Experimental Inactivation of Microalgae in Marine Ballast Water by Microbubbles Generated through Hydrodynamic Cavitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
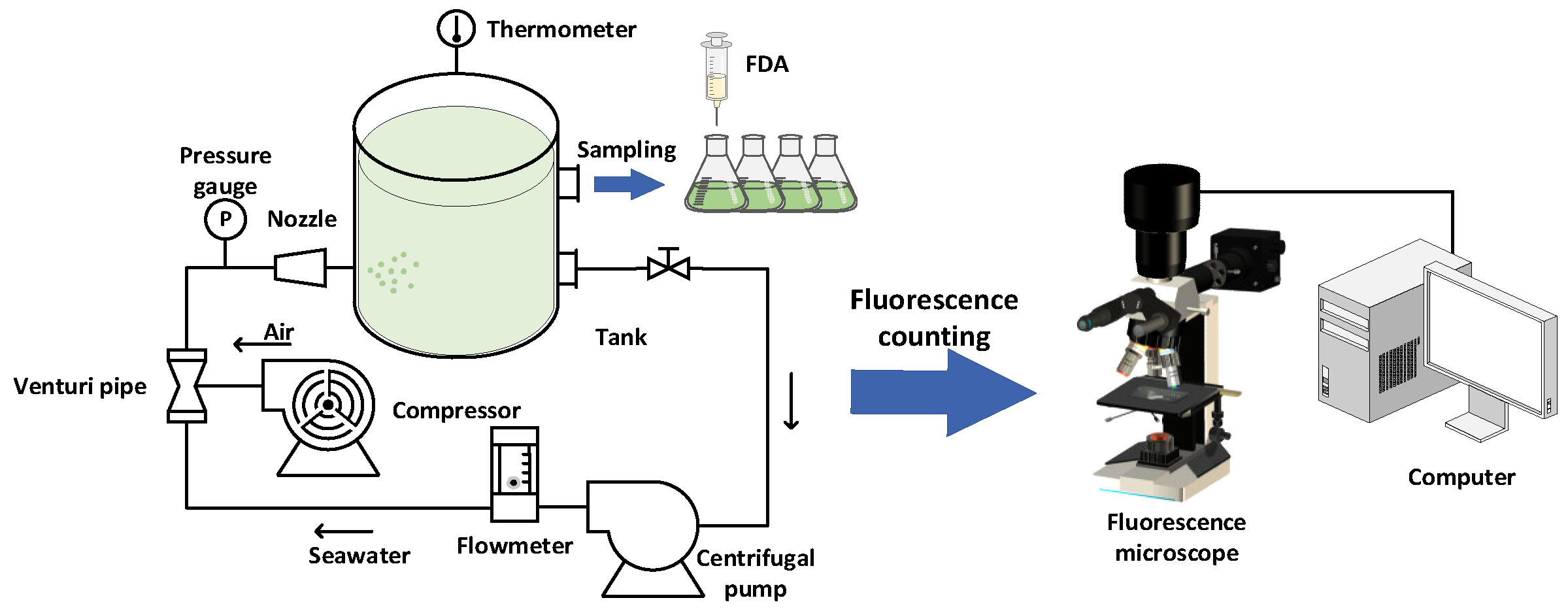
2.1. Apparatus and Species
2.2. Test Method
3. Results and Discussion
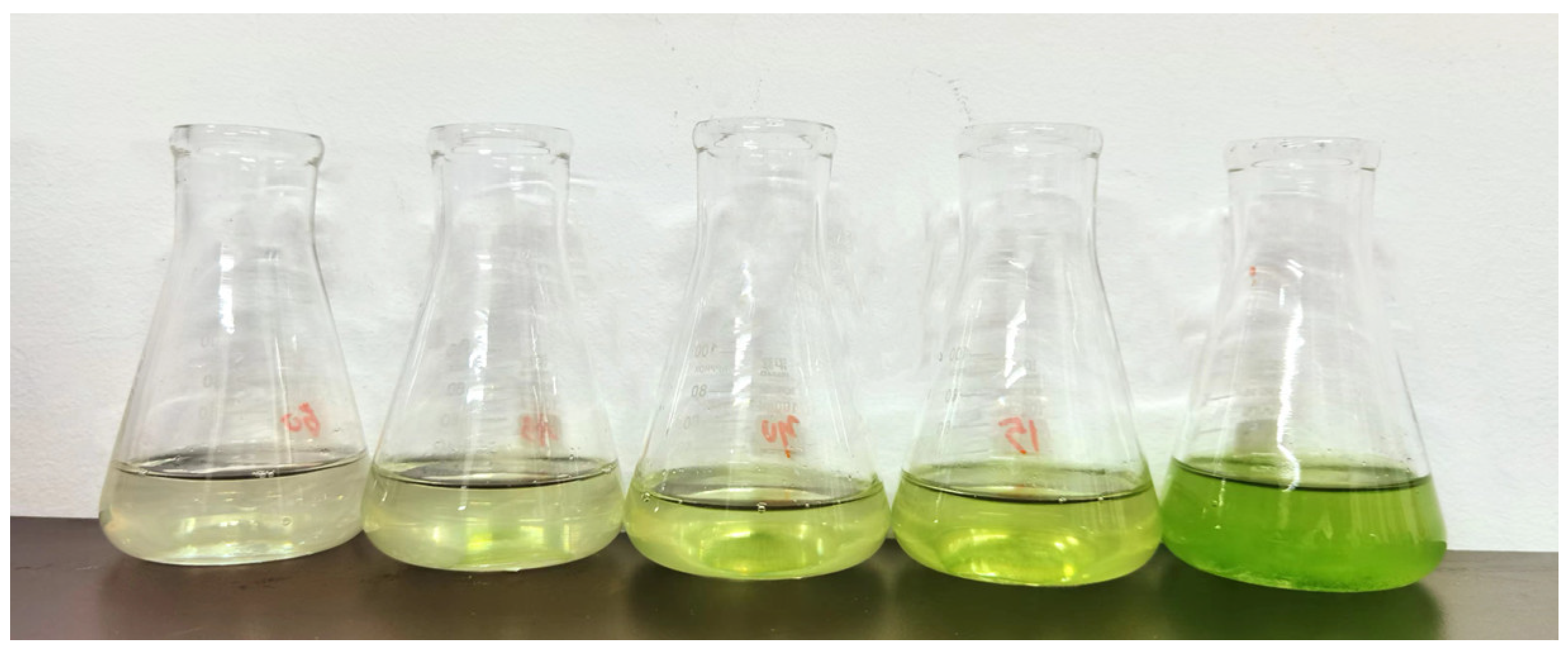
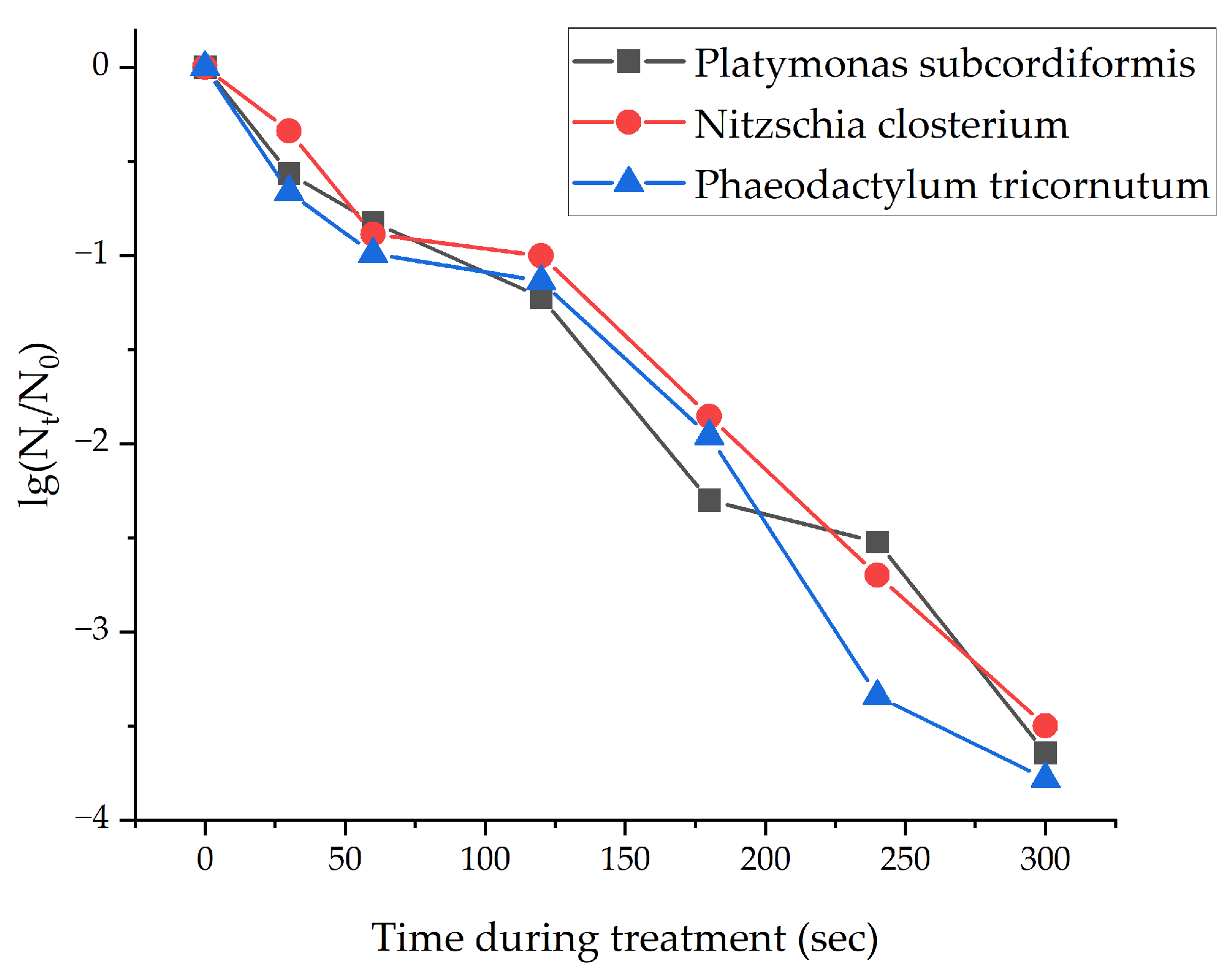
3.1. Efficiency Analysis of Microbubbles Treatment of Marine Microalgae
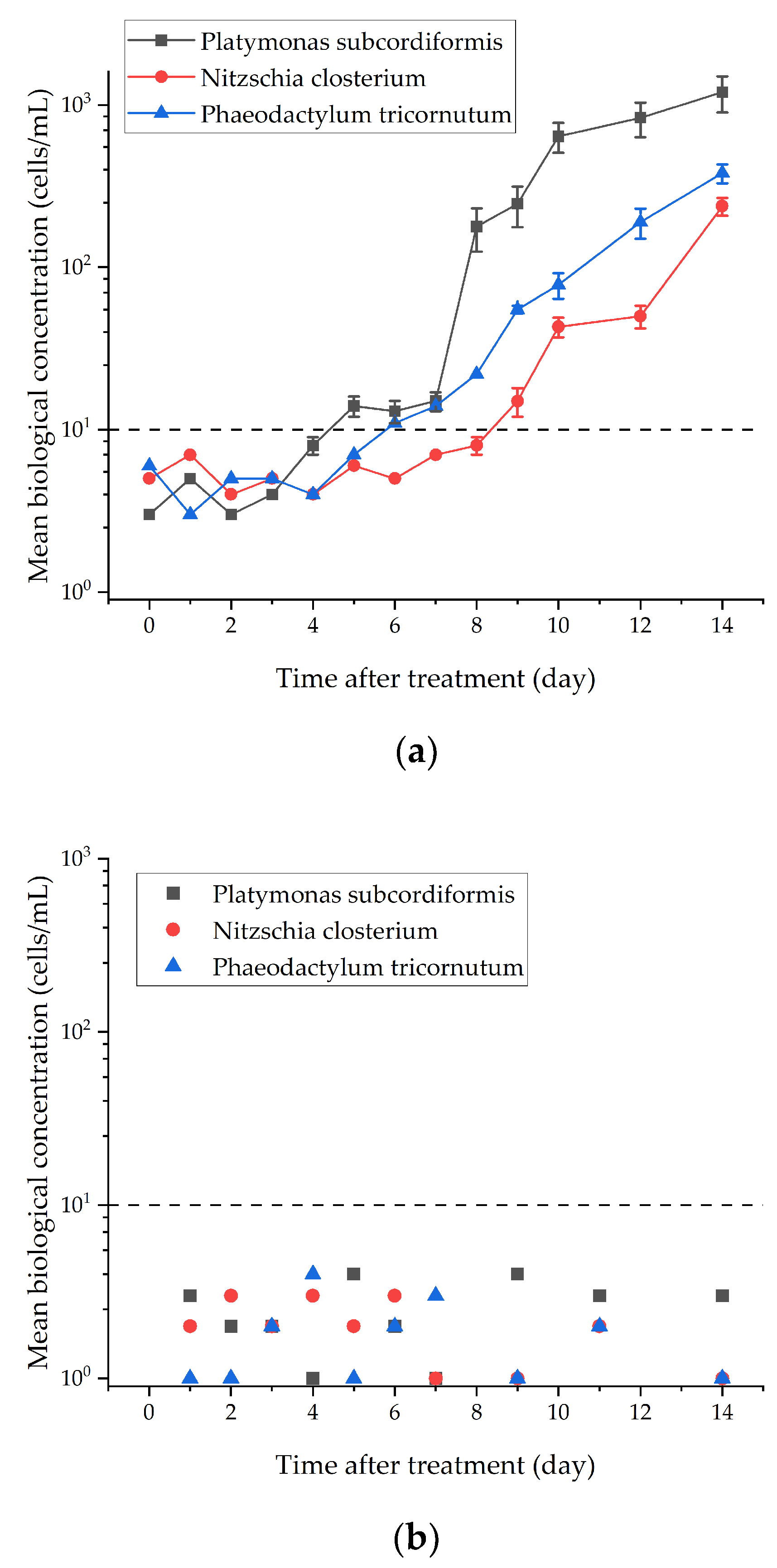
3.2. Storage Experimental Results
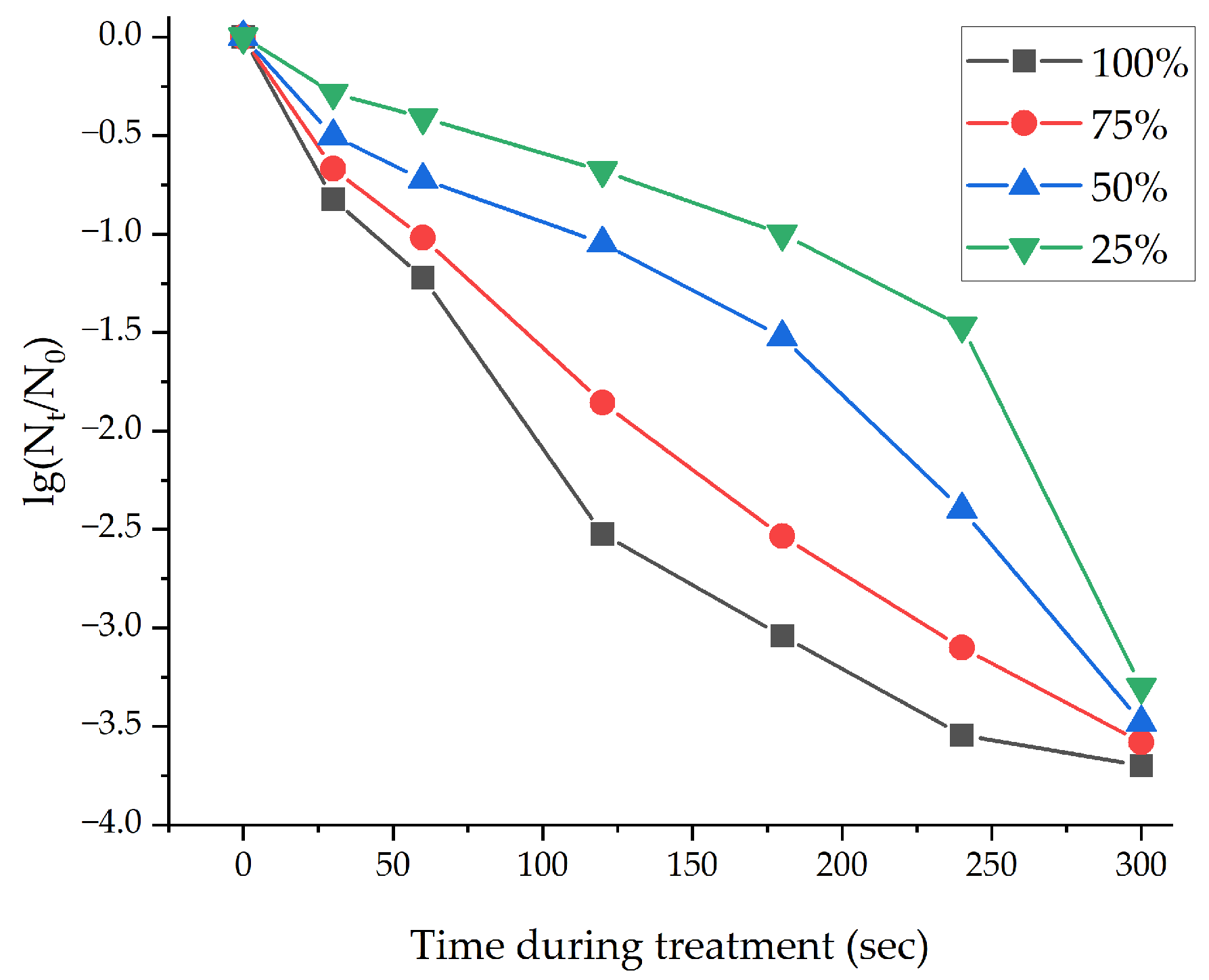
3.3. Effect of Ozone Injection Dose
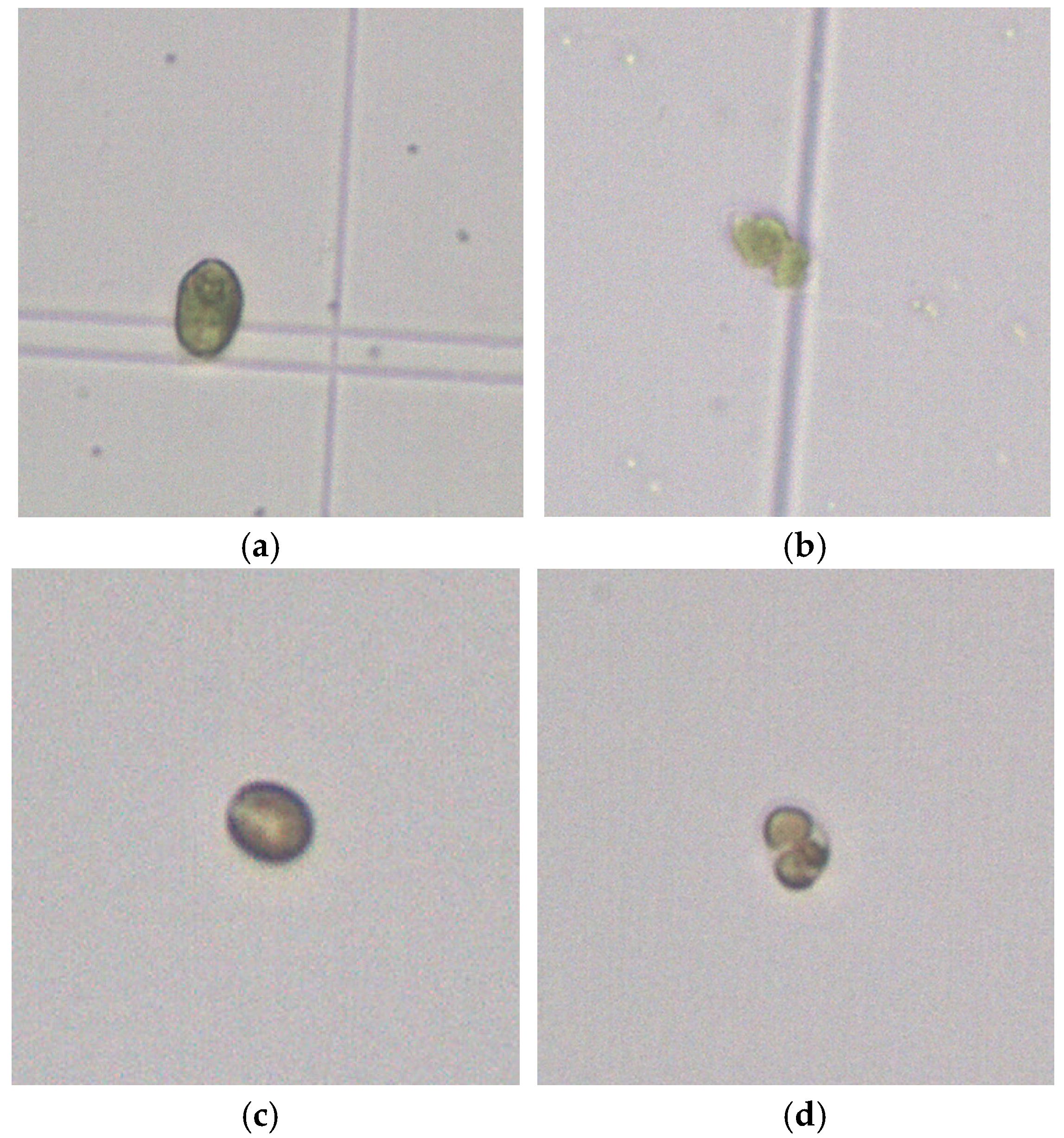
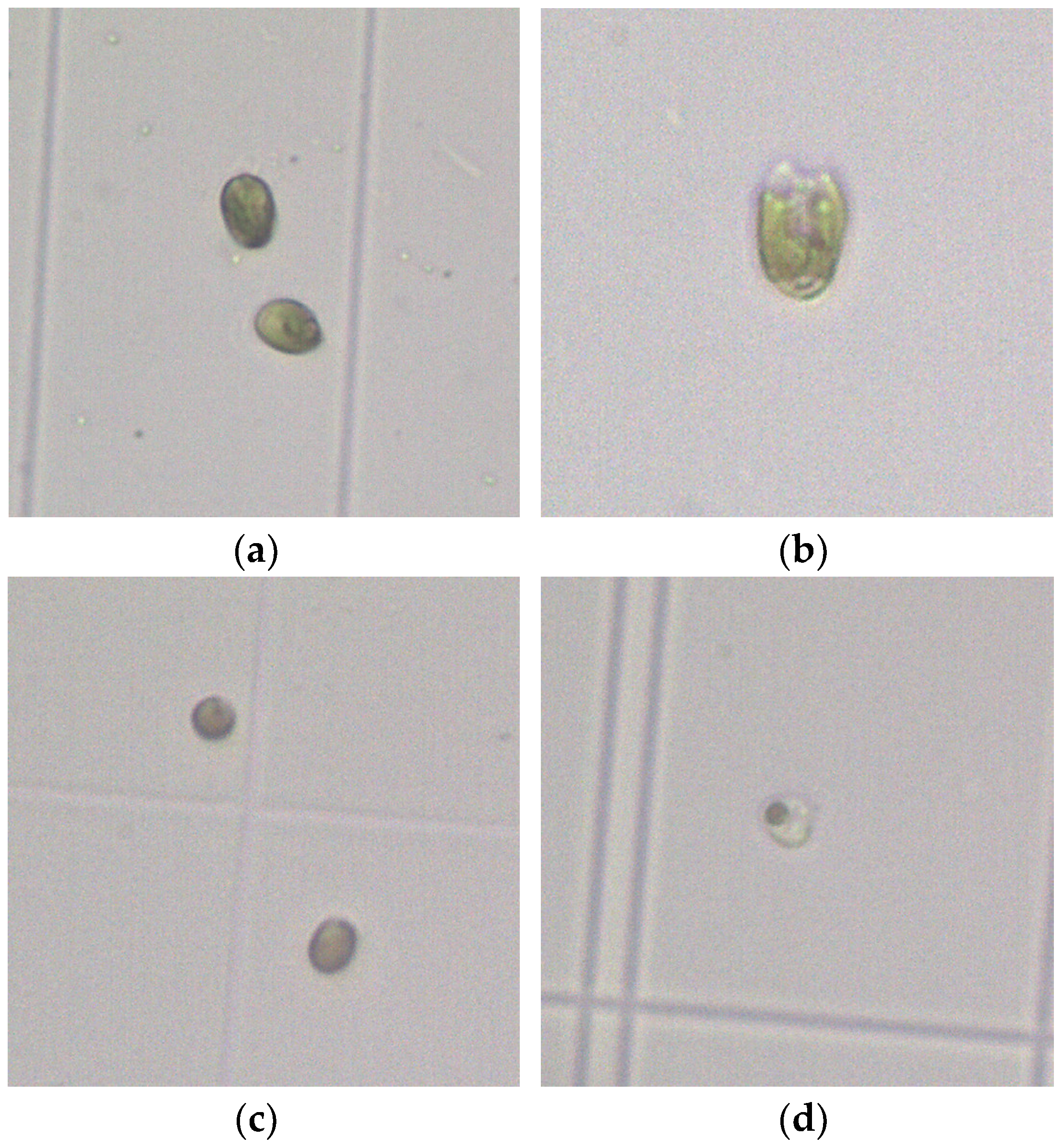
3.4. Morphological Changes of Microalgae Cells after Microbubble Treatment
3.5. The Mechanism of Microbubbles on the Inactivation Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hess-Erga, O.K.; Moreno-Andrés, J.; Enger, Ø.; Vadstein, O. Microorganisms in ballast water: Disinfection, community dynamics, and implications for management. