Abstract
The marine magnetotelluric (MMT) method is a significant tool extensively utilized in offshore studies, including the understanding of the Earth’s tectonics and hydrocarbon exploration. Conductive anisotropy and non-zero magnetic susceptibility are common phenomena observed in the Earth’s subsurface, and MMT forward modeling is the basis of practical inversion. However, numerical modeling that incorporates both conductive anisotropy and magnetic susceptibility has received limited attention. Moreover, both accuracy and efficiency are crucial in developing a 3D MMT modeling algorithm. Therefore, we developed a multi-level parallel MMT forward modeling algorithm that is capable of simultaneously modeling conductive and magnetic arbitrary anisotropic models using the vector finite element method based on the secondary field formula. The algorithm’s accuracy was validated through comparisons with previously published results for an arbitrary anisotropic model. The results show that the maximum relative error is below 2%, and the speedup reaches an impressive value of 552.41 when running with 2048 cores. Furthermore, the MMT responses of conductive anisotropy and magnetic susceptibility were comprehensively analyzed by several typical models. Our findings highlight the importance of considering magnetic susceptibility in magnetite-rich regions, particularly as the MMT responses may exhibit opposite responses for anomalies with lower resistivity and higher magnetic susceptibility compared with the surrounding rocks.
1. Introduction
The marine magnetotelluric (MMT) method is a crucial tool in electrical exploration, capable of inferring the subsurface electrical structure of the Earth by measuring naturally varying electromagnetic (EM) signals at the seafloor or ocean surface [1,2]. This technique has been widely employed in offshore research, including studies of the Earth’s tectonics hydrocarbon exploration, and so forth [3,4,5].
Conductivity and magnetic permeability are both essential physical properties of the Earth. Previous studies have shown that the susceptibility of certain geological materials significantly exceeds that of free space [6]. Common minerals exhibit a wide range of magnetic susceptibility variations, with magnetite minerals displaying exceptionally high values (~19.2 SI) [7]. For instance, Figure 1 [8] illustrates that the magnetic susceptibility of magnetite rock ranges from 0.6 SI to 1.0 SI in Huayang, Shaanxi Province, China. Although geological targets often possess both conductivity and permeability characteristics [9], the magnetic permeability in practical and numerical studies is usually assumed to be the free-space permeability (). Many studies have shown that the influence of magnetic permeability in magnetite-rich regions cannot be ignored. Zhang and Oldenburg [10] demonstrated that assuming a susceptibility value of 0 for strong magnetized examples may result in an incorrect electrical model. Thomas [11] revealed that susceptibilities greater than 0.005 can significantly affect the EM responses in layered Earth models. Sasaki et al. [12] pointed out that ignoring susceptibility may lead to misinterpretation of models with high susceptibility values. Zhang et al. [13] successfully inverted two-dimensional data while simultaneously considering both conductivity and susceptibility, highlighting the significant impact of local magnetic anomalies on MT responses.

Figure 1.
Magnetic susceptibility of magnetite in Huayang, Shaanxi Province, China (666/919 × 10−3 SI).
In recent years, there has been increased attention on magnetotelluric (MT) studies investigating the influence of conductive anisotropy [14,15,16], particularly in the development of three-dimensional (3D) forward modeling algorithms. Weidelt et al. [17] presented a staggered-grid finite difference algorithm for MT modeling in conductive anisotropic media; however, this algorithm is not convenient for dealing with irregular anomalies. Xu [18] proposed a node-based finite element (FE) method for MT modeling, but its accuracy is insufficient as it fails to satisfy the required condition of discontinuous normal electrical fields at electrical interfaces. To overcome this disadvantage of the node-based FE method, Xiao et al. [19] developed an edge-based FE method with rectangular meshes; however, this technique also faces challenges in dealing with irregular anomalies and terrain. Subsequently, Liu et al. [20] introduced a 3D adaptive FE method employing tetrahedron elements, enabling improved simulation of topography and irregular anisotropic anomalies. Additionally, Xiao et al. [21,22] contributed A- and T- algorithms based on EM potentials. Zhou et al. [23] further advanced the field by presenting a divergence scheme rooted in the edge-based FE method, while Bai et al. [24] developed a mixed algorithm that combines nodal and edge-based approaches. However, there has been limited focus on incorporating conductive anisotropy and non-zero magnetic susceptibility. Xiao et al. [25] proposed a 3D MT modeling algorithm based on the edge-based FE method, utilizing the total field formula to obtain the EM field. Yu et al. [26] provided another 3D MT modeling scheme based on the A- formula, where the EM field is obtained by differentiating potential. Notably, neither of these algorithms have been parallelized, which limits their computational efficiency and scalability.
