Sponge Community Patterns in Mesophotic and Deep-Sea Habitats in the Aegean and Ionian Seas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Sample Processing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
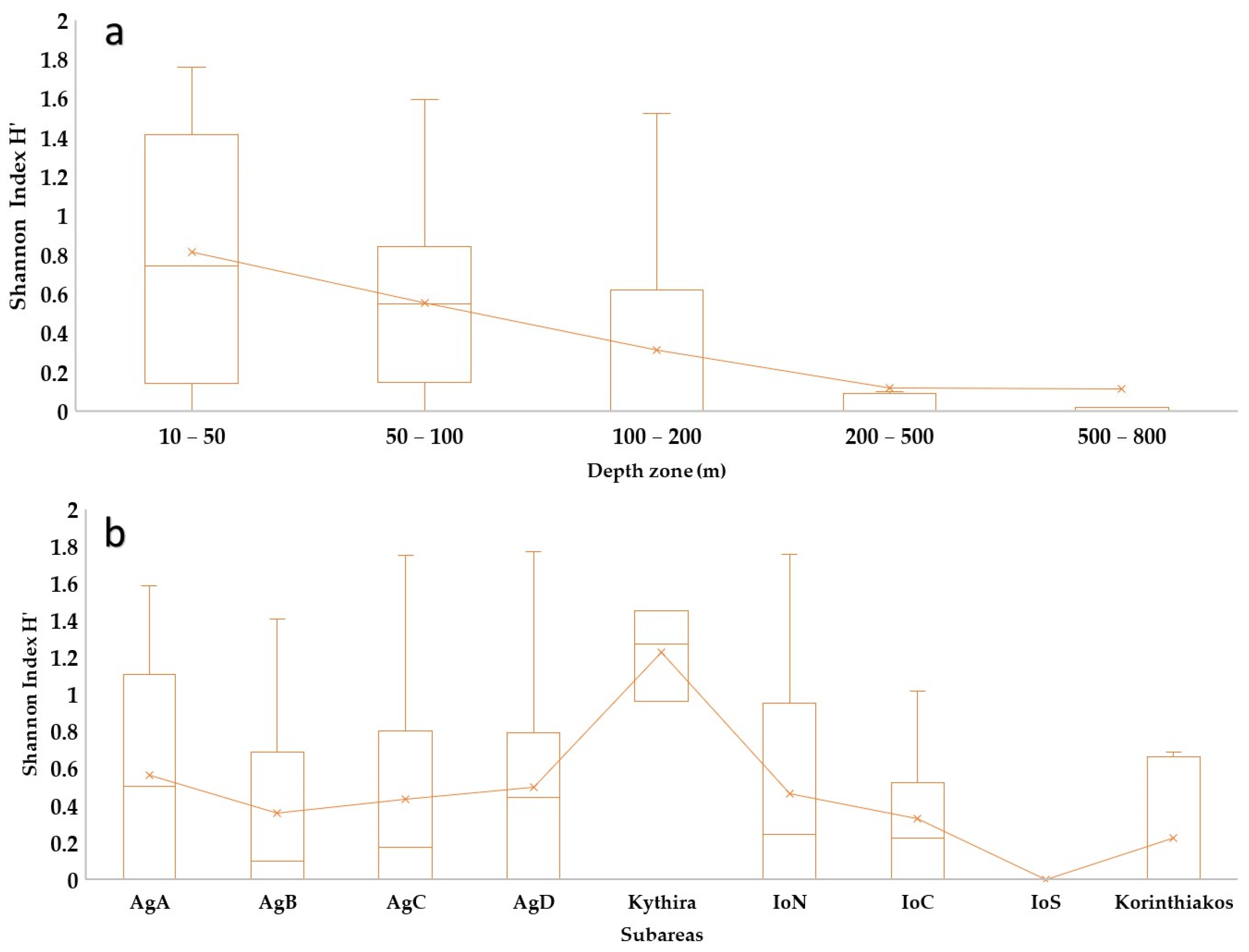
3.1. Sponge Diversity in the Two Ecoregions
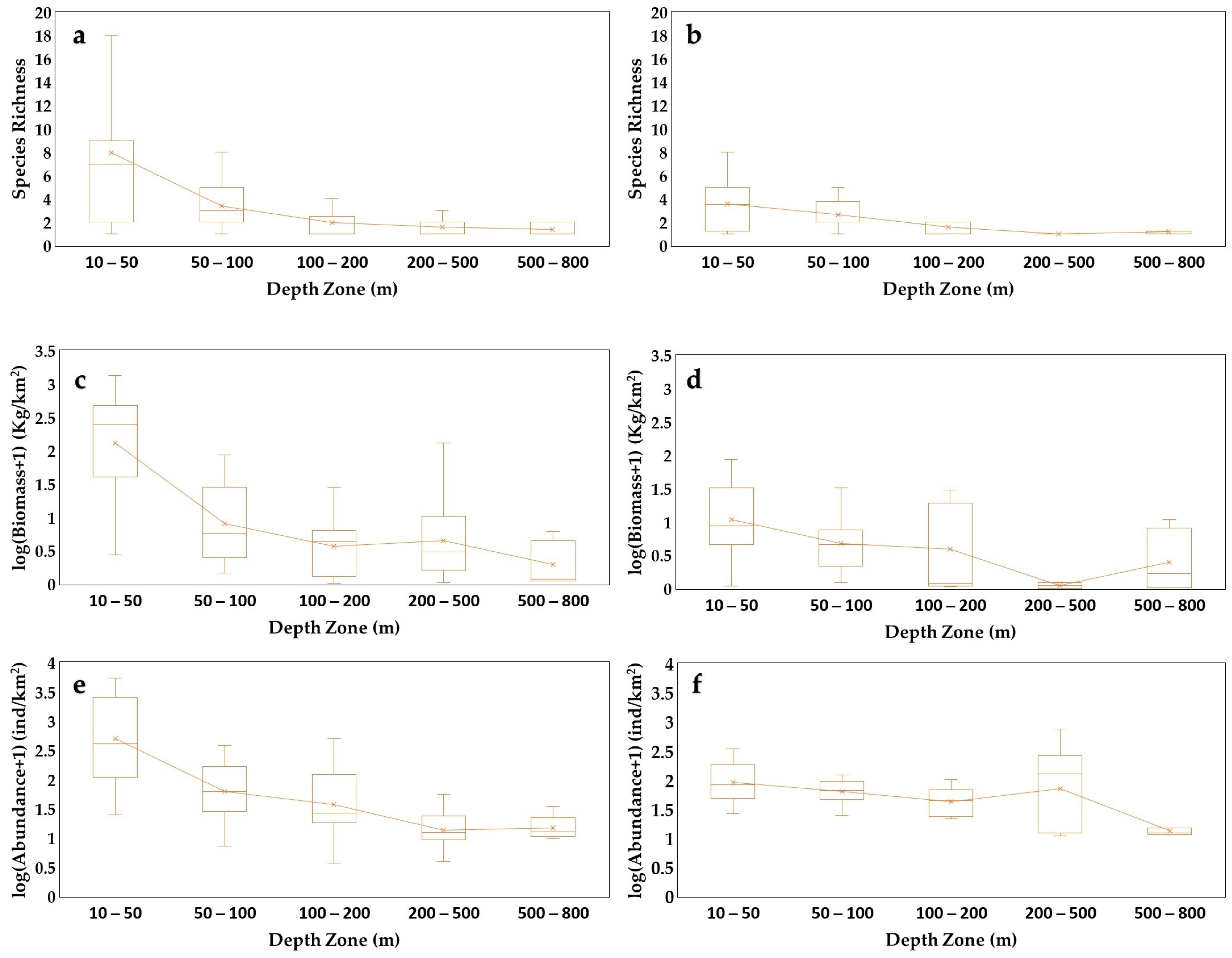
3.2. Sponge Biomass and Abundance
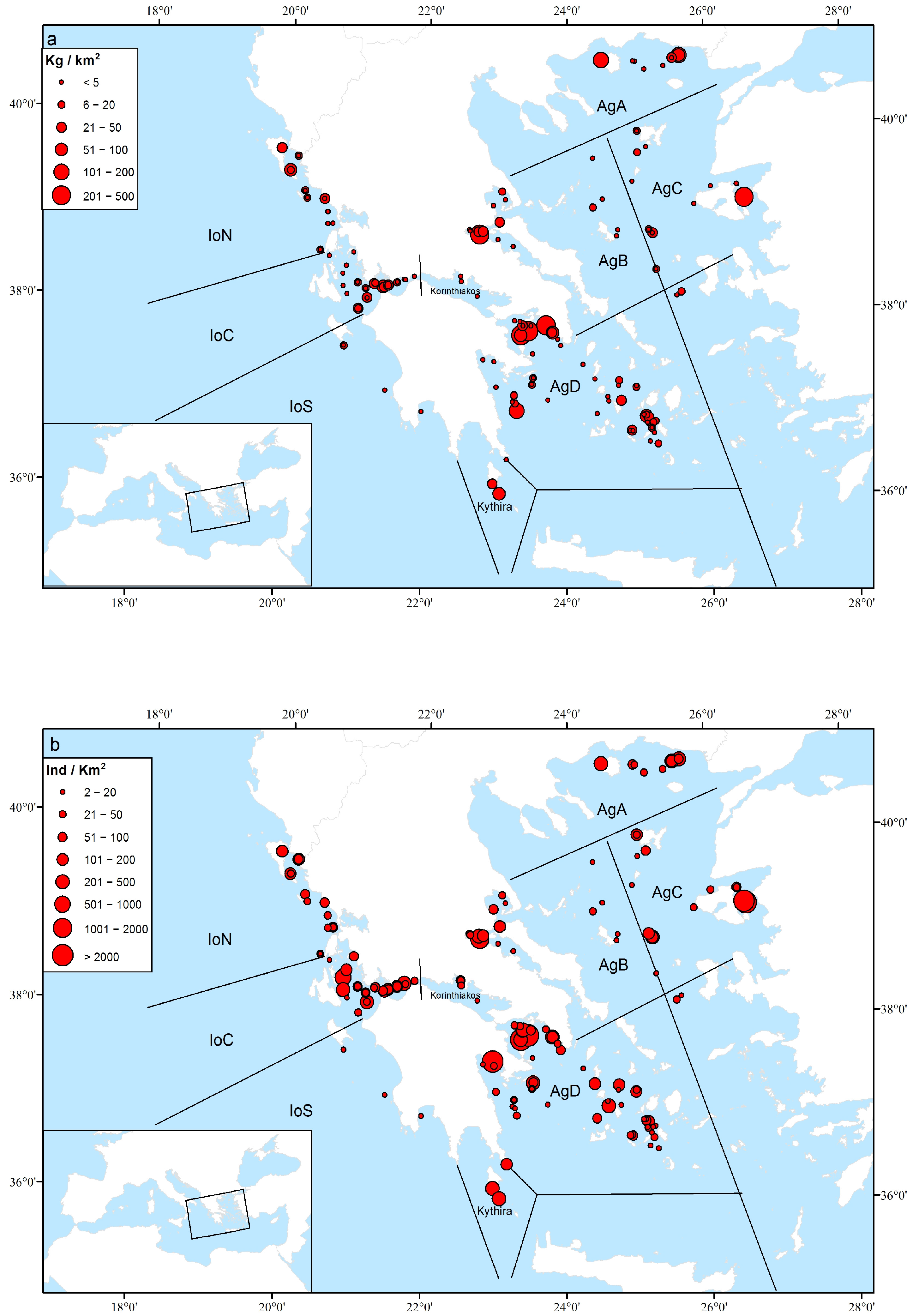
3.3. Geographical and Bathymetric Patterns
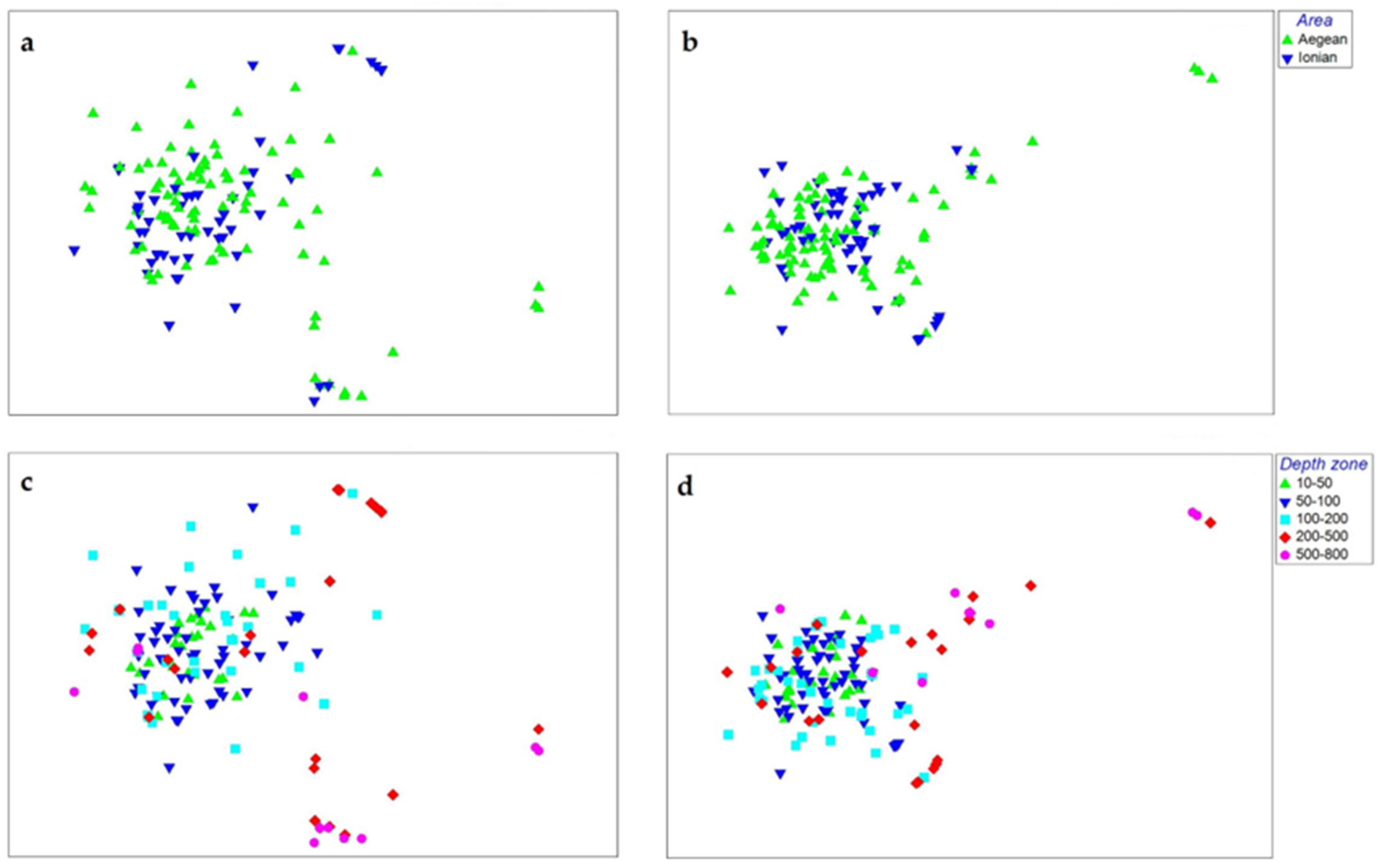
3.4. Sponge Resemblance Patterns
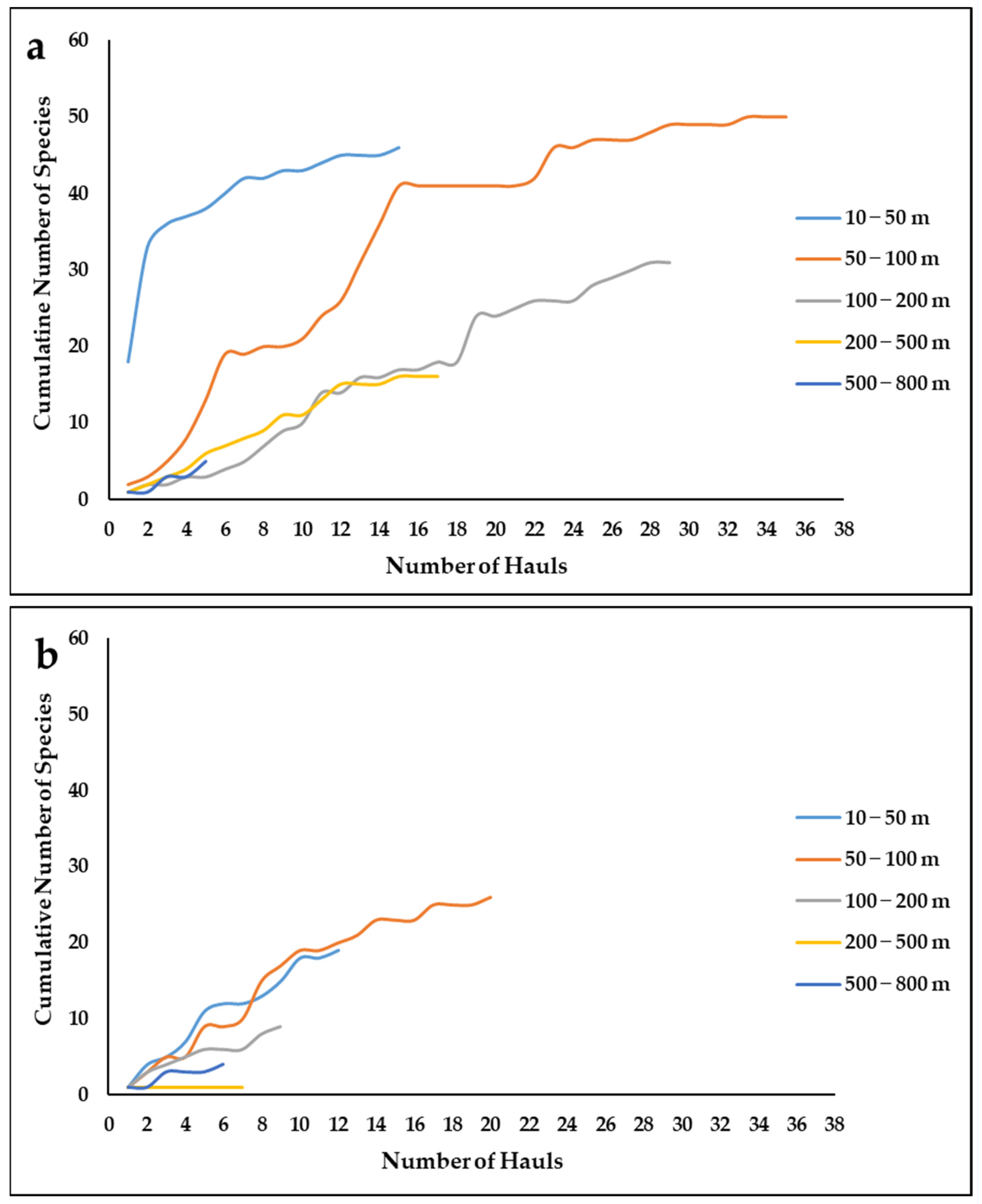
3.5. Sponge Diversity and Research Effort
4. Discussion
4.1. Sponge Diversity in the Two Ecoregions
4.2. Sponge Geographical and Bathymetric Patterns
4.3. Sponge Community Resemblance Patterns
4.4. Vulnerable and Endangered Sponge Species
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Navarro-Barranco, C.; Ambroso, S.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Grinyó, J.; Montseny, M.; Santín, A. Chapter 6—Conservation of dark habitats. In Coastal Habitat Conservation; Espinosa, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 147–170. [Google Scholar]
- Castellan, G.; Angeletti, L.; Montagna, P.; Taviani, M. Drawing the borders of the mesophotic zone of the Mediterranean Sea using satellite data. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thriestle, D. The Deep-Sea floor: An Overview; Tyler, P.A., Ed.; Ecosystems of the Deep Oceans; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 5–38. [Google Scholar]
- Danovaro, R.; Company, J.B.; Corinaldesi, C.; D’Onghia, G.; Galil, B.; Gambi, C.; Gooday, A.J.; Lampadariou, N.; Luna, G.M.; Morigi, C.; et al. Deep-Sea Biodiversity in the Mediterranean Sea: The Known, the Unknown, and the Unknowable. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Llorda, E.; Brandt, A.; Danovaro, R.; De Mol, B.; Escobar, E.; German, C.R.; Levin, L.A.; Martinez Arbizu, P.; Menot, L.; Bulh-Mortensen, P.; et al. Deep, diverse and definitely different: Unique attributes of the world’s largest ecosystem. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 2851–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardà, F.; Calafat, A.; Flexas, M.M.; Tselepides, A.; Canals, M.; Espino, M.; Tursi, A. An introduction to Mediterranean deep-sea biology. Sci. Mar. 2004, 68, 7–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzà, C.; Maldonado, M. New and rare sponges from the deep shelf of the Alboran Islant (Alboran Sea, Western Mediterranean). Zootaxa 2014, 3760, 141–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertollino, M.; Bo, M.; Canese, S.; Bavestrello, G.; Pansini, M. Deep sponge communities of the Gulf of St Eufemia (Calabria, southern Tyrrhenian Sea), with description of two new species. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. U.K. 2015, 95, 1371–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boury-Esnault, N.; Vacelet, J.; Reiswig, H.M.; Fourt, M.; Aguilar, R.; Cheveldonné, P. Mediterranean hexactinellid sponges, with the description of a new Sympagella species (Porifera, Hexactinellida). J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. U.K. 2015, 95, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idan, T.; Shefer, S.; Feldstein, T.; Yahel, R.; Huchon, D.; Ilan, M. Shedding light on an East-Mediterranean mesophotic sponge ground community and the regional sponge fauna. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, M.; Ricci, S.; Canese, S.; Cau, A.; Bavestrello, G.; Pansini, M.; Bo, M. Diversity of the sponge fauna associated with white coral banks from two Sardinian canyons (Mediterranean Sea). J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. U.K. 2019, 99, 1735–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santín, A.; Grinyó, J.; Ambroso, S.; Uriz, M.J.; Dominguez-Carrió, C.; Gili, J.M. Distribution patterns and demographic trends of demosponges at the Menorca Channel (Northwestern Mediterranean Sea). Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 173, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idan, T.; Shefer, S.; Feldstein, T.; Ilan, M. New discoveries in Eastern Mediterranean mesophotic sponge grounds: Updated checklist and description of three novel sponge species. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.; Bo, M.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Canese, S.; Canessa, M.; Cannas, R.; Cardone, F.; Carugati, L.; Cau, A.; Corriero, G.; et al. Basin-scale occurrence and distribution of mesophotic and upper bathyal red coral forests along the Italian coasts. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, R.W.M.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Vacelet, J.; Dohrmann, M.; Erpenbeck, D.; De Voogd, N.J.; Santodomingo, N.; Vanhoorne, B.; Kelly, M.; Hooper, J.N.A. Global Diversity of Sponges (Porifera). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.J. The functional roles of marine sponges. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppari, M.; Gori, A.; Viladrich, N.; Saponari, L.; Canepa, A.; Grinyó, J.; Olariaga, A.; Rossi, S. The role of Mediterranean sponges in benthic-pelagic coupling processes: Aplysina aerophoba and Axinella polypoides case studies. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 477, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouras, A.; Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Chintiroglou, H.; Dounas, C. Benthic Bionomy of the North Aegean Sea III. A comparison of the microbenthic animal assemblages associated with seven sponge species. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1985, 26, 301–319. [Google Scholar]
- Çinar, M.E.; Katağan, T.; Ergen, Z.; Sezgin, M. Zoobenthos-inhabiting Sarcotragus muscarum (Porifera: Demospongiae) from the Aegean Sea. Hydrobiologia 2002, 482, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerovasileiou, V.; Chintiroglou, C.C.; Konstantinou, D.; Voultsiadou, E. Sponges as “living hotels” in Mediterranean marine caves. Sci. Mar. 2016, 80, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, L.; Idan, T.; Shefer, S.; Ilan, M. Macrofauna Inhabiting Massive Demosponges from Shallow and Mesophotic Habitats Along the Israeli Mediterranean Coast. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021a 7, 612779. [CrossRef]
