Litter Content of Colombian Beaches and Mangrove Forests: Results from the Caribbean and Pacific Coasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
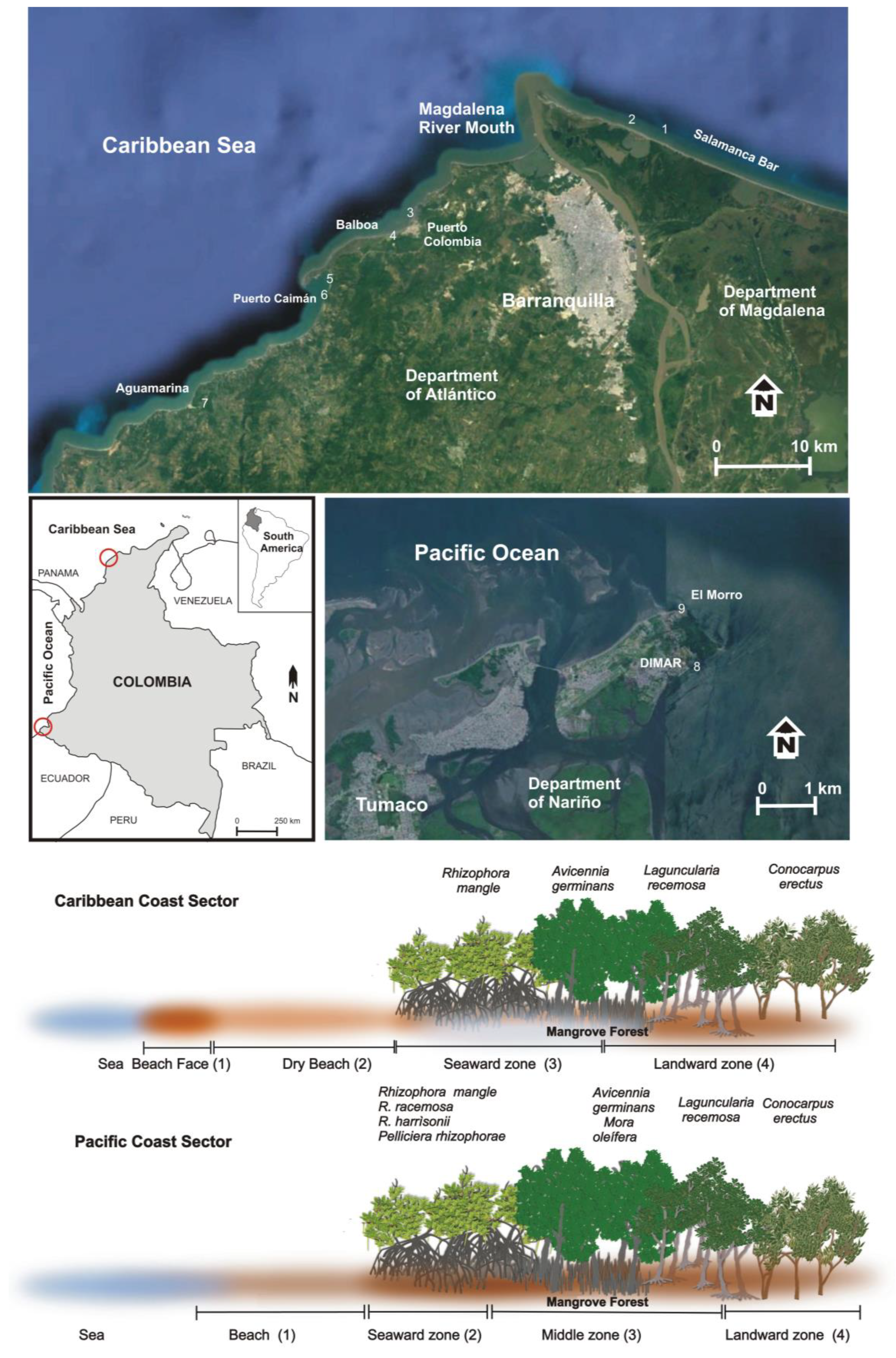
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Sites Description
2.3. Marine Littler Characterization
2.4. Statistical Approach
3. Results
3.1. Litter Abundance and Weight
3.2. Litter Composition
3.3. Litter Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution of Litter in Beach Environments
4.2. Distribution of Litter in Mangrove Forests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orthodoxou, D.L.; Loizidou, X.I.; Baldwin, C.; Kocareis, C.; Karonias, A.; Ateş, M.A. Seasonal and geographic variations of marine litter: A comprehensive study from the island of Cyprus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 177, 113495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettencourt, S.; Costa, S.; Caeiro, S. Marine litter: A review of educative interventions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, R.M.; Pinheiro, L.S.; Teixeira, C.E.P.; Paiva, B.P.; Fernandes, G.M.; Brandão, D.B.; Frota, F.F.; Filho, F.J.N.S.; Schettini, C.A.F. Marine debris on a tropical coastline: Abundance, predominant sources and fate in a region with multiple activities (Fortaleza, Ceará, northeastern Brazil). Waste Manag. 2020, 108, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.T.; Rangel-Buitrago, N. Marine litter: Solutions for a major environmental problem. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 35, 648–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Williams, A.T.; Costa, M.F.; de Jonge, V. Curbing the inexorable rising in marine litter: An overview. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 188, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Stöfen, O. Marine litter. In Handbook on Marine Environment Protection; Salomon, M., Markus, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 447–461. ISBN 9789944245326. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic pollution in the world’s oceans: More than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Williams, A.T.; Neal, W.J.; Gracia, A.; Micallef, A. Litter in coastal and marine environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 177, 113546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.Y.; Not, C.; Cannicci, S. Mangroves as unique but understudied traps for anthropogenic marine debris: A review of present information and the way forward. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolívar-Anillo, H.J.; Anfuso, G.; Chacón, S.; Badillo, M.D.; Villate, D.A.; Serrano, M.C.; Sánchez, H. Eventos naturales y actuaciones antrópicas: Impactos sobre los bosques de manglar de América del Sur. Rev. Costas 2020, 2, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villate, D.A.; Sánchez, H.; Portz, L.; Manzolli, R.P.; Bolívar-Anillo, H.J.; Anfuso, G. Mangrove forests evolution and threats in the Caribbean sea of Colombia. Water 2020, 12, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderman, J.; Hengl, T.; Fiske, G.; Solvik, K.; Adame, M.F.; Benson, L.; Bukoski, J.J.; Carnell, P.; Cifuentes-Jara, M.; Donato, D.; et al. A global map of mangrove forest soil carbon at 30 m spatial resolution. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B. The protective service of mangrove ecosystems: A review of valuation methods. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanía, J.; Urrego, L.E.; Agudelo, C.M. Recent advances in understanding Colombian mangroves. Acta Oecologica 2015, 63, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolívar-Anillo, H.J.; Sánchez, H.; Fernandez, R.; Villate, D.; Anfuso, G. An Overview on mangrove forests distribution in Colombia: An ecosystem at risk. J. Aquat. Sci. Mar. Biol. 2019, 2, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-León, R. Los manglares de Colombia y la recuperación de sus áreas degradadas: Revisión bibliográfica y nuevas experiencias. Madera Y Bosques 2003, 9, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osland, M.J.; Feher, L.C.; López-Portillo, J.; Day, R.H.; Suman, D.O.; Guzmán Menéndez, J.M.