Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Farmland Using Diverse Models: A Comparative Assessment in the Yellow River Delta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
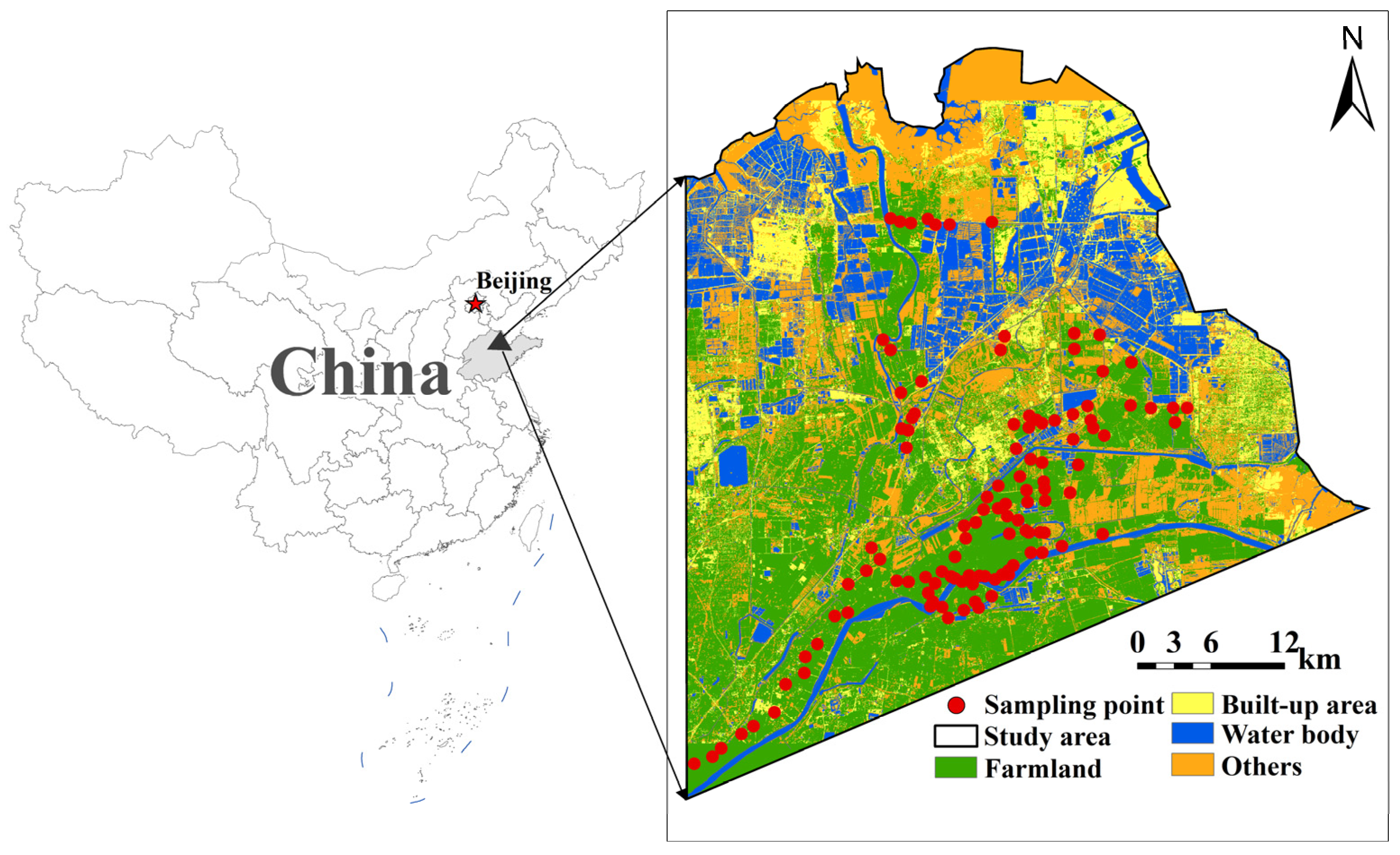
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Auxiliary Data
2.3.1. Terrain
2.3.2. Vegetation
2.3.3. Air Quality
2.3.4. Human Activity
2.4. Source Apportionment Method
2.4.1. PMF
2.4.2. Geographical Detector
2.4.3. XGBoost Model
2.4.4. Structural Equation Model
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Analysis
3.2. Source Apportionment of Heavy Metal in Soil Using the Balance of Evidence Method
3.2.1. Homology Analysis of Soil Heavy Metals
3.2.2. Source Driving Effect for Soil Heavy Metals
3.2.3. Multi-Source Path Analysis for Soil Heavy Metals
4. Discussion
4.1. Response Relationship between Sources and Soil Heavy Metals
4.2. Limitations and Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marchant, B.P.; Saby, N.; Arrouays, D. A survey of topsoil arsenic and mercury concentrations across France. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, F.; Wang, S.; Nan, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Accumulation, spatio-temporal distribution, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil-corn system around a polymetallic mining area from the Loess Plateau, northwest China. Geoderma 2017, 305, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imseng, M.; Wiggenhauser, M.; Müller, M.; Keller, A.; Frossard, E.; Wilcke, W.; Bigalke, M. The fate of Zn in agricultural soils: A stable isotope approach to anthropogenic impact, soil formation, and soil–plant cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4140–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Huang, B.; He, Y.; Kalkhajeh, Y.K. Assessment of potential health risk of heavy metals in soils from a rapidly developing region of China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2016, 22, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkett, M.O.; Akün, E. Heavy metal contents of contaminated soils and ecological risk assessment in abandoned copper mine harbor in Yedidalga, Northern Cyprus. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kumar, A.; Mehra, R.; Mishra, R. Human health risk assessment from exposure of heavy metals in soil samples of Jammu district of Jammu and Kashmir, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Liu, J.; Huang, P.; Yan, S.; Shi, X.; Ma, D. Sources, geochemical speciation, and risk assessment of metals in coastal sediments: A case study in the Bohai Sea, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Huang, B.; Xing, Z.; Hu, W. Geochemical baseline establishment and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in greenhouse soils from Dongtai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.J.; Ali, A.; DeLaune, R.D. Heavy metals and metalloid contamination in Louisiana Lake Pontchartrain Estuary along I-10 Bridge. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 44, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Men, C.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Xu, F.; Shen, Z. Spatial distribution and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in Yangtze estuary sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Feng, K.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y. Factorial Kriging analysis and sources of heavy metals in soils of different land-use types in the Yangtze River Delta of Eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2016, 23, 14957–14967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, S.; Sun, Q.; Wadood, S.A.; Guo, B. Source identification and spatial distribution of arsenic and heavy metals in agricultural soil around Hunan industrial estate by positive matrix factorization model, principle components analysis and geo statistical analysis. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2018, 159, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shit, P.K.; Bhunia, G.S.; Maiti, R. Spatial analysis of soil properties using GIS based geostatistics models. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Yue, W.; Teng, Y. Source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments and soils in an interconnected river-soil system based on a composite fingerprint screening approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Bi, X.; Ning, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, X. Apportionment of sources of heavy metals to agricultural soils using isotope fingerprints and multivariate statistical analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Su, L. Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Chen, J.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y. Enhancing apportionment of the point and diffuse sources of soil heavy metals using robust geostatistics and robust spatial receptor model with categorical soil-type data. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, S.; Yin, X.; Yu, X.; Luan, L. Arsenic accumulation, distribution and source analysis of rice in a typical growing area in north China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2019, 167, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, M.; Wu, S.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. A modified receptor model for source apportionment of heavy metal pollution in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 354, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Hu, B.; Marchant, B.P.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, Y. A methodological framework for identifying potential sources of soil heavy metal pollution based on machine learning: A case study in the Yangtze Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, L.; Huang, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Z. Application of stochastic model to assessment of heavy metal (loid) s source apportionment and bio-availability in rice fields of karst area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, A.; Yang, X.; Fan, M.; Shao, S.; Wu, J.; Wu, P.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Use of machine-learning and receptor models for prediction and source apportionment of heavy metals in coastal reclaimed soils. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, Z.; Li, F. Using ensemble models to identify and apportion heavy metal pollution sources in agricultural soils on a local scale. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Wu, X.; Ju, T.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L. Status of lead accumulation in agricultural soils across China (1979–2016). Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Xiao, R.; Ren, Z.; Lv, X. Contamination assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil through the synthesis of PMF and GeogDetector models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Lv, J. Source apportionment of potentially toxic elements in soils using APCS/MLR, PMF and geostatistics in a typical industrial and mining city in Eastern China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238513. [Google Scholar]
- Hengl, T. A Practical Guide to Geostatistical Mapping, 2nd ed.; University of Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Boettinger, J.L.; Ramsey, R.D.; Bodily, J.M.; Cole, N.J.; Stum, A.K. Landsat spectral data for digital soil mapping. In Digital Soil Mapping with Limited Data; Hartemink, A.E., McBratney, A.B., Mendonca Santos, M.L., Eds.; Springer Science: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2008; pp. 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.R. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Hass, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. In Proceedings of the Third ERTS Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 December 1973; NASA SP-351. National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1973; pp. 309–371. [Google Scholar]
- Hassoun, M.H. Fundamentals of Artificial Neural Networks; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Guo, D.; Ali, A.; Mi, S.; Liu, T.; Ren, C.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Accumulation, ecological-health risks assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in paddy soils: A case study in Hanzhong, Shaanxi, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Zhao, R.; Pan, N.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H. Source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil of Wuwei, China: Comparison of three receptor models. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0-Fundamentals and User Guide; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Hu, Y. Environmental health risk detection with GeogDetector. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 33, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Christakos, G.