Boussinesq Simulation of Coastal Wave Interaction with Bottom-Mounted Porous Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
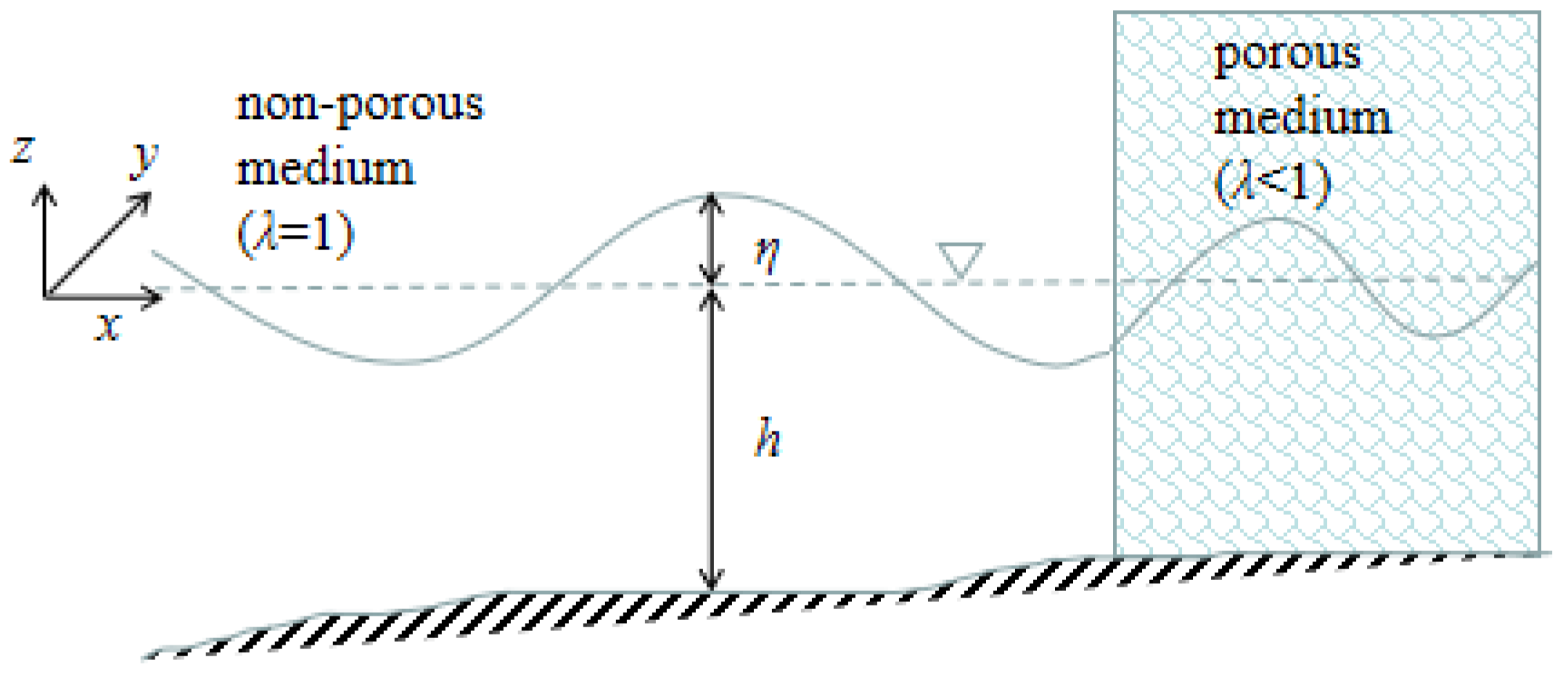
2. Model Description
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. Numerical Scheme and Boundary Conditions
2.3. GPU Implementation
3. Physical Wave Flume Experiments
4. Results and Discussion
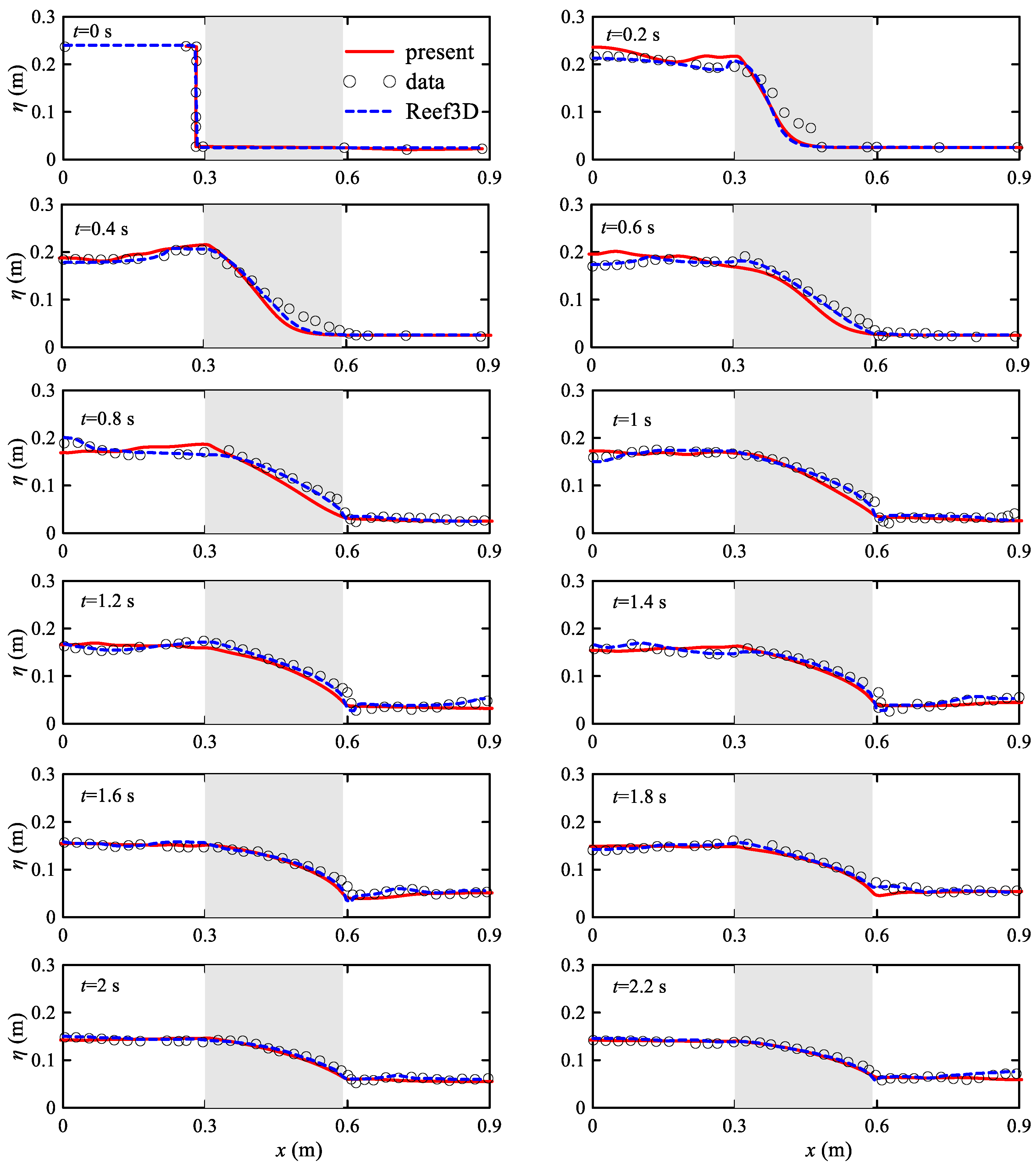
4.1. Dam Break on a Porous Structure
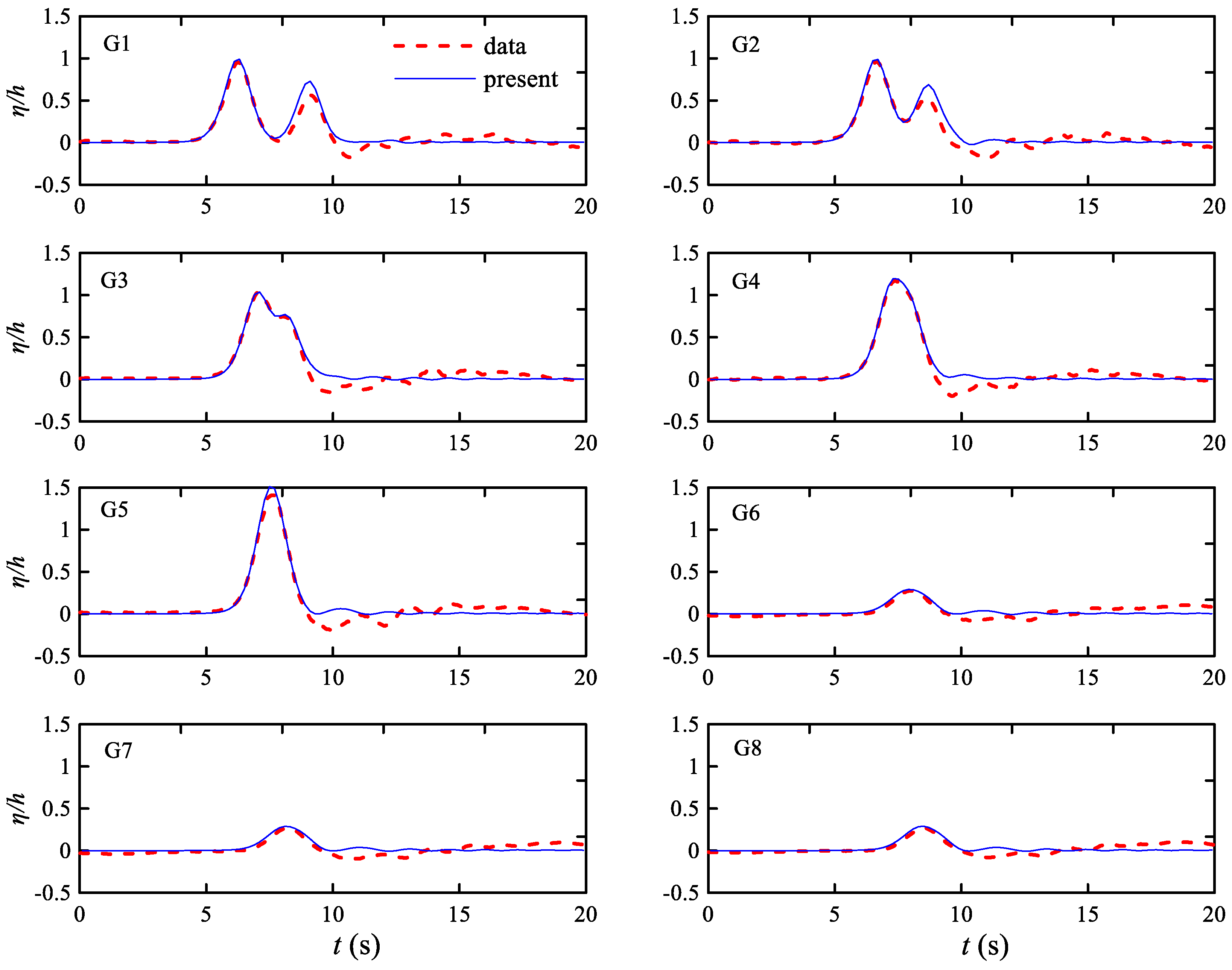
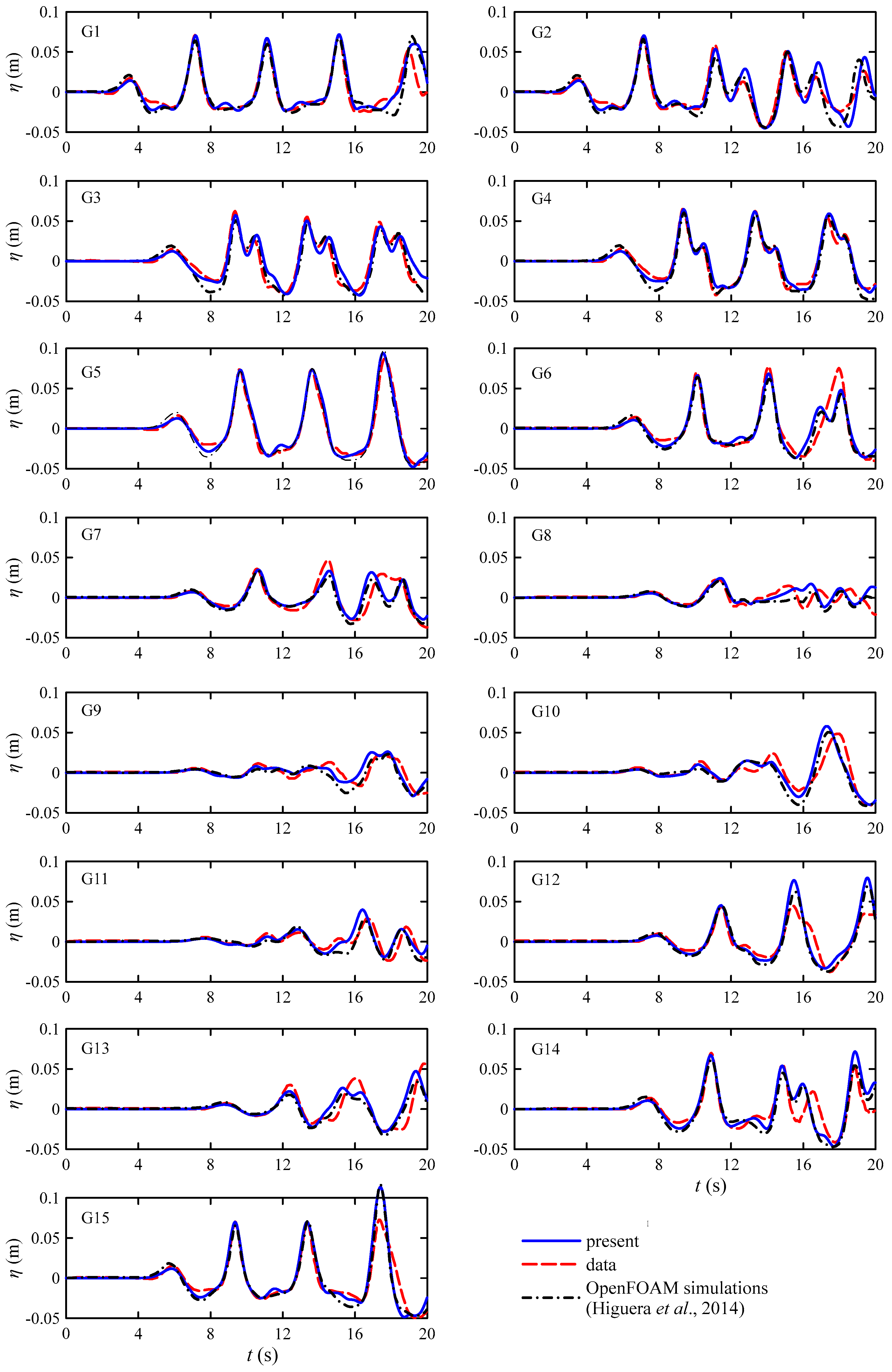
4.2. Solitary Wave Passing through Porous Breakwaters
4.3. Regular Wave Passing through Porous Breakwaters
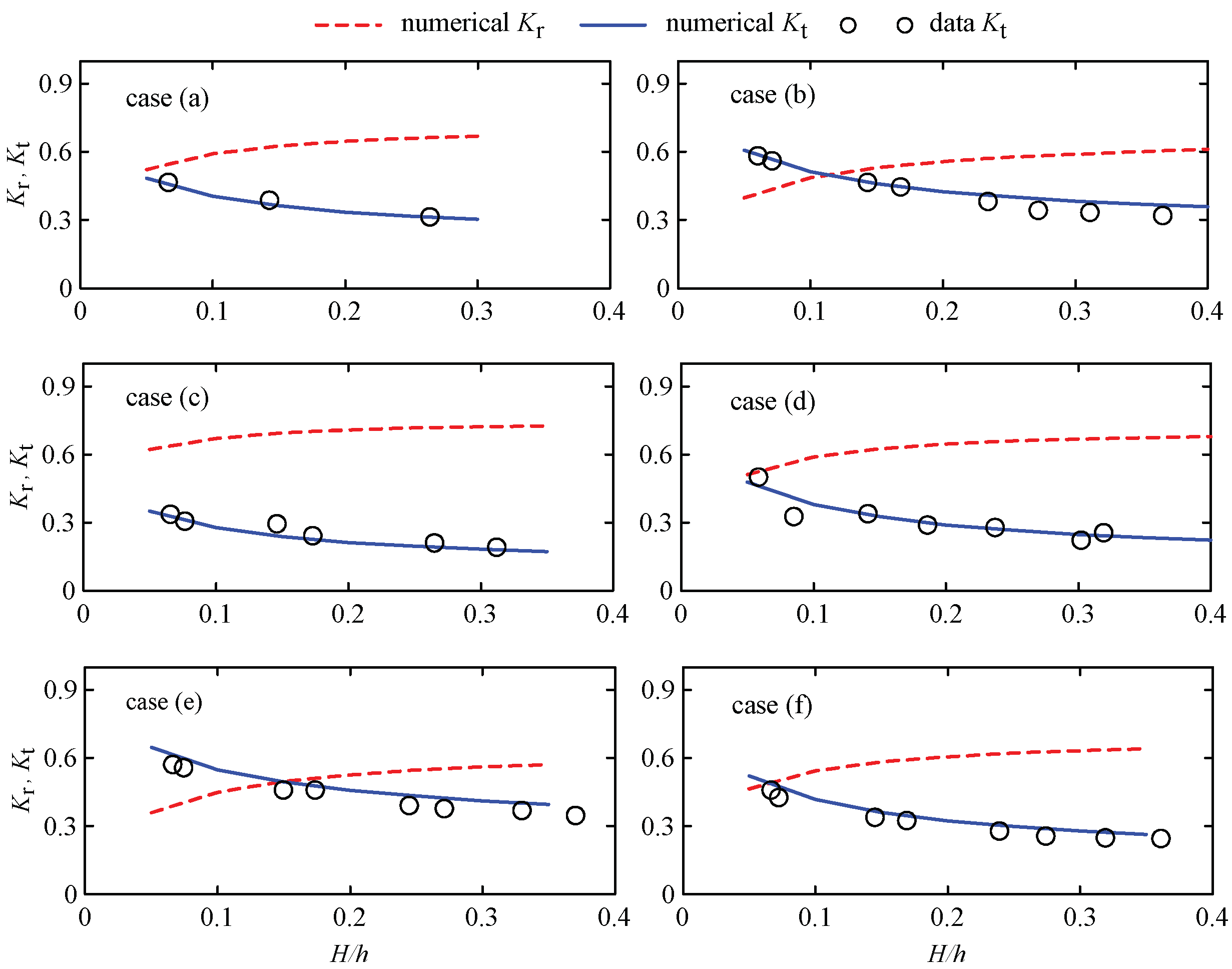
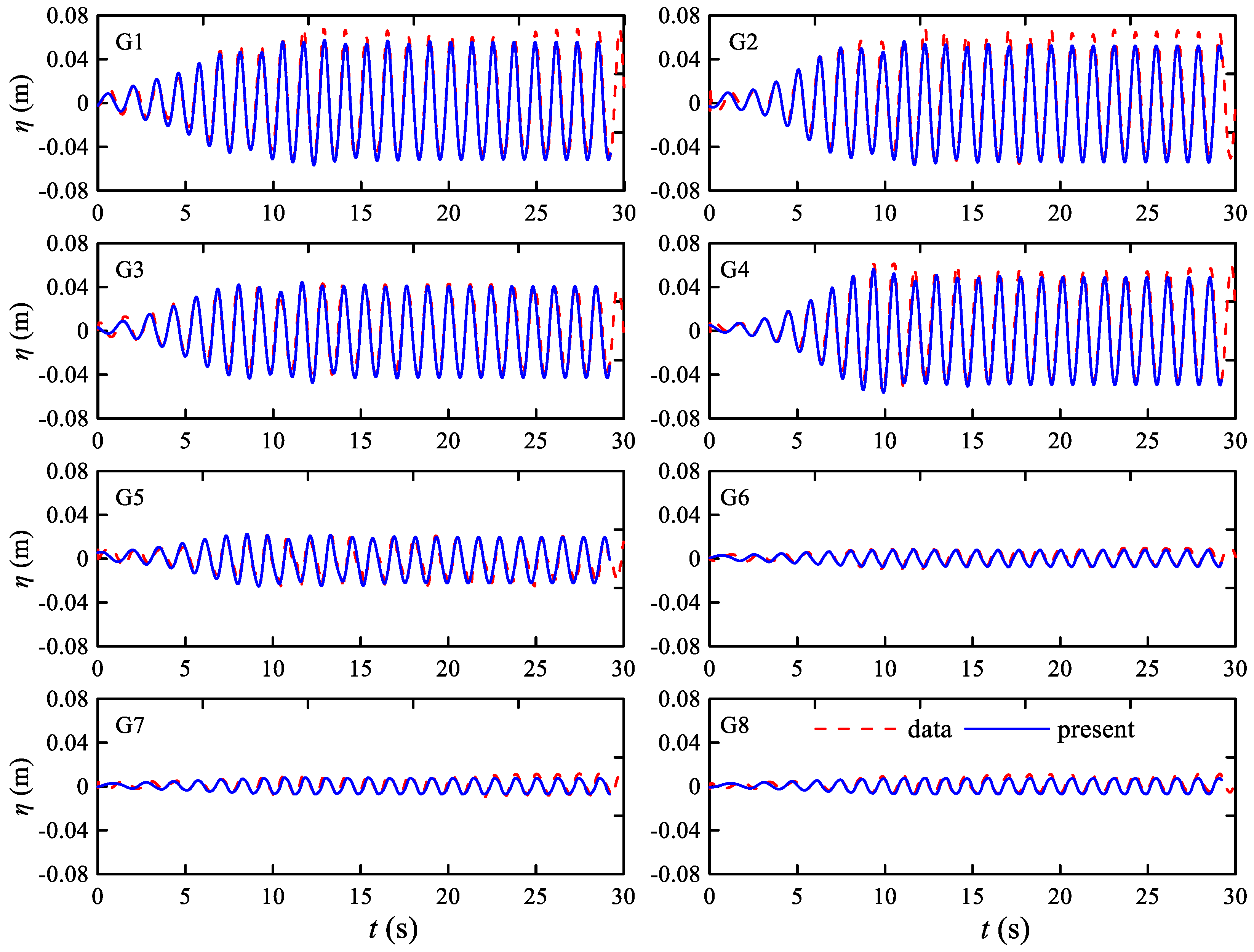
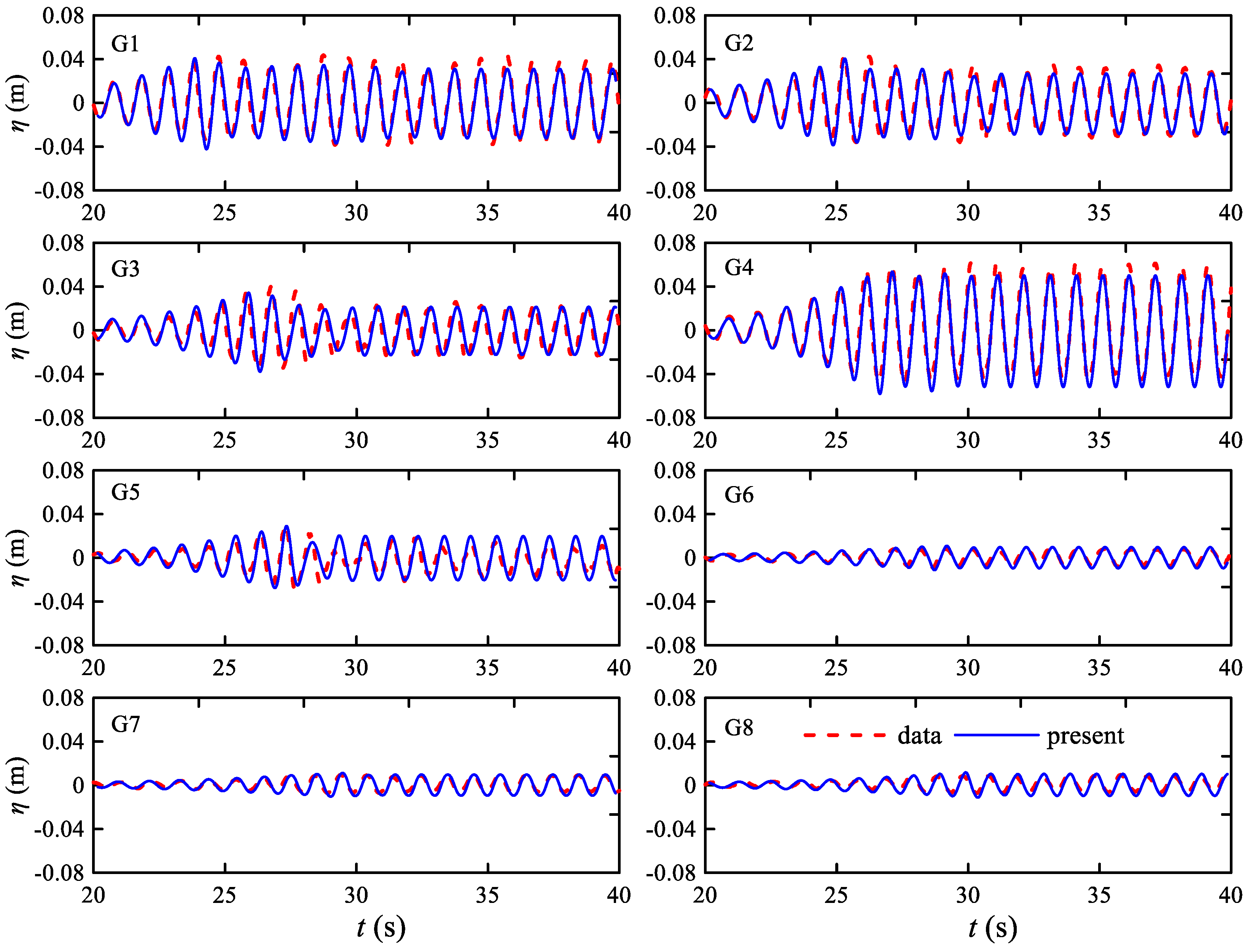
