Abstract
This study presents a thorough analysis of the sedimentology, diagenesis, and sequence stratigraphy of the Middle Jurassic Samana Suk Formation in the Hazara Basin of northern Pakistan. Focusing on two sections, namely Mera Rehmat and Por Miana, the research aims to unravel the complex geological processes within the formation. The examination of microfacies reveals nine distinct depositional textures, ranging from mudstone to wackestone, packstone, and grainstone, indicating various inner ramp environments such as open marine, lagoon, and coastal settings. Petrographic investigations shed light on diagenetic processes, including micritization, cementation, dissolution, compaction, neomorphism, and dolomitization. Six cementation types are identified, and the dolomitization patterns vary, providing insights into lagoonal environments and mudstone replacement. Sequence stratigraphic analysis uncovers intriguing patterns within the Samana Suk Formation. The high-stand system tract is characterized by mudstones, pelloidal grainstones, and dolomitized mudstones, indicating periods of high sea level. In contrast, the transgressive system tract displays ooidal grainstones, pelloidal packstones, and pel-bioclastic grainstones, representing transgression and inundation of previously exposed areas. A significant finding is the impact of diagenesis on reservoir quality parameters, specifically porosity, and permeability. Diagenetic processes, cementation types, and dolomitization patterns have significantly altered the pore network, highlighting the importance of considering diagenesis in assessing the Samana Suk Formation as a hydrocarbon reservoir. This research provides a comprehensive understanding of the sedimentology, diagenesis, and sequence stratigraphy of the Middle Jurassic Samana Suk Formation. The findings contribute to our knowledge of similar carbonate reservoirs globally, enhancing the exploration and development of hydrocarbon resources in comparable depositional environments.
1. Introduction
Reservoir characteristics are primarily controlled by depositional and diagenetic processes [1,2,3]. The geometry of the carbonate platform governs the lateral arrangement of depositional facies and the resulting primary porosity [1]. Diagenetic alterations bring about changes in the initial features of limestone deposition, leading to a redistribution of porosity. Only by researching the diagenetic history of carbonates can successive alterations and pore rearrangements of carbonate reservoirs be identified [4,5,6,7]. Although the application of sequence stratigraphy enables the anticipation of facies arrangements [8,9,10,11], there is insufficient information available regarding the depositional patterns of primary porosity and permeability within the formation [9,10,11]. The geometry, sorting, and particle size of sediments are the key factors in depositional reservoir quality. The distribution of mudstones and other fine-grained deposits that may act as seals, baffles, and barriers for fluid flow within reservoir rocks and as petroleum source rocks may be predicted using sequence stratigraphy [9,10,11]. Spatial trends in diagenesis and their influence on reservoir porosity-permeability patterns can be used to relate indirectly to relative sea-level change and the stratigraphic sequence framework [12,13]. As a result, sequence stratigraphy could be used to forecast intraformational reservoir quality. While a sequence stratigraphic framework can provide insights into facies distribution and the deposition of porosity and permeability in sedimentary successions, particularly in deltaic, coastal, and shallow marine environments, it is not applicable for inferring facies distribution and the depositional characteristics of porosity and permeability [10]. Diagenesis can be linked to sequence stratigraphy since most of the constraints on early diagenetic processes are also related to relative sea-level changes (e.g., pore water contents and flow, duration of subaerial exposure) [14,15,16,17]. As a result, integrating diagenesis with sequence stratigraphy will result in a powerful tool for predicting the geographical and temporal distribution and development of quality in clastic reservoirs [18,19]. The geographic distribution of diagenetic characteristics in different types of sedimentary successions has been extensively studied, and it has been shown that this distribution is best understood when it is connected to a stratigraphic model [14,20,21]. Carbonate successions of the Middle Jurassic, represented by the Samana Suk Formation, are located in the foreland basin of Pakistan’s Lesser Himalayas, which has been significantly altered by diagenetic processes such as dolomitization and has good outcrop exposures. Pakistan’s Indus Basin carbonate sequence is a reservoir. The Pakistani Hazara Fold and Thrust Belt, located in the Indus Basin, is bordered by the Mansehra Precambrian crystalline zone to the north, the Potwar Plateau to the south, the Kashmir Basin to the east, and the Peshawar Basin to the west, with subbasins like Kohat and Potwar. Previously, Shah et al. [22] and Rahim et al. [23] were documented the selectivity of carbonate facies in the Samana Suk Formation dolomitization process in the Por Miana and Mera Rehmat, respectively. However, these investigations were associated with vertical facies shift in one outcrop section, multiphase dolomitization, and other related diagenetic processes in the studied section.
This work examines the distribution and characterization of diagenetic heterogeneities related to sequence stratigraphic models and re-establishes the facies analysis and deposition architecture of the Samana Suk Formation. Moreover, it computes reservoir property controls and explains the Samana Suk Formation’s diagenetic history and its influence on reservoir quality evolution. This investigation will assist in modeling Jurassic play exploration in the nearby Indus Basin. The distribution and characterization of diagenetic heterogeneities within the Middle Jurassic Samana Suk Formation are of crucial importance for understanding the reservoir quality evolution and modeling Jurassic play exploration in the Indus Basin. Although previous studies have documented the selective dolomitization process and related diagenetic processes in specific sections, there is a need to establish a comprehensive understanding of the facies analysis, deposition architecture, and diagenetic history of the formation. This research aims to fill these gaps by investigating the distribution and characterization of diagenetic heterogeneities within the Samana Suk Formation using a sequence stratigraphic framework. By integrating sequence stratigraphy and diagenesis, this study seeks to provide insights into the controls on reservoir properties and the evolution of reservoir quality. The novelty of this research lies in its comprehensive approach, combining facies analysis, deposition architecture, and diagenetic history. It goes beyond previous studies that focused on vertical facies shifts in isolated sections and multiphase dolomitization. By examining the diagenetic heterogeneities within the context of sequence stratigraphic models, this study will provide a more holistic understanding of the Samana Suk Formation and its reservoir characteristics.
2. Geological Setting
The study area is in Pakistan’s Lesser Himalayan Hill Ranges, which includes the Hazara region (Figure 1). These mountain ranges are part of the large Himalayan orogenic belt’s foreland region. The study area is located on the hanging wall block of the Main Boundary Thrust (MBT). It formed as a result of the Cenozoic collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates [24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. The Indian Plate evolved during the Early Jurassic period when it was part of the southern supercontinent (i.e., Gondwanaland) that began sliding northward from neighboring Australia and Antarctica plates. Around 160 million years ago, the Indian Plate moved around 9000 km before colliding with the Eurasian Plate [31,32]. Initially, the supercontinent Pangaea was divided into Laurasia and Gondwanaland. Gondwanaland was later divided into West and East Gondwana during the Early to Middle Jurassic. During this period, this region was a part of the Indian Plate’s shelf edge, where thick depositions of platform sediments accumulated [33,34,35]. The thick shallow water carbonate platform deposits of the Samana Suk Formation, comprising oolitic, peloidal, fossiliferous, and micritic facies, were formed throughout the Toarcian to Callovian periods along the shelf margin of Neo-Tethys [34,36,37,38,39]. This formation contains most of the examined dolomites, whereas the upper and lower formations are largely undolomitized. This carbonate sequence is about 200 m thick, with lateral thickness increasing from the northwest to the southwest. Because of the restricted environment that occurred after the deposition of these shelf carbonates, as well as the deposition of pyrite-rich and belemnite-bearing black shale and siltstone during the Cretaceous period, the high-energy carbonates exhibit an unconformable contact with the Cretaceous shale (Chichali Formation) on the northern margin of the Indian plate.
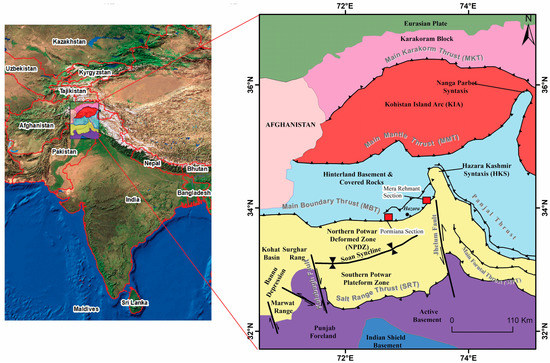
Figure 1.
Regional tectonic map of the studied section (adapted from [40]). The rectangles show the study locations.
The Indian Plate separated from Gondwanaland and began a rapid northward migration from Madagascar during the Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian). During this period, the Indian plate experienced dome uplift as a result of its passage through the Ninety-East Keregulen hotspot, which led the Rajmahal traps to erupt [41]. The domal uplift caused detritus to be eroded and spread over the basin, resulting in the deposition of Lumshiwal Sandstone. Following the formation of the Chichali and Lumshiwal Formations. The rapid northward movement resulted in the depth of the Indian Plate’s NW section and the formation of homoclinal ramps, which resulted in the deposition of micritic carbonates as the Kawagarh Formation [36,42]. The Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary denotes an unconformable contact between the overlying Cenozoic succession and the Mesozoic succession. Meanwhile, the northern half of the Indian plate underwent compression-related elevating as a result of its collision with the Kohistan-Ladakh Island arc. During this epoch, ophiolites were deposited in the northern section of the Indian Plate, such as the Muslim Bagh Waziristan-Dargai ophiolites in Pakistan [43]. The Hangu Formation, which consists of laterite, fireclay, and sandstone, was formed during this time period and represented subaerial exposure. The overlying Lokhart Limestone has lagoonal facies, while the Patala Formation has alternating shale and limestone [44]. The highest strata of the Patala Formation are composed of paleosols that reflect a Paleocene-Eocene unconformity. Later, a collision between India and the Kohistan Island Arc (KIA) resulted in sea-level regression during the Early Eocene, and thus a shallow and marginal marine and evaporitic environment prevailed in the Hill ranges [44,45]. Early Eocene Margalla Hill limestone, which mainly consists of nodular limestone [46], followed by the deposition of thinly bedded limestone of Chorgali Formation and later on Kuldana Formation (shales, marls, and limestone layers [47] and subsequent Himalayan uplift resulting in the deposition of Murree Formation [48,49]. The stratigraphic column of Hazara Basin is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Regional Stratigraphic Column of Hazara Basin, Northwest Himalayas, Pakistan.
