Implementation of International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea Using Coloured Petri Nets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- a.
- Provides a framework that allows for a team of several mariners, without much programming knowledge and with only small explantations in the ML (Meta Language) programming language [9], to define, during the system development, the rule selection for a new scenario (for example, between a cargo ship and a seaplane).
- b.
- Vessels can be classified according to their propulsion (engine, sails), their current activity (fishing, cable laying…), their limited manoeuvrability, their priorities, dangerous cargo, etc.
- c.
- Any number of exception scenarios (vessels with higher priority, importance, etc.) can be defined in this way.
- d.
- The new extensions are always made graphically in colored Petri net.
- e.
- The framework thus ensures that the rule selection for a defined scenario is handled by the system exactly as desired (without implementation/programming errors).
- f.
- A probability of destruction scenarios, which were correctly defined and fully tested earlier, is minimized.
- g.
- The implementation of the rule selection criteria for each defined scenario can be easily checked by several mutually independent persons.
- h.
- System response for each scenario can be easily verified by inserting externally generated data (vessels positions, courses, speeds, vessels types, wind direction).
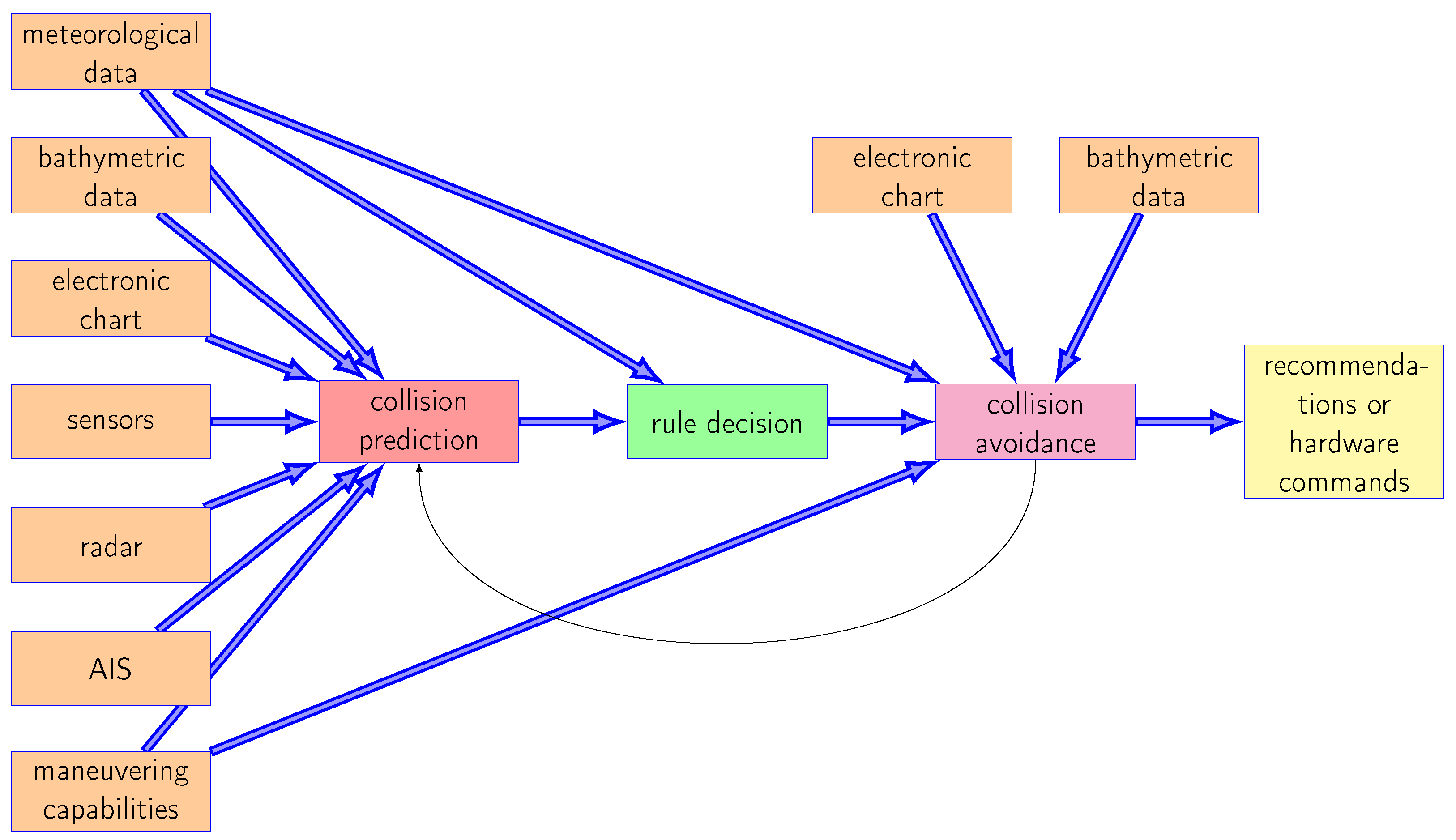
2. System Description
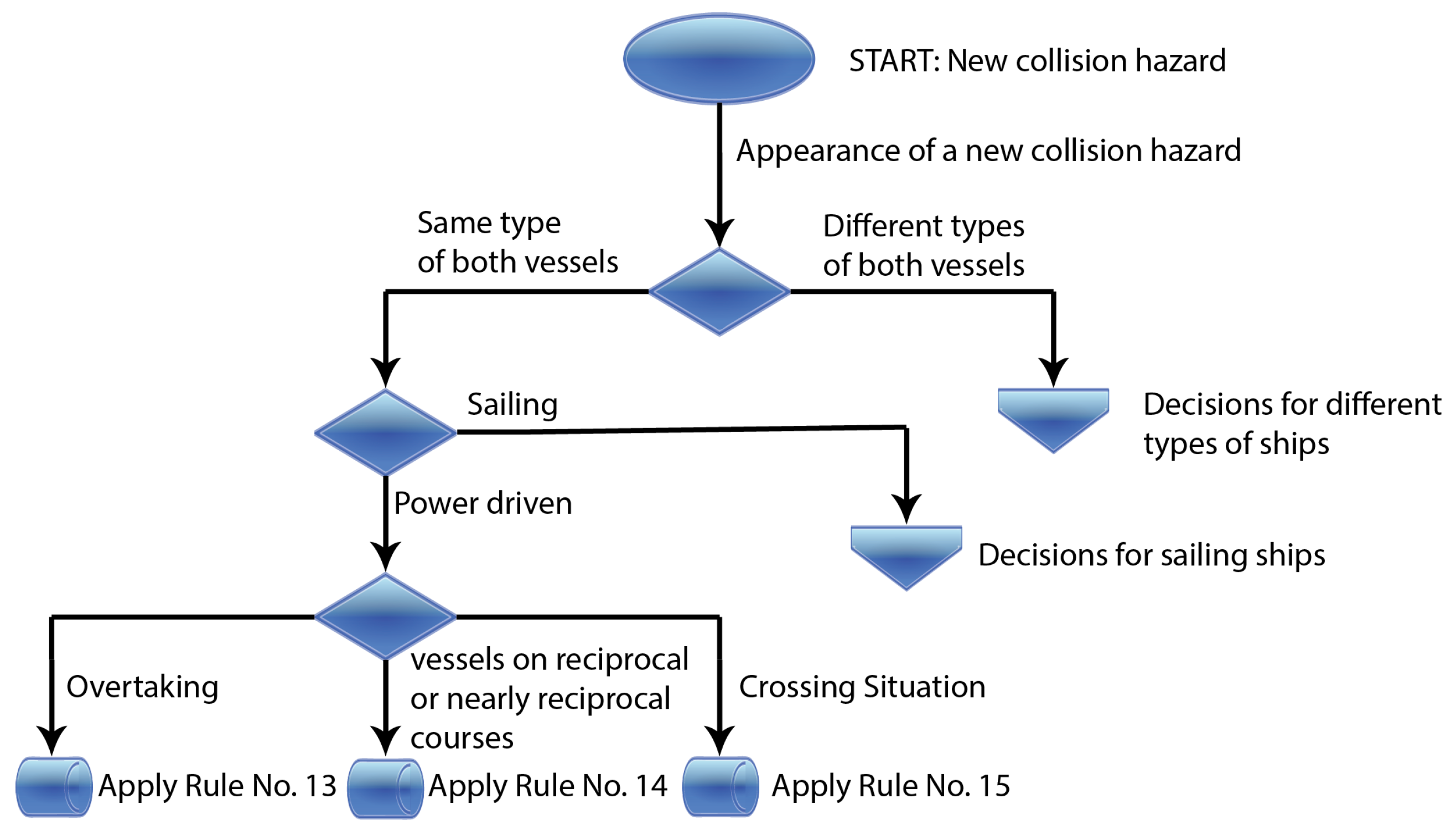
3. Rule Decision Block
4. Coloured-Petri-Net-Based Rule Decision Block
- denotes a set of places.