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, W.R.; Fernandes, F.C.; Lopes, C.C.; Lopes, R.S.; Miller, W.; Ruiz, G. Which ballast water management system will you put aboard? Remnant anxieties: A mini-review. Environments 2017, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadakis, A.; Mamais, D.; Christoulas, D.; Kabylafka, S. Ultraviolet disinfection of secondary and tertiary effluent in the Mediterranean region. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Madamwar, D.; Nakamoto, H.; Incharoensakdi, A. Resilience and self-regulation processes of microalgae under UV radiation stress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C: Photochem. Rev. 2020, 43, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.; Rigby, G.; Gollasch, S.; Voigt, M.; Hallegraeff, G.; McCollin, T.; Jelmert, A. Preventive treatment and control techniques for ballast water. In Invasive Aquatic Species of Europe. Distribution, Impacts and Management; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 484–507. [Google Scholar]
- Pećarević, M.; Mikuš, J.; Prusina, I.; Juretić, H.; Cetinić, A.B.; Brailo, M. New role of hydrocyclone in ballast water treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, C.K.; Lourenco, N.G.G.S.; Lopes, T.F.; Rall, V.L.M.; Lopes, C.A.M. Ballast water: A review of the impact on the world public health. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 14, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H. Study on the dinoflagellate cysts in ballast tank sediments of international vessels in Chinese shipyards. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 169, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ling, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, N. Formation of emerging iodinated disinfection by-products during ballast water treatment based on ozonation processes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 743, 140805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanotu, J.; Bandulasena, H.H.; Zimmerman, W.B. Microflotation performance for algal separation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, H.; Abe, A.; Katakura, R.; Kawasaki, H.; Yoshida, K.; Ishida, H. Lethality of shock pressures to a marine Vibrio sp. isolated from a ship’s ballast water. Biocontrol. Sci. 2006, 11, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.; Zhu, W.; Huang, F.; Gao, W.; Khan, N.A. Micro–nanobubble