To address the aforementioned problems, we developed a robust and scalable multi-level parallelized 3D MMT modeling scheme that is capable of handling conductive and magnetic anisotropic anomalies. Based on the second field formula, the edge-based FE method is adopted to discretize the electric governing equation. To ensure accuracy, the algorithm enables the directly computation of secondary fields by solving equations with the SuperLU_dist direct solver [27]. To enhance efficiency, a multi-level parallel algorithm has been developed. This paper is organized as follows: Firstly, we provided a concise overview of the methodology for MMT modeling in conductive and magnetic anisotropic media. Subsequently, we presented crucial components necessary for achieving accurate and efficient implementation based on the secondary field approach. Following this, we conducted tests on different typical models, and we analyzed the impact of conductive anisotropy and magnetic susceptibility.
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Differential Equations
By adopting the time dependence of , the Maxwell equations can be written as follows:
where and are the electrical and magnetic fields, respectively; and represent the magnetic permeability and the dielectric constant of the medium, respectively; is angular frequency; is electrical conductivity of the medium; and is the accumulated free charge. Both and are tensors in conductive and magnetic anisotropic media, and the resistivity utilized in this context is the reciprocal of the conductivity, namely . See [28,29] for more details of those parameters.
Displacement currents can be neglected at the frequencies used in the MMT method, namely . Two definitions are available to define and [23,24]. The former, as shown in Figure 2, is adopted here.
where is the magnetic susceptibility. By solving Equation (1) for and substituting the resulting value into Equation (2), it can be obtained that
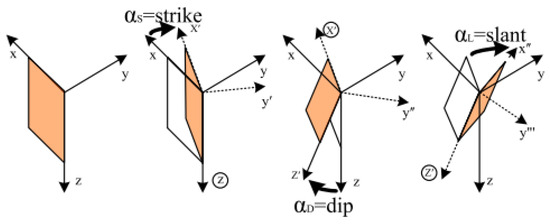
Figure 2.
Illustration of basic anisotropic parameters: transforming the observation coordinate into a general anisotropic position by successively applying three elementary Euler rotations [14].
The total electric field can be separated into the background field and the second field .
Similarly, the curl equation for the primary electric field can be obtained.
where and are the conductivity and magnetic permeability of the background, which is usually modeled as a homogeneous half-space or layered model. If the background model has a magnetic susceptibility of 0, then the magnetic permeability for the primary field model is the same as that in vacuum. Under these circumstances, Equation (9) can be modified as follows:
Subtracting Equation (10) from Equation (7) and considering Equation (8), then,
where is a unit matrix, and represents the distribution of anomalous electrical resistivity, defined as follows:
2.2. Finite Element Analysis
The Galerkin weighted residuals method is adopted here to obtain the variational equation [30]. Multiplying both sides of Equation (11) by and integrating over the entire domain, Equation (13) can be obtained:
In this equation, represents the variation of , namely .
The vector identity equation and the divergence theorem equation are expressed as follows:
where is the outward normal vector of the boundary. According to Equations (14) and (15), the first term of Equation (13) can be transformed into
where represents the entire study region, represents the boundary surface of the entire region.
The second term of Equation (13) transforms into
The first type of boundary condition is adopted, then the field value on the boundary is zero. Consequently, Equation (13) turns into
The region is discretized into hexahedral elements, as shown in Figure 3. The edge lengths in the x-, y-, and z- directions are denoted by a, b, and c, respectively, and the center coordinates are .
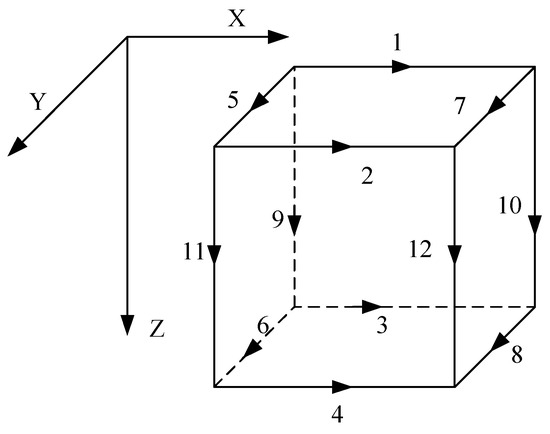
Figure 3.
Hexahedral element for vector finite element method.
We adopted a Whitney vector as the basis [30]. When the tangential field is assigned to the edges, the field components of the background field and the secondary field in the three directions can be expressed as follows, respectively:
where is the interpolation basis function [31]. Consequently, Equation (14) turns into
For a given element, the first term in Equation (21) turns into
where , and the second term in Equation (21) becomes
The third term turns into
The fourth term turns into
Extending it to all elements, then Equation (26) can be obtained for the entire computational region.
