The Role of Microplastics in Marine Pathogen Transmission: Retrospective Regression Analysis, Experimental Design, and Disease Modelling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retrospective Analysis
2.2. Experimental Studies
2.2.1. Oysters as an Experimental Model
2.2.2. Zebrafish as an Experimental Model
2.3. Disease Transmission Modelling
2.3.1. Model Schemes
2.3.2. Model Assumptions
3. Results
3.1. Retrospective Multivariate Modelling
3.2. Pathogen Transmission Modelling
3.2.1. Bivalve–Microplastic–Vibrio Disease Model
3.2.2. Fish–Microplastic–Vibrio Disease Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Úbeda, B.; Hernández-León, S.; Palma, Á.T.; Navarro, S.; García-de Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP. Emerging Issues in our Global Environment: Plastic Debris in the Ocean; UNEP Year Book 2014; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Plastic Europe. Plastics—The Facts 2014/2015: An Analysis of European Plastics Production Demand; Plastics Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, W.J.; Thomposon, R.C. Microplastics in the ocean. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.; Russell, M.; Ewins, C.; Quinn, B. The uptake of macroplastic & microplastic by demersal & pelagic fish in the Northeast Atlantic around Scotland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sequeira, I.F.; Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Worldwide contamination of fish with microplastics: A brief global overview. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, T.; Pietro, B.; Pedà, C.; Consoli, P.; Andaloro, F.; Fossi, M.C. First evidence of presence of plastic debris in stomach of large pelagic fish in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.; Van Franeker, J.; Leopold, M.; Kühn, S.; Rebolledo, E.B.; Heße, E.; Mielke, L.; IJzer, J.; Kamminga, P.; et al. Microplastic in a macro filter feeder: Humpback whale Megaptera novaeangliae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in seafood and the implications for human health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Microplastics in commercial bivalves from China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Claessens, M.; Vandegehuchte, M.B.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics are taken up by mussels (Mytilus edulis) and lugworms (Arenicola marina) living in natural habitats. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.; Hofmann, E.; Klinck, J.; Ray, S. Modeling Oyster Populations: I. A Commentary on Filtration Rate. Is Faster Always Better? Texas A&M University: College Station, TX, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzetti, E.; Sureda, A.; Tejada, S.; Faggio, C. Microplastic in marine organism: Environmental and toxicological effects. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 64, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Man, Y.B.; Mo, W.Y.; Man, K.Y.; Wong, M.H. Direct and indirect effects of microplastics on bivalves, with a focus on edible species: A mini-review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2109–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardesty, B.D.; Harari, J.; Isobe, A.; Lebreton, L.; Maximenko, N.; Potemra, J.; Van Sebille, E.; Vethaak, A.D.; Wilcox, C. Using numerical model simulations to improve the understanding of micro-plastic distribution and pathways in the marine environment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.L.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastics in the seas. Science 2014, 345, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A. Microplastics in the marine environment: Distribution, interactions and effects. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 245–307. [Google Scholar]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “plastisphere”: Microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, I.V.; Kirmizi, S.; Wichels, A.; Garin-Fernandez, A.; Erler, R.; Löder, M.; Gerdts, G. Dangerous hitchhikers? Evidence for potentially pathogenic Vibrio spp. on microplastic particles. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 120, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesy, K.; Labrenz, M.; Scales, B.S.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Oberbeckmann, S. Vibrio Colonization Is Highly Dynamic in Early Microplastic-Associated Biofilms as Well as on Field-Collected Microplastics. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vethaak, A.D.; Legler, J. Microplastics and human health. Science 2021, 371, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeilinger, A.R.; Rapacciuolo, G.; Turek, D.; Oboyski, P.T.; Almeida, R.P.; Roderick, G.K. Museum specimen data reveal emergence of a plant disease may be linked to increases in the insect vector population. Ecol. Appl. 2017, 27, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive, S.F. Guidance on Monitoring of Marine Litter in European Seas; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013; Volume 10, p. 99475. [Google Scholar]