- Goren, L.; Idan, T.; Shefer, S.; Ilan, M. Sponge-Associated Polychaetes: Not a Random Assemblage. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 695163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Aguzzi, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Corbera, J.; Dailianis, T.; et al. The Biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, Patterns, and Threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhl-Mortensen, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Gooday, A.J.; Levin, L.A.; Priede, I.G.; Buhl-Mortensen, P.; Gheerardyn, H.; King, N.J.; Raes, M. Biological structures as a source of habitat heterogeneity and biodiversity on the deep ocean margins. Mar. Ecol. 2010, 31, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, M.; Ruiz, C.; Fourt, M.; Santonja, M.; Dubois, M.; Klautau, M.; Vacelet, J.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Pérez, T. Sponge inventory of the French Mediterranean waters, with an emphasis on cave-dwelling species. Zootaxa 2018, 4466, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamouli, C.; Zenetos, A.; Kallianiotis, A.; Voultsiadou, E. Megabenthic invertebrates’ diversity in Mediterranean trawlable soft bottoms: A synthesis of the current knowledge. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.; Serena, F.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Barone, M.; Bo, M.; Arcos, J.M.; Vulcano, A.; Xavier, J. Identification Guide of Vulnerable Species Incidentally Caught in Mediterranean Fisheries; IUCN: Malaga, Spain, 2019; p. 203. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.J.; Micaroni, V.; Harris, B.; Strano, F.; Broadribb, M.; Rogets, A. Global status, impacts, and management of rocky temperate mesophotic ecosystems. Conserv. Biol. 2022, 00, e13945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, J.R.; Pomponi, S.A.; Kenchington, E.L. Editorial: Deep-sea sponge ecosystems: Knowledge-based approach towards sustainable management and conservation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1132451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Bavestrello, G.; Grinyó, J.; Dominguez-Carrió, C.; Ambroso, S.; Bo, M. Animal Forests in Deep Coastal Bottoms and Continental Shelf of the Mediterranean Sea. In Marine Animal Forests; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OCEANA; SPA/RAC–UN Environment/MAP. Guidelines for Inventorying and Monitoring of Dark Habitats in the Mediterranean Sea; Gerovasileiou, V., Aguilar, R., Marín, P., Eds.; SPA/RAC-Deep Sea Lebanon Project: Tunis, Tunisia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Salomidi, M.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Stamouli, C.; Drakopoulou, V.; Otero, M.M.; Jimenez, C.; Kiparissis, S.; Mytilineou, C.; Papadopoulou, N.; Smith, C.J.; et al. Deep-sea vulnerable benthic fauna. In Deep-Sea Atlas of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea; Otero, M., Mytilineou, C., Eds.; IUCN Gland: Malaga, Spain, 2022; pp. 123–145. [Google Scholar]