The Indian and Eurasian plates collided, resulting in the construction of an S-W-directed thrust system in the Indian plate. The major thrust systems are the Main Karakoram Thrust (MKT), the Main Mantle Thrust (MMT), the Main Boundary Thrust (MBT), and the Salt Range Thrust (SRT). The north-south compressional regime is represented by the presence of east-west trending major structures (i.e., MBT) and other local faults in the study area and its surroundings [25,26,29].
3. Material and Methods
A total of 182 thin sections were prepared from samples taken from two localities, i.e., Mera Rehmat (73°20′29″ E; 34°14′33″ N) and Por Miana (72°43′9″ E; 33°54′53″ N), both in the upper Indus basin, to develop a depositional model and explain the diagenetic history of the Samana Suk Formation. Thin-section samples were obtained every 0.5 m. Thirty-thin sections were treated with Alizarin Red-S and potassium ferrocyanide, as described by Dickson [50], and 100 were impregnated with blue-dyed epoxy resin. Thin section descriptions include the texture, size, type of allochems and diagenetic characteristics, the sequence stratigraphic effects, and the relationship between the last two. The Dunham [51] and Embry and Klovan [52] limestone classifications were used to classify the rocks. The interpretation of facies is based on rock characteristics and the diagenetic comparison of successions with well-established models [53,54,55]. According to Flügel and Munnecke [55], special attention was put on identifying standard ramp microfacies types (RMF). Plumley et al. [56] classification was used to evaluate the energy index of sedimentary facies. Overall, the texture, grain type and size, sorting, bedding style, primary sedimentary structures of the rocks, facies, interpretation of depositional setting, appearance according to lithofacies, erosive surfaces, sequence boundaries, and the impact of sequence stratigraphic events on diagnostic outcomes were described in the study thin sections. Two hundred and twenty-eight thin-sections in total were prepared and examined under a polarizing microscope to integrate lithological and diagenetic data for facies characterization, and to construct a conceptual 3-D depositional model.
4. Results
4.1. Field Observations
In the field observations, it was found that limestone and dolomite are recognizable based on their color contrast, hardness, and behavior toward acid treatment. In both sections, the limestone was mostly light to dark gray in color, thin to thickly bedded, and fine to coarsely grained (Figure 2a). The limestone was micritic in the lower part of the Mera Rehmat section and mostly dolomitized in the upper part, while it was mostly dolomitized in the Por Miana section. Moreover, it was massive, hard, and compact, with calcite veins and minor cross-bedding and fractures. Dolomites are light brown to yellowish in color. Detailed observations showed dolomitization occurred in the studied sections as (i) bedding parallel units (Figure 2b) and (ii) patchy dolomites (Figure 2c). Field observations indicate that bedding parallel or stratiform dolomites are restricted to the basal part of the studied formation, while patchy dolomite is distributed unevenly in the basal and middle parts of the section. Stylolites are abundant in the outcrops and are found both in dolomite and limestone. They are mostly filled with dark brown, patchy dolomite and are distributed at low or high angles or parallel to major bedding planes (Figure 2d). The pore-filling white saddle dolomite is present in some places at the top of the unit. Dolomitization and dedolomitization were also observed on the outcrop (Figure 2e). Various hard ground surfaces are also marked in the Mera Rehmat section, which indicates sea level fluctuations (Figure 2f).
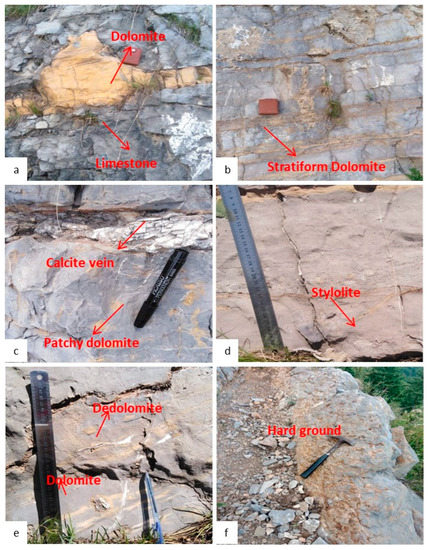

Figure 2.
Field photographs showing: (a) grey limestone and yellow dolomite, (b) bedding parallel dolomite, (c) patchy dolomite with a thin calcite vein, (d) bedding parallel stylolite, (e) dolomite and Dedolomite, and (f) erosive surface.
4.2. Microfacies Analysis
In the examined sections, nine microfacies types were recognized in the Middle Jurassic rocks.
4.2.1. Mudstone (MF-1)
In the Mera Rehmat region, this microfacies represents 20% of the overall thickness, whereas, in Por Miana, it comprises 10% of the entire thickness. In the outcrop, this facies consists of yellow sandy limestone that is faulted and fractured and contains parallel bedding stylolites with yellow dolomite patches (Figure 2). This microfacies is more common in the middle to upper Por Miana section, but it occurs at irregular intervals in the middle to the upper half of the Mera Rehmat section. This microfacies consists of 85% matrix, 5–10% dolomite rhombs, 4% twin calcite, and 1% peloids, whereas diagenetic features include twinned calcite, burrowed dolomite and stylolites, respectively (Figure 3a,b). This facies is mostly micritic in both sections (Figure 3a), with only minor cementation seen in veins.
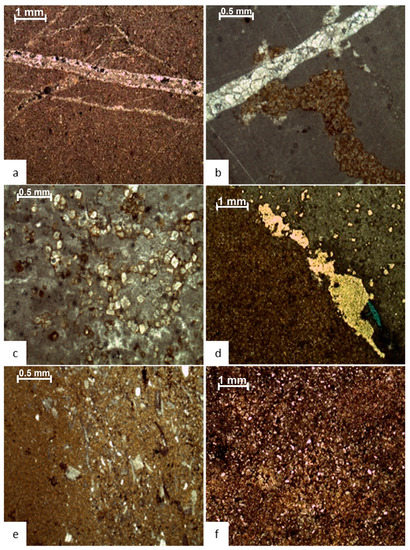
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs of microfacies of Samana Suk Formation (a,b) mudstone microfacies, (c,d) dolomitized mudstone microfacies, and (e,f) dolomite.
4.2.2. Dolomitized Mudstone (MF-2)
This facies comprises 6% of the overall thickness in the Mera Rehmat section and is evident in the first, second, and fourth cycles of the Mera Rehmat section, but less than 1% in the Por Miana section. It is composed of light gray limestone with parallel bedding stylolites within dolomite. Microscopic observations reveal that MF-2 contains 60% matrix, of which 20% are sucrosic dolomite rhombs and 5% are Fe oxides, which are scattered as authigenic minerals (Figure 3c). While the blue color of dolomites indicates diagenetic porosity (Figure 3d), Equant cement was observed scattered throughout the matrix. Along with extensive dolomitization, stylolites, parallel bedding, and calcitized euhedral cores, dedolomitization was also observed. In the case of diagenesis, the first stage consists of a matrix, the second of matrix-replacing dolomite, the third of sucrosic dolomite, and the fourth of authigenic Fe oxide.
4.2.3. Dolomite (MF-3)
This microfacies comprises 1% of the overall thickness of the Mera Rehmat section and 5% of the thickness of the Por Miana section. This outcrop is composed of medium-bedded limestone with modest cross-bedding and parallel-bedded dolomites. Flaser bedding, cross-bedding, and minor fossiliferous beds were also observed. This microfacies occurs at the base of Por Miana and in veins containing 4–5% calcite. Matrix, twin and syntaxial calcite, stylolite, pervasive dolomitization, and complete dolomitization are all diagenetic characteristics (Figure 3a–f). This microfacies exhibits dolomitization and dedolomitization in the middle and upper portions of Mera Rehmat, while the base is micritic, cemented, dolomitized, and dedolomitized. In the case of Por Miana, this facies is minor micritic and cemented, as well as dolomitized and sometimes dedolomitized. As a matrix replacement during the diagenetic stage, dolomite rhombs have formed. This facies is common near the base of the Por Miana section, and it repeatedly occurs in thin layers in the Mera Rehmat section.
4.2.4. Ooidal Grainstone (MF-4)
This microfacies comprises 10% of the thickness of the Mera Rehmat section and 3% of the thickness of the Por Miana section. On the outcrop, this facies consists of medium- to thickly bedded, sand-textured, light-gray limestone that is locally brecciated. In the Mera section, ooidal grainstones are present in the lower and middle parts, but in the Por Miana section, they are only found in the top part. This facies comprises 90% ooids, 1% bioclasts, 1% peloids, and 8% cement in thin sections (equant, blocky, twin, and syntaxial). Ooids are deformed and micritized (Figure 4a). These ooids, which are selectively dolomitized, are bound together by cement crystals. In the first step of diagenesis, micritic ooids are produced. In the second stage, calcite veins with equant cement are cut across ooids. The third diagenetic stage is stylolization, and the fourth diagenetic stage is the inflow of authigenic quartz crystals along stylolites. Large euhedral dolomite crystals with cloudy cores and saddle dolomite are very sensitive to telogenetic meteoric alterations during uplift and meteoric water inflow. This microfacies exhibits micritized (Figure 4b), calcitized, stylolites, dolomitized, and dedolomitized behavior at the base of the Mera section, and only micritization and cementation are visible in the middle and upper parts. In the Por Miana area, the upper portion of this facies is micritic, calcitized, and dolomitized.
