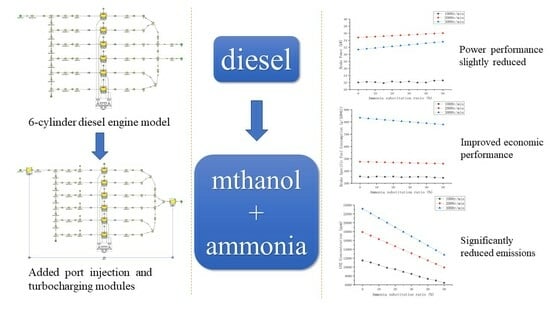
Effects of Methanol–Ammonia Blending Ratio on Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Compression Ignition Engine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
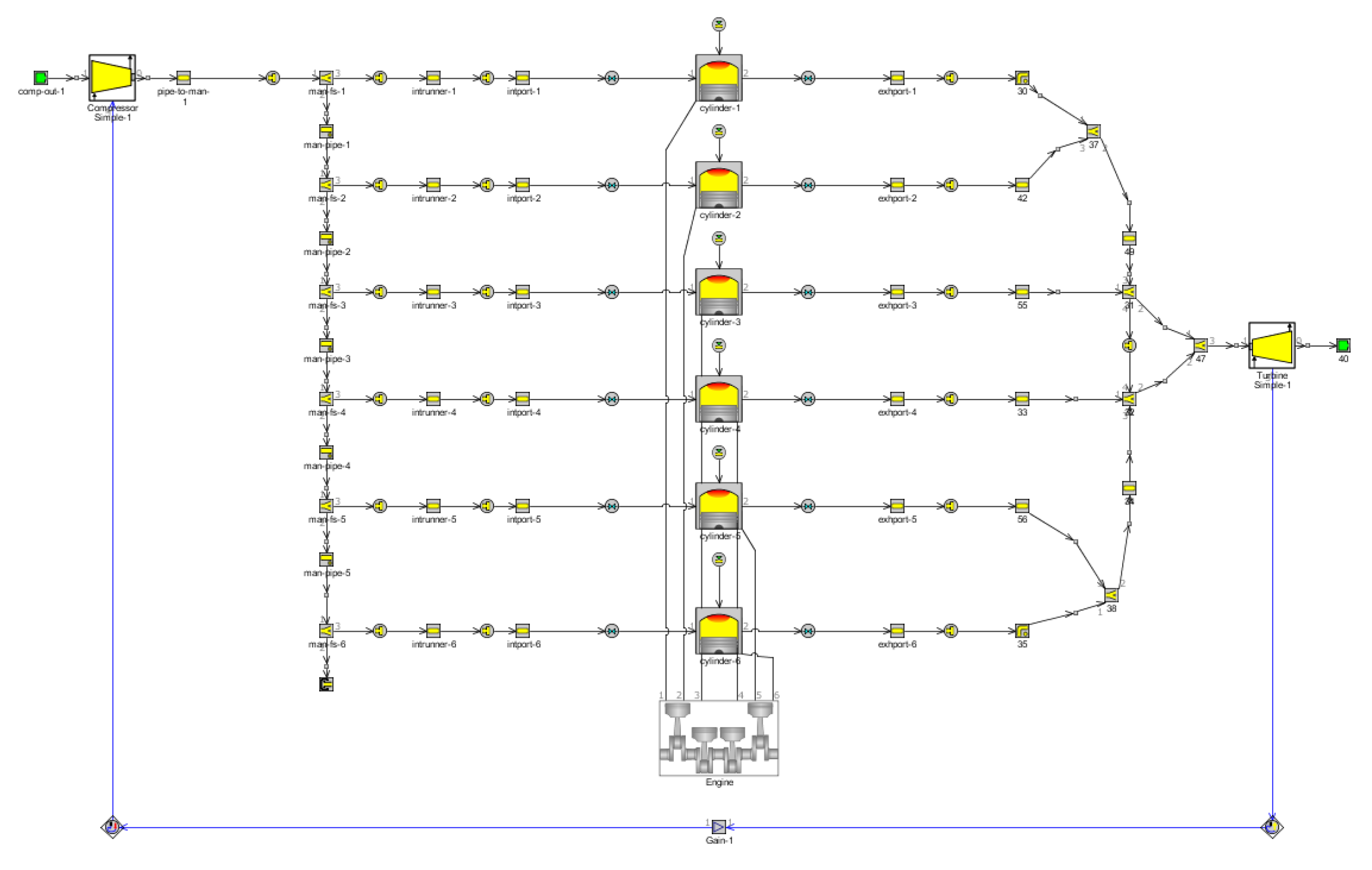
2. Simulation Principle and Model
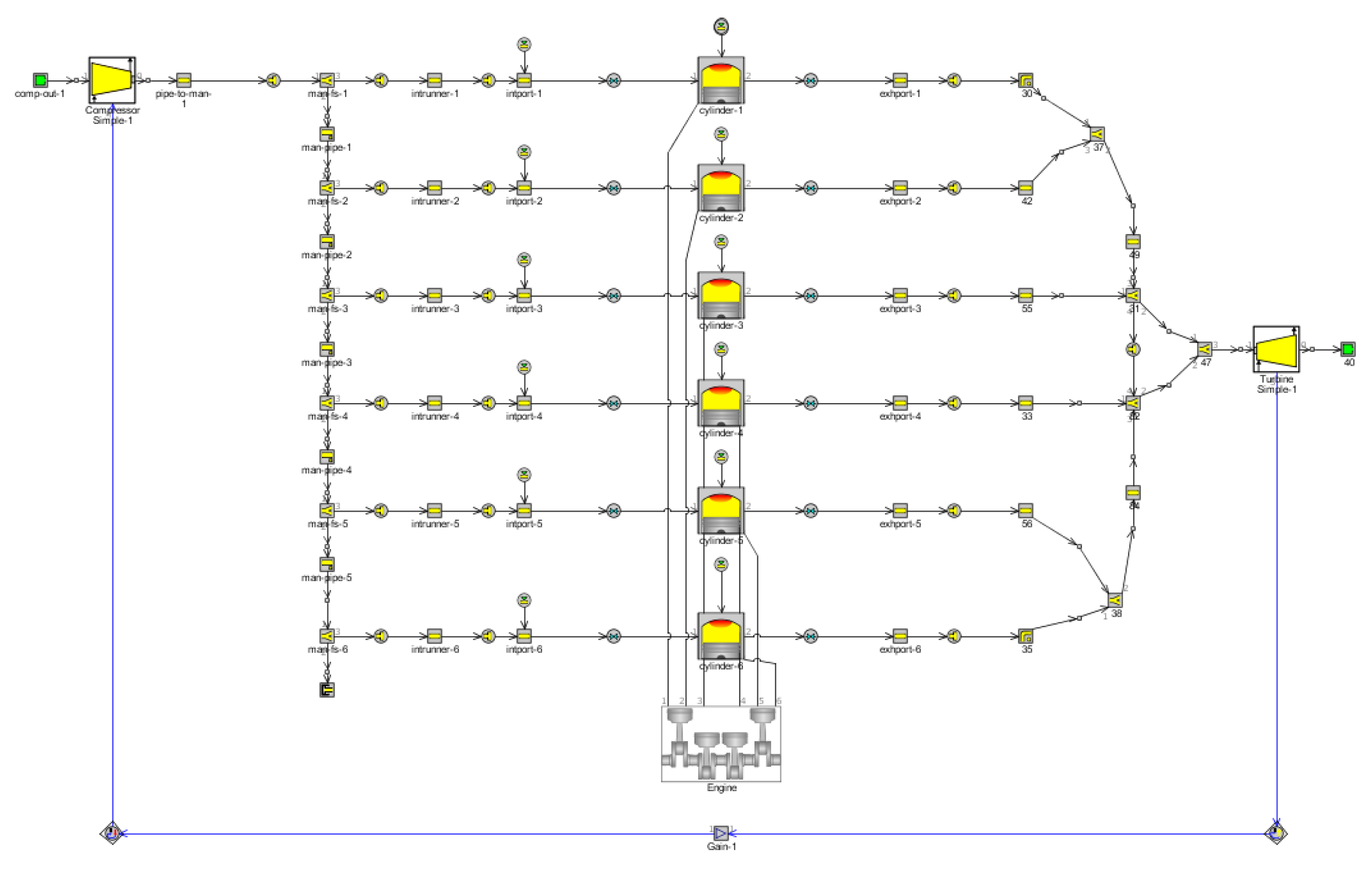
2.1. Basic Parameters and Model Establishment
2.2. Model Verification and Optimization
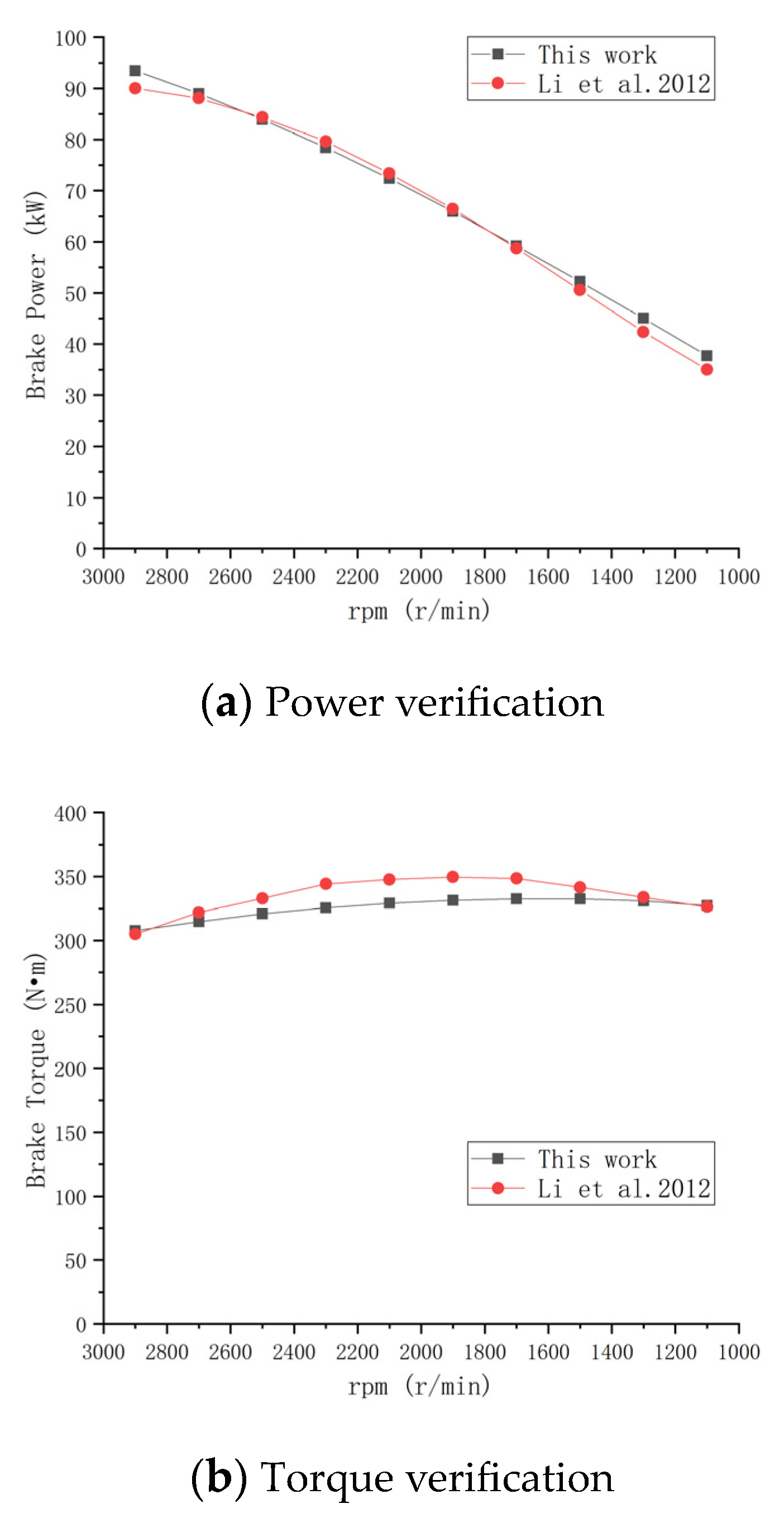
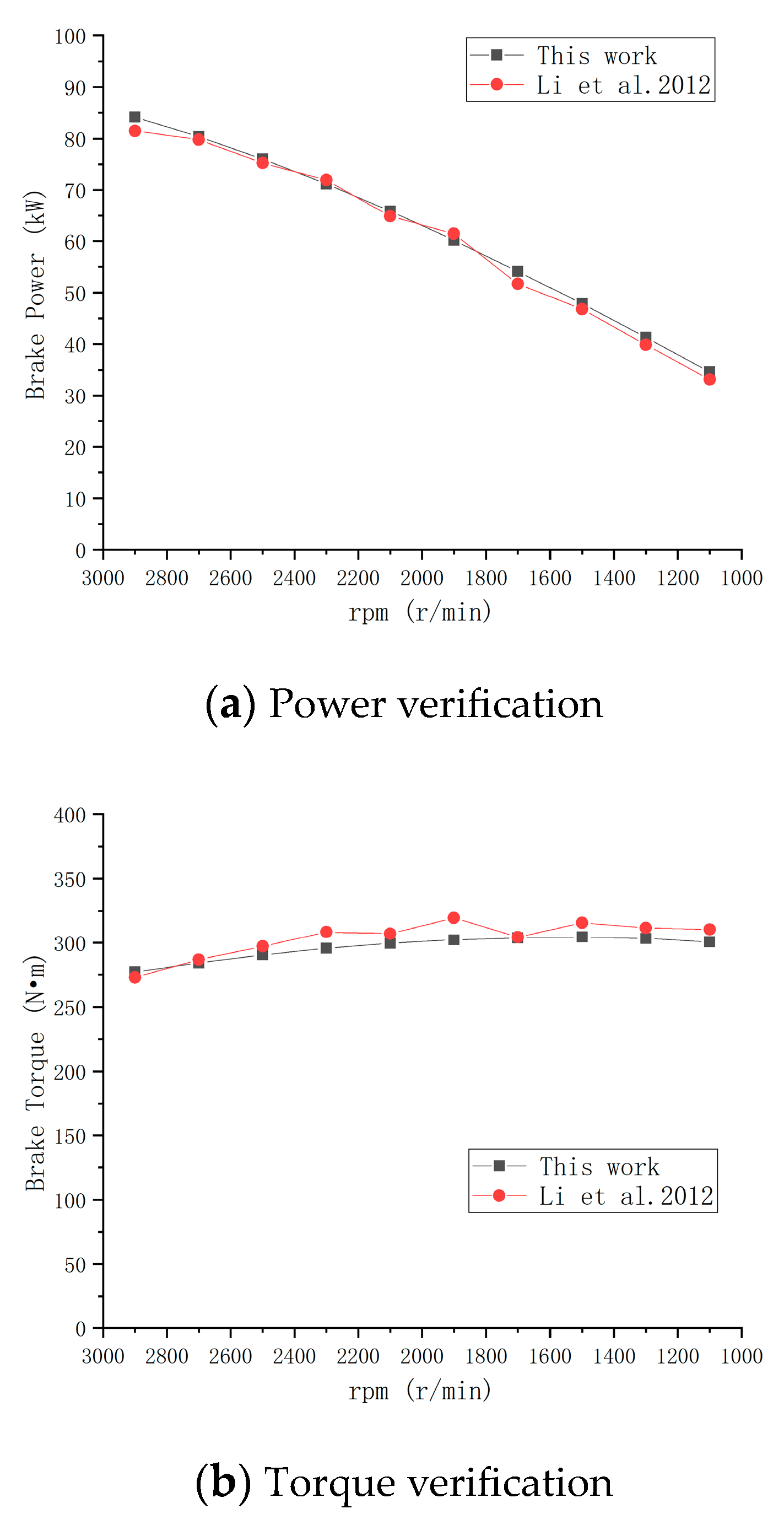
2.2.1. Model Verification
2.2.2. Model Optimization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamic Performance
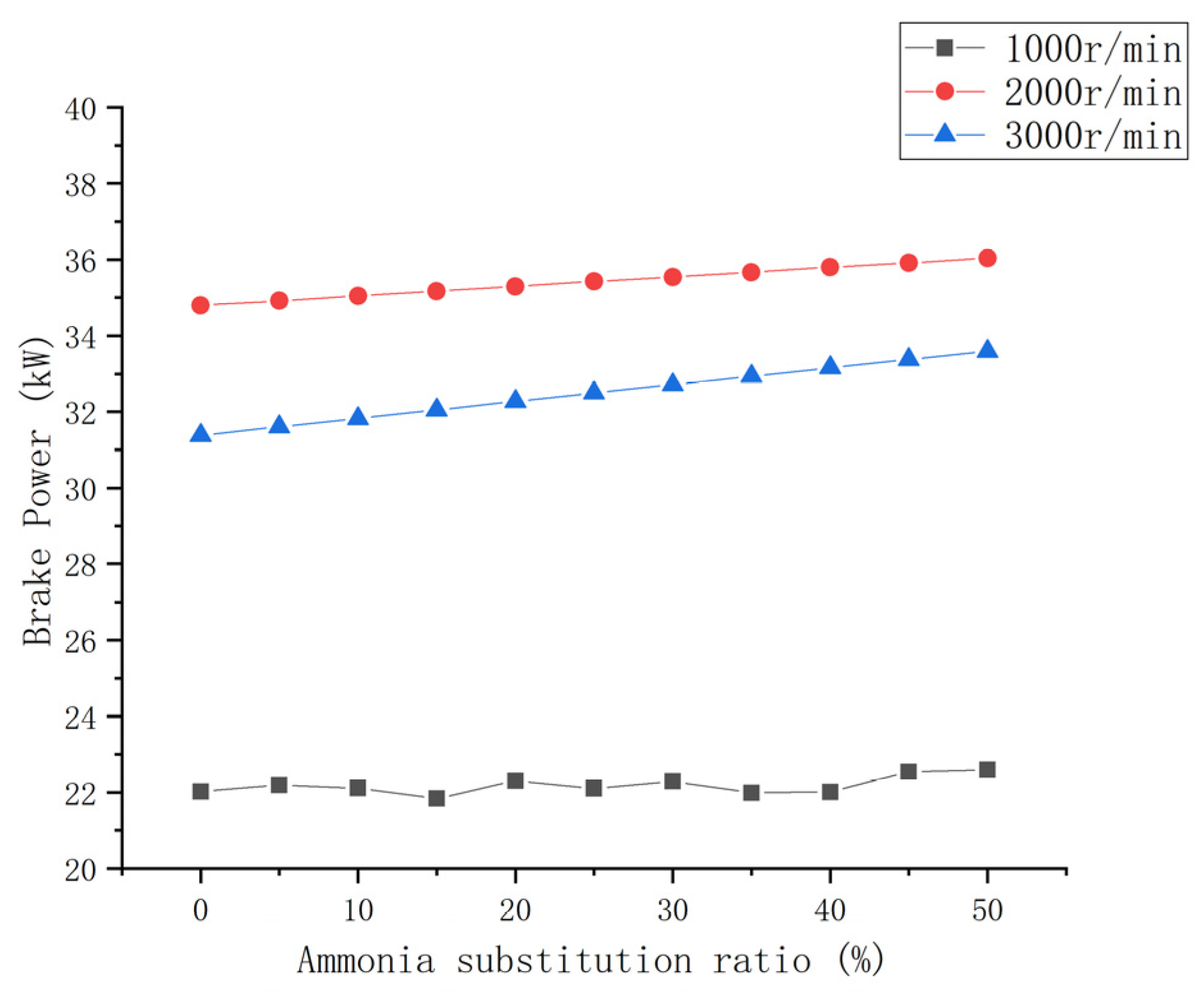
3.1.1. Brake Power
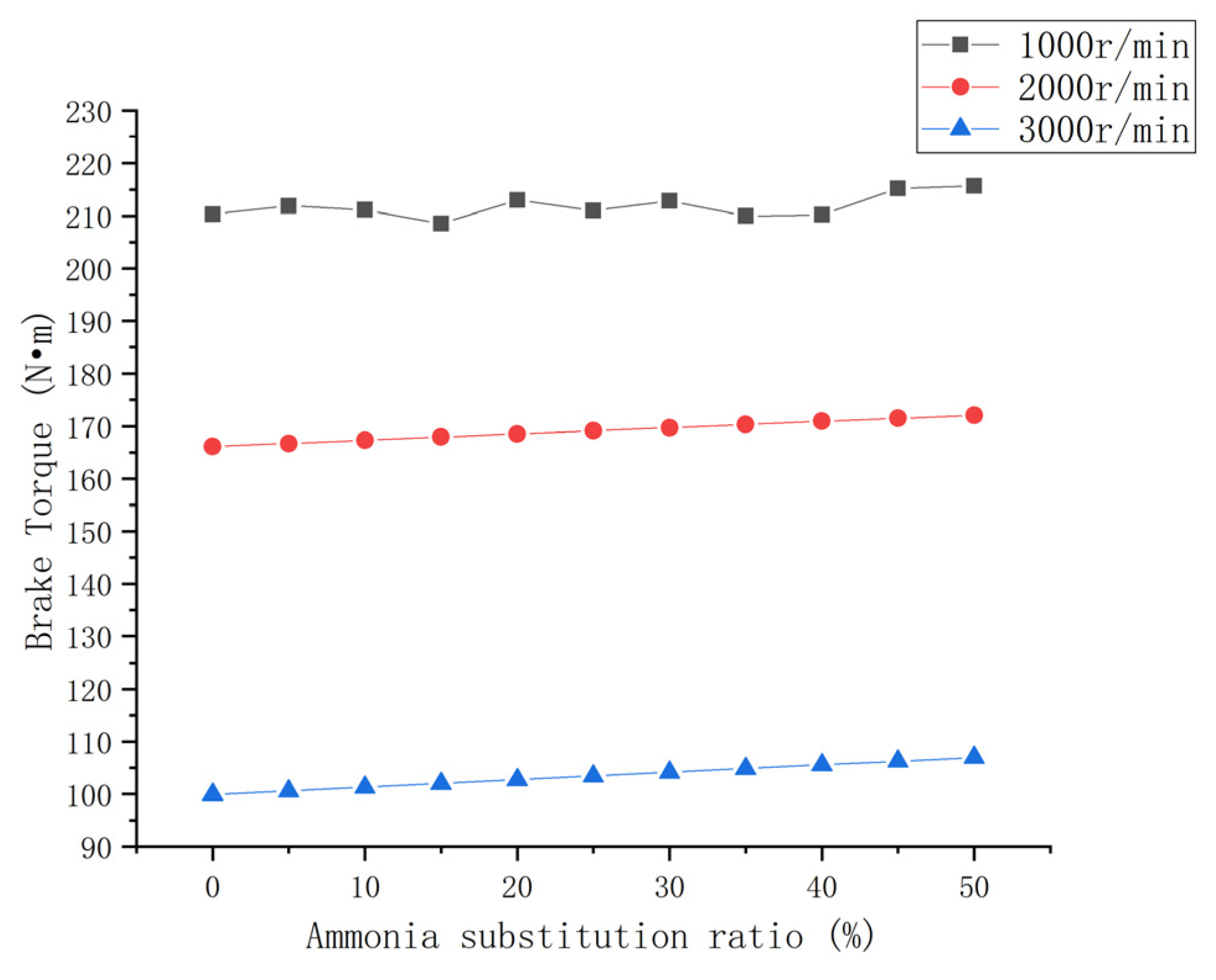
3.1.2. Brake Torque
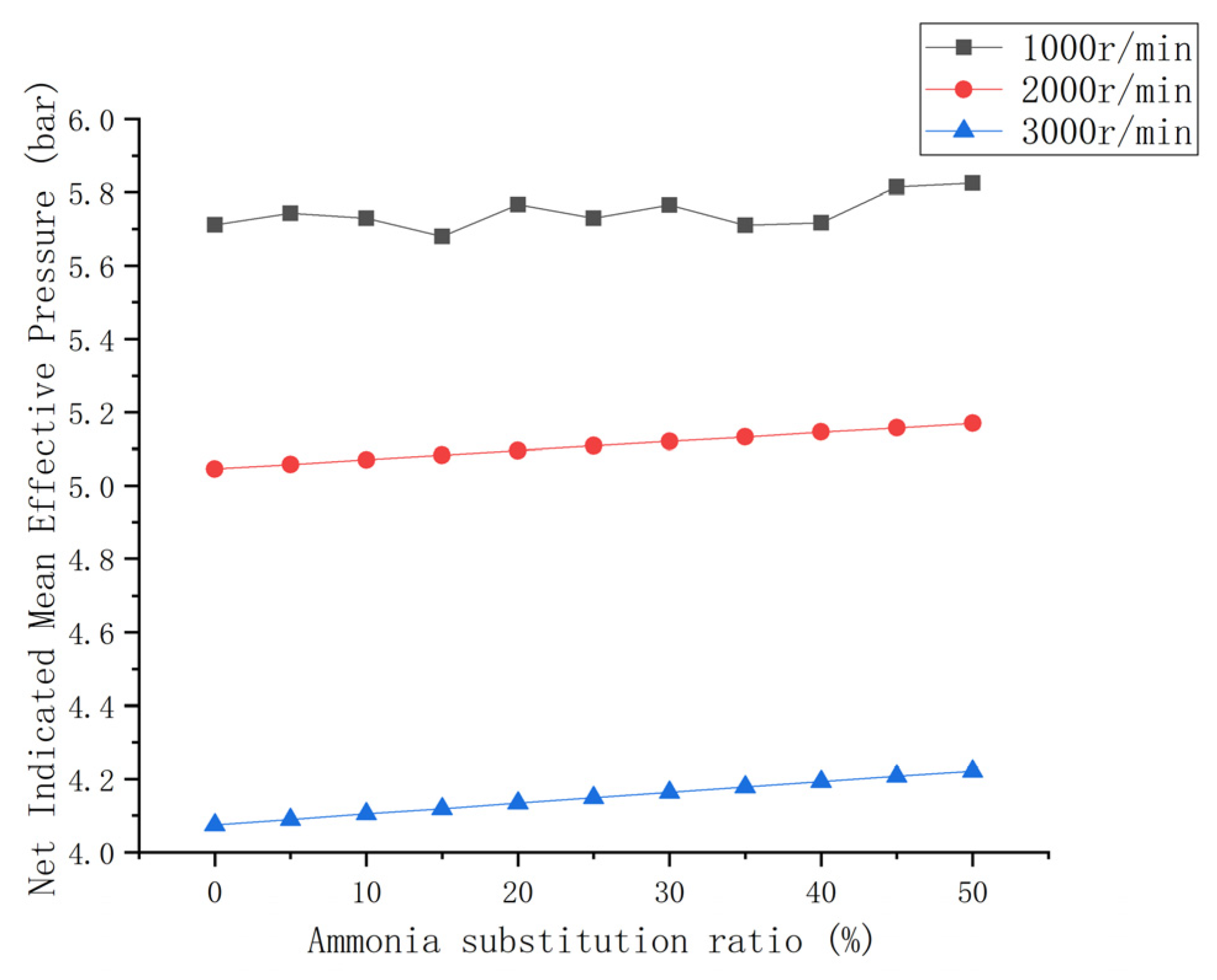
3.1.3. Mean Effective Pressure
3.2. Economic Performance
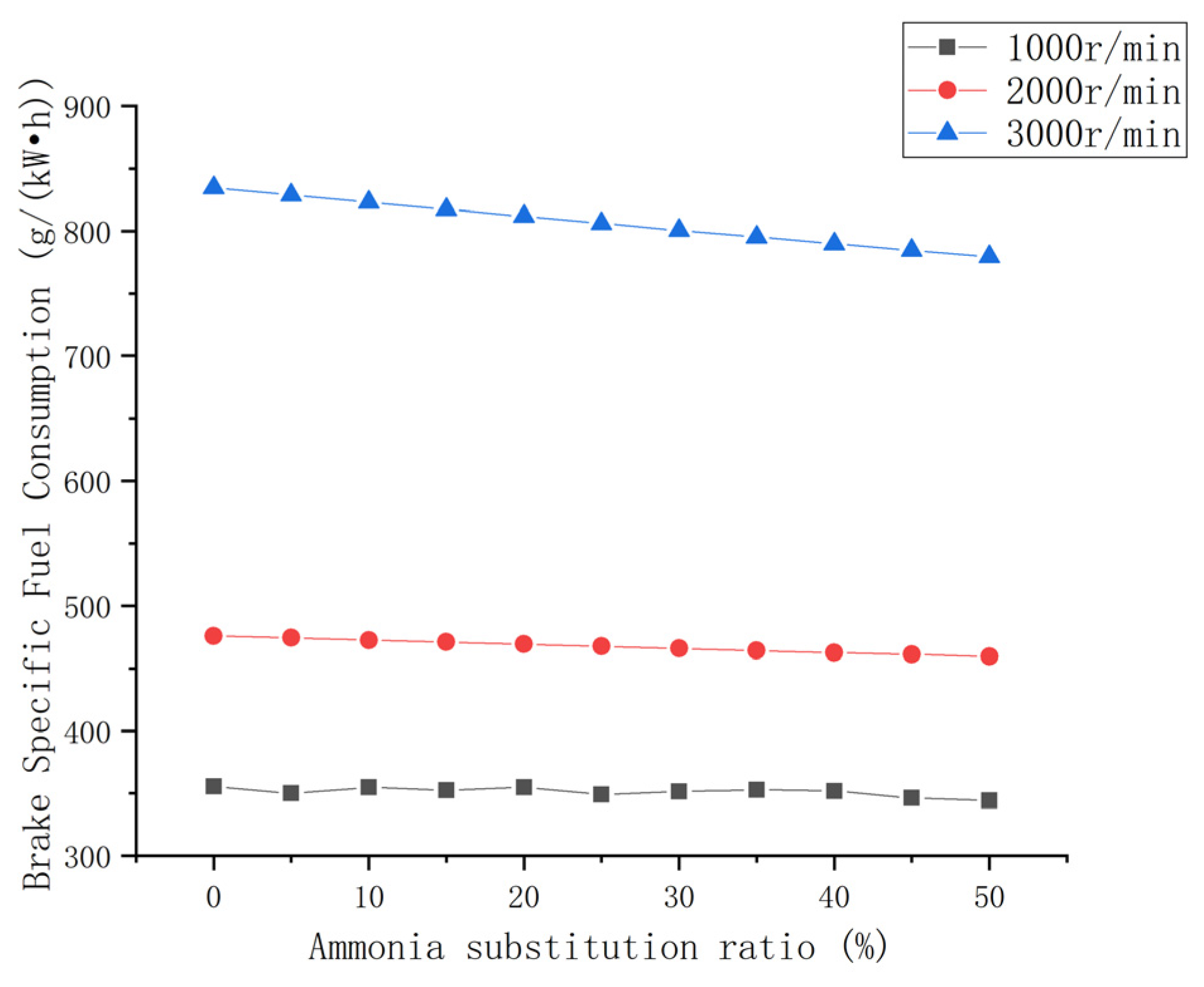
3.2.1. Brake-Specific Fuel Consumption
3.2.2. Brake Thermal Efficiency
3.3. Emission Performance
3.3.1. CO2 Emission
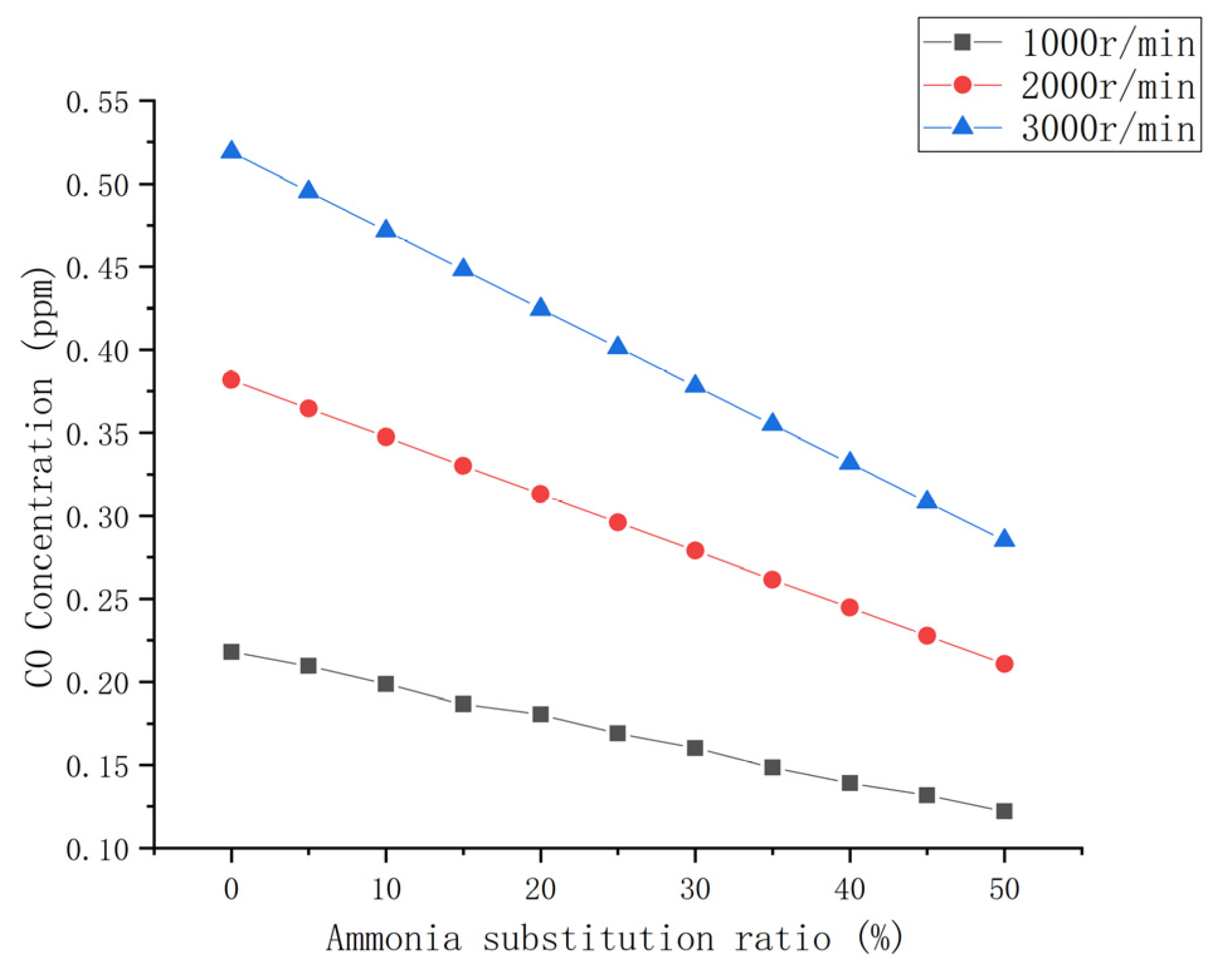
3.3.2. CO Emission
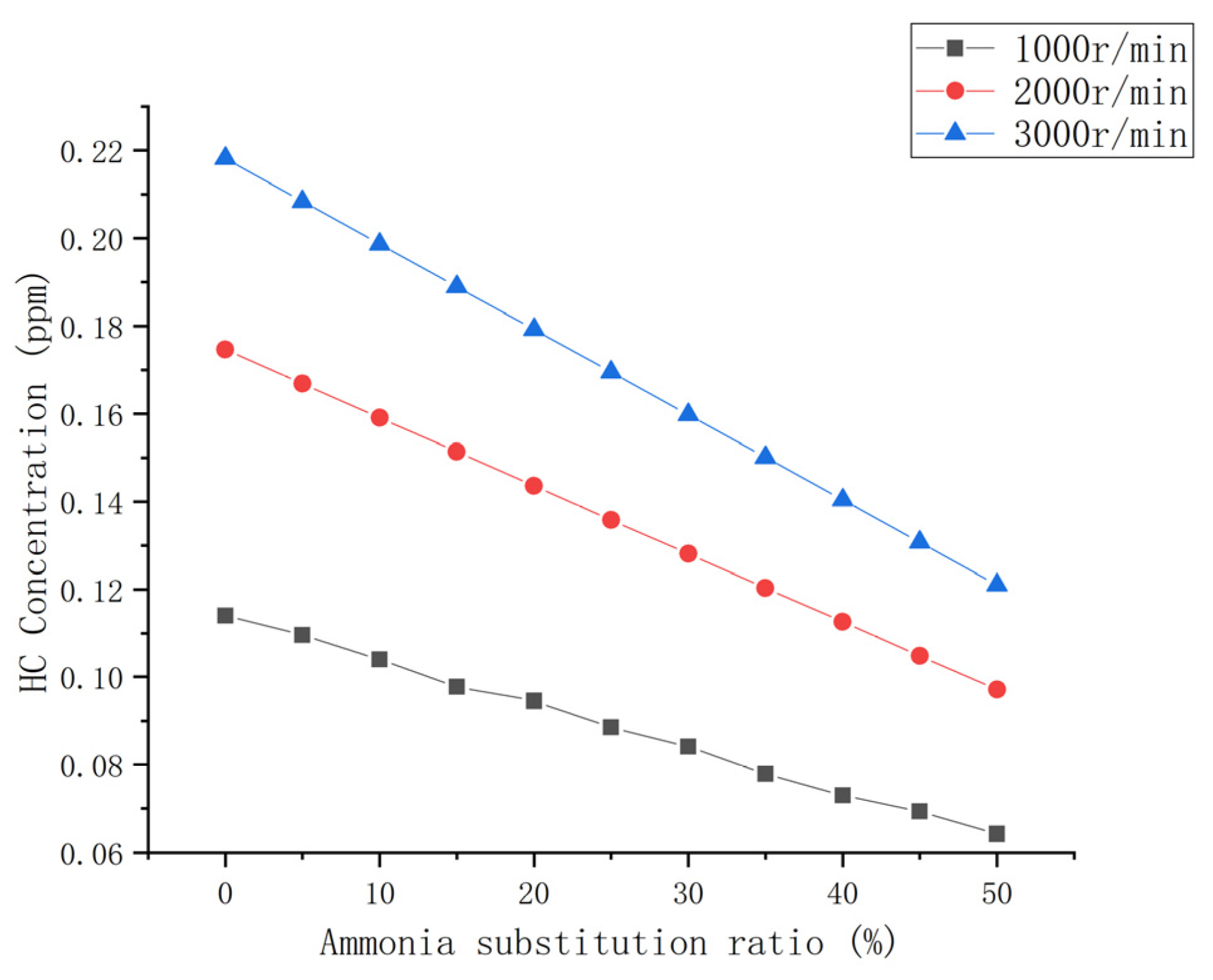
3.3.3. HC Emission
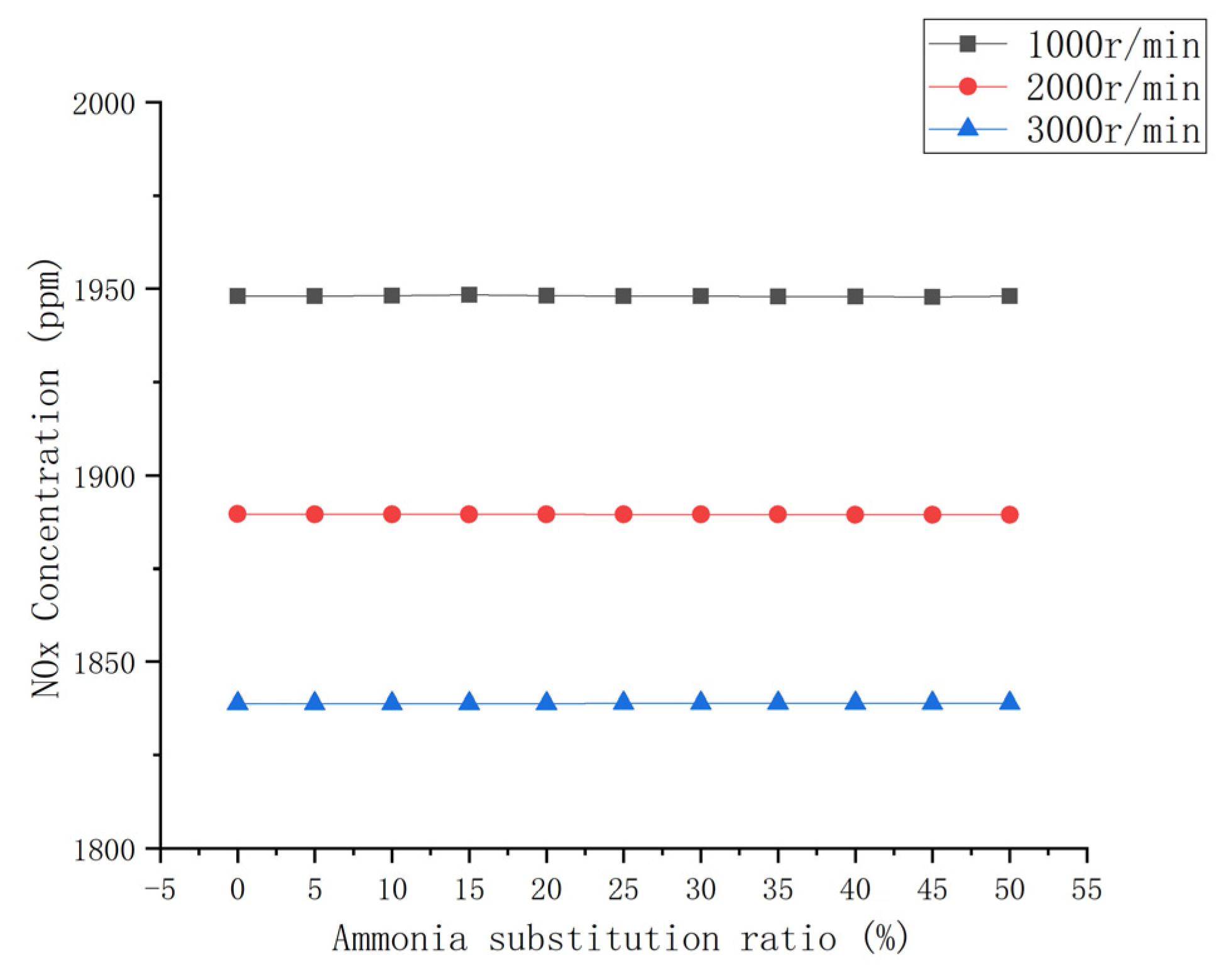
3.3.4. NOx Emission
3.4. Application Prospect
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The engine power performance parameters can be improved to a certain extent with an increase in the ammonia blending ratio. The brake power and torque of each speed condition increased by 2.5% and 7%. The increase in the mean effective pressure was small.
- (2)
- The increases in the effective fuel consumption and effective thermal efficiency at each speed condition were between 3% and 6% with an increase in the ammonia blending ratio. These increased significantly at high speeds. However, its fuel consumption and thermal efficiency were poor.