- Pansini, M.; Longo, C. A review of the Mediterranean Sea sponge biogeography with, in appendix, a list of the demosponges hitherto recorded from this sea. Biogeographia 2003, 24, 59–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerovasileiou, V.; Dailianis, T.; Sini, M.; Otero, M.D.M.; Numa, C.; Katsanevakis, S.; Voultsiadou, E. Assessing the regional conservation status of sponges (Porifera): The case of the Aegean ecoregion. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santín, A.; Grinyó, J.; Ambroso, S.; Uriz, M.J.; Gori, A.; Dominguez-Carrió, C.; Gili, J.M. Sponge assemblages on the deep Mediterranean continental shelf and slope (Menorca Channel, Western Mediterranean Sea). Deep-Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2018, 131, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Bastari, A.; Calcinai, B.; Di Camillo, C.; Pica, D.; Puce, S.; Vasilano, L.; Torsani, F. Temperate mesophotic ecosystems: Gaps and perspectives of an emerging conservation challenge for the Mediterranean Sea. Eur. Zool. J. 2019, 86, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriero, G.; Pierri, C.; Mercurio, M.; Nonnis Marzano, C.; Onen Tarantini, S.; Gravina, M.F.; Lisco, S.; Moretti, M.; De Giosa, F.; Valenzano, E.; et al. A Mediterranean mesophotic reef built by non-symbiotic scleractinians. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, F.; Corriero, G.; Longo, C.; Mercurio, M.; Onen Tarantini, S.; Gravina, M.F.; Lisco, S.N.; Moretti, M.; De Giosa, F.; Giangrande, A.; et al. Massive bioconstructions built by Neopycnodonte cochlear (Mollusca, Bivalvia) in a mesophotic environment in the central Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, F.; Corriero, G.; Longo, C.; Pierri, C.; Gimenez, G.; Gravina, M.F.; Giangrande, A.; Lisco, S.; Moretti, M.; De Giosa, F.; et al. A system of marine animal bioconstructions in the mesophotic zone along the Southeastern Italian coast. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 948836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.; Betti, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Canese, S.; Cau, A.; Andaloro, F.; Greco, S.; Bo, M. Diversity and abundance of heterobranchs (Mollusca, Gastropoda) from the mesophotic and bathyal zone of the Mediterranean Sea. Eur. Zool. J. 2022, 89, 167–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Bertolino, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Canese, S.; Giusti, M.; Angiolillo, M.; Pansini, M.; Taviani, M. Role of deep sponge grounds in the Mediterranean Sea: A case study in southern Italy. Hydrobiologia 2012, 687, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.A.; Ramírez-Amaro, S.; Ordines, F.; Cárdenas, P.; Ferriol, P.; Terrasa, B.; Massutí, E. Poorly known sponges in the Mediterranean with the detection of some taxonomic inconsistencies. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. U.K. 2020, 100, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrichetti, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Betti, F.; Coppari, M.; Toma, M.; Pronzato, R.; Canese, S.; Bertolino, M.; Costa, G.; Pansini, M.; et al. Keratose-dominated sponge grounds from temperate mesophotic ecosystems (NW Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Ecol. 2020, 41, e12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.A.; Ramírez-Amaro, S.; Ordines, F. Sponges of Western Mediterranean seamounts: New genera, new species and new records. PeerJ. 