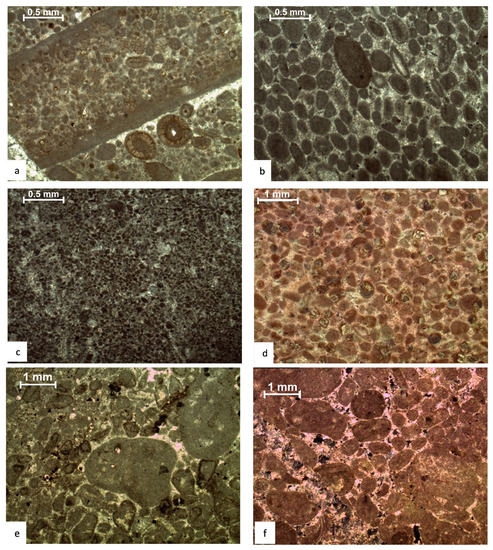
Figure 4.
Photomicrographs of microfacies of Samana Suk Formation: (a,b) ooidal grainstone, (c,d) peloidal grainstone, and (e,f) intraclastic peloidal grainstone.
4.2.5. Peloidal Grainstone (MF-5)
This microfacies accounts for 20% of the overall thickness of the Mera section and 10% of Por Miana. On the outcrop, this facies consists of stratiform yellowish dolomite with alternating layers of light and dark limestone. It is prevalent in the third and fourth depositional cycles of the Mera section, whereas it is found randomly in the Por Miana section. In thin sections, this facies is composed of 90% peloids, 6% cement, and 4% quartz. Peloids are micritic, cements are blocky and syntaxial (Figure 4c,d), and in various thin sections, tectonic/post-diagenetic stylolites were also identified. Along with stylolite, dolomite rhombs ferroan in their centers were also observed. In the first stage of diagenesis, both peloids and bioclasts are micritized. In the second stage, twin, equant, and blocky types of cement are found in various thin sections. The third stage consists of stylolites and pervasive dolomite next to the stylolite, followed by burrowed dolomite.
4.2.6. Intraclastic Peloidal Grainstone (MF-6)
This facies accounts for 1% and 4.5% in the Mera Rehmat and Por Miana sections, respectively. On the outcrop, this facies is light gray limestone with minor patches of dolomite and bedding parallel stylolites. It is found at the bottom of the first depositional cycle, and in other dispersed areas of the subsequent cycles, but in Por Miana, it is found at the bottom of the section rather than at the top. This facies comprises 30% bioclasts, 40% intraclasts, 10% micritic peloids, and 20% cement among grains, according to thin section analysis (Figure 4e,f). Diagenetic stages show micritic ooids, cement, stylolite in unstained areas, and pervasive dolomite rhombs.
4.2.7. Peloidal Ooidal Grainstone (MF-7)
This facies comprises 1% of the Por Miana sections and 9% of the Mera Rehmat section. On the outcrop, this microfacies consists of medium to thickly bedded hard and compact limestone with occasional crossbedding and brecciation in parts with patchy dolomite and bedded parallel stylolites. It is abundant in all depositional cycles and at various horizons in the Mera Rehmat section, while it is found in the lower to the middle part of the Por Miana section. In the studied thin sections, it is composed of 80% peloids and 10% ooids (Figure 5a,b). It also contains biota such as miliolides, gastropods, pelecypods, and brachiopods. In the first stage of diagenesis, micrite, micritic ooids, and peloids are prevalent; in the second stage, equant cement is found among grains, and twin calcite veins run parallel to the bedding plane; in the third stage, tectonic stylolites are evident, along which pervasive dolomite rhombs are found; in the fourth stage, selective dolomitization takes place which could be related to Himalayan tectonics; and in the final stage, dedolomitization of dolomite occurs.
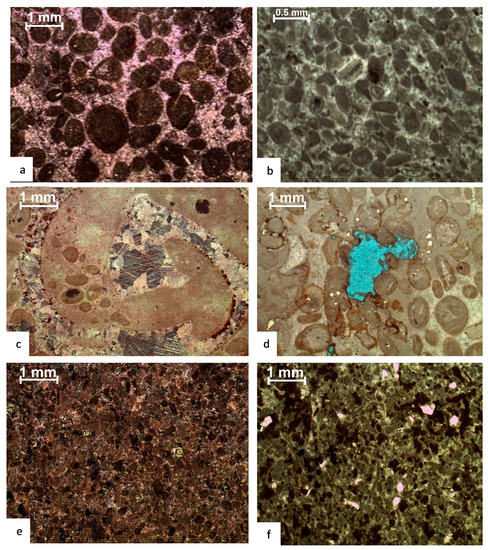
Figure 5.
Photomicrographs of microfacies of Samana Suk Formation: (a,b) peloidal ooidal grainstone, (c,d) ooidal grainstone, and (e,f) peloidal packstone.
4.2.8. Peloidal Wackestone (MF-8)
This microfacies is present in the Mera Rehmat section (1%) and in the Por Miana section (7%). On the outcrop, this microfacies displays characteristics such as thin to thickly bedded gray peloidal and oolitic limestone with yellow dolomite patches. Petrographic studies reveal that this microfacies is composed of 40% peloids, 30% matrix, 10% cement, and 10% dolomite. There are 5% quartz crystals scattered in the matrix (Figure 5c). In the first stage of diagenesis, this facies manifests as micritic peloids and matrix. Blocky cement in veins is the second diagenetic stage, tectonic stylolite with dolomite inclusions, whereas the third-stage dolomite rhombs have cloudy cores (Figure 5d). This facies is composed of bands of alternating peloids, ooids, and micrite.
4.2.9. Peloidal Packstone (MF-9)
This facies comprises 1% of the overall thickness of the Mera Rehmat layer and 10% of the Por Miana section. On the outcrop, this microfacies exhibits light gray, sandy limestone with parallel dolomite bedding. This microfacies is predominant in the first and second cycles of the Mera Rehmat section and dispersed throughout the Por Miana region. Peloids account for 85% of the microfacies, while dolomite rhombs make up the remaining 15%. Peloids and bioclasts are micritic and cemented by equant cement, while bioclasts are calcitized by twin calcite and dedolomitized scattered dolomite rhombs (Figure 5a–f). Extensive bioturbation, abundant peloids, rare smaller benthic forams, gastropods, and pelecypod fragments were also observed.
4.3. Diagenetic Processes
Carbonate rocks are very susceptible to post-depositional diageneses, such as cementation, recrystallization, compaction, and dolomitization [57]. In the examined sections, Jurassic carbonate deposits underwent a variety of diagenetic processes, including micritization, cementation, compaction (physical and chemical), dissolution, and dolomitization.
Following is a description of the various diagenetic processes impacting the carbonates under study.
4.3.1. Micritization
Micritization was readily observed in ooids and bioclasts during thin-section analysis at various Samana Suk Fm levels. Micritization has cut through the entire cortex in the ooids, following the radial pattern. Early stages of micritization in the examined sections indicate the formation of micrite envelopes surrounding grains. Certain microfacies are partly or completely micritized (Figure 6a,b), and the ooids within them are only distinguishable due to their spherical shapes and weak relics. The majority of the abundant peloids in the Samana Suk Formation seem to be micritized. In the thin section, ooids and bioclasts in various states of micritization are identifiable.
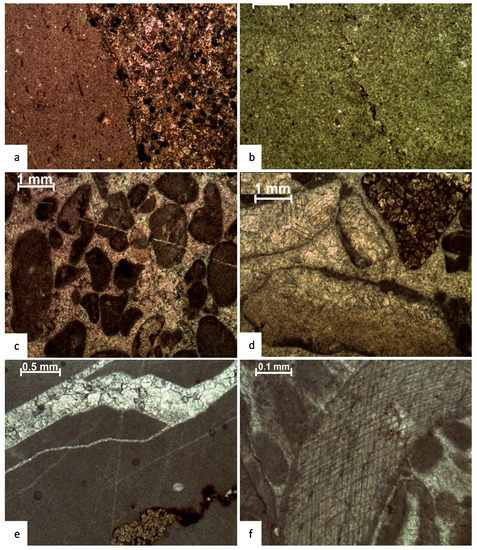
Figure 6.
Photomicrographs of diagenetic fabric (a,b) micritization and cementation, (c,d) equant cement, (e) blocky cement, and (f) syntaxial cement.
