Abstract
The impacts of climate change on ichthyoplankton have barely been examined in the Pearl River estuary (PRE). Using the fish larvae and eggs caught in the estuary in the summer from 2003 to 2018 (except for the years 2004 and 2008), the spatial and temporal variations in ichthyoplankton’s abundance, species composition, and community structure were examined and linked to the variability of the climate system. A positive/negative correlation was found between the abundance and taxonomic diversity of the fish larvae and the monthly Oceanic Niño Index. However, the variation in larval fish’s species diversity was in phase with climate change, while the variation in larval fish’s abundance had a 3-month lag behind the climate variability. The different phases of the correlations reflect a progressive change in the ichthyoplankton dynamics under the influence of climate. Furthermore, during the period of the study, the regional climate underwent an obvious transition from a “cold” to a “warm” state in the early 2010s. Associated with that, it was found that both the abundance and species composition of the ichthyoplankton exhibit a significant change around that time, particularly for the fish larvae. A further examination of the ichthyoplankton’s horizontal distributions suggests that the assemblage of ichthyoplankton in the PRE is sensitive to the La Niña conditions. This leads to an overall reduction in ichthyoplankton’s abundance and less seaward spreading of the assemblage, implying the possible impact of climate change on river discharge and then the estuarine environment.
1. Introduction
Ichthyoplankton, including the eggs and larvae of fish, is an essential component of estuarine ecosystems worldwide. As part of the lower trophic food web, the assemblages of ichthyoplankton have complex mutual effects with other plankton taxa [1]. Because of absent or weak swimming capabilities and a drifting nature, the early stages of the fish’s life history are poorly adapted to changing environmental conditions [2,3,4,5]. They can, therefore, be a good indicator of variations in the ecological environment [6]. It is also true that estuaries serve as key habitats for numerous fishes by providing food, shelter, and environmental conditions in favor of their breeding and growth [7,8,9,10,11]. The abundance and distribution of fish eggs and larvae can provide information on, for example, the spawning area [12], population size, and survival rates [13] of commercially important fish stock. Hence, the study of ichthyoplankton, including the dynamics and driving mechanism, forms a necessary basis for the sustainable utilization of fishery resources.
There are many factors affecting the composition and ecological distribution of ichthyoplankton assemblages in estuaries. Physical parameters such as temperature, salinity, river flow, turbidity, and water depth have been reported to significantly influence the structure of ichthyoplankton assemblages [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. In addition to these physical parameters, the structure and relative composition of ichthyoplankton assemblages in estuaries are further influenced by biotic processes. They include but are not limited to the location, timing, manners of spawning, larval life history, larval behavior, and rates of predation and feeding [24,25,26,27]. Meanwhile, anthropogenic behaviors, such as overfishing, coastal engineering, and pollution discharge may have effects that permanently alter the biotic and abiotic interactive processes and substantially change the ichthyoplankton population and community structure [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37].
In addition, climate change as an underlying driver of estuarine environment variability may play a critical role in affecting the population of ichthyoplankton [38]. Generally, climate change causes higher water temperatures, stronger stratification, and increased river runoff and nutrients to coastal water [39], which subsequently force ichthyoplankton assemblages to face more stressful or even fatal situations [40]. Studies in the Chesapeake Bay and Neuse River estuary and laboratory experiments revealed that the increased frequency of hypoxia under warming conditions may continue to reduce the habitat and nursery grounds, resulting in a smaller population, less migration, and limited reproduction of fish [41,42,43,44,45]. Current changes under climate variation can affect larval dispersal, retention, and recruitment as well [46]. These larvae may be translated into unfavorable areas, causing smaller recruitment [47,48,49,50]. Climate variation is also capable of influencing fish phenology by changing the temperature and/or other factors. The phenological timing of flounder migration off Plymouth, southwest UK, was found to be earlier during cold-temperature periods in the North Atlantic Oscillation [51]. Again, there are examples that climate change could disturb juvenile fish growth by mismatching the zooplankton prey in the Gironde estuary, southwest France [52].
The Pearl River estuary (hereafter referred to as the PRE) is the third-largest estuary in China. Although it is an important nursery ground for several commercially important fisheries [53], studies on the dynamics of ichthyoplankton are sparse. In this respect, Xiao et al. (2010) [54] described the distribution of fish larvae and eggs in the PRE from 2004 to 2007. They further studied the environmental factors that affected the distribution of ichthyoplankton in the period 2006–2007 [54,55]. Nevertheless, how the long-term features of ichthyoplankton assemblages in the PRE are being affected by climate fluctuations remains to be carefully examined. According to historical data, the fishery resources of the PRE are currently at a low level with an undesirable catch rate [56]. For the sustainable utilization of the fishery resources, it is of great significance to study the composition and distribution of fish eggs and larvae in the PRE.
In this context, this paper aims to explore the spatial and temporal variations in ichthyoplankton assemblage in the PRE based on a long-term dataset of fish larvae and eggs caught in the summer season from 2003 to 2018 and try to link the variations to climate change. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, the observation data and analysis methods are described. In Section 3, the variations in summer ichthyoplankton assemblage are explored, which is followed by a detailed discussion in Section 4 focusing on the potential climate influences. Finally, the conclusions are summarized in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studying Area
The area of the PRE (113–114.1° E, 21.8–22.8° N) has complex hydrodynamic conditions. The convergence of salt water and fresh water is affected by river runoff and tide, and the water exchange is also affected by the seasonal monsoon wind and the coastal current [57,58]. Lingding Bay is the largest semi-enclosed body of water of the PRE. It is trumpet-shaped with a longitudinal length of about 70 km and a gradually increasing width from north to south. The width near the bayhead is ~8 km, and the width near the mouth is ~35 km. The PRE is rich in nutrients, and the turbidity in the estuary is higher than that in the open sea. It is a suitable place for fish spawning and nursing.
The monthly runoff of the west river (the main river in the PRE) was collected from the hydrological station at Gaoyao during the period of study. The environmental data (including temperature, salinity, pH, DO, Chl-a, NO3, and PO4) of the PRE were also collected from the long-term monitoring site of the Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department (www.epd.gov.hk, accessed on 8 July 2019) (Figure 1). These data were used to investigate the impacts of climate change on the estuarine environment.