- denotes a set of transitions.
- denotes a set of arcs.
- denotes a set of colour sets.
- denotes a colour function. The colour function describes the mapping between places in and colours in .
- denotes a node function. The node function describes the mapping between arcs in and ( × ) ∪ ( × ).
- denotes an arc expression function. The node function describes the mapping between all arcs in and their associated expressions.
- denotes a transition guard function. The node function describes the mapping between all transitions in and the associated guard functions.
- denotes an initialization function. The initialization function describes the initialization of all places in .
- Name
- A colour set is required. All tokens entering and leaving this place are from this colour set.
- The initial marking defines the number and values of tokens that were initially in that location.
- Transition name
- Guard
- Time
- Code segment
- Priority
5. Use of Coloured Petri Nets for Nautical Problems
5.1. Defined Colour Sets
- Power_driven
- Sailing
- Engaged_in_fishing
- Seaplane
- Not_under_command
- Engaged_in_laying
- Engaged_in_dredging
- Engaged_in_replenishment
- Engaged_in_launching_or_recovery_of_airctaft
- Engaged_in_mine_clearance
- Engaged_in_towing
- Constrained_by_draught
- Otherwise_restricted
- Unrestricted.
- Narrow_channel.
- Traffic_separation_schema.
5.2. Defined Colour Set Products
6. Connection between Real World and CP Network
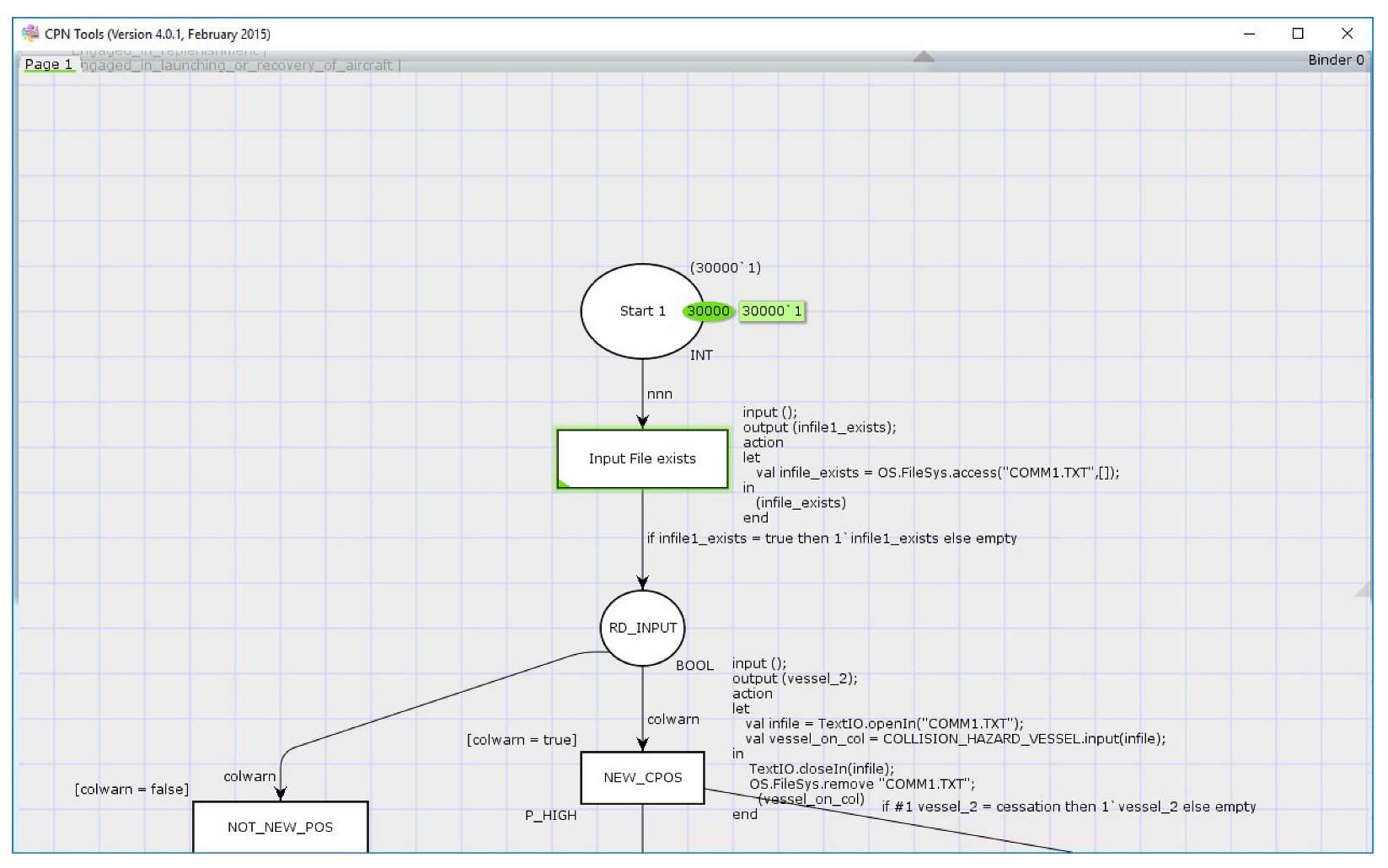
6.1. Input File comm1.txt with Information about the Possible Collision
6.2. Input File with Information about 1st Vessel Involved
6.3. Input File with Information about Wind