- Galgani, F.; Claro, F.; Depledge, M.; Fossi, C. Monitoring the impact of litter in large vertebrates in the Mediterranean Sea within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD): Constraints, specificities and recommendations. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 100, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorokhova, E. Screening for microplastic particles in plankton samples: How to integrate marine litter assessment into existing monitoring programs? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.; Otero, V.; Sobral, P. Evidence of microplastics in samples of zooplankton from Portuguese coastal waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 95, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.C.; Rosenberg, M.; Cheng, L. Increased oceanic microplastic debris enhances oviposition in an endemic pelagic insect. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmendia, L.; Soto, M.; Vicario, U.; Kim, Y.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Marigómez, I. Application of a battery of biomarkers in mussel digestive gland to assess long-term effects of the Prestige oil spill in Galicia and Bay of Biscay: Tissue-level biomarkers and histopathology. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M.; Thompson, R.C. Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system of the mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, J.B.; Willis, B.L.; Fiorenza, E.A.; Couch, C.S.; Howard, R.; Rader, D.N.; True, J.D.; Kelly, L.A.; Ahmad, A.; Jompa, J.; et al. Plastic waste associated with disease on coral reefs. Science 2018, 359, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ni, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, S. Acute microplastic exposure raises stress response and suppresses detoxification and immune capacities in the scleractinian coral Pocillopora damicornis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroja, E.; Christoforou, E.; Lindström, J.; Spatharis, S. Effects of microplastics on bivalves: Are experimental settings reflecting conditions in the field? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, H.S.; Nerheim, M.S.; Carroll, K.A.; Eriksen, M. The plastic-associated microorganisms of the North Pacific Gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 75, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M. Leaching of plastic additives to marine organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, G.R.; Matte, M.H.; Rivera, I.G.; Martins, M.T. Distribution