2021, 9, e11879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, C.; Mastrototaro, F.; Gorriero, G. Sponge fauna associated with a Mediterranean deep-sea coral bank. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 2005, 85, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrototaro, F.; D’Onghia, G.; Corriero, G.; Matarrese, A.; Maiorano, P.; Panetta, P.; Gherardi, M.; Longo, C.; Rosso, A.; Sciuto, F.; et al. Biodiversity of the white coral bank off Cape Santa Maria di Leuca (Mediterranean Sea): An update. Deep-Sea Res. Part II 2010, 57, 412–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onghia, G.; Capezzuto, F.; Cardone, F.; Carlucci, R.; Carluccio, A.; Chimienti, G.; Corriero, G.; Longo, C.; Maiorano, P.; Mastrototaro, F.; et al. Macro- and megafauna recorded in the submarine Bari Canyon (southern Adriatic, Mediterranean Sea) using different tools. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voultsiadou, E. Demosponge distribution in the eastern Mediterranean: A NW– SE gradient. Helgol Mar Res 2005, 59, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idan, T.; Goren, L.; Shefer, S.; Ilan, M. Sponges in a Changing Climate: Survival of Agelas oroides in a Warming Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 603593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idan, T.; Goren, L.; Shefer, S.; Brickner, I.; Ilan, M. Does Depth Matter? Reproduction Pattern Plasticity in Two Common Sponge Species Found in Both Mesophotic and Shallow Waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 610565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, M.D.; Fox, H.E.; Allen, G.R.; Davidson, N.; Ferdaña, Z.A.; Finlayson, M.; Halpern, B.S.; Jorge, M.A.; Lombana, A.; Lourie, S.A.; et al. Marine Ecoregions of the World: A Bioregionalization of Coastal and Shelf Areas. BioScience 2007, 57, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petza, D.; Maina, I.; Koukourouvli, N.; Dimarchopoulou, D.; Akrivos, D.; Kavadas, S.; Tsikliras, A.; Karachle, P.K.; Katsanevakis, S. Where not to fish—Reviewing and mapping fisheries restricted areas in the Aegean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2017, 18, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific, Technical and Economic Committee for Fisheries (STECF). Stock Assessments in the Mediterranean Sea 2021–Adriatic and Ionian Seas (STECF-21-15); EUR 28359 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021; ISBN 978-92-76-46195-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, J.N.A. ‘Sponguide’. Guide to Sponge Collection and Identification. 2000. Available online: http://www.qmuseum.qld.gov.au/organisation/sections/SessileMarineInvertebrates (accessed on 29 April 2023).
- Hooper, J.N.A.; van Soest, R.W.M. Systema Porifera. A Guide to the Classification of Sponges; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publ.: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- de Voogd, N.J.; Alvarez, B.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Carballo, J.L.; Cárdenas, P.; Díaz, M.C.; Dohrmann, M.; Downey, R.; Goodwin, C.; Hajdu, E.; et al. World Porifera Database. 2023. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/porifera (accessed on 29 April 2023).
