3D Numerical Modeling and Quantification of Oblique Wave Forces on Coastal Bridge Superstructures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. 3D Numerical Modeling for Wave–Bridge Interactions
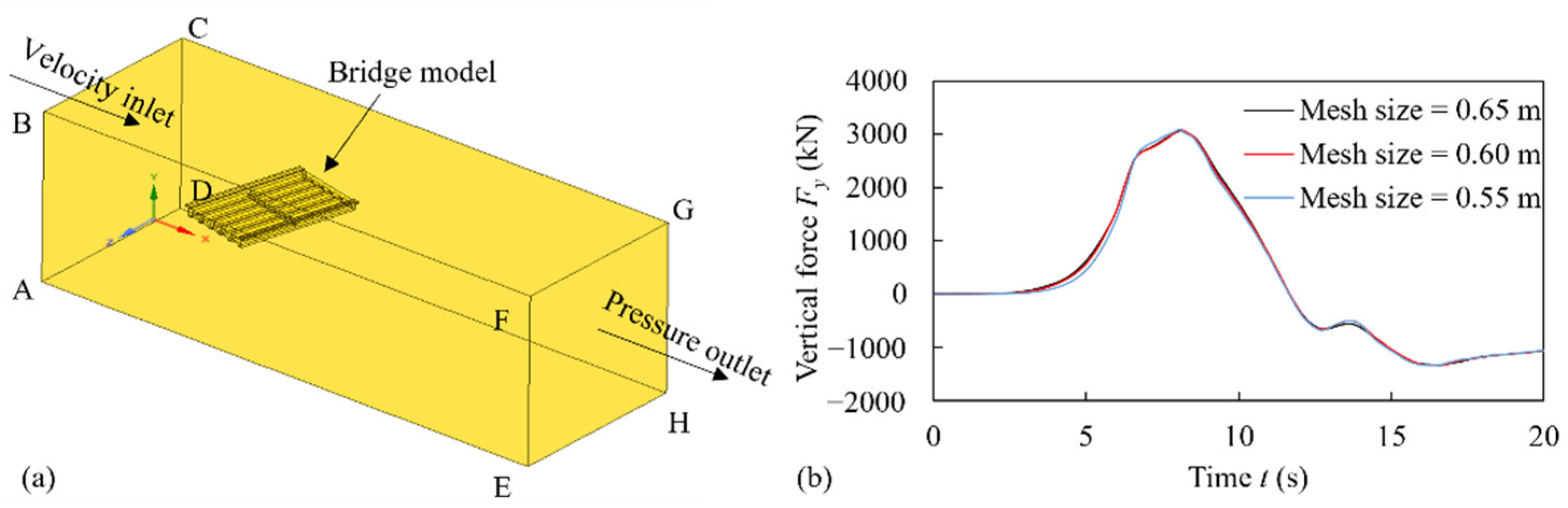
2.1. Model Setups and Boundary Conditions
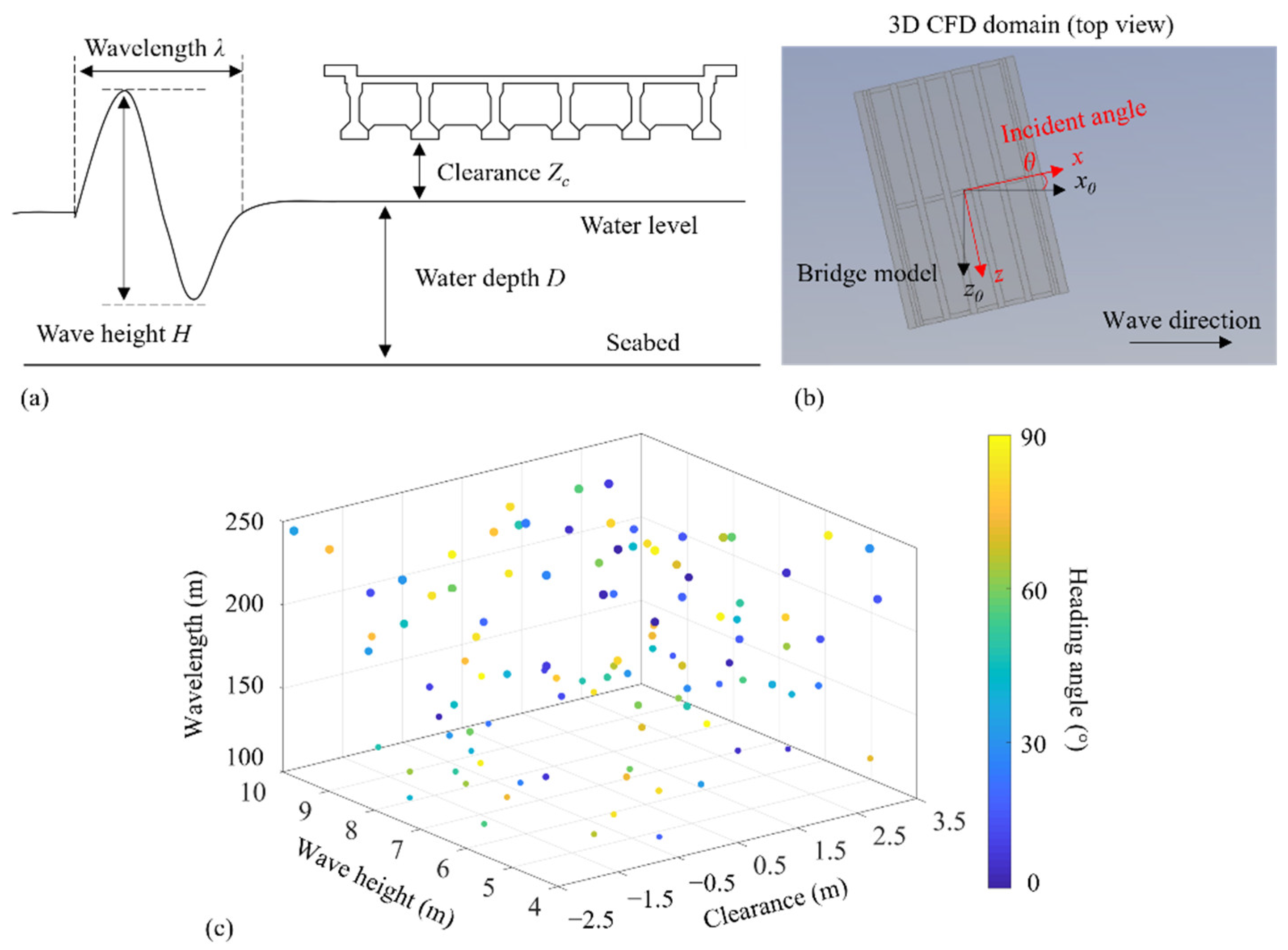
2.2. Tested Wave Cases
3. Surrogate Models for Quantification of Oblique Wave Forces
3.1. Gaussian Kriging Surrogate Model
3.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
3.3. Polynomial Chaos Expansion (PCE)
4. Oblique Wave-Induced Forces and Metamodeling
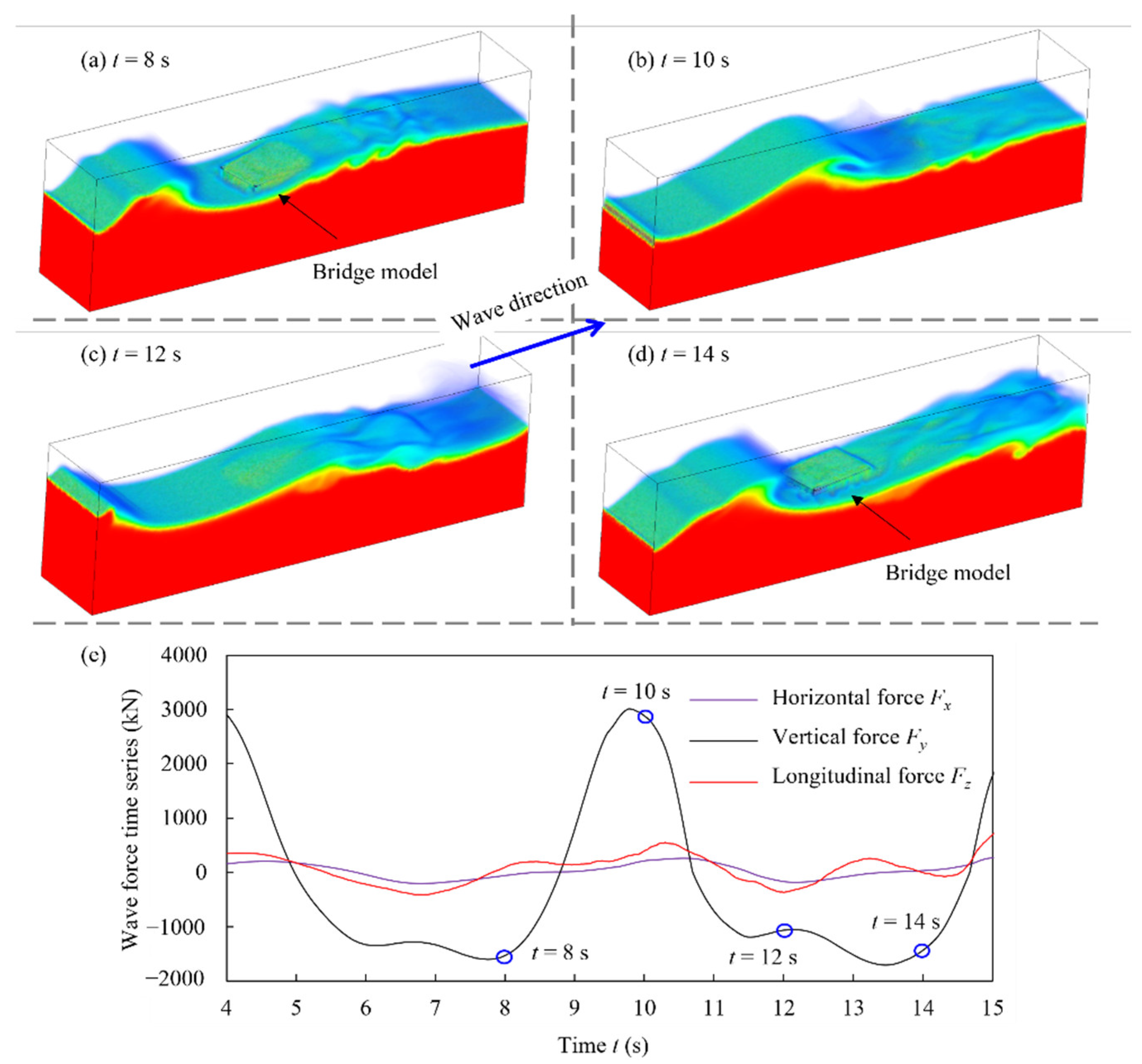
4.1. Time Histories of Oblique Wave Forces
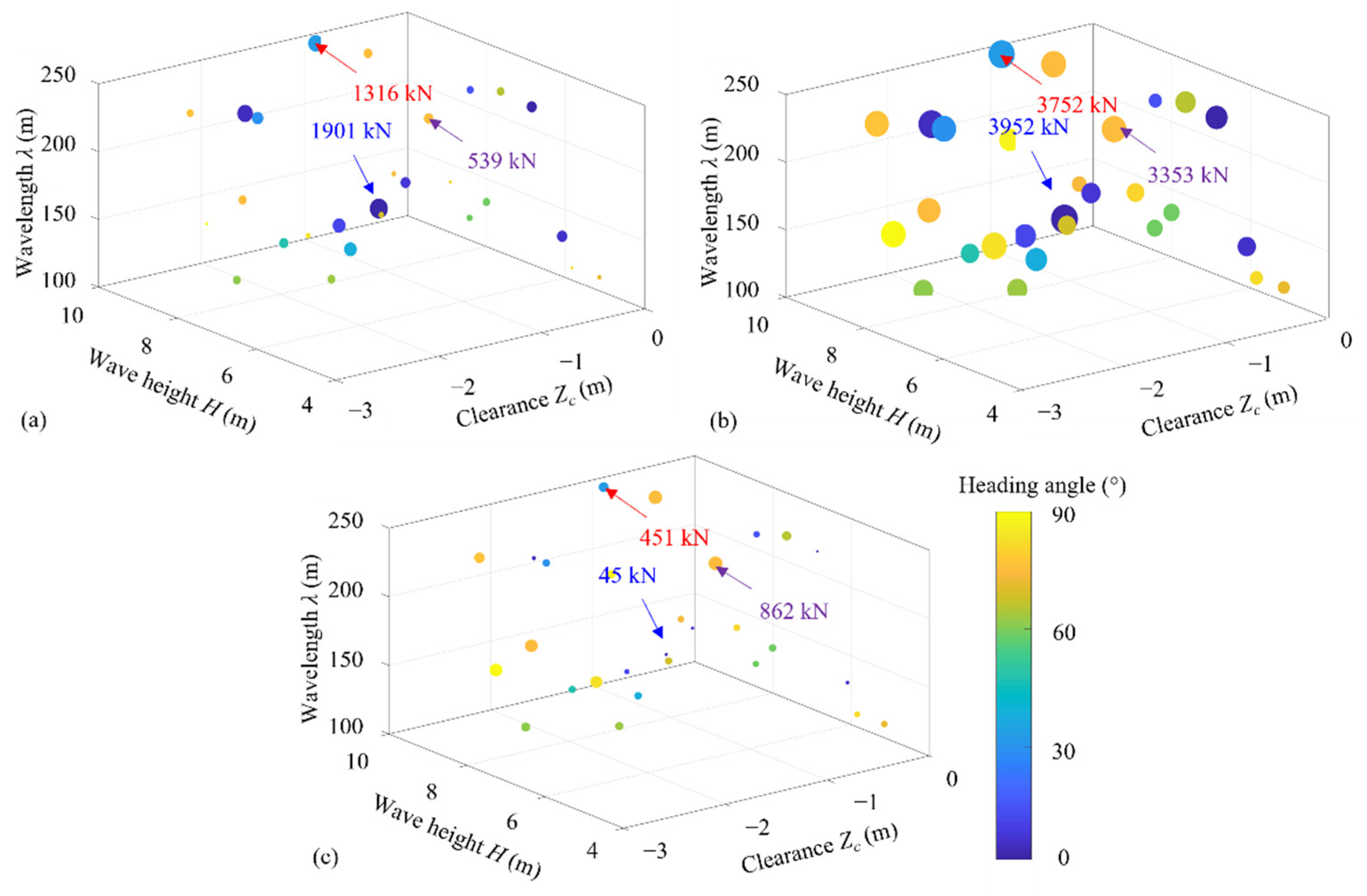
4.2. Maximum Wave Forces under Different Scenarios
4.3. Quantifications of Maximum Wave Forces Using Different Surrogate Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padgett, J.; DesRoches, R.; Nielson, B.; Yashinsky, M.; Kwon, O.S.; Burdette, N.; Tavera, E. Bridge damage and repair costs from Hurricane Katrina. J. Bridg Eng. 2008, 13, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salem, H.; Mohssen, S.; Kosa, K.; Hosoda, A. Collapse analysis of Utatsu Ohashi bridge damaged by Tohuku Tsunami using applied element method. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2014, 12, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salem, H.; Mohssen, S.; Nishikiori, Y.; Hosoda, A. Numerical collapse analysis of Tsuyagawa bridge damaged by tohoku tsunami. J. Perform. Constr Facil. 2016, 30, 04016065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataei, N.; Padgett, J.E. Fragility assessment of coastal bridges under hurricane events using enhanced probabilistic capacity models. In Advances in Hurricane Engineering: Learning from Our Past—Proceedings of the 2012 ATC and SEI Conference on Advances in Hurricane Engineering, Miami, FL, USA, 24–26 October 2012; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrati, D.; Buckle, I.; Lomonaco, P.; Yim, S. Deciphering the tsunami wave impact and associated connection forces in open-girder coastal bridges. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, T.; Istrati, D. Assessment of extreme wave impact on coastal decks with different geometries via the arbitrary lagrangian-eulerian method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrati, D.; Buckle, I.G. Tsunami Loads on Straight and Skewed Bridges–Part 2: Numerical Investigation and Design Recommendations (No. FHWA-OR-RD-21-13). 2021. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/55947 (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Istrati, D.; Buckle, I.G. Tsunami Loads on Straight and Skewed Bridges–part 1: Experimental Investigation and Design Recommendations (No. FHWA-OR-RD-21-12). 2021. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/55988 (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- AASHTO. Guide Specifications for Bridges Vulnerable to Coastal Storms; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Chen, Q. Directional spectra of hurricane-generated waves in the Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denson, K.H. Wave Forces on Causeway-Type Coastal Bridges: Effects of Angle of Wave Incidence and Cross-Section Shape; Water Resources Research Institute, Mississippi State University: Mississippi State, MS, USA; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; Available online: https://www.engineeringvillage.com/share/document.url?mid=ntis_2c04e8f791371236M45df19817173108&database=nti (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Motley, M.R.; Wong, H.K.; Qin, X.; Winter, A.O.; Eberhard, M.O. Tsunami-induced forces on skewed bridges. J. Waterw. Port. Coast. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Hong, R.; Guo, A.; Li, H. Experimental investigation of wave forces on coastal bridge decks subjected to oblique wave attack. J. Bridg Eng. 2019, 24, 04019011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Zhu, D.; Dong, Y.; Xu, G. Response-based bridge deck limit state considering component-level failure under extreme wave. Mar. Struct. 2022, 83, 103184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yuan, P. Long-term loss assessment of coastal bridges from hurricanes incorporating overturning failure mode. Adv. Bridg Eng. 2021, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonaco, P.; Istrati, D.; Maddux, T.; Buckle, I.; Yim, S.; Xiang, T. Large-scale testing of tsunami impact forces on bridges. In Proceedings of the Application of Physical Modelling in Coastal and Port Engineering and Science (COASTLAB16), Ottawa, Canada, 10–13 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, T.; Istrati, D.; Yim, S.C.; Buckle, I.G.; Lomonaco, P. Tsunami loads on a representative coastal bridge deck—Experimental study and validation of design equations. J. Waterw Port. Coast. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfaraz, M.; Pak, A. SPH numerical simulation of tsunami wave forces impinged on bridge superstructures. Coast. Eng. 2017, 121, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Elkhetali, I.; Scott, M.H. Validation of open sees for tsunami loading on bridge superstructures. J. Bridge. Eng. 2018, 23, 04018015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, A.; Istrati, D.; Buckle, I. Coupled SPH–FEM modeling of tsunami-borne large debris flow and impact on coastal structures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motley, M.R.; Lemoine, G.I.; Livermore, S.N. Three-dimensional loading effects of tsunamis on bridge superstructures. In Proceedigns of the Structures Congress 2014, Boston, MA, USA, 3–5 April 2014; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Reins, G.; Koo, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Stern, F. Plunging wave breaking: EFD and CFD. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Violent Flows, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 20–22 November 2007; Research Institute for Applied Mechanics; Kyushu University: Fukuoka, Japan, 2007; Available online: http://user.engineering.uiowa.edu/~yng/papers/ghoshs_etal_vf4.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Istrati, D. Large-scale experiments of tsunami inundation of bridges including fluid-structure-interaction. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Nevada, Reno, NV, USA, 2017. Available online: https://scholarworks.unr.edu//handle/11714/2030 (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, D. Copula-based vulnerability analysis of civil infrastructure subjected to hurricanes. Front. Built Environ. 2020, 6, 571911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y. Reliability-based retrofit assessment of coastal bridges subjected to wave forces using 3D CFD simulation and metamodeling. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2021, 38, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataei, N.; Padgett, J.E. Probabilistic modeling of bridge deck unseating during hurricane events. J. Bridg Eng. 2013, 18, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidpour, A.; Chorzepa, M.G.; Christian, J.; Durham, S. Probabilistic hurricane risk analysis of coastal bridges incorporating extreme wave statistics. Eng. Struct. 2019, 182, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Yuan, P.; Dong, Y. Probabilistic performance of coastal bridges under hurricane waves using experimental and 3D numerical investigations. Eng. Struct. 2021, 242, 112493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertsson, O.A.; Blanch, J.O. Numerical methods, finite difference. In Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics; Springer: Cham, Switzertland, 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Dong, Y.; Frangopol, D.M. Experimental and numerical investigation on wave impacts on box-girder bridges. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Dong, Y. Experimental and 3D numerical investigation of solitary wave forces on coastal bridges. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 209, 107499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, R.L. Hurricane induced wave and surge forces on bridge decks. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2008. Available online: https://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/handle/1969.1/ETD-TAMU-2008-08-48 (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Azadbakht, M. Tsunami and Hurricane Wave Loads on Bridge Superstructures. Ph.D. Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2013. Available online: https://ir.library.oregonstate.edu/concern/graduate_thesis_or_dissertations/pg15bh86v (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Istrati, D.; Buckle, I. Role of trapped air on the tsunami-induced transient loads and response of coastal bridges. Geosci. J. 2019, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bozorgnia, M.; Lee, J.J.; Raichlen, F. Wave structure interaction: Role of entrapped air on wave impact and uplift forces. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2011, 1, 57. Available online: https://icce-ojs-tamu.tdl.org/icce/index.php/icce/article/view/1358 (accessed on 3 May 2022). [CrossRef]
- Istrati, D.; Buckle, I.G.; Lomonaco, P.; Yim, S.; Itani, A. Tsunami induced forces in bridges: Large-scale experiments and the role of air-entrapment. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2017, 35, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Cai, C.S.; Hu, P.; Dong, Z. Component level–based assessment of the solitary wave forces on a typical coastal bridge deck and the countermeasure of air venting holes. Pract. Period. Struc.t Des. Constr. 2016, 21, 04016012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherenko, S.; Feil, B.; Shah, N.; Mauntz, W. The identification of model effective dimensions using global sensitivity analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.N. Sampling for qualitative research. Fam. Pract. 1996, 13, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Sahu, C.K. Driven by data or derived through physics? A review of hybrid physics guided machine learning techniques with cyber-physical system (CPS) focus. IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 71050–71073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H. Physics-informed learning of governing equations from scarce data. Nat. Commun. Vol. 2021, 12, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burhenne, S.; Jacob, D.; Henze, G.P. Sampling based on sobol′ sequences for monte carlo techniques applied to building simulations. Proceedings of Building Simulation 2011: 12th Conference of International Building Performance Simulation Association, Sydney, Australia, 14–16 November 2011; IBPSA Australasia and AIRAH: Melbourne, Australia, 2011. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257139589_Sampling_based_on_Sobol’_sequences_for_Monte_Carlo_techniques_applied_to_building_simulations (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Sun, X.; Croke, B.; Roberts, S.; Jakeman, A. Comparing methods of randomizing Sobol′ sequences for improving uncertainty of metrics in variance-based global sensitivity estimation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 210, 107499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navid, A.; Khalilarya, S.; Abbasi, M. Diesel engine optimization with multi-objective performance characteristics by non-evolutionary Nelder-Mead algorithm: Sobol sequence and Latin hypercube sampling methods comparison in DoE process. Fuel. 2018, 228, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, I.J.; Ginis, I.; Hara, T.; Tolman, H.L.; Wright, C.W.; Walsh, E.J. Numerical simulation of sea surface directional wave spectra under hurricane wind forcing. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2003, 33, 1680–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sacks, J.; Welch, W.J.; Mitchell, T.J.; Wynn, H.P. Design and analysis of computer experiments. Stat. Sci. 1989, 4, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, A.; Padgett, J.E. Investigation of multivariate seismic surrogate demand modeling for multi-response structural systems. Eng. Struct. 2020, 207, 110210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudret, B. Global sensitivity analysis using polynomial chaos expansions. Reliab. Eng. Syst. 2008, 93, 964–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatman, G.; Sudret, B. An adaptive algorithm to build up sparse polynomial chaos expansions for stochastic finite element analysis. Probabilistic. Eng. Mech. 2010, 25, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Efficient reliability analysis with a CDA-based dimension-reduction model and polynomial chaos expansion. Comput. Methods. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 373, 113467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Zhu, D.; Dong, Y. Spatial failure mechanism of coastal bridges under extreme waves using high-efficient pseudo-fluid-structure interaction solution scheme. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 240, 109894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrati, D.; Buckle, I.G. Effect of fluid-structure interaction on connection forces in bridges due to tsunami loads. In Proceedings of the 30th US-Japan Bridge Eng Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2014; Available online: https://www.pwri.go.jp/eng/ujnr/tc/g/pdf/30/30-10-2_Buckle.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Istrati, D.; Buckle, I.; Lomonaco, P.; Yim, S.; Itani, A. Large-scale experiments of tsunami impact forces on bridges: The role of fluid-structure interaction and air-venting. In Proceedings of the 26th International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 26 June–2 July 2016; The ISOPE: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2016. Available online: https://onepetro.org/ISOPEIOPEC/proceedings-abstract/ISOPE16/All-ISOPE16/ISOPE-I-16-456/16865 (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Choi, S.J.; Lee, K.H.; Gudmestad, O.T. The effect of dynamic amplification due to a structure׳ s vibration on breaking wave impact. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 96, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Zc (m) | H (m) | λ (m) | θ (°) | No. | Zc (m) | H (m) | λ (m) | θ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.94 | 4.13 | 222.90 | 15.38 | 36 | 3.18 | 6.17 | 108.88 | 54.06 |
| 2 | −0.67 | 8.98 | 128.64 | 3.12 | 37 | −0.44 | 6.50 | 239.47 | 65.71 |
| 3 | 1.69 | 9.01 | 244.07 | 55.50 | 38 | −2.39 | 9.27 | 225.99 | 77.31 |
| 4 | −1.95 | 4.97 | 216.24 | 8.92 | 39 | 2.69 | 7.45 | 161.25 | 65.89 |
| 5 | 2.03 | 7.32 | 215.06 | 70.09 | 40 | −0.01 | 9.44 | 178.24 | 75.38 |
| 6 | 0.32 | 4.56 | 130.10 | 32.48 | 41 | 0.87 | 6.31 | 138.84 | 39.25 |
| 7 | 1.19 | 7.66 | 243.33 | 80.73 | 42 | −1.34 | 4.94 | 179.85 | 59.64 |
| 8 | −1.50 | 9.22 | 115.01 | 48.03 | 43 | 2.86 | 8.41 | 139.42 | 47.34 |
| 9 | 3.29 | 5.87 | 148.12 | 23.95 | 44 | −0.93 | 9.90 | 244.60 | 33.80 |
| 10 | −0.60 | 4.28 | 137.57 | 82.31 | 45 | 1.86 | 7.25 | 138.54 | 20.80 |
| 11 | 1.35 | 4.38 | 162.77 | 13.05 | 46 | −1.75 | 7.17 | 155.87 | 13.26 |
| 12 | −2.41 | 7.51 | 242.79 | 31.53 | 47 | 2.23 | 5.15 | 154.69 | 88.49 |
| 13 | 2.63 | 5.73 | 196.50 | 79.69 | 48 | 0.24 | 4.02 | 155.28 | 71.97 |
| 14 | 0.11 | 4.01 | 122.96 | 19.05 | 49 | 0.95 | 9.04 | 200.69 | 82.34 |
| 15 | 0.72 | 6.68 | 168.66 | 31.00 | 50 | −1.60 | 4.75 | 212.99 | 80.58 |
| 16 | 2.29 | 7.97 | 134.24 | 31.79 | 51 | 3.49 | 8.05 | 219.00 | 42.53 |
| 17 | 0.21 | 7.06 | 178.11 | 40.54 | 52 | −0.40 | 9.96 | 227.20 | 75.57 |