Considering that does not always equal zero, the equation system is as follows:
The values of , , , and in an element are shown in Appendix A. The SuperLU_DIST [27], which is a parallel direct solver, is utilized to solve Equation (27), and the technique for computing is consistent with the work in [14].
Two orthogonal generating sources, namely Source A in the y-direction and Source B in the x-direction, located on the top surface of this study’s domain, are used in this paper.
3. Multi-Level Parallel Algorithm
There are several available parallel schemes in the area of MT or controlled-source EM modeling [31,32]. Our MMT parallel algorithm is implemented in the C programming language using MPICH 3.2.1, with GCC 9.3.0 as the compiler and SuperLU_dist 8.0.0 as the direct solver for solving equations. As shown in Figure 4, the overall workflow of the parallel algorithm consists of six main steps: input, pre-processing, equation assembly, equation solving, post-processing, and output. There are N processes in MPI_COMMON_WORLD. The computational domain (for all frequencies) is first divided into several groups in parallel. Then, the frequencies in each group are executed one by one, while the computations for each frequency are carried out in parallel.
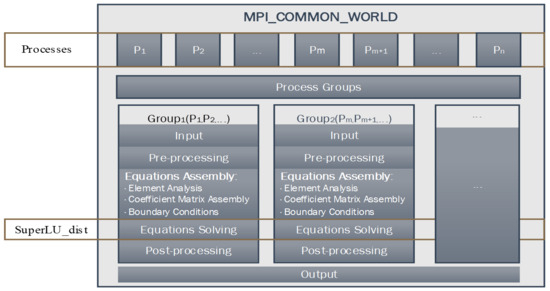
Figure 4.
The overall workflow of the parallel algorithm.
To illustrate, consider a scenario with six frequencies, 12 processes, and three groups. Initially, the total of 12 processes is divided into three groups, each group consisting of two frequencies and four processes. Each group has all the necessary information for computation, thereby reducing MPI traffic to some extent. Consequently, computations are performed in parallel both between groups and within each frequency; however, frequencies within each group are executed sequentially. Notably, all components within each frequency, including pre-processing, element analysis, matrix assembly, boundary conditions handling, equation solving, and post-processing are carried out in parallel.
4. Numerical Results
4.1. Accuracy Validation
To validate the algorithm’s correctness, a 3D conductive and magnetic arbitrary anisotropic model is designed, as shown in Figure 5. A 3D anomaly is embedded in an isotropic half-space with a resistivity of 100 . The dimensions of the anomaly are 600 m × 600 m × 600 m, and its top depth is 220 m. The principal resistivities are 50 , 100 , and 200 , respectively. The conductive Euler angles are 20°, 30°, and 10°, respectively. Its principal susceptibilities are 1, 0.5, and 0.8, and magnetic Euler angles are 45°, 20°, and 30°, respectively. The frequency computed is 10 Hz.
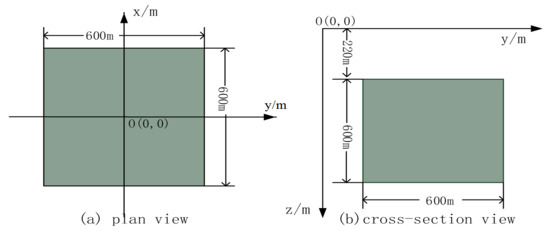
Figure 5.
The test model is a cubic anomaly embedded in a half-space of 100 , its dimensions are 600 m × 600 m × 600 m, and its top depth is 220 m: (a) plan view (left diagram); (b) cross-section view (right diagram).
The comparison between the results of this study and those of Xiao et al. [25] is shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7, respectively. In Figure 6, the upper row corresponds to Xiao’s results, which include the apparent resistivities and phases. The middle row corresponds to the results of this paper, and the bottom row shows the comparison errors. The first and second columns correspond to the apparent resistivity of the xy- and yx-modes, respectively, while the third and fourth columns correspond to the phases of the xy- and yx-modes, respectively.
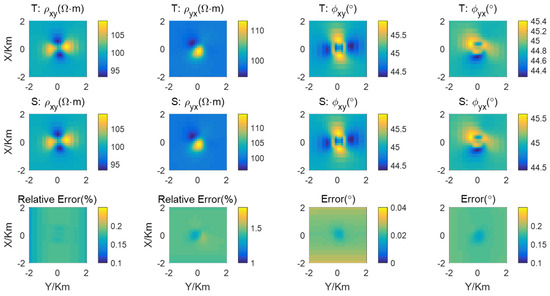
Figure 6.