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006; pp. 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- Voultsiadou, E.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Bailly, N. Porifera of Greece: An update checklist. Biodivers. Data J. 2016, 4, e7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Phorbas posidoni n.sp. (Porifera: Poecilosclerida) from the Aegean Sea, with a discussion of the family Anchinoidae. J. Nat. Hist. 1991, 25, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Koukouras, A. Contribution to the Knowledge of Keratose Sponges. (Dictyoceratida, Dendroceratida, Verongida: Demospongiae, Porifera) of the Aegean Sea. Mitteilungen aus dem Museum für Naturkunde in Berlin. Zool. Mus. Inst. Für Spez. Zool. 1993, 69, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voultsiadou, E.; Vafidis, D. Rare sponge (Porifera: Demospongiae) species from the Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 2004, 84, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacelet, J. Eponges de la Roche du Large et de l’étage bathyal de Méditerranée (Récoltes de la soucoupe plongeante Cousteau et dragages). Mémoires du Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle. Mémoires Du Muséum Natl. D’histoire Nat. 1969, 59, 145–219. [Google Scholar]
- Kefalas, E.; Tsirtsis, G.; Catritsi-Catharios, J. Distribution and ecology of Demospongiae from the circalittoral of the islands of the Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Hydrobiologia 2003, 499, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailianis, T.; Tsigenopoulos, C.S.; Dounas, C.; Voultsiadou, E. Genetic diversity of the imperilled bath sponge Spongia officinalis Linnaeus, 1759 across the Mediterranean Sea: Patterns of population differentiation and implications for taxonomy and conservation. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 3757–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voultsiadou, E.; Dailianis, T.; Antoniadou, C.; Vafidis, D.; Dounas, C.; Chintiroglou, C.C. Aegean Bath Sponges: Historical Data and Current Status. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2011, 19, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, J.R.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Diversity patterns and zoogeography of the Northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean shallow-water sponge fauna. Hydrobiologia 2012, 687, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voultsiadou, E. Reevaluating sponge diversity and distribution in the Mediterranean Sea. Hydrobiologia 2009, 628, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerovasileiou, V.; Voultsiadou, E. Marine Caves of the Mediterranean Sea: A Sponge Biodiversity Reservoir within a Biodiversity Hotspot. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M. The ecology of the sponge larva. Can. J. Zool. 2006, 84, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, S.; Uriz, M.J.; Xavier, T.; Alcoverro, T. Dispersal strategies in sponge larvae: Integrating the life history of larvae and the hydrologic component. Oecologia 2006, 149, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.; Riesgo, A. Reproduction in the Phylum Porifera: A synoptic overview. Treballs SCB 2008, 59, 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Uriz, M.J.; Turon, X.; Mariani, S. Ultrastructure and dispersal potential of sponge larvae: Tufted versus evenly ciliated parenchymellae. Mar. Ecol. 2008, 29, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skliris, N.; Sofianos, S.S.; Gkanasos, A.; Axaopoulos, P.; Mantziafou, A.; Vervatis, V. Long-term sea surface temperature variability in the Aegean Sea. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2011, 2, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou, D.; Drakopoulou, V.; Rousakis, G.; Livanos, I.; Loukaidi, V.; Kyriakidou Ch Panagiotopoulos, I.; Tsampouraki-Kraounaki, K.; Manta, K. Geomorphological Features. In Deep-Sea Atlas of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea; Otero, M., Mytilineou, C., Eds.; IUCN Gland: Malaga, Spain, 2022; pp. 20–121. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.J.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Mytilineou, C.H.; Jimenez, C.; Papadopoulou, K.; Salomidi, M.; Sakellariou, D.; Drakopoulou, V.; Otero, M. Revisiting underwater surveys to uncover sites of conservation interest. In Deep-Sea Atlas of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea; Otero, M., Mytilineou, C., Eds.; IUCN Gland: Malaga, Spain, 2022; pp. 146–172. [Google Scholar]
- Voultsiadou, E. Sponge diversity in the Aegean Sea: Check list and new information. Ital. J. Zool. 2005, 72, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, N.; Gertman, I.; Herut, B. Temporal evolution of physical and chemical characteristics of the water column in the easternmost Levantine basin (Eastern Mediterranean Sea) from 2002 to 2010. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 135, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansini, M.; Musso, B. Sponges from trawl-exploitable bottoms of Ligurian and Tyrrhenian seas: Distribution and ecology. Mar. Ecol. 1991, 12, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilan, M.; Gugel, J.; Galil, B.S.; Janussen, D. Small bathyal sponge species from the east Mediterranean revealed by a non- regular soft bottom sampling technique. Ophelia 2003, 3, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.K.; Roberts, E.M.; Rapp, H.T.; Davies, A.J. Spatial patterns of arctic sponge ground fauna and demersal fish are detectable in autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) imagery. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2019, 153, 103137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, M.; Costa, G.; Carella, M.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Cerrano, C.; Pansini, M.; Quarta, G.; Calcagnile, L.; Bavestrello, G. The dynamics of a Mediterranean coralligenous sponge assemblage at decennial and millennial temporal scales. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spedicato, M.T.; Massutí, E.; Mérigot, B.; Tserpes, G.; Jadaud, A.; Relini, G. The MEDITS trawl survey specifications in an ecosystem approach to fishery management. Sci. Mar. 2019, 83S1, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CLASS/Orders/Species | Aegean Sea | Ionian Sea | Depth (m) | F | mDb | mDa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEMOSPONGIAE | ||||||