of potentially pathogenic vibrios in oysters from a tropical region. J. Food Prot. 1994, 57, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoste, A.; Jalabert, F.; Malham, S.; Cueff, A.; Gelebart, F.; Cordevant, C.; Lange, M.; Poulet, S. A Vibrio splendidus strain is associated with summer mortality of juvenile oysters Crassostrea gigas in the Bay of Morlaix (North Brittany, France). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2001, 46, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toranzo, A.E.; Magariños, B.; Romalde, J.L. A review of the main bacterial fish diseases in mariculture systems. Aquaculture 2005, 246, 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, X.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zu, Y.; Li, W. Zebrafish as a useful model for zoonotic Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenicity in fish and human. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 55, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, J.A.; Wedderbum, R.W.M. Generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 1972, 135, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, P.; Nelder, J.A. Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1989; p. 500. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Generalized Additive Models; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Eubank, R. Monotone Regression Splines in Action: Comment. Stat. Sci. 1988, 3, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, G. Spline Models for Observational Data; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Gijbels, I. Local Polynomial Modelling and Its Applications; Number 66 in Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability Series; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wand, M.P.; Jones, M.C. Kernel Smoothing; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wand, M.P. A comparison of regression spline smoothing procedures. Comput. Stat. 2000, 15, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Marron, J. Fast implementation of nonparametric curve estimators. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1994, 3, 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Golub, G.; Heath, M.; Wahba, G. Generalized cross-validation as a method for choosing a good ridge parameter. Technometrics 1979, 21, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, D.; Sheather, S.J.; Wand, M.P. An Effective Bandwidth Selector for Local Least Squares Regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marron, J.S. Bootstrap bandwidth selection. In Exploring the Limits of Bootstrap; LePage, R., Billard, L., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, M.R. Key Concepts in Model Selection: Performance and Generalizability. J. Math. Psychol. 