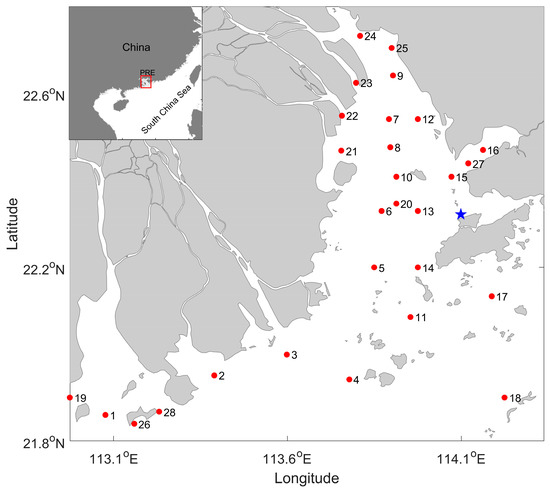
Figure 1.
Enlarged view of the Pearl River estuary (PRE) with an indication of the geographic location. The red dots represent the stations where the ichthyoplankton data were collected. The blue start represents the long-term monitoring site of the Hong Kong EPD.
The local climate variability, which is mainly driven by the ENSO (El Niño-Southern Oscillation), can be inferred based on the Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) [59]. The time-series data of the index was obtained from the web (https://ggweather.com/enso/oni.htm, accessed on 8 July 2019) and is calculated based on the anomalies of the averaged sea surface temperature in the area of the east-central equatorial Pacific Ocean, which is called the Niño3.4 region (5S to 5N; 170° W to 120° W). In the present study, warm events (El Niño) are defined as having ONI values over 5 °C for consecutive overlapping 3-month periods at or above the +0.5 °C anomaly. Similarly, cold events (La Niña) are defined as having ONI values over 5 °C for consecutive overlapping 3-month periods at or below the −0.5 °C anomaly.
2.2. Ichthyoplankton Sampling and Processing in the Lab
The locations for ichthyoplankton data collection (including fish larvae and eggs) are shown in Figure 1. The collection was conducted each summer (mainly in August) from 2003 to 2018 (except for the years 2004 and 2008). According to the Chinese marine survey regulations, the sampling was made by a single large plankton net (80 cm in diameter and 0.505 mm in mesh size), which was towed horizontally for 10 min (0.5 m below the surface water) with a speed of ~1.5 knots. Therefore, we simply calculated the water volume by multiplying the diameter of the plankton net by a speed of ~1.5 knots and multiplying it by 10 min during the tow period. The ind(individual)/tow was the recording unit of ichthyoplankton. The sampled fish larvae and eggs were preserved in a 5% formaldehyde seawater solution. After being brought back to the laboratory, the fish eggs and larvae were counted separately and identified under an anatomic microscope using the identification keys provided in the references [60,61]. Samples of fish larvae and eggs were recorded by species. For species that could not be identified, families were used instead.
2.3. Data Analyses
The Spearman coefficient was calculated to determine the correlation of ichthyoplankton abundance and taxonomic diversity with the ONI. It was also used to determine the correlation between the ONI and estuarine environmental factors. Before the calculation, the data were preprocessed using . The Spearman rank correlation coefficient converts multiple vectors into a rank vector, and its formula is as follows:
where is the result of the Spearman rank correlation coefficient. The degree of correlation is within the range of [−1, 1]. N is the sum of quadrate numbers, and is the rank difference of the variables and .
Pianka’s (1971) [62] Index of Relative Importance (IRI) was used to calculate the dominant species in the community of fish larvae and eggs. The formula is as follows:
where W is the individual mass proportion of the whole catch and is often ignored because the mass of larval fish or eggs themselves is very small. N is the proportion of horizontally caught fish larvae or eggs in the total catch, and F is the proportion of occurrence frequency of larval fish or eggs in this taxon. In this study, the dominant species (taxon) are defined with an IRI value of over 100 [63]. If the IRI index value is larger than one hundred, the species (taxon) will be considered a dominant species (taxon); otherwise, if the IRI index value is less than 100 but larger than 10, the species (taxon) will be defined as a common species (taxon).
To calculate the taxonomic diversity, we use the following:
Margalef species richness index (D):
Pielou evenness index (J):
Shannon–Wiener diversity index (H):
In these equations, S represents the number of species, M represents the total catch, and means the proportion of taxon in the total catch.
Similarity analysis (ANOSIM) [64] was conducted to compare the ichthyoplankton’s community structure between different years using the RStudio program.
Finally, the caught fish larvae and eggs can be clustered into four categories according to the study of Yang et al. (1990) [65]: (1) the freshwater type, mainly Cyprinidae—in the present study, no ichthyoplankton were caught belonging to this type; (2) the brackish type, which mainly live in the temperature range of 12–22 °C and the salinity range of 0.12–12‰—representative taxa are the species of Gobiidae, Mugilidae, Liza sp., etc.; (3) the neritic type, most of which prefer a higher temperature range of 18–30 °C and stained water with salinity lower than 26‰—representative taxa are Stolephorus sp., Hemiramphus sp., Sardinella sp., etc.; (4) the coastal type, whose adults live away from the coast where the depth is more than 30 m—representative taxa are Sillago sihama, Leiognathidae, Sparidae, etc.
3. Results
3.1. Abundance Dynamics
The catches from 2003 to 2018 showed a large yearly variation in the summer abundance of ichthyoplankton (Figure 2). Relative to the multi-year mean value (0.34 ind/m3), the abundance of fish larvae was high in the years 2006, 2014, 2016, and 2017 and low in the years 2003, 2005, 2007, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2015, and 2018 (note there were no data from 2004 and 2008). The highest catch (1.97 ind/m3) was recorded in 2017, and the catch reached its lowest value (0.03 ind/m3) in 2012. For the fish eggs, the temporal variation in the abundance is different. Relative to the multi-year mean value (0.85 ind/m3), the abundance of fish eggs was high in the years 2005, 2007, 2010, 2011, 2014, and 2016 and low in the years 2003, 2006, 2009, 2012, 2013, 2015, 2017, and 2018 (Figure 2b). The highest catch (1.99 ind/m3) was recorded in 2011, and the catch again reached its lowest value (0.09 ind/m3) in 2012.
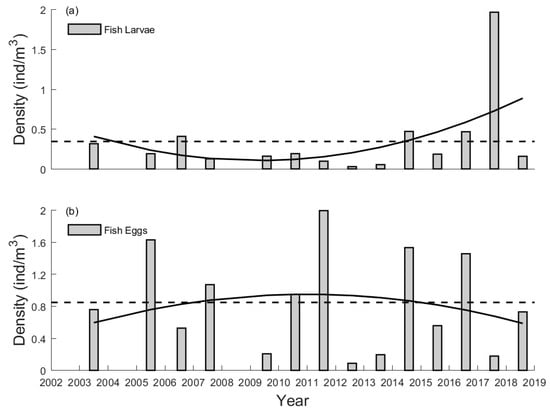
Figure 2.