- (3)
- The emissions of CO and CO2 in the engine exhaust decreased up to approximately 50% with an increase in the ammonia blending ratio. HC emissions were significantly reduced. The total amount and NOx remained generally unchanged.
- (4)
- The overall performance of the engine at medium speed was the best. The power output was maximized while maintaining low emissions and high efficiency.
- (5)
- In the simulation, simplified treatments were applied to the heat transfer and the combustion model of the engine. More in-depth studies of chemical reaction mechanisms are needed to further improve the simulation. More experiments are needed for further model calibration.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| N0 | mass fraction of ammonia is 0% |
| N50 | mass fraction of ammonia is 50% |
| BSFC | brake-specific fuel consumption |
| BTE | brake thermal efficiency |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| HC | hydrocarbon |
| NOx | oxides of nitrogen |
References
- Anika, O.C.; Nnabuife, S.G.; Bello, A.; Okoroafor, E.R.; Kuang, B.; Villa, R. Prospects of low and zero-carbon renewable fuels in 1.5-degree net zero emission actualisation by 2050: A critical review. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, M.; Zhang, H.; Yin, H.; Ding, Y. Emission control status, and future perspectives of diesel trucks in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, M.; Chojnowski, J.; Szamrej, G. A Review of Low-CO2 Emission Fuels for a Dual-Fuel RCCI Engine. Energies 2021, 14, 5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Gu, Z.; Zhu, C. A review of low and zero carbon fuel technologies: Achieving ship carbon reduction targets. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 54, 102762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, M.; Ventura, M.; Soares, C.G. Optimization procedure to minimize fuel consumption of a four-stroke marine turbocharged diesel engine. Energy 2019, 168, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatuğ, Ç.; Tadros, M.; Ventura, M.; Soares, C.G. Strategy for ship energy efficiency based on optimization model and data-driven approach. Ocean Eng. 2023, 279, 114397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axsen, J.; Wolinetz, M. What does a low-carbon fuel standard contribute to a policy mix? An interdisciplinary review of evidence and research gaps. Transp. Policy 2023, 133, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatuğ, Ç.; Ceylan, B.O.; Ejder, E.; Arslanoğlu, Y. Investigation and Examination of LNG, Methanol, and Ammonia Usage on Marine Vessels. In Decarbonization of Maritime Transport. Energy, Environment, and Sustainability; Zincir, B., Shukla, P.C., Agarwal, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Atnaw, S.M.; Ramaya, A.V.; Alemayehu, G. A comprehensive review on the effect of ethers, antioxidants, and cetane improver additives on biodiesel-diesel blend in CI engine performance and emission characteristics. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 108, 101227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, M.; Szamrej, G. Experimental Evaluation of the Effect of Replacing Diesel Fuel by CNG on the Emission of Harmful Exhaust Gas Components and Emission Changes in a Dual-Fuel Engine. Energies 2023, 16, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, S.; Turner, J.W.; Sileghem, L.; Vancoillie, J. Methanol as a fuel for internal combustion engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2019, 70, 