4.3.2. Cementation
According to sedimentological characteristics, numerous generations of calcite cement with little dolomite input were identified. In the Samana Suk Formation, the six cement types listed below have been identified:
- (a)
- The most common type of cement was the equant calcite spar, which filled pores and skeletal chambers, and veins (Figure 6c–e);
- (b)
- Granular blocky or equant calcite cement: The crystal boundaries in this cement are frequently irregular to curved, but occasionally straight. This cement resulted from aragonite leaching since it is present in both intergranular pores and molds. The crystal’s size increased from the mold’s perimeter to its center. Occasionally, crystals exhibit intense twinning;
- (c)
- Coarse, blocky calcite cement is the most prevalent type of cement in the Samana Suk Fm. Clear, coarse to very coarse calcite cement (Figure 6e). In thin sections, it appeared to have straight boundaries on one side and curved boundaries on the other. It completely fills all accessible intergranular pores. Sometimes, thin isopachous cement is used to line molds, and the remaining space is filled with a single calcite crystal;
- (d)
- This cement was evident in compacted grainstones with syntaxial overgrowths. Syntaxial overgrowth (Figure 6f) is difficult to distinguish from poikilotopic cement and frequently replaces bioclasts;
- (e)
- Poikilotopic cement: This form of cement in the Samana Suk Formation is a highly coarse-grained, poikilotopic (Figure 7a), clear, blocky, calcite cement that fills pore spaces surrounding multiple grains. It has a diameter of several millimeters;
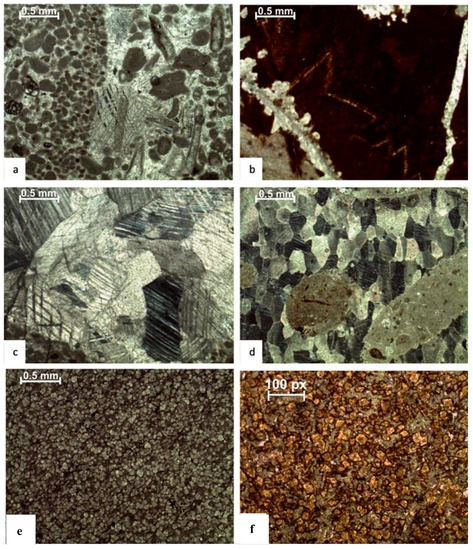 Figure 7. Photomicrographs of diagenetic fabric (a) poikilotopic cement, (b) ferroan dolomite cement, (c,d) twin calcite, and (e,f) dolomitization.
Figure 7. Photomicrographs of diagenetic fabric (a) poikilotopic cement, (b) ferroan dolomite cement, (c,d) twin calcite, and (e,f) dolomitization. - (f)
- Ferroan dolomite cement; molds and intergranular pores include dark brown to reddish brown, anhedral to subhedral, coarsely crystalline ferroan and non-ferroan dolomite and twin calcite (Figure 7b–d).
4.3.3. Dissolution
Dissolution is common in the examined intervals, indicating late-stage porosity development (Figure 8). Moldic (Figure 8c), vuggy, and inter- and intra-particle (Figure 8a,b) porosity are all types of dissolution-associated porosity.
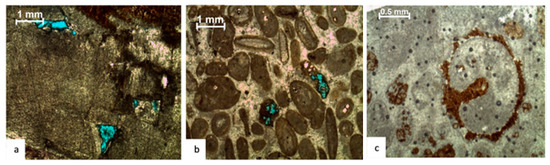
Figure 8.
Photomicrographs of diagenetic fabric showing dissolution (a) inter-particle porosity, (b) intra-particle porosity, and (c) moldic porosity.
4.3.4. Mechanical and Chemical Compaction
The depth-dependent porosity distribution and compaction trends are influenced by various textures, diagenetic conditions, and mineralogies [58,59]. Various horizons record the detailed distribution of these features in individual microfacies. In the investigated section, broken and cracked ooids along the lamellae and broken cortical layers are common. Mudstone (micrite) is often converted into microspar owing to compaction; however, compaction is not uniform across all microfacies (Figure 9b).
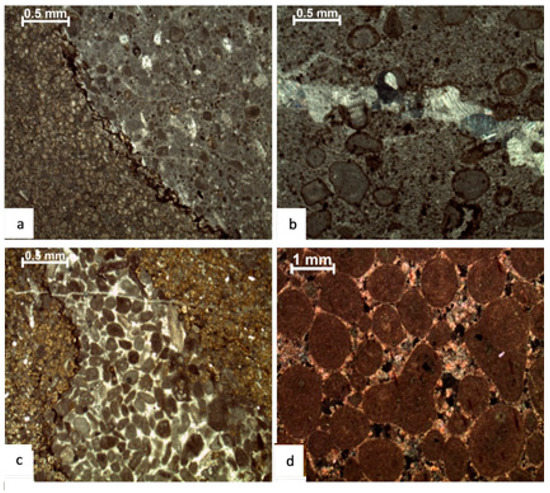
Figure 9.
Photomicrographs showing mechanical and chemical compaction (a) sutured seams, (b) broken micritic envelope, (c) grain interpenetration, and (d) sutured contacts.
Sutured seams (Figure 9a), microstylolites, and stylolites identified in sections constitute the pressure solution (Figure 9a,c). Sutured seams and microstylolites are mostly horizontal and parallel to bedding planes, indicating that overburden stresses most likely caused the pressure solution phenomenon. The initial pressure solution is concentrated at grain contacts in grainstone (Figure 9d), resulting in sutured contacts and grain interpenetration (Figure 9c).
4.3.5. Neomorphism
Calcite largely replaced aragonitic allochems in the section studied (i.e., shell fragments). Petrographic investigations demonstrated that microcrystalline calcite recrystallized into equant calcite spars of varying crystal sizes. Aggregational neomorphism results from partial to total recrystallization of the skeletal components. The different skeletal grains, echinoderms, foraminifera, algal grains, and other bioclasts coated with micritic envelopes and exhibiting aggradation neomorphism, suggestive of subaerial diagenesis, support this process.
4.3.6. Dolomitization
Pore-filling dolomite plays a major role in the diagenetic process in the section (Figure 10). The Samana Suk Formation contains dolomite in several forms: (a) layered thin beds; (b) burrowed dolomite (Figure 10e); (c) patches, clusters, matrix replacive and dispersed dolomite crystals (Figure 10c,d); (d) grain-selective (Figure 10f) and matrix-selective dolomite (Figure 10a); (e) molds and fracture-filling dolomite; and (f) pervasive dolomite. The parent rock is occasionally visible in the dolomitized layer (Figure 10b). Fine to medium-crystalline, anhedral to subhedral mosaics of dolomite crystals pervade several thin sections (Figure 7e,f). This widespread dolomite formed early in the diagenetic period.
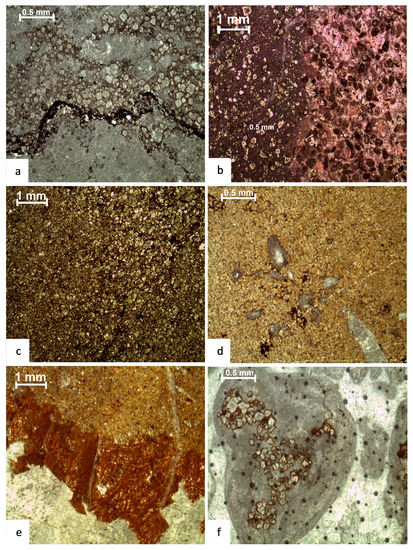
Figure 10.
Photomicrographs reflecting different types of dolomitization (a) pervasive dolomitization, (b) layered, (c,d) matrix repulsive, (e) burrowed dolomite, and (f) grain selective.
The dolomite crystals that have replaced the allochems are rich in inclusions, but the crystals formed in the intergranular spaces are finer and coarser. Crystal size grows toward the pore center in molds. Very fine crystalline subhedral dolomite was used to fill the intergranular pore spaces. Dolomite is also observed as cement in the slightly dolomitized mudstones.
4.4. Sequence Stratigraphy
The Samana Suk Formation represents deposition in three different environments: open marine, lagoon, and shoreline/coastline. According to the microfacies and sequence stratigraphic data, the Samana Suk Formation is composed of a 2nd-order local cycle, which is equivalent to the global sequences reported by Haq et al. [60]. Similarly, the Samana Suk Formation’s 3rd-order sequences comprise five High-stand Systems Tracts (HSTs), five Transgressive Systems Tracts (TST) in the Mera Rehmat section (Figure 11), and three TST and two Highstand Systems in the Por Miana section (Figure 12). The Samana Suk Formation has recorded third-order system tracts (Figure 11 and Figure 12).

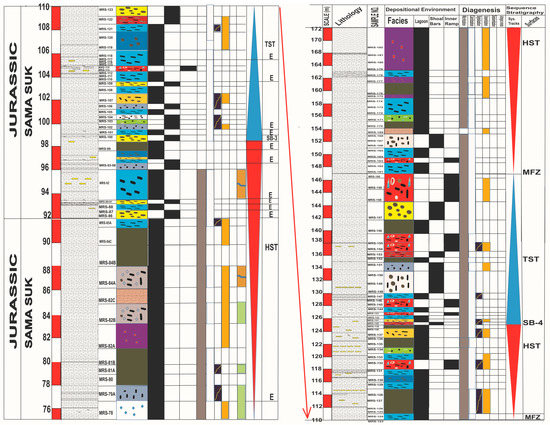
Figure 11.
Litholog showing microfacies distribution, diagenetic and sequence stratigraphic attributes of Mera Rehmat section.
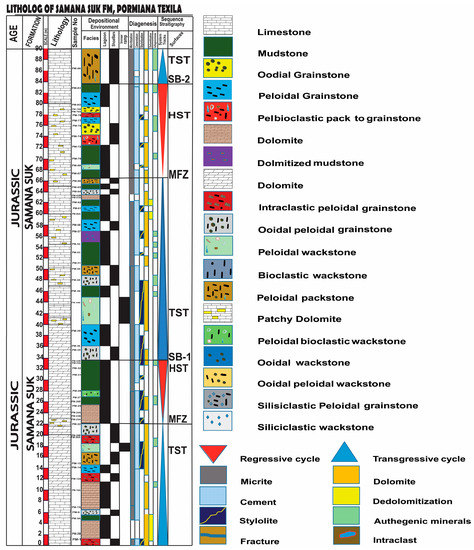
Figure 12.
Litholog showing microfacies distribution, diagenetic, and stratigraphic sequence attributes in the Por Miana section.
4.4.1. Depositional Sequence 1
A TST near the base of the Mera Rehmat section makes sharp contact with the underlying Datta FM. This section begins with siliciclastic wackestone facies displaying underlying formation inclusions, followed by a lagoonal to inner ramp setting (Figure 13).
