Three New Species of Free-Living Marine Nematodes of the Order Enoplida Filipjev, 1929 (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
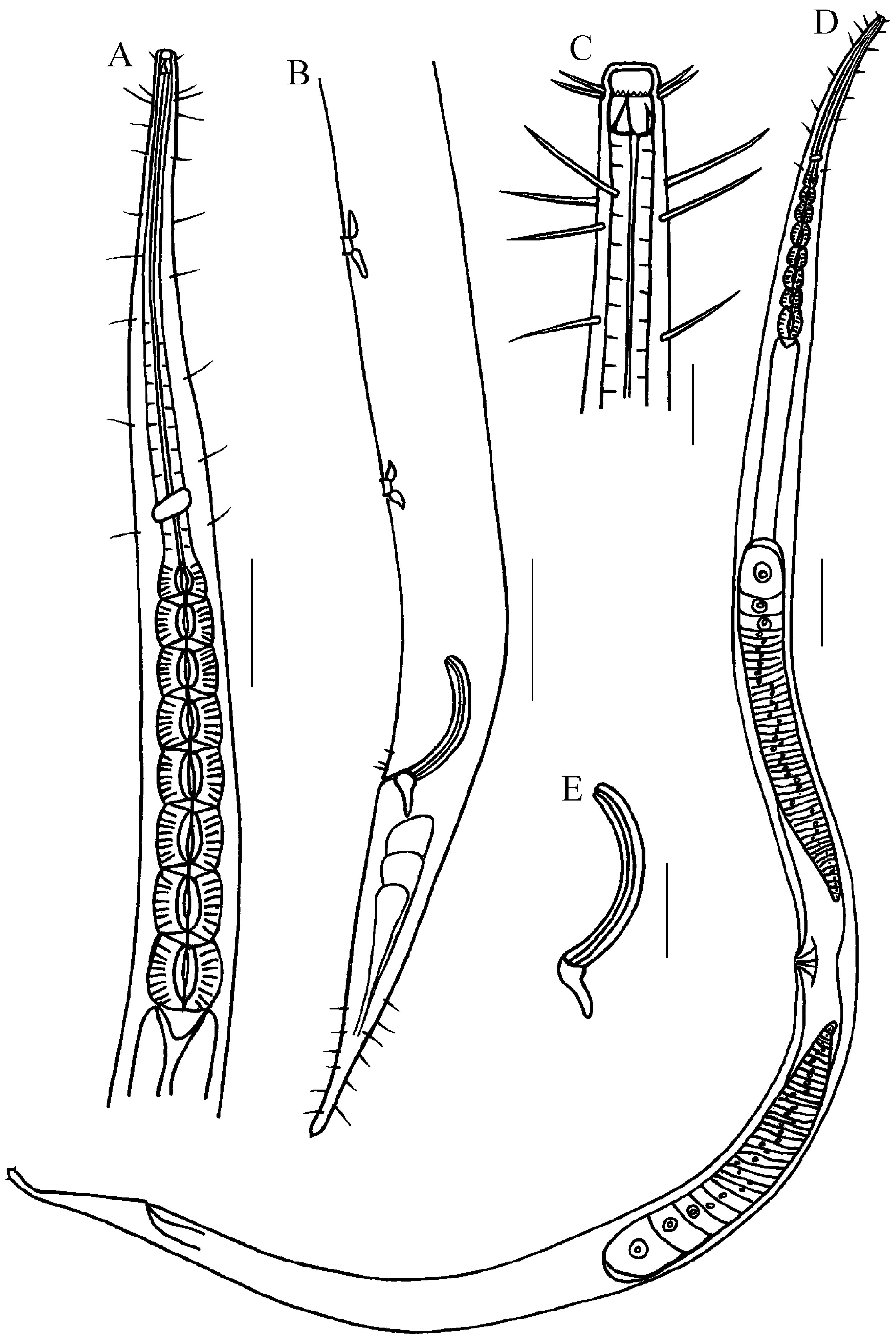
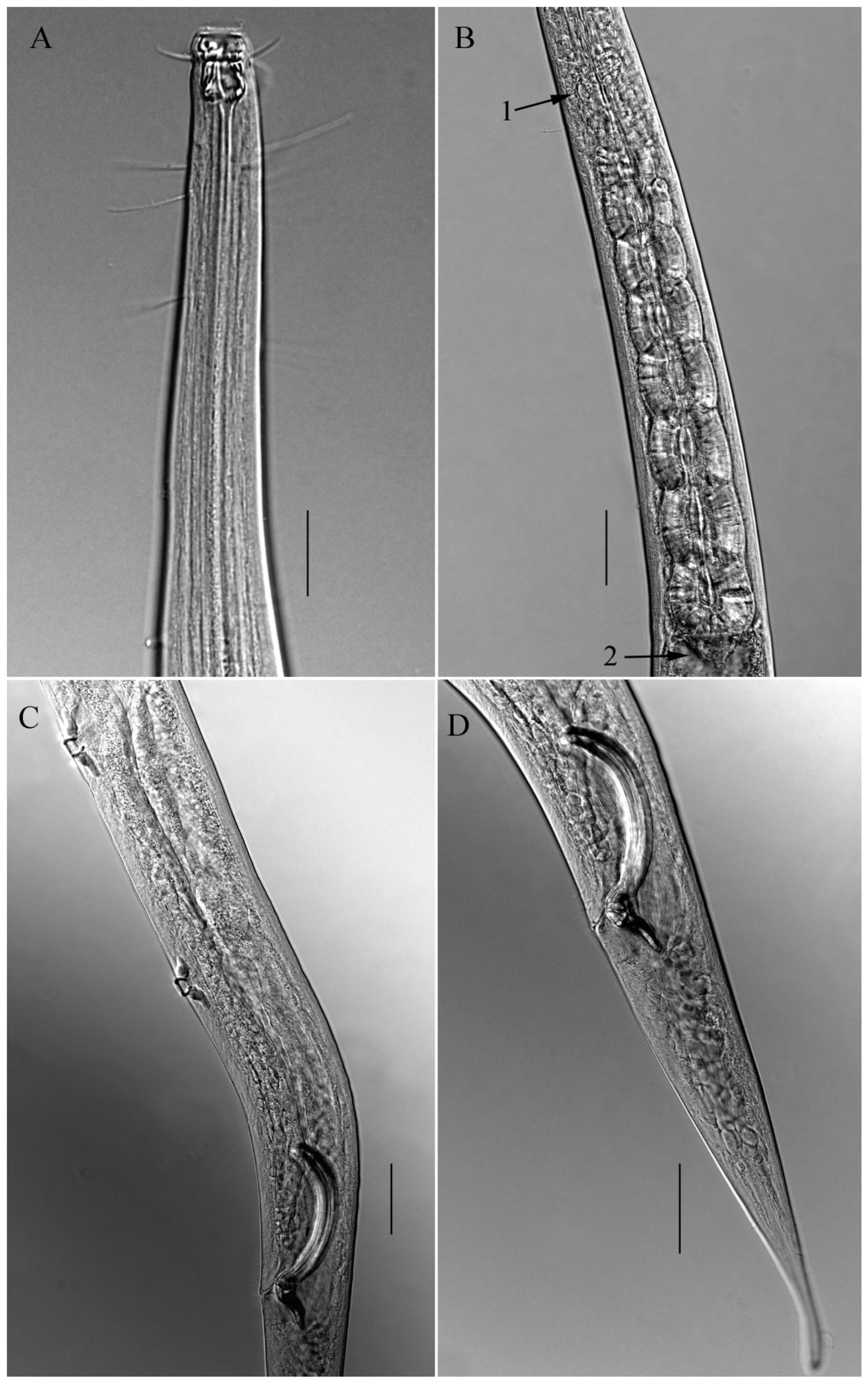
3.1. Description of Belbolla octobulba sp. nov. (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4)
3.1.1. Type Material
3.1.2. Etymology
3.1.3. Type Locality and Habitat
3.1.4. Measurements
3.1.5. Description
3.1.6. Differential Diagnosis and Discussion

3.1.7. Updated Key to Species of the Genus Belbolla (Based on Huang and Zhang, 2005) [10]
- -
- Presence of precloacal supplements …2
- Pharynx with four or seven bulbs…3
- -
- Pharynx with eight, nine or ten bulbs …7
- Four pharyngeal bulbs; male with two papilliform and two winged precloacal supple ments…B. vietnamica Gagarin & Nguyen Dinh Tu, 2016 [32]
- -
- Seven pharyngeal bulbs; male with two precloacal supplements…4
- Precloacal supplements winged; gubernacular apophysis absent …5
- -
- Precloacal supplements not winged; gubernacular apophysis present…6
- Spicules slender with handle-shaped proximal end, gubernaculum absent…B. heptabulba (Timm, 1961) Andrássy, 1973 [8,33]
- -
- Spicules broad with tapered proximal end, gubernaculum present…B. sinica Wang, Guo & Wang, 2022 [4]
- Tail conico-cylindrical, spicules broad, 1.3–1.5 abd…B. warwicki Huang & Zhang, 2005 [10]