43–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.R.; Maurya, R.K.; Mishra, P. Assessment of performance, combustion and emissions characteristics of methanol-diesel dual-fuel compression ignition engine: A review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 8, 638–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, X.; Liu, Z. The effect of methanol production and application in internal combustion engines on emissions in the context of carbon neutrality: A review. Fuel 2022, 320, 123902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Qu, Q.; Chen, M.; Lyu, H.; Sun, J. Advancements in methanol distillation system: A comprehensive overview. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 199, 130–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, N.; Viswanathan, K.; Karthic, S.; Ekambaram, P.; Wu, W.; Vo, D.-V.N. Split injection strategies based RCCI combustion analysis with waste cooking oil biofuel and methanol in an open ECU assisted CRDI engine. Fuel 2022, 319, 123710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Li, Z. Effects of hydrogen-rich products from methanol steam reforming on the performance enhancement of a medium-speed marine engine. Energy 2022, 256, 124540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Li, B.; Tian, H.; Leng, X.; Dong, D.; Long, W. Study on the performance of diesel-methanol diffusion combustion with dual-direct injection system on a high-speed light-duty engine. Fuel 2022, 317, 123414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Cordtz, R.F.; Thomsen, T.B.; Førby, N.L.; Schramm, J. Application of methanol with an ignition improver in a small marine CI engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 271, 116311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.O.; Osman, A.I.