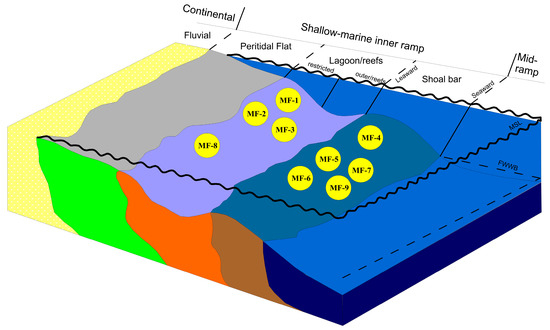
Figure 13.
Hypothetical depositional model for Samana Suk Formation.
Micritization and cementation are prevalent diagenetic features with stylolites and authigenic content in alternate bands of grainstone, wackestone, and mudstone with minor peloidal intraclastic facies. While the uppermost ooidal grainstone is the Maximum Flooding Zone (MFZ), dolomitization and dedolomitization occur at the end of this transgression cycle. The MFZ is represented by the topmost ooidal grainstone in the Mera Rehmat section. The TST in Por Miana is characterized by the repetitive deposition of peloidal grainstone and intraclastic peloidal grainstone, as well as lagoonal facies such as peloidal packstone and wackestone. Micritization and calcitization are early diagenetic features, whereas stylization and dolomitization are late diagenetic features, with minimal authigenic content in the intraclastic peloidal grainstone as the last diagenetic phase. Por Miana is distinguished by the presence of dolomite at the base, which is followed by intraclastic peloidal grainstone. The packstone and wackestone facies exhibit micritization, cementation, dolomitization, and stylolization. Dedolomitization and authigenic minerals were also observed in intra-clastic peloidal grainstone microfacies (Figure 14).
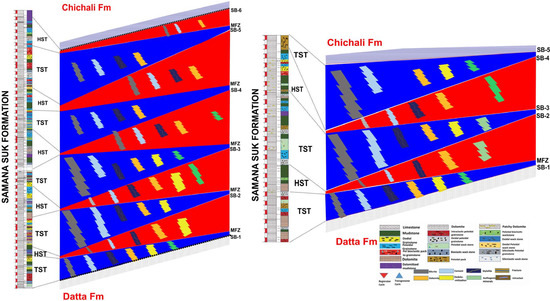
Figure 14.
The model represents the overall interplay of sequence stratigraphic architecture of the Samana Suk Formation.
4.4.2. Depositional Sequence 2
The Mera Rehmat’s HST of DS2 is characterized by the deposition of mudstones and repeated dolomitized mudstone and peloidal grainstone facies of the lagoon. These facies have been micritized, calcitized, and stylolized. In the last diagenetic stage, dolomitized mudstone is dolomitized and dedolomitized. Dolomite, mudstone, and bioclastic peloidal and bioclastic wackestones characterize the HST in the Por Miana region. The lagoonal environment defines this area (Figure 12)—micritized, calcitized, and dolomitized mudstone and dolomite facies containing authigenic inclusions in mudstone. Micritization, calcitization, and stylolization are early stages of diagenesis in peloidal bioclastic wackestone. The Mera Rehmat section’s TST of the depositional sequence is described by the deposition of ooidal grainstone, ooidal peloidal grainstone, dolomitized mudstone, peloidal packstone, and pel-bioclastic packstone to grainstone facies, which represent the lagoon to inner ramp environment and sea level transgression. These facies are micritized and calcitized, whereas the highest flooding zone is dolomitized ooidal grainstone at the top of the cycle. The TST of DS2 in the Por Miana section is characterized by the presence of peloidal grainstone, ooidal peloidal grainstone, mudstone, dolomitized mudstone, and peloidal packstone facies, all of which are micritized except for dolomite. The peloidal wackestone, dolomite, and mudstone facies lack cementation. Stylolite is observed at the base of TST in peloidal grainstone, peloidal ooidal grainstone, peloidal wackestone, and mudstone facies, and in lesser amounts at the top. Dolomitization often occurs in mudstone, peloidal wackestone, and dolomite facies. Dolomitized mudstone facies towards the top have some authigenic material (Figure 14).
4.4.3. Depositional Sequence 3
Dolomite at the bottom of the HST of DS3 in the Mera Rehmat section and peloidal and ooidal grainstones that look similar to lagoonal and shoal bars set it apart. All facies are micritized and calcitized. Peloidal and ooidal grainstones are stylolized, dolomitized, and dedolomitized at the base of the cycle. Por Miana’s High Systems Trajectory represents the peloidal grainstone, ooidal grainstone, mudstone, pel-bioclastic pack-to-grainstone, and intraclastic peloidal grainstone, which characterize the depositional environment ranging from lagoon to shoal bar. All facies are micritized and calcitized except for peloidal wackestone, which lacks cement. The mudstone and ooidal grainstone facies are dolomitized and include authigenic minerals. A sequence boundary is marked at the top of HST due to the presence of an erosive surface. The transgressive systems tract (TST) of DS3 in the Mera Rehmat section is marked by repeated ooidal grainstone, peloidal grainstone, mudstone, intraclastic peloidal grainstone, and the topmost peloidal wackestone facies. From lagoonal mud to the inner ramp’s peloidal wackestone facies, these facies ultimately mark the depositional environment. The top is marked by a maximum flooding surface. The TST of DS3 in the section is marked by a single peloidal packstone facie that is micritized, calcitized, dolomitized and includes authigenic content (Figure 14).
4.4.4. Depositional Sequence 4
In the Mera Rehmat section, the fourth cycle of the Middle Jurassic Samana Suk Formation comprises a TST with peloidal grainstone, ooidal grainstone, peloidal bioclastic grainstone, and intraclastic peloidal grainstone facies. Micritization and cementation episodes affect these grainstones, while dolomites occur at three horizons. Stylolites are observed in peloidal and ooidal grainstones at specific horizons within the TST. The HST in the Mera Rehmat section consists of basal thick mudstone facies, followed by peloidal grainstone, ooidal wackestone, pelbioclastic pack to grainstone, and peloidal ooidal grainstone facies. The topmost layer represents a thin mudstone facies marking the sequence boundary. Dolomites and stylolites are confined to the peloidal ooidal grainstone and pelbioclastic pack to grainstone facies within the HST. It is important to note that this sequence is not observed in the Por Miana section, indicating lateral facies variations within the Samana Suk Formation. These precise observations provide valuable insights into the sedimentological and diagenetic characteristics of the Middle Jurassic carbonates in the Mera Rehmat section.
4.4.5. Depositional Sequence 5
In the Mera Rehmat section, the TST of the fourth cycle in the Middle Jurassic Samana Suk Formation comprises the following facies: six units of pelbioclastic pack to grainstone, three units of peloidal grainstone, ooidal grainstone, mudstone, intraclastic peloidal grainstone, bioclastic grainstone, and peloidal ooidal grainstone. Stylolites and dolomites are observed at three horizons within the pelbioclastic pack to grainstone facies towards the top, at the base of the intraclastic peloidal grainstone facies, and in the middle part of the peloidal grainstone facies. Above the transgressive surface, the HST in the Mera Rehmat section includes the following facies: peloidal grainstone, dolomitized mudstone, dolomite, mudstone, peloidal grainstone, and pelbioclastic pack to grainstone. Dolomites are also present in the pelbioclastic pack to grainstone facies, which marks the MFZ. It is important to note that this specific sequence is not observed in the Por Miana section, indicating lateral facies variations within the Samana Suk Formation. These precise observations provide valuable insights into the facies distribution, diagenetic features such as stylolites and dolomites, and the stratigraphic architecture of the Mera Rehmat section in the Middle Jurassic Samana Suk Formation.
5. Discussion
5.1. Depositional Environment
The variety of microfacies within the Samana Suk Formation suggests a complex depositional history with different energy conditions, ranging from hypersaline supratidal to high-energy marine environments, highlighting the dynamic nature of the depositional setting.
MF-1: Mudstone facies-1 often follows transgressions in sequence stratigraphy (Figure 11 and Figure 12). The mudstone texture, dolomitized lime mud matrix, and absence of marine biota all point to low-energy depositional conditions. The presence of lime mud in microfacies suggests a calm water condition. This non-laminated, unfossiliferous, homogenous micritic mudstone microfacies is characteristic of a low-energy supratidal environment, most likely mudflats or tidal ponds. This facies coincides with Flügel and Munnecke’s [55] SMF-23 and Wilson’s FZ-8 [53].
MF-2: These mudstones are often deposited along the edge of shoals, where energy shifts are frequent, and the resultant sedimentary facies assemblage consists of alternating grainstone and mudstone layers [61]. This facies is similar to SMF-23 of Flügel and Munnecke [55] and FZ-8 of Wilson [53].
MF-3: Diagenetic dolomite rhombs replaced the matrix. Low faunal contents suggest a tidal flat-deposited lime-mudstone parent rock. This facies matches Flügel and Munnecke [55] SMF-23 and Wilson FZ-8 Wilson [53].
MF-4: Ooids mostly form on high-energy shoals of the inner shelf within the platform interior and are limited to near-coast, marginal marine environments. Ooids are first deposited along with gastropods in the low-energy lagoon setting. Encrusted and micritized ooids form grapestone fabric. Later, ooids and intraclasts are reworked to the high-energy inner shelf and deposited above Fair Weather Wave Base (FWWB) in typical marine conditions. This facies matches Flügel and Munnecke [55] SMF-23 and Wilson FZ-8 Wilson [53].
