A New Boundary Condition Framework for Particle Method by Using Local Regular-Distributed Background Particles—The Special Case for Poisson Equation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Governing Equations
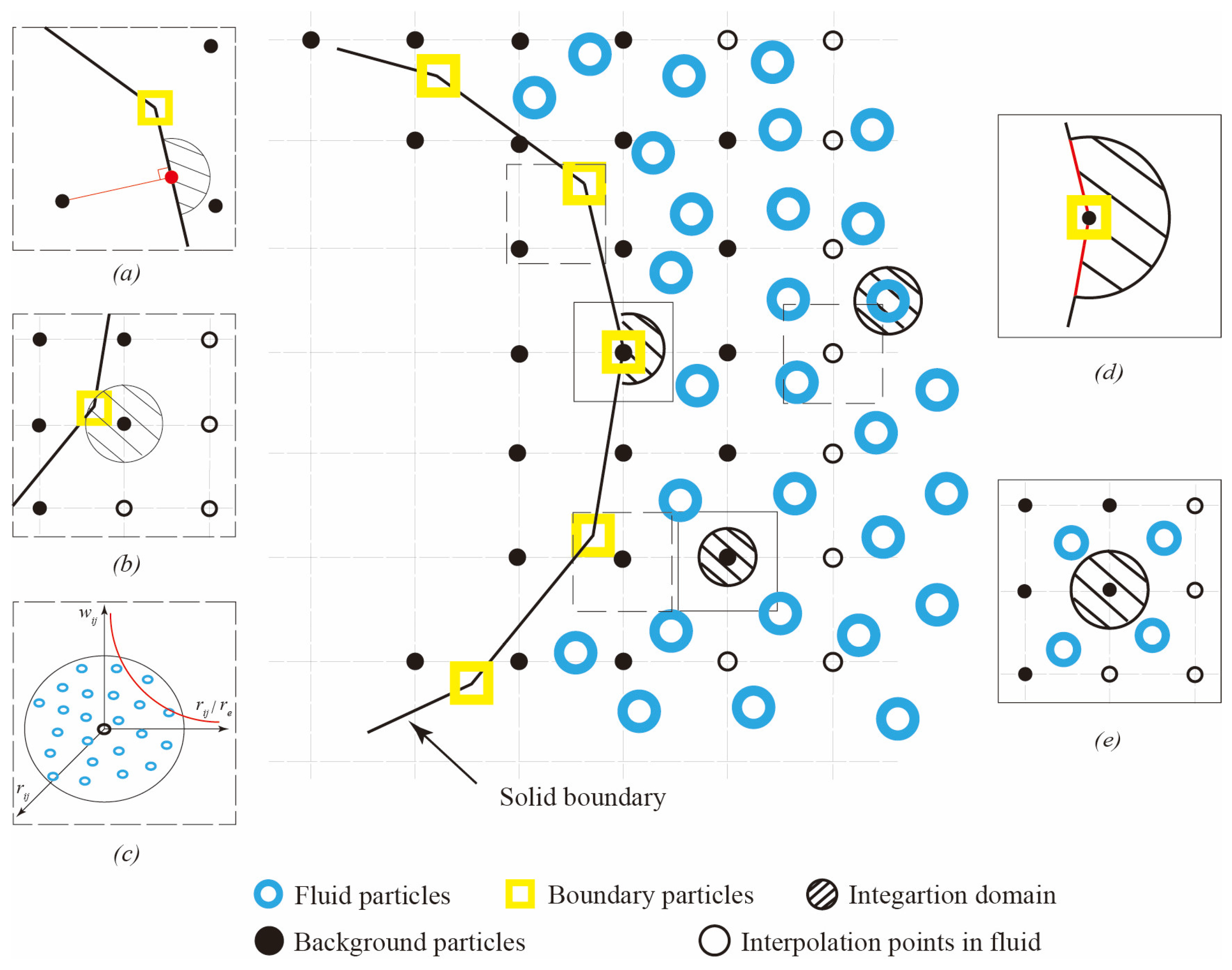
2.2. Enhancing the Boundary Condition Accuracy by Local Regular-Distributed Particles
2.3. Weak Form Poisson Equation and Imposing Boundary Condition
2.4. Closure Equations for the Background Particles
2.4.1. Closure Equations for Different Parts of Background Particles
2.4.2. Gauss–Legendre Quadrature Formula
2.5. Different Interpolation Techniques
2.5.1. Least Square Type Interpolation Based on Taylor Series Expansion
2.5.2. Moving Particle Semi-Implicit Method (MPS)
3. Numerical Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of Boundary Local Background Particles Method
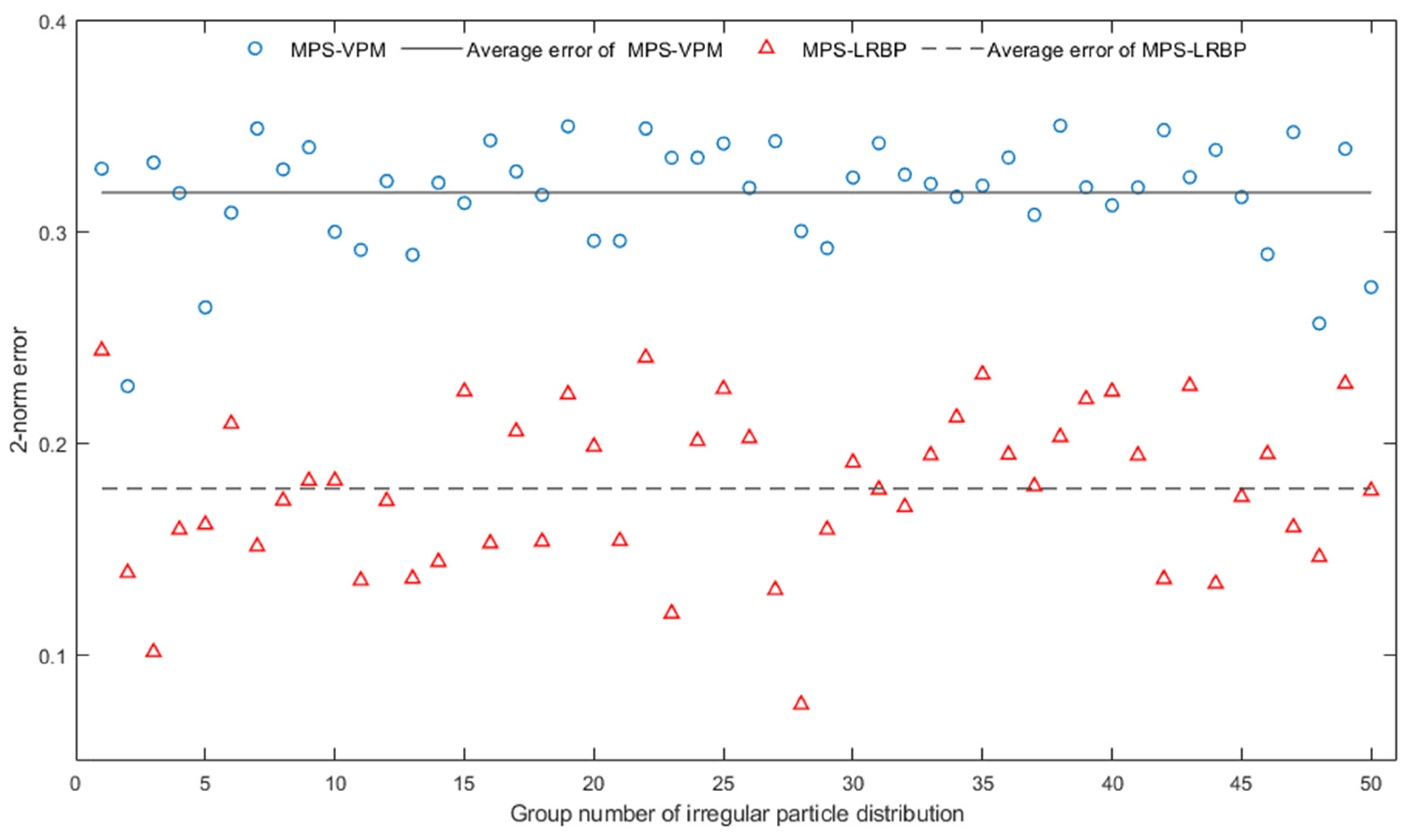
3.2. Different Choice of Interpolation Methods for Inner Areas
3.3. Different Shapes for the Boundary
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Z.; Liu, G.; Zou, L.; Zheng, H.; Djidjeli, K. Investigation of Non-Linear Ship Hydroelasticity by CFD-FEM Coupling Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hu, T.; Sun, Z.; Wang, S.; Shi, S.; Zhang, Z. A delta SPH-SPIM coupled method for fluid-structure interaction problems. J. Fluid Struct. 2021, 101, 103210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, M.H.; Park, J. Development of Moving Particle Simulation Method for Multiliquid-Layer Sloshing. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 350165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Djidjeli, K.; Xing, J.T.; Cheng, F. Coupled MPS-modal superposition method for 2D nonlinear fluid-structure interaction problems with free surface. J. Fluid Struct. 2016, 61, 295–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyer, A.; Gotoh, H. A Multiphase Compressible-Incompressible Particle Method for Water Slamming. Int. J. Offshore Polar 2016, 26, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, A.Z.; Shi, Y.; Pan, G. Recent developments on the water entry impact of wedges and projectiles. Ships Offshore Struct. 2022, 17, 695–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Djidjeli, K.; Xing, J.T. The weak coupling between MPS and BEM for wave structure interaction simulation. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2017, 82, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyer, A.; Tsuruta, N.; Shimizu, Y.; Gotoh, H. Multi-resolution MPS for incompressible fluid-elastic structure interactions in ocean engineering. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 82, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Khayyer, A.; Gotoh, H.; Park, J. Development of a fully Lagrangian MPS-based coupled method for simulation of fluid-structure interaction problems. J. Fluid Struct. 2014, 50, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Lo, E.Y.M. Incompressible SPH method for simulating Newtonian and non-Newtonian flows with a free surface. Adv. Water Resour. 2003, 26, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshizuka, S.; Oka, Y. Moving-particle semi-implicit method for fragmentation of incompressible fluid. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 1996, 123, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solenthaler, B.; Pajarola, R. Predictive-Corrective Incompressible SPH. ACM T Graph. 2009, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihmsen, M.; Cornelis, J.; Solenthaler, B.; Horvath, C.; Teschner, M. Implicit Incompressible SPH. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2014, 20, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomeritae, N.; Bui, H.H.; Daly, E. Modeling Transitions between Free Surface and Pressurized Flow with Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 144, 4018012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.J. Simulating free-Surface flows with sph. J. Comput. Phys. 1994, 110, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Koshizuka, S.; Oka, Y. Modelling of a single drop impact onto liquid film using particle method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2004, 45, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.J.; Kajtar, J.B. SPH particle boundary forces for arbitrary boundaries. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2009, 180, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jeun, G. Coupling of rigid body dynamics and moving particle semi-implicit method for simulating isothermal multi-phase fluid interactions. Comput. Method Appl. M 2011, 200, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaram, K.T. Gauss Legendre quadrature over a unit circle. Int. J. Eng. Tech. Res. 2013, 2, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Shivaram, K.T. Generalised Gaussian Quadrature over a Sphere. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2013, 4, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, C.G.; Gao, M.; Luo, C. A new particle method for simulation of incompressible free surface flow problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2012, 89, 1582–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I.; Green, A.E. Mechanism of the Production of Small Eddies from Large Ones. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1937, 158, 499–521. [Google Scholar]