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Al-Rawashdeh, H.; Abu-Jrai, A.; Ahmad, R.; Gomaa, M.R.; Deka, T.J.; Rooney, D.W. An experimental study of engine characteristics and tailpipe emissions from modern DI diesel engine fuelled with methanol/diesel blends. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 220, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Juangsa, F.B.; Irhamna, A.R.; Irsyad, A.R.; Hariana, H.; Darmawan, A. Ammonia utilization technology for thermal power generation: A review. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 111, 101365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Rengel, M.M.; Martín, M. A zero CO2 emissions large ship fuelled by an ammonia-hydrogen blend: Reaching the decarbonisation goals. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 293, 117497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurien, C.; Mittal, M. Utilization of green ammonia as a hydrogen energy carrier for decarbonization in spark ignition engines. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2023, 48, 28803–28823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manigandan, S.; Ryu, J.I.; Kumar, T.P.; Elgendi, M. Hydrogen and ammonia as a primary fuel—A critical review of production technologies, diesel engine applications, and challenges. Fuel 2023, 352, 129100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Pan, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Wei, H. Effects of intake parameters and compression ratio on ammonia combustion and emissions in SI engines. Fuel 2023, 354, 129382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddeen, K.; Tang, Q.; Shi, H.; Magnotti, G.; Turner, J. A novel multiple spark ignition strategy to achieve pure ammonia combustion in an optical spark-ignition engine. Fuel 2023, 349, 128741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Duan, L. Research progress of ammonia combustion toward low carbon energy. Fuel Process. Technol. 