Abstract
This study focuses on the prediction of technical efficiency of narrow-crested submerged permeable rubble-mound breakwaters, in terms of wave attenuation. A number of existing formulae for estimating wave transmission coefficient for submerged breakwaters can be found in the literature, whereas in this work further improvement for that estimation has been achieved mainly through physical modelling. A series of 2D experiments under scale were conducted for regular and random waves providing data on wave transmission coefficient and respective wave breaking characteristics. A Boussinesq-type wave model capable of simulating wave propagation for regular waves over porous submerged breakwaters was also used in order to provide additional wave transmission information. Data analysis showed that wave breaking mechanism significantly affects wave energy dissipation and, therefore, wave breaking occurrence and type can be directly linked to wave transmission coefficient for a given structure’s geometry and sea state. The result of this work is the proposal of a set of simple semi-empirical equations for predicting wave transmission coefficient over small profile porous submerged breakwaters in relevance to the parameterization of the expected dominant wave breaking mechanism.
1. Introduction
With a view to minimizing environmental impact of coastal protection measures, submerged breakwaters have been adopted as a shore protection alternative to their emerged counterparts. This is because they can enhance water renewal of inshore waters, avoid degradation of the aesthetic value of the landscape, occupy relatively smaller seabed areas, etc. Beyond their basic role of coastal stabilization, submerged breakwaters also gain attention as it has been deduced that they may function as artificial marine habitats like natural reefs [1]. This is applicable especially to rubble-mound submerged permeable breakwaters. In this work, technical efficiency of those coastal protection structures of minimum sea bed occupation is studied, specifically the trapezoidal, narrow-crested, homogenous rubble-mound, steep-sloped submerged breakwater layout (SPB). When addressing wave energy abstraction, such structures are expected to be effective for up to average surface wave exposure due to their submergence. Also, they are intended for micro-tidal environments as in the Mediterranean, the Caribbean, and the Baltic Sea due to the critical impact the freeboard has on the efficiency of a submerged structure in reducing wave heights. Nevertheless, due to environmental considerations such as the ones mentioned above, they do gather research interest. Aiming at furthering the acceptance of small profile SPBs as coastal defense structures, this study focuses on parameterizing wave energy dissipation, expressed in terms of wave transmission coefficient (Kt), in relation to certain physical processes giving satisfactory prediction accuracy, acceptable for technical design.
Several attempts on predicting Kt for single submerged porous breakwaters based on various data sets have been carried out. Existing formulae’ reviews summarizing them and assessing their accuracy can be found in the literature [2,3,4]. Also, a few studies (e.g., [5,6]) addressed multiple trapezoidal structures. In contrast to most approaches [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19], the method considered in this study is based on physical wave breaking characteristics. It has been indicated that wave breaking is a significant factor affecting wave transmission over submerged breakwaters [2]. This is the core novelty advanced in this study by highlighting the strong dependence of wave transmission level to the corresponding type of wave breaking induced by the submerged obstacle. Surely technical efficiency of SPBs also depends on other wave energy dissipating phenomena like the turbulence generated by water movement through the pores between the stones. This work suggests correlating wave breaking macro-features over SPBs with Kt for predicting the latter in a rather reasonable way by taking into account such crucial physical processes. The method applied to acquire the information needed for this task was mainly based on carrying out a series of 2D experiments combining Kt with relevant wave breaking characteristics. The models tested were under scale and overall dimensions considered real life applications of SPBs. It is typical in such research to evaluate Kt by assuming 2D conditions. However, a few works also treated 3D configurations, thus capturing diffraction effects by submerged [20] or low-crested [21] breakwater heads.
Beyond semi-empirical approaches on estimating Kt, several wave models of different types have been developed that can predict the wave transformation due to the presence of submerged obstacles, by treating the surface elevation time-series. The authors of [22] presented a one-dimensional Boussinesq model with improved linear dispersion characteristics capable of predicting the non-linear wave transformations over impermeable barred topographies. The Boussineq-type model was extended to include the effect of structural porosity [23,24,25]. Another Boussinesq-type model in conjunction with a macroscopic drag formula was introduced by [26]. A fully dispersive and highly non-linear Boussinesq-type model was presented [27] and extended by [28], to include the effects of structural porosity, steep slopes, and relevant wave breaking prediction. In another approach, ref. [29] developed a 1DH model based on the non-linear shallow water equations and two vertical dimensional (2DV) model based on Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations (RANS) that are capable of simulating wave interaction with permeable and impermeable coastal structures. Ref. [30] simulated wave interaction with porous structures by introducing an improved smoothed particle hydrodynamic (SPH) model based on RANS equations and a large eddy simulation (LES) model. The authors of [31] formulated a non-hydrostatic model based on a non-linear shallow water equation (NSWE) to investigate wave evolution on a water channel with a submerged trapezoidal breakwater.
Data analysis showed that if the main wave breaking mechanism is predicted for a given structure’s geometry and sea state, it can then lead to Kt by simple linear semi-empirical equations suitable mainly for small profile porous submerged breakwaters, the type of structure addressed herein. The method proposed was also compared to a widely accepted Formula [9] based on a large number of experimental results, showing satisfactory performance on estimating Kt.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
Experiments associated with the present study were conducted in the three-dimensional basin D1 of the Laboratory of Harbour Works at the National Technical University of Athens, Greece. Part of the basin was transformed into four parallel tangent canals with 0.80 m width and 22.00 m length suitable for carrying out 2D experiments. More details for this facility can be found in previous experimental work [32]. Experiments involving regular and irregular waves under breaking and non-breaking conditions over various SPB physical models were conducted, and layouts according to three different stone mean diameters (dn50) that were tested were constructed in three of the total existing four canals.
Five physical models of submerged breakwaters made of uniform natural stones of porosity close to 0.5 were made with crest widths (B) varying from 3dn50 to 5dn50, namely SPB1 with dn50 around 0.10 m and B equal to 0.30 m; SPB2a and SPB2b with dn50 around 0.08 m and respective B equal to 0.28 m and 0.40 m; SPB3a and SPB3b with dn50 around 0.06 m and respective B equal to 0.25 m and 0.35 m. All structures displayed slope (m) of 1:1.5 at both sides and height (hs) equal to 0.33 m. The SPB1 was tested for a sea depth (d) of 0.43 m giving a free board (F) of 0.10 m, while the other four models were tested for two sea depths of 0.38 m and 0.43 m giving F of 0.05 m and 0.1 m, respectively.
