Ectopleura crocea (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) Identified as a Predator of Pelagic Fish Eggs through Cytochrome c Oxidase I Metabarcoding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Analysis
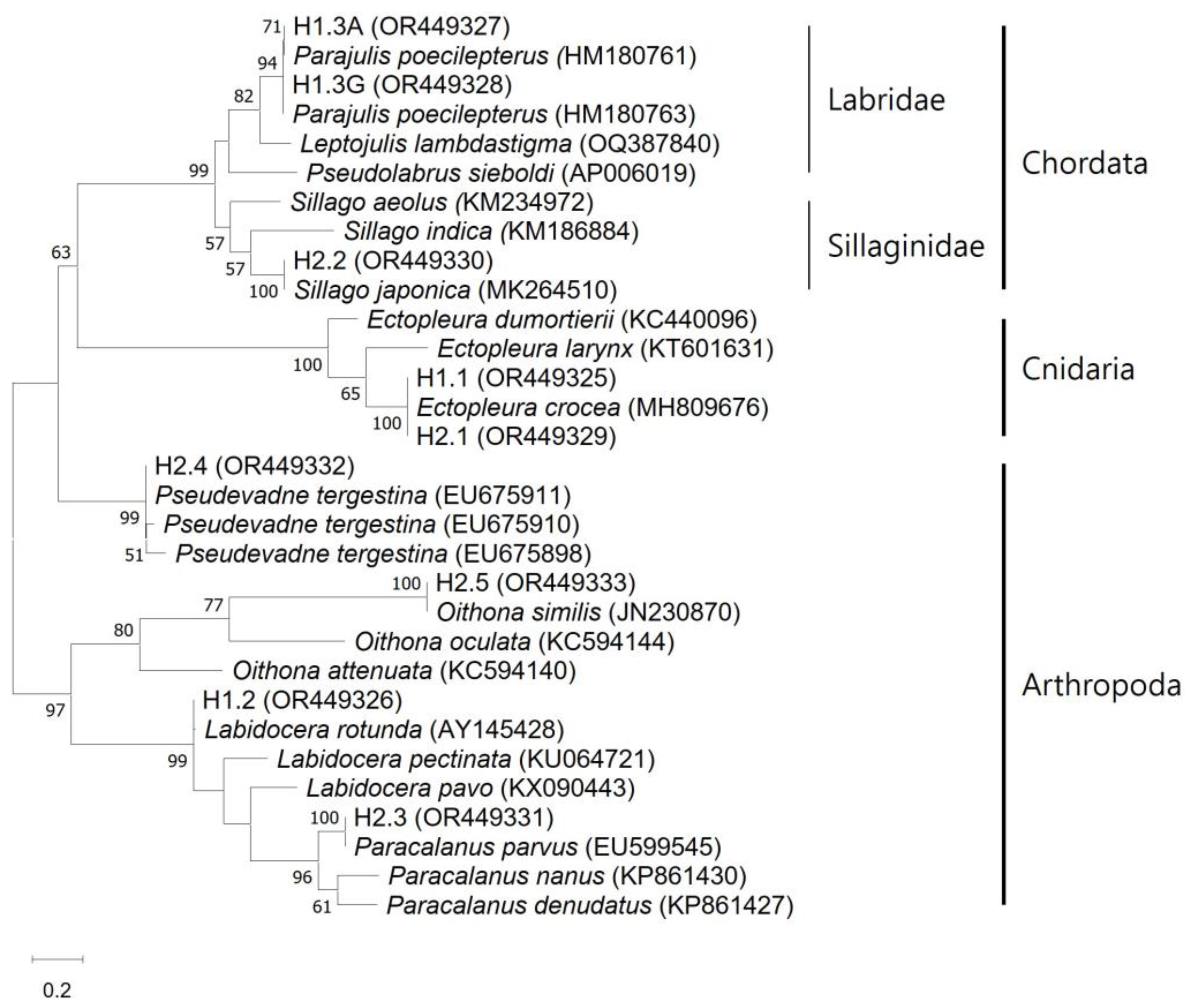
3. Results
3.1. Morphology of Hydroids
3.2. Identification of Ectopleura crocea and Prey via Metabarcoding
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kendall, A.W.; Ahlstrom, E.H.; Moser, H.G. Early life history stages of fishes and their characters. In Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes; Moser, H.G., Richards, W.J., Cohen, D.M., Fahay, M.P., Kendall, A.W., Richardson, S.L., Eds.; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists Special Publication: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1984; pp. 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Houde, E.D. Fish early life dynamics and recruitment variability. Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 1987, 2, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Cushing, D.H. A link between science and management in fisheries. Fish. Bull. 1974, 72, 859–864. [Google Scholar]
- Bunn, N.A.; Fox, C.J.; Webb, T. A Literature Review of Studies on Fish Egg Mortality: Implications for the Estimation of Spawning Stock Biomass by the Annual Egg Production Method; Centre for Environment, Fisheries, and Aquaculture Science: Lowestoft, UK, 2000; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.R. Inferences regarding predation on the early life stages of cod and other fishes. In The Propagation of Cod Gadus morhua L.; Dahl, E., Danielssen, D.S., Moksness, E., Solemdal, P., Eds.; Flodevigen Rapportser: Arendal, Norway, 1984; pp. 533–562. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, M.R. Field investigations of the early life stages of marine fish. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1992, 28, 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, C.J.; Taylor, M.I.; Van der Kooij, J.; Taylor, N.; Milligan, S.P.; Albaina, A.; Pascoal, S.; Lallias, D.; Maillard, M.; Hunter, E. Identification of marine fish egg predators using molecular probes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 462, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, A.; Baker, R.; Loneragan, N.; Sheaves, M. Standardising fish stomach content analysis: The importance of prey condition. Fish. Res. 2017, 196, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.T.; Chen, K.C.; Wu, J.H. Identification of marine fish eggs in Taiwan using light microscopy, scanning electric microscopy and mtDNA sequencing. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 53, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Choi, H.C.; Kim, S.; Oh, H.J.; Youn, S.H. Discovery of pelagic eggs of two species from the rare mesopelagic fish genus Trachipterus (Lampriformes: Trachipteridae). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J.; Glöckner, G.; Jahn, R.; Enke, N.; Gemeinholzer, B. Metabarcoding vs. morphological identification to assess diatom diversity in environmental studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, A.E.; Pearman, J.K.; Borja, A.; Carugati, L.; Carvalho, S.; Danovaro, R.; Dashfield, S.; David, R.; Féral, J.P.; Olenin, S. A comparative analysis of metabarcoding and morphology-based identification of benthic communities across different regional seas. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 8908–8920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.; Shokralla, S.; Costa, M.H.; Hajibabaei, M.; Costa, F.O. DNA metabarcoding for high-throughput monitoring of estuarine macrobenthic communities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmerling, N.; Zuqert, O.; Amitai, G.; Gurevich, T.; Armoza-Zvuloni, R.; Kolesnikov, I.; Berenshtein, I.; Melamed, S.; Gilad, S.; Benjamin, S.; et al. Quantitative species-level ecology of reef fish larvae via metabarcoding. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.U.; Choi, H.; Jeon, M.S.; Kim, E.J.; Jeong, H.G.; Kim, S.; Kim, C.G.; Hwang, H.J.; Purnaningtyas, D.W.; Lee, S.; et al. Zooplankton diversity monitoring strategy for the urban coastal region using metabarcoding analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbart, M.; Kerr, M.; Schram, M.J.; Williams, I.; Koziol, G.; Peebles, E.; Stallings, C.D. Evaluation of DNA metabarcoding for identifying fish eggs: A case study on the West Florida Shelf. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, G.; Keskin, E.; Demirel, N. Comparison of fish prey contribution in the diet of European hake by visual assessment of stomach contents and DNA metabarcoding. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2023, 106, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzano, G.N. Trophic ecology of a benthic intertidal hydroid, Tubularia crocea, at Mar del Plata, Argentina. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.E.; Marques, A.C.; Migotto, A.E.; Calder, D.R.; Hand, C.; Rees, J.T.; Haddock, S.H.D.; Dunn, C.W.; Pugh, P.R. Hydrozoa: Polyps, Hydromedusae, and Siphonophora. In The Light and Smith Manul, 4th ed.; Carlton, J.T., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 118–167. [Google Scholar]
- Kamita, T.; Sato, T.N. Marine fauna at Jinsen (Incheon) Bay, Corea. J. Chosen Nat. Hist. Soc. 1941, 8, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, R.J. Studies in the marine hydroids in Korea (2). J. Korean Res. Inst. Better Liv. Ewha Womans Univ. 1969, 2, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H. Invertebrate Fauna of Korea. No. 1. Cnidaria: Hydrozoa: Thecata. Thecates; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2010; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, P.; Yoon, T.J.; Shin, S. Environmental DNA and specific primers for detecting the invasive species Ectopleura crocea (Hydrozoa: Anthoathecata) in seawater samples. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oregon Estuarine Invertebrates: Rudys’ Illustrated Guide to Common Species (Third Edition). Available online: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/c.php?g=542184&p=3886596 (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Leray, M.; Yang, J.Y.; Meyer, C.P.; Mills, S.C.; Agudelo, N.; Ranwez, V.; Boehm, J.T.; Machida, R.J. A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: Application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Front. Zool. 2013, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Chin, B.S.; Park, G.S.; Kim, S. Evidence of intrusion of a rare species, Peristedion liorhynchus, into Korean waters based on high-throughput sequencing of the mixed fish eggs. Korean J. Icthyol. 2022, 34, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation. Preparing 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Amplicons for the Illumina MiSeq System. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/16s/16s-metagenomic-library-prep-guide-15044223-b.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Bushnell, B.; Rood, J.; Singer, E. BBMerge–accurate paired shotgun read merging via overlap. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunsicker, M.E.; Ciannelli, L.; Bailey, K.M.; Buckel, J.A.; White, J.W.; Link, J.S.; Essington, T.E.; Gaichas, S.; Anderson, T.W.; Brodeur, R.D.; et al. Functional responses and scaling in predator–prey interactions of marine fishes: Contemporary issues and emerging concepts. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Youn, S.H. Integrated Ecosystem Assessments for Fisheries Management in the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea, and the East/Japan Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, K.J.; Milton, A.M. Multi-species fish foraging associations during tool use by the graphic tuskfish Choerodon graphicus (De Vis 1885) (Labridae). Mar. Ecol. 2021, 42, e12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Malagón, M.A.; Speakman, C.N.; Sutton, G.J.; Angel, L.P.; Arnould, J.P. Temporal and spatial isotopic variability of marine prey species in south-eastern Australia: Potential implications for predator diet studies. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyslop, E.J. Stomach contents analysis—A review of methods and their application. J. Fish Biol. 1980, 17, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, C.M.; Riera, R.; Leite, T.; Díaz-Santana-Iturrios, M.; Rosa, R.; Pardo-Gandarillas, M.C. Stomach content analysis in cephalopods: Past research, current challenges, and future directions. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2021, 31, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.J.