- -
- Tail long, filiform, spicules slender, 2.5 abd…B. gracilis Gagarin & Thanh, 2016 [34]
- Pharynx with eight bulbs…8
- -
- Pharynx with nine or ten bulbs…15
- Spicules 10.8 abd long with knob-like proximal end; five papilliform supplements…B. longispiculata Nasira, Shahina & Shamim, 2014 [28]
- -
- Spicules shorter than 2 abd; two precloacal supplements…9
- Gubernacular apophysis longer than half spicule length …10
- -
- Gubernacular apophysis shorter than half spicule length …11
- -
- Precloacal supplements 0.5–0.9 abd long, eight or nine pharyngeal bulbs…B. zhangi Guo & Warwick, 2001 [11]
- Spicule with swollen distal tip …B. stenocephalum Huang & Zhang, 2005 [10]
- -
- Spicule with tapered distal tip …12
- Distance between posterior supplement and proximal end of spicule equal or shorter than spicule length; gubernacular apophysis about one third of spicule length…13
- -
- Distance between posterior supplement and proximal end of spicule longer than spicule length; gubernacular apophysis one fifth to one sixth of spicule length…14
- Body length 1.9 mm, spicules 39 µm, tail 5.7 abd with half posterior cylindrical part…B. teissieri (Luc. et de Conink, 1959) Andrássy, 1973 [8,29]
- -
- Body length 3.2 mm, spicules 115 µm, tail 4.3 abd with one-fourth posterior cylindrical part…B. octobulba sp. nov.