2023, 248, 107821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Long, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wei, Y. Effects of ammonia addition on the performance and emissions for a spark-ignition marine natural gas engine. Energy 2023, 272, 127092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, S.; Bai, X.-S.; Repo, J.A.; Hautala, S.; Hyvönen, J. Performance and emission characteristics of an ammonia/diesel dual-fuel marine engine. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 185, 113631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, X.; Hashemi, H.; Glarborg, P.; Lowe, V.M.; Marshall, P.; Fernandes, R.; Shu, B. An experimental and modeling study on auto-ignition kinetics of ammonia/methanol mixtures at intermediate temperature and high pressure. Combust. Flame 2022, 242, 112160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Dong, D.; Wei, F.; Long, W.; Wang, Y.; Cong, L.; Dong, P.; Tian, H.; Wang, P. Chemical mechanism of ammonia-methanol combustion and chemical reaction kinetics analysis for different methanol blends. Fuel 2023, 341, 127697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Xi, Z.; Hu, S.; Chu, X. Effect of methanol blending on the high-temperature auto-ignition of ammonia: An experimental and modeling study. Fuel 2023, 339, 126911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liao, C.; Liu, J. Harmonic analysis and optimization of the intake system of a gasoline engine using GT-power. Energy Procedia 2012, 14, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ye, Y. Experimental