Summer abundance (in density) of fish larvae and eggs in the PRE from 2003 to 2018. The dashed line represents the multi-year mean value and the solid line is the regression based on a quadratic function. (a) Fish Larvae (b) Fish Eggs.
For the abundance of both fish larvae and eggs, there is also a long-term variation existing during this period. As shown in Figure 2, the abundance of fish larvae features a concave-shaped trend of change and a turning point in the early 2010s. In contrast, the abundance of fish eggs features a dome-shaped trend of change and a turning point in the early 2010s as well. It is found that before that time, the abundance anomalies of the fish larvae and eggs (normalized by the multi-year mean) are nearly opposite (Figure S1). However, they have reversed since then (except for the abnormal year 2017). The abrupt change in the phase relationship reflects the potential impact of the environment on the summer ichthyoplankton abundance. Therefore, the estuarine condition of the PRE could be significantly different before and after the early 2010s, thus leading to a prolonged variation in the ichthyoplankton abundance.
The mean spatial patterns of the summer ichthyoplankton abundances are presented in Figure 3. The result shows a very different horizontal distribution of the fish larvae and the eggs in the PRE. Specifically, the fish larvae have a much higher abundance in the low-salinity region (<5 PSU) of Lingding Bay. In addition, there is a small isolated area of high fish larvae abundance located at the mouth of the estuary. In comparison, the distribution of fish eggs is spread more seaward. There is a significantly larger number of eggs located along a high gradient of salinity, reflecting a possible influence from the river flow.
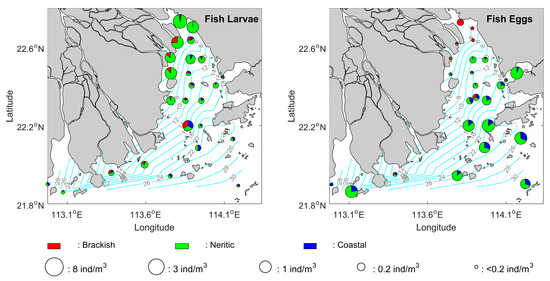
Figure 3.
Circle: mean abundance distribution of the fish larvae and eggs in the PRE. Colors: partitions among the brackish, neritic, and coastal species of fish larvae and eggs in the PRE. The light blue represents the contour lines of the corresponding mean surface salinity field.
3.2. Composition, Dominant Taxa, and Community Structure
From 2003 to 2018, a total of 44,473 fish eggs and 22,924 fish larvae were caught in the summer. Among these, 49 taxa of fish larvae belonging to 27 families and 41 taxa of fish eggs belonging to 24 families were identified (Table S1a,b). For the convenience of analysis, they were further clustered into four categories: freshwater, brackish, neritic, and coastal, according to the work by Yang et al. (1990) [65]. In terms of the fish larvae, the neritic type was the one with the most species identified. This type of larval fish also had the largest abundance, accounting for 88.93% of the total catch. In comparison, although the coastal type also had a large number of identified species, the abundance accounted for only 4.32% of the total catch. This value was even smaller than that of the brackish type (6.43%), despite there being only five identified fish larvae species falling into this category. Due to the small fraction, the freshwater type is ignored in the following analysis. In terms of the fish eggs, the neritic type again was the most abundant, accounting for 65.34% of the total catch. The coastal type, however, was the one with the most species identified, accounting for 23.21% of the total catch in abundance. The remaining 10% of the total catch was mainly of the brackish type, with six species identified.
Based on the IRI index, there are two dominant fish larvae species in the PRE, Sardinella sp. and Ambassis gymnocephalus, and all belong to the neritic type. In addition, there are seven common fish larvae species. Among those, two are the brackish type, four of which are the neritic type, and one is the coastal type. In comparison, the fish eggs have four dominant species, which include the Ambassis gymnocephalus and two Stolephorus sp. in the neritic type, and an unknown species of the Cynoglossidae family in the coastal type. Furthermore, there are nine common fish egg species. Among those, one is the brackish type, five are the neritic type, and three are the coastal type.
The community structure of the summer ichthyoplankton also showed a large yearly variation. As shown in Figure 4, the neritic type of fish larvae was the main category of the composition (except for the year 2005). However, the dominant species was not the same all the time. From 2006 to 2011, Sardinella sp. had a clear trend of diminished dominance. Since 2012, it resumed its previous abundance and quickly became the dominant one again. It is worth noting that over the same period of 2006–2011, the brackish/coastal type of fish larvae featured an increased/decreased proportion in the composition. These changes are coincident with the variation in Sardinella sp. and stopped abruptly in the year 2012. This again indicates a strong environmental change in the PRE, which subsequently altered the ichthyoplankton’s summer community structure. Compared to the fish larvae, the composition of fish eggs did not display a clear pattern of variation. The sporadic occurrences of significant changes in the structure of the assemblage may also have been a result of strong perturbations of the estuarine environment.
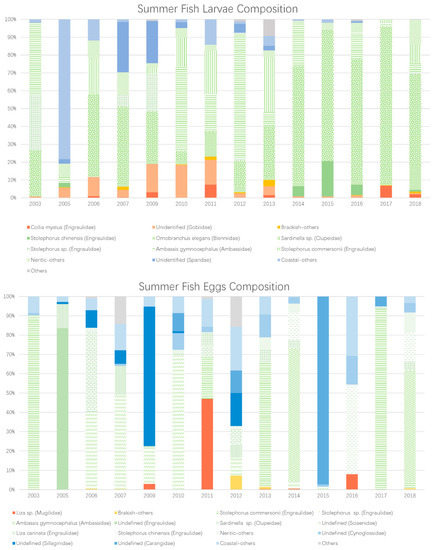
Figure 4.
Circle: mean abundance distribution of the fish larvae and eggs in the PRE. Colors: partitions among the brackish, neritic, and coastal species of fish larvae and eggs in the PRE. The light blue represents the contour lines of the corresponding mean surface salinity field.
Finally, the horizontal distributions of the ichthyoplankton composition show that the neritic type of fish larvae and eggs are the most commonly observed species in the PRE during the summer season (Figure 3). The coastal type of fish eggs can also be found in a relatively large amount but are mainly located in the outer region of the estuary, while the brackish type of ichthyoplankton has a better chance to be seen in the upper region of the estuary.
