Effect of Aquaculture Reclamation on Sediment Nitrates Reduction Processes in Mangrove Wetland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
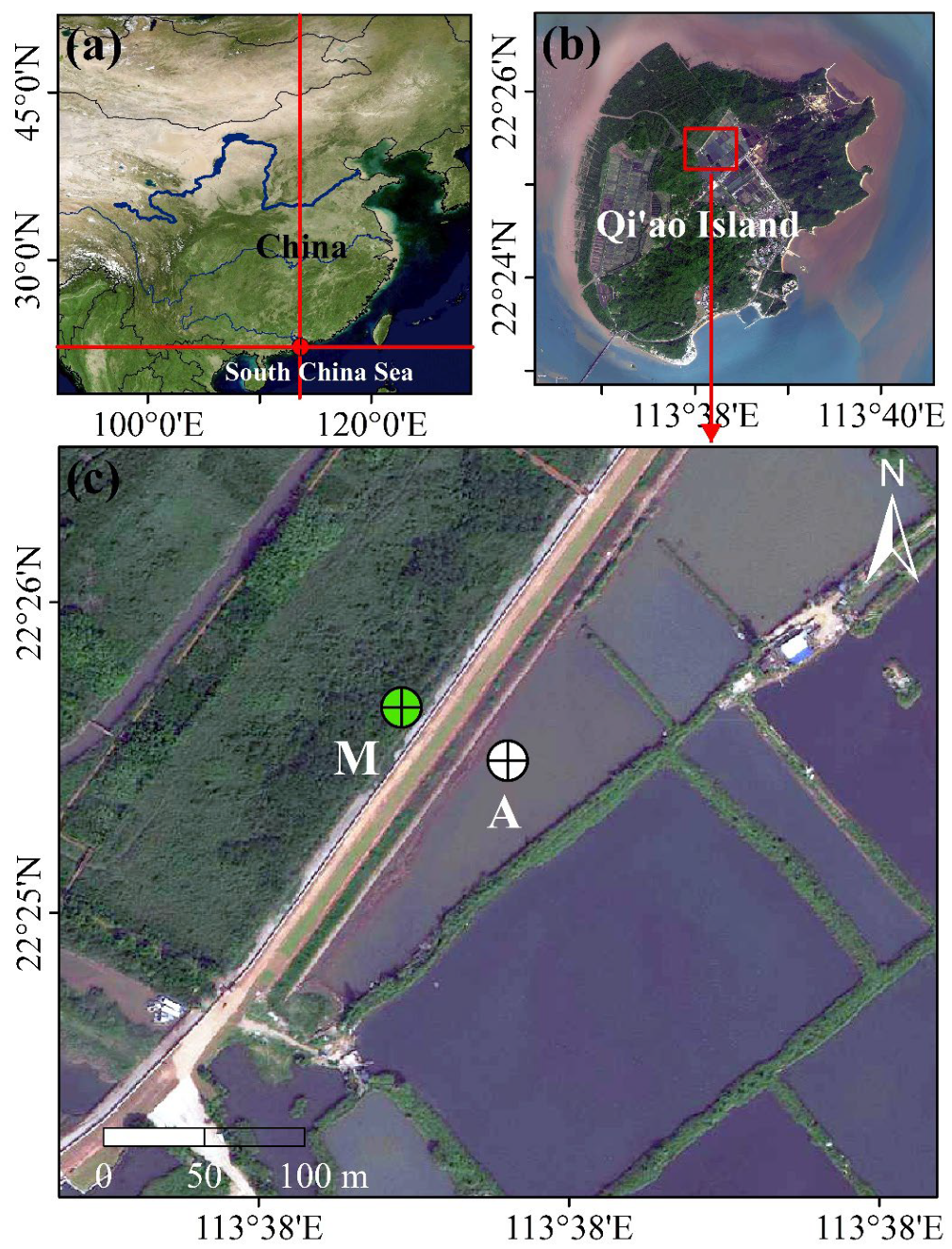
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Determination of Environmental Parameters
2.3. Sediment Incubation Experiments
2.4. Extraction of DNA and Quantification of N-Cycling Related Genes
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Physiochemical Characteristics
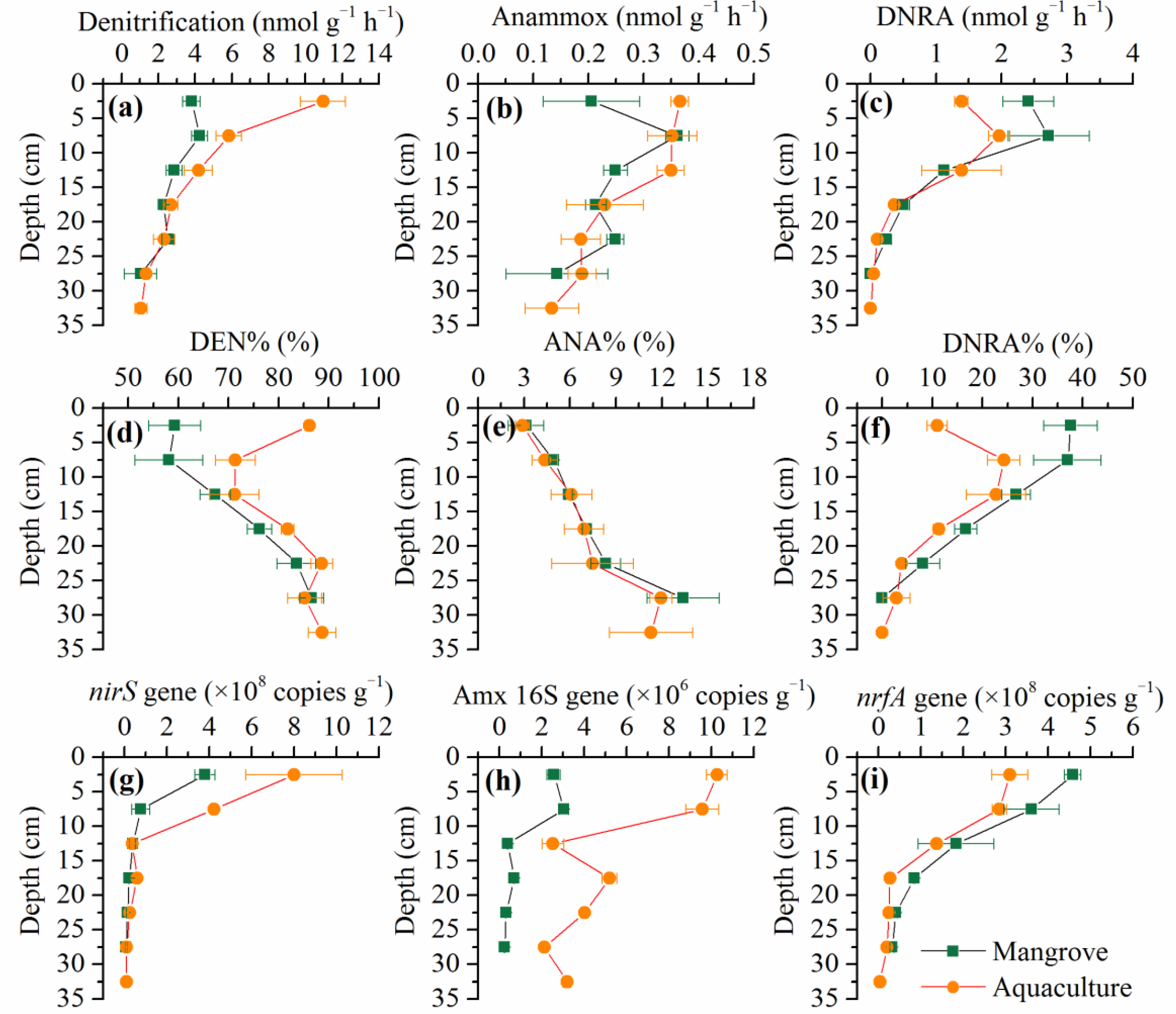
3.2. Spatial Variations of NOx− Reduction Pathways
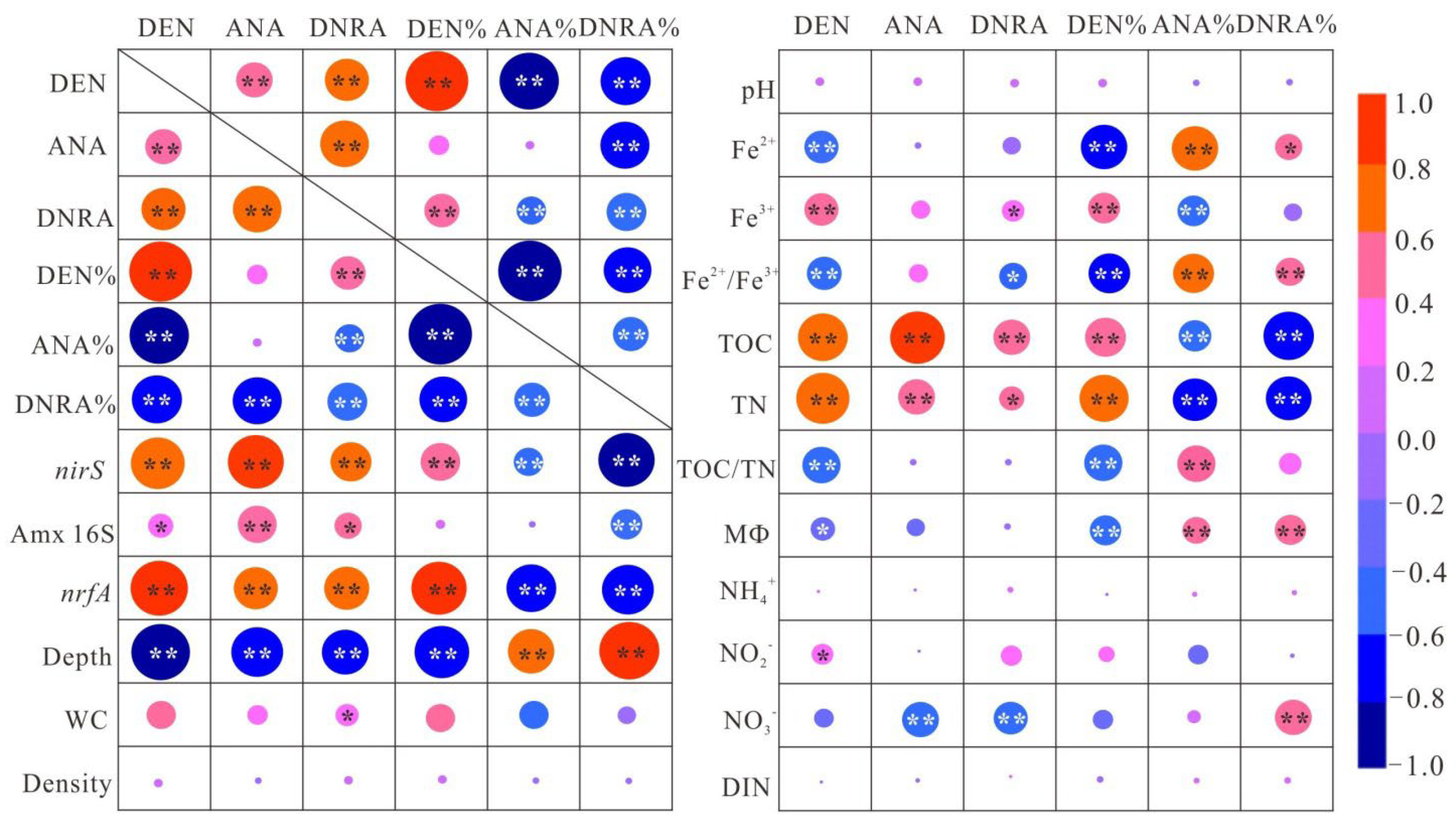
3.3. Environmental Factors Affecting N-Cycling Rates
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Environmental Variables on NOx− Reduction Processes
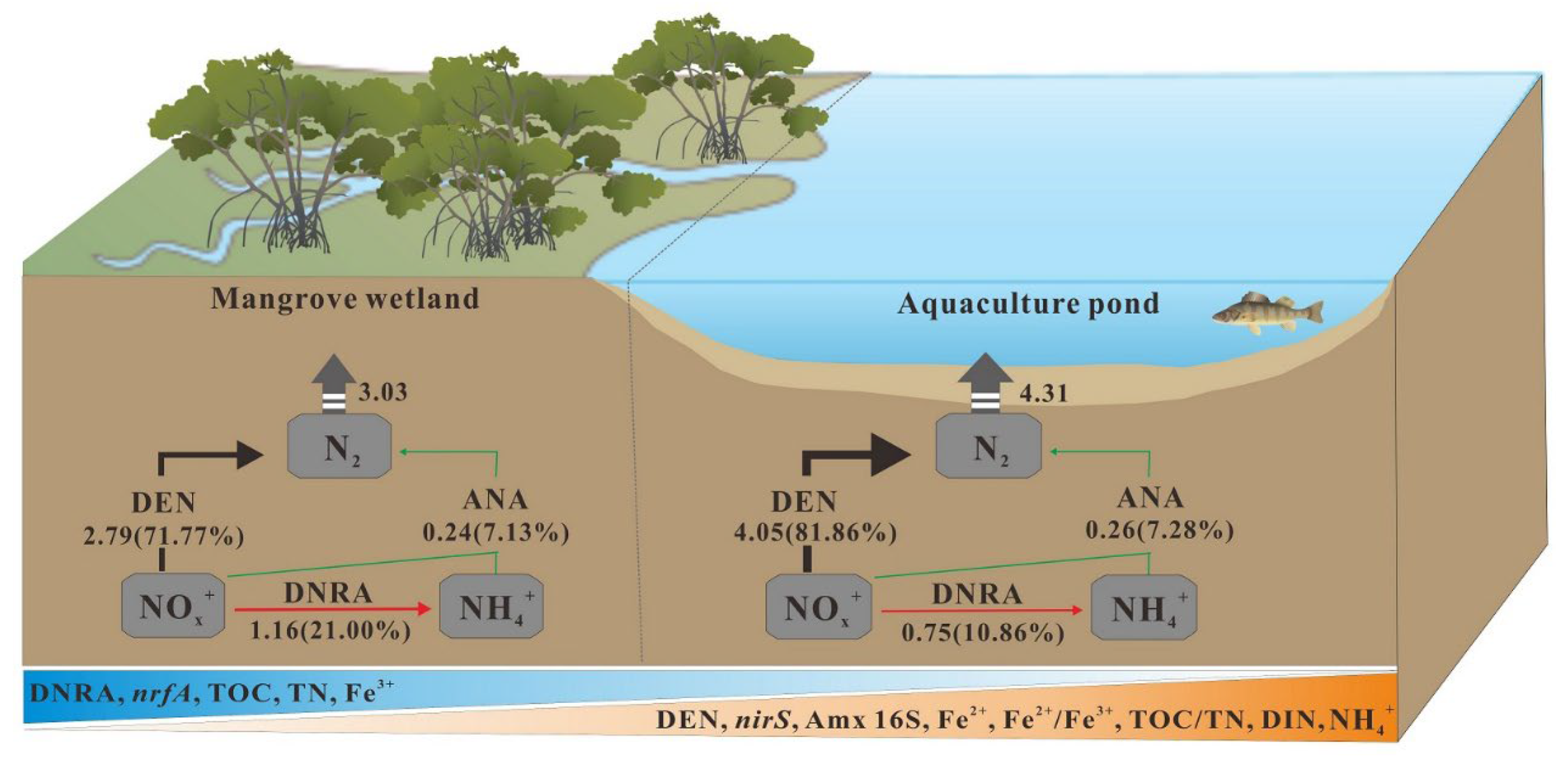
4.2. Effects of Aquaculture Reclamation on Mangrove Sediment NOx− Reduction Processes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabral, H.; Fonseca, V.; Sousa, T.; Leal, M.C. Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Marine Pollution: An Overlooked Interaction in Coastal and Estuarine Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Li, X.; Gao, D.; Liu, M.; Cheng, L. Ammonium Production and Removal in the Sediments of Shanghai River Networks: Spatiotemporal Variations, Controlling Factors, and Environmental Implications. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2461–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Gao, D.; Lu, K.; Li, X. Bacterial Community Shifts Driven by Nitrogen Pollution in River Sediments of a Highly Urbanized City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, H.; Gao, D.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X. Sediment nitrate reduction processes in response to environmental gradients along an urban river-estuary-sea continuum. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesch, D.F. Challenges and opportunities for science in reducing nutrient over-enrichment of coastal ecosystems. Estuaries 2002, 25, 886–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Lin, X.; Yin, K. Effects of marine produced organic matter on the potential estuarine capacity of NOx− removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X. Increased nutrient loads from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River have led to increased Harmful Algal Blooms. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.; Eate, V.; Eyre, B.; Holland, D.; Cook, P. Hypoxic events stimulate nitrogen recycling in a shallow salt-wedge estuary: The Yarra River estuary, Australia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1427–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liu, M.; Hou, L.; Gao, D.; Li, X.; Lu, K.; Gao, J. Nitrogen Losses in Sediments of the East China Sea: Spatiotemporal Variations, Controlling Factors, and Environmental Implications. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2699–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Sardans, J.; Le, Y.; Yan, R.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Tong, C. Biogeochemical behavior of P in the soil and porewater of a low-salinity estuarine wetland: Availability, diffusion kinetics, and mobilization mechanism. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Yin, G.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, F. Gross Nitrogen Mineralization in Surface Sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Lin, X.; Hu, W.; Zeng, F.; He, L.; Yin, K. Nitrogen cycling processes in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary: Spatial variations, controlling factors, and environmental implications. CATENA 2021, 206, 105545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Lin, X.; Yin, K. Effects of algal-derived organic matter on sediment nitrogen mineralization and immobilization in a eutrophic estuary. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Lin, X. Shifts in the relative abundance and potential rates of sediment ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria along environmental gradients of an urban river–estuary–adjacent sea continuum. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.M.; Sui, S.S. The mangrove wetland resources and their conservation in China. J. Nat. Res. 2001, 16, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Lin, X. Bait input altered microbial community structure and increased greenhouse gases production in coastal wetland sediment. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.E.; Casey, D. Creation of a high spatio-temporal resolution global database of continuous mangrove forest cover for the 21st century (CGMFC-21). Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 25, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.R.; Friess, D.A. Rates and drivers of mangrove deforestation in Southeast Asia, 2000–2012. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, N.; Lucas, R.; Bunting, P.; Hardy, A.; Rosenqvist, A.; Simard, M. Distribution and Drivers of Global Mangrove Forest Change 1996–2010. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovai, A.S.; Twilley, R.R.; Castañeda-Moya, E.; Riul, P.; Cifuentes-Jara, M.; Manrow-Villalobos, M.; Horta, P.A.; Simonassi, J.C.; Fonseca, A.L.; Pagliosa, P.R. Global controls on carbon storage in mangrove soils. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.E.; Friess, D.A. Global carbon stocks and potential emissions due to mangrove deforestation from 2000 to 2012. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Guo, Q.; Lai, D.Y.; Zhao, G.; Li, L.; Tong, C. Ebullition was a major pathway of methane emissions from the aquaculture ponds in southeast China. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Dai, P.; Lin, X.; Lin, L.; Hetharua, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y. Nitrogen loss by anaerobic ammonium oxidation in a mangrove wetland of the Zhangjiang Estuary, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harhangi, H.R.; Le Roy, M.; van Alen, T.; Hu, B.; Groen, J.; Kartal, B.; Tringe, S.G.; Quan, Z.-X.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Op den Camp, H.J.M. Hydrazine synthase, a unique phylomarker with which to study the presence and biodiversity of anammox bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2012, 78, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comer-Warner, S.A.; Nguyen, A.T.; Nguyen, M.N.; Wang, M.; Turner, A.; Le, H.; Sgouridis, F.; Krause, S.; Kettridge, N.; Nguyen, N.; et al. Restoration impacts on rates of denitrification and greenhouse gas fluxes from tropical coastal wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 803149577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, F.; Chang, C. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium conserves nitrogen in anthropogenically affected subtropical mangrove sediments in Southeast China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.O.; Michotey, V.D.; Guasco, S.; Bonin, P.C.; Bharathia, P.A.L. Denitrification prevails over anammox in tropical mangrove sediments (Goa, India). Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 74, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.X.; Feng, J.X.; Liu, K.; Wang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Guan, D. Changes of ecosystem carbon stock following the plantation of exotic mangrove Sonneratia apetala in Qi’ao Island, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 717137142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Retrieval of mangrove aboveground biomass at the individual species level with worldview-2 images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12192–12214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Lin, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, X. Natural N-bearing nanoparticles in sediments of a shallow bay of the south china: A new N form in N-cycling. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Huang, J.; Lu, J.; Su, M.; Hu, B.; Lin, X. Geochemical and microbial insights into vertical distributions of genetic potential of N-cycling processes in deep-sea sediments. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zheng, P.; Zou, S.; Sun, F.; Zhang, X.; Gong, J. Seagrass (Zostera marina) promotes nitrification potential and selects specific ammonia oxidizers in coastal sediments. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3259–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovley, D.R.; Phillips, E.J.P. Rapid assay for microbially reducible ferric iron in aquatic sediments. Appl Env. Microb 1987, 53, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Liu, C.; Li, M.; Lin, X. Sediment nitrate dissimilatory reduction processes along a salinity gradient in an estuarine and coastal wetland, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, X. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in sediments of urban river networks: Spatiotemporal variations and environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Schimel, J.P.; Holden, P.A. Variations in microbial community composition through two soil depth profiles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, K.; Kandeler, E.; Nagel, P.; Scheu, S.; Ruess, L. Functional microbial community response to nutrient pulses by artificial groundwater recharge practice in surface soils and subsoils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 72, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, B.; Zhang, H.; Luo, W.; Sun, S.; Cheng, F.; Li, Z. Nitrogen loss through denitrification, anammox and Feammox in a paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hong, Y.; Wilson, S.J.; Song, B. Microbial nitrogen loss by coupled nitrification to denitrification and anammox in a permeable subterranean estuary at Gloucester Point, Virginia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hong, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y. Variations in nitrogen removal rates and microbial communities over sediment depth in Daya Bay, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Wu, D.; Jin, B.; Huang, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, X. Soil dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in the Spartina alterniflora invasion chronosequences of a coastal wetland of southeastern China: Dynamics and environmental implications. Plant Soil 2017, 421, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.D.; Liu, S.M.; Marchant, H.; Kuypers, M.M.M.; Lavik, G. Anammox, denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in the East China Sea sediment. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 6851–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strous, M.; Pelletier, E.; Mangenot, S.; Rattei, T.; Lehner, A.; Taylor, M.W.; Horn, M.; Daims, H.; Bartol-Mavel, D.; Wincker, P.; et al. Deciphering the evolution and metabolism of an anamox bacterium from a community genome. Nature 2006, 440, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, M.C.; Kemp, W.M. The coupling of nitrification and denitrification in two estuarine sediments 1, 2. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1984, 29, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, E.K.; Roberts, K.L.; Burdorf, L.D.W.; Cook, P.; Thamdrup, B. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium coupled to Fe(II) oxidation in sediments of a periodically hypoxic estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, E.K.; Thamdrup, B. The fate of nitrogen is linked to iron(II) availability ina freshwater lake sediment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 205, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.F.; Xiao, C.C.; Lu, J.H.; Zhang, Y. Fe(III)/Fe(II) forwarding a new anammox-like process to remove high-concentration ammonium using nitrate as terminal electron acceptor. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Hong, Y.; Wilson, A.M.; Jiao, J.J.; Shananan, M. Nitrogen fate in a subtropical mangrove swamp: Potential association with seawater-groundwater exchange. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Li, S.; Ye, F.; Hong, Y.; Lü, M.; Camp, H.J.M.O.D.; Wang, Y. Artificial ponds as hotspots of nitrogen removal in agricultural watershed. Biogeochemistry 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, G.; Peng, Y.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Yin, C. Anammox bacterial abundance, activity, and contribution in riparian sediments of the Pearl River Estuary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8834–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Liu, M.; Hou, L.; Lai, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Zeng, A.; Zheng, Y.; Han, P.; Yang, Y.; et al. Effects of shrimp-aquaculture reclamation on sediment nitrate dissimilatory reduction processes in a coastal wetland of southeastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Song, A.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Yan, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, N. Saltmarsh sediments with wastewater input emit more carbon greenhouse gases but less N2O than mangrove sediments. CATENA 2022, 213, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Label | Depth | WC | Density | pH | Fe2+ | Fe3+ | Fe2+/Fe3+ | TOC | TN | TOC/TN | MΦ | NO2− | NH4+ | NO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | % | g mL−1 | mg Fe g−1 | Mg Fe g−1 | mg C g−1 | mg N g−1 | μm | μg N g−1 | μg N g−1 | μg N g−1 | ||||
| Mangrove | ||||||||||||||
| H1-1 | 0–5 | 49.82 | 1.37 | 7.48 | 0.87 | 4.59 | 0.19 | 12.61 | 1.42 | 7.48 | 6.70 | 0.06 | 5.25 | 0.66 |
| H1-2 | 5–10 | 51.30 | 1.40 | 7.89 | 0.56 | 5.38 | 0.10 | 8.23 | 1.07 | 7.71 | 9.02 | 0.15 | 2.96 | 0.55 |
| H1-3 | 10–15 | 49.30 | 1.54 | 7.66 | 0.44 | 5.55 | 0.08 | 6.76 | 0.85 | 7.94 | 5.78 | 0.09 | 2.46 | 0.32 |
| H1-4 | 15–20 | 50.16 | 1.45 | 7.74 | 0.42 | 4.55 | 0.09 | 6.15 | 0.71 | 8.68 | 5.61 | 0.06 | 2.00 | 0.44 |
| H1-5 | 20–25 | 53.21 | 1.18 | 7.68 | 1.23 | 4.18 | 0.29 | 5.61 | 0.64 | 8.81 | 22.55 | 0.08 | 3.33 | 0.51 |
| H1-6 | 25–30 | 53.80 | 0.91 | 7.67 | 1.24 | 5.91 | 0.21 | 5.30 | 0.61 | 8.72 | 18.13 | 0.13 | 2.44 | 0.59 |