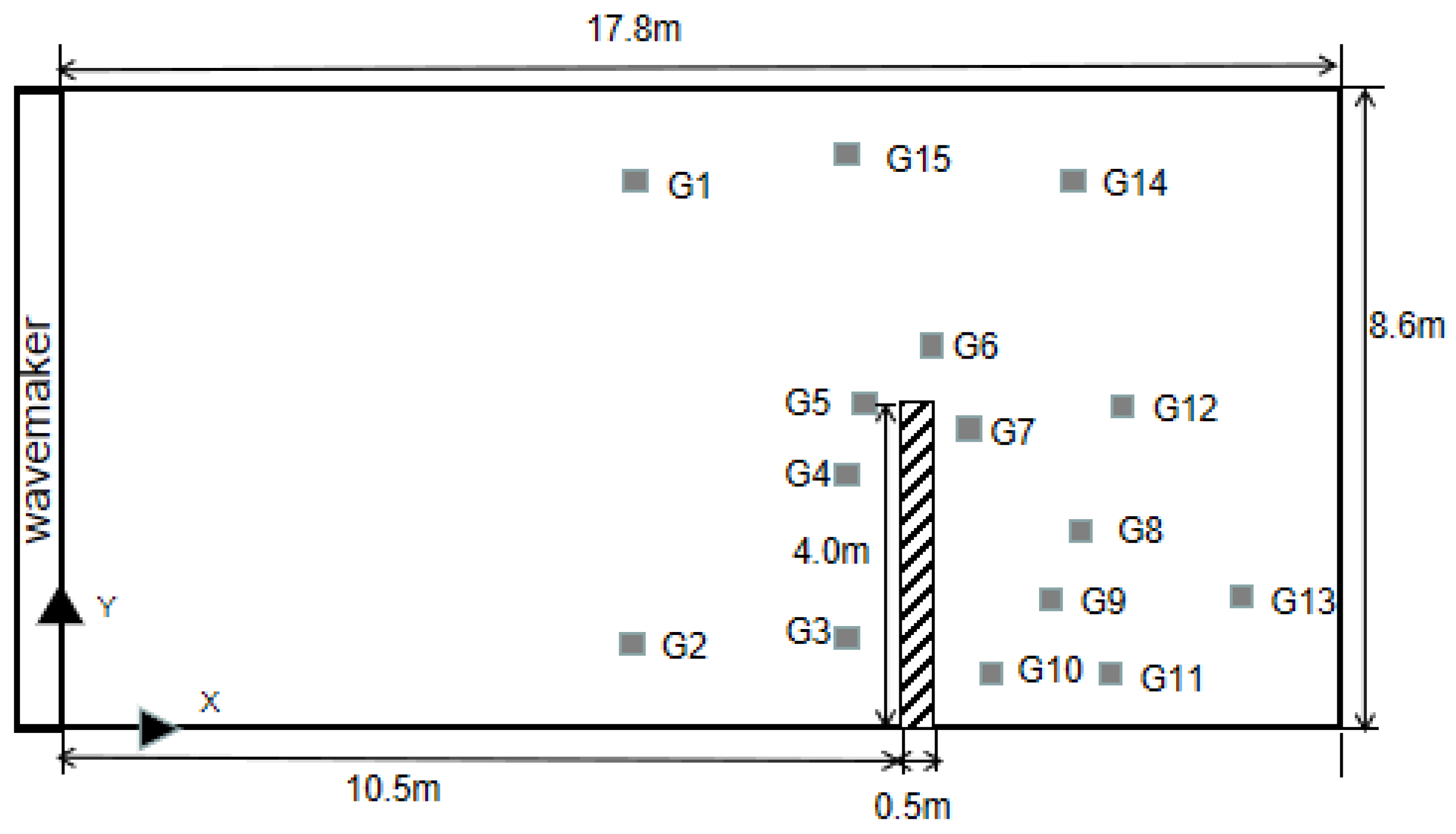
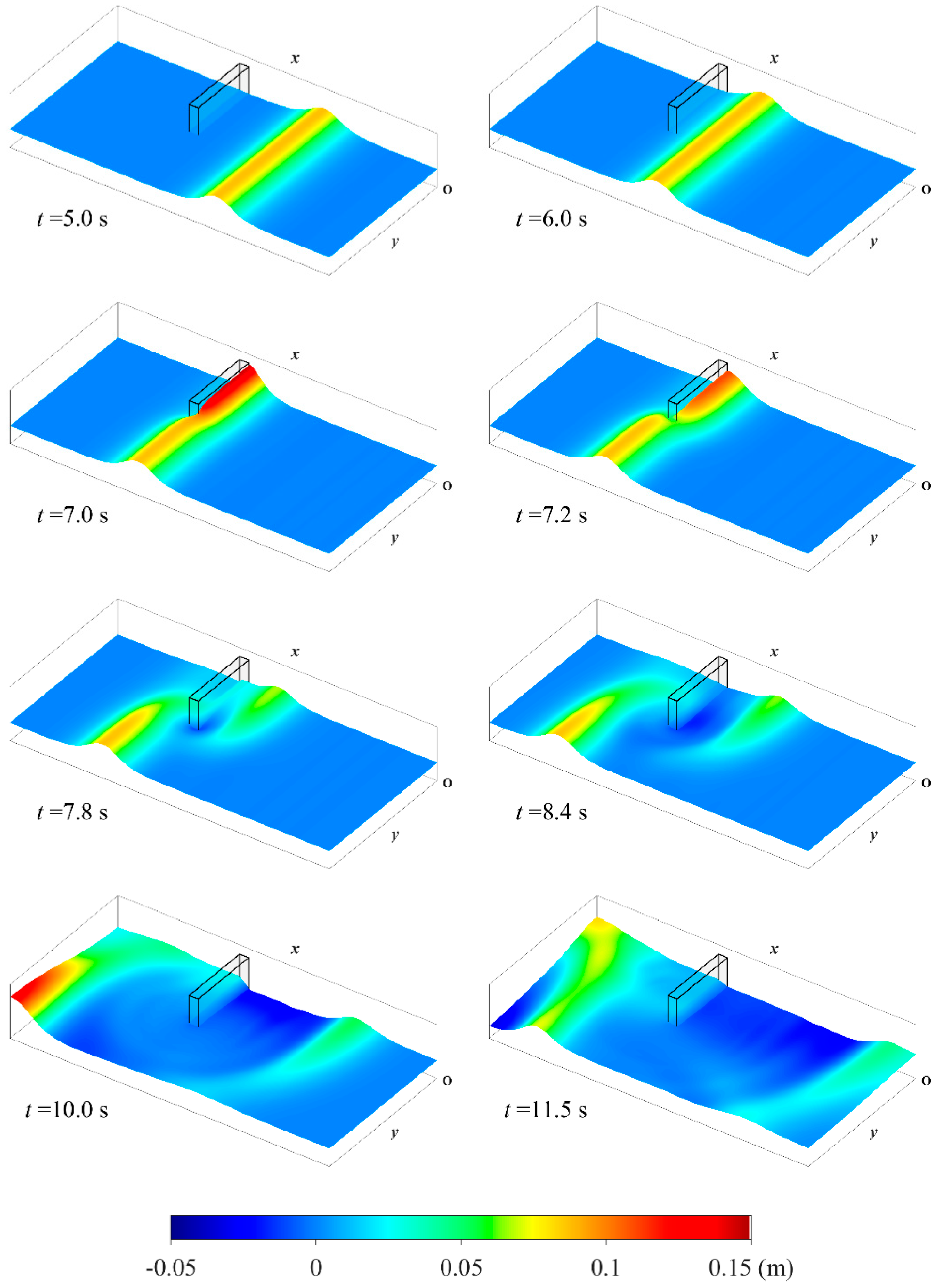
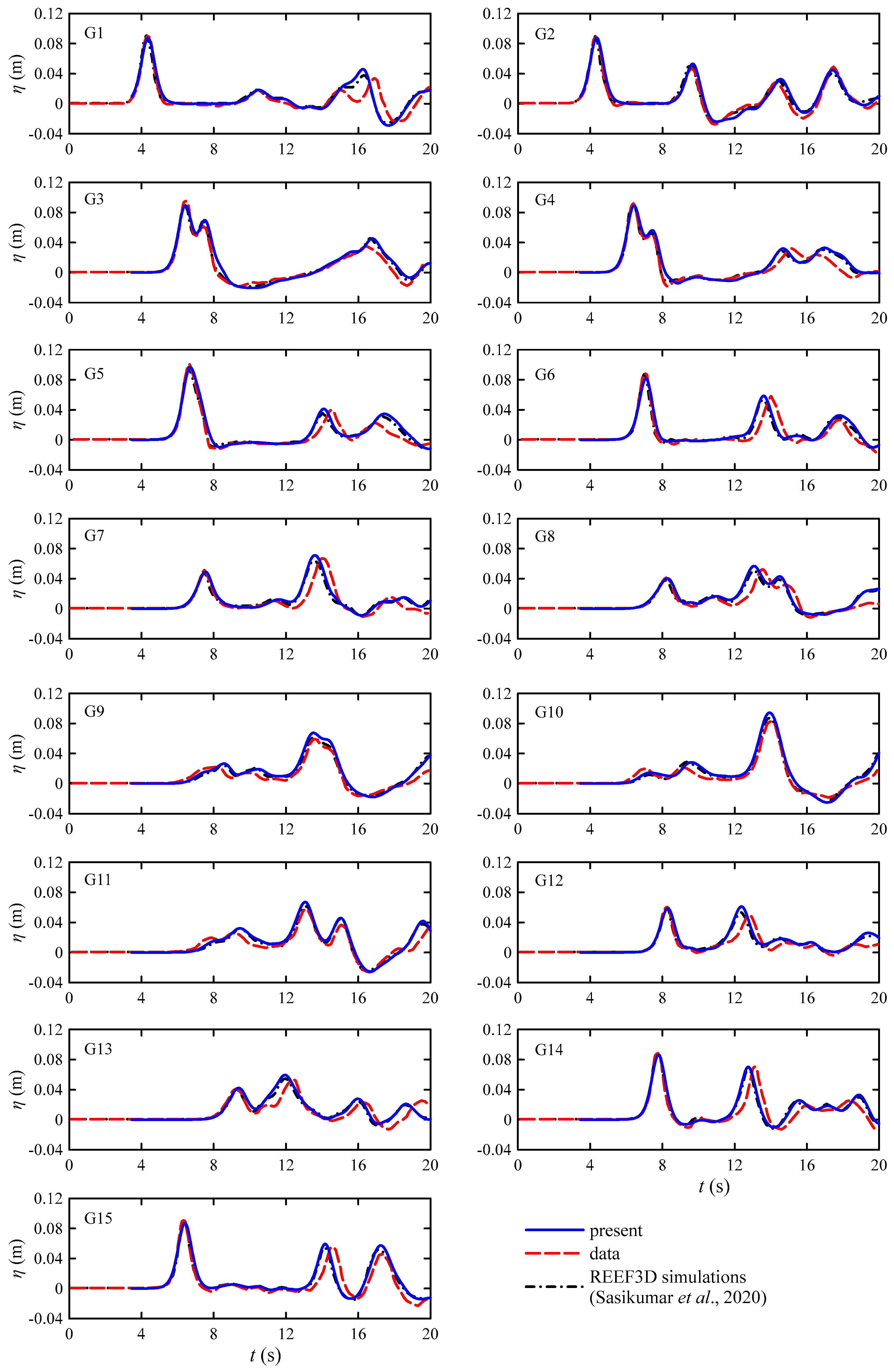
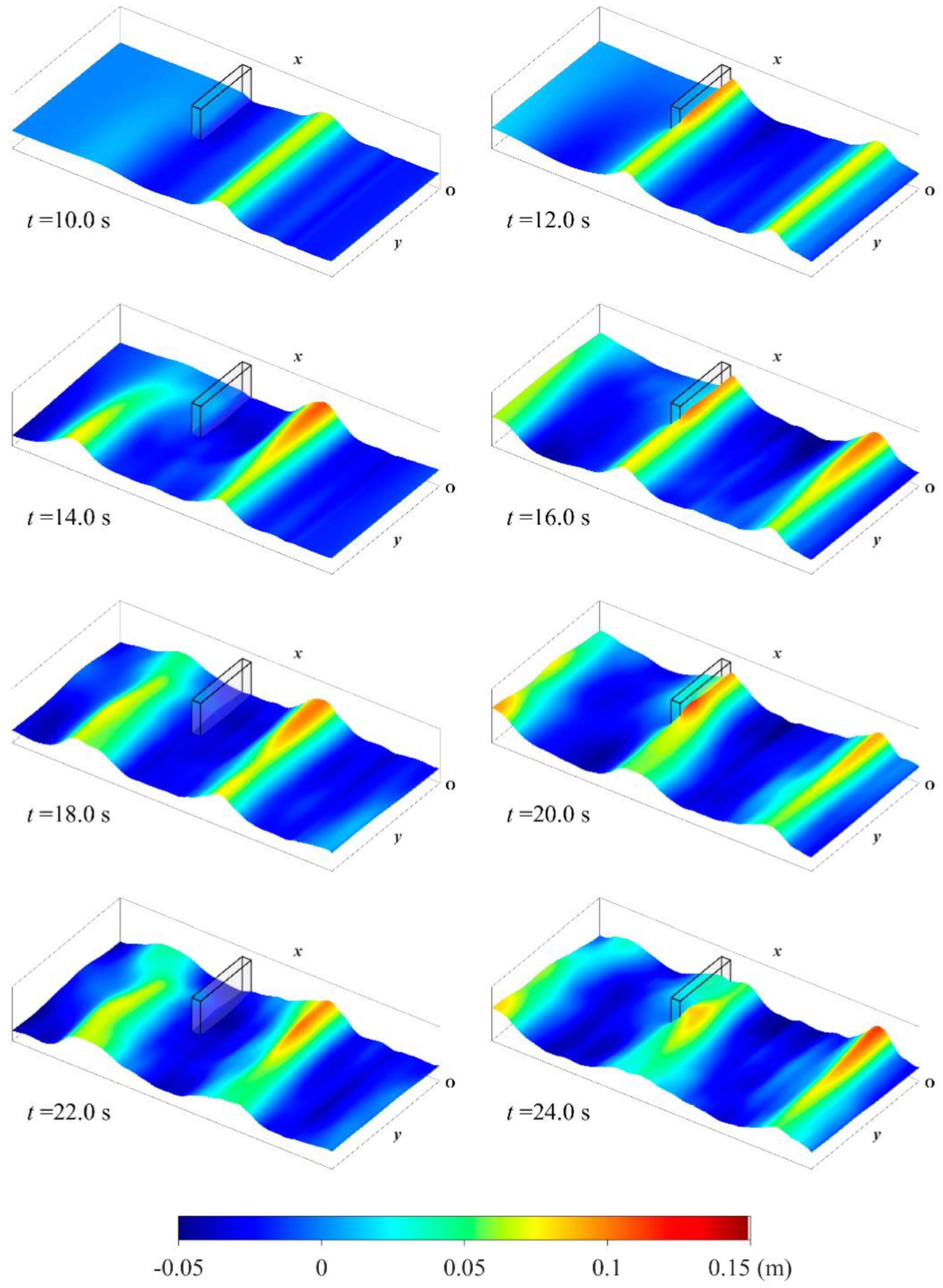
4.4. Wave Passing through Porous Breakwater in a Wave Basin
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, P.L.F.; Lin, P.; Chang, K.A.; Sakakiyama, T. Numerical modeling of wave interaction with porous structures. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1999, 125, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.Z.; Jiang, C.B.; Wang, Y.Y. A coupled numerical model of wave interaction with porous medium. Ocean Eng. 2009, 36, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera, P.; Lara, J.L.; Losada, I.J. Three-dimensional interaction of waves