3.3. Taxonomic Diversity
The total number of species in the ichthyoplankton assemblage is an unambiguous index of species richness. As shown in Figure 5, fish larvae displayed the highest number of species in 2013 and 2016, followed by 2011 and 2007, with a value >20, while the lowest species number (<10) was found in 2003, 2012, and 2017. In other years, the number of species fluctuated in between these values. In comparison, the fish eggs always had a smaller overall number of species than the fish larvae. However, they were more stable in the year-to-year variation.
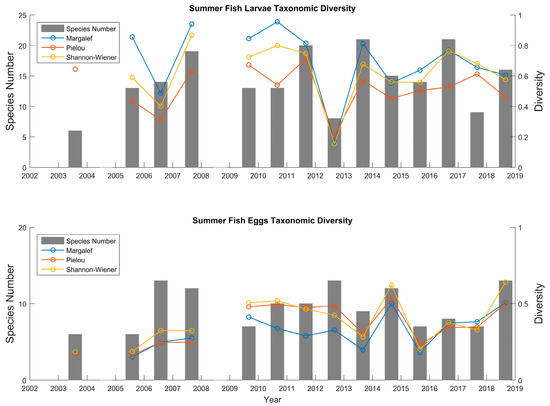
Figure 5.
Spatially averaged species number and taxonomic diversity for the fish larvae and eggs from 2003 to 2018.
Several indices (Margalef richness index, Pielou evenness index, and Shannon–Wiener diversity index) were spatially averaged and calculated to show the comprehensive characteristics of the ichthyoplankton community’s ecological diversity and heterogeneity. Overall, all the indices varied similarly. For the fish larvae, the Margalef richness index, Pielou evenness index, and Shannon–Wiener-diversity index were low in 2006 and 2012. The highest Margalef richness index appeared in 2010, the Pielou evenness index was at its peak in 2007, and the Shannon–Wiener diversity index was higher (around 0.7) in 2011 than in the other years. For the fish eggs, these indices became flatter. In contrast, the fish larvae have a relatively higher diversity than the eggs in terms of both richness and evenness, since there is a larger number of species found in the catch (Figure 5).
3.4. Impacts of Climate Change on the Ichthyoplankton
3.4.1. Abundance
A strong positive correlation was found between the summer ichthyoplankton abundance and the monthly ONI (Table 1). For the fish larvae, the correlation coefficient can be up to r = 0.71 if the ONI leads the observations by 3 months. The abundance of fish eggs shows a similar degree of correlation. However, the ONI has to be 7–12 months ahead of the observations.

Table 1.
Correlations of the fish larval and egg abundance with the monthly ONI (* means p < 0.05).
Climate change may contribute to the long-term variation in the summer ichthyoplankton abundance in the PRE. As shown in Figure S2, the ONI in the period 2006–2012 reveals a strong negative phase of ENSO. It also indicates a short period of weak climate variability in the period 2013–2014 and the strong El Niño of 2015–2016. Since the shift in the climate state matches the timings of the observed abundance variations (Figure 2 and Figure S1), the climate variability is thought to be a key mechanism driving the estuarine environmental change and then leading to the long-term variation in the summer ichthyoplankton abundance.
To give a physical sense of the connection between climate change and the variations in summer ichthyoplankton abundance, correlation analyses were made between the ONI and the estuarine environment of the PRE. As demonstrated in Table S2, the river runoff is the only environmental factor that shows a correlation with the ONI. In addition, it has a strong connection with the estuarine temperature and salinity (r > 0.5, p < 0.01). Therefore, river runoff may be the specific driver of the estuary’s environmental change under the influence of climate. To verify this, we also compared the monthly Gaoyao river discharge, from 2015 to 2018. During the strong El Niño of 2015–2016, the river flow was increased 2–3 months earlier (Figure 6). This confirms the 3-month lead of ONI in the correlation analysis with the fish larvae and thus demonstrates the role of climate change on the estuarine environment through river runoff.
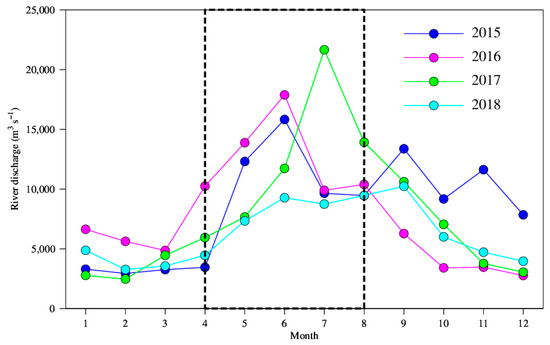
Figure 6.
Monthly river discharge at the Gaoyao hydrological station, from 2015 to 2018.
3.4.2. Composition and Taxonomic Diversity
The dendrogram resulting from the two-way cluster analysis using the 14-year data from the Bray–Curtis similarity matrix of taxa proportion shows the change in the ichthyoplankton composition around the early 2010s. As shown in Figure S3, the years 2010–2013 are clustered together and separated from the following sampling period, in particular, during the strong 2015–2016 El Niño event. Although the result of grouping is robust based on the ANOSIM test, since it gives a statistical value of 0.83 (p = 0.002), the analysis does not mean the different composition is fully a result of climate change. Nevertheless, Figure S3 suggests that the structural change in the ichthyoplankton assemblage does not cross the boundary of the biological groups and occurs only within the neritic category. The larval fish Ambassis gymnocephalus (F11) was the dominant species in the grouping years 2010–2013, which was then replaced by Sardinella sp. (F12) in the grouping of the later years following the climate variability.
The association of ENSO with the taxonomic diversity of the ichthyoplankton was also examined based on the Spearman analysis. Table 2 shows that for the larval fish, both the Margalef richness number and the Shannon–Wiener diversity index have a strong negative correlation with the ONI. For the fish eggs, however, there is no such reliable relationship found in the same analysis. In addition, the analysis shows that the phase relationship of the correlation for species richness and diversity is different from the result for abundance since the correlation coefficients are greatest at a null phase difference.

Table 2.
Correlations between the taxonomic diversity and monthly ONI (** means p < 0.01, * means p < 0.05).
3.4.3. Spatial Distribution
The changes in the ichthyoplankton’s horizontal distribution may also reflect a possible underlying cause of the climate impact during the period from 2003 to 2018. For both fish larvae and eggs, the spatial patterns of El Niño over the years more resemble their climatological distributions, even though some variations were shown in the ichthyoplankton’s species composition near the river mouth (Figure 7). In contrast, the corresponding spatial patterns of fish larvae and eggs during the years of La Niña show some changes. The overall abundance of fish larvae within the estuary has been significantly reduced. In addition, there is a larger gradient of abundance decrease along the main axis of the estuary from the head to the mouth. These changes can be confirmed in a similar comparison of the spatial distributions based on the years of groups (Figure S3) since they can also loosely be regarded as a separation between the climate condition of El Niño and La Niña (Figure 8).