MF-5: This facies is deposited at lower water depths than the packstone facies in a high-energy shallow subtidal shoal environment. It is interpreted as a carbonate shoal deposit above the normal wave base. Grainstone texture and broken fragments of bioclasts imply high-energy environments, whereas peloids indicate a low-energy environment. Thus, lagoonal tidal inlets with high-energy settings can deposit microfacies. The bioclasts imply a shallow environment with normal salinity and may have been transferred to lagoonal tidal inlets by storm surges or waves. This facies corresponds to SMF 16 of Wilson [53] and Flügel and Munnecke [55].
MF-6: Many peloids indicate low energy. Bioclasts, pelecypods, brachiopods, and other skeletal fragments suggest a shallow, normal-salinity marine environment. Intraclasts, bioclasts, and ooids indicate high energy above the fair-weather wave base. These allochems and fossils indicate that the microfacies is deposited in the near-shore zone of the inner shelf during storms. The peloids of low-energy conditions are reworked into such high-energy settings. The facies correspond to SMF 16 of Wilson [53] and Flügel and Munnecke [55].
MF-7: Micritic envelopes and selective micritization have been observed. Due to biogenic encrustations, micritized ooids occur in protected lagoonal environments. Peloids, milliolids, and gastropods are also indicative of lagoonal environments. The presence of bioclasts, pelecypods, brachiopods, and other skeletal fragments suggests a shallow marine environment with normal salinity. The ooids develop in the high-energy shoal environments of the inner shelf’s interior, which are restricted to near-coast marginal marine environments. The dominance of sparite further supports the high-energy condition. Initially, ooids are reworked and deposited in the low-energy lagoon with miliolids and gastropods. The ooids are encrusted and micritized to form a fabric of grapestone. Later, the ooids and intraclasts are redistributed to the inner shelf with high energy and deposited in typical marine conditions above the FWWB [62]. The facies match [53] and [55] SMF 16.
MF-8: The rich lime mud matrix with limited fauna suggests a lagoonal environment with low circulation [62]. The facies match [53] and [55] in SMF 16.
MF-9: Extensive bioturbation, abundant peloids, rare smaller benthic forams, gastropods, and pelecypod fragments in the micritic matrix suggest a low-energy, shallow subtidal lagoonal environment. Pseudo-ooids imply sporadic, moderate energy. Iron oxides surrounding grains suggest slow sedimentation. This facies implies warm, moderate to highly agitated, shallow water up to 5 m in the shoal (Figure 11 and Figure 12). The facies match [53] and [55] in SMF 16.
The Samana Suk Formation exhibits a diverse range of microfacies, each indicative of specific depositional environments. The presence of MF-1, characterized by non-laminated, unfossiliferous mudstone with dolomitized lime mud matrix, calcite-filled evaporative molds, and absence of marine biota, suggests a low-energy hypersaline deposition in a supratidal environment, possibly mudflats or tidal ponds [22]. MF-2, which comprises alternating grainstone and mudstone layers, is typically found along the edges of shoals where frequent energy shifts occur [63]. MF-3, with diagenetic dolomite rhombs and low faunal content, suggests deposition on tidal flats. MF-4 corresponds to high-energy shoals within the platform interior, featuring ooides and grapestone fabric, indicating deposition in near-coast, marginal marine environments [64]. MF-5 is interpreted as a carbonate shoal deposit in a high-energy shallow subtidal shoal environment, with grainstone texture, broken fragments of bioclasts, and peloids indicating both high- and low-energy environments. MF-6 represents the near-shore zone of the inner shelf during storms, with peloids, bioclasts, pelecypods, and ooids suggesting high-energy deposition. MF-7 shows micritic envelopes, selective micritization, and encrusted ooids, indicating protected lagoonal environments [55]. MF-8 suggests a lagoonal environment with low circulation, while MF-9 implies a low-energy, shallow subtidal lagoonal setting with extensive bioturbation, peloids, benthic foraminifera, and gastropods [65].
5.2. Diagenetic History and Sequence Stratigraphy
The diagenetic history of the Samana Suk Formation is characterized by a series of processes and products that have influenced the sedimentary rocks. After sediment deposition and early grain settlement, a microbial activity played a significant role in filling grain pores with micrite and forming micrite envelopes around ooids and other allochems. Endolithic fungi, algae, and bacteria are believed to be responsible for this micritization process [59,66,67]. The extensive micritization observed in the formation indicates a slow sedimentation rate, allowing ample time for blue-green algae to transform grains before burial [68]. Micritization varies across different horizons, with some mudstones exhibiting more extensive micritization compared to grainstones and dolostones. Thin-section studies have revealed ooids and bioclasts in various stages of micritization, often displaying a radial pattern that extends throughout the entire cortex. Bacterial boring can lead to the complete loss of primary particle texture and subsequent micritization [69,70].
Additionally, diagenetic processes such as calcitization of dolomite, dedolomitization, and early aragonite dissolution have played a role in the formation. Calcitization occurs due to changes in pore water chemistry from marine to meteoric composition, resulting in the transformation of dolomite to calcite [71]. Dissolution of aragonite skeletal detritus, mainly gastropods and bivalves, has been observed, with isopachous bladed and blocky types of cement filling moldic pores, indicating early dissolution. Pressure solution diagenesis, characterized by chemical compaction, occurs as a result of gravity loading or unilateral tectonic stress, leading to the development of microstylolites, sutured seams, and stylolites. Pressure solution dissolution at grain contacts and solution seams or stylolites causes calcite to re-precipitate as cement in surrounding limestone, reducing porosity [72,73,74,75].
Dolomitization is another important diagenetic process observed in the Samana Suk Formation. It is associated with the evaporation of marine pore water, particularly in near-shore environments and the mixed meteoric/marine pore water zone. Dolomitization occurs during a relative sea-level fall when the mixed marine/meteoric pore-water zone shifts landwards. These highly dolomitized zones can impede vertical hydrocarbon flow due to their tight nature and the presence of organic matter from decayed cyanobacteria [13].
Early diagenetic processes and products in the formation vary depending on the system tract. The shelf regions experience the formation of carbonate sediments, often cemented by marine aragonite and/or high-Mg calcite rims and pore-filling cement, during the HST. In the more exposed sections of the ramp and platform sediments, meteoric water flow influences the diagenetic processes, while deeper and more buried regions may undergo marine pore-water diagenesis. The variation in pore-water composition is attributed to the “floating” of meteoric waters over denser marine pore waters [76]. As the HST deposits become subaerial, meteoric water percolation leads to the dissolution of marine grains and types of cement, forming karstic structures as they reach the sequence boundary [77,78]. Carbonate deposits along the TST and approaching the maximum flooding surface (MFS) exhibit increased marine carbonate types of cement, such as aragonite/high-Mg calcite rims and syntaxial overgrowths, as well as dolomitization. This is attributed to the migration of the marine pore-water zone into the basin and the mixing of meteoric and seawater in the sediments [15].
The diagenetic sequence of the Samana Suk Formation Involves four settings: marine, mixed marine-meteoric, burial, and uplifting [64]. Micritization occurred during early marine diagenesis, influenced by endolithic algal borings [62,79]. Micritization varies across horizons, with extensive micritization in mudstones. Ooids and bioclasts show radial micritization patterns. Dolomitization likely happened in mixed marine-meteoric water. Calcitization of dolomite to calcite is common below the sequence boundary. Early dissolution of aragonite skeletal debris is observed, and moldic pores are filled with isopachous bladed and blocky cements. Pressure-solution diagenesis, driven by gravity and tectonic stress, leads to chemical compaction, microstylolite development, and concentration of dolomite and quartz along seams. Burial diagenesis is marked by fractures, grain distortion, stylolites, and cementation. Dissolution and cementation occur during both initial deposition and subsequent uplift [80].
Sequence stratigraphy is crucial for understanding the deposition and pore development in carbonates and is essential for reservoir evaluation. Carbonates are more susceptible to sequential changes compared to siliciclastics due to their unstable mineralogy, making even small sea-level fluctuations capable of altering pore-water chemistry and pore types [20]. The Samana Suk Formation consists of three depositional settings: open marine, lagoon, and beach. Shah [34] suggested that the formation was deposited around 10 million years ago (170–160 Ma) based on biostratigraphic evidence. The presence of different facies at varying depths within the vertical stratigraphic column indicates sea-level fluctuations and the occurrence of both deeper and shallower environments. Additionally, the formation exhibits HST and TST, which were marked based on microfacies and field evidence. The formation comprises calm lagoonal deposits, including Mudstone, Dolo-Mudstone, and Bioclastic Mud-Wackestone microfacies, indicating a sea-level lowstand during HST. A transition to retrogradational Mudstone deposition signifies the onset of TST.