6.4. Output File with Information about Corrective Action
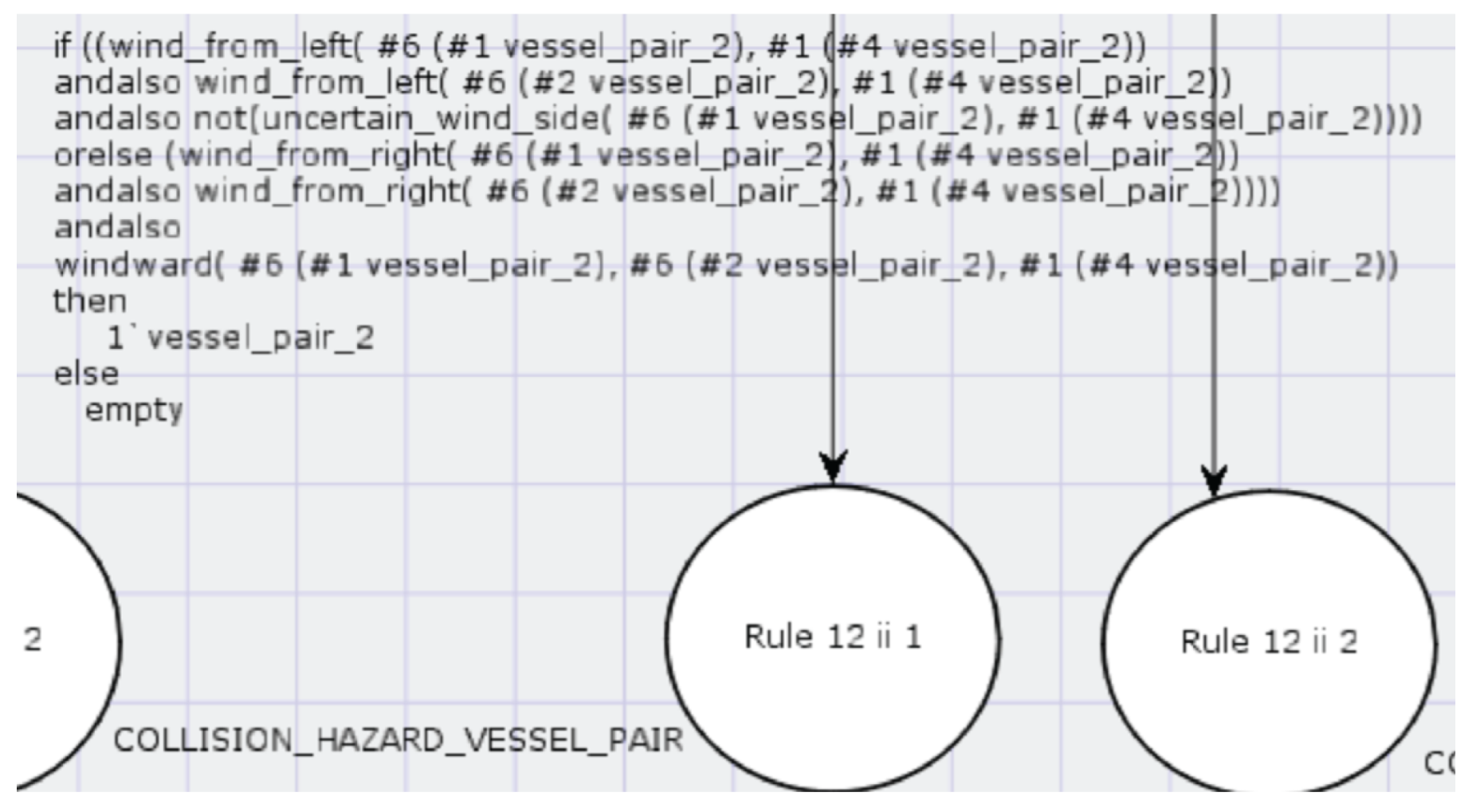
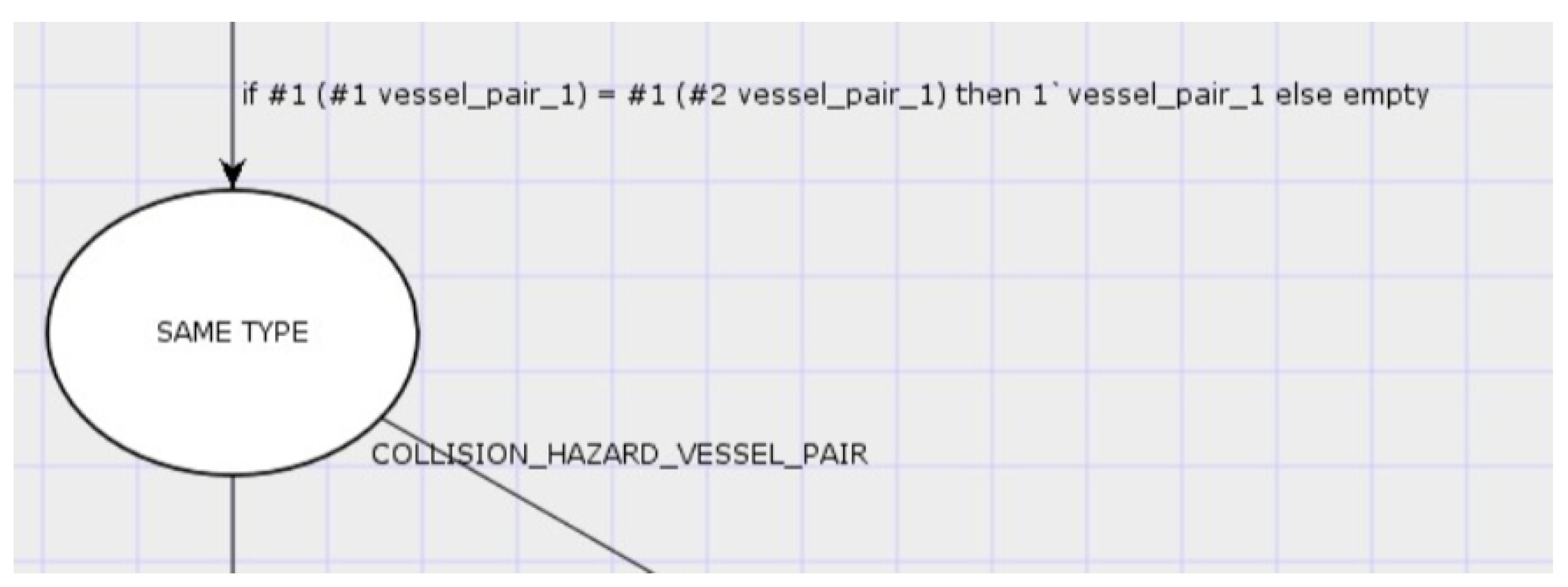
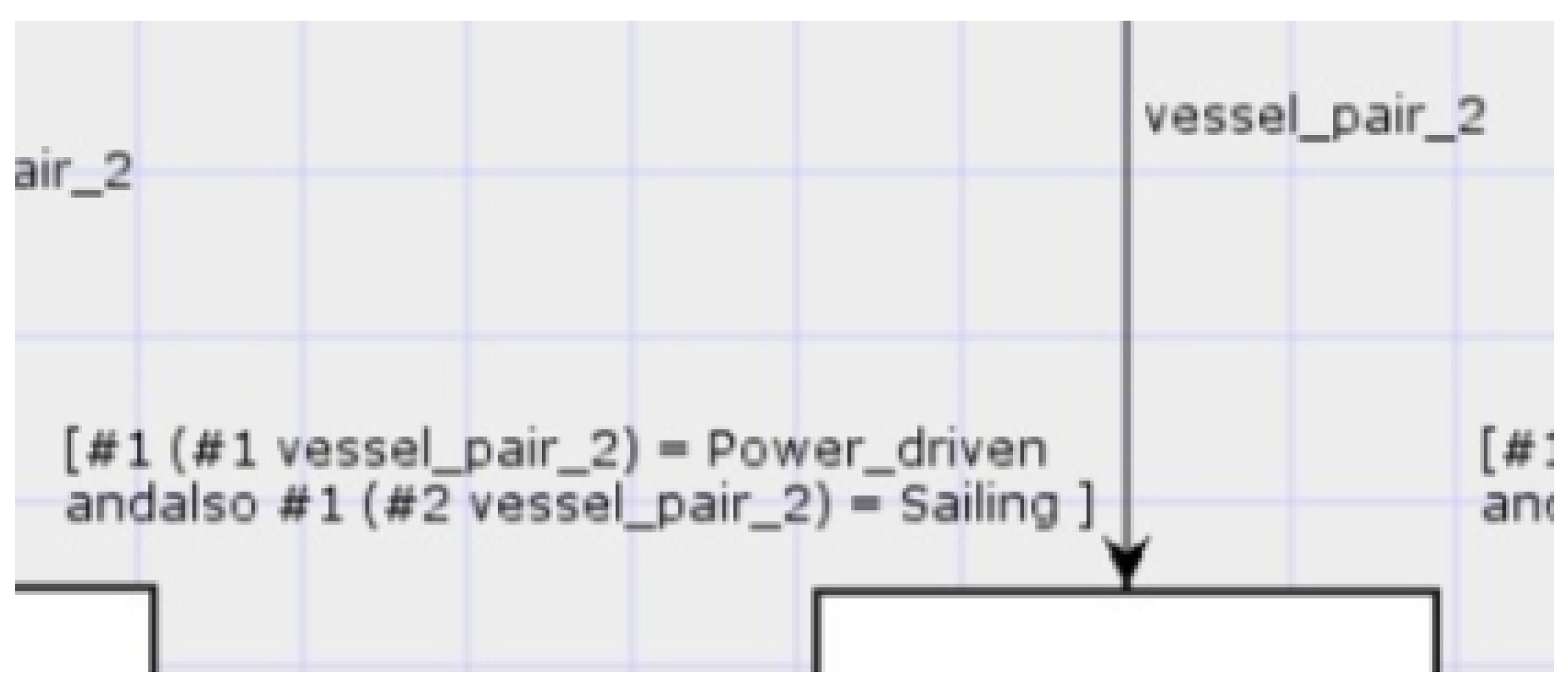
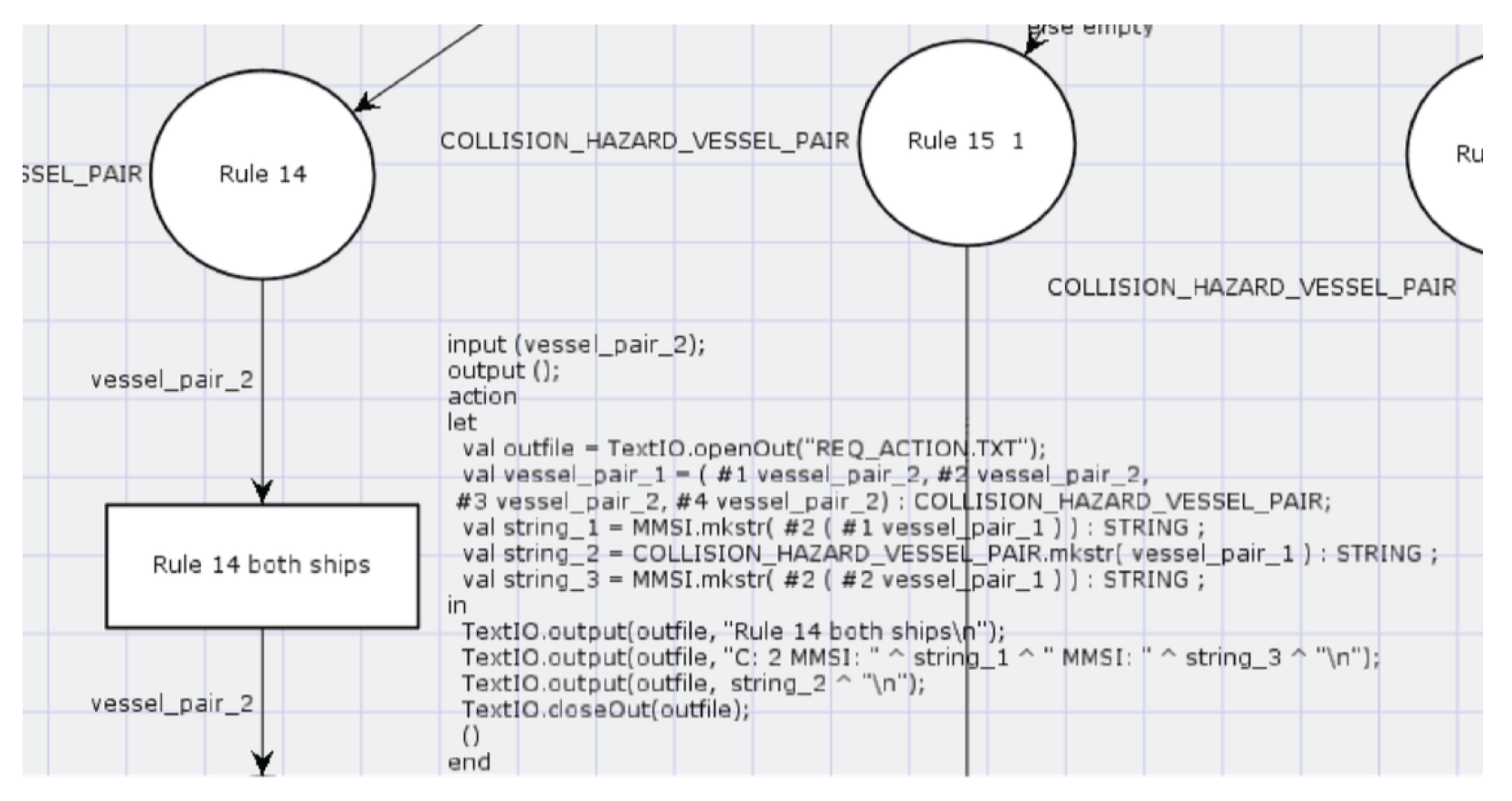
7. Use of Arcs and Transitions
8. Use of User-Defined ML Functions in Arc Inscriptions
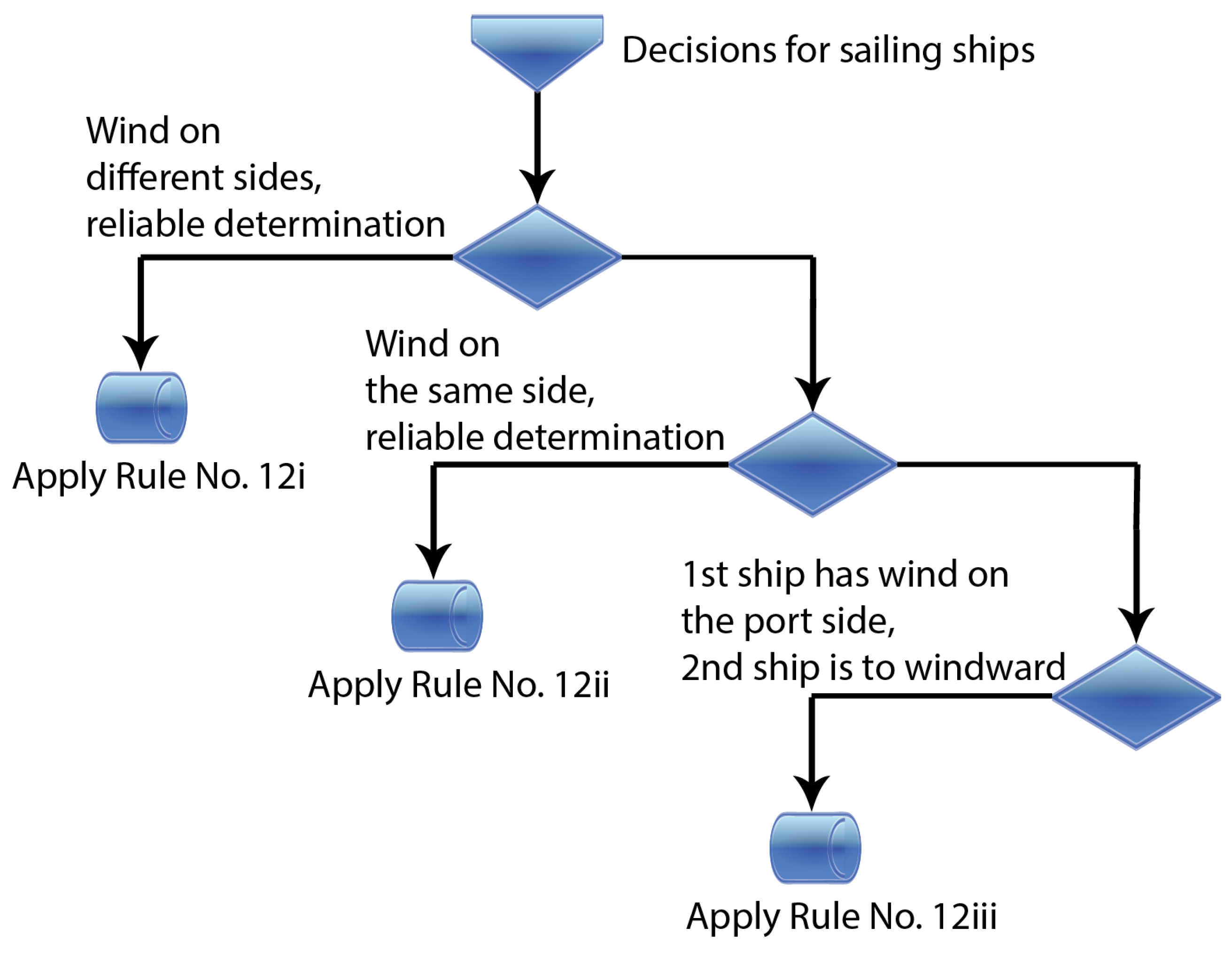
- #1 (#4 vessel_pair_2), according to the definitions of the colour sets in Section 5.2. The used function wind_from_left returns true if the wind comes from the left side of the ship. The direction of the first ship is given by
- #6 (#1 vessel_pair_2), according to the definition of the colour sets in Section 5.2. The direction of the second ship is given by
- #6 (#2 vessel_pair_2). The token vessel_pair_2 colour value comes from the colour set COLLISION _HAZARD _VESSEL _PAIR.