In regard to SPB geometry and water depth, in total nine different sections of SPBs were formed and tested. The wave maker’s paddle was located 7.5 m from the upstream toe of the SPB models and a dissipative layer, made of gravel beach topped with wire mess cylinders, was formed starting around 4.0 m from the downstream toe. The plane of the sea bed was horizontal along the flumes. Testing scale was around 1:10 following Froude scaling similarity, and the submerged bars were designed as statically stable. A view from the facility during experiments is given in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
View of the experimental layout from the downstream area during wave tests.
In order to calculate Kt as the ratio of the incoming to the transmitted wave height, two resistant-type wave gauges were used to measure water surface elevation, placed at two specific locations along the canals. Each structure was tested separately from the others. During wave runs, in order to minimize effects between the models, wire mess cylinders functioning as wave energy absorbers were used. The first gauge, used to measure the characteristics of the incident wave, was placed 1.0 m up-wave from the offshore slope toe while the other was positioned 1.6 m inshore from the downslope toe of the SPBs in order to take measurements of the transmitted wave characteristics. The gauge signals were recorded by a personal computer loaded with the WaveData acquisition and analysis software of HR Wallingford. The software controlling the wave paddle did not cope with re-reflection absorption. The issue was addressed by a suitable treatment of the numerical output, which gave higher weight to the measurements in the time window prior to the re-reflection arriving at the gauges. In general, contamination of the used signal was insignificant especially for the runs with irregular waves. In each run, data were recorded simultaneously from the two stations at a sampling frequency of 100 Hz (dt = 0.01 s). In total, 16,400 data points per gauge for each regular wave run and 92,200 data points for the irregular ones were taken. In Figure 2, the overall geometry of the physical models and location of wave gauges placed for measuring Kt is displayed. The structures were tested for regular waves with incoming wave height (Hi) ranging from 0.045 m to 0.173 m and wave period (T) ranging from 1.0 s to 2.2 s. As for irregular waves, the respective range covered from 0.031 m to 0.132 m for the incoming significant height (Hs) and from 1.0 s to 2.2 s for the wave peak period (Tp). Incident wave characteristics correspond to statistical analysis of free surface elevation measurements for the upstream section. Summary of B, Dn50, and sea state for each SPB model is given in Table 1. Incoming wave data for all scenarios are given in Table A1 for regular and Table A2 for irregular waves.
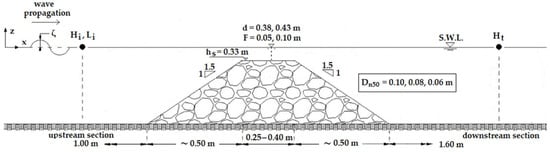
Figure 2.
Layout of the physical rubble-mound models tested and location of measurements.

Table 1.
Sea state and basic structural features for SPB models tested.
Wave breaking occurrence was visually observed, and its main characteristics were noted down. For regular waves, a certain wave breaking mechanism was deduced for each wave test, while for irregular wave conditions, following a Jonswap spectrum, various wave breaking types were observed for each test as expected. In general, with the interest mostly concentrated on the visual observations for regular waves, wave breaking classification considered that wave breaking evolution over submerged structures is a complex phenomenon and may vary: from mixed spilling to plunging with or without bore formation, bore, collapsing to surging, and two steps spilling with or without plunging wave breakers. Details for this wave breaking type classification can be found in the literature [33]. In order to simplify the wave breaking types, transmitted waves were sorted in four groups according to the dominant breaker type evolution: the non-breaking, the spilling, the plunging, and the “other” (such as bore and collapsing) with a view to parameterization of each type, in order to implement it subsequently for irregular waves. Data results of Kt for regular waves in relation to the above simplified wave breaking classification are given in Table A1. The Kt values for irregular wave tests are also presented in Table A2.
2.2. Numerical Model
Considering wave models as described in the introduction, a Boussinesq-type numerical wave model capable of simulating wave propagation of incoming regular waves over porous submerged breakwaters was also used in order to provide additional wave transmission coefficient information. Wave propagation over the SPBs tested experimentally was simulated utilizing the fully dispersive and highly nonlinear Boussinesq-type model [28], referred to as a modified version (mCM14) of a previous one [27] that was based on Boussinesq equations by [34]. Validation with the experimental data showed that the numerical model is capable of reproducing Kt for short waves. Thus, it was applied for wave tests with incoming wave height (Hi) ranging from 0.06 m to 0.12 m and wave period (T) ranging from 1.0 s to 1.25 s. In this way, certain gaps on Kt values for wave tests not conducted experimentally were filled. Results are given in Table A3.
2.3. Breaker Type Classification
2.3.1. Regular Waves
Parameterization of breaker type was performed following a previous approach for submerged breakwaters, based on two non-dimensional parameters [33] given as R*d and ξB, their relevance to certain limit values defining wave breaking features for regular waves, with:
and
where Lo is the deep water wave length, Hi the incident wave height, F the free board in the absence of waves, m the sloping, B the crest width, and hs the structure’s height.
In Equation (1), P denotes a notional permeability [35], equal to 0.6 for permeable rubble-mound homogenous structures. This value was applied to the physical models tested in this study. The P value decreases for lower porosity rubble-mounds and may take a value down to 0.4 for structures made of smaller or graded stones or in structures with a core.
Certain modifications were made on these parameters in order to correlate them closer with the main type of wave breaking also including the non-breaking occurrence not considered in previous studies. Initially, in R*d and ξB, Lo was replaced by the incoming wave length Li computed at the depth close to the front toe of the breakwater but not that close to be affected by shoaling due to the structure, where the incident wave characteristics were measured.
Then, R*d was multiplied by two additional non-dimensional factors c1 and c2. The first one takes into account a width (Bch) that loosely can characterize wave-structure interaction in terms of momentum flux. Its calculation is based on the estimation of a characteristic water depth (dch), where the mean of the product of ux∙C, integrated along the height of the water column at the structure location, matches the local ux∙C value. Parameter ux is the orbital horizontal velocity and C is the wave celerity, both calculated through linear theory. After applying this process for a wide range of wave scenarios and for depths up to 1.0 m, considering testing scale around 1:10, Bch was defined as follows:
Now factor c1, denoting somehow the wave-structure geometrical interaction, can be expressed by:
Factor c2 takes into account Bch as well, but also dn50, and an equivalent freeboard Feq defined as [33]:
where As is the cross-sectional area of the structure and Lm its width along the base with c2 defined by:
where is the median nominal diameter of the breakwater structure. It should be added here that the freeboard in the absence of waves is actually modified by waves through their setup resulting from eventual wave breaking forced by the structure; see e.g., [21]. This contribution was indirectly taken into account in this study by the identification of the breaker type associated to the corresponding measurements that finally supported the proposed formulae, as it will be seen in the following.