| 18 | 1.03 | 4.95 | 117.76 | 83.08 | 53 | 1.55 | 9.06 | 241.85 | 9.13 |
| 19 | −1.73 | 9.60 | 210.34 | 6.44 | 54 | −2.24 | 9.24 | 141.95 | 89.81 |
| 20 | 3.34 | 8.00 | 102.23 | 40.36 | 55 | 2.52 | 9.54 | 233.94 | 81.73 |
| 21 | −0.34 | 7.53 | 227.04 | 16.11 | 56 | −0.25 | 5.44 | 141.36 | 7.90 |
| 22 | 1.52 | 5.97 | 124.06 | 58.38 | 57 | 0.64 | 5.92 | 235.77 | 86.25 |
| 23 | −2.16 | 6.49 | 241.83 | 87.56 | 58 | −1.08 | 8.63 | 109.80 | 38.79 |
| 24 | 2.39 | 4.92 | 189.10 | 10.92 | 59 | 3.01 | 5.74 | 206.18 | 87.48 |
| 25 | −0.13 | 4.81 | 116.15 | 71.56 | 60 | −0.67 | 6.26 | 164.58 | 59.01 |
| 26 | 0.55 | 4.61 | 103.85 | 19.18 | 61 | 1.63 | 6.76 | 233.72 | 56.90 |
| 27 | −1.09 | 4.12 | 206.00 | 29.54 | 62 | −2.00 | 8.96 | 158.58 | 75.97 |
| 28 | 3.10 | 6.71 | 174.95 | 43.25 | 63 | 1.20 | 4.21 | 199.88 | 26.22 |
| 29 | −0.79 | 8.29 | 164.40 | 74.89 | 64 | −1.56 | 7.86 | 104.96 | 63.49 |
| 30 | 1.75 | 9.40 | 216.25 | 87.73 | 65 | 3.27 | 9.53 | 202.37 | 19.00 |
| 31 | −2.07 | 5.27 | 191.06 | 69.09 | 66 | −0.56 | 5.40 | 242.79 | 3.88 |
| 32 | 2.18 | 6.95 | 107.42 | 72.17 | 67 | 1.43 | 9.68 | 128.24 | 11.09 |
| 33 | 0.47 | 4.51 | 247.45 | 30.33 | 68 | −2.47 | 7.88 | 120.04 | 62.42 |
| 34 | 1.08 | 7.85 | 199.41 | 19.79 | 69 | 2.57 | 6.21 | 168.67 | 3.71 |
| 35 | −1.44 | 8.76 | 124.70 | 83.24 | 70 | 0.75 | 7.79 | 156.22 | 78.15 |
| No. | Fx-max (kN) | Fy-max (kN) | Fz-max (kN) | No. | Fx-max (kN) | Fy-max (kN) | Fz-max (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 74.33 | 118.88 | 11.85 | 36 | 381.84 | 236.57 | 297.03 |
| 2 | 1900.79 | 3952.66 | 46.00 | 37 | 357.08 | 2290.60 | 393.53 |
| 3 | 848.28 | 2680.82 | 569.96 | 38 | 288.16 | 3192.11 | 506.35 |
| 4 | 579.70 | 2026.92 | 49.00 | 39 | 447.60 | 644.45 | 438.13 |
| 5 | 325.02 | 1559.30 | 417.89 | 40 | 539.81 | 3353.63 | 862.02 |
| 6 | 320.77 | 708.66 | 107.75 | 41 | 635.92 | 933.15 | 230.84 |
| 7 | 168.13 | 1764.98 | 484.21 | 42 | 216.61 | 1417.98 | 191.23 |
| 8 | 502.52 | 1826.05 | 243.77 | 43 | 1237.72 | 718.86 | 564.73 |
| 9 | 360.88 | 164.86 | 48.83 | 44 | 1316.40 | 3752.72 | 451.41 |
| 10 | 48.84 | 908.83 | 170.35 | 45 | 1181.32 | 1104.69 | 204.05 |
| 11 | 178.98 | 427.54 | 26.76 | 46 | 970.81 | 2642.00 | 125.28 |
| 12 | 755.85 | 3232.77 | 260.52 | 47 | 4.98 | 418.91 | 182.02 |
| 13 | 80.60 | 340.80 | 186.42 | 48 | 95.18 | 821.20 | 162.72 |
| 14 | 186.33 | 699.87 | 51.65 | 49 | 213.54 | 2563.57 | 788.73 |
| 15 | 778.37 | 1611.61 | 233.25 | 50 | 57.52 | 1709.83 | 213.47 |
| 16 | 1376.21 | 1063.41 | 406.01 | 51 | 715.33 | 831.02 | 295.57 |
| 17 | 749.23 | 1961.12 | 323.20 | 52 | 446.95 | 3399.66 | 840.53 |