- Bardazzi, A.; Lugni, C.; Antuono, M.; Graziani, G.; Faltinsen, O.M. Generalized HPC method for the Poisson equation. J. Comput. Phys. 2015, 299, 630–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Grid | Nx | Ny | Order of Convergence | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS | MPS–LRBP | MPS–VPM | ||||||
| 1st | 21 | 21 | ||||||
| 2.5714 | 2.5700 | 2.4922 | 2.4855 | 1.2605 | 0.6855 | |||
| 2nd | 41 | 41 | ||||||
| 2.6201 | 2.5897 | 2.3156 | 2.2794 | 1.0774 | 0.6919 | |||
| 3rd | 61 | 61 | ||||||
| 2.6250 | 2.5774 | 1.5935 | 1.5686 | 0.9137 | 0.5662 | |||
| 4th | 81 | 81 | ||||||
| 2.6196 | 2.5599 | 3.9045 | 3.7851 | 1.0827 | 1.5220 | |||
| 5th | 101 | 101 | ||||||
| 2.6106 | 2.5416 | 0.3337 | 0.8071 | 1.2138 | 2.4241 | |||
| 6th | 121 | 121 | ||||||
| 2.6000 | 2.5238 | 3.3926 | 3.1212 | 1.2980 | 1.9567 | |||
| 7th | 141 | 141 | ||||||
| 2.5889 | 2.5069 | 4.8021 | 4.0767 | 1.3334 | 0.3329 | |||
| 8th | 161 | 161 | ||||||
| 2.5776 | 2.4910 | 3.0669 | 2.8146 | 1.3413 | 0.3075 | |||
| 9th | 181 | 181 | ||||||
| 2.5665 | 2.4761 | 1.3129 | 1.6320 | 1.5538 | 0.1371 | |||
| 10th | 201 | 201 | ||||||
| Mean value | 2.5977 | 2.5374 | 2.5793 | 2.5078 | 1.2305 | 0.9582 | ||
| Global value | 2.6035 | 2.5590 | 2.4752 | 2.4301 | 1.1550 | 1.0167 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Dou, L.; Mu, Z.; Tan, S.; Zong, Z.; Djidjeli, K.; Zhang, G. A New Boundary Condition Framework for Particle Method by Using Local Regular-Distributed Background Particles—The Special Case for Poisson Equation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112183
Sun Z, Dou L, Mu Z, Tan S, Zong Z, Djidjeli K, Zhang G. A New Boundary Condition Framework for Particle Method by Using Local Regular-Distributed Background Particles—The Special Case for Poisson Equation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(11):2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112183
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhe, Liyuan Dou, Zongbao Mu, Siyuan Tan, Zhi Zong, Kamal Djidjeli, and Guiyong Zhang. 2023. "A New Boundary Condition Framework for Particle Method by Using Local Regular-Distributed Background Particles—The Special Case for Poisson Equation" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 11: 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112183
APA StyleSun, Z., Dou, L., Mu, Z., Tan, S., Zong, Z., Djidjeli, K., & Zhang, G. (2023). A New Boundary Condition Framework for Particle Method by Using Local Regular-Distributed Background Particles—The Special Case for Poisson Equation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(11), 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112183