In accordance with the above modifications made mainly on R*d, the set of surf similarity type non-dimensionless parameters named R and ξm herein becomes:
and
The R and ξm values were calculated for each regular wave test carried out on physical models and was correlated to the main wave breaking type visually observed, namely the plunging, spilling, “other”, and non-breaking as previously mentioned. Plots of ξm-R showed gathering of scenarios with the same wave breaking type to certain areas of the diagram as presented in Figure 3. These sub areas where the majority of tests had a certain breaking type were delineated by T1 and T2 curves described by:
and
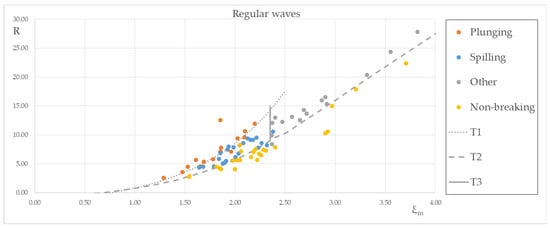
Figure 3.
Breaker types parameterization for regular waves.
Curve T1 separates plunging from spilling breaking events, while T2 functions as a boundary for spilling and “other” breakers from cases for non-breaking wave occurrence. Moreover, there is a certain ξm value that separates spilling from “other” types of breaking equal to 2.35 (line T3 in Figure 2). In general, spilling and plunging breakers appear for ξm lower than 2.35. Sub areas for each wave breaking type are distinguished in Table 2.

Table 2.
Breaker type in relevance to R, ξm parameters for regular waves.
As it can be seen in Figure 3, determination of the boundary line T1 (Equation (9)) for ξm greater than 2.35 was not possible as testing conditions did not cover this area of the diagram. Thus, the relevant limit where plunging breaking type occurs was not defined there.
The next step was to investigate the relevance of Kt to the breaker type. To do so, additional Kt data derived from the numerical model described in Section 2.2 were also used. The breaker type identification for the numerical simulations followed Table 2. The relation of R to Kt values showed that for each breaker type there is a different range of Kt values, quite distinct for plunging and non-breaking waves with spilling and “other” types covering more or less a common area on the Kt–R plane and showing a trend with a mean value of Kt between the relevant mean values for plunging and non-breaking wave tests (Figure 4). In the following, types spilling and “other” were unified in one type for simplicity. The unified type was named spilling+ breaking type. The Kt values that were numerically calculated contributed in examining further the consistence of the wave breaking type’s sub-areas defined by the experimental data, to the expected wave energy abstraction level. Results showed that the derived boundaries distinguished reasonably well the Kt values between sub-areas in the ξm–R plane of the numerical simulations’ wave tests.
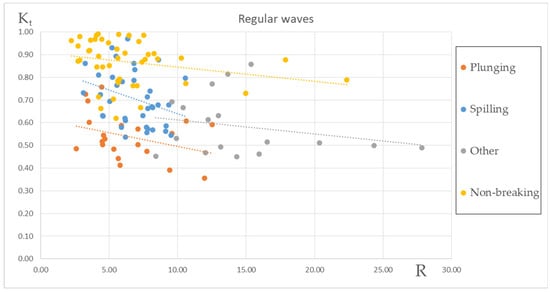
Figure 4.
Correlation of Kt values to R parameter and linear approximation from regression analysis for each wave breaking type (dotted lines) for regular waves.
2.3.2. Irregular Waves
Data analysis for regular waves showed that the Kt value depends significantly on wave breaking occurrence and type. This observation was extended to the irregular wave tests. As a single breaker type cannot be identified visually for such runs, calculation of ξm and R values for each irregular wave test was performed considering the peak wave period Tp instead of T in regular waves, the relevant peak wave length Lp instead of Li at the sea depth associated to the incoming wave train, and the significant wave height Hs instead of Hi. Table 2 was then applied in order to estimate the dominant breaking form in irregular waves. Results are presented in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Breaker types parameterization for irregular waves.
In order to estimate the T1 boundary line for ξm greater than 2.35 not defined for regular waves, Kt data for irregular waves for submerged structures of geometries close to the tested models but of lower porosity [36] were used. For this data series, P was taken around 0.4 in Equation (7) and the extension of the curve T1 (see Figure 5) distinguished reasonably the wave breaking type according to the Kt values. This process is further discussed in Section 4.
Investigation of the relevance of Kt to R for any breaker type showed that for each breaker type likewise for regular waves, there is a certain range of Kt values close to a straight line (Figure 6).
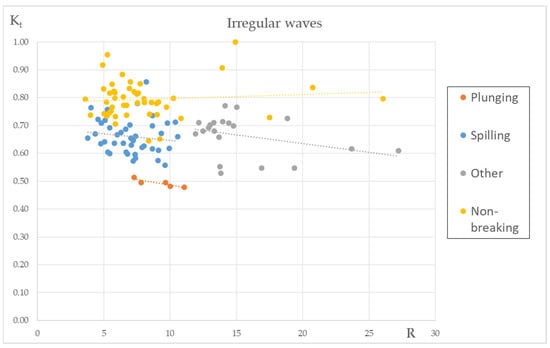
Figure 6.
Correlation of Kt values to R parameter and linear approximation from regression analysis for each wave breaking type (dotted lines) for irregular waves.
As noted for regular waves, spilling and “other” breakers present a similar range for Kt values more distinct for the irregular wave tests and for simplicity can be gathered in one general group denoted as spilling+. This is further supported in irregular waves, where no clear boundary between typical spilling and bore/surging breaking types can be accurately defined.
3. Results
The Kt parameterization for irregular waves was based on the predicted dominant breaker characteristic. Three main types are considered: plunging, spilling+, and non-breaking. Similarly to the methodology applied for regular wave conditions, the set of R and ξm values is calculated as:
where
Feq from Equation (5), and
Consecutively, for every given ξm, the relation of the R value to T1 and T2 boundary lines (Equations (9) and (10)) is checked according to Table 3, and the breaker type is defined.

Table 3.