technology and water-related application. Water Supply 2020, 20, 2021–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Qin, F.G.; Jiang, R.; Kang, S. Interpreting the influence of liquid temperature on cavitation collapse intensity through bubble dynamic analysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 69, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedadi, M.; Choubey, A.; Nomura, K.I.; Kalia, R.K.; Nakano, A.; Vashishta, P.; Van Duin, A.C.T. Structure and dynamics of shock-induced nanobubble collapse in water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 014503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.T.; Jayaprakash, A.; Kapahi, A.; Choi, J.K.; Chahine, G.L. Modelling of material pitting from cavitation bubble collapse. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 755, 142–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Kang, C.H.; Park, J.J.; Kim, H.S.; Om, A.S.; Yoon, J.Y. An experimental study on the thermal performance of a novel hydrodynamic cavitation reactor. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018, 99, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Song, Y.; Yu, S. Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa using hydrodynamic cavitation: Performance and mechanisms. Water Res. 2014, 62, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, T.; Wu, S.; Mortimer, R.J.; Pan, G. Nanobubble technology in environmental engineering: Revolutionization potential and challenges. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7175–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wang, R.; Tang, J.; Yang, L.; Feng, Z.; Xu, C.; Yang, F.; Gu, N. Dynamic tracking of bulk nanobubbles from microbubbles shrinkage to collapse. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 589, 124430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, H. A review of bulk nanobubbles and their roles in flotation of fine particles. Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, L.; Yang, H.; Gui, X.; Schönherr, H.; Kappl, M.; Cao, Y.; Xing, Y. Recent advances for understanding the role of nanobubbles in particles flotation. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 291, 102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Xu, G. Mass transfer of nanobubble aeration and its effect on biofilm growth: Microbial activity and structural properties. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 703, 134976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrins, J.C.; Cordell, J.R.; Ferm, N.C.; Grocock, J.L.; Herwig, R.P. Mesocosm experiments for evaluating the biological efficacy of ozone treatment of marine ballast water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 1756–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.A.; Gensemer, R.W.; Mitchelmore, C.L.; Stubblefield, W.A.; van Genderen, E.; Dawson, R.; Orano-Dawson, C.E.; Bearr, J.S.; Mueller, R.A.; Cooper, W.J. Shipboard trials of an ozone-based ballast water treatment system. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1571–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Species | The Processing Time Required When the Inactivation Rate Reaches 99% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Biological Concentration: 104–105 Cells/mL | Initial Biological Concentration: 103–104 Cells/mL | Initial Biological Concentration: 102–103 Cells/mL | |
| Platymonas subcordiformis | 65 min | 40 min | 20 min |
| Nitzschia closterium | 65 min | 40 min | 15 min |
| Phaeodactylum tricornutum | 65 min | 40 min | 20 min |
| Species | The Processing Time Required When the Inactivation Rate Reaches 99% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Biological Concentration: 104–105 Cells/mL | Initial Biological Concentration: 103–104 Cells/mL | Initial Biological Concentration: 102–103 Cells/mL | |
| Platymonas subcordiformis | 300 s | 180 s | 60 s |
| Nitzschia closterium | 300 s | 180 s | 60 s |
| Phaeodactylum tricornutum | 300 s | 180 s | 60 s |
| Injection Dose | Total Residual Oxidant (mg/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | After 1 Day | After 2 Days | After 5 Days | After 7 Days | After 14 Days | |
| 100% | 1.36 | 0.88 | 0.56 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| 75% | 0.96 | 0.74 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| 50% | 0.52 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 25% | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Lu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Hong, J.; Cui, M. Experimental Inactivation of Microalgae in Marine Ballast Water by Microbubbles Generated through Hydrodynamic Cavitation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020241
Wang B, Lu H, Zhang H, Li W, Hong J, Cui M. Experimental Inactivation of Microalgae in Marine Ballast Water by Microbubbles Generated through Hydrodynamic Cavitation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(2):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020241
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Baojun, Hao Lu, Hongpeng Zhang, Wei Li, Jiaju Hong, and Mingsheng Cui. 2023. "Experimental Inactivation of Microalgae in Marine Ballast Water by Microbubbles Generated through Hydrodynamic Cavitation" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 2: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020241
APA StyleWang, B., Lu, H., Zhang, H., Li, W., Hong, J., & Cui, M. (2023). Experimental Inactivation of Microalgae in Marine Ballast Water by Microbubbles Generated through Hydrodynamic Cavitation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(2), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020241