| Agelasida | ||||||
| Agelas oroides (Schmidt, 1864) | x | 37–250 | 4.49 | 0.93 | 0.66 | |
| Axinellida | ||||||
| Axinella cannabina (Esper, 1794) c | x | x | 34–119 | 9.62 | 0.37 | 1.63 |
| Axinella damicornis (Esper, 1794) | x | 37–74 | 1.92 | 0.04 | 0.18 | |
| Axinella polypoides Schmidt, 1862 c | x | 38–86 | 3.21 | 0.18 | 0.44 | |
| Axinella sp.1 | x | 38–43 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.07 | |
| Axinella sp.2 | x | 65–118 | 1.28 | 0.01 | 0.15 | |
| Axinella verrucosa (Esper, 1794) | x | x | 38–154 | 2.56 | 0.19 | 0.40 |
| Raspailia (Raspailia) viminalis Schmidt, 1862 | x | x | 34.5–210 | 5.77 | 0.01 | 0.65 |
| Raspailiidae sp. | x | x | 24.7–53.7 | 3.21 | 0.10 | 0.27 |
| Bubarida | ||||||
| Acanthella acuta Schmidt, 1862 | x | 26.3–101 | 5.77 | 6.36 | 18.01 | |
| Bubaris sp. | x | 85–166 | 1.92 | 0.01 | 0.07 | |
| Dictyonella incisa (Schmidt, 1880) | x | 45.4–84.2 | 1.28 | 0.12 | 0.32 | |
| Dictyonella obtusa (Schmidt, 1862) | x | 90–91 | 0.64 | 0.03 | 0.07 | |
| Chondrillida | ||||||
| Chondrilla nucula Schmidt, 1862 | x | 40–163.4 | 2.56 | 0.73 | 3.09 | |
| Chondrosiida | ||||||
| Chondrosia reniformis Nardo, 1847 | x | x | 26.3–118 | 7.05 | 5.76 | 16.68 |
| Clionaida | ||||||
| Cliona celata Grant, 1826 | x | x | 35–68.4 | 4.49 | 0.36 | 0.89 |
| Desmacellida | ||||||
| Desmacella annexa Schmidt, 1870 b | x | x | 78–154 | 1.92 | 0.02 | 0.19 |
| Desmacella inornata (Bowerbank, 1866) b | x | x | 37–774 | 1.92 | 0.00 | 0.17 |
| Dictyoceratida | ||||||
| Dysidea avara (Schmidt, 1862) | x | x | 37–74 | 7.69 | 1.41 | 1.84 |
| Dysidea fragilis (Montagu, 1814) | x | x | 53–91 | 1.92 | 0.02 | 0.15 |
| Fasciospongia cavernosa (Schmidt, 1862) | x | 40–113.7 | 2.56 | 0.97 | 1.10 | |
| Hyrtios collectrix (Schulze, 1880) | x | x | 45.4–96 | 3.21 | 0.15 | 0.36 |
| Ircinia paucifilamentosa Vacelet, 1961 | x | 65–74 | 1.28 | 0.06 | 0.13 | |
| Ircinia sp. | x | 92–98 | 0.64 | 0.13 | 0.07 | |
| Ircinia variabilis (Schmidt, 1862) | x | x | 37–334 | 10.26 | 22.12 | 4.98 |
| Pleraplysilla spinifera (Schulze, 1879) | x | 60–63 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| Sarcotragus foetidus Schmidt, 1862 c | x | x | 38–185.6 | 12.82 | 22.38 | 4.32 |
| Scalarispongia scalaris (Schmidt, 1862) | x | x | 43–102 | 3.85 | 1.89 | 0.66 |
| Spongia (Spongia) nitens (Schmidt, 1862) | x | 40–45 | 1.28 | 0.46 | 0.41 | |
| Spongia (Spongia) officinalis Linnaeus, 1759 d | x | x | 32–109 | 8.33 | 1.77 | 0.96 |
| Spongia (Spongia) virgultosa (Schmidt, 1868) | x | 43–48 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 0.07 | |
| Haplosclerida | ||||||
| Haliclona (Gelius) sp. | x | x | 65–113.7 | 3.21 | 0.05 | 0.37 |
| Haliclona (Haliclona) simulans (Johnston, 1842) | x | 45.4–100.8 | 3.21 | 0.04 | 0.26 | |
| Haliclona (Reniera) cf. fulva | x | 136.8–173 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.06 | |
| Haliclona (Reniera) sp.1 | x | 45.4–166 | 5.13 | 0.30 | 1.39 | |
| Haliclona (Soestella) mucosa (Griessinger, 1971) | x | 136.8–173 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.06 | |
| Haliclona sp. | x | 76.6–83.9 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.07 | |
| Petrosia (Petrosia) ficiformis (Poiret, 1789) | x | 43–84 | 1.92 | 0.41 | 0.82 | |
| Siphonochalina coriacea Schmidt, 1868 a | x | 91–100 | 1.92 | 0.01 | 0.06 | |
| Poecilosclerida | ||||||
| Chondropsidae sp. | x | 40–45.4 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.17 | |
| Echinoclathria sp. | x | 45–47 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.06 | |
| Echinoclathria translata (Pulitzer-Finali, 1978) b | x | 62.5–77.2 | 1.28 | 0.01 | 0.14 | |
| Microcionidae sp. | x | 85–87 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| Mycale (Aegogropila) contarenii (Lieberkühn, 1859) | x | 50–54 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.06 | |
| Mycale (Aegogropila) retifera Topsent, 1924 | x | 100–103 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 0.07 | |
| Mycale (Aegogropila) syrinx (Schmidt, 1862) | x | x | 45.4–113.7 | 3.21 | 0.12 | 0.50 |
| Mycale (Aegogropila) tunicata (Schmidt, 1862) | x | x | 43–65 | 1.28 | 0.02 | 0.14 |
| Mycale (Mycale) lingua (Bowerbank, 1866) | x | x | 42–48 | 1.92 | 0.08 | 0.29 |
| Mycale (Mycale) massa (Schmidt, 1862) | x | x | 26.3–91 | 7.69 | 2.21 | 5.01 |
| Mycale sp. | x | 51.8–54.5 | 1.28 | 0.01 | 0.11 | |
| Myxilla (Myxilla) rosacea (Lieberkühn, 1859) | x | 45–99 | 4.49 | 0.40 | 0.87 | |
| Phorbas fictitius (Bowerbank, 1866) | x | 40–45 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.08 | |
| Phorbas posidoni Voultsiadou-Koukoura & van Soest, 1991 | x | 40–97 | 2.56 | 0.03 | 0.21 | |
| Phorbas sp. | x | x | 43–77 | 2.56 | 0.33 | 0.68 |
| Ulosa digitata (Schmidt, 1866) | x | x | 23.6–843 | 20.51 | 0.74 | 2.20 |
| Polymastiida | ||||||
| Polymastia mamillaris (Müller, 1806) a | x | 50–54 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.06 | |
| Suberitida | ||||||
| Aaptos sp. | x | 40–45.4 | 0.64 | 0.03 | 0.08 | |
| Axinyssa aurantiaca (Schmidt, 1864) b | x | 42.8–77.2 | 1.28 | 0.17 | 0.14 | |
| Axinyssa sp. | x | 120–129 | 0.64 | 0.14 | 0.05 | |
| Halichondria sp. | x | 65–250.7 | 1.28 | 0.03 | 0.09 | |
| Halichondriidae sp.1 | x | x | 40–334 | 3.21 | 0.47 | 0.29 |
| Halichondriidae sp.2 | x | 37–45 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.14 | |
| Hymeniacidon perlevis (Montagu, 1814) b | x | 78–81 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.07 | |
| Hymeniacidon sp. | x | 23.3–53.7 | 4.49 | 0.53 | 1.23 | |
| Laminospongia subtilis Pulitzer-Finali, 1983 | x | 273–334 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.03 | |
| Rhizaxinella elongata (Ridley & Dendy, 1886) | x | x | 40–113.7 | 1.28 | 0.02 | 0.20 |
| Rhizaxinella pyrifera (Delle Chiaje, 1828) | x | x | 40–754 | 4.49 | 0.02 | 1.12 |
| Spongosorites sp. | x | 39–95 | 3.21 | 0.33 | 0.51 | |
| Stylocordyla pellita (Topsent, 1904) b | x | 533–606 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.03 | |
| Suberites domuncula (Olivi, 1792) | x | x | 32–225 | 16.03 | 0.35 | 6.00 |
| Suberites ficus (Johnston, 1842) | x | x | 41–154 | 7.69 | 0.82 | 1.83 |
| Topsentia sp.1 | x | 110–285 | 1.92 | 0.03 | 0.10 | |
| Topsentia sp.2 | x | 397–563 | 2.56 | 0.23 | 0.08 | |
