The Influence of Crest Width and Working States on Wave Transmission of Pile–Rock Breakwaters in the Coastal Mekong Delta
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Laboratory Experiments
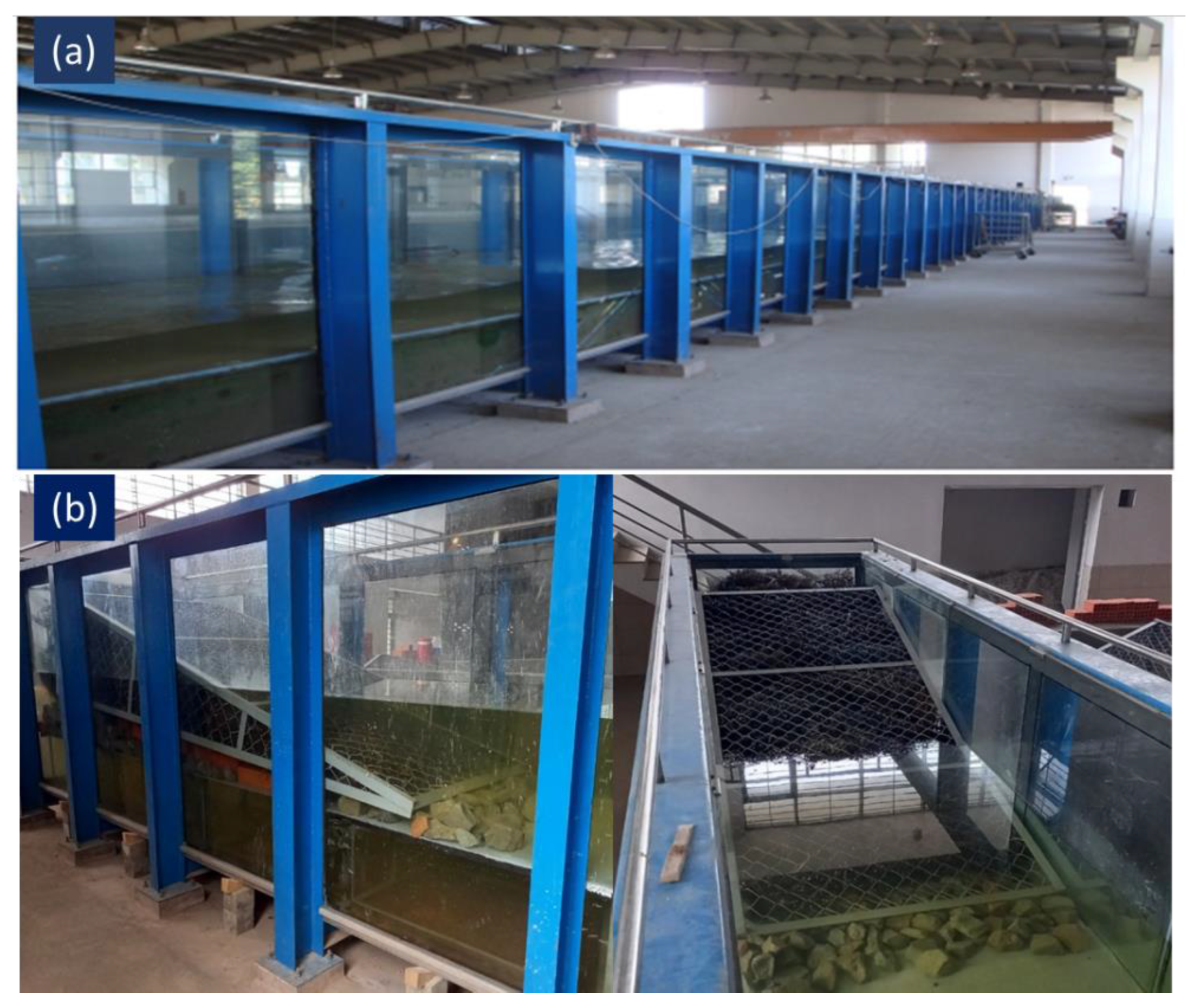
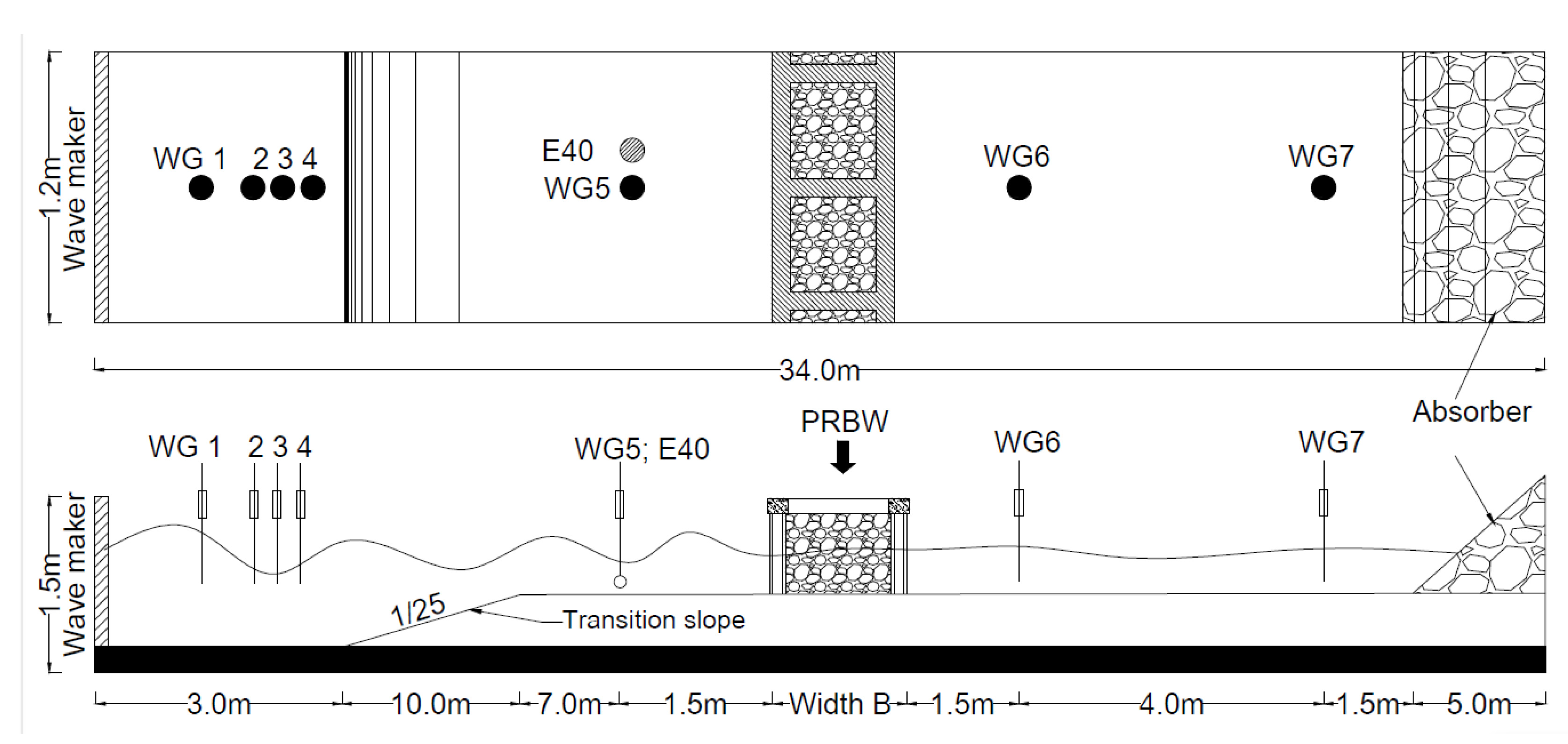
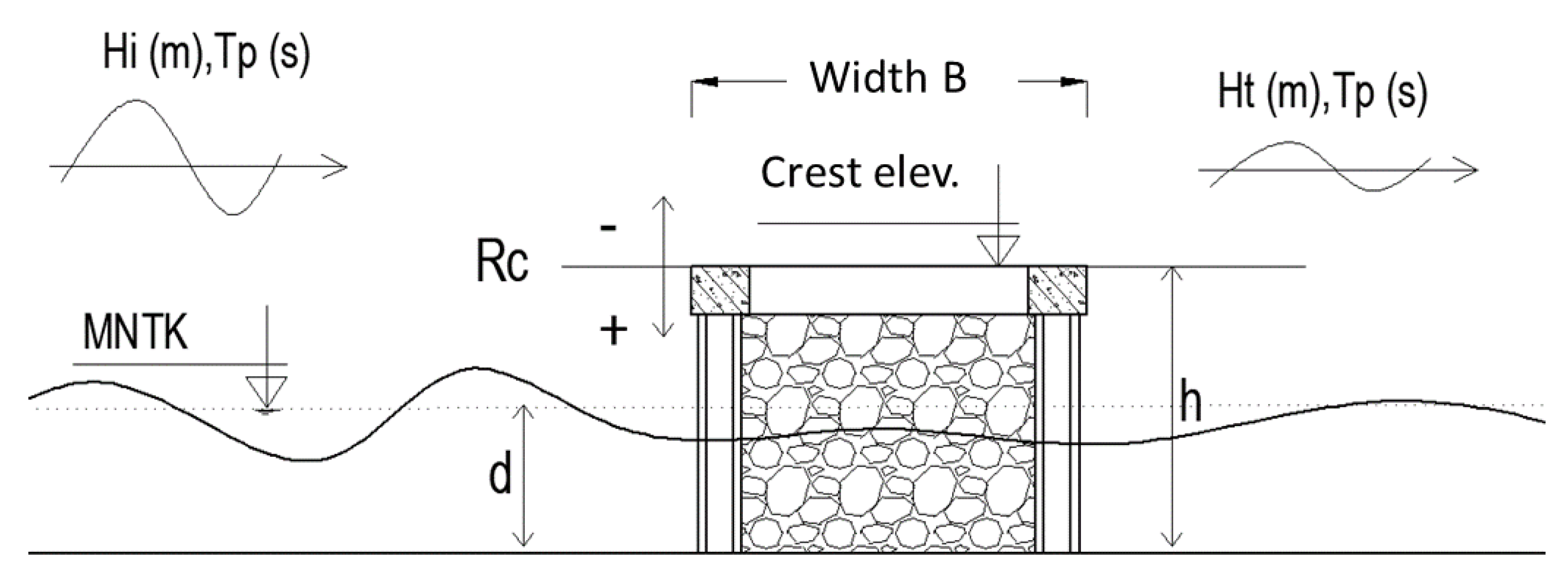
2.1. Experiment Equipment Setup
2.2. Installation of Equipment and Model Setup