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H. Mangrove forests in a rapidly changing world: Global change impacts and conservation opportunities along the Gulf of Mexico coast. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 214, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, H.; Bolívar-Anillo, H.J.; Villate, D.; Escobar-Olaya, G.; Anfuso, G. Influencia de los impactos antrópicos sobre la evolución del bosque de manglar en Puerto Colombia (Mar Caribe colombiano). Rev. Latinoam. Recur. Nat. 2019, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios, M.L.; Cantera, J.R.; Peña, E.J. Carbon stocks in mangrove forests of the Colombian Pacific. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 227, 106299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, M.L.; Cantera, J.R. Mangrove timber use as an ecosystem service in the Colombian Pacific. Hydrobiologia 2017, 803, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Almahasheer, H.; Duarte, C.M. Mangrove forests as traps for marine litter. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Baalkhuyur, F.; Valluzzi, L.; Saderne, V.; Cusack, M.; Almahasheer, H.; Krishnakumar, P.K.; Rabaoui, L.; Qurban, M.A.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; et al. Exponential increase of plastic burial in mangrove sediments as a major plastic sink. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Obbard, J.P. Microplastics in Singapore’s coastal mangrove ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, C.A.M.M.; Costa, T.M. Evaluation of solid residues removed from a mangrove swamp in the São Vicente Estuary, SP, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, J.; Nandhini, A.R.; Velayudhaperumal, P.; Sillanpää, M. Microplastics in mangroves and coral reef ecosystems: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Ordóñez, O.; Castillo-Olaya, V.A.; Granados-Briceño, A.F.; Blandón, L.M.; Espinosa, L.F. Marine litter and microplastic pollution on mangrove soils of the Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta, Colombian Caribbean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, O.; Bayona, M.R. Impactos de la contaminación por basura marina en el ecosistema de manglar de la Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta, Caribe colombiano. Rev. Cienc. Mar. Y Costeras 2019, 11, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riascos, J.M.; Valencia, N.; Peña, E.J.; Cantera, J.R. Inhabiting the technosphere: The encroachment of anthropogenic marine litter in neotropical mangrove forests and its use as habitat by macrobenthic biota. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Ordóñez, O.; Saldarriaga-Vélez, J.F.; Espinosa-Díaz, L.F. Marine litter pollution in mangrove forests from Providencia and Santa Catalina islands, after hurricane IOTA path in the Colombian Caribbean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Castillo, L.; Álvares, R. Evaluación de suelos de manglar en dos localidades de la ensenada de Tumaco. Arqivos Cienc. Mar. 2011, 44, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal, B.; Sidman, G.; Pearson, T. Assessment of Mangrove Ecosystems in Colombia and Their Potential for Emissions Reductions and Restoration; Winrock International: Arlington, VA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Stronkhorst, J.; Levering, A.; Hendriksen, G.; Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Appelquist, L.R. Regional coastal erosion assessment based on global open access data: A case study for Colombia. J. Coast. Conserv. 