Breaker type in relevance to R parameter for irregular waves.
After the prediction of the wave breaking feature, the Kt value is calculated by simple linear equations, one for each breaker type, extracted through linear regression of the experimental Kt data in conjunction to the non-dimensional parameter described as:
The result of the semi-empirical Kt prediction model proposed herein is the following:
The above formulation is aligned with what one would expect by considering the physical process of wave breaking that controls the phenomenon. Indeed, the three main breaking classes extract a progressively lower amount of wave energy in the order noted in Equation (15), giving thus a correspondingly higher transmission coefficient.
4. Discussion
The applicability range of the model, derived solely by the experiments framing this work is for Hs/F values from 0.40 to 1.50 and for Lm/Lp from 0.3 to 1.0. Additionally, the relative depth F/d was approximately between 0.10 and 0.25. It should be pointed out that only a few wave scenarios were categorized as plunging for the irregular wave tests, thus information from regular waves giving an average Kt value of 0.5 was also considered in defining the relevant Kt equation. Root mean squared error (RMSE) was employed as a reliability indicator to assess the proposed formula as compared to the experimental data, where:
N is the number of data, and Ktm and Kte are the predicted by the model and experimentally measured values of Kt, respectively. Their relation is shown in Figure 7. For the total number of all 115 data measurements, RMSE calculated was equal to a quite satisfactory value of 0.08.
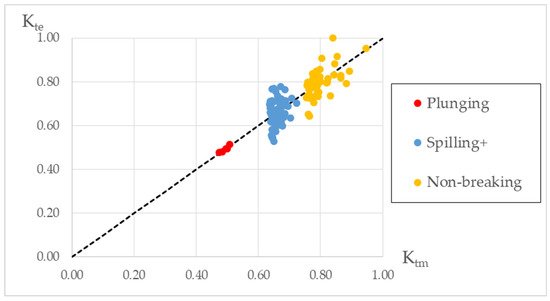
Figure 7.
Comparison between Kt calculated with the proposed model (Ktm) and Kt measured experimentally (Kte).
Despite the fact that various data sets of Kt values for submerged structures are mentioned in [3], for the small profile SPBs investigated in this study (narrow crested, homogenous, statically stable rubble-mound and steep sloped trapezoidal bars of a relative depth F/d approximately between 0.10 and 0.25 for up to average wave exposure) and especially for irregular waves, such data were limited. Thus, the need for the experiments framing this work was apparent. Additionally, information of combined Kt values and the physical process of wave breaking has not been previously conducted systematically as herein, despite the fact that wave breaking type obviously dominates the resulting transmission coefficient. Moreover, comparison to a widely accepted existing formula for irregular waves [12] was performed, initially introduced by [9] and incorporated in commonly used technical manuals [37,38] by implementing it on the experimental set-ups and Kt data of this study. The approach according to [25] is described by the equation:
where Hsi is the significant wave height of the incident wave and ξop a breaker parameter based on wave steepness given by:
where Lop is the deep water peak wave length and m is the leeward sloping of the structure. It is noted that Formula (17) is based on a number of experimental results including earlier published data.
Despite the fact that this formula is considered to present a high level of accuracy, it is limited for Kt values lower than 0.8. This means that it cannot be used for a range of cases with non-breaking waves thus not giving information for cases under which wave energy dissipation is low. A check for 88 of the total 115 irregular wave tests for which Kt values from Equation (17) were calculated lower than 0.8 gave an RMSE score close to 0.125, greater than the relevant value for the proposed method covering all scenarios.
The proposed method was compared to some Kt values from a previous experiment on a narrow-crested SPB in order to examine its reliability. Data on Kt measurements, not used in the formulae production of this study, on a narrow-crested SPB were identified [35], and according to [36], 11 irregular wave tests were assorted. The geometry of the structure was hs = 0.40 m, B = 0.30 m, dn50 = 0.035 m, m = 1:2, and F around 0.09 m, while wave characteristics ranged for Tp from 1.94 s to 2.6 s and Hs from 0.11 m to 0.254 m. The Hs/F values ranged from 1.20 to 2.70 and Lm/Lp from 0.25 to 0.80. The proposed method resulted in RMSE equal to 0.065 while Formula (17) gave an RMSE equal to 0.12.
Moreover, a comparison with experimental data for submerged rubble-mound breakwaters with core of small dn50 was executed in order to also investigate the extension of boundary line T1 (Equation (9)) for ξm values greater than 2.35, and it was assumed that the algebraic expression of curve T1 would not change. To this end, experimental data from the literature for narrow-crested submerged breakwaters with core were used [36]. The geometry of two given structures with armor layer of dn50 = 0.04 m and 0.06 m, respectively, was for both hs = 0.46 m, B = 0.34 m, m = 1:1:5, and F ranging from 0.04 to 0.09 m, Tp from 0.99 s to 1.91 s and Hs from 0.067 m to 0.14 m. In total, Kt data for 14 irregular wave tests was distinguished. By applying the hypothesis that the T1 boundary line between plunging and spilling breaking waves is suitable for every ξm value, the proposed method resulted in RMSE equal to 0.14 while Formula (17) had the same RMSE. For further investigation, another set of experimental data for a submerged breakwater with a core was used for comparison [39]. The relevant structure with armor layer of dn50 = 0.16 m had hs = 0.66 m, B = 0.3 m, m = 1:1:5 and F = 0.09 m, Tp from 1.33 to 2.0 s, and Hs from 0.12 to 0.187 m. In total, six irregular wave tests were used. The proposed method resulted in RMSE equal to 0.27 while Formula (17) gave an RMSE close to 0.38. Considerable differentiation on Kt values was observed for these wave tests defined as plunging breakers according to the proposed method. Based on the above experiments for submerged breakwaters with core, the plunging leg of the equation was re-examined, and for 11 predicted plunging breaking wave tests from [36,39], linear regression analysis of Kt gave the following equation:
When this expression was applied, RMSE slightly improved to 0.13 for the first set of experiments [36], while it dropped significantly to 0.07 for the other one [39]. An overall view of the final results is presented in Figure 8. It should be noted that wave height for the scenarios from literature was expressed in Hmo. Thus Hmo values were converted to Hs prior to comparison with the present model.