The comparison between the results of this paper and the solutions of the total field [25] is presented. The first row corresponds to the results of the total field, the second row corresponds to the results of this paper, and the bottom row corresponds to the comparison errors. The first and second columns correspond to the apparent resistivity of the xy- and yx-modes, respectively, while the third and fourth columns correspond to the phases of the xy- and yx-modes, respectively.
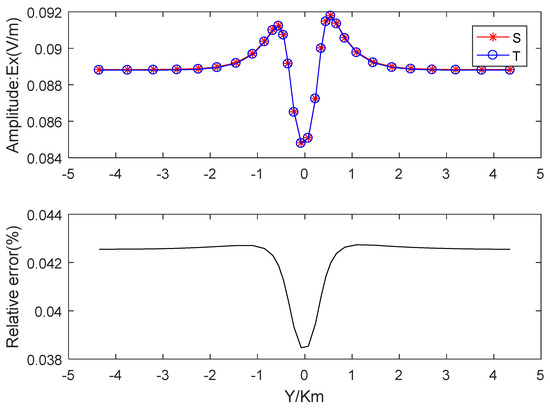
Figure 7.
The comparison between the electric fields of this paper and those of the total field method (Xiao, et al., 2020 [25]). ‘S*’ denotes the electric field of Source B along y = 0 m at the Earth’s surface, while ‘To’ represents the electric field of Source B along y = 0 m at the Earth’s surface.
The electric fields along y = 0 m at the Earth’s surface generated by Source B are further validated. In Figure 7, the electric fields from this paper and those from Xiao et al. (2020) [25] are shown in the upper subplot, while the relative errors are displayed in the bottom subplot.
4.2. Scalability Test
The scalability of the parallel algorithm is tested by computing a model with over one million unknowns (16 frequencies are equally sampled in logarithmic space between 0.001 Hz and 100 Hz). The grid dimensions are 76, 76, and 71 in the x-, y-, and z-directions, respectively.
A series of strong scalability tests were conducted on the Tianhe supercomputer with FT processors (National Supercomputer Center in Tianjin, Tianjin, China). Each computation node contains 64 cores running at a frequency of 2.0 GHz frequency, with 128 GB memory, while also exhibiting lower power consumption. The speedup and parallel efficiency are shown in Figure 8.
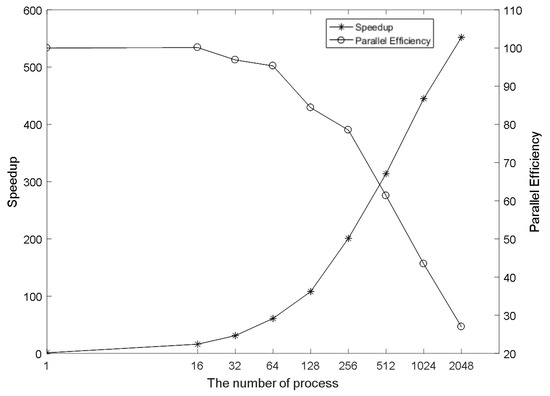
Figure 8.
Scalability test of 16 frequencies.
4.3. Typical Models
To eliminate the influence of magnetic susceptibility in marine environments, several representative marine models have been designed.
4.3.1. Cases with Single Anomaly
As shown in Figure 9, there is a layered marine medium with a 3D rectangular block embedded in the underlying half-space. The resistivities of the air, seawater, first layer (layer1), and half-space are 1012 , 0.4 , 10 and 100 , respectively. The thickness of the seawater layer is 300 m, and the thickness of the first layer is 100 m. The dimensions of the 3D anomaly are 1000 m × 1000 m × 100 m in the x-, y-, and z-directions, respectively. Its top depth is 200 m. A magnetic case and a conductive anisotropic and magnetic case are studied, respectively.
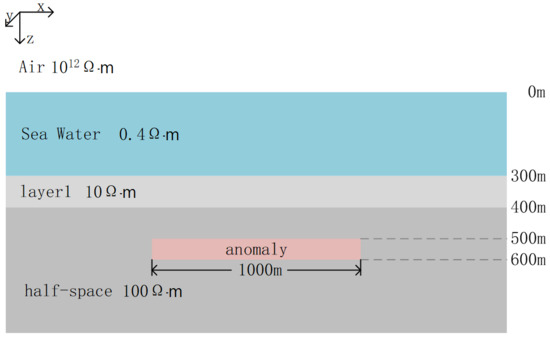
Figure 9.
Marine model with single anomaly: the 3D anomaly’s top depth is 200 m, and its dimensions are 1000 m × 1000 m × 100 m in the x-, y-, and z-directions, respectively.