- The wings of supplement almost equal to the diameter of its central part…B. sundoensis (Micoletzky, 1930) Andrássy, 1973 [8,30]
- -
- Spicule with a hook at the distal end…B. intarma Belogurov & Belogurova, 1980 [35]
- -
- Spicule without hook at the distal end…16
- Gubernacular apophysis shorter than 25 µm…17
- -
- Gubernacular apophysis longer than 40 µm…18
- -
- Female having nine pharyngeal bulbs…B. wonkimi Rho, Lee, Lee & Min, 2020 [37]
- Male having ten pharyngeal bulbs, a = 19.8…B. insula Belogurov, Fadeeva & Belogurova, 1983 [38]
- -
- Male having nine pharyngeal bulbs, a = 34.5–41.5…B. huanghaiensis Huang & Zhang, 2005 [10]
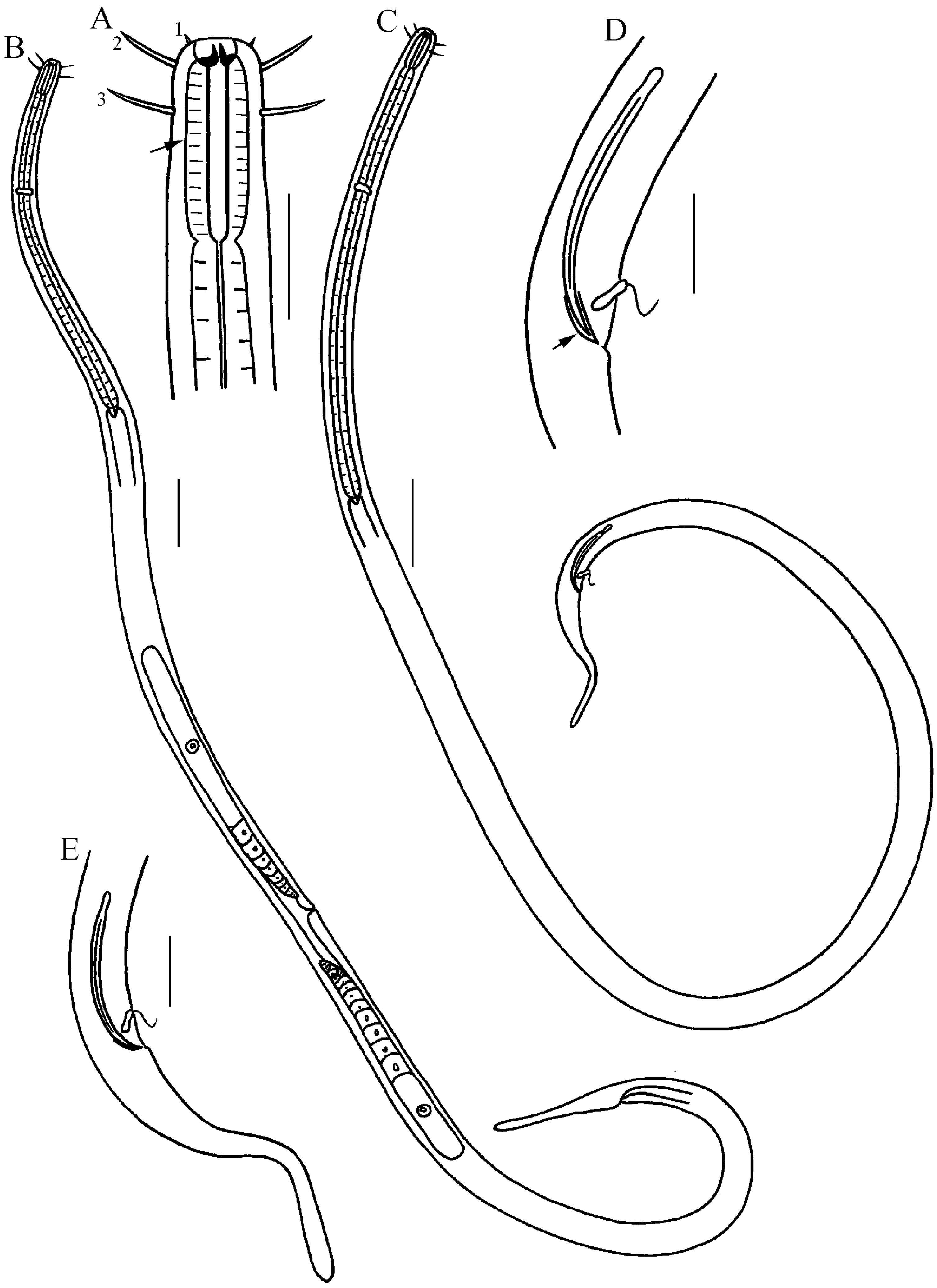
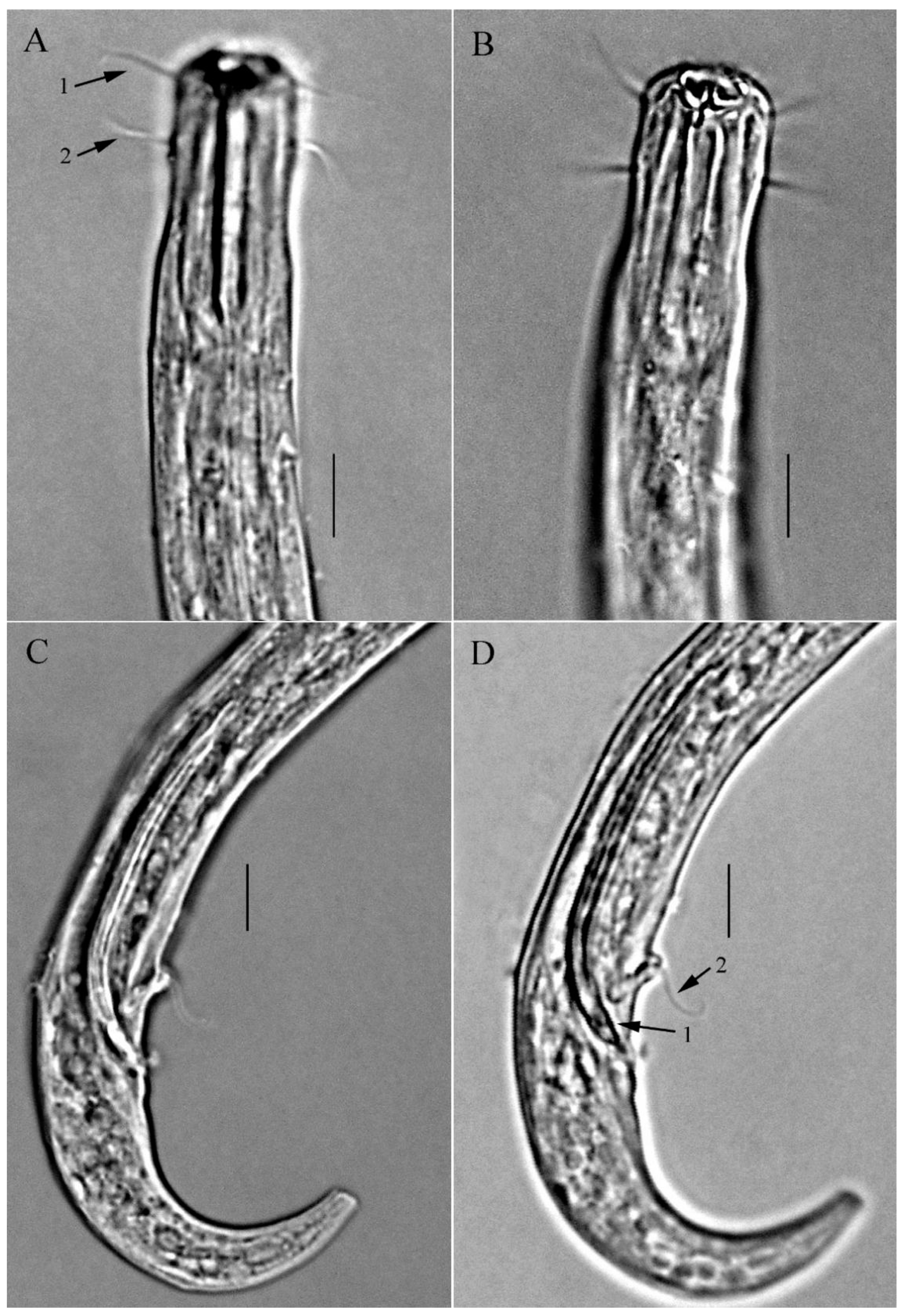
3.2. Description of Ironella gracilis sp. nov. (Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7)
3.2.1. Type Material
3.2.2. Etymology
3.2.3. Type Locality and Habitat
3.2.4. Measurements
3.2.5. Description
3.2.6. Differential Diagnosis and Discussion
3.2.7. Identification Key to Species of Ironella (Updated from Platonova & Mokievsky [14])
- Lips twisted at anterior ends into horizontal tubes, microodontia present…I. prismato laima Cobb, 1920 [5]
- -
- Lips not twisted, microodontia absent…2
- Distance between the circles of outer labial setae and cephalic setae equal to l/6 cbd… I. cobbi Timm, 1954 [13]
- -
- Distance between the circles of cephalic setae equal to 1/3 cbd…3
- Vestibulum separated and with sclerotized walls…I. gracilis sp. nov.