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Park, Y.S.; Kwak, I.S. Analysis of food preference and competition based on stomach contents of fish species inhabiting fresh and brackish waters in South Korea. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2023, 32, 64–79. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.J.; Mcveagh, S.M.; Allain, V.; Sanchez, C. DNA identification of gut contents of large pelagic fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 37, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, E.; Hirsch, P.E.; Bussmann, K.; Wiegleb, J.; Jermann, H.P.; Muller, R.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Adrian-Kalchhauser, I. Predation on native fish eggs by invasive round goby revealed by species-specific gut content DNA analyses. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. 2020, 30, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, D.J.; DiBattista, J.D.; Stat, M.; Arrigoni, R.; Reimer, J.; Terraneo, T.I.; Villalobos, R.; Nowicki, J.P.; Bunce, M.; Berumen, M.L. DNA metabarcoding confirms primary targets and breadth of diet for coral reef butterflyfishes. Coral Reefs 2023, 42, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.H. Fish mitochondrial genomics: Sequence, inheritance and functional variation. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibulskis, K.; McKenna, A.; Fennell, T.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.; Getz, G. ContEst: Estimating cross-contamination of human samples in next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2601–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiévet, A.; Bernard, V.; Tenreiro, H.; Dehainault, C.; Girard, E.; Deshaies, V.; Hupe, P.; Delattre, O.; Stern, M.H.; Stoppa-Lyonnet, D.; et al. ART-DeCo: Easy tool for detection and characterization of cross-contamination of DNA samples in diagnostic next-generation sequencing analysis. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurasz, H.; Pawłowski, T.; Perlejewski, K. Contamination issue in viral metagenomics: Problems, solutions, and clinical perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 745076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Taxonomy | Sample | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | Species | H1 | H2 | ||||||
| Rep. (accession number) | Reads | Ref. accession number | Paired identity | Rep. (accession number) | Reads | Ref. accession number | Paired identity | ||
| Cnidaria | Ectopleura crocea | H1.1 (OR449325) | 5477 | MH809676 | 100.0 | H2.1 (OR449329) | 1345 | MH809676 | 100.0 |
| Chordata | Parajulis poecilepterus | H1.3A (OR449327) | 102 | HM180761 | 100.0 | ||||
| Parajulis poecilepterus | H1.3G (OR449328) | 146 | HM180763 | 100.0 | |||||
| Sillago japonica | H2.2 (OR449330) | 1054 | MK264510 | 100.0 | |||||
| Arthropoda | Labidocera rotunda | H1.2 (OR449326) | 934 | AY145428 | 99.4 | ||||
| Paracalanus parvus | H2.3 (OR449331) | 801 | KC784345 | 100.0 | |||||
| Pseudevadne tergestina | H2.4 (OR449332) | 621 | EU675911 | 100.0 | |||||
| Oithona similis | H2.5 (OR449333) | 298 | JN230870 | 100.0 | |||||
| Total | 6659 | 4119 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.-Y.; Kim, S. Ectopleura crocea (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) Identified as a Predator of Pelagic Fish Eggs through Cytochrome c Oxidase I Metabarcoding. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112178
Choi H-Y, Kim S. Ectopleura crocea (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) Identified as a Predator of Pelagic Fish Eggs through Cytochrome c Oxidase I Metabarcoding. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(11):2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112178
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hae-Young, and Sung Kim. 2023. "Ectopleura crocea (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) Identified as a Predator of Pelagic Fish Eggs through Cytochrome c Oxidase I Metabarcoding" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 11: 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112178
APA StyleChoi, H.-Y., & Kim, S. (2023). Ectopleura crocea (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) Identified as a Predator of Pelagic Fish Eggs through Cytochrome c Oxidase I Metabarcoding. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(11), 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112178






