Behavioural Responses to Ultrasound Antifouling Systems by Adult Solitary Ascidians
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
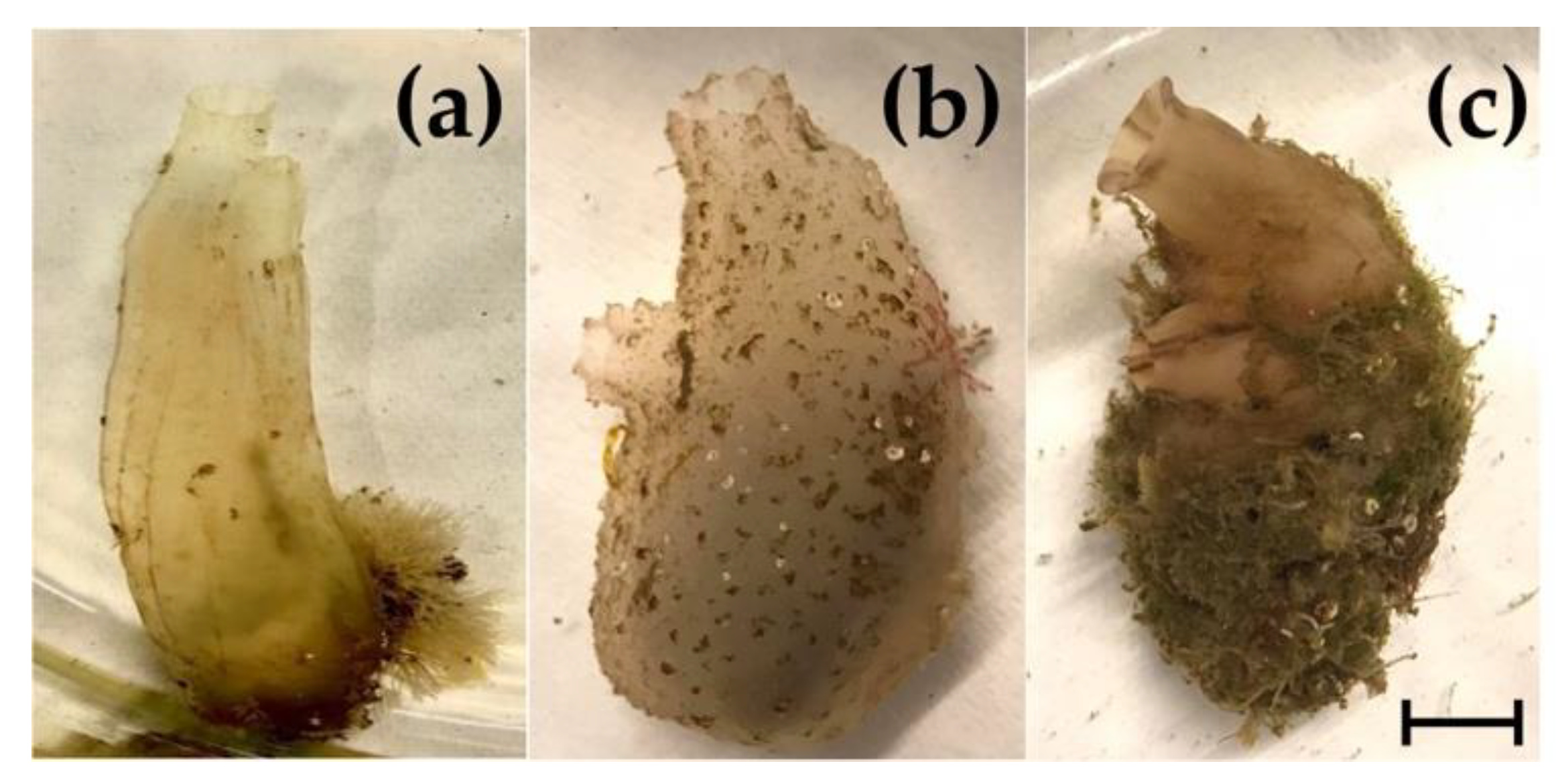
2.1. Animals
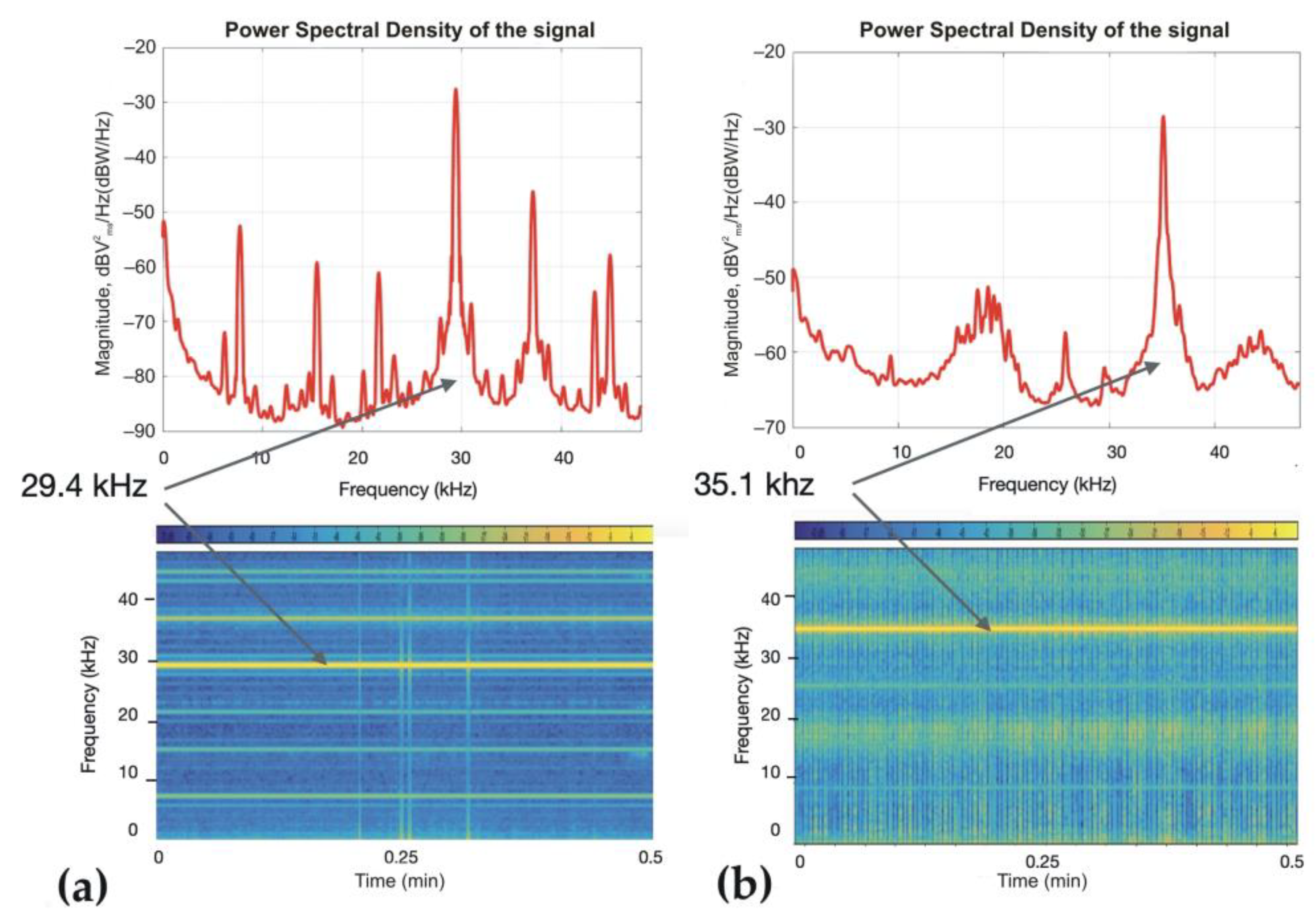
2.2. Ultrasound Devices
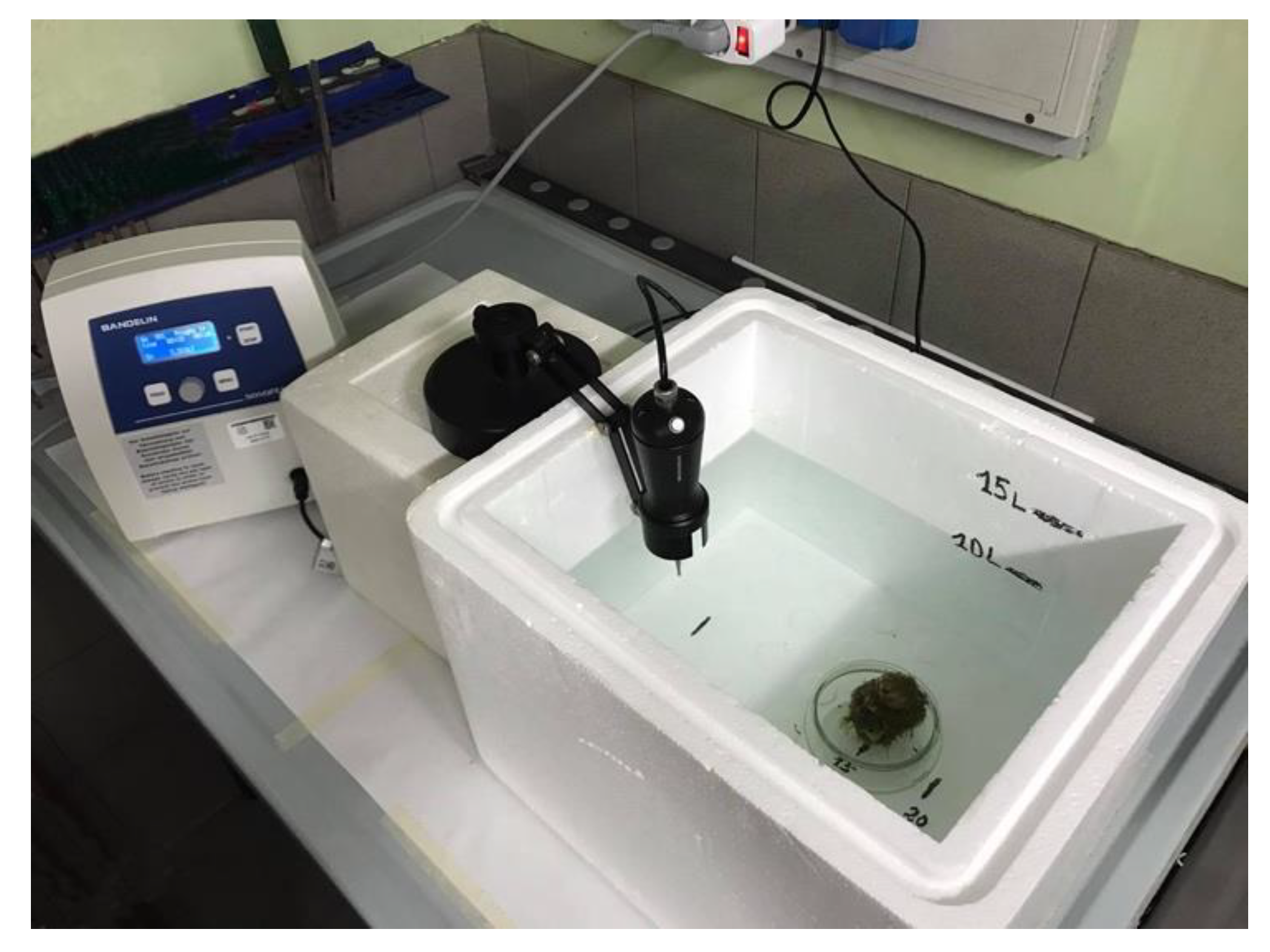
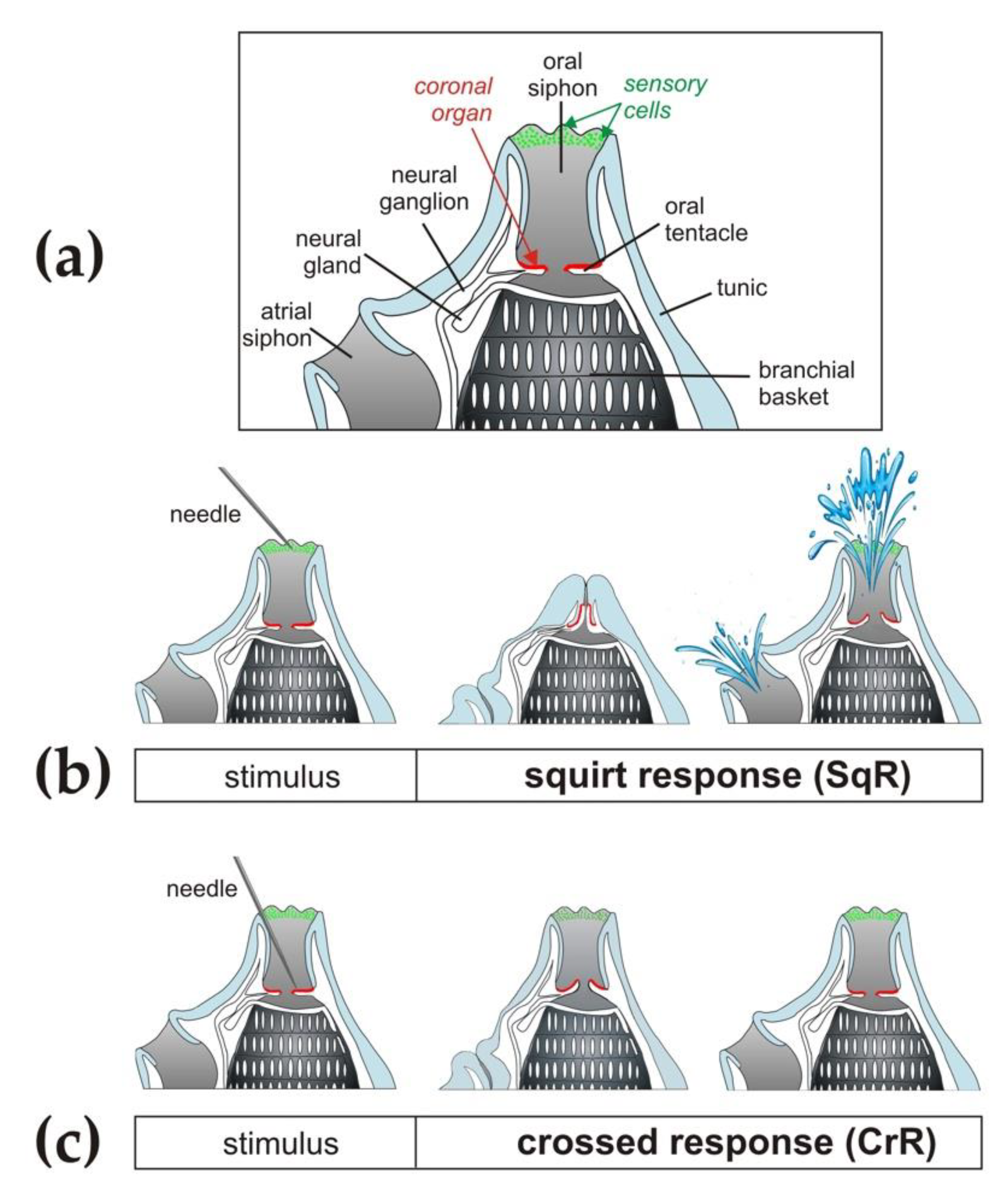
2.3. Experimental Setup
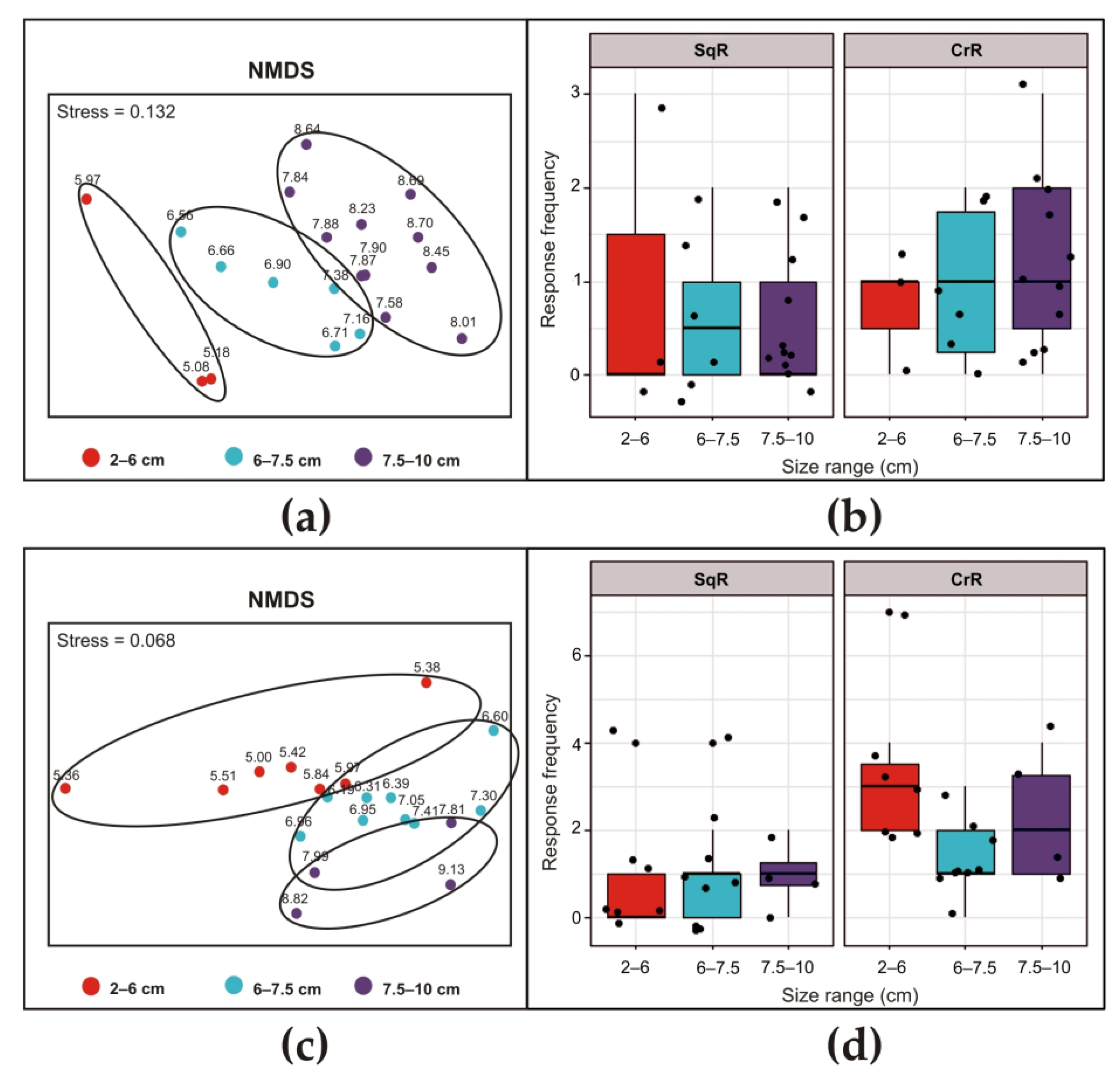
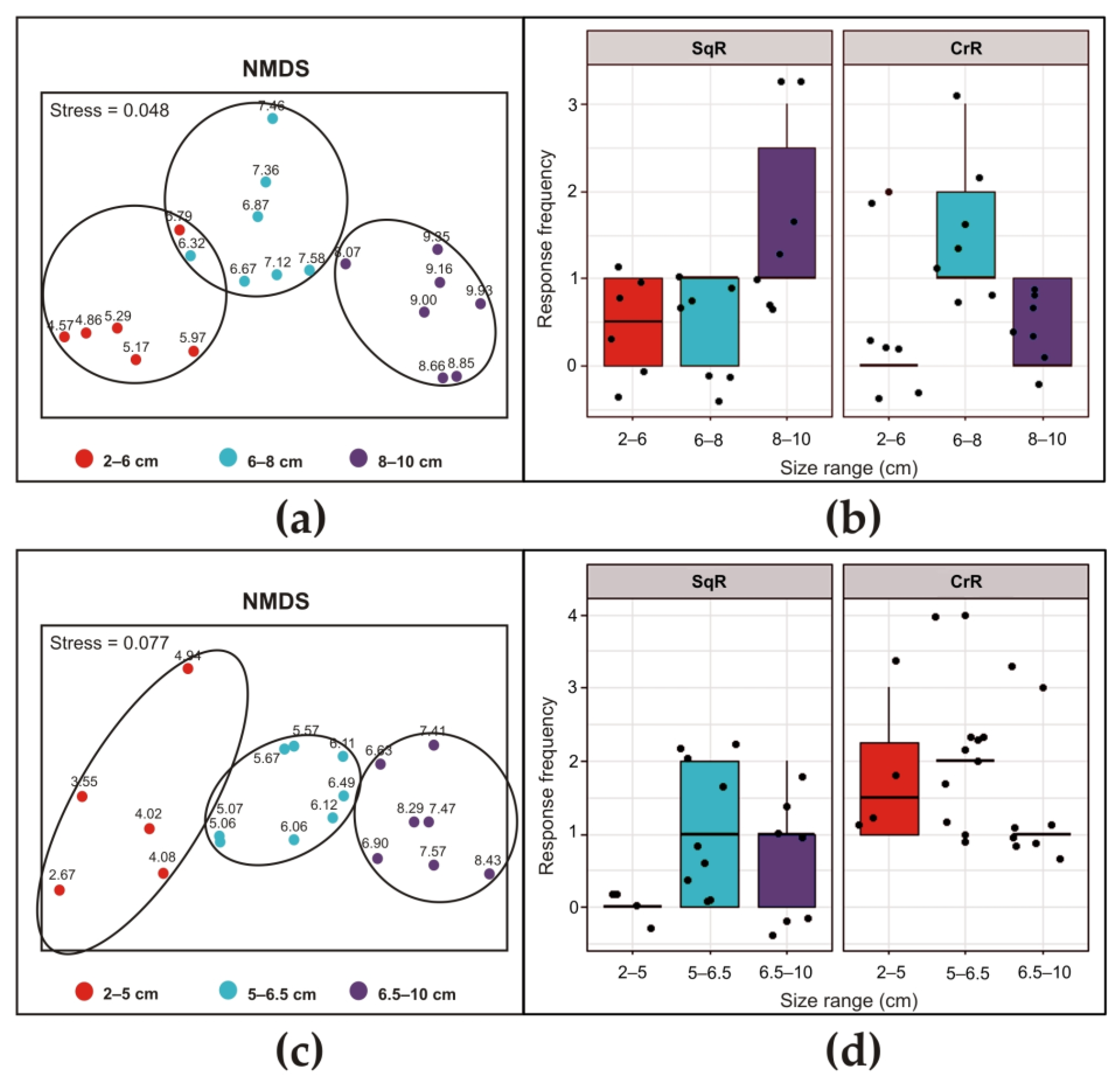
2.4. Statistical Analysis
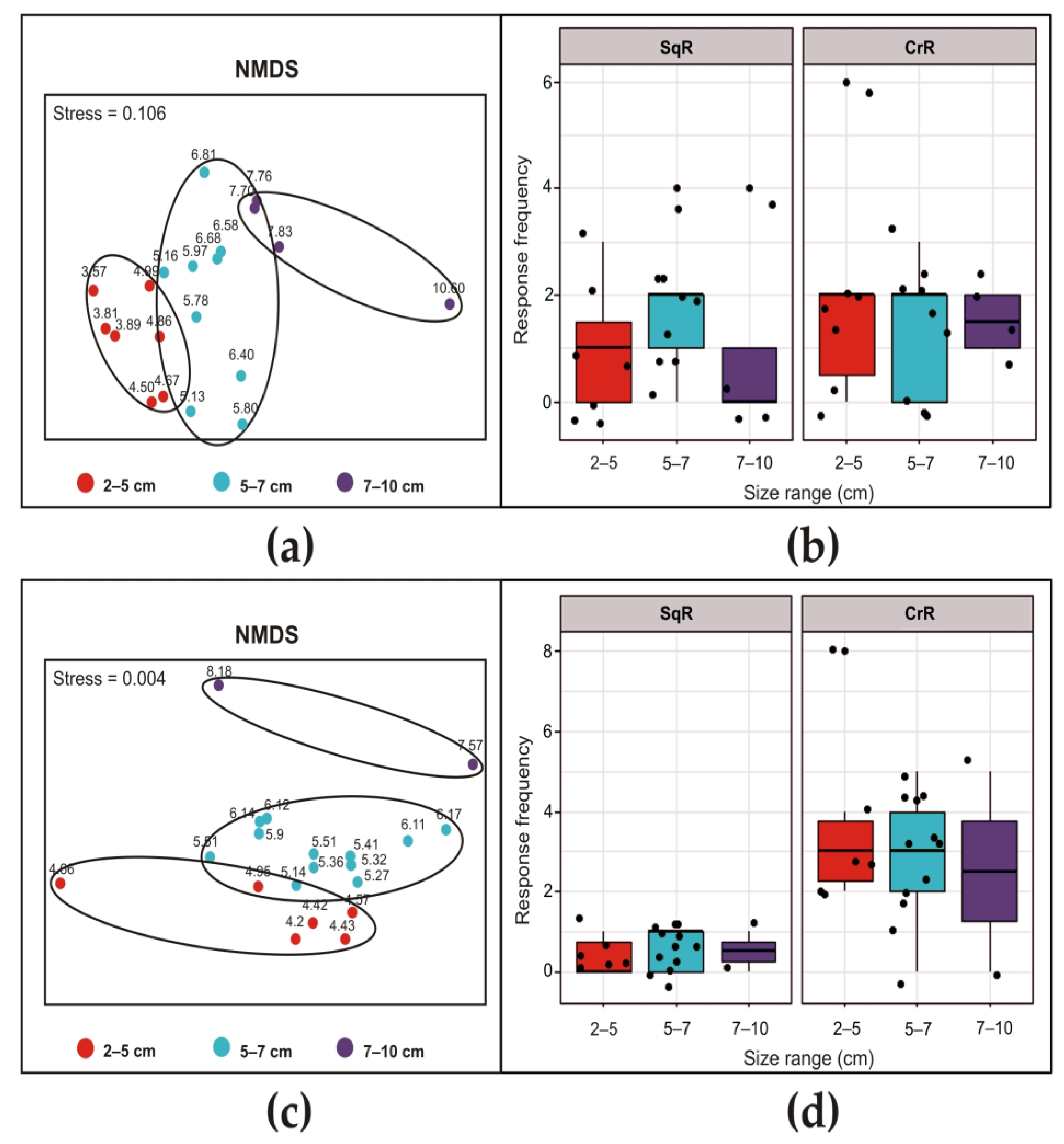
3. Results
3.1. Siphon Responses in the Absence of Stimuli
3.2. Siphon Responses after Exposure to a Brief Ultrasound Input
3.2.1. Ciona intestinalis
3.2.2. Ascidiella aspersa
3.2.3. Styela plicata
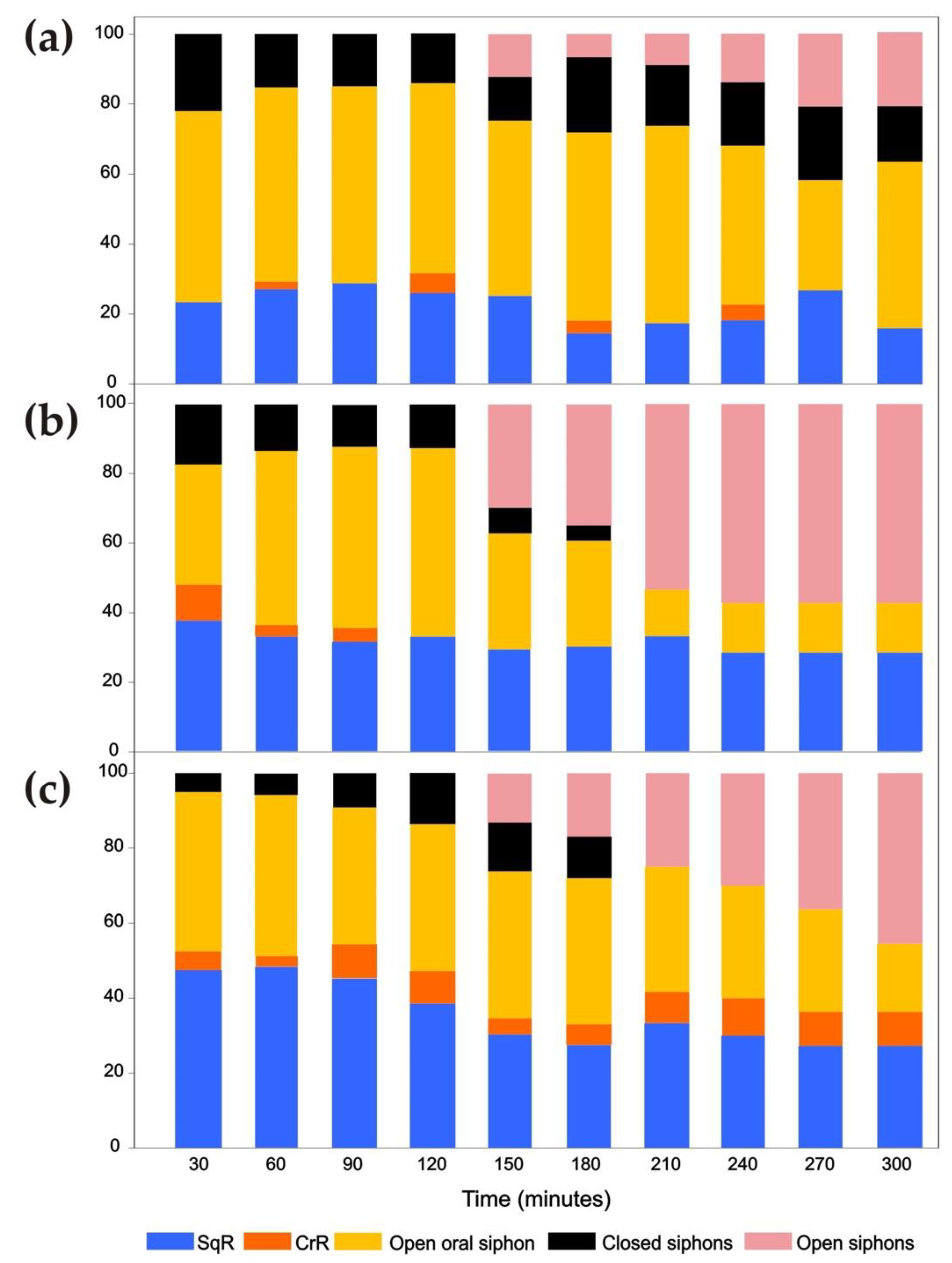
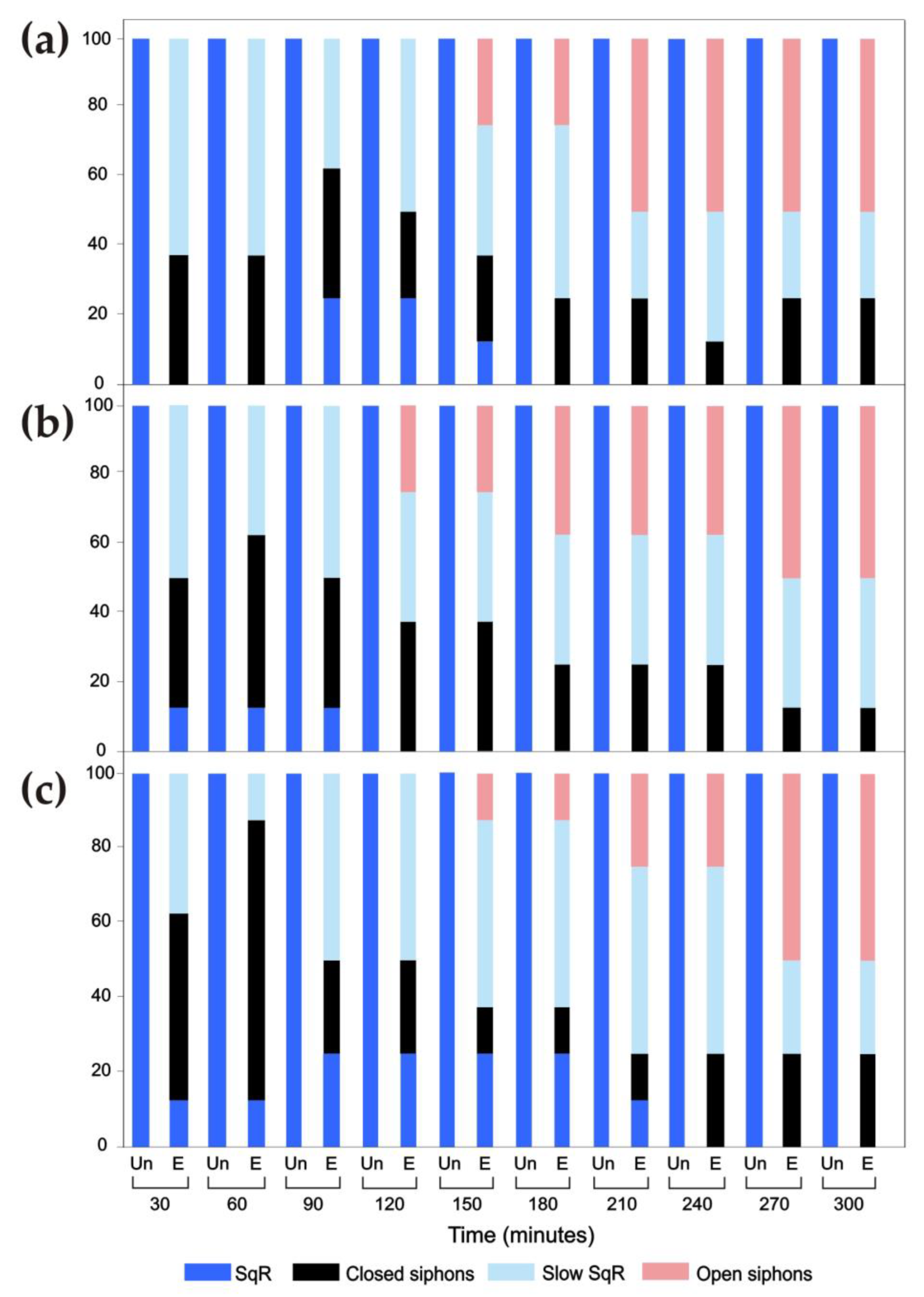
3.3. Siphon Responses during Continuous Ultrasound Exposure
3.4. Responses of the Oral Siphon to a Mechanical Stimulus during Continuous Ultrasound Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pavan, G. Bioacustica e ecologia acustica. In Acustica. Fondamenti e Applicazioni; Spagnolo, R., Ed.; UTET Università: Turin, Italy, 2015; pp. 803–828. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.M.; Chapuis, L.; Collin, S.P.; Costa, D.P.; Devassy, R.P.; Eguiluz, V.M.; Erbe, C.; Gordon, T.A.C.; Halpern, B.S.; Harding, H.R.; et al. The soundscape of the Anthropocene Ocean. Science 2021, 371, eaba4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- William, R.; Wright, A.J.; Ashe, E.; Blight, L.K.; Bruintjes, R.; Canessa, R.; Clark, C.W.; Cullis-Suzuki, S.; Dakin, D.T.; Erbe, C.; et al. Impacts of anthropogenic noise on marine life: Publication patterns, new discoveries, and future directions in research and management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 115, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D. Technology evolution and advances in fisheries acoustic. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2011, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, J.A. Anthropogenic and natural sources of ambient noise in the ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 395, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C. Effects of underwater noise on marine mammals. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 730, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Southall, B.L.; Bowles, A.E.; Ellison, W.T.; Finneran, J.J.; Gentry, R.L.; Greene, C.R., Jr.; Kastak, D.; Ketten, D.R.; Miller, J.H.; Nachtigall, P.E.; et al. Marine mammal noise-exposure criteria: Initial scientific recommendations. Bioacoustics 2008, 17, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacek, D.P.; Thorne, L.H.; Johnston, D.W.; Tyack, P.L. Responses of cetaceans to anthropogenic noise. Mamm. Rev. 2007, 37, 81–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilgart, L.S. The impacts of anthropogenic ocean noise on cetaceans and implications for management. Can. J. Zool. 2007, 85, 1091–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C.; Dunlop, R.; Dolman, S. Effects of noise on marine mammals. In Effects of Anthropogenic Noise on Animals; Slabbekoorn, H., Dooling, R., Popper, A., Fay, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 66, pp. 277–309. [Google Scholar]
- Ketten, D.R. Marine mammal auditory systems: A summary of audiometric and anatomical data and implications for underwater acoustic impacts. Polarforschung 2004, 72, 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Popper, A.N. Effects of Mid- and High-Frequency Sonars on Fish; Naval Undersea Warfare Center Division (U.S.A.): Providence, RI, USA, 2008; Contract No. N66604-07M-6056. [Google Scholar]
- Kunc, H.P.; McLaughlin, K.E.; Schmidt, R. Aquatic noise pollution: Implications for individuals, populations, and ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichegru, L.; Nyengera, R.; McInnes, A.M.; Pistorius, P. Avoidance of seismic survey activities by penguins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popper, A.N.; Hawkins, A.D. An overview of fish bioacoustics and the impacts of anthropogenic sounds on fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 692–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Franco, E.; Pierson, P.; Di Iorio, L.; Calò, A.; Cottalorda, J.M.; Derijard, B.; Guidetti, P. Effects of marine noise pollution on Mediterranean fishes and invertebrates: A review. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2020, 159, 111450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morely, E.L.; Jones, G.; Radford, A.N. The importance of invertebrates when considering the impacts of anthropogenic noise. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20132683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, M.; Kaifu, K.; Mooney, T.A.; Nedelec, S.L.; Olivier, F.; Radford, A.N.; Vazzana, M.; Wale, M.A.; Semmens, J.M.; Simpson, S.D.; et al. Marine invertebrates and noise. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1129057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, K.; Popper, A.N.; Hawkins, A.D.; Akamatsu, T.; André, M.; Branstetter, B.K.; Lammers, M.; Radford, C.A.; Stansbury, A.L.; Aran Mooney, T. Auditory sensitivity in aquatic animals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 3097–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wale, M.A.; Briers, R.A.; Diele, K. Marine invertebrate anthropogenic noise research: Trends in methods and future directions. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2021, 173, 112958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charifi, M.; Sow, M.; Ciret, P.; Benomar, S.; Massabuau, J.C. The sense of hearing in the pacific oyster, Magallana gigas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, A.N.; Salmon, M.; Horch, K.W. Acoustic detection and communication by decapod crustaceans. J. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 187A, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Soto, N.A. Peer-reviewed studies on the effects of anthropogenic noise on marine invertebrates: From scallop larvae to giant squid. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II; Popper, A., Hawkins, A., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 875, pp. 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, T.A.; Samson, J.E.; Schlunk, A.D.; Zacarias, S. Loudness-dependent behavioural responses and habituation to sound by the longfin squid (Doryteuthis pealeii). J. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 202A, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewtrell, J.L.; McCauley, R.D. Impact of air gun noise on the behaviour of marine fish and squid. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2012, 64, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.R.; Mann, D.A.; Kimbro, D.L. Predatory fish sounds can alter crab foraging behaviour and influence bivalve abundance. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20140715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solan, M.; Hauton, C.; Godbold, J.A.; Wood, C.L.; Leighton, T.G.; White, P. Anthropogenic sources of underwater sound can modify how sediment-dwelling invertebrates mediate ecosystem properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillis, A.; Eggleston, D.B.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R. Oyster larvae settle in response to habitat-associated underwater sounds. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittenberger, A.; van Stelt, R.C. Artificial structures in harbours and their associated ascidian fauna. Aquat. Invasions 2011, 6, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsin, R.L. The ship hull fouling penalty. Biofouling 2003, 19, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazue, G.; Viennet, R.; Hihn, J.Y.; Carpentier, L.; Devidal, P.; Albaina, I. Large-scale ultrasonic cleaning system: Design of a multi-transducer device for boat cleaning (20 kHz). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.P.; Bendick, J.A.; Holm, E.R.; Hertel, W.M. Economic impact of biofouling on a naval surface ship. Biofouling 2011, 27, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H.; Scardino, A.J.; Dylejko, P.G.; Fletcher, L.E.; Juniper, R. The effect of vibration frequency and amplitude on biofouling deterrence. Biofouling 2013, 29, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.; Rigby, G.; Gollasch, S.; Voight, M.; Hallegraeff, G.M.; McCollin, T.; Jelmert, A. Preventive treatment and control techniques for ballast water. In Invasive Aquatic Species of Europe. Distribution, Impacts and Management; Leppakoski, E., Gollasch, S., Olenin, S., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 484–507. [Google Scholar]
- Legg, M.; Yücel, M.K.; Garcia del Carrelan, I.; Kappatos, V.; Selcuk, C.; Gan, T.H. Acoustic methods for biofouling control: A review. Ocean Eng. 2015, 103, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.F.; Lee, H.P.; Chaw, K.C.; Miklas, J.; Teo, S.L.M.; Dickinson, G.H.; Birch, W.R.; Khoo, B.C. Effect of ultrasound on cyprids and juvenile barnacles. Biofouling 2011, 27, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Lee, H.P.; Khoo, B.C. Inhibitory effect of ultrasound on barnacle (Amphibalanus amphitrite) cyprid settlement. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 409, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Lee, H.P.; Teo, S.L.M.; Khoo, B.C. Inhibition of barnacle cyprid settlement using low frequency and intensity ultrasound. Biofouling 2012, 28, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, N.; Chakravarty, P.; Khandeparker, L.; Anil, A.C.; Pandit, A.B. Quantification of the energy required for the destruction of Balanus amphitrite larva by ultrasonic treatment. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2010, 90, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, H.; Takahashi, K.; Kanamaru, D. Inhibitory effect of ultrasonic waves on the larval settlement of the barnacle, Balanus amphitrite in the laboratory. Mar. Fouling 1995, 12, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.D.; Radford, A.N.; Tickle, E.J.; Meekan, M.G.; Jeffs, A.G. Adaptive avoidance of reef noise. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilgart, L.S. The Impact of Ocean Noise Pollution on Fish and Invertebrates; Report by Ocean Care & Dalhousie University; Ocean Care: Wädenswil, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Callow, J.A.; Callow, M.E. Trends in the development of environmentally friendly fouling-resistant marine coatings. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 210–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.N.; Ambrosio, L.J.; Edwards, C. Anthropogenic sound in the sea: Are ascidians affected? Gulf Caribb. Res. 2021, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S. The physiology of the Ascidia atra Leseuer. I. General physiology. J. Exp. Zool. 1918, 25, 229–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S. The physiology of the Ascidia atra Leseuer. II. Sensory physiology. J. Exp. Zool. 1918, 25, 261–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, E.C. The physiology of the nervous system of the tunicates. I: The relation of the nerve ganglion to sensory response. J. Exp. Zool. 1919, 28, 307–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, L.; Pennati, R. Tunicata. In Structure and Evolution of Invertebrate Nervous Systems; Schmidt-Rhaesa, A., Harzsch, S., Purschke, G., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 699–718. [Google Scholar]