| Listing 1. CPN Tools, Definition of the fuction wind_from_left. |
| fun wind_from_left(v1: REAL, v2: REAL) = |
| let |
| val from_left = false ; |
| in |
| if v1 < 180.0 |
| then |
| if v2 > v1 andalso v2 < (v1 + 180.0) |
| then |
| true |
| else |
| false |
| else |
| if v2 > v1 |
| then |
| true |
| else |
| if v2 < (v1 - 180.0) |
| then |
| true |
| else |
| false |
| end; |
| Listing 2. CPN Tools, Definition of the fuction wind_from_left. |
| fun windward(v1: REAL, v2: REAL, v3: REAL) = |
| let |
| val first_ship_winward = false ; |
| in |
| if abs(v1 - v3) < 180.0 |
| then |
| if abs(v2 - v3) < 180.0 |
| then |
| if abs(v1 - v3) < abs(v2 - v3) |
| then |
| true |
| else |
| false |
| else |
| if abs(v1 - v3) < abs(360.0 - abs(v2 - v3)) |
| then |
| true |
| else |
| false |
| else |
| if abs(v2 - v3) < 180.0 |
| then |
| if abs(360.0 - abs(v1 - v3)) < abs(v2 - v3) |
| then |
| true |
| else |
| false |
| else |
| if abs(360.0 - abs(v1 - v3)) < abs(360.0 - abs(v2 - v3)) |
| then |
| true |
| else |
| false |
| end; |
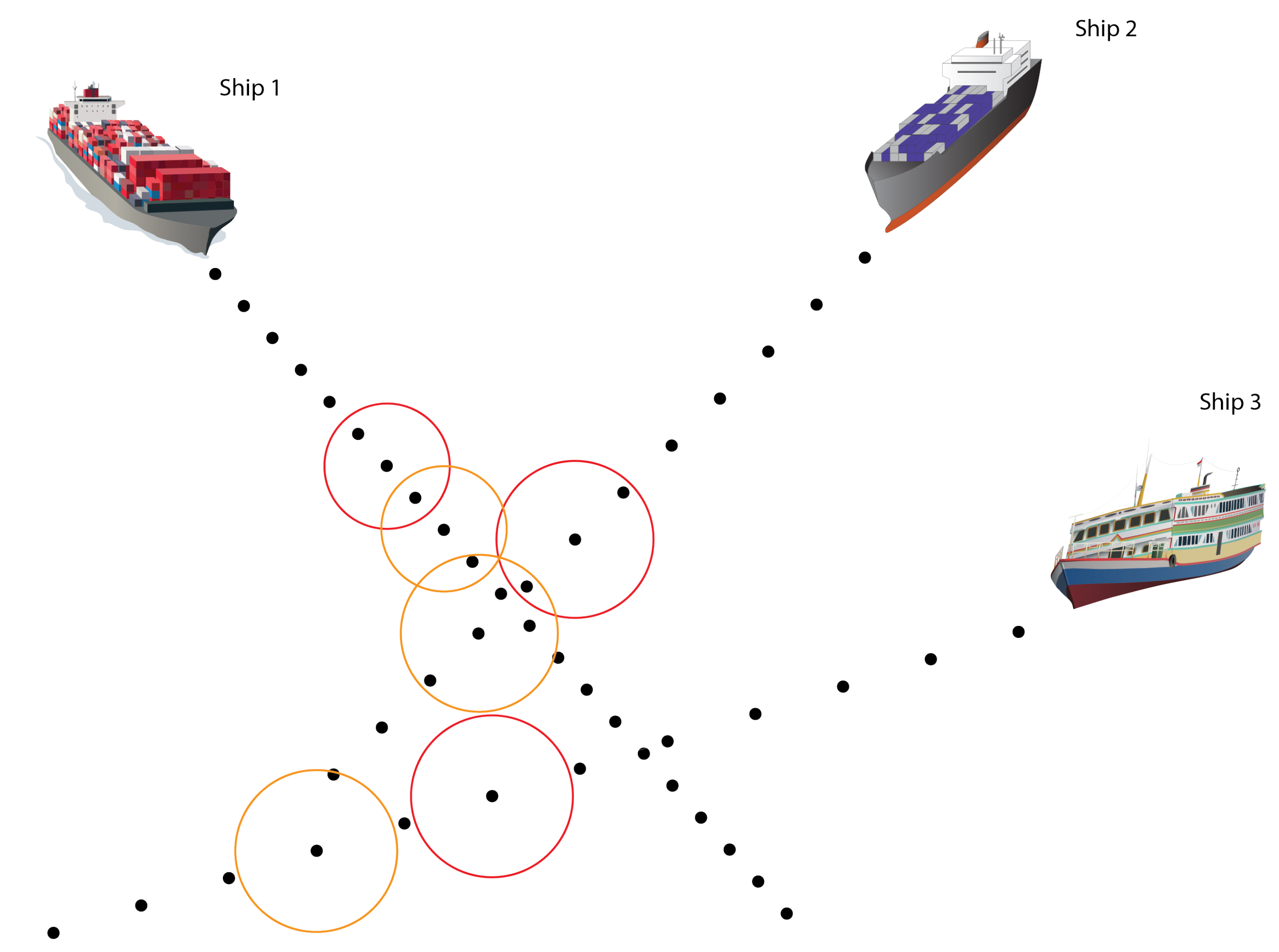
9. Test Method
10. Results
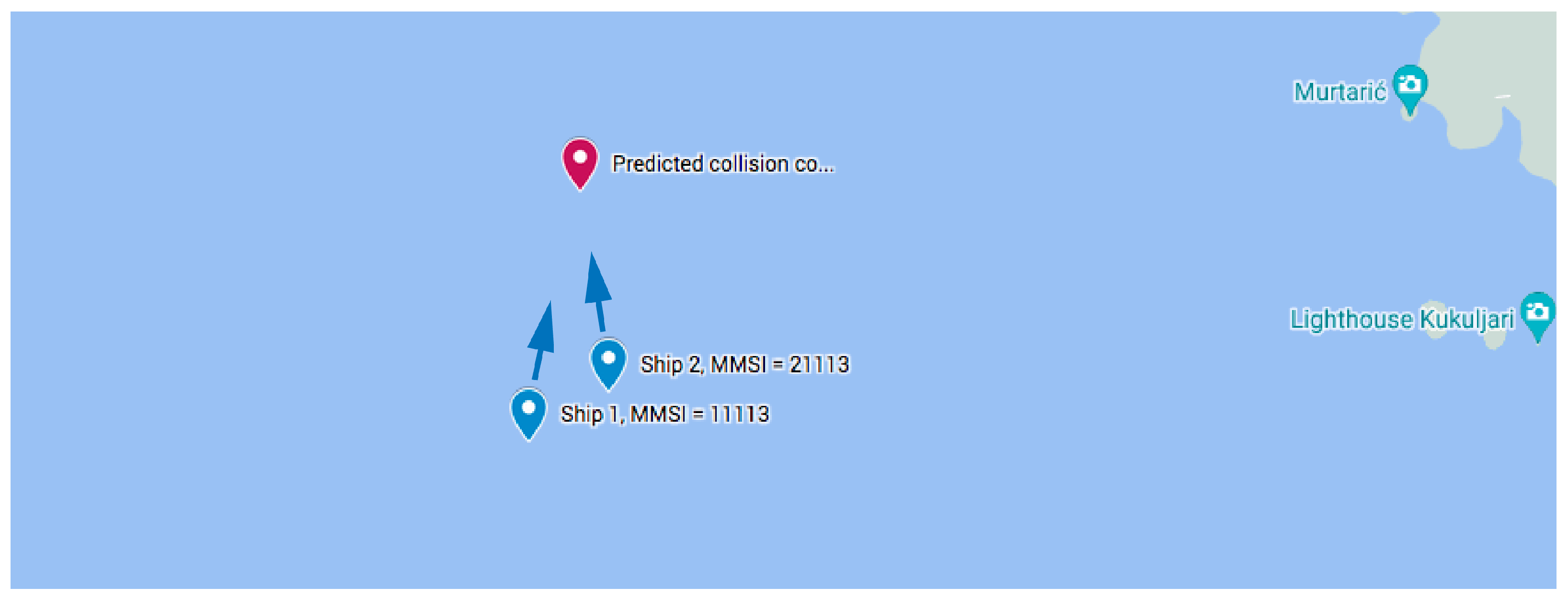
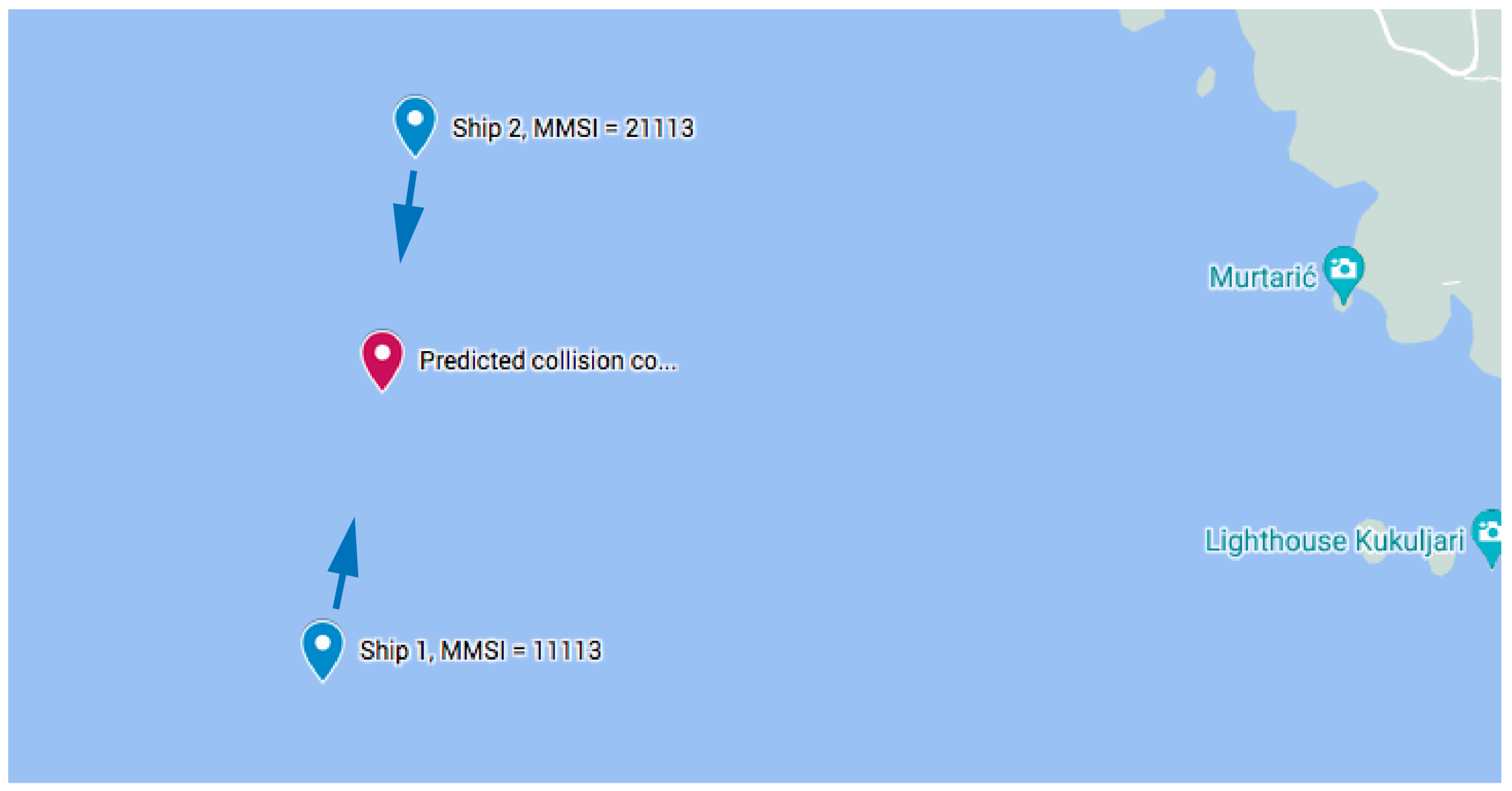
10.1. Two Power-Driven Ships
- Input Informations from collision prediction block to the presented subsystem:
- Output Information from the presented subsystem:
- Information input to the presented subsystem:
- Information output from the presented subsystem:
- Information input to the presented subsystem:
- Information output from the presented subsystem:
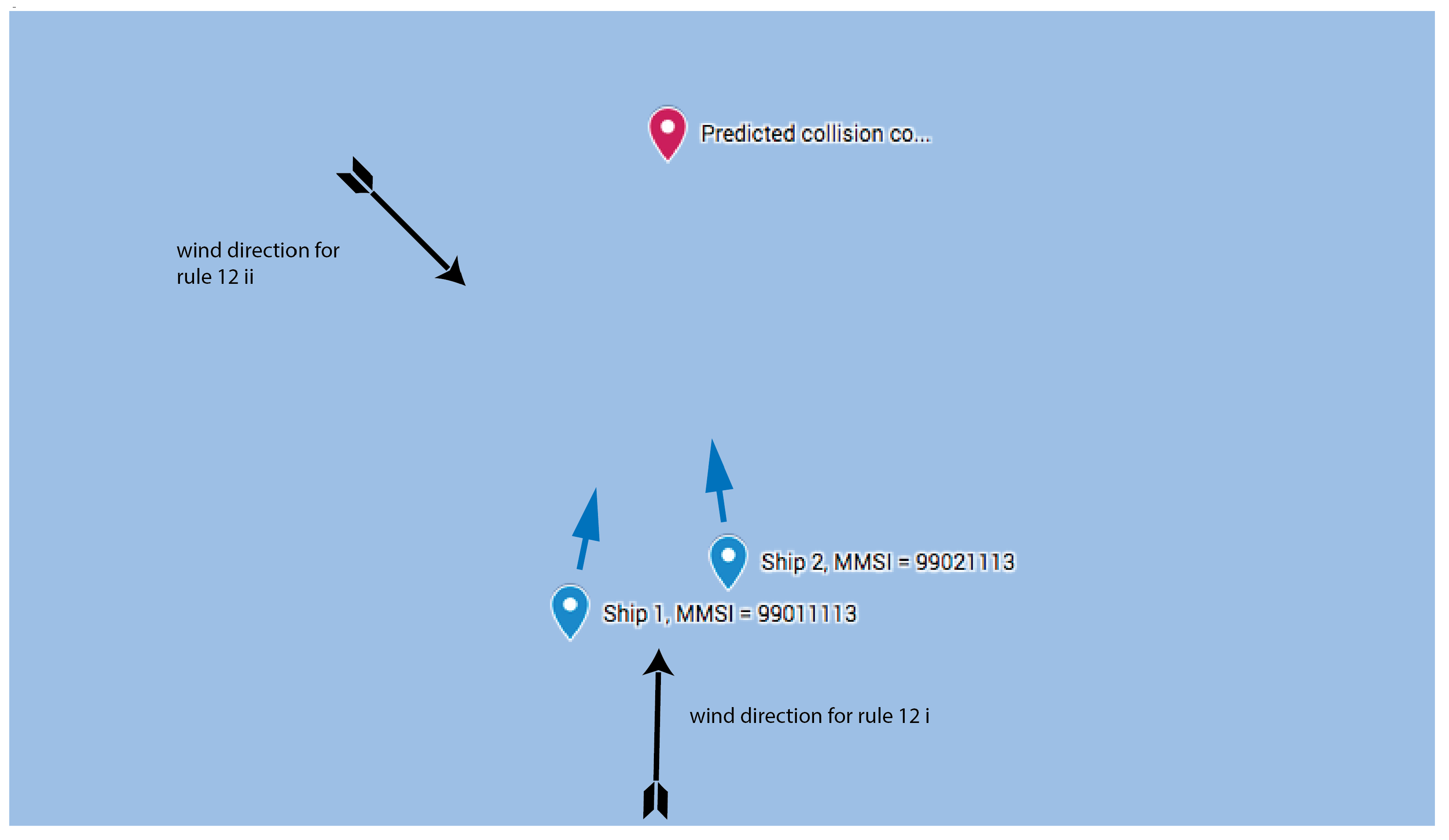
10.2. Two Sailing Ships
- Information input to the presented subsystem:
- Information output from the presented subsystem:
- Information input to the presented subsystem:
- Information output from the presented subsystem:
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, T.; Liu, C.; Xu, S.; Hu, Q.; Li, C. COLREGS-Complied Automatic Collision Avoidance for the Encounter Situations of Multiple Vessels. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Maritime Organization (IMO). COLREG—Preventing Collisions at Sea. Available online: https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Safety/Pages/Preventing-Collisions.aspx (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Heiberg, A.; Larsen, T.N.; Meyer, E.; Rasheed, A.; San, O.; Varagnolo, D. Risk-based implementation of COLREGs for autonomous surface vehicles using deep reinforcement learning. Neural Netw. 2022, 152, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, P.N.; Papageorgiou, D.; Blanke, M.; Galeazzi, R.; Lützen, M.; Mogensen, J.; Bennedsen, M.; Hansed, D. COLREGs-based Situation Awareness for Marine Vessels—A Discrete Event Systems Approach. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 14501–14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Hydrographic Oganization. S-100 Specification Numbers. 2020. Available online: http://s100.iho.int/S100/home/s-100-specification-numbers (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Brozović, V.; Bošnjak, R.; Kezić, D.; Brozović, F. Storage of the Ship maneuvering Capabilities into the Postgres Database. In Proceedings of the ICTS2022, Portotoz, Slovenia, 23–24 May 2022; pp. 69–75, ISBN 978-961-7041-11-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, H.; Yin, Y. Ship’s trajectory planning for collision avoidance at sea based on modified artificial potential field. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Robotics and Automation Engineering (ICRAE), Shanghai, China, 29–31 December 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Negenborni, R.R.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M. Ship collision avoidance methods: State-of-the-art. Saf. Sci. 2020, 121, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansner, E.R.; Reppy, J.H. The Standard ML Basis Manual; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004; ISBN 978-0-521-79478-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, K. Coloured Petri Nets—Basic Concepts, Analysis Methods and Practical Use; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 1, ISBN 978-3-662-03241-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, K. Coloured Petri Nets—Basic Concepts, Analysis Methods, and Practical Use; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; Volume 2, ISBN 978-0-387-58276-4. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, K. Coloured Petri Nets—Basic Concepts, Analysis Methods and Practical Use; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 3, ISBN 978-3-642-60794-3. [Google Scholar]
- Jašić, D.; Belamarić, G.; Gundić, A. International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea = Međunarodna Pravila o Izbjegavanju Sudara na Moru; Sveučilište u Zadru, Pomorski Odjel: Zadar, Croatia, 2011; ISBN 978-953-331-000-8. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Negenborni, R.R.; va Gelder, P.H.A.J.M. A ship collision avoidance system for human-machine cooperating during collision avoidance. Ocean Eng. 2020, 217, 107913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozović, V.; Bošnjak, R.; Kezić, D.; Vojović, I. Real Time Prediction of the Ship Position with the PostGIS Function ST_PROJECT. In Proceedings of the ICTS2022, Portotoz, Slovenia, 23–24 May 2022; pp. 76–81, ISBN 978-961-7041-11-8. [Google Scholar]
- Shmelova, T.; Sikirda, Y.; Rizun, N.; Kucherov, D.; Dergachov, K. Automated Systems in the Aviation and Aerospace Industries; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-522-57710-2. [Google Scholar]