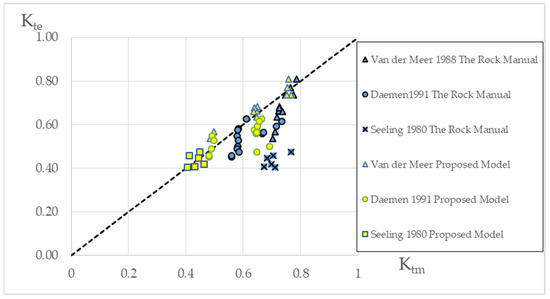
Figure 8.
Comparison for Kt calculated with the proposed model, Formula (19) (Ktm-axis), and Kt measured experimentally from literature (Kte).
Extension of the derived model to layered submerged rubble-mound breakwaters is foreseen as it is common practice to build layouts with a core, when a higher level of technical efficiency, i.e., lower Kt, is sought after. Examination of both the existing formula applied and the proposed method’s performance for such cases showed that further research would be welcome. However, based on the analysis on some previous experiments for submerged breakwaters with core, an approximation was derived for cases with plunging wave breaking prediction (Equation (19)), but requires further investigation. More experimental data on correlating Kt with breaker type are needed in order to better determine the subareas between spilling and plunging breaking waves. Specifically, lowering of the permeability due to a core is more probable to induce intense wave breakers meaning more energy loss, leading probably to modification of the corresponding breaker type areas in the ξm–R plane especially for plunging waves in comparison to homogenous counterparts. Thus, further evaluation of the proposed equation predicting Kt for plunging waves should be undertaken for low permeability (or multi-layered) breakwaters.
5. Conclusions
In this article, a simple but reliable method is presented to calculate the transmission coefficient for irregular waves propagating over submerged breakwaters. It is based mainly on process-based considerations, such as type of wave breaking and nominal interaction between wave and structure. The method has been developed based on numerous experimental measurements for such breakwaters of high permeability that display enhanced environmental merits, enriched by results from a suitable numerical model. Its applicability range covers primarily the said breakwater types, but a number of further checks showed that it can be extended to also include submerged breakwaters of reduced permeability. In general, the proposed model shows a good performance, superior to that from a well-established formula, reproduced also in EurOtop. Further research is suggested to confirm the previously mentioned extension of the method to cover virtually all types of practically applicable submerged breakwaters for coastal protection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.R. and C.M.; methodology, E.R. and C.M.; software, I.R.; validation, I.R.; formal analysis, E.R.; writing—original draft preparation, E.R.; writing—review and editing, E.R., I.R., and C.M.; visualization, E.R. and C.M.; supervision, C.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Experimental data framing this work are available in Appendix A.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the head and staff of the laboratory of Harbour Works, National Technical University of Athens, for providing the installations for the experiments framing this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
List of regular incident wave tests characteristics, Kt values, and breaker type where (P) is for plunging, (S) is for spilling, (O) is for “other”, and (x) is for non-breaking waves.
Table A1.
List of regular incident wave tests characteristics, Kt values, and breaker type where (P) is for plunging, (S) is for spilling, (O) is for “other”, and (x) is for non-breaking waves.
| # | T (s) | Hi (m) | Kt | Breaker Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPB1 F = 0.10 m | 1 | 1 | 0.078 | 0.85 | x |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.066 | 0.98 | x | |
| 3 | 1.3 | 0.08 | 0.76 | x | |
| 4 | 1.45 | 0.122 | 0.89 | S | |
| 5 | 1.85 | 0.145 | 0.79 | S | |
| SPB2a F = 0.05 m | 6 | 1 | 0.098 | 0.72 | S |
| 7 | 1.15 | 0.141 | 0.50 | P | |
| 8 | 1.25 | 0.051 | 0.45 | O | |
| 9 | 1.25 | 0.066 | 0.53 | O | |
| 10 | 1.25 | 0.096 | 0.57 | P | |
| 11 | 1.45 | 0.079 | 0.80 | S | |
| 12 | 1.6 | 0.083 | 0.61 | O | |
| 13 | 1.7 | 0.125 | 0.55 | P | |
| 14 | 1.85 | 0.107 | 0.47 | O | |
| 15 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.49 | O | |
| 16 | 2 | 0.052 | 0.50 | O | |
| 17 | 2 | 0.08 | 0.46 | O | |
| 18 | 2.2 | 0.152 | 0.36 | P | |
| SPB2a F = 0.10 m | 19 | 1 | 0.078 | 0.85 | x |
| 20 | 1 | 0.113 | 0.88 | x | |
| 21 | 1.15 | 0.066 | 0.98 | x | |
| 22 | 1.3 | 0.07 | 0.90 | x | |
| 23 | 1.3 | 0.08 | 0.76 | S | |
| 24 | 1.45 | 0.12 | 0.93 | x | |
| 25 | 1.45 | 0.13 | 0.80 | S | |
| 26 | 2 | 0.14 | 0.57 | S | |
| SPB2b F = 0.05 m | 27 | 1 | 0.093 | 0.60 | P |
| 28 | 1.25 | 0.087 | 0.41 | P | |
| 29 | 1.25 | 0.097 | 0.48 | S | |
| 30 | 1.5 | 0.081 | 0.68 | S | |
| 31 | 1.5 | 0.089 | 0.66 | S | |
| 32 | 1.5 | 0.095 | 0.63 | S | |
| 33 | 1.6 | 0.08 | 0.56 | S | |
| 34 | 1.6 | 0.082 | 0.59 | S | |
| 35 | 1.7 | 0.118 | 0.47 | P | |
| 36 | 1.85 | 0.11 | 0.39 | P | |
| 37 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.51 | O | |
| 38 | 2 | 0.075 | 0.49 | O | |
| 39 | 2.1 | 0.062 | 0.52 | O | |
| SPB2b F = 0.10 m | 40 | 1 | 0.085 | 0.87 | x |
| 41 | 1.25 | 0.173 | 0.49 | P | |
| 42 | 1.3 | 0.065 | 0.91 | x | |
| 43 | 1.5 | 0.094 | 0.77 | S | |
| 44 | 1.6 | 0.075 | 0.67 | O | |
| 45 | 1.6 | 0.141 | 0.63 | S | |
| 46 | 1.8 | 0.115 | 0.61 | S | |
| 47 | 2 | 0.093 | 0.45 | O | |
| 48 | 2.2 | 0.108 | 0.67 | S | |
| SPB3a F = 0.05 m | 49 | 1 | 0.07 | 0.79 | x |
| 50 | 1.15 | 0.105 | 0.58 | S | |
| 51 | 1.25 | 0.094 | 0.96 | x | |
| 52 | 1.3 | 0.082 | 0.88 | S | |
| 53 | 1.45 | 0.141 | 0.50 | P | |
| 54 | 1.6 | 0.112 | 0.54 | S | |
| 55 | 1.7 | 0.131 | 0.68 | S | |
| 56 | 1.85 | 0.074 | 0.73 | x | |
| 57 | 2 | 0.052 | 0.79 | x | |
| 58 | 2 | 0.084 | 0.86 | x | |
| 59 | 2.2 | 0.138 | 0.63 | O | |
| SPB3a F = 0.10 m | 60 | 1 | 0.073 | 0.99 | x |
| 61 | 1.25 | 0.122 | 0.89 | S | |
| 62 | 1.3 | 0.089 | 0.99 | x | |
| 63 | 1.45 | 0.159 | 0.63 | S | |
| 64 | 1.5 | 0.126 | 0.78 | x | |
| 65 | 1.5 | 0.15 | 0.69 | S | |
| 66 | 1.8 | 0.079 | 0.89 | x | |
| 67 | 1.8 | 0.105 | 0.90 | x | |
| 68 | 2 | 0.088 | 0.77 | x | |
| SPB3b F = 0.05 m | 69 | 1 | 0.066 | 0.83 | S |
| 70 | 1.15 | 0.053 | 0.87 | x | |
| 71 | 1.15 | 0.101 | 0.54 | P | |
| 72 | 1.3 | 0.079 | 0.86 | S | |
| 73 | 1.45 | 0.145 | 0.44 | P | |
| 74 | 1.5 | 0.115 | 0.59 | P | |
| 75 | 1.6 | 0.102 | 0.57 | S | |
| 76 | 1.7 | 0.123 | 0.74 | S | |
| 78 | 1.8 | 0.07 | 0.77 | x | |
| 79 | 2 | 0.075 | 0.81 | O | |
| 80 | 2.1 | 0.057 | 0.88 | x |

Table A2.