- Fedele, M. Sulla organizzazione e le caratteristiche funzionali dell’attività nervosa dei Tunicati. I. Ricerche sul sistema nervoso periferico degli Ascidiacea. In Atti della Reale Accademia dei Lincei Rendiconti; Classe di Scienze Fisiche Matematiche e Naturali; Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei: Rome, Italy, 1923; Volume 32, pp. 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, R.H. Ciona. In L.M.B.C. Memoirs on Typical British Marine Plants and Animals; University Press of Liverpool: Liverpool, UK, 1953; Volume 35, pp. 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- Mackie, G.O.; Wyeth, R.C. Conduction and coordination in deganglionated ascidians. Can. J. Zool. 2000, 78, 1626–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burighel, P.; Lane, N.J.; Gasparini, F.; Tiozzo, S.; Zaniolo, G.; Carnevali, M.D.; Manni, L. Novel, secondary sensory cell organ in ascidians: In search of the ancestor of the vertebrate lateral line. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 461, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burighel, P.; Caicci, F.; Manni, L. Hair cells in non-vertebrate models: Lower chordates and molluscs. Hear. Res. 2011, 273, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, L.; Caicci, F.; Gasparini, F.; Zaniolo, G.; Burighel, P. Hair cells in ascidians and the evolution of lateral line placodes. Evol. Dev. 2004, 6, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, L.; Lane, N.J.; Joly, J.S.; Gasparini, F.; Tiozzo, S.; Caicci, F.; Zaniolo, G.; Burighel, P. Neurogenic and non-neurogenic placodes in ascidians. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2004, 302, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, L.; Mackie, G.O.; Caicci, F.; Zaniolo, G.; Burighel, P. Coronal organ of ascidians and the evolutionary significance of secondary sensory cells in chordates. J. Com. Neurol. 2006, 495, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, G.O.; Burighel, P. The nervous system in adult tunicates: Current research directions. Can. J. Zool. 2005, 83, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigon, F.; Stach, T.; Caicci, F.; Gasparini, F.; Burighel, P.; Manni, L. Evolutionary diversification of secondary mechanoreceptor cells in tunicata. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, L.; Anselmi, C.; Burighel, P.; Martini, M.; Gasparini, F. Differentiation and induced sensorial alteration of the coronal organ in the asexual life of a tunicate. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2018, 58, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, G.O.; Burighel, P.; Caicci, F.; Manni, L. Innervation of ascidian siphons and their responses to stimulation. Can. J. Zool. 2006, 84, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicci, F.; Degasperi, V.; Gasparini, F.; Zaniolo, G.; Del Favero, M.; Burighel, P.; Manni, L. Variability of hair cells in the coronal organ of ascidians (Chordata, Tunicata). Can. J. Zool. 2010, 88, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, R.; Mastrototaro, F. Ascidiacea of the European Waters; Edagricole: Milan, Italy, 2017; pp. 1–430. [Google Scholar]
- Hotta, K.; Dauga, D.; Manni, L. The ontology of the anatomy and development of the solitary ascidian Ciona: The swimming larva and its metamorphosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R. emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 1.8.5. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.6-4. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 2 June 2022).
- Paplou, V.; Schubert, N.; Pyott, S.J. Age-related changes in the cochlea and vestibule: Shared patterns and processes. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 680856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, J.R. The ascidians (Tunicata) from Chindo Islands, Korea. Anim. Syst. Evol. Divers. 1995, 11, 125–145. [Google Scholar]
- Tatián, M.; Schwindt, E.; Lagger, C.; Varela, M.M. Colonization of Patagonian harbours (SW Atlantic) by an invasive sea squirt (Chordata, Ascidiacea). Spixiana 2010, 33, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.B. Habituation of the polychaete Nereis to sudden stimuli. 1. General properties of the habituation process. Anim. Behav. 1960, 8, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burighel, P.; Sorrentino, M.; Zaniolo, G.; Thorndyke, M.C.; Manni, L. The peripheral nervous system of an ascidian, Botryllus schlosseri, as revealed by cholinesterase activity. Invertebr. Biol. 2001, 120, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, G. The response mechanism in ascidians. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 1952, 31, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charifi, M.; Miserazzi, A.; Sow, M.; Perrigault, M.; Gonzalez, P.; Ciret, P.; Benomar, S.; Massabuau, J.C. Noise pollution limits metal bioaccumulation and growth rate in a filter feeder, the pacific oyster Magallana gigas. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.; Cheesman, S.; Breithaupt, T.; Elliott, M. Sensitivity of the mussel Mytilus edulis to substrate-borne vibration in relation to anthropogenically generated noise. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 538, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, T.; Clements, J.C.; Comeau, L.A.; Cervello, G.; Tremblay, R.; Olivier, F.; Chauvaud, L.; Bernier, R.Y.; Lamarre, S.G. Effects of anthropogenic sounds on the behavior and physiology of the Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1104526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trickey, J.S.; Cárdenas-Hinojosa, G.; Rojas-Bracho, L.; Schorr, G.S.; Rone, B.K.; Hidalgo-Pla, E.; Rice, A.; Baumann-Pickering, S. Ultrasonic antifouling devices negatively impact Cuvier’s beaked whales near Guadalupe Island, México. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1005. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varello, R.; Asnicar, D.; Boaga, J.; Cima, F. Behavioural Responses to Ultrasound Antifouling Systems by Adult Solitary Ascidians. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061115
Varello R, Asnicar D, Boaga J, Cima F. Behavioural Responses to Ultrasound Antifouling Systems by Adult Solitary Ascidians. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(6):1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061115
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarello, Roberta, Davide Asnicar, Jacopo Boaga, and Francesca Cima. 2023. "Behavioural Responses to Ultrasound Antifouling Systems by Adult Solitary Ascidians" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 6: 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061115
APA StyleVarello, R., Asnicar, D., Boaga, J., & Cima, F. (2023). Behavioural Responses to Ultrasound Antifouling Systems by Adult Solitary Ascidians. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(6), 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061115