2.3. Experimental Scenarios
2.3.1. Wave Conditions
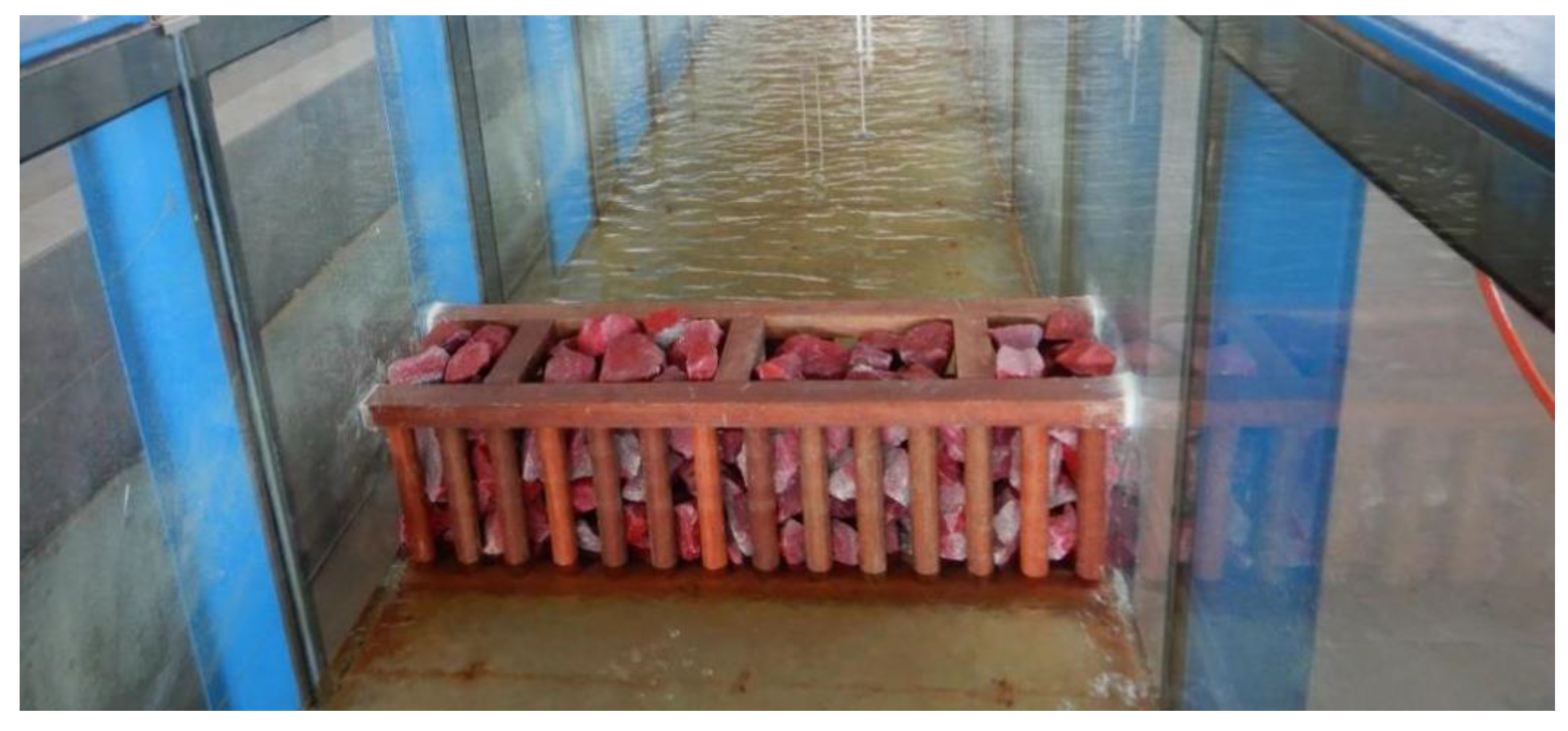
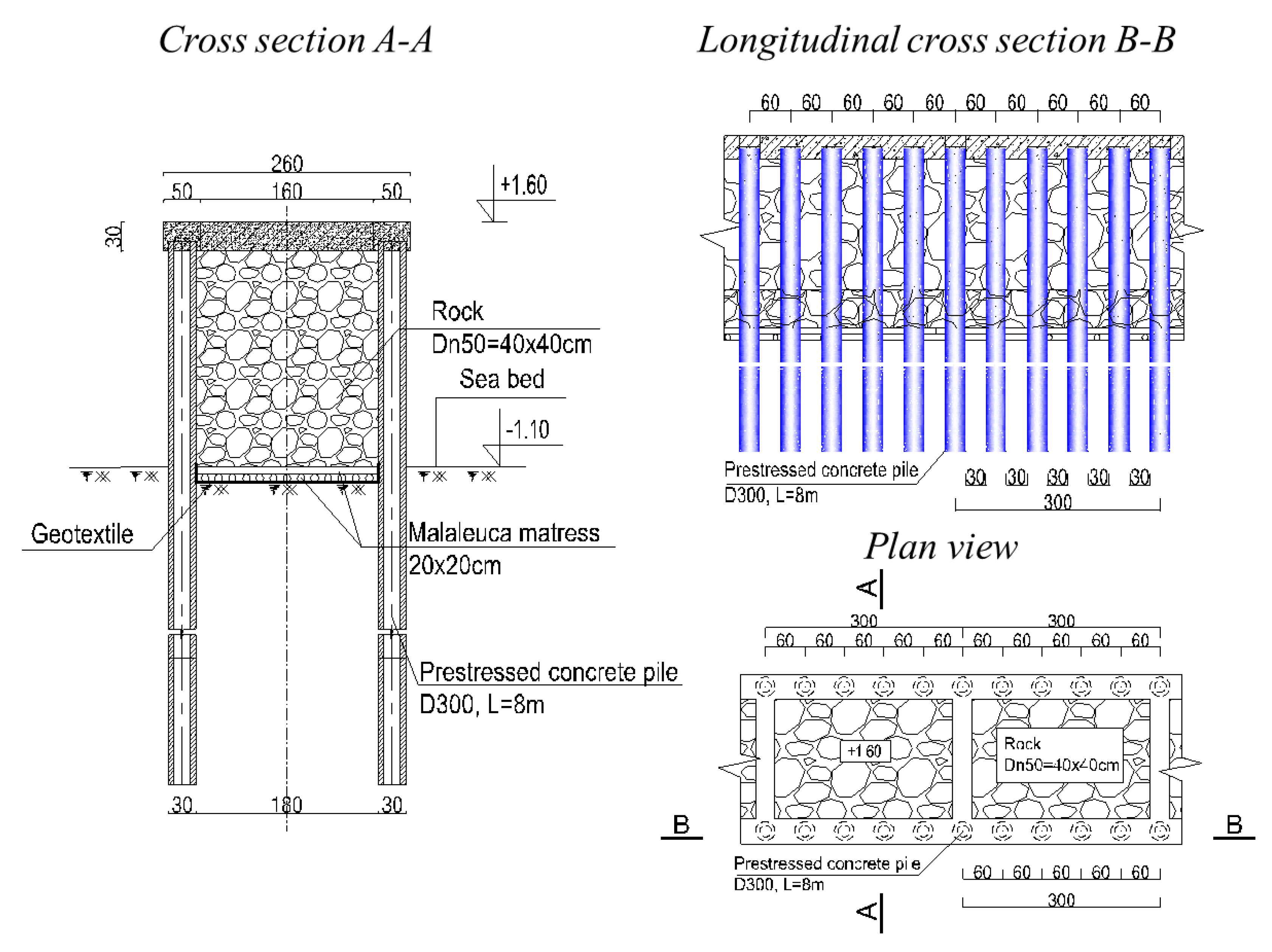
2.3.2. Experimental Structures
2.3.3. Testing Scenarios
- One test without PRBW and three tests with three crest widths (B24, B38, and B52);
- Seven tests with a changing water level and crest freeboard (Rc);
- Tests changing ten parameters of the waves (Hs, Tp, and L).