6. Conclusions
This study conducted a detailed analysis of the sedimentology, diagenesis, and sequence stratigraphy of the Middle Jurassic Samana Suk Formation in the Hazara Basin of northern Pakistan. Two sections, Mera Rehmat and Por Miana, were specifically studied to unravel the complex geological processes within the formation. The examination of microfacies in the studied sections identified nine distinct depositional textures, ranging from mudstone to wackestone, packstone, and grainstone. These variations indicate the presence of different inner ramp environments, including open marine, lagoon, and coastal settings. Petrographic investigations provided insights into the diagenetic processes that have affected the formation. The identified diagenetic processes include micritization, cementation, dissolution, compaction, neomorphism, and dolomitization. Six different cementation types were identified, and the patterns of dolomitization varied, particularly highlighting lagoonal environments and mudstone replacement. This study also conducted a stratigraphic sequence analysis, which revealed interesting patterns within the Samana Suk Formation. The high-stand system tract was characterized by mudstones, pelloidal grainstones, and dolomitized mudstones, indicating periods of high sea level. On the other hand, the transgressive system tract displayed ooidal grainstones, pelloidal packstones, and pel-bioclastic grainstones, representing transgression and inundation of previously exposed areas. One significant finding of this study was the impact of diagenesis on reservoir quality parameters, specifically porosity, and permeability. The various diagenetic processes, cementation types, and dolomitization patterns significantly altered the pore network within the formation. This highlights the importance of considering diagenesis when assessing the Samana Suk Formation as a potential hydrocarbon reservoir. Overall, this research provides a comprehensive understanding of the sedimentology, diagenesis, and sequence stratigraphy of the Middle Jurassic Samana Suk Formation. The findings contribute to our knowledge of similar carbonate reservoirs globally and can enhance the exploration and development of hydrocarbon resources in comparable depositional environments. The results presented in this study are precise, coherent, consistent, and clear, providing valuable insights into the geological processes within the formation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.S. and S.Q.; methodology, S.Q., M.M.S. and H.T.J.; software, S.Q., M.M.S., H.T.J. and A.S.; validation, M.M.S. and H.T.J.; formal analysis, S.Q., M.M.S. and A.S.; investigation, S.Q., M.M.S., H.T.J., G.K., A.S. and E.B.; resources, M.M.S.; data curation, S.Q. and M.M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Q. and M.M.S.; writing—review and editing, H.T.J., M.M.S., G.K., A.S. and E.B.; visualization, M.M.S.; supervision, M.M.S.; project administration, M.M.S.; funding acquisition, G.K., and H.T.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this work is available on request to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lucia, F.J. Petrophysical rock properties. In Carbonate Reservoir Characterization: An Integrated Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ahr, W.M. Geology of Carbonate Reservoirs: The Identification, Description and Characterization of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Carbonate Rocks; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Beigi, M.; Jafarian, A.; Javanbakht, M.; Wanas, H.A.; Mattern, F.; Tabatabaei, A. Facies analysis, diagenesis and sequence stratigraphy of the carbonate-evaporite succession of the Upper Jurassic Surmeh Formation: Impacts on reservoir quality (Salman Oil Field, Persian Gulf, Iran). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 129, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaupp, R.; Matter, A.; Platt, J.; Ramseyer, K.; Walzebuck, J. Diagenesis and fluid evolution of deeply buried Permian (Rotliegende) gas reservoirs, northwest Germany. AAPG Bull. 1993, 77, 1111–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzullo, S.J. Diagenesis in a sequence-stratigraphic setting: Porosity evolution in periplatform carbonate reservoirs, Permian Basin, Texas and New Mexico. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1994, 11, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiatt, E.E.; Kyser, T.K. Links between depositional and diagenetic processes in basin analysis: Porosity and permeability evolution in sedimentary rocks. In Fluids Basin Evolution; Short Course; Mineralogical Association of Canada: Québec City, QC, Canada, 2000; Volume 28, pp. 63–92. [Google Scholar]
- Janjuhah, H.T.; Salim, A.M.A.; Ghosh, D.P.; Wahid, A. Diagenetic process and their effect on reservoir quality in Miocene carbonate reservoir, Offshore, Sarawak, Malaysia. In ICIPEG 2016, Proceedings of the International Conference on Integrated Petroleum Engineering and Geosciences, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–17 August 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 545–558. [Google Scholar]
- Posamentier, H.W.; Vail, P.R. Eustatic controls on clastic deposition II—Sequence and systems tract models. In Sea-Level Changes: An Integrated Approach; Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Posamentier, H., Van Wagoner, J., Ross, C.A., Kendall, C.G., Eds.; Society for Sedimentary Geology: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wagoner, J.C.; Mitchum, R.M.; Campion, K.M.; Rahmanian, V.D. Siliciclastic Sequence Stratigraphy in Well Logs, Cores, and Outcrops: Concepts for High-Resolution Correlation of Time and Facies; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, D.; Myers, K.J. Sequence Stratigraphy; Black Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Posamentier, H.W.; Allen, G.P. Siliciclastic Sequence Stratigraphy—Concepts and Applications; SEPM Concepts in Sedimentology and Paleontology; SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1999; Volume 7, 210p. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Mehrabi, H.; Enayati-Bidgoli, A.H.; Omidvar, M. Coupled imprints of tropical climate and recurring emergence on reservoir evolution of a mid Cretaceous carbonate ramp, Zagros Basin, southwest Iran. Cretac. Res. 2012, 37, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, A.A.; Mørk, A.; Emadi, M.A. Sequence stratigraphically controlled diagenesis governs reservoir quality in the carbonate Dehluran Field, southwest Iran. Pet. Geosci. 2006, 12, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, S.; Ketzer, J.M.; De Ros, L.F. Spatial and temporal distribution of diagenetic alterations in siliciclastic rocks: Implications for mass transfer in sedimentary basins. Sedimentology 2000, 47, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.E. Carbonate diagenesis and sequence stratigraphy. In Sedimentology Review 1; Wright, V.P., Ed.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1993; pp. 51–72. [Google Scholar]
- South, D.L.; Talbot, M.R. The sequence stratigraphic framework of carbonate diagenesis within transgressive fan-delta deposits: Sant Llorenç del Munt fan-delta complex, SE Ebro Basin, NE Spain. Sediment. Geol. 2000, 138, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketzer, J.M.; Holz, M.; Morad, S.; Al-Aasm, I.S. Sequence stratigraphic distribution of diagenetic alterations in coal-bearing, paralic sandstones: Evidence from the Rio Bonito Formation (early Permian), southern Brazil. Sedimentology 2003, 50, 855–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, S.; Tucker, M.E. Diagenesis of Barremian-Aptian platform carbonates (the Urgonian Limestone Formation of SE France): Near-surface and shallow-burial diagenesis. Sedimentology 1995, 42, 853–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booler, J.; Tucker, M.E. Distribution and geometry of facies and early diagenesis: The key to accommodation space variation and sequence stratigraphy: Upper Cretaceous Congost Carbonate platform, Spanish Pyrenees. Sediment. Geol. 2002, 146, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, S.; Al-Aasm, I.S.; Nader, F.H.; Ceriani, A.; Gasparrini, M.; Mansurbeg, H. Impact of diagenesis on the spatial and temporal distribution of reservoir quality in the Jurassic Arab D and C members, offshore Abu Dhabi oilfield, United Arab Emirates. GeoArabia 2012, 17, 17–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjuhah, H.T.; Alansari, A.; Ghosh, D.P.; Bashir, Y. New approach towards the classification of microporosity in Miocene carbonate rocks, Central Luconia, offshore Sarawak, Malaysia. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2018, 3, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.M.; Rahim, H.U.; Hassan, A.; Mustafa, M.R.; Ahmad, I. Facies control on selective dolomitization and its impact on reservoir heterogeneities in the Samana Suk Formation (middle Jurassic), Southern Hazara Basin (NW Himalaya, Pakistan): An outcrop analogue. Geosci. J. 2020, 24, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, H.-u.; Qamar, S.; Shah, M.M.; Corbella, M.; Martín-Martín, J.D.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Navarro-Ciurana, D.; Lianou, V.; Kontakiotis, G. Processes Associated with Multiphase Dolomitization and Other Related Diagenetic Events in the Jurassic Samana Suk Formation, Himalayan Foreland Basin, NW Pakistan. Minerals 2022, 12, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, H.U.; Shah, M.M.; Corbella, M.; Navarro-Ciurana, D. Diagenetic evolution and associated dolomitization events in the middle Jurassic Samana Suk Formation, Lesser Himalayan Hill Ranges, NW Pakistan. Carbonates Evaporites 2020, 35, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeats, R.S.; Hussain, A. Timing of structural events in the Himalayan foothills of northwestern Pakistan. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1987, 99, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPietro, J.A.; Pogue, K.R. Tectonostratigraphic subdivisions of the Himalaya: A view from the west. Tectonics 2004, 23, TC5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.T.; Moon, C.J. Mineralogy, geochemistry and genesis of the ferromanganese ores from Hazara area, NW Himalayas, northern Pakistan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2004, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.U.; Seno, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Khan, T. Timing of collision of the Kohistan–Ladakh Arc with India and Asia: Debate. Isl. Arc 2011, 20, 308–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Ding, L.; Khan, M.A.; Jadoon, I.A.K.; Haneef, M.; Baral, U.; Cai, F.; Wang, H.; Yue, Y. Tectonic implications of detrital zircon ages from lesser Himalayan Mesozoic-Cenozoic strata, Pakistan. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2018, 19, 1636–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, K.A.; Arif, M.; Basit, A.; Ahmad, S.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Kontakiotis, G. Sedimentological Controls on the Reservoir Characteristics of the Mid-Triassic Tredian Formation in the Salt and Trans-Indus Surghar Ranges, Pakistan: Integration of Outcrop, Petrographic, and SEM Analyses. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Himalayan orogen as constrained by along-strike variation of structural geometry, exhumation history, and foreland sedimentation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 76, 1–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Goswami, A.; Scotese, C.R. The longest voyage: Tectonic, magmatic, and paleoclimatic evolution of the Indian plate during its northward flight from Gondwana to Asia. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 238–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Garzanti, E. Jurassic carbonate microfacies and relative sea-level changes in the Tethys Himalaya (southern Tibet). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 456, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.I. Stratigraphy of Pakistan (memoirs of the geological survey of Pakistan). Geol. Surv. Pak. 2009, 22, 381. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, M.; Naseem, A.A.; Saleem, M.; Rehman, J.u.; Kontakiotis, G.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Khan, E.U.; Antonarakou, A.; Khan, I.; Rehman, A.u. Sedimentary Facies, Architectural Elements, and Depositional Environments of the Maastrichtian Pab Formation in the Rakhi Gorge, Eastern Sulaiman Ranges, Pakistan. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, N.; Chaudhry, M.N. Geology of Hettangian to middle Eocene rocks of Hazara and Kashmir basins, Northwest lesser Himalayas, Pakistan. Geol. Bull. Panjab Univ. 2008, 43, 131–152. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, H.S.; Fayaz, M.; Haneef, M.; Hanif, M.; Jan, I.U.; Gul, B. Microfacies and diagenetic-fabric of the Samana Suk Formation at Harnoi Section, Abbottabad, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Himal. Earth Sci. 2013, 46, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.K.; Lashari, R.A.; Sahito, A.G.; Kontakiotis, G.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Mughal, M.S.; Bilal, A.; Mehmood, T.; Majeed, K.U. Sedimentological and Petrographical Characterization of the Cambrian Abbottabad Formation in Kamsar Section, Muzaffarabad Area: Implications for Proto-Tethys Ocean Evolution. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, A.; Yang, R.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Mughal, M.S.; Li, Y.; Kontakiotis, G.; Lenhardt, N. Microfacies analysis of the Palaeocene Lockhart limestone on the eastern margin of the Upper Indus Basin (Pakistan): Implications for the depositional environment and reservoir characteristics. Depos. Rec. 2023, 9, 152–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basharat, M.; Qasim, M.; Shafique, M.; Hameed, N.; Riaz, M.T.; Khan, M.R. Regolith thickness modeling using a GIS approach for landslide distribution analysis, NW Himalayas. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 2466–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzanti, E. Himalayan ironstones, “superplumes”, and the breakup of Gondwana. Geology 1993, 21, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, A.; Yang, R.; Mughal, M.S.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Zaheer, M.; Kontakiotis, G. Sedimentology and Diagenesis of the Early–Middle Eocene Carbonate Deposits of the Ceno-Tethys Ocean. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, M.Q.; Windley, B.F.; Khan, A. The Waziristan ophiolite, Pakistan; general geology and chemistry of chromite and associated phases. Econ. Geol. 1985, 80, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.; Imraz, M.; Ali, F.; Haneef, M.; Saboor, A.; Iqbal, S.; Ahmad, S. The inner ramp facies of the Thanetian Lockhart Formation, western Salt Range, Indus Basin, Pakistan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 4911–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Shah, M.M.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Trave, A.; Antonarakou, A.; Kontakiotis, G. Multiphase Diagenetic Processes and Their Impact on Reservoir Character of the Late Triassic (Rhaetian) Kingriali Formation, Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan. Minerals 2022, 12, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Munir, M.u.H.; Adatte, T.; Riaz, M.T.; Basharat, M.; Ahmed, K.S.; Sarfraz, Y.; Khan, J.; Mughal, M.S. Multi-proxy approach of the stratigraphy, geochemistry, and sedimentology of Eocene Margalla Hill Limestone: Case study from Muzaffarabad area, Sub-Himalayas, Pakistan. Geol. J. 2022, 57, 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Khan, J.; Hanif, M.; Baumgartner-Mora, C.; Sarfraz, Y.; Ahmed, K.S.; Riaz, M.T.; Baumgartner, P.O.; ul Hassan Munir, M.; Wazir, A. Eocene nannofossils and paleoenvironmental reconstruction of the Kuldana Formation in Yadgar area, Muzaffarabad, northern Pakistan. Palaeoworld 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critelli, S.; Garzanti, E. Provenance of the lower Tertiary Murree redbeds (Hazara-Kashmir Syntaxis, Pakistan) and initial rising of the Himalayas. Sediment. Geol. 1994, 89, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.K.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Shahzad, S.M.; Kontakiotis, G.; Saleem, M.H.; Khan, U.; Zarkogiannis, S.D.; Makri, P.; Antonarakou, A. Depositional Sedimentary Facies, Stratigraphic Control, Paleoecological Constraints, and Paleogeographic Reconstruction of Late Permian Chhidru Formation (Western Salt Range, Pakistan). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, J.A.D. A modified staining technique for carbonates in thin section. Nature 1965, 205, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, R.J. Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional textures. In Classification of Carbonate Rocks—A Symposium; AAPG Datapages Inc.: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Embry, A.F.; Klovan, J.E. A late Devonian reef tract on northeastern Banks Island, NWT. Bull. Can. Pet. Geol. 1971, 19, 730–781. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.L. The lower carboniferous Waulsortian facies. In Carbonate Facies in Geologic History; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975; pp. 148–168. [Google Scholar]
- Buxton, M.W.N.; Pedley, H.M. Short Paper: A standardized model for Tethyan Tertiary carbonate ramps. J. Geol. Soc. 1989, 146, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flügel, E.; Munnecke, A. Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks: Analysis, Interpretation and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 976. [Google Scholar]
- Plumley, W.J.; Risley, G.A.; Graves Jr, R.W.; Kaley, M.E. Energy index for limestone interpretation and classification. In Classification of Carbonate Rocks—A Symposium; AAPG Datapages Inc.: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Janjuhah, H.T.; Alansari, A. Offshore carbonate facies characterization and reservoir quality of Miocene rocks in the southern margin of South China Sea. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2020, 94, 1547–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Kominz, M.; Reuning, L.; Gallagher, S.J.; Takayanagi, H.; Ishiwa, T.; Knierzinger, W.; Wagreich, M. Quantitative compaction trends of Miocene to Holocene carbonates off the west coast of Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 68, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjuhah, H.T.; Alansari, A.; Santha, P.R. Interrelationship between facies association, diagenetic alteration and reservoir properties evolution in the Middle Miocene carbonate build up, Central Luconia, Offshore Sarawak, Malaysia. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, B.U.; Hardenbol, J.; Vail, P.R. Mesozoic and Cenozoic chronostratigraphy and cycles of sea-level change. In Sea-Level Changes: An Integrated Approach; Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Posamentier, H., Van Wagoner, J., Ross, C.A., Kendall, C.G., Eds.; Society for Sedimentary Geology: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.M.; Ahmed, I. Diagenetic Studies and Its Implications on the Reservoir Character of the Anisian-Norian (Triassic) Kingriali Formation, Salt Range (Pakistan). In Proceedings of the AAPG/SEG International Conference & Exhibition, Cancun, Mexico, 6–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wadood, S.A.; Boli, G.; Xiaowen, Z.; Hussain, I.; Yimin, W. Recent development in the application of analytical techniques for the traceability and authenticity of food of plant origin. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngia, N.R.; Hu, M.; Gao, D. Hydrocarbon reservoir development in reef and shoal complexes of the Lower Ordovician carbonate successions in the Tazhong Uplift in central Tarim basin, NW China: Constraints from microfacies characteristics and sequence stratigraphy. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 2693–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadood, B.; Khan, S.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Ahmad, S.; Jiao, X. Sequence Stratigraphic Framework of the Jurassic Samana Suk Carbonate Formation, North Pakistan: Implications for Reservoir Potential. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Movahed, F.; Aleali, M.; Ghazanfari, P. Facies Analysis, Depositional Environment and Diagenetic Features of the Qom Formation in the Saran Semnan, Central Iran. Open J. Geol. 2016, 6, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathurst, R.G.C. Boring algae, micrite envelopes and lithification of molluscan biosparites. Geol. J. 1966, 5, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobluk, D.R.; Risk, M.J. Micritization and carbonate-grain binding by endolithic algae. AAPG Bull. 1977, 61, 1069–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Smosna, R.; Koehler, B. Tidal Origin of a Mississippian Oolite on the West Virginia Dome: Chapter 11. In Mississippian Oolites and Modern Analogs; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, C.T. Grain susceptibility to the effects of microboring: Implications for the preservation of skeletal carbonates. Sedimentology 1998, 45, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjuhah, H.T.; Kontakiotis, G.; Wahid, A.; Khan, D.M.; Zarkogiannis, S.D.; Antonarakou, A. Integrated porosity classification and quantification scheme for enhanced carbonate reservoir quality: Implications from the miocene malaysian carbonates. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjuhah, H.T.; Salim, A.M.A.; Alansari, A.; Ghosh, D.P. Presence of microporosity in Miocene carbonate platform, Central Luconia, offshore Sarawak, Malaysia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathurst, R.G.C. Carbonate Sediments and Their Diagenesis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Halley, R.B.; Scholle, P.A. Radiaxial fibrous calcite as early-burial, open-system cement: Isotopic evidence from Permian of China. AAPG Bull. 1985, 69, 261–262. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, C.H. Diagenetic environments of porosity modification and tools for their recognition in the geologic record. Carbonate Reserv. Porosity Evol. Diagenesis A Seq. Stratigr. Framew. Dev. Sedimentol. 2001, 55, 61–88. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, M.K.; Janjuhah, H.; Sanjuan, J.; Maalouf, E. Impact of diagenesis and pore aspects on the petrophysical and elastic properties of carbonate rocks from southern Lebanon. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchon, B.; Friedman, I. Geochemistry and origin of formation waters in the western Canada sedimentary basin—I. Stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1969, 33, 1321–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Hunter, I.G. Messinian (late Miocene) karst on Grand Cayman, British West Indies; an example of an erosional sequence boundary. J. Sediment. Res. 1994, 64, 531–541. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.W.; Snyder, S.W.; Hine, A.C. High-resolution seismic expression of karst evolution within the Upper Floridan aquifer system; Crooked Lake, Polk County, Florida. J. Sediment. Res. 1994, 64, 232–244. [Google Scholar]
- Janjuhah, H.T.; Sanjuan, J.; Alqudah, M.; Salah, M.K. Biostratigraphy, Depositional and Diagenetic Processes in Carbonate Rocks from Southern Lebanon: Impact on Porosity and Permeability. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 1668–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Xie, E.; Zhang, Y.; Qing, H.; Luo, X.; Sun, C. Structural Diagenesis in Carbonate Rocks as Identified in Fault Damage Zones in the Northern Tarim Basin, NW China. Minerals 2019, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).