- -
- Vestibulum not separated and not sclerotized…. I. riemanni Platonova & Mokievsky, 1994 [14]

3.3. Description of Oxystomina longiseta sp. nov. (Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10)
3.3.1. Type Material
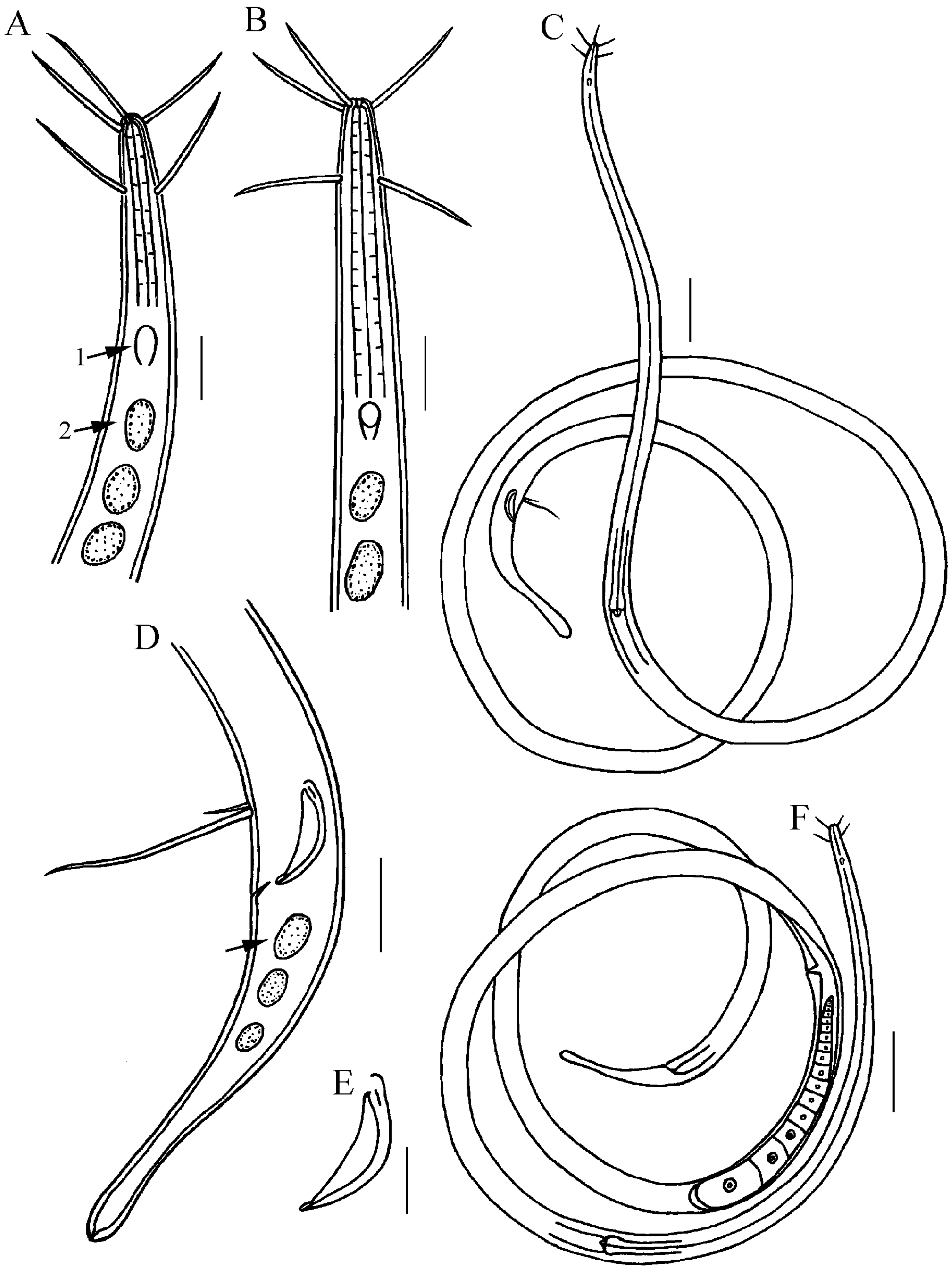

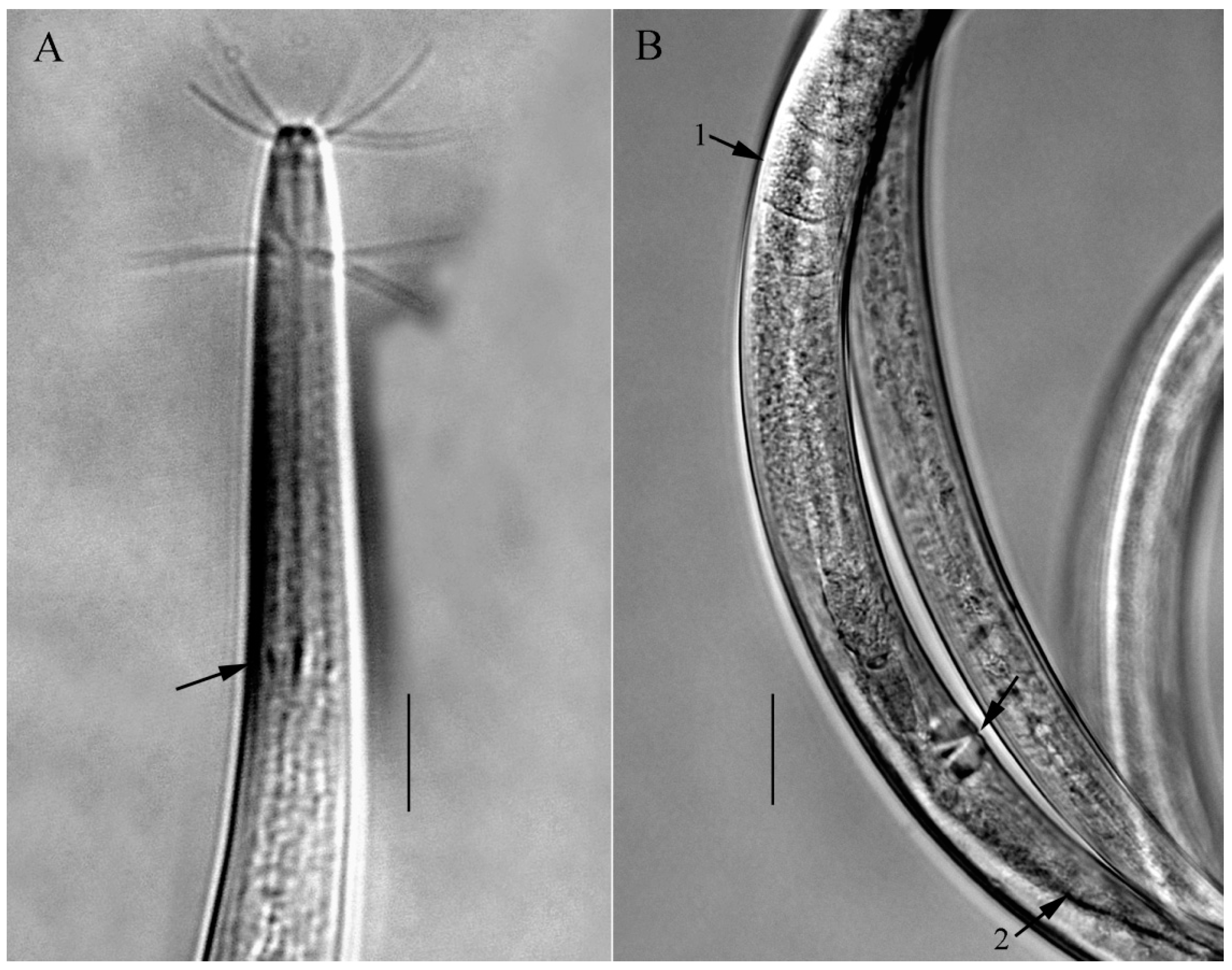
3.3.2. Etymology
3.3.3. Type Locality and Habitat
3.3.4. Measurements
3.3.5. Description
3.3.6. Differential Diagnosis and Discussion
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heip, C.; Vincx, M.; Vranken, G. The ecology of marine nematodes. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1985, 23, 399–489. [Google Scholar]
- Hodda, M. Phylum Nematoda: A classification, catalogue and index of valid genera, with a census of valid species. Zootaxa 2022, 5114, 1–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.D.; Hao, Y.D.; Huang, Y. Descriptions of Leptolaimus sinensis sp. nov. and Perspiria brevicaudata sp. nov. (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China. Zootaxa 2023, 5258, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.N.; Guo, W.; Wang, C.M. Two new species, Parabathylaimus gracilis sp. nov. and Belbolla sinica sp. nov. (Nematoda: Enoplida), from Yangma Island of the Yellow Sea, China. Zootaxa 2022, 5200, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, N.A. One hundred new nemas (type species of 100 new genera). Contrib. A Sci. Nematol. 1920, 9, 217–343. [Google Scholar]
- Leduc, D.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Verdon, V.; Xu, Y. Phylogenetic position of the enigmatic deep-sea nematode order Rhaptothyreida: A molecular analysis. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2018, 122, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Leduc, D.; Fu, S.J.; Zhao, Z.Q. New nematode species from the continental slope of New Zealand (Chromadorea, Microlaimida, and Chromadorida), and unexpected placement of the genus Molgolaimus Ditlevsen, 1921. Mar. Biodiv. 2019, 49, 2267–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrássy, I. Über vier homonyme Nematodengattungen. Nematologica 1973, 19, 403–404. [Google Scholar]
- Filipjev, I.N. Free-living marine Nematodes of the Sevastopol Area. Pt. I. Trudy Osoboi Zoologicheskoi Laboratorii Sebastopolskoi Stantsii Rossiikoi 1918, 4, 1–614. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.N. Three new species of the genus Belbolla (Nematoda: Enoplida) from the Yellow Sea, China. J. Nat. Hist. 2005, 39, 1689–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Q.; Warwick, R.M. Three new species of free-living nematodes from the Bohai Sea, China. J. Nat. Hist. 2001, 35, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Man, J.G. Onderzoekingen over vrij in de aarde levende Nematoden. Tijdschr. Ned. Dierk. Vereen. 1876, 2, 78–196. [Google Scholar]
- Timm, R.W. A survey of the marine nematodes of Chesapeake Bay, Maryland. Cathol. Univ. Am. Biol. Stud. 1954, 23, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Platonova, T.A.; Mokievsky, V.O. Revision of the marine nematodes of the family Ironidae (Nematoda: Enoplida). Zool. Inst. St. Petersburg Zoosyst. Ross. 1994, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Riemann, F. Die interstitielle Fauna im Elbe-Aestuar. Verbreitung und Systematik. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1966, 1, 1–279. [Google Scholar]
- Filipjev, I.N. Free-living marine Nematodes of the Sevastopol area. Trudy Osob. Zool. Lab. Sebastop. Biol. Sta. 1921, 2, 351–614. [Google Scholar]