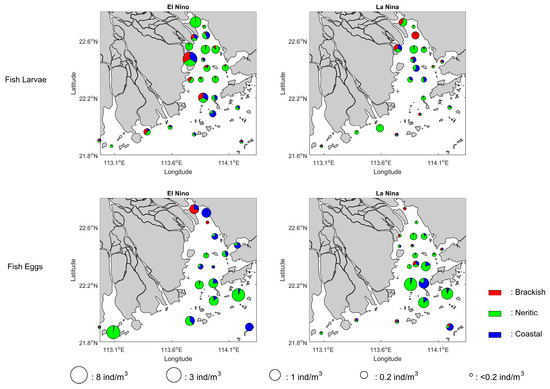
Figure 7.
Abundance distribution and the associated partitions among the brackish, neritic, and coastal species of fish larvae and eggs associated with the El Niño and La Niña conditions.
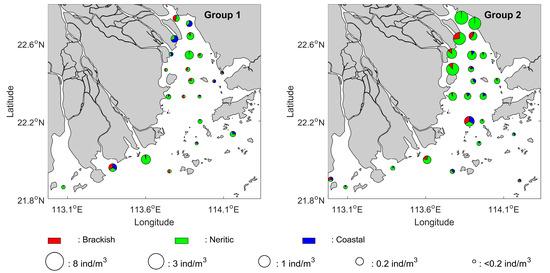
Figure 8.
Same as Figure 7 but using the years of groups determined in the dendrogram analysis.
4. Discussion
4.1. Correlation of the Summer Ichthyoplankton Abundance with Climate Change
In this study, we confirmed the correlation between climate change and the long-term variation in ichthyoplankton abundance in the PRE. The effect of climate change on the variations in ichthyoplankton abundance has long been recognized [4,66,67,68,69]. Such a relationship is expected to be variable from region to region or from species to species [70,71,72]. For example, Hsieh et al. (2021) [73] reported that the abundance of mesopelagic fish larvae decreases during El Niño events in the Gaoping estuary, southwest of Taiwan Island. In contrast, the Strait of Georgia (British Columbia, Canada), influenced by freshwater from the Fraser River, features a higher larval fish abundance and diversity under El Niño conditions and a lower larval fish abundance and diversity under La Niña conditions [74]. In contrast, Attrill and Power (2002) [75] compared the relationship between the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) and the abundance of juvenile fish in the Thames estuary and the North Sea in the south. They found no correlation between the estuarine juvenile fish and NAO, but the juvenile fish of marine groups was significantly correlated with climate oscillation. In the present study, we demonstrate a positive correlation between ENSO and the abundance of summer ichthyoplankton in the PRE. It was found that the correlation of fish larvae with the ENSO had a 3-month phase lag. This resembles the finding in the Columbia River estuary, where the concentration of larval fish is positively correlated with the ONI index 2–3 months early [76]. Nevertheless, the 7-to12-month phase lag in the correlation of fish eggs with the ENSO is a somewhat surprising finding, since it has not been reported in previous studies. The broad temporal range of the correlation suggests that it may be a spurious result affected by the inability of the data to resolve the seasonality of ichthyoplankton abundance in the PRE.
The shift in the climate system from a “cold” to a “warm” state in the early 2010s had significant effects on many local estuarine environments [77,78,79]. Dang (2019) [80] found that the Mekong River discharge increased by 30% during the 2011 La Niña but decreased by 20% in the 2015 El Niño. During the strong La Niña in 2010–2011, the water temperature around the Australian coast area declined by ~0.2% [81]. In the PRE, studies of saltwater intrusion suggest a significant change in the estuarine environment since 2012 [82]. From 2005 to 2012, there was a strong intrusion of saltwater, which became much weaker in the period 2012–2016. The changes in the estuarine hydrodynamics are mainly associated with more/less river discharge and stronger easterly/northeasterly winds during most El Niño/La Niña periods in this region [82]. Thus, the long-term variation in ENSO may be the mechanism driving the change in ichthyoplankton dynamics in the early 2010s.
4.2. Temporal Changes in the Ichthyoplankton’s Composition and Diversity under the Influence of Climate
Our results suggest that the change in the ichthyoplankton’s community structure is more relevant to the climate condition changes(Table 2). This is different from the abundance response (Table 1). The different phase relationships mean the abundance and structure of the ichthyoplankton may have diverse responses to ENSO and may change progressively under the influence of climate.
In previous studies, the different phase response of the ichthyoplankton’s abundance and diversity to climate change is not a common phenomenon or was simply ignored [75,83,84]. However, some studies have pointed out the possible differences. For example, off the Oregon coast, Auth et al. (2011) [76] found that the highest value of the larval diversity of fish lagged the ONI index by 2 months, while the decrease in larval concentration responded to the increase in the ONI index with a 5-month delay. In the Vaza Barris estuarine system (NE Brazil), Achirus sp. and Trinectes sp. grew in abundance during high-temperature and -salinity conditions due to the influence of climate, which led to a change in the composition of local fish larvae assemblage [85]. Similarly, the drought climate caused a decrease in the catadromous fish larvae in the Coorong estuary, Australia, which then led to reduced diversity [86].
The negative correlation between ONI and the Shannon–Wiener index indicates a decreased larval fish diversity during a positive phase of ENSO. Such a response of fish larvae to climate change may differ from one estuary to another [87,88,89]. For example, an increase in diversity was observed in the Mullica River–Great Bay area when the climate drove a warmer water temperature [89]. While 43 fish species were recorded from 2003 to 2010 in the Mendego Estuary, this number decreased by 20 species during the wetter climate conditions between 1988 and 1992 [90].
The shift in the climate state in the early 2010s not only causes a long-term variation in the abundance but also has a strong influence on the ichthyoplankton’s community structure. It was also found in the Huanghe (Yellow) River estuary, where the clustering of species composition resembles our results and shows a different assemblage before and after the year 2013 [91]. Moreover, the composition of fish larvae can be affected by climate change in different ways [92,93,94,95]. In the present study, the change in the dominant larval fish species from Ambassis gymnocephalus to Sardinella sp. is associated with the change from a “cold” to a “warm” climate state. This suggests a possible role of temperature or associated factors in the species composition. In Sepetiba Bay of the southeast Brazilian coast, it was also reported that, from 1948 to 2016, the pelagic ichthyofauna such as Sardinella brasiliensis grew in abundance as a response to climate change, while the abundance of the subtropical species decreased accordingly with the warming condition, resulting in a change in the ichthyoplankton’s composition [96].