3. Results and Discussion
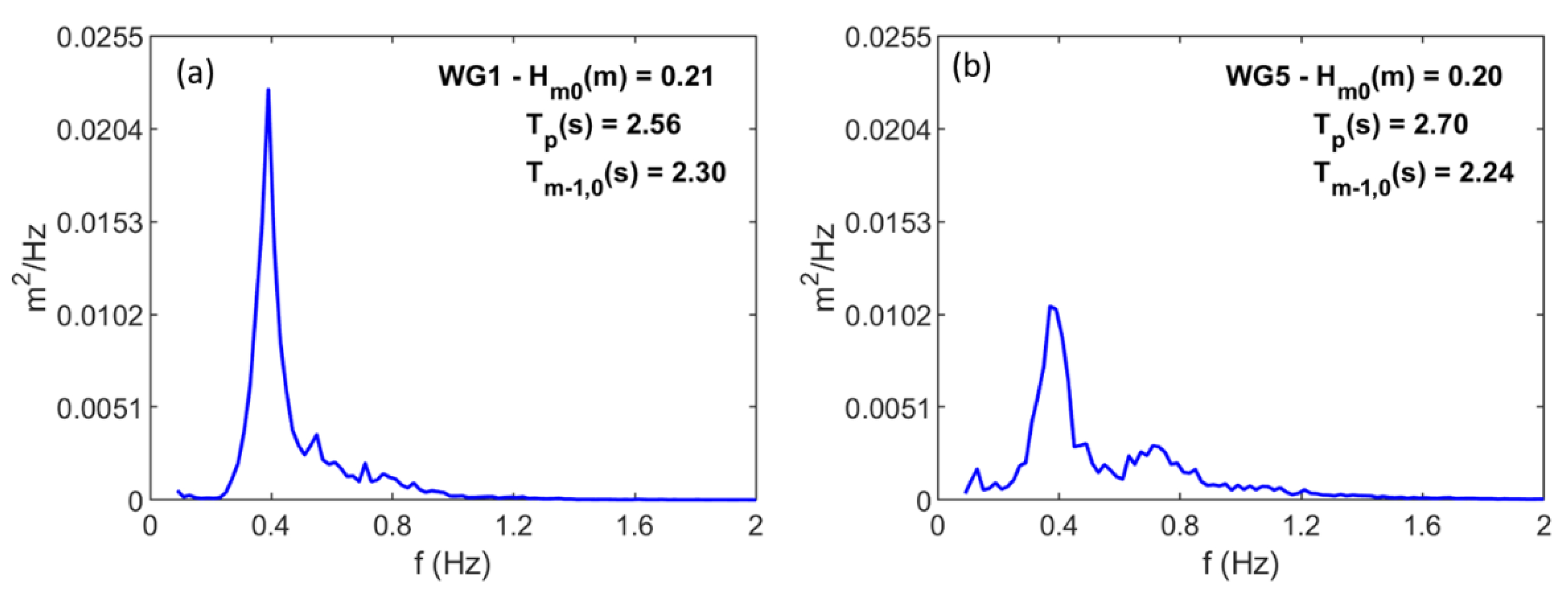
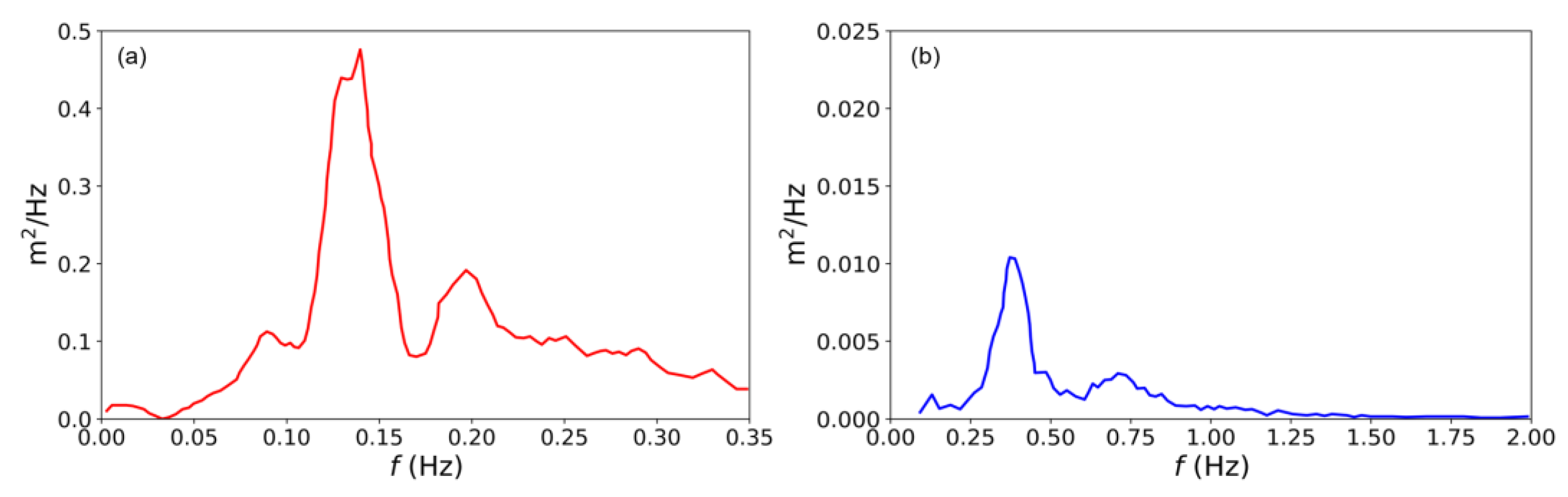
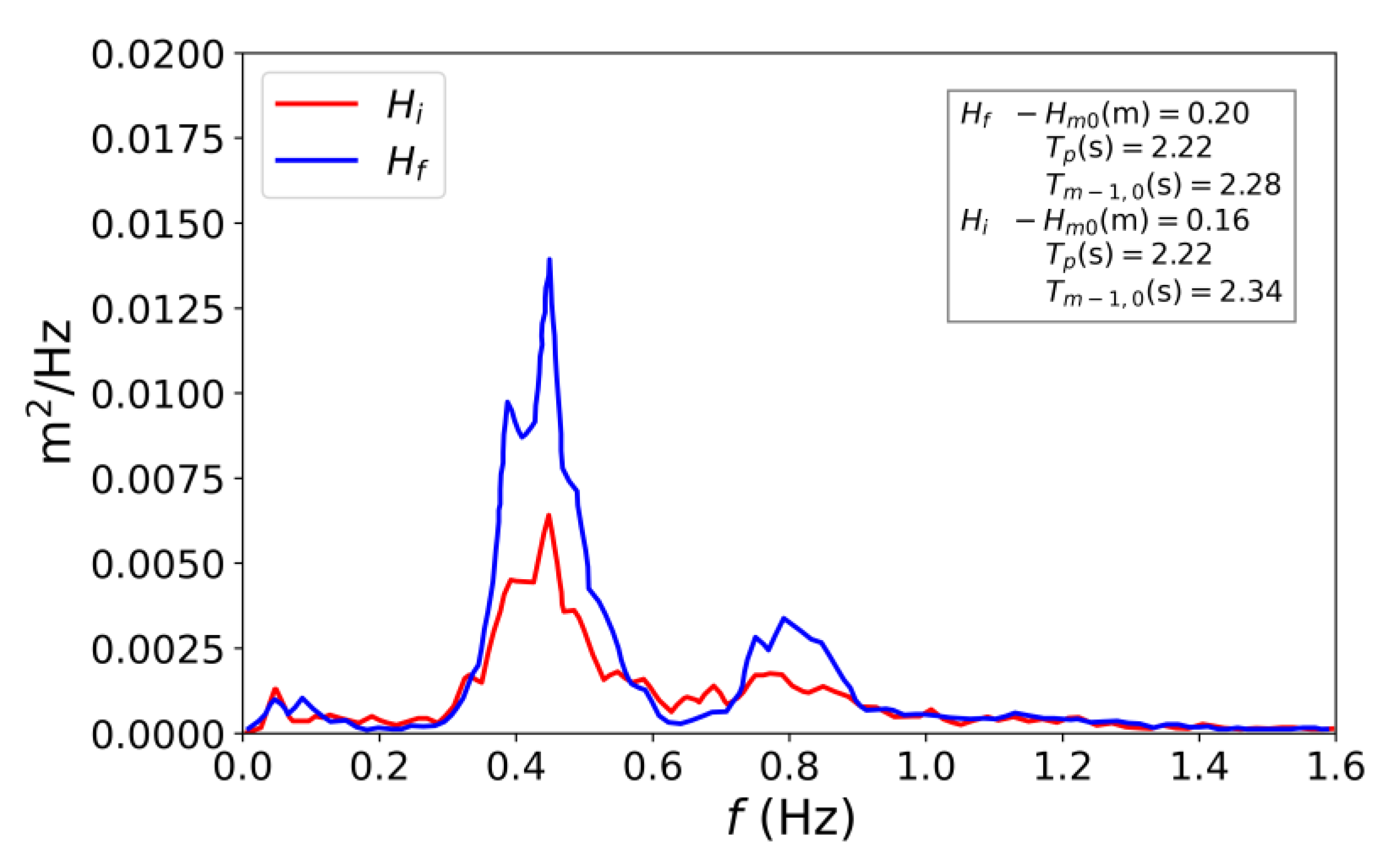
3.1. Wave Spectrum Validation
3.2. Experimental Analysis
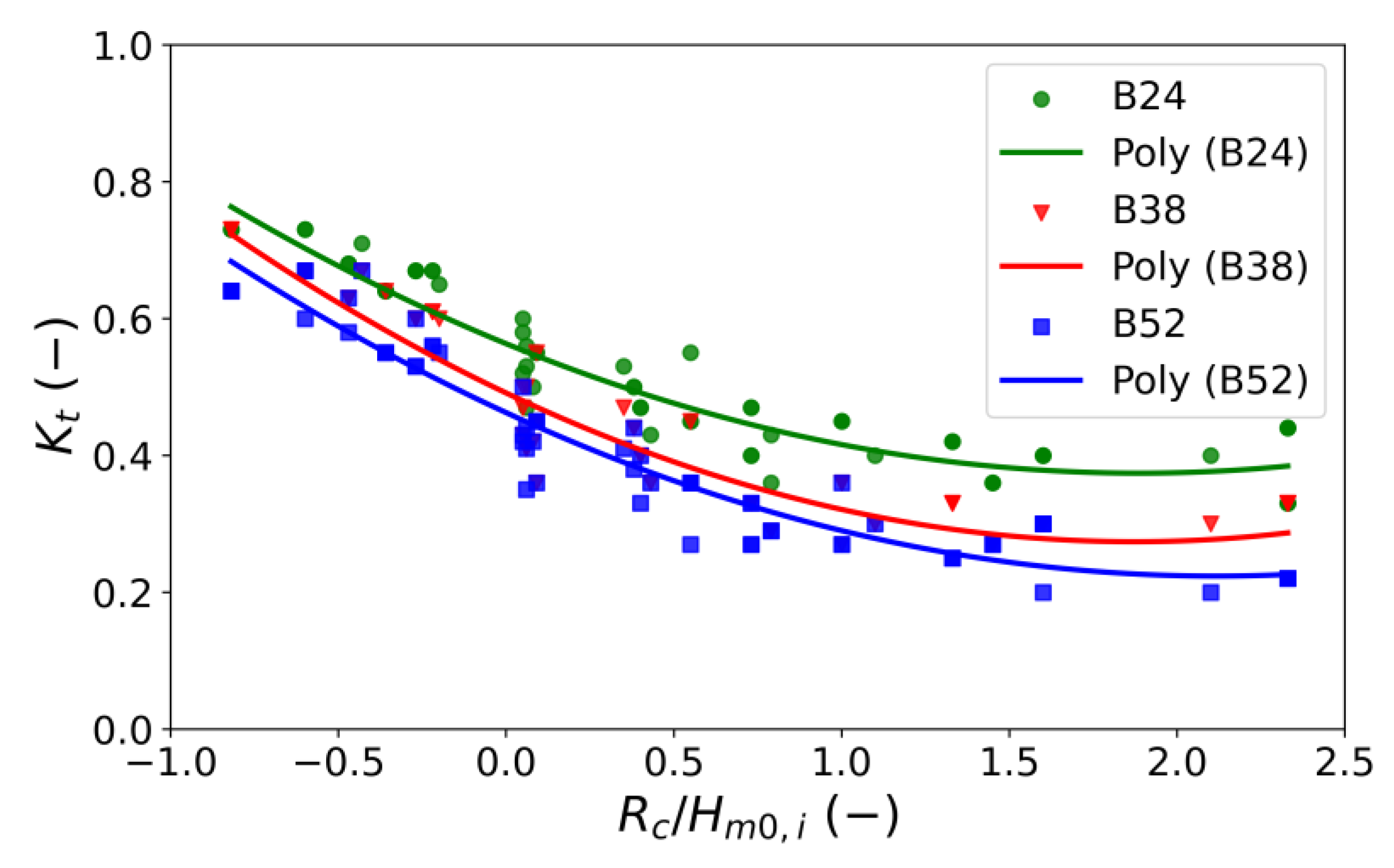
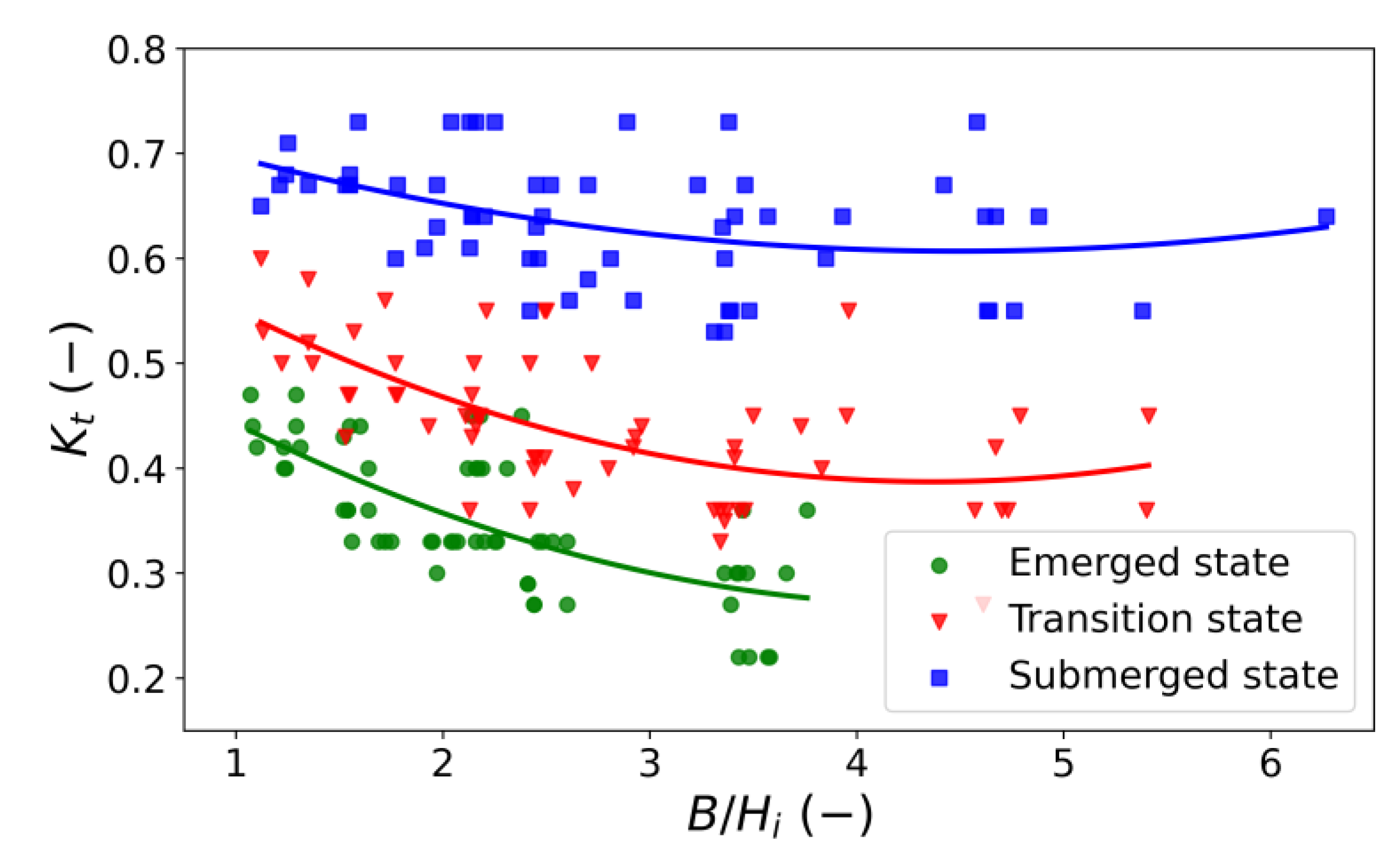
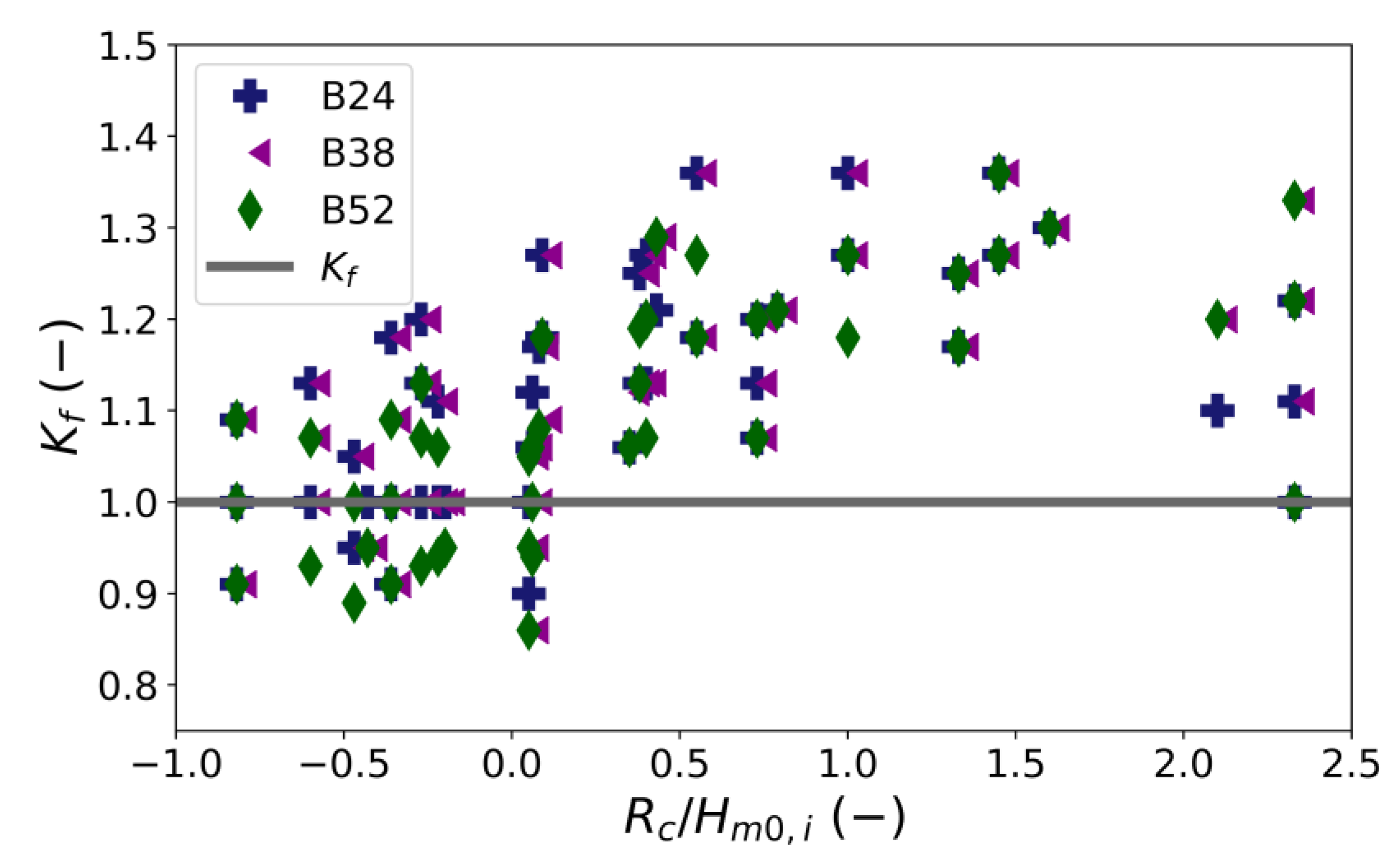
3.2.1. The Effect of Crest Width on the Wave Transmission Coefficient
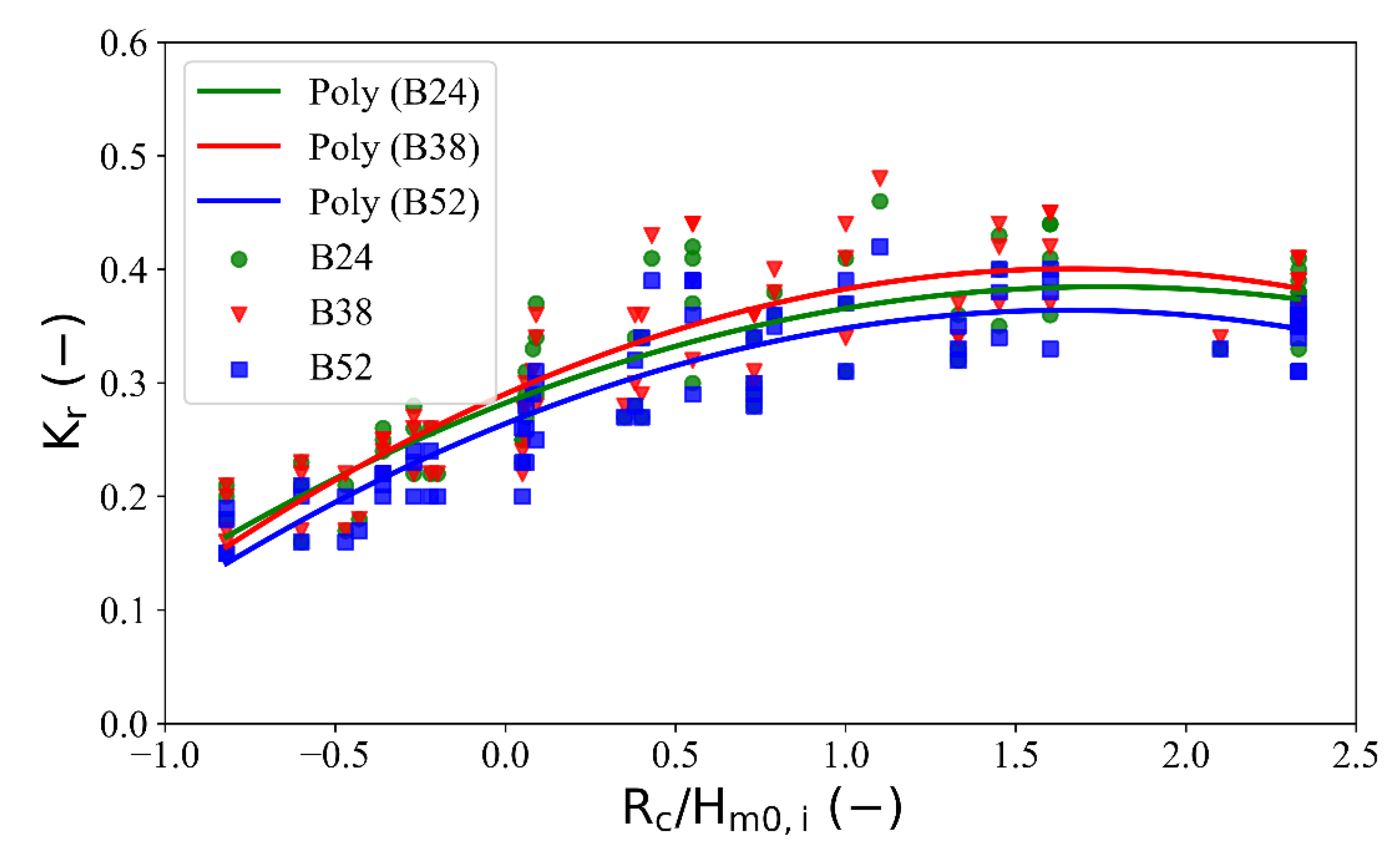
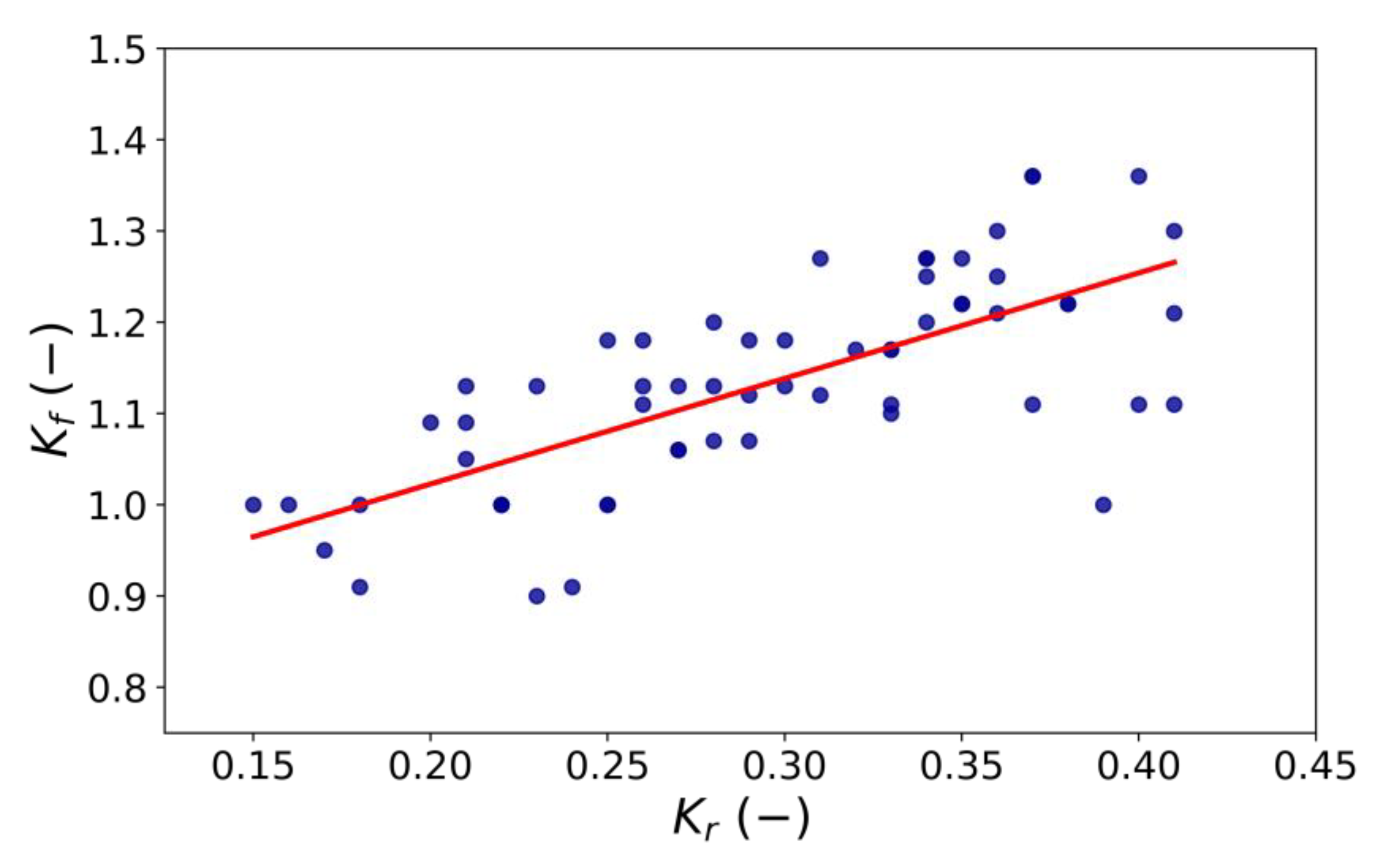
3.2.2. The Effect of Crest Width on the Wave Reflection Coefficient
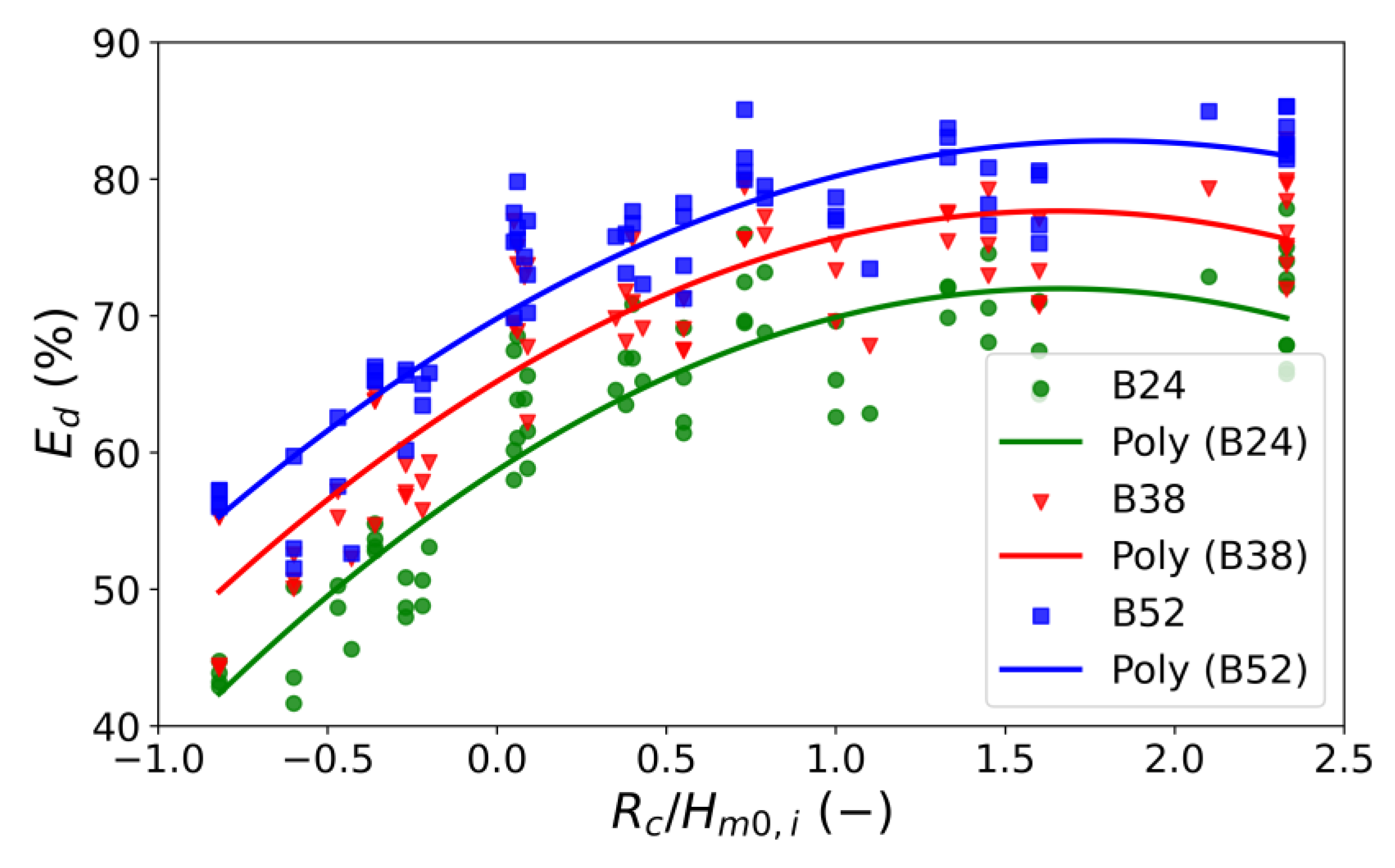
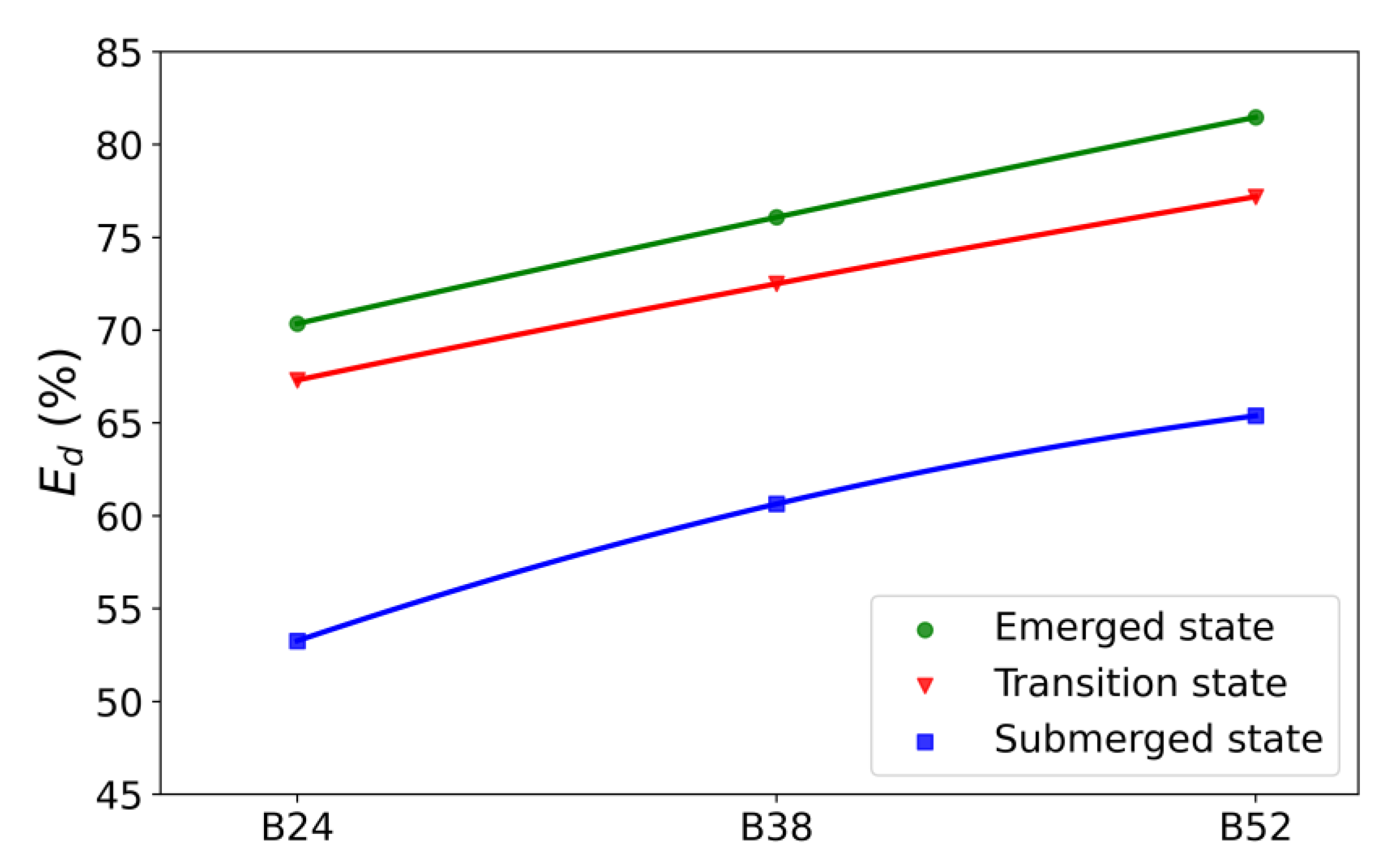
3.2.3. The Effect of Crest Width on Energy Dissipation
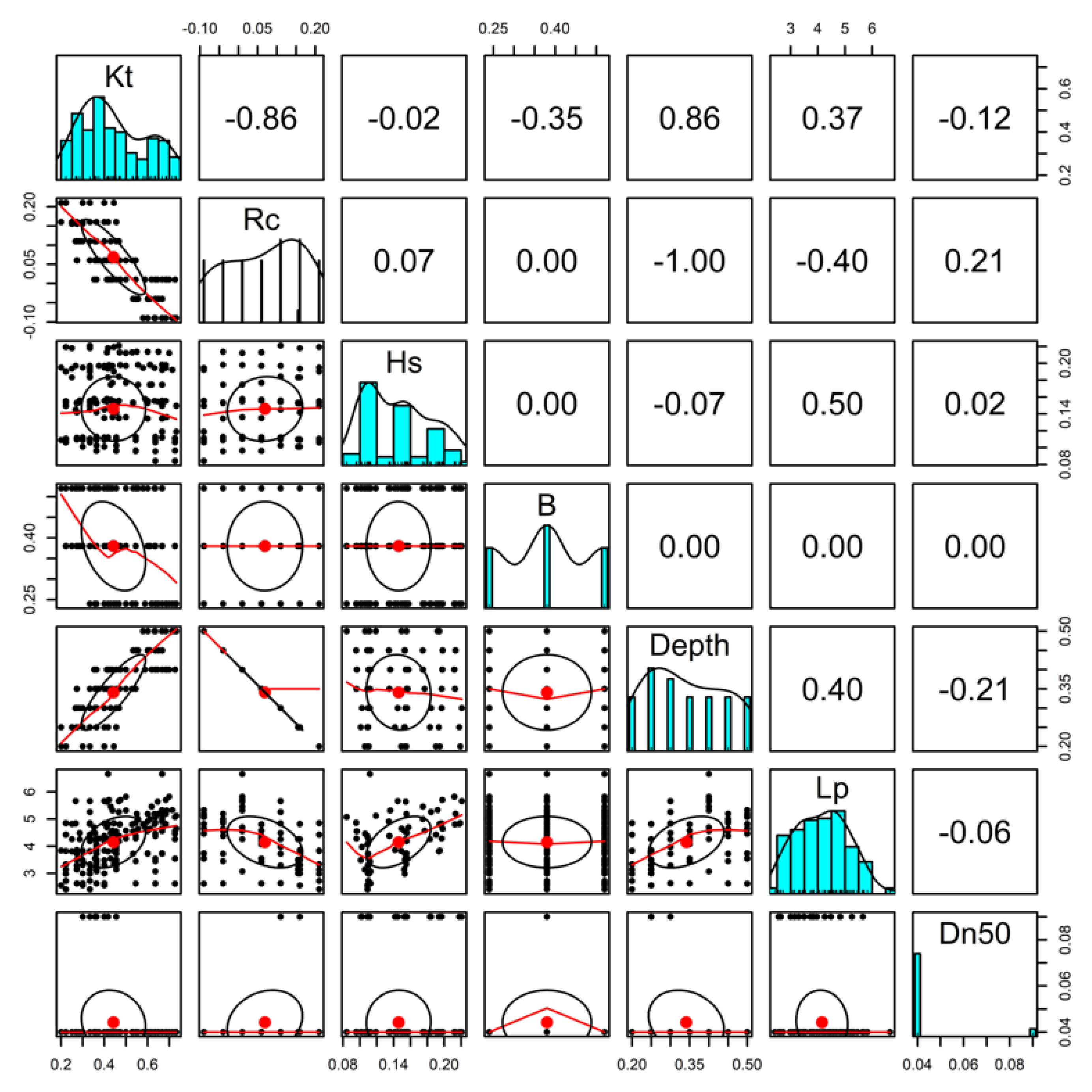
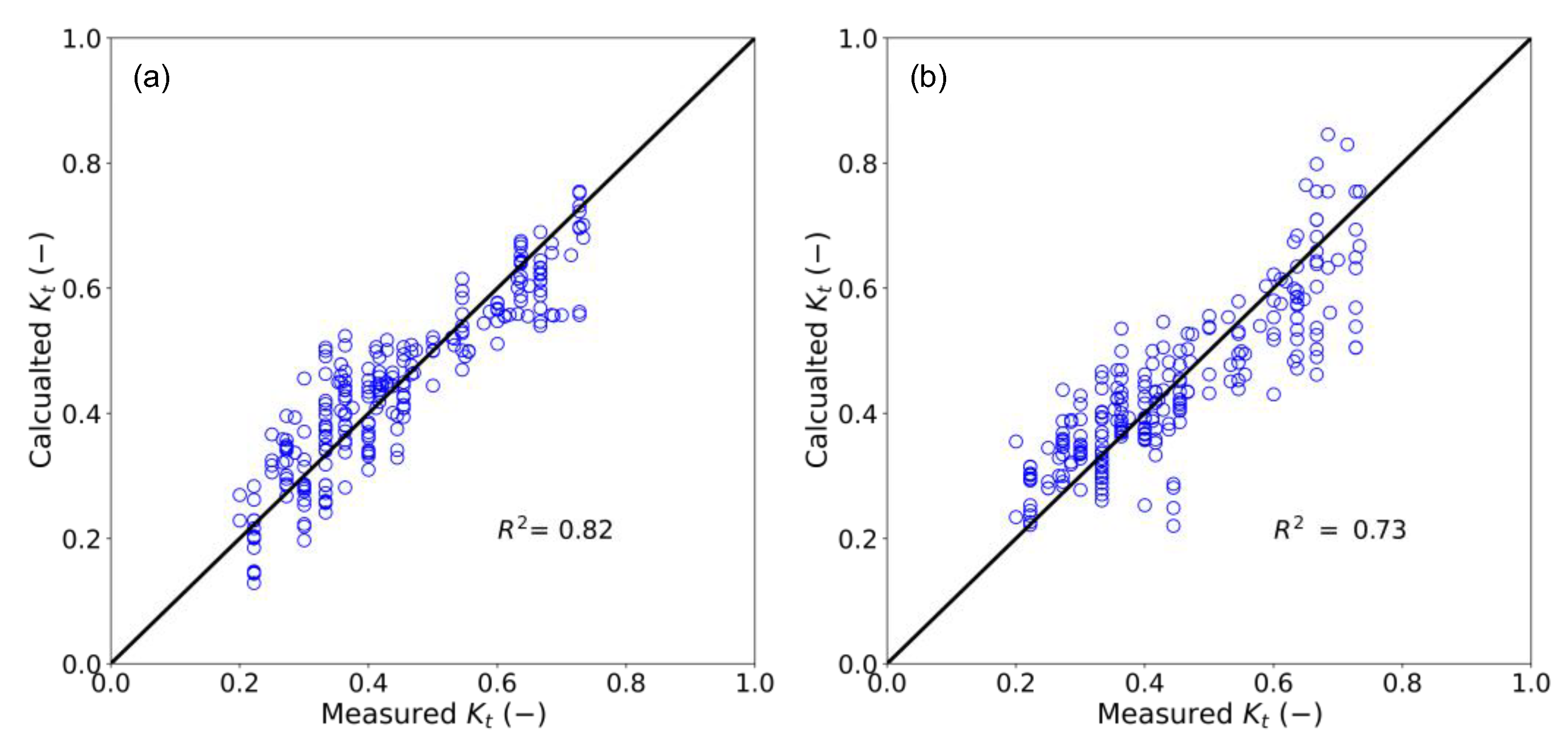
3.3. Development of Experimental Equations for the Wave Transmission Coefficient
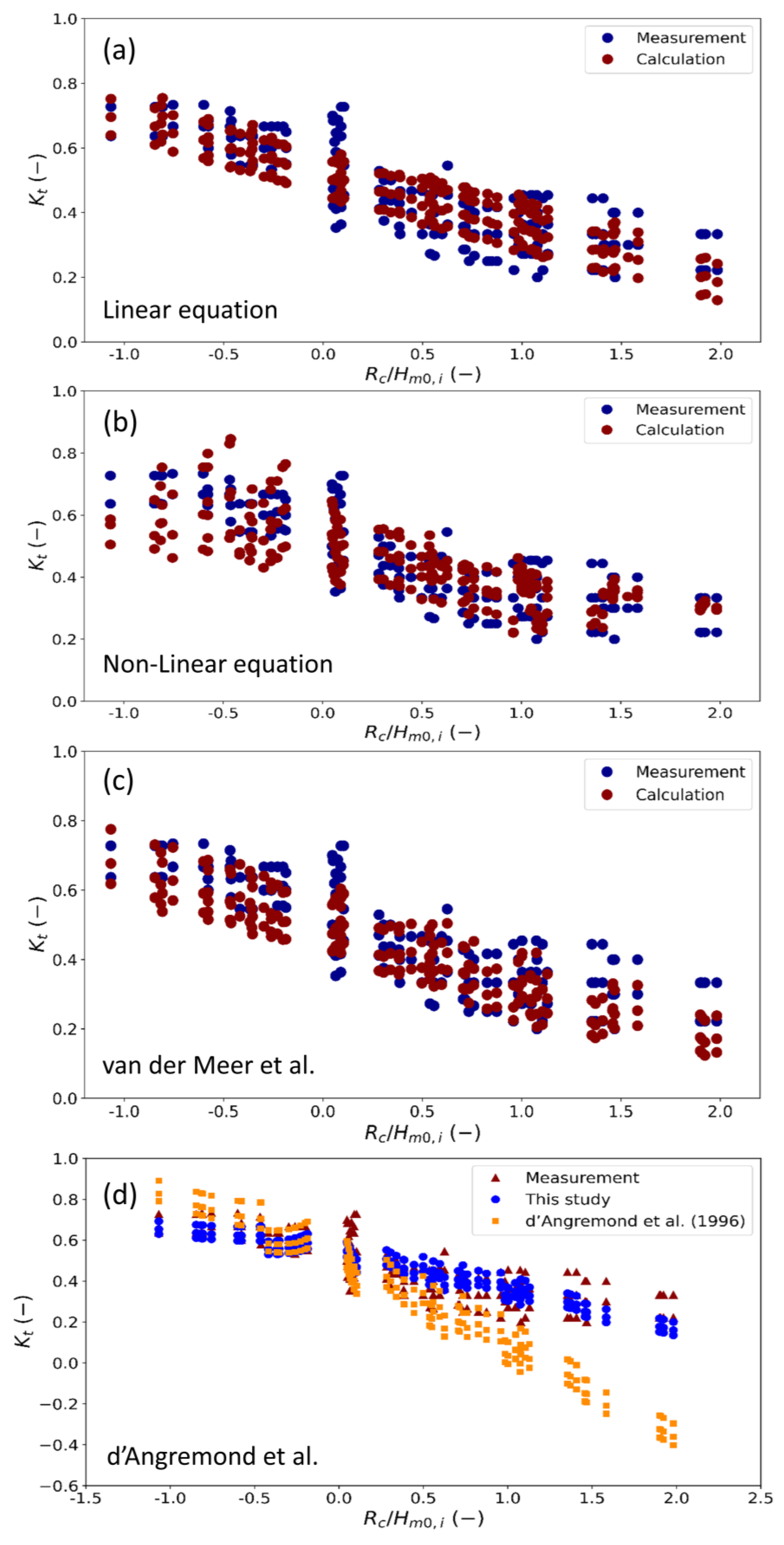
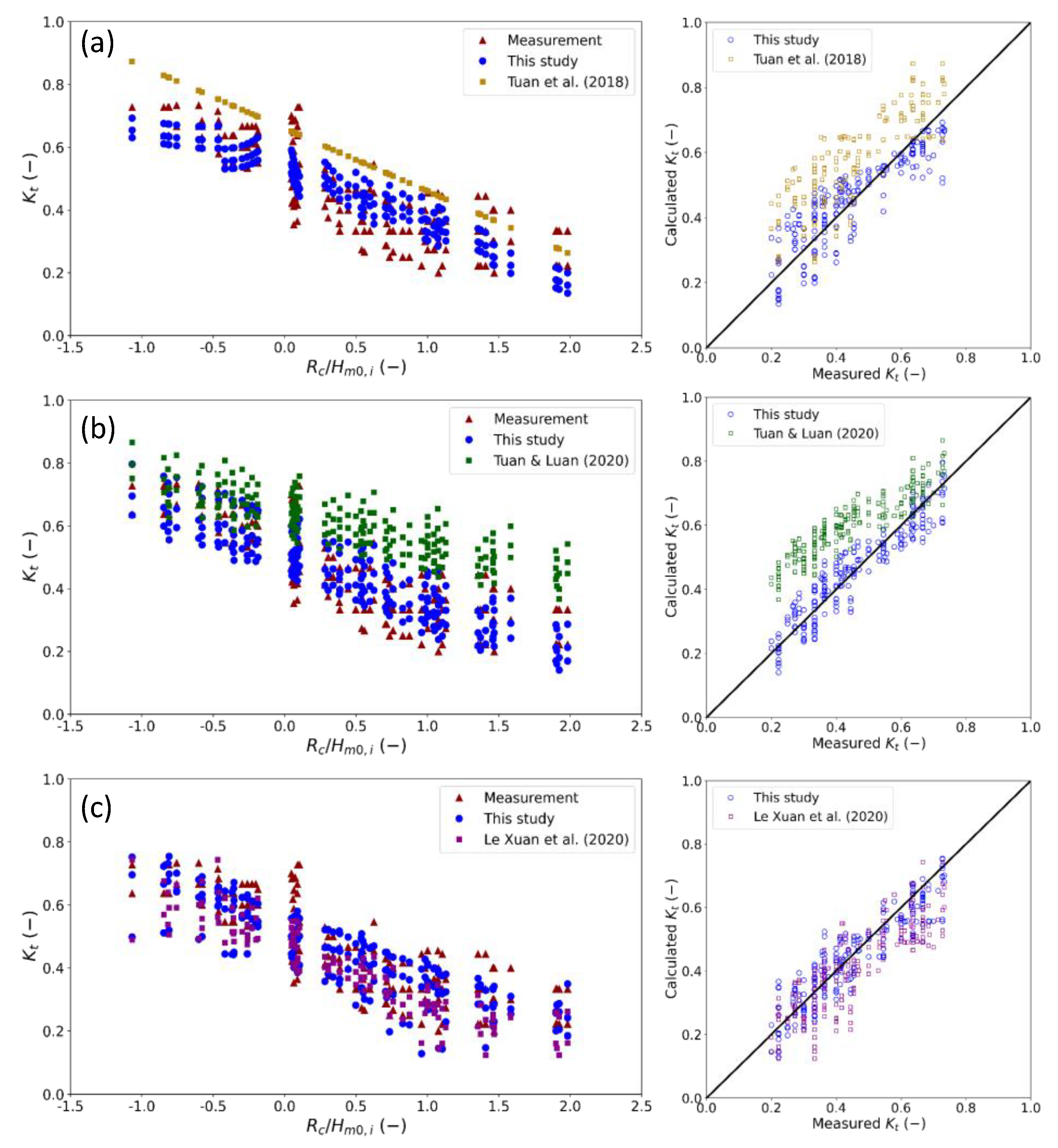
3.4. Comparison of Different Empirical Formulas for Pile–Rock Breakwaters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kondolf, G.M.; Rubin, Z.K.; Minear, J.T. Dams on the Mekong: Cumulative Sediment Starvation. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5158–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Annandale, G.; Rubin, Z. Sediment Starvation from Dams in the Lower Mekong River Basin: Magnitude of the Effect and Potential Mitigation Opportunities. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress, The Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Minderhoud, P.S.J.; Coumou, L.; Erkens, G.; Middelkoop, H.; Stouthamer, E. Mekong Delta Much Lower than Previously Assumed in Sea-Level Rise Impact Assessments. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thanh, V.Q.; Reyns, J.; Van, S.P.; Anh, D.T.; Dang, T.D.; Roelvink, D. Sediment Transport and Morphodynamical Modeling on the Estuaries and Coastal Zone of the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 186, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, V.Q.; Reyns, J.; Wackerman, C.; Eidam, E.F.; Roelvink, D. Modelling Suspended Sediment Dynamics on the Subaqueous Delta of the Mekong River. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 147, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Manh, N.; Dung, N.V.; Hung, N.N.; Kummu, M.; Merz, B.; Apel, H. Future Sediment Dynamics in the Mekong Delta Floodplains: Impacts of Hydropower Development, Climate Change and Sea Level Rise. Glob. Planet. Change 2015, 127, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erban, L.E.; Gorelick, S.M.; Zebker, H.A. Groundwater Extraction, Land Subsidence, and Sea-Level Rise in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.D.; Cochrane, T.A.; Arias, M.E. Future Hydrological Alterations in the Mekong Delta under the Impact of Water Resources Development, Land Subsidence and Sea Level Rise. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 15, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Ma, X.; Dong, G.; Chen, H.; Liu, Q.; Zang, J. Investigation on the Effects of Bragg Reflection on Harbor Oscillations. Coast. Eng. 2021, 170, 103977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, T.; San, D.C.; Schmitt, K. Shoreline Management Guidelines: Coastal Protection in the Lower Mekong Delta. Dtsch. Ges. Für. Int. ZsGiZ GmbH Manag. Nat. Resour. Coast. Zone Soc. Trang. Prov. 2013, 1, 