, S.W.; Schouten, S.; Koning, E.; Brummer, G.; Damsté, J.S.S. A 90 kyr upwelling record from the northwestern Indian ocean using a novel long-chain diol index. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 276, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassinot, F.C.; Marzin, C.; Braconnot, P.; Marti, O.; Mathien-Blard, E.; Lombard, F.; Bopp, L. Holocene evolution of summer winds and marine productivity in the tropical Indian ocean in response to insolation forcing: Data-model comparison. Clim. Past 2011, 7, 485–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaji, Y.; Kawahata, H.; Ohkouchi, N.; Ogawa, N.O.; Tamaki, K. Varying responses to Indian monsoons during the past 220 kyr recorded in deep-sea sediments in inner and outer regions of the gulf of aden. J. Geophys. Res-Ocean. 2016, 120, 7253–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolla, V.; Coumes, F. Morpho-Acoustic and Sedimentologic Characteristics of the Indus Fan. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1983, 3, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Magaña, V.O.; Palmer, T.N.; Shukla, J.; Tomas, R.A.; Yanai, M. Monsoons: Processes, predictability, and the prospects for prediction. J. Geophys. Res-Ocean. 1998, 103, 14451–14510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronan, D.S.; Damiani, V.V.; Kinsman, D.; Thiede, J. Sediments from the Gulf of Aden and Western Indian Ocean. Initial Rep. Deep. Sea Drill. Proc. 1974, 24, 1047–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Zhai, S. Hydrothermal signature in the axial-sediments from the carlsberg ridge in the northwest Indian ocean. J. Mar. Syst. 2018, 180, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Han, X.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. The temporal variability of hydrothermal activity of wocan hydrothermal field, carlsberg ridge, northwest Indian ocean. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 2021, 103999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, A.C. Geochemical studies of detrital heavy minerals and their application to provenance research. Geol. Soc. 1991, 57, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, S.F.; Stow, D.A.V.; Croudace, I.W. Mineralogy and geochemistry of Bay of Bengal deep-sea fan sediments, ODP Leg 116: Evidence for an Indian subcontinent contribution to distal fan sedimentation. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1998, 131, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, A.C.; Whitham, A.G.; Fanning, C.M. Provenance of Late Cretaceous to Paleocene submarine fan sandstones in the Norwegian Sea: Integration of heavy mineral, mineral chemical and zircon age data. Sediment. Geol. 2005, 182, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.G.; Melcher, F.; Fuessl, M.; Weber, B. Accessory minerals in cassiterite: A tool for provenance and environmental analyses of colluvial-fluvial placer deposits (NE Bavaria, Germany). Sediment. Geol. 2006, 191, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wei, T.; Wei, W. Diagnostic heavy minerals in Plio-Pleistocene sediments of the Yangtze Coast, China with special reference to the Yangtze River connection into the sea. Geomorphology 2009, 113, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevastjanova, I.; Hall, R.; Alderton, D. A detrital heavy mineral viewpoint on sediment provenance and tropical weathering in SE Asia. Sediment. Geol. 2012, 280, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Jin, B.F.; Zhao, B.C. Transparent heavy minerals and magnetite geochemical composition of the Yangtze River sediments: Implication for provenance evolution of the Yangtze Delta. Sediment. Geol. 2018, 364, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.F.; Yue, W.; Wang, K.S. The crystallochemistry characteristics and genetic analysis of amphibole in the sediments of the Huanghe River. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2013, 35, 131–143, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, D.; Ravenne, C.; Marechal, B.; Moutte, J. Geochemical variability induced by entrainment sorting: Quantified signals for provenance analysis. Sediment. Geol. 2004, 171, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A.; Zussman, J. An Introduction to the Rock Forming Minerals; Longman: London, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.H. Hornblende genetic mineral family and its application. J. Chang. Inst. Geol. 1986, 9, 41–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Y.; Sun, D.S.; Yin, H.A. Genetic Mineralogy and Prospecting Mineralogy; Chongqing Publishing House: Chongqing, China, 1988. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Derkachev, A.N.; Nikolaeva, N.A. Associations of heavy minerals in sediments of western part of south china sea. Geol. Pac. Ocean 1999, 14, 503–534. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.T.; Li, W.R.; Shi, Z.B. Characteristics of heavy minerals in clastic sediments of Yellow River provenance. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2003, 23, 7–21, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.B.; Yang, S.Y.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Li, J.; Bai, F.L. The clastic mineral composition of the sediments of the Yellow River system and the constraint of sedimentary dynamic environment. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2010, 30, 73–85, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, F.C.; Oberti, R.; Harlow, G.E.; Maresch, W.V.; Martin, R.F.; Schumacher, J.C.; Welch, M.D. IMA report: Nomenclature of the amphibole supergroup. Am. Miner. 2012, 97, 2031–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.F.; Yue, W.; Wang, K.S. Chemical composition of detrital amphibole in the sediments of the Huanghe River, Liaohe River and Yalu River, and its implication for sediment provenance. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 36, 11–21, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.M.; Jin, B.F.; Yue, W.; Dang, L.L.; Wang, M.Y.; Kong, Q.X. Type and genesis of amphibole in the Huanghe River and Changjiang River estuaries and significance of its provenance. Geosci. J. 2021, 25, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, P.R.; Munschy, M.; Ségoufin, J. Structure and early evolution of the Arabian Sea and east Somali Basin. Geophys. J. Int. 1998, 134, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yan, W.; Zhong, L.; Xia, Z.; Wang, S. Provenance of heavy mineral deposits on the northwestern shelf of the South China Sea, evidence from single-mineral chemistry. Mar. Geol. 2015, 363, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudholkar, A.V.; Ambre Kodagali, V.N.; Ranade, G.H.; Kak, R.; Valsangkar, A.B. Geomorphological and petrological observations along a segment of slow-spreading Carlsberg Ridge. Curr. Sci. India 2002, 82, 982–989. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.R. Calculated Fe3+ and Fe2+ contents by electron probe analysis values. Acta Mineral. Sin. 1983, 12, 55–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, J.C.; Wang, L.B. Estimation of iron trivalent ratio in electron probe analysis of amphibole. Acta Petrol. Et Mineral. 2001, 20, 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.C.; Rutherford, M.J. Experimental calibration of the aluminum-in-hornblende geobarometer with applicable to long valley caldera (california) volcanic rocks. Geology 1989, 17, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberti, R.; Cannillo, E.; Toscani, G. How to name amphiboles after the IMA 2012 report: Rules of thumb and a new PC program for monoclinic amphiboles. Period. Miner. 2012, 81, 257–267. [Google Scholar]
- Leake, B.E. Nomenclature of amphiboles. Am. Mineral. 1978, 63, 1023–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Bong, W.; Matsumura, K.; Yokoyama, K.; Nakai, I. Provenance study of early and middle bronze age pottery from Kaman-Kalehyük, Turkey, by heavy mineral analysis and geochemical analysis of individual amphibole grains. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 2165–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mange, M.A.; Morton, A.C. Geochemistry of heavy minerals. Dev. Sedimentol. 2007, 58, 345–391. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.Z.; Bai, X.R.; Chen, W. Genetic Mineralogy; China University of Geosciences Press: Beijing, China, 1991. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.Y.; Jin, B.F.; Liu, J.; Gao, M.S.; Gao, J.H.; Jia, J.J. Genetic types and provenance indication of clastic amphibole in the South Yellow Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1382352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ding, Z.L. Analysis of heavy mineral composition and sand source in sandy land of Northeast China. Chin. Sci. D Earth Sci. 2007, 37, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.Q. Typomorphic characteristics and genetic significance of hornblende in granitoids from Hengduan Mountains. J. Mineral. 1990, 10, 35–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Pan, Z.L.; Weng, L.B. Systematic Mineralogy; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1982. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.S.; Shi, X.F.; Lin, Z.H. Assemblages, provinces and provenances of Heavy Minerals on the shelf of the southern Yellow Sea and northern East China Sea. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2003, 21, 31–40, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, D.; Clift, P.D.; Kulhanek, D.K.; Mishra, R.; Hahn, A.; Gurumurthy, G.P.; Scardia, G. Deep sea drilling in the Arabian Sea: Constraining Tectonic-Monsoon Interactions in South Asia. Integr. Ocean. Drill. Program Prelim. Rep. 2015, 355, 6–46. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Xiang, R.; Liu, S.; Khokiattiwong, S.; Kornkanitnan, N.; Fan, J.; Wen, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J. Holocene indian summer monsoon variations inferred from end-member modeling of sediment grain size in the andaman sea. Quat. Int. 2020, 558, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Wei, J.; Lau, W.K.; Pu, B.; Wang, C. Interactions of Asian mineral dust with Indian summer monsoon: Recent advances and challenges. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 215, 103562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.L.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.X.; Li, S.Z.; Xiao, C.F.; Chen, L. Source-sink processes, paleoenvironment and paleomonsoon evolution in the Northeast Indian Ocean. Earth Sci. Front. 2022, 5, 102–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hadiseh, R.S.; Hesamaddin, M.; Mohssen, M. Geochemistry and geochronology of amphibolites from the Sirjan area, Sanandaj-Sirjan zone of Iran: Jurassic metamorphism prior to Arabia and Eurasia collision. J. Geodyn. 2021, 143, 101786. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.F.; Xiao, P.X.; Guo, L.; Xi, D.R. Opening of an early Paleozoic limited oceanic basin in the northern Altyn area: Constraints from plagiogranites in the Hongliugou-Lapeiquan ophiolitic mélange. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.K.; Huang, Q.T.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.X.; Song, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J. Metamorphic temperature and pressure of the Daru Co amphibolite in western Bangong-Nujiang Suture Zone and their geological significance. Chin. J. Geol. 2023, 58, 1503–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Rui, X.; Guo, K.; He, J.; Yang, W. Ocean ridge granite and its geochemical characteristics in western Qinghai-Xizang plateau. Chin. J. Geochem. 2001, 20, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanless, V.; Perfit, M.R.; Ridley, W.I.; Wallace, P.J.; Grimes, C.B.; Klein, E.M. Volatile abundances and oxygen isotopes in basaltic to dacitic lavas on mid-ocean ridges: The role of assimilation at spreading centers. Chem. Geol. 2011, 287, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanless, V.; Shaw, A. Lower crustal crystallization and melt evolution at mid-ocean ridges. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, C.Z.; Mitchell, R.; Wen, Y. Petrogenesis of Dacites in a Triassic Volcanic Arc in the South China Sea: Constraints from Whole Rock and Mineral Geochemistry. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 9, 780007. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).