Measuring Bed Exchange Properties of Cohesive Sediments Using Tripod Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Field Measurements
2.2. The K-P Model and Data Processing
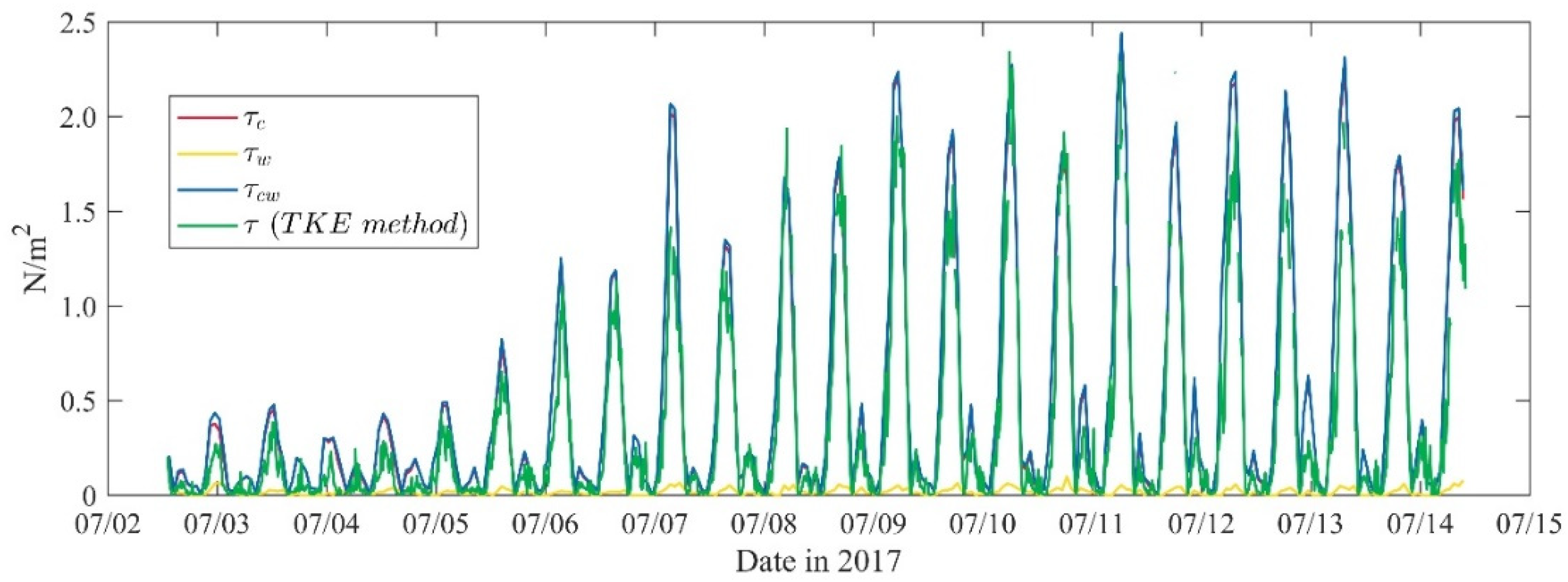
2.3. The Bed Shear Stress
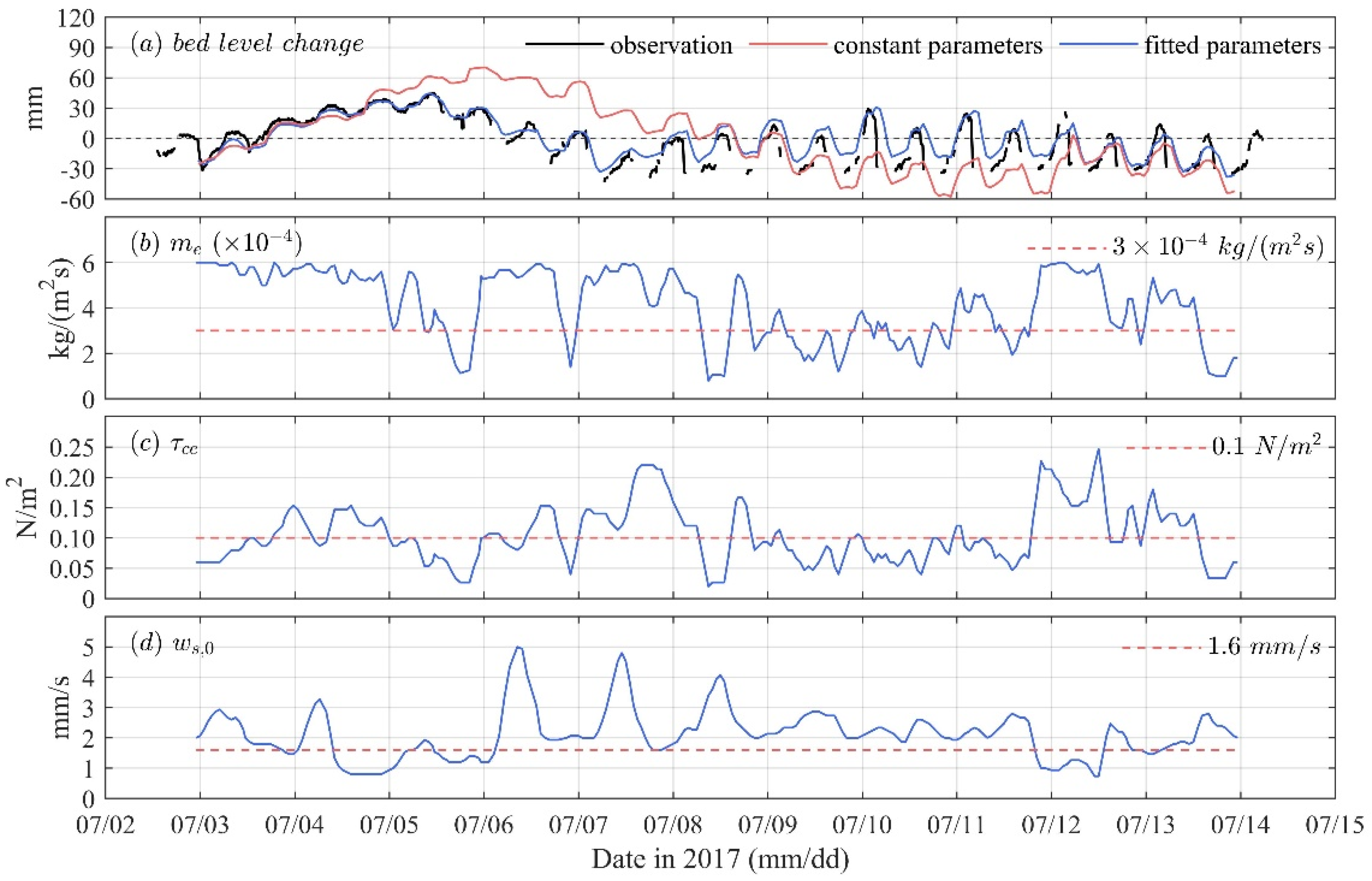
2.4. Data Fitting Methodology
3. Observational Data
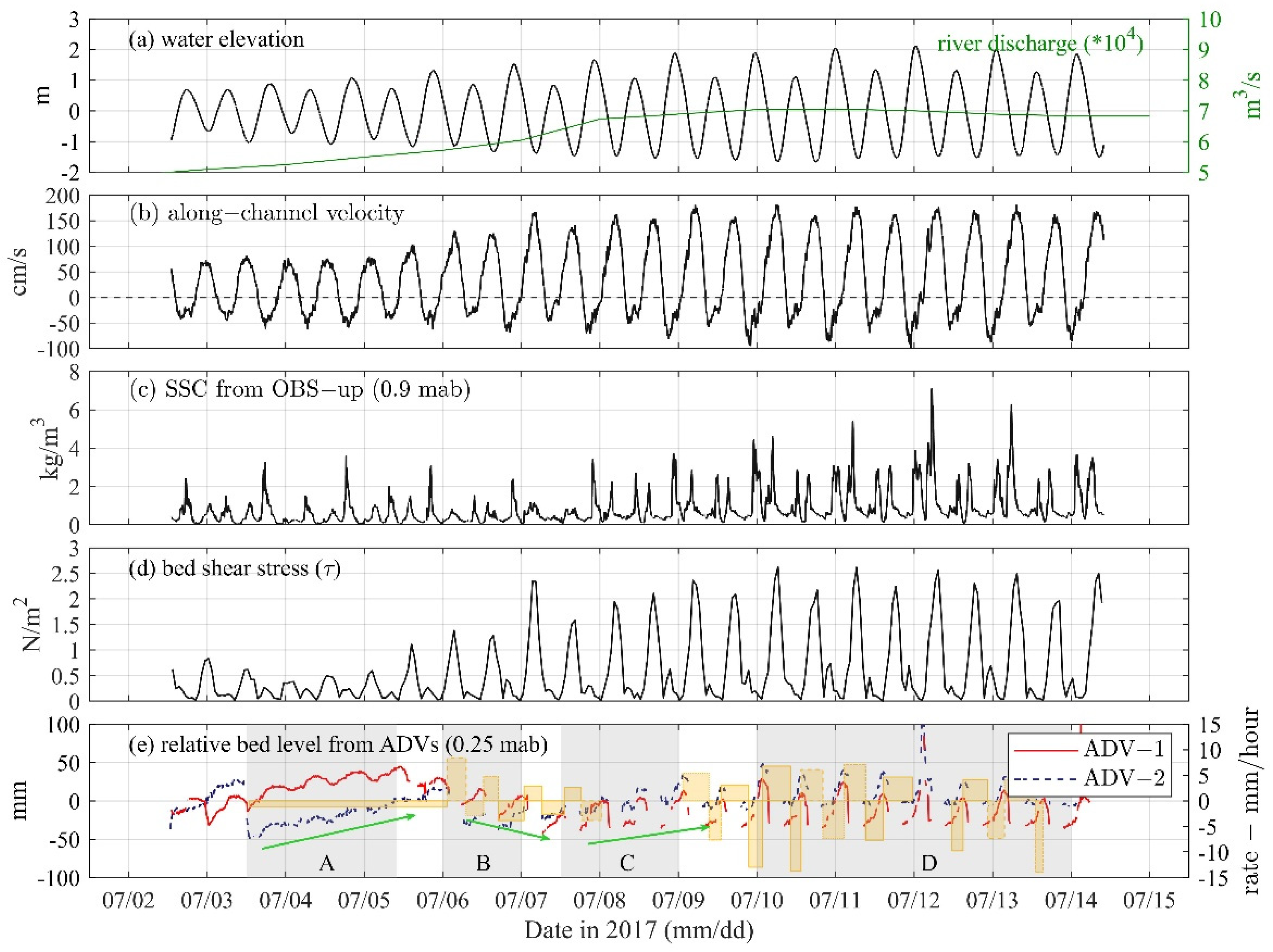
3.1. General Observations
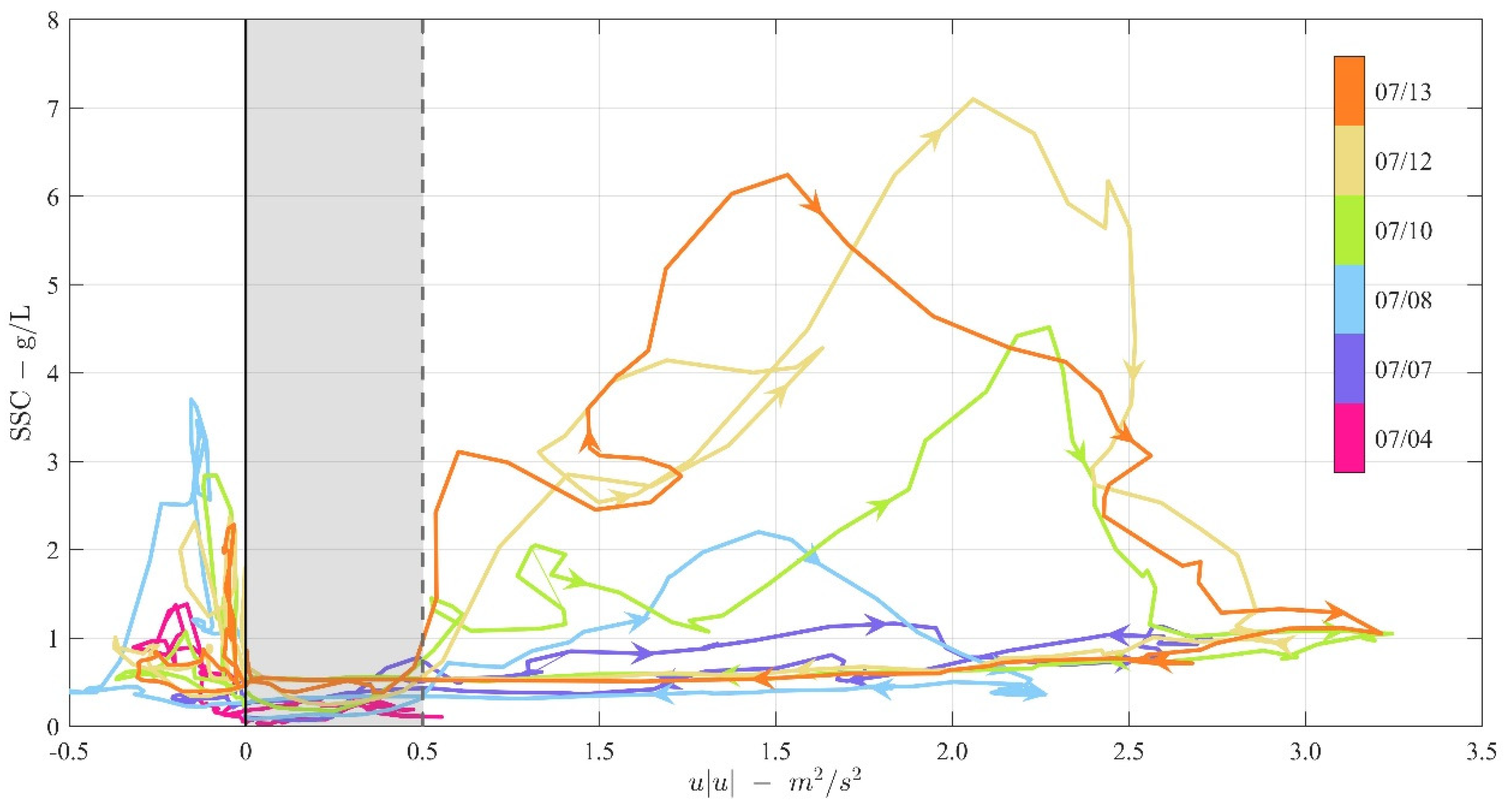
3.2. Sediment Dynamics
4. A parameter Space Diagram for the K-P Formulations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ariathurai, C.R. A Finite Element Model for Sediment Transport in Estuaries; University of California, Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Krone, R.B. Flume Studies of the Transport of Sediment in Estuarial Shoaling Processes: Final Report; Hydraulic Engineering Laboratory and Sanitary Engineering Research Laboratory, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Partheniades, E.A. Erosion and Deposition of Cohesive Soils. J. Hydraul. Div. 1965, 1, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterwerp, J.C.; van Kesteren, W.G.M. Introduction to the Physics of Cohesive Sediment Dynamics in the Marine Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; ISBN 0444515534. [Google Scholar]
- de Nijs, M.A.J.; Pietrzak, J.D. Saltwater Intrusion and ETM Dynamics in a Tidally-Energetic Stratified Estuary. Ocean Model 2012, 49–50, 60–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, L.P.; Halka, J.P. Assessing the Paradigm of Mutually Exclusive Erosion and Deposition of Mud, with Examples from Upper Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Geol. 1993, 114, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Maren, D.S.; Winterwerp, J.C.; Wu, B.S.; Zhou, J.J. Modelling Hyperconcentrated Flow in the Yellow River. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, Y.M.; Schuttelaars, H.M.; Schramkowski, G.P.; Brouwer, R.L. Modeling the Transition to High Sediment Concentrations as a Response to Channel Deepening in the Ems River Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 1578–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Shen, F.; Guo, W.; Chen, C.; Ding, P. Estimation of Critical Shear Stress for Erosion in the Changjiang Estuary: A Synergy Research of Observation, GOCI Sensing and Modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 8439–8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, L.P. Modeling a Dynamically Varying Mixed Sediment Bed with Erosion, Deposition, Bioturbation, Consolidation, and Armoring. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 1263–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; van der Wegen, M.; Jagers, B.; Coco, G. Modelling the Role of Self-Weight Consolidation on the Morphodynamics of Accretional Mudflats. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 76, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterwerp, J.C.; Zhou, Z.; Battista, G.; Van Kessel, T.; Jagers, H.R.A.; Van Maren, D.S.; Van Der Wegen, M. Efficient Consolidation Model for Morphodynamic Simulations in Low-SPM Environments. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, A.J.; Dyer, K.R. Mass Settling Flux of Fine Sediments in Northern European Estuaries: Measurements and Predictions. Mar. Geol. 2007, 245, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Friedrichs, C.T. Size and Settling Velocities of Cohesive Flocs and Suspended Sediment Aggregates in a Trailing Suction Hopper Dredge Plume. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S50–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsby, R.L.; Manning, A.J.; Spearman, J.; Whitehouse, R.J.S. Settling Velocity and Mass Settling Flux of Flocculated Estuarine Sediments. Mar. Geol. 2013, 339, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, C.L.; Grant, J.; Daborn, G.R.; Black, K. Sea Carousel-A Benthic, Annular Flume. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1992, 34, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickhudt, P.J.; Friedrichs, C.T.; Sanford, L.P. Mud Matrix Solids Fraction and Bed Erodibility in the York River Estuary, USA, and Other Muddy Environments. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, W.; Ding, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.B.; Gu, J. Formation of Concentrated Benthic Suspension in a Time-Dependent Salt Wedge Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 8581–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.B.; Ke, K.; Yi, J.; Ding, P. Dynamic Response of the Fluid Mud to a Tropical Storm. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC015419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, R.; Soulsby, R.; Roberts, W.; Mitchener, H. Dynamics of Estuarine Muds; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 2000; ISBN 0-7277-3762-7. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, O.S. Spectral Wave-Current Bottom Boundary Layer Flows. In Proceedings of the Coastal Engineering 1994, Kobe, Japan, 23–28 October 1994; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 384–398. [Google Scholar]
- Dankers, P.J.T.; Winterwerp, J.C.; van Kesteren, W.G.M. A Preliminary Study on the Hindered Settling of Kaolinite Flocs. In Proceedings in Marine Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 8, pp. 227–241. ISBN 9780444521637. [Google Scholar]
- Dankers, P.J.T.; Winterwerp, J.C. Hindered Settling of Mud Flocs: Theory and Validation. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- te Slaa, S.; He, Q.; van Maren, D.S.; Winterwerp, J.C. Sedimentation Processes in Silt-Rich Sediment Systems. Ocean Dyn. 2013, 63, 399–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-C.; Friedrichs, C.T.; Maa, J.P.