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, V.T.; Nguyen, H.H.; Pham, D.H.; Nguyen, D.N.; Nguyen, T.T. Hollow Cylinder Breakwater for Dissipation of Wave Energy to Protect the West Coast of Ca Mau Province in Vietnam. In Vietnam Symposium on Advances in Offshore Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 599–605. [Google Scholar]
- Le Xuan, T.; Ba, H.T.; Le Manh, H.; Do Van, D.; Nguyen, N.M.; Wright, D.P.; Bui, V.H.; Mai, S.T.; Anh, D.T. Hydraulic Performance and Wave Transmission through Pile-Rock Breakwaters. Ocean Eng. 2020, 218, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Van Tam, N.; Parnell, K.E. Community Perspectives on an Internationally Funded Mangrove Restoration Project: Kien Giang Province, Vietnam. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 119, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Parnell, K.E. Gradual Expansion of Mangrove Areas as an Ecological Solution for Stabilizing a Severely Eroded Mangrove Dominated Muddy Coast. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 107, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luom, T.T.; Phong, N.T.; Anh, N.T.; Tung, N.T.; Tu, L.X.; Duong, T.A. Using Fine-Grained Sediment and Wave Attenuation as a New Measure for Evaluating the Efficacy of Offshore Breakwaters in Stabilizing an Eroded Muddy Coast: Insights from Ca Mau, the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhan, N.H. Assessing the impact of embankment to create beach in the west coast of Ca Mau province. Assess. Impact. Embankment Create Beach West Coast Ca Mau Prov. 2013, 17, 4–18. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Hur, D.