- Chitwood, B.G. Nomenclatorial notes, l. Proc. Helminth. Soc. Wash. 1935, 2, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bütschli, O. Zur Kenntnis der freilebenden Nematoden, insbesondere der des Kieler Hafens. Abh. Senck. Naturf Gesel. 1874, 9, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, W. Reports of the Lund University Chile expedition 1948–1949: 1. Enoploidea. Acta Univ. Lund 1953, 49, 1–155. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, S.A. Diagnosen neuer Nematoden aus der Kieler Bucht. Kieler Meeresforsch. 1956, 12, 85–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzen, S. Entwurf eines phylogenetischen Systems der freilebenden Nematoden. Verött Inst. Meeresforsch. Bremerh. 1981, 7, 1–472. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, D.; Takeda, N.; Tsune, A.; Murakami, C. Three new species of free-living marine nematodes (Nematoda: Enoplida) from the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone (CCFZ), North Pacific. Zootaxa 2020, 4859, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platonova, T.A. Exploration of the fauna of the seas VIII (XVI). Fauna and flora of the Possjet Bay of the Sea of Japan. Zool. Inst. Acad. Sci. USSR 1971, 8, 72–108. [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge, V.N.; Bouwman, L.A. A simple density separation technique for quantitative isolation of meiobenthos using the colloidal silica Ludox-TM. Mar. Biol. 1977, 42, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Zhou, R.G.; Zhu, H.L.; Guo, Y.Q. Two new species of free-living marine nematode of the genus Anticyathus Cobb, 1920 (Linhomoeidae) from Mangroves Sediment of Shenzhen and Shantou, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, A.D.; Warwick, R.M. Meiofauna techniques. In Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos; Holme, N.A., McIntyre, A.D., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1984; pp. 217–244. [Google Scholar]
- Inglis, W.G. Two new species of free-living marine nematodes from the west coast of Scotland. Hydrobiologia 1961, 18, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasira, K.; Shahina, F.; Shamim, S. Descriptions of Bathyeurystomina minima sp. n. and Belbolla longispiculata sp. n. with observations on Pareurystomina vaughtae and Eurystomina indica (Enoplida: Enchelidiidae) from Pakistan. Int. J. Nematol. 2014, 24, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Luc, M.; De Coninck, L.A. Nématodes libres marins de la région de Roscoff. Archs Zool. Exp. Gén. 1959, 98, 103–165. [Google Scholar]
- Micoletzky, H. Freilebende marine Nematoden von den Sunda-Inseln. I. Enoplidae. (Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen’s Pacific Expedition 1914-16 53) (edited by H. A. KREIS). Vidensk. Meddr Dansk Naturh. Foren. 1930, 87, 243–339. [Google Scholar]
- Juario, J.V. Neue freilebende Nematoden aus dem Sublitoral der Deutschen Bucht. Veröff. Inst. Meeresforsch. Bremerh. 1974, 14, 275–303. [Google Scholar]
- Gagarin, V.G.; Nguyen, D.T. Adoncholaimus minor sp. n. and Belbolla vietnamica sp. n. (Nematoda, Enoplida) from mangrove forest of the Yen River Estuary in Vietnam. Int. J. Nematol. 2016, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Timm, R.W. The Marine Nematodes of the Bay of Bengal. Proc. Pak. Acad. Sci. 1961, 1, 25–88. [Google Scholar]