2018, 22, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C. Cambios Recientes del Nivel del Mar en Colombia. In Deltas de Colombia: Morfodinámica y Vulnerabilidad Ante el Cambio Global; Restrepo, J., Ed.; EAFIT Universidad Press: Medellin, Colombia, 2008; pp. 103–122. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto de Investigaciones Marinas y Costeras (INVEMAR). Climatologie de la vitesse et la direction des vent pour le mar territoriale sous juridiction colombianne 8° a 19° N e 69° a 84° W. In Atlas ERS 1 et 2 et Quickscat, Colombie; INVEMAR: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Osorio, A.F.; Mesa, J.C.; Bernal, G.R.; Montoya, R.D. Reconstrucción de cuarenta años de datos de oleaje en el mar Caribe colombiano empleando el modelo WWIIITM y diferentes fuentes de datos. Boletín Científico CIOH 2009, 56, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L. Clima marítimo, procesos de erosión/acreción y amenazas/vulnerabilidades por erosión: Caso de estudio de la barrera costera de Puerto Velero, Departamento del Atlántico. Master´s Thesis, Universidad del Norte, Barranquilla, Colombia, 2021; pp. 1–121. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, A.M.; Sánchez, R. Evaluación de la amenaza por tsunami en poblaciones del sur, centro y norte del litoral Pacífico colombiano. Boletín Científico CIOH 2019, 38, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, I.; Morton, R. Pacific Coast of Colombia. In Encyclopedia of the World’s Coastal Landforms; Bird, E., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Tovilla, C.; Orihuela, D.E. Impacto del huracán Rosa sobre los bosques de manglar de la costa norte de Nayarit, México. Madera Y Bosques 2004, 10, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Varela, Z.E.; Rosado-Porto, D.; Bolívar-Anillo, H.J.; González, C.P.; Pantoja, B.G.; Alvarado, D.E.; Anfuso, G. Preliminary microbiological coastal water quality determination along the department of Atlántico (Colombia): Relationships with beach characteristics. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto de Investigaciones Marinas y Costeras (INVEMAR). Actualizacion y Ajuste del Diagnóstico y Zonificación de los Manglares de la Zona Costera del Departamento del Atlantico, Caribe Colombiano; INVEMAR: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2005; pp. 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Botero, C.M.; Tamayo, D.; Zielinski, S.; Anfuso, G. Qualitative and quantitative beach cleanliness assessment to support marine litter management in tropical destinations. Water 2021, 13, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Monroy, O. Estado de los manglares en Colombia año 2000. In Informe del Estado de los Ambientes Marinos y Costeros en Colombia: Año 2000; Instituto de Investigaciones Marinas y Costeras (INVEMAR): Santa Marta, Colombia, 2000; pp. 48–68. [Google Scholar]
- Mejía-Rentería, J.C.; Castellanos-Galindo, G.A.; Cantera-Kintz, J.R.; Hamilton, S.E. A comparison of Colombian Pacific mangrove extent estimations: Implications for the conservation of a unique neotropical tidal forest. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 212, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, O.; Espinosa, L. Contaminación por hidrocarburos en sedimentos de manglar del estuario del río Mira, Pacífico colombiano, afectados por derrames de petróleo crudo. Bull. Mar. Coast. Res. 2019, 48, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, A.; Salazar, J.; Indaburu, M.; Rubio, J.; Quiroz, F.; Vargas, J.; Palacios, J. Estudio de caso: Tumaco 2000-2015; USAID: Arlington, VA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–104.