For the magnetic case, the 3D anomaly’s resistivity is set to 100 , which is the same as the half-space, while its susceptibility is set to be −0.5, 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2.0, respectively. The apparent resistivities and phases of 10 Hz are shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11, respectively. The first to second rows correspond to the xy- and yx-modes, respectively, while the first to fifth columns correspond to susceptibilities of −0.5, 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2, respectively.
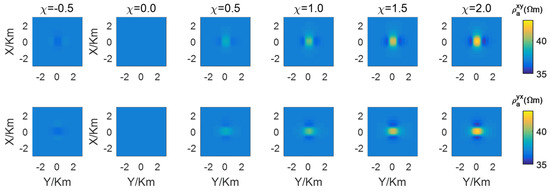
Figure 10.
The apparent resistivities of the marine model with single anomaly.
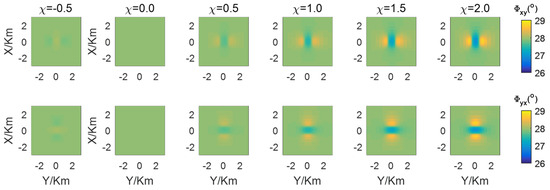
Figure 11.
The phases of the marine model with single anomaly.
For the conductive anisotropic and magnetic case, the axial resistivities are 30 , 50 , and 60 in the x-, y-, and z-directions, respectively. Its susceptibility values are set to be 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2.0, respectively. The apparent resistivities and phases at 10 Hz are shown in Figure 12 and Figure 13, respectively. The first to second rows correspond to the xy- and yx-modes, respectively, while the first to fifth columns correspond to susceptibilities of 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2, respectively.
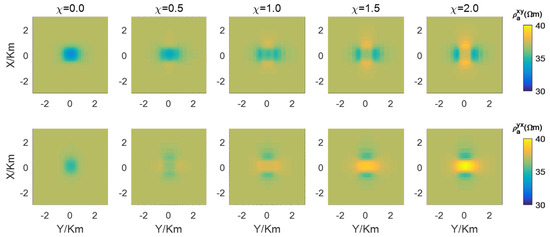
Figure 12.
The apparent resistivities of the conductive anisotropic and magnetic case are presented. The first to second rows correspond to xy- and yx-modes, respectively, while the first to fifth columns correspond to susceptibilities of 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2, respectively.
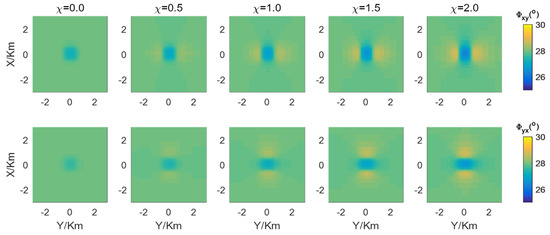
Figure 13.
The phases of the conductive anisotropic and magnetic case are presented. The first to second rows correspond to the xy- and yx-modes, respectively, while the first to fifth columns correspond to susceptibilities of 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2, respectively.
4.3.2. Case with Synthetic Anomalies
The synthetic model is shown in Figure 14. There is another 3D anomaly (anomaly2) located beneath the first 3D anomaly (anomaly1). The dimensions of anomaly2 are 1000 m × 1000 m × 160 m in the x-, y-, and z-directions, respectively. In this case, anomaly1 is an axial conductive anisotropic block with three principal resistivities of 30 , 50 , and 60 , respectively. While anomaly2 is a magnetic block with a susceptibility of 0, 1, and 2, respectively. The frequency computed here is also 10 Hz.
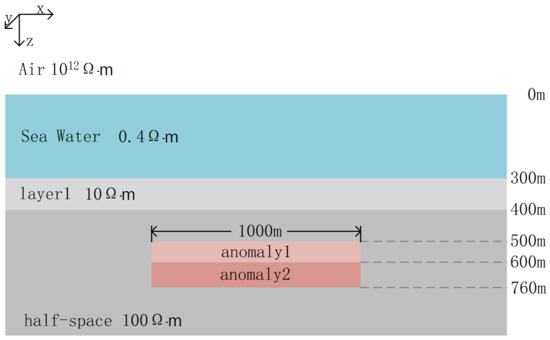
Figure 14.
Marine model with synthetic anomalies: anomaly1’s dimensions are 1000 m × 1000 m 100 m in the x-, y- and z-directions, respectively. Its top depth is 200 m. Anomaly2’s dimensions are 1000 m × 1000 m × 160 m in the x-, y-, and z-directions, respectively. Its top depth is 300 m.
The apparent resistivities and phases are presented in Figure 15 and Figure 16, respectively. The first to second rows correspond to the xy-, and yx-modes, respectively, while the first to fifth columns correspond to susceptibilities of 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2, respectively.