study and Analysis on the performance of methanol/Diesel mixed fuel Diesel engine. Diesel Engine 2012, 5, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Hu, D.; Yang, C.; Duan, B.; Wang, Y. Study on the performance of premixed natural gas/ammonia engine with diesel ignition. Energy 2023, 271, 127056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Hu, D.; Yang, C.; Duan, B.; Wang, Y. Effect of different ammonia mixing methods for diesel ignition on combustion and emission performance of high pressure common rail engine. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 111, 101402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Feng, Y.; Jin, S. Generation mechanism and emission characteristics of N2O and NO in ammonia-diesel dual-fuel engine. Energy 2023, 284, 129291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Yang, C.; Hu, D.; Duan, B.; Wang, Y. Study on dual injection strategy of diesel ignition ammonia/hydrogen mixture fuel engine. Fuel 2023, 348, 128526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, K.N.; Gore, M.; Liu, H.; Fang, T. Experimental characterization of ammonia, methane, and gasoline fuel mixtures in small scale spark ignited engines. Appl. Energy Combust. Sci. 2023, 16, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | Ammonia | Methanol | Diesel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density/g·cm−3 | 0.77 (Liquid) | 0.79 | 0.84 |
| Spontaneous combustion temperature/°C | 650 | 464 | 316 |
| Vaporization latent heat/kJ·kg−1 | 1370 | 1100 | 260 |
| Low calorific value/kJ·kg−1 | 18,610 | 19,660 | 42,700 |
| Octane number | 110 | 110 | N/A |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Compression ratio | 16.5 |
| Bore/mm | 105 |
| Stroke/mm | 125 |