- Williams, A.T.; Micallef, A. Beach Management, Principles & Practice; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 1–480. ISBN 978-1-84407-435-8. [Google Scholar]
- YIN, C.S.; Chai, Y.J.; Carey, D.; Yusri, Y.; Barry, G.J. Anthropogenic marine debris accumulation in mangroves on Penang island, Malaysia. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2020, 15, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Enviroment Programme/Mediterranean Action Plan. Marine Litter Assessment in the Mediterranean; UNEP/MAP: Athens, Greece, 2015; pp. 1–86. [Google Scholar]
- Joint Research Centre of the European Commission. Guidance on Monitoring of Marine Litter in European Seas; JRC: Luxembourg, 2013; pp. 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- Cheshire, A.C.; Adler, E.; Barbière, J.; Cohen, Y.; Evans, S.; Jarayabhand, S.; Jeftic, L.; Jung, R.T.; Kinsey, S.; Kusui, E.; et al. UNEP/IOC Guidelines on Survey and Monitoring of Marine Litter; UNEP Regional Seas Reports and Studies, No. 186; IOC Technical Series No. 83; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2009; pp. 1–120. ISBN 978-92-807-3027-2. [Google Scholar]
- Alkalay, R.; Pasternak, G.; Zask, A. Clean-coast index-A new approach for beach cleanliness assessment. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2007, 50, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y. A nationwide assessment of litter on China’s beaches using citizen science data. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonidi, A.; Latifi, P.; Kazemi, Z.; Kazemi, Z.; Morovati, M.; Farzadkia, M.; Torkashvand, J. Development a new index for littered waste assessment in different environments: A study on coastal and urban areas of northern Iran (Caspian Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, R.; Curtis, T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Velez, A.; Gracia, A.; Mantilla-Barbosa, E.; Arana, V.A.; Trilleras, J.; Arroyo-Olarte, H. Litter impacts on cleanliness and environmental status of Atlantico department beaches, Colombian Caribbean coast. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 179, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Williams, A.; Anfuso, G. Killing the goose with the golden eggs: Litter effects on scenic quality of the Caribbean coast of Colombia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcés-Ordóñez, O.; Espinosa, L.F.; Pereira, R.; Costa, M. The impact of tourism on marine litter pollution on Santa Marta beaches, Colombian Caribbean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portz, L.; Manzolli, R.P.; Villate-Daza, D.A.; Fontán-Bouzas, Á. Where does marine litter hide? The Providencia and Santa Catalina Island problem, Seaflower reserve (Colombia). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 151878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.; Rangel-Buitrago, N.G.; Anfuso, G.; Cervantes, O.; Botero, C.M. Litter impacts on scenery and tourism on the Colombian north Caribbean coast. Tour. Manag. 2016, 55, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portz, L.; Portantiolo, R.; Vasquez, G.; Laiton, L.; Villate, D.; Ivar do Sul, J.A. Marine litter arrived: Distribution and potential sources on an unpopulated atoll in the Seaflower biosphere reserve, Caribbean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Gracia, A.; Velez-Mendoza, A.; Carvajal-Florián, A.; Mojica-Martinez, L.; Neal, W.J. Where did this refuse come from? Marine anthropogenic litter on a remote island of the Colombian Caribbean sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Ordóñez, O.; Espinosa, L.F.; Pereira, R.; Issa, B.B.; Meigikos, R. Plastic litter pollution along sandy beaches in the Caribbean and Pacific coast of Colombia. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Ordóñez, O.; Espinosa, L.F.; Costa, M.; Salles, L.B.; Meigikos, R. Abundance, distribution, and characteristics of microplastics in coastal surface waters of the Colombian Caribbean and Pacific. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43431–43442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Williams, A.; Anfuso, G.; Arias, M.; Gracia, A. Magnitudes, sources, and management of beach litter along the Atlantico department coastline, Caribbean coast of Colombia. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 138, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, I.C.; Lovelock, C.E.; Berger, U.; McKee, K.L.; Joye, S.B.; Ball, M.C. Biocomplexity in mangrove ecosystems. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo, J.D.; Zapata, P.; Díaz, J.M.; Garzón-Ferreira, J.; García, C.B. Fluvial fluxes into the Caribbean Sea and their impact on coastal ecosystems: The Magdalena River, Colombia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 50, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, A.; Restrepo, J.C.; Ortiz, J.C.; Pierini, J.; Otero, L. Suspended sediment transport in the Magdalena River (Colombia, South America): Hydrologic regime, rating parameters and effective discharge variability. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; Van Der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsband, C.; Herzke, D. Plastic litter in the European Arctic: What do we know? Emerg. Contam. 2019, 5, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addamo, A.M.; Laroche, P.; Hanke, G. Top Marine Beach Litter Items in Europe; JRC: Luxembourg, 2017; pp. 1–118. ISBN 978-92-79-87711-7. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.T.; Randerson, P.; Di Giacomo, C.; Anfuso, G.; Macias, A.; Perales, J.A. Distribution of beach litter along the coastline of Cádiz, Spain. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziane, F.; Nachite, D.; Anfuso, G. Artificial polymer materials debris characteristics along the Moroccan Mediterranean coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio-Montesinos, F.; Anfuso, G.; Ramírez, M.O.; Smolka, R.; Sanabria, J.G.; Enríquez, A.F.; Arenas, P.; Bedoya, A.M. Beach litter composition and distribution on the Atlantic coast of Cádiz (SW Spain). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 34, 101050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachite, D.; Maziane, F.; Anfuso, G.; Williams, A.T. Spatial and temporal variations of litter at the Mediterranean beaches of Morocco mainly due to beach users. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 179, 104846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavers, J.L.; Dicks, L.; Dicks, M.R.; Finger, A. Significant plastic accumulation on the Cocos (Keeling) Islands, Australia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Castro-Barros, J.D.; Gracia, A.; Villamil, J.D.; Williams, A.T. Litter impacts on beach/dune systems along the Atlantico Department, the Caribbean Coastline of Colombia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Velez, A.; Mantilla-Barbosa, E.; Arroyo-Olarte, H.; Arana, V.A.; Trilleras, J.; Gracia, A.; Neal, W.J.; Williams, A.T. Plastic pollution on the Colombian central Caribbean beaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topçu, E.N.; Tonay, A.M.; Dede, A.; Öztürk, A.A.; Öztürk, B. Origin and abundance of marine litter along sandy beaches of the Turkish Western Black Sea Coast. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 85, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, C.; Corbau, C.; Simeoni, U.; Mistri, M. Marine litter on Mediterranean shores: Analysis of composition, spatial distribution and sources in north-western Adriatic beaches. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitaka, T.Y.; von Blottnitz, H. Accumulation and characteristics of plastic debris along five beaches in Cape Town. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, G.; Zviely, D.; Ribic, C.A.; Ariel, A.; Spanier, E. Sources, composition and spatial distribution of marine debris along the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.R.; Shirgaonkar, S.S.; Patil, R.B. Plastic marine debris: Sources, distribution and impacts on coastal and ocean biodiversity. PENCIL Publ. Biol. Sci. 2016, 3, 40–54. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Caselles, C.; Viejo, J.; Martí, E.; González-Fernández, D.; Pragnell-Raasch, H.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Montero, E.; Arroyo, G.M.; Hanke, G.; Salvo, V.S.; et al. An inshore–offshore sorting system revealed from global classification of ocean litter. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convey, P.; Barnes, D.K.A.; Morton, A. Debris accumulation on oceanic island shores of the Scotia Arc, Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2002, 25, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.Y.; Vorsatz, L.D.; Not, C.; Cannicci, S. Landward zones of mangroves are sinks for both land and water borne anthropogenic debris. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivar do Sul, J.A.; Costa, M.F.; Silva-Cavalcanti, J.S.; Araújo, M.C.B. Plastic debris retention and exportation by a mangrove forest patch. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, B.K.; Mullarney, J.C.; Bryan, K.R.; Henderson, S.M. The effect of pneumatophore density on turbulence: A field study in a Sonneratia-dominated mangrove forest, Vietnam. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 147, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, E.M.; Dohmen-Janssen, C.M.; Narra, P.M.F.; van den Berg, N.J.F.; Siemerink, M.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Wave attenuation in mangroves: A quantitative approach to field observations. Coast. Eng. 2014, 94, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.M.; Catherine, S.M.P.; Takaijudin, H. Effectiveness of mangrove forests in surface wave attenuation: A review. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 5, 4483–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfuso, G.; Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Correa, I. Evolution of sandspits along the Caribbean coast of Colombia: Natural and human influences. In Sand and Gravel Spits; Randazzo, G., Jackson, D.W.T., Cooper, J.A.G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–19. ISBN 9783319137162. [Google Scholar]
- Ainali, N.M.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Aging effects on low- and high-density polyethylene, polypropylene and polystyrene under UV irradiation: An insight into decomposition mechanism by Py-GC/MS for microplastic analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 158, 105207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagut, E.; Cabrera, E. Situación de riesgo en la ensenada de Tumaco. Boletín Científico CCCP 1997, 6, 8–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.; Simmons, S.L. The degradation of plastic litter in rivers: Implications for beaches. J. Coast. Conserv. 1996, 2, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreo, N.A.S.; Siblos, S.K.V.; Macusi, E.D. Anthropogenic marine debris (AMD) in mangrove forests of Pujada Bay, Davao Oriental, Philippines. J. Mar. Isl. Cult. 2021, 9, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, S.; Xavier, K.A.M.; Deshmukhe, G.; Jaiswar, A.K.; Bhusan, S.; Sukla, S.P. Anthropogenic pressure on mangrove ecosystems: Quantification and source identification of surficial and trapped debris. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suyadi; Manullang, C.Y. Distribution of plastic debris pollution and it is implications on mangrove vegetation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto de Investigaciones Marinas y Costeras (INVEMAR). Propuesta de Estandarización de los Levantamientos Geomorfológicos en la Zona Costera del Caribe Colombiano; INVEMAR: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2012; pp. 1–110. [Google Scholar]