List of irregular incident wave tests characteristics and Kt values.
Table A2.
List of irregular incident wave tests characteristics and Kt values.
| # | T (s) | Hs (m) | Kt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPB1 F = 0.10 m | 1 | 1 | 0.066 | 0.82 |
| 2 | 1.15 | 0.079 | 0.8 | |
| 3 | 1.3 | 0.086 | 0.8 | |
| 4 | 1.3 | 0.102 | 0.75 | |
| 5 | 1.45 | 0.087 | 0.82 | |
| 6 | 1.5 | 0.095 | 0.82 | |
| 7 | 1.6 | 0.102 | 0.81 | |
| 8 | 1.85 | 0.102 | 0.78 | |
| 9 | 2 | 0.107 | 0.77 | |
| SPB2a F = 0.05 m | 10 | 1 | 0.064 | 0.69 |
| 11 | 1.15 | 0.063 | 0.70 | |
| 12 | 1.15 | 0.074 | 0.66 | |
| 13 | 1.25 | 0.04 | 0.73 | |
| 14 | 1.25 | 0.052 | 0.69 | |
| 15 | 1.25 | 0.07 | 0.67 | |
| 16 | 1.25 | 0.083 | 0.63 | |
| 17 | 1.3 | 0.049 | 0.71 | |
| 18 | 1.3 | 0.087 | 0.62 | |
| 19 | 1.45 | 0.062 | 0.71 | |
| 20 | 1.45 | 0.095 | 0.61 | |
| 21 | 1.6 | 0.073 | 0.66 | |
| 22 | 1.6 | 0.113 | 0.56 | |
| 23 | 1.7 | 0.092 | 0.54 | |
| 24 | 1.85 | 0.087 | 0.55 | |
| 25 | 2 | 0.046 | 0.61 | |
| 26 | 2 | 0.075 | 0.55 | |
| 27 | 2.2 | 0.073 | 0.55 | |
| SPB2a F = 0.10 m | 28 | 1 | 0.065 | 0.83 |
| 29 | 1.15 | 0.076 | 0.82 | |
| 30 | 1.3 | 0.093 | 0.75 | |
| 31 | 1.3 | 0.11 | 0.71 | |
| 32 | 1.3 | 0.124 | 0.67 | |
| 33 | 1.45 | 0.092 | 0.77 | |
| 34 | 1.45 | 0.108 | 0.73 | |
| 35 | 1.6 | 0.12 | 0.68 | |
| 36 | 1.7 | 0.116 | 0.66 | |
| 37 | 1.7 | 0.129 | 0.64 | |
| 38 | 1.85 | 0.107 | 0.64 | |
| 39 | 2 | 0.109 | 0.65 | |
| SPB2b F = 0.05 m | 40 | 1 | 0.063 | 0.63 |
| 41 | 1.15 | 0.075 | 0.60 | |
| 42 | 1.25 | 0.037 | 0.70 | |
| 43 | 1.25 | 0.061 | 0.64 | |
| 44 | 1.45 | 0.089 | 0.57 | |
| 45 | 1.6 | 0.109 | 0.51 | |
| 46 | 1.7 | 0.113 | 0.50 | |
| 47 | 1.85 | 0.099 | 0.49 | |
| 48 | 2 | 0.039 | 0.62 | |
| 49 | 2 | 0.07 | 0.53 | |
| 50 | 2 | 0.11 | 0.48 | |
| 51 | 2.2 | 0.115 | 0.48 | |
| SPB2b F = 0.10 m | 52 | 1 | 0.063 | 0.79 |
| 53 | 1.15 | 0.076 | 0.74 | |
| 54 | 1.3 | 0.107 | 0.65 | |
| 55 | 1.45 | 0.09 | 0.73 | |
| 56 | 1.6 | 0.117 | 0.64 | |
| 57 | 1.7 | 0.124 | 0.60 | |
| 58 | 1.85 | 0.106 | 0.60 | |
| 59 | 2 | 0.109 | 0.60 | |
| 60 | 2 | 0.122 | 0.60 | |
| SPB3a F = 0.05 m | 61 | 1 | 0.049 | 0.80 |
| 62 | 1.15 | 0.06 | 0.78 | |
| 63 | 1.15 | 0.077 | 0.70 | |
| 64 | 1.25 | 0.043 | 0.91 | |
| 65 | 1.25 | 0.068 | 0.78 | |
| 66 | 1.3 | 0.099 | 0.65 | |
| 67 | 1.45 | 0.073 | 0.73 | |
| 68 | 1.45 | 0.099 | 0.62 | |
| 69 | 1.6 | 0.115 | 0.57 | |
| 70 | 1.7 | 0.088 | 0.67 | |
| 71 | 1.7 | 0.115 | 0.62 | |
| 72 | 1.85 | 0.079 | 0.71 | |
| 73 | 1.85 | 0.097 | 0.68 | |
| 74 | 2 | 0.044 | 0.80 | |
| 75 | 2 | 0.07 | 0.73 | |
| 76 | 2 | 0.103 | 0.68 | |
| 77 | 2.2 | 0.106 | 0.70 | |
| SPB3a F = 0.10 m | 78 | 1 | 0.053 | 0.85 |
| 79 | 1.15 | 0.06 | 0.88 | |
| 80 | 1.3 | 0.085 | 0.82 | |
| 81 | 1.3 | 0.101 | 0.74 | |
| 82 | 1.3 | 0.115 | 0.72 | |
| 83 | 1.45 | 0.092 | 0.77 | |
| 84 | 1.45 | 0.105 | 0.70 | |
| 85 | 1.6 | 0.126 | 0.67 | |
| 86 | 1.7 | 0.122 | 0.74 | |
| 87 | 1.85 | 0.104 | 0.74 | |
| 88 | 2 | 0.111 | 0.74 | |
| 89 | 2.2 | 0.109 | 0.80 | |
| SPB3b F = 0.05 m | 90 | 1 | 0.042 | 0.83 |
| 91 | 1.15 | 0.056 | 0.86 | |
| 92 | 1.25 | 0.031 | 1.00 | |
| 93 | 1.25 | 0.06 | 0.85 | |
| 94 | 1.3 | 0.068 | 0.78 | |
| 95 | 1.3 | 0.099 | 0.64 | |
| 96 | 1.45 | 0.072 | 0.74 | |
| 97 | 1.45 | 0.097 | 0.63 | |
| 98 | 1.6 | 0.115 | 0.58 | |
| 99 | 1.7 | 0.086 | 0.71 | |
| 100 | 1.7 | 0.113 | 0.65 | |
| 101 | 1.85 | 0.094 | 0.71 | |
| 102 | 2 | 0.043 | 0.84 | |
| 103 | 2 | 0.07 | 0.77 | |
| 104 | 2 | 0.109 | 0.66 | |
| 105 | 2.2 | 0.107 | 0.71 | |
| SPB3b F = 0.10 m | 106 | 1 | 0.043 | 0.95 |
| 107 | 1.15 | 0.06 | 0.92 | |
| 108 | 1.3 | 0.102 | 0.76 | |
| 109 | 1.45 | 0.093 | 0.78 | |
| 110 | 1.6 | 0.121 | 0.72 | |
| 111 | 1.7 | 0.12 | 0.77 | |
| 112 | 1.7 | 0.132 | 0.76 | |
| 113 | 2 | 0.11 | 0.78 | |
| 114 | 2.2 | 0.12 | 0.78 |

Table A3.
List of regular incident wave tests characteristics and Kt values, simulated by the mCM14 Boussinesq-type numerical model [28].
Table A3.
List of regular incident wave tests characteristics and Kt values, simulated by the mCM14 Boussinesq-type numerical model [28].
| # | T (s) | Hi (m) | Kt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPB2a F = 0.05 m | 10 | 1 | 0.067 | 0.97 |
| 11 | 1 | 0.099 | 0.76 | |
| 12 | 1.25 | 0.063 | 0.67 | |
| 13 | 1.25 | 0.082 | 0.67 | |
| 14 | 1.25 | 0.119 | 0.59 | |
| SPB2a F = 0.10 m | 28 | 1 | 0.063 | 0.95 |
| 29 | 1 | 0.082 | 0.96 | |
| 30 | 1.25 | 0.059 | 0.88 | |
| 31 | 1.25 | 0.082 | 0.79 | |
| 32 | 1.25 | 0.117 | 0.99 | |
| SPB2b F = 0.05 m | 40 | 1 | 0.058 | 0.93 |
| 41 | 1 | 0.102 | 0.73 | |
| 42 | 1.25 | 0.061 | 0.56 | |