-Y.; Wright, L.D. Estimating Bottom Stress in Tidal Boundary Layer from Acoustic Doppler Velocimeter Data. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2000, 126, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsby, R.L. The Bottom Boundary Layer of Shelf Seas. In Physical Oceanography of Coastal and Shelf Seas; Johns, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; Volume 35, pp. 189–266. [Google Scholar]
- Soulsby, R.L.; Dyer, K.R. The Form of the Near-Bed Velocity Profile in a Tidally Accelerating Flow. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdows, J.; Friend, P.L.; Bale, A.J.; Brinsley, M.D.; Pope, N.D.; Thompson, C.E.L. Inter-Comparison between Five Devices for Determining Erodability of Intertidal Sediments. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Dong, P.; Mamat, M.; Nik, W.B.W.; Mohd, M.H. The Critical Shear Stresses for Sand and Mud Mixture. Appl. Math. Sci. 2011, 5, 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Winterwerp, J.C.; van Kesteren, W.G.M.; van Prooijen, B.; Jacobs, W. A Conceptual Framework for Shear Flow-Induced Erosion of Soft Cohesive Sediment Beds. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117, C10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, C.L.; Daborn, G.; Christian, H.; Atkinson, A.; Robertson, A. In Situ Erosion Measurements on Fine-Grained Sediments from the Bay of Fundy. Mar. Geol. 1992, 108, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Maren, D.S.; Cronin, K. Uncertainty in Complex Three-Dimensional Sediment Transport Models: Equifinality in a Model Application of the Ems Estuary, The Netherlands. Ocean Dyn. 2016, 66, 1665–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agrawal, Y.C.; Pottsmith, H.C. Instruments for Particle Size and Settling Velocity Observations in Sediment Transport. Mar. Geol. 2000, 168, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugate, D.C.; Friedrichs, C.T. Determining Concentration and Fall Velocity of Estuarine Particle Populations Using Adv, Obs and Lisst. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 1867–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Instrument Deployed | Distance above Bed (m) | Sampling Interval (min) | Sampling Configuration | Survey Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADCP upward | 1.2 | / | 120 s (1 h for wave observation) | Profile velocity, waves |
| ADCP downward | 1.0 | / | 120 s | Profile velocity |
| PCM | 1.15 | 2 | 0.2 Hz (every first 50 s) | Velocity |
| ADV | 0.25 | 10 | 16 Hz (every first 70 s) | Near-bed velocity |
| OBS | 0.9 | / | 100 s | Salinity, temperature, turbidity, pressure |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Ge, J.; van Maren, D.S.; Gu, J.; Ding, P.; Wang, Z. Measuring Bed Exchange Properties of Cohesive Sediments Using Tripod Data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111713
Zhou Z, Ge J, van Maren DS, Gu J, Ding P, Wang Z. Measuring Bed Exchange Properties of Cohesive Sediments Using Tripod Data. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(11):1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111713
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zaiyang, Jianzhong Ge, Dirk Sebastiaan van Maren, Jinghua Gu, Pingxing Ding, and Zhengbing Wang. 2022. "Measuring Bed Exchange Properties of Cohesive Sediments Using Tripod Data" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 11: 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111713
APA StyleZhou, Z., Ge, J., van Maren, D. S., Gu, J., Ding, P., & Wang, Z. (2022). Measuring Bed Exchange Properties of Cohesive Sediments Using Tripod Data. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(11), 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111713