- Shmelova, T.; Sikirda, Y.; Sterenharz, A. Artificial Intelligence Applications in the Aviation and Aerospace Industries; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-799-81417-7. [Google Scholar]
- Piera, M.A.; Radanovic, M.; Leal, X. Multi-agent systems for air traffic conflicts resolution by using a causal analysis of spatio-temporal interdependencies. In Proceedings of the SCSC 2016, Montreal, QC, Canada, 24–27 July 2016; pp. 1–8, ISBN 978-1-5108-2424-9. [Google Scholar]
- Brozović, V.; Bošnjak, R.; Kezić, D.; Bojić, F. S-101 charts, Database Tables for S-101 charts, Autonomous Vessel. In Proceedings of the IMSC 2021, Varna, Bulgaria, 9–10 September 2021; pp. 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolka, G. Programmierung—Eine Einführung in die Informatik Mit Standard ML; Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag GmbH: Munich, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-486-58601-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.R.; Rischel, H. Introduction to Programmierung Using SML; Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 1999; ISBN 0-201-39820-6. [Google Scholar]
- The PostgreSQL Global Development Group. PostgreSQL 14.1 Documentation. 2021. Available online: https://www.postgresql.org/files/documentation/pdf/14/postgresql-14-A4.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- The Open Source Geospatial Foundation. PostGIS 3.3.0 dev Manual. 2022. Available online: https://postgis.net/docs/manual-dev/ (accessed on 13 March 2023).



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brozovic, V.; Kezic, D.; Bosnjak, R.; Krile, S. Implementation of International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea Using Coloured Petri Nets. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071322
Brozovic V, Kezic D, Bosnjak R, Krile S. Implementation of International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea Using Coloured Petri Nets. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(7):1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071322
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrozovic, Vladimir, Danko Kezic, Rino Bosnjak, and Srecko Krile. 2023. "Implementation of International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea Using Coloured Petri Nets" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 7: 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071322
APA StyleBrozovic, V., Kezic, D., Bosnjak, R., & Krile, S. (2023). Implementation of International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea Using Coloured Petri Nets. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(7), 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071322