| 43 | 1.25 | 0.08 | 0.54 | |
| 44 | 1.25 | 0.122 | 0.52 | |
| SPB2b F = 0.10 m | 52 | 1 | 0.061 | 0.92 |
| 53 | 1 | 0.08 | 0.94 | |
| 54 | 1.25 | 0.063 | 0.62 | |
| 55 | 1.25 | 0.08 | 0.66 | |
| 56 | 1.25 | 0.123 | 0.73 | |
| SPB3a F = 0.05 m | 61 | 1 | 0.062 | 0.98 |
| 62 | 1 | 0.106 | 0.81 | |
| 63 | 1.25 | 0.065 | 0.69 | |
| 64 | 1.25 | 0.084 | 0.71 | |
| 65 | 1.25 | 0.119 | 0.78 | |
| SPB3a F = 0.10 m | 78 | 1 | 0.062 | 0.97 |
| 79 | 1 | 0.102 | 0.98 | |
| 80 | 1.25 | 0.058 | 0.88 | |
| 81 | 1.25 | 0.079 | 0.89 | |
| 82 | 1.25 | 0.124 | 0.97 | |
| SPB3b F = 0.05 m | 90 | 1 | 0.061 | 0.85 |
| 91 | 1 | 0.102 | 0.70 | |
| 92 | 1.25 | 0.062 | 0.58 | |
| 93 | 1.25 | 0.084 | 0.62 | |
| 94 | 1.25 | 0.123 | 0.53 | |
| SPB3b F = 0.10 m | 106 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.92 |
| 107 | 1 | 0.104 | 0.96 | |
| 108 | 1.25 | 0.064 | 0.70 | |
| 109 | 1.25 | 0.084 | 0.71 | |
| 110 | 1.25 | 0.122 | 0.86 |
References
- Kontaxi, C.; Memos, C.D. Submerged Breakwaters as Artificial Habitats. In Proceedings of the 31st IAHR Congress, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 11–16 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, V.C.; Memos, C.D. Wave Transmission over Submerged Breakwaters: Performance of Formulae and Models. In Proceedings of the 16th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Lisbon, Portugal, 1–6 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brancasi, A.; Leone, E.; Francone, A.; Scaravaglione, G.; Tomasicchio, G.R. On Formulae for Wave Transmission at Submerged and Low-Crested Breakwaters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, N.; Vicinanza, D.; Contestabile, P. Determining Wave Transmission over Rubble-Mound Breakwaters: Assessment of Existing Formulae through Benchmark Testing. Water 2023, 15, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, H.; Khan, M.B.M. Numerical Modeling for Wave Attenuation in Double Trapezoidal Porous Structures. J. Ocean Eng. 2019, 184, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.M.; Behera, H. Analysis of Wave Action through multiple Submerged Porous Structures. J. Offshore Mech. Arctic Eng. 2019, 142, 011101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, J.W. Data on Wave Transmission Due to Overtopping; Delft Hydraulics: Delft, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meer, J.W.; Daemen, I.F. Stability and wave transmission at low-crested rubble-mound structures. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean. Eng. 1994, 120, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Angremond, K.; van der Meer, J.W.; de Jong, R.J. Wave Transmission at Low-Crested Structures. In Coastal Engineering 1996; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 2418–2427. [Google Scholar]
- Seabrook, S.R.; Hall, K.R. Wave Transmission at Submerged Rubblemound Breakwaters. In Coastal Engineering 1998; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 1999; pp. 2000–2013. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, M.; Vicinanza, D.; Buccino, M. Large-Scale Experiments On The Behaviour Of Low Crested And Submerged Breakwaters In Presence Of Broken Waves. In Coastal Engineering 2002; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2003; pp. 1900–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Briganti, R.; van der Meer, J.; Buccino, M.; Calabrese, M. Wave Transmission Behind Low-Crested Structures. In Coastal Structures 2003; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2004; pp. 580–592. [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer, J.W.; Briganti, R.; Zanuttigh, B.; Wang, B. Wave Transmission and Reflection at Low-Crested Structures: Design Formulae, Oblique Wave Attack and Spectral Change. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccino, M.; Calabrese, M. Conceptual Approach for Prediction of Wave Transmission at Low-Crested Breakwaters. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean. Eng. 2007, 3, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, Y.; Ahrens, J.P. New Formulation of Wave Transmission Over And Through Low-Crested Structures. In Coastal Engineering 2008; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2009; pp. 3530–3541. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasicchio, G.R.; D’Alessandro, F. Wave Energy Transmission through and over Low Crested Breakwaters. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.X.; Li, X. Design Formulas of Transmission Coefficients for Permeable Breakwaters. Water Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 457–467. [Google Scholar]