5. Conclusions
The spatial and temporal variations in summer ichthyoplankton in the PRE were examined in the period from 2003 to 2018. The results demonstrate significant climate impacts on the variations that occurred independently of space and time. For the fish larvae, there is a strong positive correlation between the abundance and the ONI and a strong negative correlation between the taxonomic diversity and the ONI. For fish eggs, no such reliable relationships were found, even though Spearman analysis showed a correlation between the abundance and the ONI if the latter led the observations by 7–12 months. Our results also show that the phase relationship of the correlation with the larval fish’s abundance and taxonomic diversity is different, which may reflect a progressive change in the ichthyoplankton assemblage under climate influences. During this period of the study, the regional climate has undergone an obvious transition from a “cold” to a “warm” state in the early 2010s. Similarly, the study shows that both the abundance and composition of the ichthyoplankton exhibit a significant change in dynamics around that time, particularly for the fish larvae. Finally, the significant changes in the ichthyoplankton’s horizontal distribution during La Niña reflect a lower level of river discharge, which may cause fewer nutrients to be carried to the estuary and cause less primary production when nutrients are lacking. When there is no food, there are fewer fish and therefore less spawning. The estuarine environment changes may be responsible for an overall reduction in the ichthyoplankton’s abundance and less seaward spreading of the assemblage in the PRE and vice versa.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jmse11010209/s1, Table S1a: Fish larvae composition and guilds. Dominant species are labeled “***”, and common species are labeled “**”. Species with an abundance lower than 0.01% of the total catch are ignored. Table S1b: Fish egg composition and guilds. Dominant species are labeled “***”, and common species are labeled “**”. Species with an abundance lower than 0.01% of the total catch are ignored. Table S2: Correlations among the environmental factors and monthly ONI (** means p < 0.01, * means p < 0.05). Only the correlation coefficients greater than 0.5 are in bold for the environmental factors. Table S3. The Oceanic Niño Index (ONI). Figure S1: Abundance anomalies for the fish larvae and eggs. Figure S2: Monthly Ocean Niño index from 2003 to 2018. The dashed line is the same as in Figure S1 to indicate the long-term abundance variations for the fish larvae and eggs. Figure S3: Dendrogram from the two-way cluster analysis using the 14-year data from the Bray–Curtis similarity matrix of taxa proportion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.H. and Z.L.; methodology, Z.L.; software, S.L.; validation, J.H. and Z.L.; formal analysis, S.L.; investigation, S.L. and Z.L.; resources, J.H.; data curation, S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.; writing—review and editing, Z.L.; visualization, S.L.; supervision, Z.L. and J.H.; project administration, J.H.; funding acquisition, J.H. and Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Innovation Group Project of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai) (No. 311021006).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to South China Sea Environmental Monitoring Center for their summer surface ichthyoplankton data. We thank the reviewers for their insightful comments, which improved the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sanvicente-Añorve, L.; Soto, L.A.; Espinosa-Fuentes, M.L.; Flores-Coto, C. Relationship patterns between ichthyoplankton and zooplankton: A conceptual model. Hydrobiologia 2006, 559, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.; Morais, P.; Chícharo, M.A. Ichthyoplankton dynamics in the Guadiana estuary and adjacent coastal area, South-East Portugal. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 70, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolan, J.M. Larval fish assemblage response to freshwater inflows: A synthesis of five years of ichthyoplankton monitoring within Nueces Bay, Texas. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2008, 82, 275–296. [Google Scholar]
- Primo, A.L.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Marques, S.C.; Pardal, M.Â. Impact of climate variability on ichthyoplankton communities: An example of a small temperate estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 91, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xian, W.; Liu, S. Ichthyoplankton assemblage structure of springs in the Yangtze Estuary revealed by biological and environmental visions. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S.; Cabral, H.; Elliott, M. Do fish larvae have advantages over adults and other components for assessing estuary ecological quality? Ecol. Indic. 2015, 55, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. The ecological characteristics of distribution of eggs, larvae and juveniles of the Engraulis Japonicus (Temminck & Schlegel) and Anchoviella Commersonii (LECÉPÈDE) in the Chang Jiang River estuary. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1989, 20, 217–229. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Jiang, M.; Zang, Z. An investigation of fish eggs, larvae and juveniles in the Chang Jiang Estuary. J. Fish. Sci. China 1999, 6, 63–64. [Google Scholar]
- Light, P.R.; Able, K.W. Juvenile Atlantic menhaden (Brevoortia tyrannus) in Delaware Bay, USA are the result of local and long-distance recruitment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 57, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, N.A.; Sutherland, K.; Wooldridge, T.H. Diet and prey selection in late-stage larvae of five species of fish in a temperate estuarine nursery. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 36, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S. Research Adavance in Estuarine Ichthyuoplankton Ecology. Stud. Mar. Sin. 2016, 51, 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xian, W.; Liu, S. Seasonal variations of the ichthyoplankton assemblage in the Yangtze Estuary and its relationship with environmental factors. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.L.; Jacobson, L.D.; Barnes, J.T. Biology and population dynamics of cowcod (Sebastes levis) in the southern California Bight. Fish. Bull. 2003, 101, 260–280. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, B.K.; Keuren, D.V.; Clancy, M. Timing and size of blooms of the ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi in relation to temperature in Narragansett Bay, RI. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, S.C.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Marques, J.C.; Neto, J.M.; Pardal, M.A. Zooplankton and ichthyoplankton communities in a temperate estuary: Spatial and temporal patterns. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, N. Ichthyoplankton dynamics in a highly urbanized estuary. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015, 11, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, F.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Lek, S. Temporal patterns of larval fish occurrence in a large subtropical river. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0146441. [Google Scholar]