- Gerigny, O.; Brun, M.; Fabri, M.C.; Tomasino, C.; Le Moigne, M.; Jadaud, A.; Galgani, F. Seafloor litter from the continental shelf and canyons in French Mediterranean water: Distribution, typologies and trends. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, R.; Dimech, M. Litter as a source of habitat islands on deep water muddy bottoms. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Médit. 2007, 38, 567. [Google Scholar]
- Maghsodian, Z.; Sanati, A.M.; Tahmasebi, S.; Shahriari, M.H.; Ramavandi, B. Study of microplastics pollution in sediments and organisms in mangrove forests: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Colombian Caribbean Coast | ||||||||
| Site Number and Location | Distance of the Mangrove Forest from the Shoreline | Zone 1 Cross-Shore Dimension/Surface of Beach Face | Zone 2 Cross-Shore Dimension/Surface of Dry Beach | Zone 3 Cross-Shore Dimension/Surface Seaward Mangrove Zone | Zone 4 Cross-Shore Dimension/Surface of Landward Mangrove Zone | Mangrove Specie/ Density | Pneumatophores and Seedlings | Other Plants |
| 1-Salamanca A | 30 m | 10 m/100 m2 | 20 m/200 m2 | 10 m/100 m2 | − | A. germinans, R. mangle/Low | Yes | − |
| 2-Salamanca B | 2 m | 2 m/20 m2 | − | 10 m/100 m2 | − | L. racemosa, A. germinans/High | Yes | Batis marítima |
| 3-Puerto Colombia | 13 m | 3 m/30 m2 | 10 m/100 m2 | 15 m/150 m2 | 8 m/80 m2 | C. erectus, A. germinans/High | Yes | Prosopis juliflora Batis marítima |
| 4-Balboa | 0 m | − | − | 10 m/100 m2 | 10 m/100 m2 | A. germinans/Low | Yes | Batis marítima |
| 5-Puerto Caimán A | 0 m | − | − | 10 m/100 m2 | − | C. erectus A. germinans/Low | No | Batis marítima Portulaca oleracea |
| 6-Puerto Caimán B | 5 m | 5 m/50 m2 | − | 10 m/100 m2 | − | C. erectus A. germinans/Low | No | Batis marítima |
| 7-Aguamarina | 22 m | 2 m/20 m2 | 20 m/200 m2 | 10 m/100 m2 | − | Conocarpus erectus/Low | No | − |
| Colombian Pacific Coast | ||||||||
| Site | Distance of the Mangrove Forest from the Low Tide Position | Zone 1 Beach (Lower Foreshore) | Zone 2 Mangrove Seaward Zone (Middle Foreshore) | Zone 3 Mangrove Middle Zone (Middle Foreshore) | Zone 4 Mangrove Landward Zone (Upper Foreshore) | Mangrove Specie/ Density | Pneumatophores and Seedlings | Other Plants |
| 8-Complejo DIMAR | 93 m | 93 m/930 m2 | 12 m/120 m2 | 15 m/150 m2 | 4 m/40 m2 | Rhizophora racemosa R. mangle, A. germinans, L. Racemosa/ High | Yes | Acrosticum danaeifolium |
| 9-El Morro * | − | − | 11 m/110 m2 | 38 m/380 m2 * | 12/120 m2 | R. Racemosa, R. Mangle, L. Racemosa/ High | Yes | Acrosticum danaeifolium |
| Site | Coast | Zone | TOTAL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 1-Salamanca A | Caribbean | 0.060 0.21 | 0.590 3.26 | 1.240 29.28 | − | 0.620 9.00 |
| 2-Salamanca B | Caribbean | 0 0 | − | 0.570 27.94 | − | 0.475 23.28 |
| 3-Puerto Colombia | Caribbean | 6.933 76.04 | 1.030 2.54 | 0.813 35.19 | 0.875 17.48 | 1.397 25.59 |
| 4-Balboa | Caribbean | − | − | 1.230 44.69 | 2.890 67.39 | 2.060 56.04 |
| 5-Puerto Caimán A | Caribbean | − | − | 1.640 27.02 | − | 1.640 27.02 |
| 6-Puerto Caimán B | Caribbean | 0 0 | − | 0.990 18.73 | − | 0.660 12.48 |
| 7-Aguamarina | Caribbean | 0 0 | 2.725 15.59 | 1.400 18.17 | − | 2.141 15.42 |
| 8-Complejo DIMAR | Pacific | 0 0 | 0.083 8.34 | 1.067 101.72 | 4.775 196.63 | 0.291 19.45 |
| 9-El Morro | Pacific | − | 0.773 144.51 | 0.132 25.24 | 0 0 | 0.221 41.78 |
| Material | Caribbean Sea Sites (%) | Pacific Ocean Sites (%) | Total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloth | 0.51 | 2.46 | 0.97 |