-S. Deformation of Multi-Directional Random Waves Passing over an Impermeable Submerged Breakwater Installed on a Sloping Bed. Ocean Eng. 2004, 31, 1295–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, D.-S.; Lee, K.-H.; Choi, D.-S. Effect of the Slope Gradient of Submerged Breakwaters on Wave Energy Dissipation. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2011, 5, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, C.-P.; Chen, H.-B.; Lee, F.-C. Wave Transformation over Submerged Permeable Breakwater on Porous Bottom. Ocean Eng. 2006, 33, 1623–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Hsiao, S.-C. Propagation of Solitary Waves over a Submerged Permeable Breakwater. Coast. Eng. 2013, 81, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Ma, X.; Zang, J.; Dong, G.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, L. Numerical Investigation of Harbor Oscillations Induced by Focused Transient Wave Groups. Coast. Eng. 2020, 158, 103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, J.W.; Daemen, I.F. Stability and Wave Transmission at Low-Crested Rubble-Mound Structures. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1994, 120, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Angremond, K.; Van Der Meer, J.W.; De Jong, R.J. Wave Transmission at Low-Crested Structures. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Orlando, FL, USA, 2–6 September 1996; pp. 2418–2427. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meer, J.W.; Briganti, R.; Zanuttigh, B.; Wang, B. Wave Transmission and Reflection at Low-Crested Structures: Design Formulae, Oblique Wave Attack and Spectral Change. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, T.T.; Trong, L.M. Monsoon Wave Transmission at Bamboo Fences Protecting Mangroves in the Lower Mekong Delta. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 101, 102259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, T.Q.; San, D.C.; Duong, D.V. Research on the Wave Reduction Efficiency of Perforated Hollow Breakwater on the Wave Flume. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2018. Available online: https://vawr.org.vn/Upload/BaibaoKH/thieu-quang-tuan-49-2018.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2022). (In Vietnamese).




| Dimension | Scenarios | Actual (cm) | Model (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Height | - | 280 | 40 |
| Length | - | 850 | 120 |
| Width (B) | B24 | 170 | 24 |
| B38 | 270 | 38 | |
| B52 | 370 | 52 | |
| Rock mix | - | 30–50 | 4–7 |
| Centrifugal pile diameter | - | 30 | 4 |
| Scenarios | Water Depth D (cm) and Crest Freeboard Rc (cm) | Wave Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| No PRBW B24 B38 B52 | D = 20 cm (Rc = +20 cm) D = 25 cm (Rc = +15 cm) D = 30 cm (Rc = +10 cm) D = 35 cm (Rc = +5.0 cm) D = 40 cm (Rc = +0.0 cm) D = 45 cm (Rc = −5.0 cm) D = 50 cm (Rc = −10 cm) | Hs = 12 cm; Tp = 1.51 s Hs = 12 cm; Tp = 1.89 s Hs = 12 cm; Tp = 2.27 s Hs = 12 cm; Tp = 2.65 s Hs = 17 cm; Tp = 1.89 s Hs = 17 cm; Tp = 2.27 s Hs = 17 cm; Tp = 2.65 s Hs = 22 cm; Tp = 2.27 s Hs = 22 cm; Tp = 2.65 s Hs = 27 cm; Tp = 2.65 s |
| Empirical Equations | R2 | MSE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| van der Meer et al. (2005) | 0.88 | 0.0028 | 0.053 |
| d.Angremond et al. (1996) | 0.78 | 0.0041 | 0.064 |
| Linear equation (current study) | 0.82 | 0.0033 | 0.058 |