- Kingsford, M.J.; Suthers, I.M. Dynamic estuarine plumes and fronts: Importance to small fish and plankton in coastal waters of NSW, Australia. Cont. Shelf Res. 1994, 14, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta-Bergan, A.; Barletta, M.; Saint-Paul, U. Structure and seasonal dynamics of larval fish in the caeté river estuary in north brazil. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wu, Z.; Tan, X.; Huang, L.; Rad, S. Ontogenetic structure and temporal patterns of summer ichthyoplankton in upper course of the Xijiang river, SW China. Water 2021, 13, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattrick, P.; Strydom, N.A. Composition, abundance, distribution and seasonality of larval fishes in the shallow nearshore of the proposed Greater Addo Marine Reserve, Algoa Bay, South Africa. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, N.A.; Coetzer, C.J.; Pattrick, P. The complex early life history of marine estuarine-opportunist fish species, Solea turbynei (Soleidae) from temperate South Africa. Sci. Mar. 2015, 79, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfirrmann, B.W.; Matthew, E.K.; Marvin, M.M.; Brendan, D.T. Summer Ichthyoplankton Assemblage diversity within a southeastern United States Estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2021, 44, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, E.; Pina, T.; Chícharo, M.A. The distribution of estuarine fish larvae: Nutritional condition and co-occurrence with predators and prey. Acta Oecologica 2000, 21, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, G.C.; Potter, I.C. Do the characteristics of the ichthyoplankton in an artificial and a natural entrance channel of a large estuary differ? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campfield, P.A.; Houde, E.D. Ichthyoplankton community structure and comparative trophodynamics in an estuarine transition zone. Fish. Bull. 2011, 109, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, S.A.; Stige, L.C.; Neuheimer, A.B.; Bogstad, B.; Durant, J.M. Match-mismatch dynamics in the Norwegian-Barents Sea system. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 650, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmore, A.R.; Norman, L.; Strong, J. Oxygen concentrations, temperatures and salinities in the Gippsland Lakes, Victoria 1987–88, and survival of black bream Acanthopagrus butcherii. Environ. Prot. Auth. Sci. Rep. Ser. 1990, 89, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Caddy, J.F. Toward a comparative evaluation of human impacts on fishery ecosystems of enclosed and semi-enclosed seas. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1993, 1, 57–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caddy, J.F. Marine catchment basin effects versus impacts of fisheries on semi-enclosed seas. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, I.T.; Parslow, J.S.; Grayson, R.B.; Molloy, R.P.; Andrewartha, J.; Sakov, P.; Tan, K.S.; Walker, S.J.; Wallace, B.B. Nutrient cycling and water quality in the lakes. In Gippsland Lakes Environmental Study: Assessing Options for Improving Water Quality and Ecological Function; CSIRO: Glen Osmond, SA, Australia, 2001; pp. 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J. Overview of hypoxia around the world. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitburg, D. Effects of hypoxia, and the balance between hypoxia and enrichment, on coastal fishes and fisheries. Estuaries 2002, 25, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalov, G.M. Overfishing drives a trophic cascade in the Black Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 225, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalov, G.M. Long-term changes in fish abundance and environmental indices in the Black Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 255, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T. Long-term impacts of anthropogenic forcing on the Black Sea ecosystem. Oceanography 2005, 18, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nack, C.C.; Swaney, D.P.; Limburg, K.E. Historical and Projected Changes in Spawning Phenologies of American Shad and Striped Bass in the Hudson River Estuary. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2019, 11, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeing, W.J.; Duffy-Anderson, J.T. Ichthyoplankton dynamics and biodiversity in the Gulf of Alaska: Responses to environmental change. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, N.N.; Diaz, R.J.; Justic, D. Global change and eutrophication of coastal waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.A.; Morgan, J.D.; Vijayan, M.M. Biological indicators of aquatic ecosystem stress. In Physiological and condition-related indicators of environmental stress in fish; Adams, S.M., Ed.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002; pp. 111–148. ISBN 1888569433. [Google Scholar]
- Coutant, C.C.; Benson, D.L. Summer habitat suitability for striped bass in Chesapeake Bay: Reflections on a population decline. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1990, 119, 757–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, S.B.; Gerken, M.; Hartman, K.J.; Demers, E. Effects of hypoxia on food consumption and growth of juvenile striped bass (Morone saxatilis). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 381, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.A.; Adamack, A.T.; Murphy, C.A.; Sable, S.E.; Kolesar, S.E.; Craig, J.K.; Breitburg, D.L.; Thomas, P.; Brouwer, M.H.; Cerco, C.F. Does hypoxia have populationlevel effects on coastal fish? Musings from the virtual world. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 381, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.A.; Rice, J.A. Effects of hypoxia-induced habitat compression on growth of juvenile fish in the Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina, USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 497, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, R.T.; Secor, D.H. Application of the nurseryrole hypothesis to an estuarine fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 291, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessig, J.M.; Woodley, C.M.; Cech, J.J.; Hansen, L.J. Effect of global climate change on marine and estuarine fishes and fisheries. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2004, 14, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iles, T.D.; Sinclair, M. Atlantic herring: Stock discreteness and abundance. Science 1982, 215, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortier, L.; Leggett, W.C. Small-scale covariability inthe abundance of fish larvae and their prey. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1984, 41, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, R.K.; Lwiza, K.M.; Paris, C.B.; Olson, D.B. Connectivity of marine populations: Open or closed? Science 2000, 287, 857–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.G. The potential impacts of global climate change on marine protected areas. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2002, 11, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genner, M.J.; Sims, D.W.; Wearmouth, V.J.; Southhall, E.J.; Southward, A.J.; Henderson, P.A.; Hawkings, S.J. Regional climatic warming drives long-term community changes of British marine fish. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevillot, X.; Drouineau, H.; Lambert, P.; Carassou, L.; Sautour, B.; Lobry, J. Toward a phenological mismatch in estuarine pelagic food web? PLoS One 2017, 12, e0173752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, M.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y. Food habits of 8 species of economical fishes in the Pearl River estuary shallow waters. J. South. Agric. 2016, 47, 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, R.; OU, Q.; Fang, H. Relationship between abundance distribution of fish eggs, larvae and juveniles and environmental factors in the Pearl River Estuary water in spring. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2010, 29, 488–494. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y.; He, W. Species composition and abundance distribution of ichthyoplankton in the Pearl River Estuary. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2013, 32, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Liang, J. Fishery resources and economic benefits of fishermen in Lingding Bay of the Pearl River Estuary (in Chinese). Theor. Res. Urban Constr. 2012, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Z.; Ma, R.; Gao, G.; Chen, C.; Beardsley, R.C. Impact of multichannel river network on the plume dynamics in the Pearl River estuary. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2015, 120, 5766–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, T.; Gan, J. A numerical study of coupled estuary–shelf circulation around the Pearl River Estuary during summer: Responses to variable winds, tides and river discharge. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2015, 117, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Chan, J. Impacts of land use changes and synoptic forcing on the seasonal climate over the Pearl river delta of China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okiyama, M. An Atlas of the Early Stage Fishes in Japan; Okiyama, M., Ed.; Scripps Institution of Oceanography: San Diego, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, R. Eggs and Larvae of Fish in Offshore China and Its Adjacent Waters; Quan, L., Huang, Q., Eds.; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pianka, E.R. Ecology of the Agamid lizard Amphibolurus isolepis in Western Australia. Copeia 1971, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y. The Temporal and Spatial Variation of Fish Recruitment Resources in Yangtze River Estuary. Master’s Thesis, The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Clare, E.P.; Thompson, R.A.; Sax, D.F.; Morse, R.E.; Perretti, C.J. Decadal regime shifts in southern California’s ichthyoplankton assemblage. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 607, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Wu, G.; Sun, J. The investigation of pelagic eggs, larvae and juveniles of fishes at the mouth of the Changjiang River and adjacent areas. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1990, 21, 346–355. [Google Scholar]