| 18 | 54.36 | 336.82 | 221.63 | 53 | 1315.23 | 3034.26 | 148.19 |
| 19 | 1430.87 | 3716.05 | 81.63 | 54 | 45.55 | 3360.03 | 740.43 |
| 20 | 1389.92 | 1120.65 | 477.58 | 55 | 229.58 | 1829.72 | 711.40 |
| 21 | 292.00 | 951.00 | 193.00 | 56 | 622.32 | 1841.32 | 67.71 |
| 22 | 413.38 | 473.73 | 286.93 | 57 | 21.30 | 1646.42 | 326.69 |
| 23 | 46.68 | 2406.67 | 310.56 | 58 | 936.88 | 2576.45 | 259.62 |
| 24 | 131.35 | 225.82 | 14.91 | 59 | 14.68 | 225.35 | 147.93 |
| 25 | 111.04 | 790.88 | 192.60 | 60 | 332.66 | 1470.05 | 262.32 |
| 26 | 429.13 | 817.47 | 74.79 | 61 | 448.49 | 1305.80 | 300.98 |
| 27 | 296.63 | 1090.63 | 91.20 | 62 | 396.52 | 2913.42 | 740.31 |
| 28 | 499.00 | 539.47 | 181.89 | 63 | 156.04 | 566.40 | 42.33 |
| 29 | 130.72 | 1206.10 | 209.91 | 64 | 372.10 | 2219.16 | 313.96 |
| 30 | 101.10 | 2192.40 | 839.84 | 65 | 1514.30 | 1482.25 | 264.18 |
| 31 | 186.17 | 1802.30 | 234.10 | 66 | 596.26 | 2679.94 | 26.79 |
| 32 | 368.53 | 379.54 | 645.14 | 67 | 670.14 | 3477.37 | 225.47 |
| 33 | 457.91 | 1727.20 | 158.39 | 68 | 367.81 | 2151.41 | 381.46 |
| 34 | 1069.10 | 2450.47 | 234.21 | 69 | 588.66 | 928.00 | 31.33 |
| 35 | 141.47 | 3448.73 | 653.86 | 70 | 305.21 | 1731.20 | 642.15 |
| 3-Order PCE | Kriging | ANN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fx-max | R2 | 0.8924 | 0.8274 | 0.8567 |
| RMSE | 142.7 | 180.7 | 134.1 | |
| Fy-max | R2 | 0.9161 | 0.8725 | 0.9044 |
| RMSE | 308.3 | 379.9 | 323.4 | |
| Fz-max | R2 | 0.9476 | 0.8324 | 0.8979 |
| RMSE | 52.3 | 93.5 | 16.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Dong, Y. 3D Numerical Modeling and Quantification of Oblique Wave Forces on Coastal Bridge Superstructures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070860
Jia L, Zhang Y, Zhu D, Dong Y. 3D Numerical Modeling and Quantification of Oblique Wave Forces on Coastal Bridge Superstructures. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(7):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070860
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Lei, Yu Zhang, Deming Zhu, and You Dong. 2022. "3D Numerical Modeling and Quantification of Oblique Wave Forces on Coastal Bridge Superstructures" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 7: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070860
APA StyleJia, L., Zhang, Y., Zhu, D., & Dong, Y. (2022). 3D Numerical Modeling and Quantification of Oblique Wave Forces on Coastal Bridge Superstructures. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(7), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070860