2000, 44, 205–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J.H. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Green, P.J. Reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo computation and Bayesian model determination. Biometrika 1995, 82, 711–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, L.; Mallick, B. Variable selection for regression models. Indian J. Stat. (Spec. Issue Bayesian Anal.) 1998, 60, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.; Casella, G. The Bayesian Lasso. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2008, 103, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S-Plus, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A. Subset Selection in Regression; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sestelo, M.; Villanueva, N.M.; Meira-Machado, L.; Roca-Pardiñas, J. FWDselect: An R Package for Variable Selection in Regression Models. R J. 2016, 8, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagno, V.; de Mazancourt, C. glmulti: An R package for easy automated model selection with (Generalized) Linear Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 34, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Mou, H.; Lin, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Junaid, M.; Wang, J. Microplastics in Mollusks: Research Progress, Current Contamination Status, Analysis Approaches, and Future Perspectives. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 62, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ashton-Alcox, K.A.; Powell, E.N. Histological Techniques for Marine Bivalve Molluscs: Update; OAA/National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science: Bethlehem, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Iriarte, A.; Villate, F.; Uriarte, I.; Bidegain, G.; Barroeta, Z. Shifts in neritic copepod communities off the Basque coast (southeastern Bay of Biscay) between 1998 and 2015. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 79, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. Stable and efficient multiple smoothing parameter estimation for generalized additive models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2004, 99, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.; Pya, N.; Safken, B. Smoothing parameter and model selection for general smooth models (with discussion). J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 1548–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Horin, T.; Bidegain, G.; Huey, L.; Nárvaez, D.A.; Bushek, D. Parasite transmission through suspension feeding. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 131, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantet, F.; Hervio-Heath, D.; Caro, A.; Le Mennec, C.; Monteil, C.; Quéméré, C.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A.; Colwell, R.R.; Monfort, P. Quantification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio vulnificus and Vibrio cholerae in French Mediterranean coastal lagoons. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Pan, J.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Bartlam, M.; Wang, Y. Selective enrichment of bacterial pathogens by microplastic biofilm. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Perrein-Ettajani, H.; Bruneau, M.; Akcha, F.; Sussarellu, R.; Rouxel, J.; Costil, K.; Decottignies, P.; Cognie, B.; et al. Realistic environmental exposure to microplastics does not induce biological effects in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Shan, E.; Wang, Q. Oxidative stress biomarkers, physiological responses and proteomic profiling in oyster (Crassostrea gigas) exposed to microplastics with irregular-shaped PE and PET microplastic. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidegain, G.; Powell, E.E.; Klinck, J.M.; Ben-Horin, T.; Hofmann, E.E. Microparasitic disease dynamics in benthic suspension feeders: Infective dose, non-focal hosts, and particle diffusion. Ecol. Model. 2016, 328, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidegain, G.; Powell, E.E.; Klinck, J.M.; Ben-Horin, T.; Hofmann, E.E. Marine infectious disease dynamics and outbreak thresholds: Contact, transmission, pandemic infection, and the potential role of filter feeders. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.P.; Neely, M.N. Trolling for the ideal model host: Zebrafish take the bait. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, C.; Kim, C.H. Zebrafish as a model for infectious disease and immune function. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2008, 25, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, H.M.; Withey, J.H.; Neely, M.N. Zebrafish as a model for zoonotic aquatic pathogens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 46, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Runft, D.L.; Mitchell, K.C.; Abuaita, B.H.; Allen, J.P.; Bajer, S.; Ginsburg, K.; Neely, M.N.; Withey, J.H. Zebrafish as a natural host model for Vibrio cholerae colonization and transmission. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and toxic effects in liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidegain, G.; Powell, E.; Klinck, J.; Hofmann, E.; Ben-Horin, T.; Bushek, D.; Ford, S.; Munroe, D.; Guo, X. Modeling the transmission of Perkinsus marinus in the Eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica. Fish. Res. 2017, 186, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, J.P.; Smith, L.D.; Heyward, A.J.; Baird, A.H.; Pratchett, M.S. Recovery of an isolated coral reef system following severe disturbance. Science 2013, 340, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, C.; Jean, F.; Ford, S.E.; Powell, E.N.; Klinck, J.M.; Hofmann, E.E.; Flye-Sainte-Marie, J. A theoretical individual-based model of brown ring disease in Manila clams Venerupis philippinarum. J. Sea Res. 2014, 91, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega Thurber, R.L.; Burkepile, D.E.; Fuchs, C.; Shantz, A.A.; McMinds, R.; Zaneveld, J.R. Chronic nutrient enrichment increases prevalence and severity of coral disease and bleaching. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Kim, M.; Rueda, L.; Rochman, C.; VanWormer, E.; Moore, J.; Shapiro, K. Association of zoonotic protozoan parasites with microplastics in seawater and implications for human and wildlife health. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Tolman, M.; Thames, H.D.; Withers, H.R.; Mason, K.A.; Transtrum, M.K. The limitations of model-based experimental design and parameter estimation in sloppy systems. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1005227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowley, J.; Baker-Austin, C.; Porter, A.; Hartnell, R.; Lewis, C. Oceanic hitchhikers–assessing pathogen risks from marine microplastic. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
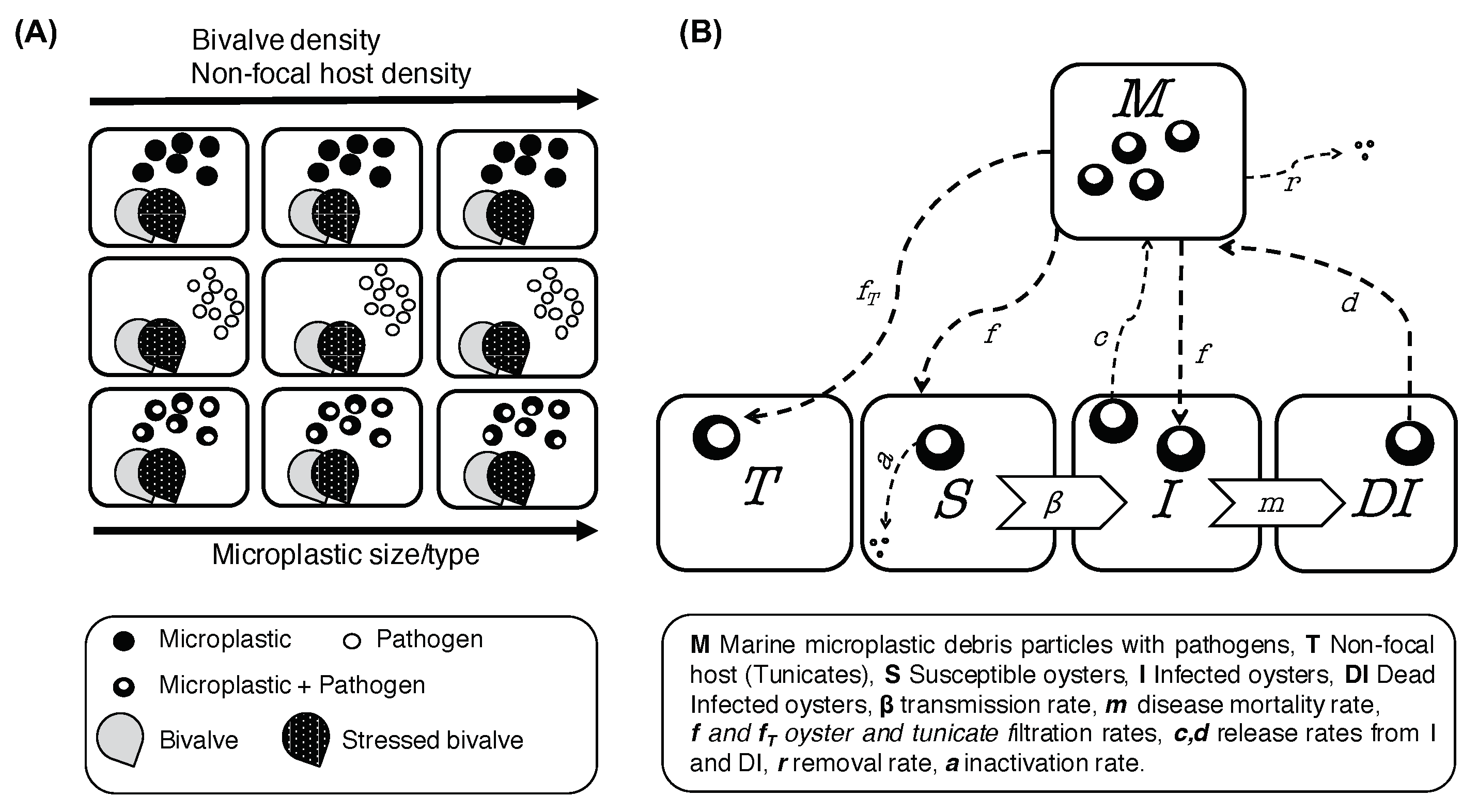


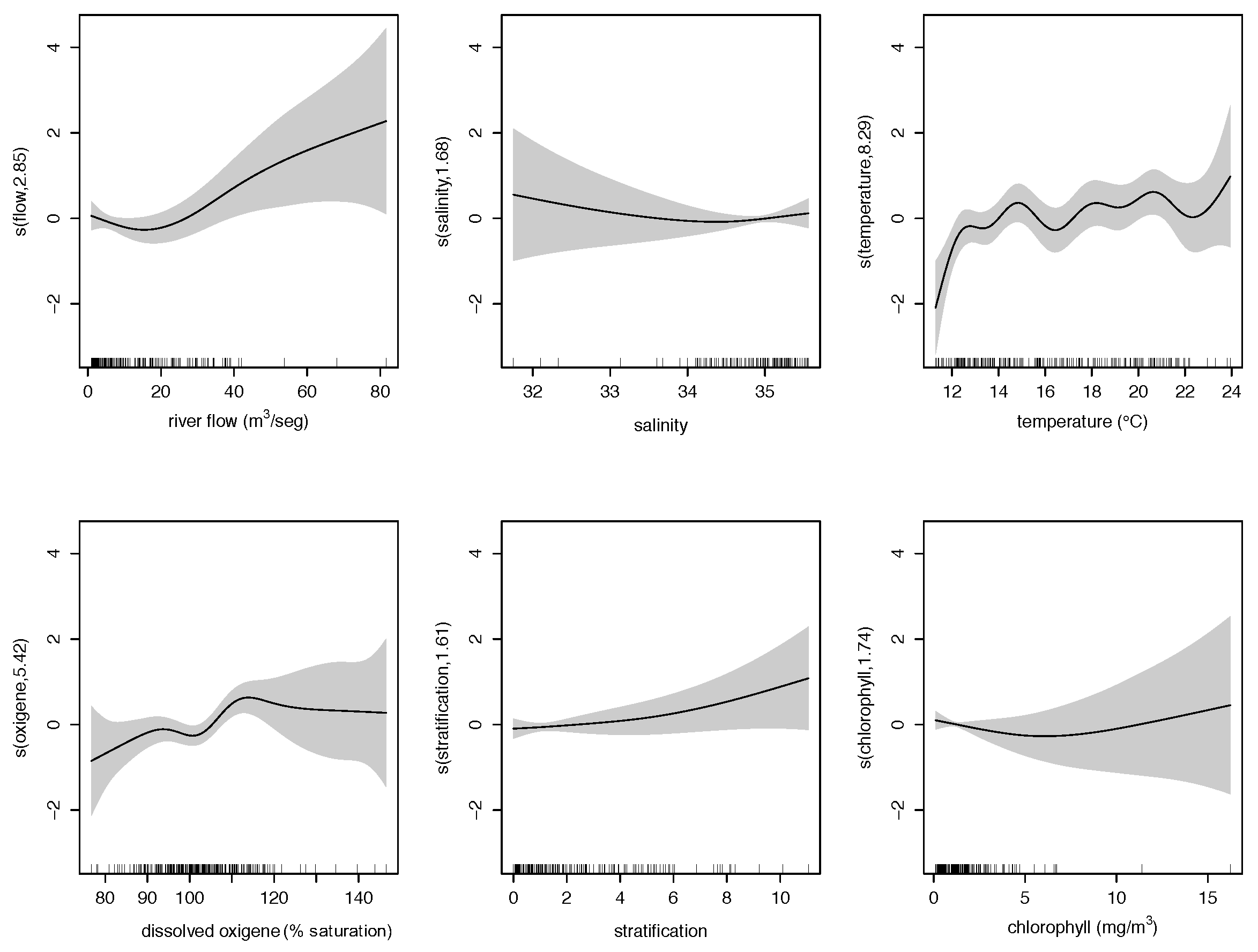
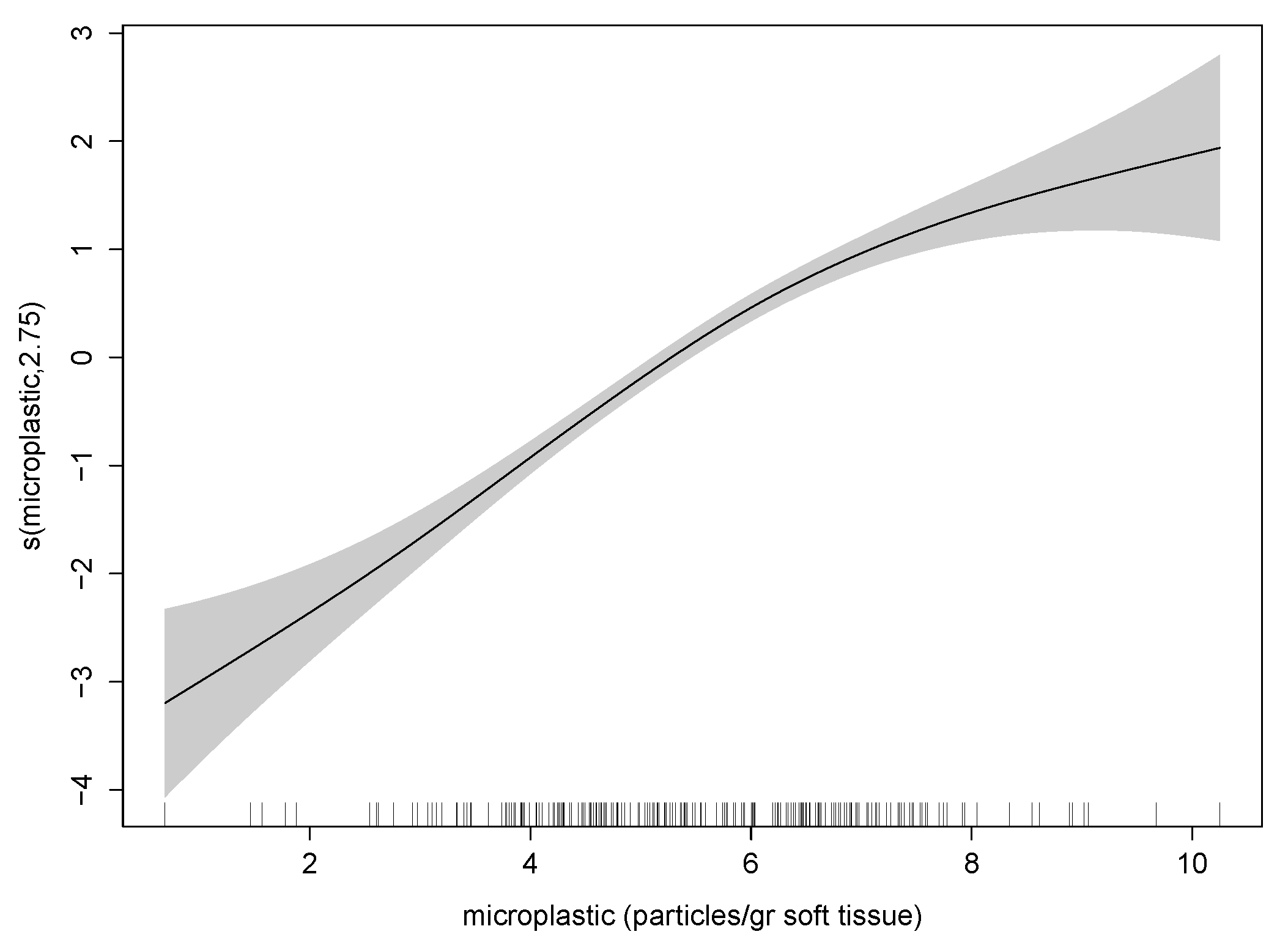
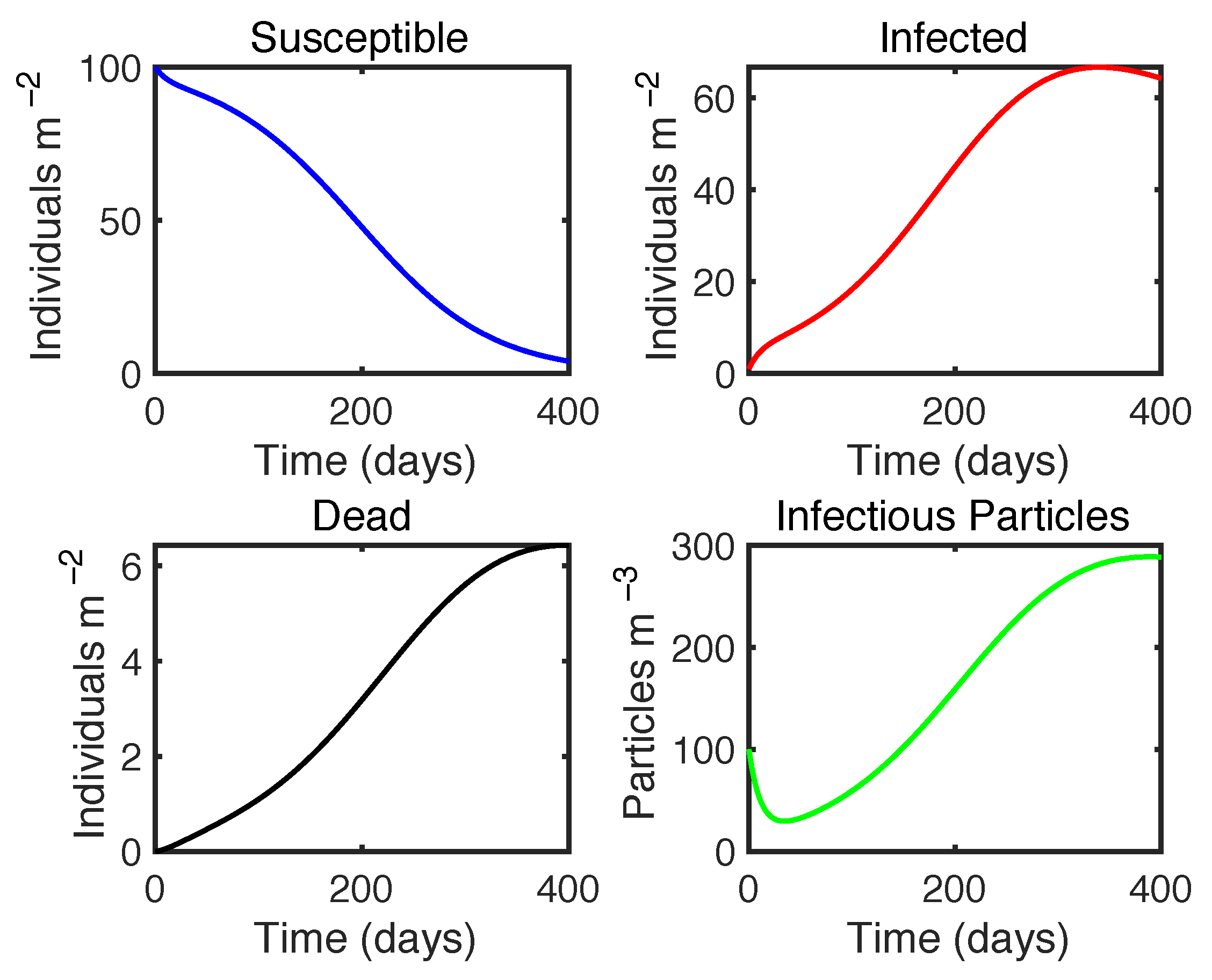

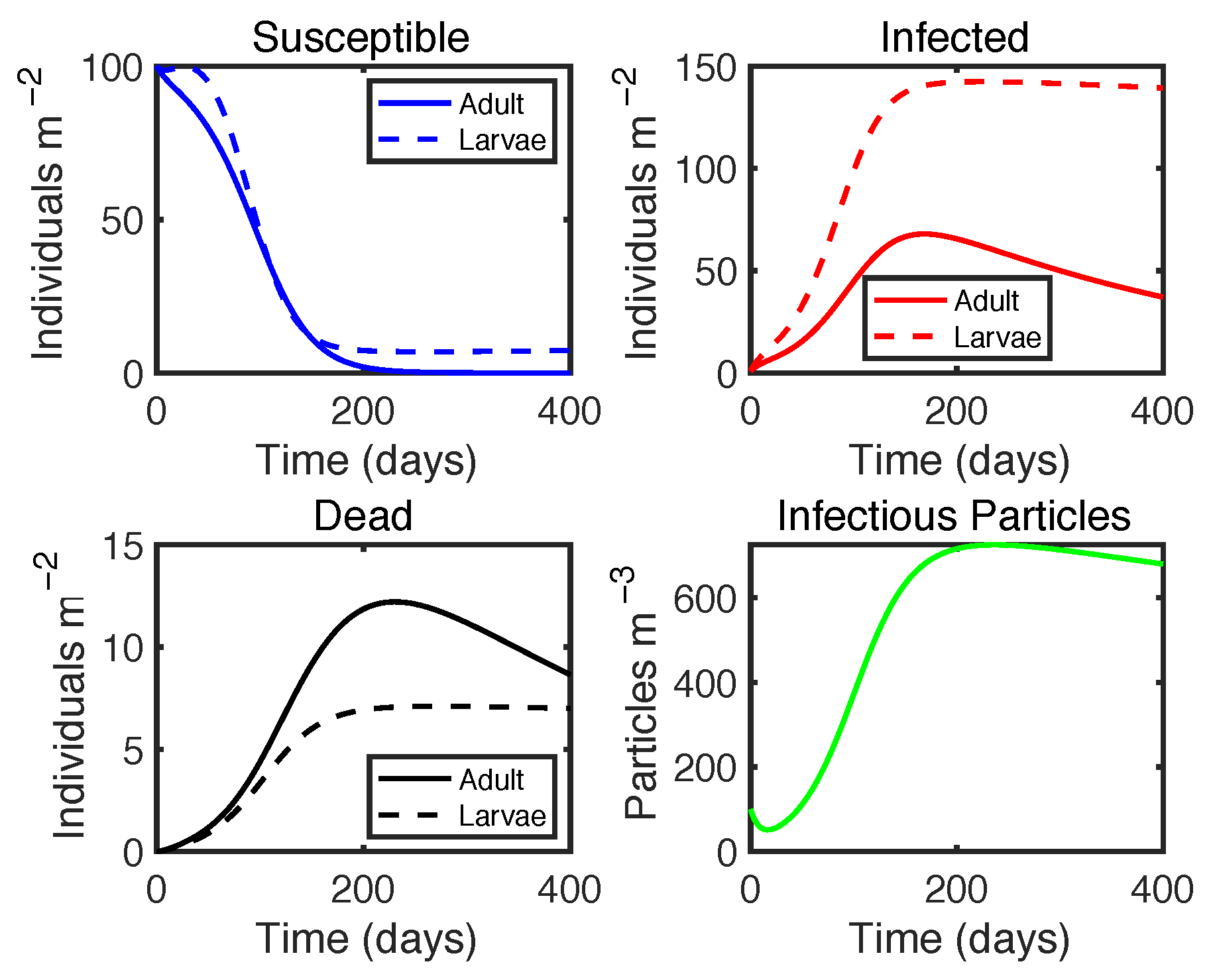
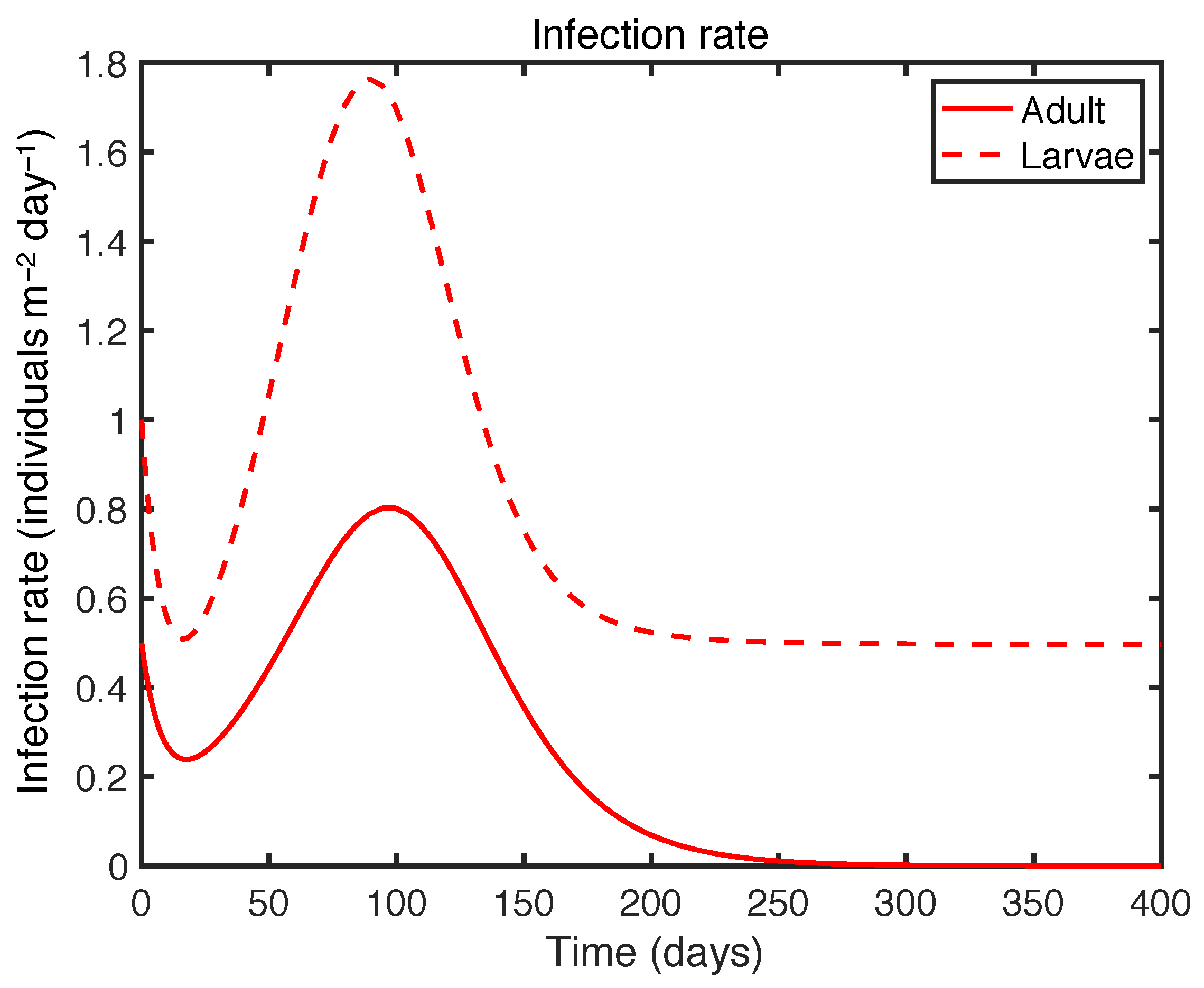
| Variable | Definition | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Susceptible hosts in the population | Number of individuals | |
| Infected individuals in the population | Number of individuals | |