| Connecting rod length/mm | 220 |
| Fuel supply advance angle/(°) | 12 |
| Rated speed/(r/min) | 2800 |
| Rated power/kW | 95.6 |
| Speed (r/min) | 2900 | 2700 | 2500 | 2300 | 2100 | 1900 | 1700 | 1500 | 1300 | 1100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel injection quantity (mg) | 48 | 47.5 | 47 | 46.5 | 46 | 45.5 | 45 | 44.5 | 44 | 43.5 |
| Speed (r/min) | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel injection quantity (mg) | 43.5 | 46 | 48.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Lyu, Z.; Luo, P.; Zhang, G.; Ying, W.; Chen, A.; Xiao, H. Effects of Methanol–Ammonia Blending Ratio on Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Compression Ignition Engine. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122388
Huang Z, Lyu Z, Luo P, Zhang G, Ying W, Chen A, Xiao H. Effects of Methanol–Ammonia Blending Ratio on Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Compression Ignition Engine. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(12):2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122388
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zan, Zhaochun Lyu, Peifang Luo, Guoqing Zhang, Wenxuan Ying, Aiguo Chen, and Hua Xiao. 2023. "Effects of Methanol–Ammonia Blending Ratio on Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Compression Ignition Engine" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 12: 2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122388
APA StyleHuang, Z., Lyu, Z., Luo, P., Zhang, G., Ying, W., Chen, A., & Xiao, H. (2023). Effects of Methanol–Ammonia Blending Ratio on Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Compression Ignition Engine. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(12), 2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122388