- Sindhu, S.; Shirlal, K.G.; Manu. Prediction of Wave Transmission Characteristics at Submerged Reef Breakwater. Procedia Eng. 2015, 116, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdistani, S.M.; Tomasicchio, G.R.; D′Alessandro, F.; Francone, A. Formula for Wave Transmission at Submerged Homogeneous Porous Breakwaters. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 266, 113053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metallinos, S.A.; Klonaris, T.G.; Memos, C.; Dimas, A.A. Hydrodynamic Conditions in a Submerged Porous Breakwater. J. Ocean Eng. 2019, 172, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicinanza, D.; Cáceres, I.; Buccino, M.; Gironella, X.; Calabrese, M. Wave Disturbance behind Low-Crested Structures: Diffraction and Overtopping Effects. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.A.; Sørensen, O.R. A New Form of the Boussinesq Equations with Improved Linear Dispersion Characteristics 2: A Slowly Varying Bathymetry. Coast. Eng. 1992, 18, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgeris, I.; Karambas, V.T.; Prinos, P. Boussinesq Modeling of Wave Interaction with Porous Submerged Breakwaters. In Coastal Engineering 2004: (In 4 Volumes); World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2004; pp. 604–616. [Google Scholar]
- Metallinos, S.A.; Memos, C. Wave-induced Kinematics inside Submerged Porous Structures. J. Hydraul. Res. 2012, 50, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metallinos, S.A.; Emmanouilidou, A.M.; Memos, C. Wave-induced Pore Pressures in Submerged Rubble-mound Breakwaters Simulated by a Compound Boussinesq Model. J. Hydraul. Res. 2014, 52, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.C.; Hu, K.C.; Hwung, H.H. Extended Boussinesq Equations for Water-Wave Propagation in Porous Media. J. Eng. Mech. 2010, 136, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chondros, M.K.; Memos, C.D. A 2DH non Linear Boussinesq-type Wave Model of Improved Dispersion, Shoaling and Wave Generation Characteristics. Coast. Eng. 2014, 91, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metallinos, A.; Repousis, E.; Memos, C. Wave Propagation over a Submerged Porous Breakwater with steep slopes. Ocean Eng. 2016, 111, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gent, M.R.A. The Modelling of Wave Action on and in Coastal Structures. Coast. Eng. 1994, 22, 311–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, R.; Wen, H.; Dong, P.; Wang, Y. Numerical Simulation of Wave Interaction with Porous Structures using an Improved Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamic Method. Coat. Eng. 2014, 88, 88–100. [Google Scholar]
- Magdalena, I.; Rif’atin, H.Q.; Kusuma, M.; Reeve, D.E. A non-Hydrostatic Model for Wave Evolution on a Submerged Trapezoidal Breakwater. Results Appl. Math. 2023, 18, 100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memos, C.; Malliouri, D.; Kazakidou, E.; Tsoukala, V. Impact of Wavelength on the Stability of Rubble Mound Breakwaters. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science, Santander, Spain, 22–26 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, M.; Buccino, M.; Pasanisi, F. Wave Breaking Macrofeatures on a Submerged Rubble Mound Breakwater. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2008, 1, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.A.; Schäffer, H.A. Higher-order Boussinesq-type Equations for Surface Gravity Waves: Derivation and Analysis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1998, 356, 3123–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, J.W. Rock Slopes and Gravel Beaches under Wave Attack. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 1988. no. 396. [Google Scholar]
- Daemen, I.F.R. Wave Transmission at Low Crested Structures; Delft Hydraulics Report H 462; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- CIRIA; CUR; CETMEF. The Rock Manual. The Use of Rock in Hydraulic Engineering; C683; CIRIA: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- EurOtop. Manual on Wave Overtopping of Sea Defences and Related Structures. An Overtopping Manual Largely Based on European Research, but for Worldwide Application. 2018. Available online: www.overtopping-manual.com (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Seeling, W.N. Two-Dimensional Tests of Wave Transmission and Reflection Characteristics of Laboratory Breakwaters; Technical Report No. 80-1; US army, Corps of Engineers, CERC: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).