- Beamish, R.J. Climate and exceptional fish production off the West Coast of North America. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 2270–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenseth, N.C.; Mysterud, A.; Ottersen, G.; Hurrell, J.W.; Chan, K.; Lima, M. Ecological effects of climate fluctuations. Science 2002, 297, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchis, L.I.; Balance, L.T.; Watson, W. Temporal variability of neustonic ichthyoplankton assemblages of the eastern Pacific warm pool: Can community structure be linked to climate variability? Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Papers 2009, 56, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asch, R.G. Climate change and decadal shifts in the phenology of larval fishes in the California Current ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4065–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koslow, J.A.; Goericke, R.; Watson, W. Fish assemblages in the Southern California Current: Relationships with climate, 1951–2008. Fish. Oceanogr. 2013, 22, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynou, F.; Sabatés, A.; Salat, J. Clues from the recent past to assess recruitment of Mediterranean small pelagic fishes under sea warming scenarios. Clim. Chang. 2014, 126, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.W.; Bouchard, C.; Robert, D.; Fortier, L. Spatiotemporal occurrence of summer ichthyoplankton in the southeast Beaufort Sea. Polar Biol. 2015, 38, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.; Lo, W.; Liao, C.; Meng, P. Shifts in the Assemblage of Summer Mesopelagic Fish Larvae in the Gaoping Waters of Southwestern Taiwan: A Comparison between El Niño Events and Regular Years. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Dower, J.F.; McKinnell, S.M.; Pepin, P.; Pakhomov, E.A.; Hunt, B.P. Interannual variability in the abundance and composition of spring larval fish assemblages in the Strait of Georgia (British Columbia, Canada) from 2007 to 2010. Fish. Oceanogr. 2016, 26, 638–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attrill, M.J.; Power, M. Climatic influence on a marine fish assemblage. Nature 2002, 417, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auth, T.D.; Brodeur, R.D.; Soulen, H.L.; Ciannelli, L.; Peterson, W.T. The response of fish larvae to decadal changes in environmental forcing factors off the Oregon coast. Fish. Oceanogr. 2011, 20, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boening, C.; Willis, J.K.; Landerer, F.W.; Nerem, R.S.; Fasullo, J. The 2011 La Niña: So strong, the oceans fell. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, H.K.; Chen, C.; Hou, W.P.; Liau, J.M.; Choi, Y.Y. Intrusion of kuroshio helps to diminish coastal hypoxia in the coast of northern south china sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 565952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Távora, J.; Ehf, B.; Lpb, B.; Pmso, B. El-Niño southern oscillation (enso) effects on the variability of patos lagoon suspended particulate matter. Sciencedirect. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 40, 101495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.H. Impact of ENSO on water discharge and sediment load in lower Mekong River. J. Clim. Chang. Sci. 2019, 9, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, P.A.; Bonham, P.; Thomson, P.; Rochester, W.; Doblin, M.A.; Waite, A.M.; Richardson, A.; Rousseaux, C.S. Climate variability drives plankton community composition changes: The 2010–2011 El Niño to La Niña transition around Australia. J. Plankton Res. 2015, 37, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lin, H.; Gong, W. Intraseasonal and interannual variabilities of saltwater intrusion during dry seasons and the associated driving forcings in a partially mixed estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 174, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloterdijk, H.; Brehmer, P.; Sadio, O.; Müller, H.; Döring, J.; Ekau, W. Composition and structure of the larval fish community related to environmental parameters in a tropical estuary impacted by climate change. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 197, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyah, N.; Webber, M.; Prospere, K. An assessment of the larval fish diversity within a coastal marine reserve Larval fish diversity within a marine reserve. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 43, 101655. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, R.V.; Severi, W. Dynamics of early life-history stages of fish along an estuarine gradient. Fish. Oceanogr. 2019, 28, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampatti, B.P.; Bice, C.M.; Jennings, P.R. Temporal variability in fish assemblage structure and recruitment in a freshwater-deprived estuary: The Coorong, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2010, 61, 1298–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.R.; Austen, M.C.; Boucher, C.; Heip, C.; Hutchings, P.A.; King, G.M.; Koike, I.; Lambshead, P.J.; Snelgrove, P. Global Change and Biodiversity Linkages across the Sediment–Water Interface. BioScience 2000, 50, 1108–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehn, J.D.; Hobday, A.J.; Pratchett, M.S.; Gillanders, B.M. Climate change and Australian marine and freshwater environments, fishes and fisheries: Synthesis and options for adaptation. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1148–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morson, J.M.; Grothues, T.; Able, K.W. Change in larval fish assemblage in a USA east coast estuary estimated from twenty-six years of fixed weekly sampling. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0224157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyitrai, D.; Martinho, F.; Dolbeth, M.; Baptista, J.; Pardal, M.A. Trends in estuarine fish assemblages facing different environmental conditions: Combining diversity with functional attributes. Aquat Ecol. 2012, 46, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Luo, X. Spatiotemporal distribution of fish eggs and larvae in the Huanghe (Yellow) River estuary, China in 2005–2016. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Li, L.C.; Chong, V.C.; Ching, C.N.; Ooi, A.L.; Loh, K. Effect of coastal development on larval fish abundance in Klang Strait (Malaysia). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 46, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheaves, M. Nature and consequences of biological connectivity in mangroves systems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 302, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuheimer, A.B.; Thresher, R.E.; Lyle, J.M.; Semmens, J.M. Tolerance limit for fish growth exceeded by warming waters. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2011, 1, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, S.; Sponaugle, S.; Hauff, M.; Cowen, R.K. Combined effects of elevated pCO2, temperature, and starvation stress on larvae of a large tropical marine fish. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 74, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, F.G.; Teixeira, T.P.; Guedes, A.P.; Azevedo, M.C.; Pessanha, A.L. Shifts in the abundance and distribution of shallow water fish fauna on the southeastern Brazilian coast: A response to climate change. Hydrobiologia 2018, 814, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).