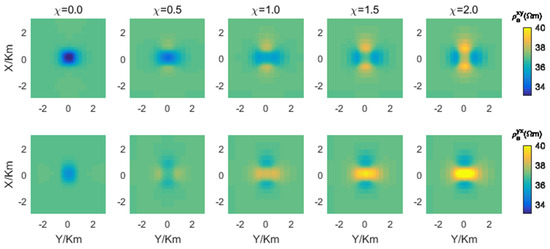
Figure 15.
The apparent resistivities of the marine model with synthetic anomalies. The first to second rows correspond to the xy-, and yx-modes, respectively, while the first to fifth columns correspond to susceptibilities of 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2, respectively.
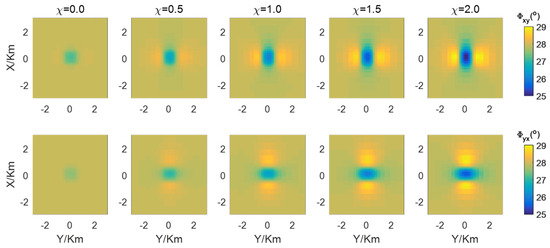
Figure 16.
The phases of the marine model with synthetic anomalies. The first to second rows correspond to the xy-, and yx-modes, respectively, while the first to fifth columns correspond to susceptibilities of 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2, respectively.
5. Analysis and Discussion
5.1. Accuracy Validation
The conductive and magnetic arbitrary anisotropic model is utilized to comprehensively verify the accuracy of this algorithm. As shown in Figure 6, the relative errors of the xy-mode apparent resistivities are below 1.2%, and those of the yx-mode apparent resistivities are less than 0.15%. Moreover, the errors of the xy-mode phases do not exceed 0.3254°, and for the yx-mode phases, they remain below 0.03°. As shown in Figure 7, the relative errors of the electric fields of Source B along the y = 0 m at the Earth’s surface are less than 0.05%. Given that the relative errors of the apparent resistivities are significantly lower than 5%, the errors of the phases are considerably less than 1°, and the relative errors of electric fields are far below 0.05%, the results of this algorithm exhibit a high level of agreement with the findings of Xiao et al. [25].
5.2. Scalability Test
In this section, the degree of freedom (Dof), the run-time, and the number of nonzero elements (NoN) are discussed in detail.
With the grid dimensions of 76, 76, and 71 in the x-, y-, and z-directions, respectively, the Dof of one frequency is 1,263,647, which is more than 1,000,000. For the 16 frequencies tested in this Section, the Dof is 20,218,352, which exceeds 20,000,000. The serial computation time is 116.92 h, while the parallel computation time using 2048 processes only needs 12.70 min. As shown in Figure 7, the speedup shows a remarkable improvement with the increase in processes. For the parallelized algorithm running with 2048 processes, the speedup over the serial version reaches an impressive value of 552.41 and is accompanied by a parallel efficiency of 26.97%. Due to the independence of calculations between different frequencies, this naturally leads to a task-level parallelism among them. Notably, the speedup will further increase with an increasing number of unknowns or processes, and the computation time will further decrease with a higher CPU frequency. The scalability test reveals that the multi-level parallel algorithm exhibits exceptional scalability.
The memory required to run this code is closely related to two aspects: (1) the storage strategy of matrices, which is further closely connected to the NoN of the coefficient matrices in Equation (27); and (2) the choice of the direct or iterative solver to solving Equation (27), which is also closely related to the NoN. Therefore, we only analyze the NoN here. Since it is the hexahedral cell and the edge-based FE method are adopted in this context, the NoN of the left or right coefficient matrices in Equation (27) can be obtained by
where represents the edges of the entire computational domain, and , , denote the number of cells in the x-, y-, and z-directions, respectively.
For each frequency, two orthogonal sources are adopted. Therefore the of the tested model with 16 frequencies is 64 times Formula (29), amounting to 2,613,227,456. Furthermore, given that the matrix coefficients are complex values with double precision, it takes 38.94 GB to store the non-zero coefficients alone. The data are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Statistics including Dofs, NoNs, runtime, and memory required.
5.3. Typical Models
For the convenience of expression, in this section we hereby define as the magnetic susceptibility of anomalies, as the resistivity of the surrounding rock where the anomaly is embedded, and and as the principal resistivities in the x- and y-directions, respectively.
5.3.1. Cases with Single Anomaly
Cases with a single anomaly include the magnetic case and the conductive anisotropic and magnetic case.