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lv, X. The association between heavy metal soil pollution and stomach cancer: A case study in Hangzhou City, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhao, G.; He, B.; Li, Q.; Dong, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. XGBoost-based method for flash flood risk assessment. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, M. A data augmentation approach to XGboost-based mineral potential mapping: An example of carbonate-hosted Zn Pb mineral systems of Western Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 228, 106811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, R.; Ye, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, D.; Hua, K. Winter wheat SPAD estimation from UAV hyperspectral data using cluster-regression methods. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 105, 102618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdullah, A.A.; Iqbal, M.; Zahid, M.; Khan, K.; Amin, M.N.; Jalal, F.E. Prediction of rapid chloride penetration resistance of metakaolin based high strength concrete using light GBM and XGBoost models by incorporating SHAP analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yan, K.; Ji, G. Optimization and prediction in the early design stage of office buildings using genetic and XGBoost algorithms. Build Environ. 2022, 218, 109081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zheng, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, F. Estimation of daily maize transpiration using support vector machines, extreme gradient boosting, artificial and deep neural networks models. Agr. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Guo, W.; Zheng, J. Soil prediction for coastal wetlands following Spartina alterniflora invasion using Sentinel-1 imagery and structural equation modeling. Catena 2019, 173, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, D.; Xiong, G.; Duan, Y.; Cai, C.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Tao, S.; Liu, W. Structural equation modeling of PAHs in ambient air, dust fall, soil, and cabbage in vegetable bases of Northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, R.; Cao, H.; Tan, W. Factor contribution to soil organic and inorganic carbon accumulation in the Loess Plateau: Structural equation modeling. Geoderma 2019, 352, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Song, X.; Cui, D. Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the topsoil of the Yellow River Delta. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Yuanan, H.; He, K.; Sun, Z.; Chen, G.; Cheng, H. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metal (loid) s in the agricultural soils of an industrializing region and associated model uncertainty. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, G.; Zhang, D.; Lei, M. An integrated method for source apportionment of heavy metal (loid) s in agricultural soils and model uncertainty analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Su, L.; Liu, M. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil and associated model uncertainty. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.M.; Fitzsimmons, J.N.; Adams, H.M.; Dellapenna, T.M.; Brandon, A.D. A time-series of heavy metal geochemistry in sediments of Galveston Bay estuary, Texas, 2017–2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burak, D.L.; Fontes, M.P.; Santos, N.T.; Monteiro, L.V.S.; de Sousa Martins, E.; Becquer, T. Geochemistry and spatial distribution of heavy metals in Oxisols in a mineralized region of the Brazilian Central Plateau. Geoderma 2010, 160, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Pan, N.; Lin, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Teng, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y. A partition computing-based positive matrix factorization (PC-PMF) approach for the source apportionment of agricultural soil heavy metal contents and associated health risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adgate, J.L.; Willis, R.D.; Buckley, T.J.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Rhoads, G.G.; Lioy, P.J. Chemical mass balance source apportionment of lead in house dust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, S.K.; Tung, T.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. Heavy metal contamination prediction using ensemble model: Case study of Bay sedimentation, Australia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Teng, Y. Source apportionment and source-oriented risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of an urban river-lake system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Deng, Q.; Lin, Q.; Zeng, C.; Zhong, C. Cadmium source identification in soils and high-risk regions predicted by geographical detector method. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Hu, J. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and quantitative source apportionment in surface sediments along a partially mixed estuary (Modaomen, China). Chemosphere 2019, 225, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Xiao, R.; Christakos, G.; Langousis, A.; Ren, Z.; Tian, Y.; Lv, X. Comprehensive assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in Shanghai agricultural soils with different fertility levels. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; Guan, Q.; Ma, Y.; Ni, F.; Yang, E.; Zhang, J. Heavy metal pollution levels, source apportionment and risk assessment in dust storms in key cities in Northwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Yin, M.; Ma, X.; Yu, X.; Guo, X.; Du, N.; Eller, F.; Guo, W. Soil salinity, not plant genotype or geographical distance, shapes soil microbial community of a reed wetland at a fine scale in the Yellow River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G. Upscaling remote sensing inversion and dynamic monitoring of soil salinization in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamulki, S.; Harrison, R.M.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Webster, C.P. N2O, NO and NO2 fluxes from a grassland: Effect of soil pH. Soil Biol. Bioche. 1997, 29, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.I.; Park, H.J.; Lee, K.S.; Lim, S.S.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, S.I.; Chang, S.; Lee, S.; Choi, W.J. δ13C, δ15N, N concentration, C/N, and Ca/Al of Pinus densiflora foliage in Korean cities of different precipitation pH and atmospheric NO2 and SO2 levels. Ecol. Indicat. 2018, 88, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.J.; Clemente, R.; Bernal, M.P. Contrasting effects of manure and compost on soil pH, heavy metal availability and growth of Chenopodium album L. in a soil contaminated by pyritic mine waste. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.N.; Nagendran, R. Influence of initial pH on bioleaching of heavy metals from contaminated soil employing indigenous Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Song, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Duan, T.; Cai, Y. Coupling soil washing with chelator and cathodic reduction treatment for a multi-metal contaminated soil: Effect of pH controlling. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 448, 142178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cortijo, J.; Ruiz-Canales, A. Effect of heavy metals on rice irrigated fields with waste water in high pH Mediterranean soils: The particular case of the Valencia area in Spain. Agr. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jia, J.; Wen, X. Heavy metals in wetland soils along a wetland-forming chronosequence in the Yellow River Delta of China: Levels, sources and toxic risks. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.T.; Wang, X.M.; Wu, N.; Chen, L.X.; Yuan, M.; Hu, J.C.; Chen, Y.E. Temporal and spatial biomonitoring of atmospheric heavy metal pollution using moss bags in Xichang. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, M.; Antonucci, A.; Owczarek, M.; Guidotti, M.; Astolfi, M.L.; Manigrasso, M.; Avino, P.; Bhattacharya, B.; Protano, C. Air quality assessment in different environmental scenarios by the determination of typical heavy metals and Persistent Organic Pollutants in native lichen Xanthoria parietina. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.; Lin, C.; Lu, S.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. Effect of air quality improvement by urban parks on mitigating PM2. 5 and its associated heavy metals: A mobile-monitoring field study. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yan, J.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Chen, M.; Lü, G. PM2. 5-bound heavy metals from the major cities in China: Spatiotemporal distribution, fuzzy exposure assessment and health risk management. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Franklin, M.; Fallah-Shorshani, M.; Shafer, M.; McConnell, R.; Fruin, S. Exposure models for particulate matter elemental concentrations in Southern California. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guan, Q.; Tian, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Pan, N. Contamination characteristics, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil in the Hexi Corridor. Catena 2020, 191, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, D.; Holm, P.E.; Ou, Q.; Hu, W. Quantitative source apportionment, risk assessment and distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soils from southern Shandong Peninsula of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Fu, W. Risk assessment, spatial patterns and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a typical Chinese hickory plantation region of southeastern China. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Cheng, G.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yuan, W. Source apportionment of heavy metal and their health risks in soil-dustfall-plant system nearby a typical non-ferrous metal mining area of Tongling, Eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.T.; Lin, C.; Shern, C.; Yeh, G.; Le, V.G.; Tran, H.T. Contamination, ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments and water of a contaminated river in Taiwan. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyad, M.T.; Khan, S.; Malik, A. Genotoxic hazard and oxidative stress induced by wastewater irrigated soil with special reference to pesticides and heavy metal pollution. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chu, C.; Wei, H.; Zhang, L.; Ahmad, Z.; Wu, S.; Xie, B. Ameliorative effects of silicon fertilizer on soil bacterial community and pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) grown on soil contaminated with multiple heavy metals. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.A.; Bedade, D.K.; Al-Ethawi, L.; Al-Waleed, S.M. Assessment of physiochemical properties and concentration of heavy metals in agricultural soils fertilized with chemical fertilizers. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, C.; Zheng, X.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, B.; Hu, Y.; et al. Combined apatite, biochar, and organic fertilizer application for heavy metal co-contaminated soil remediation reduces heavy metal transport and alters soil microbial community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, H.; Mansouri, B.; Kiani, A.; Omer, A.K.; Tazik, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, G.; Sharafi, K. Ecological risk assessment and heavy metals accumulation in agriculture soils irrigated with treated wastewater effluent, river water, and well water combined with chemical fertilizers. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Elements | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV (%) | BG | Excessive Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 9.78 | 31.3 | 22.3 | 4.79 | 22 | 8.60 | 100 |
| Cd | 0.13 | 0.91 | 0.36 | 0.19 | 53 | 0.13 | 99.1 |
| Cr | 53.8 | 197 | 123 | 30.3 | 25 | 62.0 | 98.2 |
| Cu | 12.7 | 38.8 | 23.0 | 4.98 | 22 | 22.6 | 47.8 |
| Ni | 17.8 | 45.1 | 30.1 | 5.64 | 19 | 27.1 | 66.4 |
| Pb | 10.4 | 45.4 | 21.8 | 6.67 | 31 | 23.6 | 30.1 |
| Zn | 25.7 | 86.1 | 43.7 | 11.8 | 28 | 63.3 | 7.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, H.; Xie, Y.; Hu, Y. Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Farmland Using Diverse Models: A Comparative Assessment in the Yellow River Delta. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11051069
Huang W, Wang S, Wang L, Song Y, Zhu Y, Yang H, Xie Y, Hu Y. Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Farmland Using Diverse Models: A Comparative Assessment in the Yellow River Delta. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(5):1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11051069
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wei, Shuhuan Wang, Lu Wang, Yingqiang Song, Yue Zhu, Hao Yang, Yingkai Xie, and Yueming Hu. 2023. "Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Farmland Using Diverse Models: A Comparative Assessment in the Yellow River Delta" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 5: 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11051069
APA StyleHuang, W., Wang, S., Wang, L., Song, Y., Zhu, Y., Yang, H., Xie, Y., & Hu, Y. (2023). Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Farmland Using Diverse Models: A Comparative Assessment in the Yellow River Delta. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(5), 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11051069