| Tethyida | ||||||
| Tethya aurantium (Pallas, 1766) c | x | 34–154 | 3.21 | 0.09 | 0.76 | |
| Tethya citrina Sarà & Melone, 1965 c | x | 43–48 | 1.28 | 0.28 | 2.49 | |
| Tetractinellida | ||||||
| Astrophorina sp. | x | 748–754 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.03 | |
| Discodermia cf. polymorpha Pisera & Vacelet, 2011 | x | 110–173 | 1.92 | 0.03 | 0.79 | |
| Erylus discophorus (Schmidt, 1862) | x | 136.8–309 | 1.28 | 0.10 | 0.09 | |
| Geodia cydonium (Linnaeus, 1767) c | x | 26.3–154 | 3.85 | 12.4 | 0.87 | |
| Pachastrella monilifera Schmidt, 1868 | x | x | 100–724 | 8.33 | 2.66 | 0.39 |
| Penares euastrum (Schmidt, 1868) | x | 146–148 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 0.34 | |
| Penares helleri (Schmidt, 1864) | x | 78.6–369 | 3.21 | 0.52 | 1.79 | |
| Stelletta grubii Schmidt, 1862 | x | 23.6–41 | 0.64 | 0.20 | 0.05 | |
| Stryphnus mucronatus (Schmidt, 1868) | x | 43–265 | 1.28 | 0.24 | 0.08 | |
| Thenea muricata (Bowerbank, 1858) | x | x | 92–342 | 7.05 | 0.02 | 4.61 |
| Verongiida | ||||||
| Aplysina aerophoba (Nardo, 1833) c | x | x | 34–311 | 16.03 | 8.60 | 2.91 |
| HOMOSCLEROMORPHA | ||||||
| Homosclerophorida | ||||||
| Plakortis simplex Schulze, 1880 | x | 500–525 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| Biomass | ||||
| AgA | AgB | AgC | AgD | Kythira |
| Geodia cydonium (43.1%) Ircinia variabilis (28.8%) | Geodia cydonium (56.6%) | Sarcotragus foetidus (43.6%) Geodia cydonium (23.2%) | Ircinia variabilis (34.8%) Sarcotragus foetidus (19.9%) | Ircinia variabilis (34%) Sarcotragus foetidus (29.6%) |
| Abundance | ||||
| AgA | AgB | AgC | AgD | Kythira |
| Cliona celata (13.9%) Tethya aurantium (10.8%) Hymeniacidon sp. (10.5%) Ulosa digitata (7.3%) Geodia cydonium (7.1%) Ircinia variabilis (5.5%) | Mycale massa (52.7%) | Suberites domuncula (17.8%) Tethya citrina (12.3%) Penares helleri (8.2%) Sarcotragus foetidus (8.1%) Fasciospongia cavernosa (5.1%) | Acanthella acuta (33.4%) Chondrosia reniformis (30%) | Ircinia variabilis (26.7%) Sarcotragus foetidus (19.5%) Discodermia cf. polymorpha (10.1%) |
| Biomass | |||
| IoN | IoC | IoS | Korinthiakos Gulf |
| Aplysina aerophoba (41.7%) Spongia officinalis (18.3%) | Ircinia variabilis (23.9%) Spongia officinalis (21.1%) Suberites ficus (14.2%) | Pachastrella monilifera (98.5%) | Axinella verrucosa (69.5%) |
| Abundance | |||
| IoN | IoC | IoS | Korinthiakos Gulf |
| Suberites domuncula (3%) Ulosa digitata (12.3%) Raspailia viminalis (11.2%) Aplysina aerophoba (10.1%) Spongosorites sp. (9.9%) | Thenea muricata (44.9%) Ulosa digitata (9.8%) | Pachastrella monilifera (42.6%) Suberites domuncula (28.7%) | Axinella verrucosa (24.8%) Ircinia variabilis (24.5%) |
| Biomass | ||||
| 10–50 m | 50–100 m | 100–200 m | 200–500 m | 500–800 m |
| Ircinia variabiliss (24%) Sarcotragus foetidus (23.8%) Geodia cydonium (14.8%) | Sarcotragus foetidus (29.8%) Ircinia variabilis (17.3%) Geodia cydonium (10.1%) | Ircinia variabilis (33%) Sarcotragus foetidus (32%) | Pachastrella monilifera (71.3%) | Topsentia sp.2 (95.1%) |
| Abundance | ||||
| 10–50 m | 50–100 m | 100–200 m | 200–500 m | 500–800 m |
| Acanthella acuta (26.6%) Chondrosia reniformis (24.5%) | Haliclona (Reniera) sp. (8.7%) Suberites ficus (7.8%) Suberites domuncula (7.7%) Myxilla rosacea (7.5%) Sarcotragus foetidus (6.8%) Aplysina aerophoba (6%) Rhizaxinella pyrifera (3.5%) Agelas oroides (3.4%) | Penares helleri (23.1%) Ircinia variabilis (12.8%) Discodermia cf. polymorpha (11%) Thenea muricata (5.1%) | Pachastrella monilifera (20.8%) Thenea muricata (12.1%) Aplysina aerophoba (10.4%) Agelas oroides (7.4%) | Rhizaxinella pyrifera (29.1%) Topsentia sp.2 (24.5%) |
| Presence | ||||
| 10–50 m | 50–100 m | 100–200 m | 200–500 m | 500–800 m |
| Aplysina aerophoba (P = 8) Dysidea avara (P = 7) | Sarcotragus foetidus (P = 9) Aplysina aerophoba (P = 6) Myxilla rosacea (P = 6) | Haliclona sp.1 (P = 4) Ircinia variabilis (P = 4) Sarcotragus foetidus (P = 4) Suberites domuncula (P = 4) | Pachastrella monilifera (P = 7) | Pachastrella monilifera (P = 2) Topsentia sp.2 (P = 2) |
| Biomass | ||||
| 10–50 m | 50–100 m | 100–200 m | 200–500 m | 500–800 m |
| Aplysina aerophoba (39.9%) Spongia officinalis (30.4%) | Ircinia variabilis (35.8%) Sarcotragus foetidus (16.5%) | Suberites ficus (47.7%) Spongia officinalis (27.1%) | Thenea muricata (100%) | Pachastrella monilifera (99%) |
| Abundance | ||||
| 10–50 m | 50–100 m | 100–200 m | 200–500 m | 500–800 m |
| Ulosa digitata (17.6%) Rhizaxinella pyrifera (12.9%) Spongia officinalis (9.6%) Aplysina aerophoba (8.8%) Spongosorites sp. (7%) | Suberites domuncula (16.1%) Ulosa digitata (14.7%) Mycale massa (10.3%) Ircinia variabilis (8.9%) | Suberites ficus (34.6%) Raspailia vimilaris (20.9%) | Thenea muricata (100%) | Pachastrella monilifera (41.6%) Ulosa digitata (29.4%) |
| Presence | ||||
| 10–50 m | 50–100 m | 100–200 m | 200–500 m | 500–800 m |
| Ulosa digitata (P = 8) Spongia officinalis (P = 5) Raspailia vimilaris (P = 4) | Ulosa digitata (P = 9) Suberites domuncula (P = 6) Mycale massa (P = 4) | Raspailia vimilaris (P = 3) Suberites domuncula (P = 3) | Thenea muricata (only representative) | Pachastrella monilifera (P = 3) Ulosa digitata (P = 2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stamouli, C.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Voultsiadou, E. Sponge Community Patterns in Mesophotic and Deep-Sea Habitats in the Aegean and Ionian Seas. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112204
Stamouli C, Gerovasileiou V, Voultsiadou E. Sponge Community Patterns in Mesophotic and Deep-Sea Habitats in the Aegean and Ionian Seas. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(11):2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112204
Chicago/Turabian StyleStamouli, Caterina, Vasilis Gerovasileiou, and Eleni Voultsiadou. 2023. "Sponge Community Patterns in Mesophotic and Deep-Sea Habitats in the Aegean and Ionian Seas" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 11: 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112204
APA StyleStamouli, C., Gerovasileiou, V., & Voultsiadou, E. (2023). Sponge Community Patterns in Mesophotic and Deep-Sea Habitats in the Aegean and Ionian Seas. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(11), 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112204