Magnetic case. As shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11, when is −0.5 the apparent resistivities and phases are somewhat similar to those of a low-resistive anomaly. When is 0, the apparent resistivities and phases remain unchanged due to the magnetic case turning into the layered background model. However, as susceptibility increases, the apparent resistivities become higher and the phases become lower. This indicates that a positive susceptibility in a magnetic anomaly will result in higher apparent resistivities and lower phases, somewhat resembling a high-resistive anomaly, while a negative susceptibility in a magnetic anomaly will result in lower apparent resistivities and higher phases, resembling a lower-resistive anomaly to some extent. These findings are consistent with previous research by Xiao et al. [25], who explained this phenomenon using the analytical solutions of an axial conductive and magnetic anisotropic half-space.
Conductive anisotropic and magnetic case. The results presented in Figure 12 and Figure 13 demonstrate a transition from lower to higher apparent resistivities, accompanied by significant variations in the phases. Specifically, the xy-mode apparent resistivities exhibit noticeably lower values when is 0, 0.5, 1, or 1.5, while they tend to manifest higher values when is 2. Through parameter analysis, it is observed that the value in the x-direction increases when varies from 0 to 2, and the maximum value 90 approaches (100 ). On the other hand, the yx-mode’s apparent resistivities display obviously lower values when is set at either 0 or 0.5 but show clearly higher values when is set at 1.0, 1.5, or 2.0. Parameter analysis reveals that the value of in the y-direction is no less than when . This phenomenon is also consistent with the conclusions in [25].
5.3.2. Case with Synthetic Anomalies
The results, as shown in Figure 15 and Figure 16, demonstrate a transition from lower to higher apparent resistivities with significant variations in phases. When the magnetic susceptibility of anomaly2 is 0, indicating that it is identical to the surrounding rocks, the apparent resistivities and phases are solely influenced by anomaly1, resulting in lower apparent resistivities. The xy-mode apparent resistivities manifest as obvious lower apparent resistivities when is set to 0, 0.5, 1, or 1.5, while they exhibit almost higher values when equals 2. On the other hand, the yx-mode apparent resistivities manifest as noticeably lower apparent resistivities for values of 0 and 0.5, while they manifest obvious higher values for values of 1, 1.5, or 2.
In this case, anomaly1 is a conductive axial anisotropic yet non-magnetic block, while anomaly2 beneath it is a magnetic but non-conductive block. Additionally, the size of anomaly2 is larger than that of anomaly1. Despite the presence of these two distinct anomalies, the explanation provided in Section 5.3.1 remains applicable for elucidating the behavior of MMT’s responses. However, it is crucial to note that MMT’s responses are not solely dependent on conductivity and magnetic susceptibility; they are also closely linked to the size and location of these anomalies.
6. Conclusions
In this study, we developed an accurate and efficient 3D MMT modeling algorithm based on the secondary field formula, utilizing the edge-based finite element method and integrating multi-level parallel technology to investigate MMT responses in complex media with conductive and magnetic anisotropy. The accuracy of the algorithm was validated through comparisons with previously published results for a conductive and magnetic arbitrary anisotropic model, while its efficiency was confirmed via scalability tests. The scalability test indicates that the computational efficiency can be significantly improved with the implementation of parallel technology. Therefore, the algorithm is beneficial for practical inverse problems that rely on a fast-forward modeling scheme.
More importantly, it can be concluded that the susceptibility has a considerable influence on MMT’s responses in practical MMT works conducted in magnetite-rich regions, as demonstrated through several typical modeling tests in this study:
- (1)
- For a single conductive and magnetic anomaly, such as an anomaly with lower resistivity and higher susceptibility than the surrounding rocks, the apparent resistivities and phases can even be reversed due to the influence of susceptibility.
- (2)
- For synthetic anomalies, such as the combination of a conductive anomaly and a magnetic anomaly, the responses of the conductive anomaly can be affected or even covered by the influence of the magnetic anomaly.