| Dead infected individuals in the population | Number of individuals | |
| M | Marine microplastic debris particles with adhered pathogens | Number of particles |
| T | Alternate non-competent reservoir hosts | Number of individuals |
| Parameter | Definition | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission rate in oysters | individual day | |
| Transmission rates in fish | individual day | |
| m | Disease mortality rate in oysters | day |
| Disease mortality rate in fish | day | |
| g | Growth rate from larvae to adult | day |
| Removal rate of dead individuals by scavengers or decay | day | |
| Average number of per I | MMD particles | |
| Average number of per T | MMD particles | |
| Average per | MMD particles | |
| Release rate of particles from I | day | |
| Release rate of particles from T | day | |
| Release rate of particles from DI | day | |
| r | Loss rate of MMD particles from the local environment | day |
| Filtration/feeding rate of S and I | m individual day | |
| Filtration/feeding rate of T | m individual day | |
| Inactivation of pathogens in S and I | day | |
| Inactivation of pathogens in T | day |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bidegain, G.; Sestelo, M.; Luque, P.L.; Uriarte, I.; Iriarte, A.; Villate, F. The Role of Microplastics in Marine Pathogen Transmission: Retrospective Regression Analysis, Experimental Design, and Disease Modelling. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121837
Bidegain G, Sestelo M, Luque PL, Uriarte I, Iriarte A, Villate F. The Role of Microplastics in Marine Pathogen Transmission: Retrospective Regression Analysis, Experimental Design, and Disease Modelling. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(12):1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121837
Chicago/Turabian StyleBidegain, Gorka, Marta Sestelo, Patricia L. Luque, Ibon Uriarte, Arantza Iriarte, and Fernando Villate. 2022. "The Role of Microplastics in Marine Pathogen Transmission: Retrospective Regression Analysis, Experimental Design, and Disease Modelling" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 12: 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121837
APA StyleBidegain, G., Sestelo, M., Luque, P. L., Uriarte, I., Iriarte, A., & Villate, F. (2022). The Role of Microplastics in Marine Pathogen Transmission: Retrospective Regression Analysis, Experimental Design, and Disease Modelling. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(12), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121837