- Gagarin, V.G.; Thanh, N.V. Two new nematode species (Nematoda) from the mangroves of the Yen River Delta, Vietnam. Inland Water Biol. 2016, 9, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belogurov, O.I.; Belogurova, L.S. Morphology of Belbolla intarma sp. n., diagnosis and a table for the species of the genus Belbolla. Biologiya Morya 1980, 4, 74–77. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Allgén, C.A. Pacific Freeliving Marine Nematodes. (Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen’s Pacific Expedition 1914-16. LXXVI). Vidensk. Meddr. Fra Dansk Naturh. Foren. 1951, 113, 263–411. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, H.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.J.; Min, W. A new free-living marine nematode species of the genus Belbolla (Enoplida, Enchelidiidae) from a subtidal zone of the East Sea, Korea, with some ecological and biogeographical information. Environ. Biol. Res. 2020, 38, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belogurov, O.I.; Fadeeva, L.S.; Belogurova, L.S. Studies of Nematodes of the Subfamily Eurystomininae (Enoplida, Enchelidiidae) from the Far East Seas of the USSR. Zool. Zh. 1983, 62, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Filipjev, I.N. Les Nématodes libres des mers septentrionales appartenant a la famille des Enoplidae. Arch. Naturgesch. 1927, 91, 1–216. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, S.A. Brasilianische Meeres-Nematoden I. Bol. Inst. Ocean. São Paulo 1956, 5, 3–69. [Google Scholar]

| Characters | Holotype | Paratype | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ♀1 | ♀2 | ||
| Body length | 3185 | 4076 | 3853 |
| Maximum body diameter | 96 | 139 | 134 |
| Head diameter | 14 | 18 | 11 |
| Length of cephalic setae | 10 | 10 | 9 |
| Length of buccal cavity | 21 | 21 | 17 |
| Width of buccal cavity | 10 | 11 | 11 |
| Nerve ring from anterior end | 335 | 368 | 341 |
| Length of pharynx | 717 | 760 | 740 |
| Body diameter at pharyngeal base | 80 | 100 | 91 |
| Number of pharyngeal bulbs | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Tail length | 274 | 273 | 248 |
| Body diameter at cloaca or anus | 64 | 62 | 62 |
| Spicule length along arc | 124 | - | - |
| Length of gubernacular apophysis | 38 | - | - |
| Length of anterior supplement | 53 | - | - |
| Length of posterior supplement | 42 | - | - |
| Posterior supplement from cloaca | 251 | - | - |
| Distance between both supplements | 185 | - | - |
| Vulva from anterior end | - | 1986 | 1853 |
| Body diameter at vulva | - | 138 | 120 |
| V% | - | 49 | 48 |
| a | 33.0 | 29.3 | 28.8 |
| b | 4.4 | 5.4 | 5.2 |
| c | 11.6 | 14.9 | 15.5 |
| c′ | 4.3 | 4.4 | 4.0 |
| Characters | Holotype | Paratypes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ♂1 | ♂2 | ♀1 | ♀2 | ||
| Total body length | 1469 | 1357 | 1244 | 1623 | 1513 |
| Maximum body diameter | 19 | 18 | 19 | 27 | 26 |
| Head diameter | 14 | 14 | 14 | 18 | 18 |
| Length of inner labial setae | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Length of outer labial setae | 9 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 8 |
| Length of cephalic setae | 9 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 9 |
| Distance between outer labial setae and cephalic seta | 7 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Depth of buccal cavity | 26 | 29 | 26 | 34 | 33 |
| Width of buccal cavity | 4 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 7 |
| Nerve ring from anterior end | 106 | 103 | 93 | 113 | 117 |