- (3)
- The marine geological environment of practical MMT works is extremely intricate. It needs more attention for the influences of susceptibility, especially in magnetite-rich regions though non-zero susceptibility and conductive anisotropy complicate MMT’s responses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.X., Z.Z. and Y.W.; methodology, T.X., Z.Z., X.Z., J.Z., B.Y. and C.G.; formal analysis, T.X. and J.L.; writing—original draft preparation: T.X. and Z.Z.; writing—review and editing: Z.Z., X.Z. and C.G.; funding acquisition, T.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was co-funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42104078) and Henan Province Science Foundation for Youths (242300420600, NSFRF240709).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data associated with this research are available and can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. The Values of , , , and
, , and are side lengths of the hexahedral element in the -, -, and -directions, respectively. ,
- (1)
- The values of
- (2)
- The values of
- (3)
- The values of
- (4)
- The values of
References
- Zhdanov, M.S.; Wan, L.; Gribenko, A.; Čuma, M.; Key, K.; Constable, S. Large-scale 3D inversion of marine magnetotelluric data: Case study from the Gemini prospect, Gulf of Mexico. Geophysics 2011, 76, F77–F87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worzewski, T.; Jegen, M.; Kopp, H.; Brasse, H.; Castillo, W.T. Magnetotelluric image of the fluid cycle in the Costa Rican subduction zone. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Reyes, O.; Queralt, P.; Piñas-Varas, P.; Ledo, J.; Rojas, O. Electromagnetic Subsurface Imaging in the Presence of Metallic Structures: A Review of Numerical Strategies. Surv. Geophys. 2024, 34, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, S.; Key, K.; Lewis, L. Mapping offshore sedimentary structure using electromagnetic methods and terrain effects in marine magnetotelluric data. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 176, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, K.; Constable, S. Coast effect distortion of marine magnetotelluric data: Insights from a pilot study offshore northeastern Japan. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2011, 184, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.O.; Racic, L.; Grauch, V.J.S. Magnetic methods in near-surface geophysics. In Near-Surface Geophysics; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2005; pp. 151–176. [Google Scholar]
- Mickus, K. Magnetic Method. 2023. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228994566_Magnetic_Method (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Chen, L.; Xiao, T.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. One-dimensional magnetotelluric modeling in magnetic and resistive axial anisotropic media. Prog. Geophys. 2022, 37, 2373–2380. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Oldenburg, D.W. Recovering magnetic susceptibility from electromagnetic data over a one-dimensional earth. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 130, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Oldenburg, D.W. Simultaneous reconstruction of 1-D susceptibility and conductivity from EM data. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1996; pp. 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, L. Electromagnetic sounding with susceptibility among the model parameters. Geophysics 1977, 42, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.J. Multidimensional inversion of loop-loop frequency-domain EM data for resistivity and magnetic susceptibility. Geophysics 2010, 75, F213–F223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, S.; Li, M.; Ma, X.; Li, W. Two-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion considering resistivity and magnetic permittivity. J. East China Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2018, 41, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Pek, J.; Santos, F.A. Magnetotelluric impedances and parametric sensitivities for 1-D anisotropic layered media. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Maurer, H.M. Electromagnetic induction in a layered earth with arbitrary anisotropy. Geophysics 2001, 66, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pek, J. Adaptive finite element modelling of two-dimensional magnetotelluric fields in general anisotropic media. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 175, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidelt, P.; Oristaglio, M.; Spies, B. 3-D conductivity models: Implications of electrical anisotropy. Three-Dimens. Electromagn. 1999, 7, 119–137. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z. Research on Three-Dimensional Magnetotelluric Modeling in General Anisotropic Media. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.-Y. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric modeling in anisotropic media using edge-based finite element method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 149, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y. Adaptive finite element modelling of three-dimensional magnetotelluric fields in general anisotropic media. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 151, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric modelling in anisotropic media using the A-phi method. Explor. Geophys. 2019, 50, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y. 3D MT modeling using the T–Ω method in general anisotropic media. J. Appl. Geophys. 2019, 160, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hu, X.; Xiao, T.; Cai, H.; Li, J.; Peng, R.; Long, Z. Three-dimensional edge-based finite element modeling of magnetotelluric data in anisotropic media with a divergence correction. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 189, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, N.; Zhou, J.; Hu, X.; Han, B. 3D edge-based and nodal finite element modeling of magnetotelluric in general anisotropic media. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 158, 104975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; He, G.; Liu, J. Magnetotelluric responses of three-dimensional conductive and magnetic anisotropic anomalies. Geophys. Prospect. 2020, 68, 1016–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Chen, Z.; Wu, X.; Kong, W.; Chen, H.; Li, T.; Feng, X. Unstructured Grid Finite Element Modeling of the Three-Dimensional Magnetotelluric Responses in a Model with Arbitrary Conductivity and Magnetic Susceptibility Anisotropies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SuperLU: Home Page. Available online: https://www.nersc.gov (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Cullity, B.D.; Graham, C.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Greiner, W. Classical Electrodynamics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.M. The Finite Element Method in Electromagnetics, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Reyes, O.; Modesto, D.; Queralt, P.; Marcuello, A.; Ledo, J.; Amor-Martin, A.; de la Puente, J.; García-Castillo, L.E. 3D magnetotelluric modeling using high-order tetrahedral Nédélec elements on massively parallel computing platforms. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 160, 105030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Reyes, O.; de la Puente, J.; Cela, J.M. PETGEM: A parallel code for 3D CSEM forward modeling using edge finite elements. Comput. Geosci. 2018, 119, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).