| Non-linear equation (current study) | 0.73 | 0.0044 | 0.066 |
| Tuan et al. (2018) | 0.04 | 0.0224 | 0.150 |
| Tuan and Luan. (2020) | 0.22 | 0.0285 | 0.169 |
| Le Xuan et al. (2020) | 0.61 | 0.0086 | 0.093 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, N.-M.; Van, D.D.; Le Duy, T.; Pham, N.T.; Duc Dang, T.; Tanim, A.H.; Wright, D.; Thanh, P.N.; Anh, D.T. The Influence of Crest Width and Working States on Wave Transmission of Pile–Rock Breakwaters in the Coastal Mekong Delta. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111762
Nguyen N-M, Van DD, Le Duy T, Pham NT, Duc Dang T, Tanim AH, Wright D, Thanh PN, Anh DT. The Influence of Crest Width and Working States on Wave Transmission of Pile–Rock Breakwaters in the Coastal Mekong Delta. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(11):1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111762
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Nguyet-Minh, Duong Do Van, Tu Le Duy, Nhat Truong Pham, Thanh Duc Dang, Ahad Hasan Tanim, David Wright, Phong Nguyen Thanh, and Duong Tran Anh. 2022. "The Influence of Crest Width and Working States on Wave Transmission of Pile–Rock Breakwaters in the Coastal Mekong Delta" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 11: 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111762
APA StyleNguyen, N.-M., Van, D. D., Le Duy, T., Pham, N. T., Duc Dang, T., Tanim, A. H., Wright, D., Thanh, P. N., & Anh, D. T. (2022). The Influence of Crest Width and Working States on Wave Transmission of Pile–Rock Breakwaters in the Coastal Mekong Delta. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(11), 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111762