| Glass | 0.99 | 3.85 | 1.67 |
| Metal | 0.25 | 3.30 | 0.97 |
| Paper and cardboard | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.17 |
| Plastic | 94.72 | 89.51 | 93.61 |
| Rubber | 3.15 | 0.36 | 2.50 |
| Processed wood | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.03 |
| Other | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.09 |
| Caribbean Sea Sites | % | Pacific Ocean Sites | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foamed plastic pieces (2.5–50 cm) | 24.4 | Film plastic pieces (2.5–50 cm) | 26.6 |
| Hard plastic pieces (2.5–50 cm) | 20.2 | Hard plastic pieces (2.5–50 cm) | 13.9 |
| Caps/lids | 10.1 | Bags (e.g., shopping) | 13.5 |
| Drinks (bottles, containers, drums) < 2 L | 9.1 | Hard plastic cups | 13.1 |
| Crisp/sweet packets and lolly sticks | 4.8 | Glass fragments (2.5–50 cm) | 5.6 |
| Hard plastic cups | 4.7 | Metal fragments (2–50 cm) | 5.0 |
| Food wrappers | 3.8 | Food wrappers | 4.4 |
| Drinks (bottles, containers and drums) > 2 L | 3.6 | Clothing | 4.2 |
| Footwear (flip-flops) | 2.6 | Drinks (bottles, containers, drums) < 2 L | 3.4 |
| Foam (insulation & packaging) | 2.5 | Tubes | 2.2 |
| Site | Coast | Zone 1 | Zone 2 | Zone 3 | Zone 4 | TOTAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Salamanca A | Caribbean | Very Clean | Dirty | Extremely Dirty | − | Dirty |
| 2-Salamanca B | Caribbean | Very Clean | − | Dirty | − | Moderate |
| 3-Puerto Colombia | Caribbean | Extremely Dirty | Extremely Dirty | Dirty | Dirty | Extremely Dirty |
| 4-Balboa | Caribbean | − | − | Extremely Dirty | Extremely Dirty | Extremely Dirty |
| 5-Puerto Caimán A | Caribbean | − | − | Extremely Dirty | − | Extremely Dirty |
| 6-Puerto Caimán B | Caribbean | Very Clean | − | Dirty | − | Dirty |
| 7-Acuamarina | Caribbean | Very Clean | Extremely Dirty | Extremely Dirty | − | Extremely Dirty |
| 8-Complejo DIMAR | Pacific | Very Clean | Very Clean | Very Clean | Clean | Moderate |
| 9-El Morro | Pacific | − | Dirty | Clean | Very Clean | Clean |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolívar-Anillo, H.J.; Asensio-Montesinos, F.; Reyes Almeida, G.; Solano Llanos, N.; Sánchez Moreno, H.; Orozco-Sánchez, C.J.; Villate Daza, D.A.; Iglesias-Navas, M.A.; Anfuso, G. Litter Content of Colombian Beaches and Mangrove Forests: Results from the Caribbean and Pacific Coasts. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020250
Bolívar-Anillo HJ, Asensio-Montesinos F, Reyes Almeida G, Solano Llanos N, Sánchez Moreno H, Orozco-Sánchez CJ, Villate Daza DA, Iglesias-Navas MA, Anfuso G. Litter Content of Colombian Beaches and Mangrove Forests: Results from the Caribbean and Pacific Coasts. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(2):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020250
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolívar-Anillo, Hernando José, Francisco Asensio-Montesinos, Giovanna Reyes Almeida, Nataly Solano Llanos, Hernando Sánchez Moreno, Christian J. Orozco-Sánchez, Diego Andrés Villate Daza, María Auxiliadora Iglesias-Navas, and Giorgio Anfuso. 2023. "Litter Content of Colombian Beaches and Mangrove Forests: Results from the Caribbean and Pacific Coasts" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 2: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020250
APA StyleBolívar-Anillo, H. J., Asensio-Montesinos, F., Reyes Almeida, G., Solano Llanos, N., Sánchez Moreno, H., Orozco-Sánchez, C. J., Villate Daza, D. A., Iglesias-Navas, M. A., & Anfuso, G. (2023). Litter Content of Colombian Beaches and Mangrove Forests: Results from the Caribbean and Pacific Coasts. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(2), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020250