| Mean | 51.26 | 1.31 | 7.69 | 0.79 | 5.03 | 0.16 | 7.11 | 0.88 | 8.22 | 11.30 | 0.09 | 3.07 | 0.51 | |
| SD | 1.86 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 0.68 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.31 | 0.58 | 7.24 | 0.04 | 1.16 | 0.12 | |
| Aquaculture | ||||||||||||||
| S1-1 | 0–5 | 50.15 | 1.37 | 7.59 | 1.29 | 4.85 | 0.27 | 11.89 | 1.11 | 10.75 | 7.93 | 0.08 | 1.29 | 0.36 |
| S1-2 | 5–10 | 46.55 | 1.45 | 7.60 | 1.14 | 4.29 | 0.27 | 7.53 | 0.75 | 10.05 | 17.83 | 0.09 | 54.25 | 0.33 |
| S1-3 | 10–15 | 48.69 | 1.50 | 7.60 | 1.36 | 4.52 | 0.30 | 6.48 | 0.58 | 11.08 | 14.97 | 0.10 | 11.56 | 0.54 |
| S1-4 | 15–20 | 36.82 | 1.56 | 7.77 | 1.20 | 3.29 | 0.37 | 5.02 | 0.47 | 10.68 | 14.11 | 0.08 | 5.94 | 0.50 |
| S1-5 | 20–25 | 37.66 | 1.66 | 7.64 | 1.64 | 3.28 | 0.50 | 4.64 | 0.47 | 9.78 | 9.06 | 0.07 | 10.68 | 0.53 |
| S1-6 | 25–30 | 36.76 | 1.55 | 7.46 | 1.49 | 2.96 | 0.50 | 4.72 | 0.48 | 9.91 | 11.96 | 0.07 | 15.62 | 0.79 |
| S1-7 | 30–35 | 37.61 | 1.63 | 7.28 | 1.93 | 2.12 | 0.91 | 3.67 | 0.40 | 9.15 | 18.83 | 0.07 | 12.62 | 0.73 |
| Mean | 42.03 | 1.53 | 7.56 | 1.44 | 3.62 | 0.44 | 6.28 | 0.61 | 10.20 | 13.53 | 0.08 | 15.99 | 0.54 | |
| SD | 6.11 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.97 | 0.23 | 2.78 | 0.25 | 0.67 | 4.14 | 0.01 | 17.51 | 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, L.; Huang, J. Effect of Aquaculture Reclamation on Sediment Nitrates Reduction Processes in Mangrove Wetland. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070857
Hao L, Huang J. Effect of Aquaculture Reclamation on Sediment Nitrates Reduction Processes in Mangrove Wetland. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(7):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070857
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Lin, and Jiafang Huang. 2022. "Effect of Aquaculture Reclamation on Sediment Nitrates Reduction Processes in Mangrove Wetland" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 7: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070857
APA StyleHao, L., & Huang, J. (2022). Effect of Aquaculture Reclamation on Sediment Nitrates Reduction Processes in Mangrove Wetland. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(7), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070857