| Length of pharynx | 316 | 304 | 284 | 326 | 329 |
| Body diameter at pharyngeal base | 17 | 17 | 19 | 25 | 25 |
| Length of cardia | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 10 |
| Spicule length along arc | 61 | 57 | 57 | - | - |
| Length of gubernaculum | 7 | 7 | 7 | - | - |
| Vulva from anterior end | - | - | - | 825 | 797 |
| V% | - | - | - | 50.8 | 52.7 |
| Body diameter at cloaca or anus | 16 | 15 | 15 | 17 | 16 |
| Tail length | 99 | 96 | 85 | 110 | 122 |
| a | 77.3 | 75.4 | 65.5 | 60.1 | 58.2 |
| b | 4.6 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 5 | 4.6 |
| c | 14.8 | 14.1 | 14.6 | 14.8 | 12.4 |
| c′ | 6.2 | 6.4 | 5.7 | 6.5 | 7.6 |
| Characters | Holotype | Paratypes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ♂1 | ♂1 | ♀1 | ♀2 | ♀3 | ||
| Total body length | 2387 | 2221 | 2205 | 2019 | 2349 | 2540 |
| Maximum body diameter | 20 | 21 | 21 | 19 | 23 | 23 |
| Head diameter | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Length of outer labial setae | 13 | 16 | 17 | 13 | 14 | 14 |
| Length of cephalic setae | 14 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 13 |
| Distance between two circles of setae | 11 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 11 | 11 |
| Length of amphidial fovea | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 |
| Width of amphidial fovea | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4.5 | 4 | 4 |
| Amphid from anterior end | 30 | 29 | 32 | 38 | 32 | 31 |
| Body diameter at amphid level | 9 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 8 |
| Length of pharynx | 486 | 532 | 460 | 476 | 503 | 562 |
| Body diameter at pharyngeal base | 19 | 19 | 20 | 18 | 20 | 19 |
| Spicule length along arc | 26 | 27 | 26 | - | - | - |
| Length of precloacal setae | 35/8 | 41/11 | 38/8 | - | - | - |
| From precloacal setae to cloaca | 19 | 18 | 18 | - | - | - |
| Body diameter at cloaca or anus | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 17 |
| Tail length | 90 | 86 | 85 | 80 | 85 | 82 |
| Vulva from anterior end | - | - | - | 1019 | 1200 | 1305 |
| Body diameter at vulva | - | - | - | 20 | 24 | 24 |
| V% | - | - | - | 50.5 | 51.1 | 51.4 |
| a | 119 | 106 | 105 | 106 | 102 | 111 |
| b | 4.9 | 4.2 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 4.7 | 4.5 |
| c | 26.5 | 25.8 | 25.9 | 25.2 | 27.6 | 31.0 |
| c′ | 4.7 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 4.4 | 4.7 | 4.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ban, S.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y. Three New Species of Free-Living Marine Nematodes of the Order Enoplida Filipjev, 1929 (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112202
Ban S, Sun J, Huang Y. Three New Species of Free-Living Marine Nematodes of the Order Enoplida Filipjev, 1929 (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(11):2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112202
Chicago/Turabian StyleBan, Shuyan, Jing Sun, and Yong Huang. 2023. "Three New Species of Free-Living Marine Nematodes of the Order Enoplida Filipjev, 1929 (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 11: 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112202
APA StyleBan, S., Sun, J., & Huang, Y. (2023). Three New Species of Free-Living Marine Nematodes of the Order Enoplida Filipjev, 1929 (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(11), 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112202