and porous coastal structures using OpenFOAM®. Part I: Formulation and validation. Coast. Eng. 2014, 83, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, A.; Kamath, A.; Bihs, H. Modeling porous coastal structures using a level set method based VRANS-solver on staggered grids. Coast. Eng. J. 2020, 62, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cea, L.; Vázquez-Cendón, E. Unstructured finite volume discretization of two-dimensional depth-averaged shallow water equations with porosity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2010, 63, 903–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K. A finite volume method for numerical simulation of shallow water models with porosity. Comput. Fluids 2014, 104, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, M.B.; Petersen, H.M.; Skovgaard, O. On the numerical modelling of short waves in shallow water. J. Hydraul. Res. 1978, 16, 173–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.A.; Warren, I.R. Performance of a numerical short-wave model. Coast. Eng. 1984, 8, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.L.F.; Wen, J. Nonlinear diffusive surface waves in porous media. J. Fluid Mech. 1997, 347, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.N.; Lee, C.; Jung, T.H. Extended Boussinesq equations for waves in porous media. Coast. Eng. 2018, 139, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S. Incompressible SPH flow model for wave interactions with porous media. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Namin, M.M. Moving particle method for modeling wave interaction with porous structures. Coast. Eng. 2013, 74, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Wen, H.; Dong, P.; Wang, Y. Improved SPH simulation of wave motions and turbulent flows through porous media. Coast. Eng. 2016, 107, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIKE Powered by DHI. Available online: https://www.mikepoweredbydhi.com (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- Kirby, J.T.; Wei, G.; Chen, Q.; Kennedy, A.; Dalrymple, R.A. FUNWAVE 1.0 Fully Nonlinear Boussinesq Wave Model Documentation and User’s Manual; University of Delaware: Newwark, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lynett, P.J. A Multi-Layer Approach to Modeling Generation, Propagation, and Interaction of Water Waves. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, E.C.; Isobe, M.; Watanabe, A. Boussinesq equations for wave transformation on porous beds. Coast. Eng. 1997, 30, 125–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.C.; Liu, P.L.F.; Chen, Y. Nonlinear water waves propagating over a permeable bed. In Proceedings of the Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences of the Conference, Ithaca, NY, USA, 8 June 2002; pp. 1291–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, E.C.; Chen, Q. Numerical modeling of nonlinear water waves over heterogeneous porous beds. Ocean Eng. 2007, 34, 1303–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.C.; Hu, K.C.; Hwung, H.H. Extended Boussinesq equations for water-wave propagation in porous media. J. Eng. Mech. 2010, 136, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peregrine, D.H. Long waves on a beach. J. Fluid Mech. 1967, 27, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.A. Wave reflection from a vertical permeable wave absorber. Coast. Eng. 1983, 7, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynett, P.; Liu, P.; Losada, I.; Vidal, C. Solitary wave interaction with porous breakwaters. J. Waterw. Port. Coast. Ocean Eng. 2000, 126, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Y. Long Waves in ocean and coastal waters. J. Eng. Mech. 1981, 107, 501–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.A.; Sørensen, S.R. A new form of the Boussinesq equations with improved linear dispersion characteristics. Part 2. A slowly-varying bathymetry. Coast. Eng. 1992, 18, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Kirby, J.T.; Harris, J.C.; Geiman, J.D.; Grilli, S.T. A high-order adaptive time-stepping TVD solver for Boussinesq modeling of breaking waves and coastal inundation. Ocean Model 2012, 43–44, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Zou, Z.; Dong, P.; Liu, Z.; Gui, Q.; Yin, J. An efficient shock capturing algorithm to the extended Boussinesq wave equations. Appl. Ocean Res. 2013, 43, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Liu, Z.; Zou, Z. Fully Nonlinear Modeling Wave Transformation over Fringing Reefs Using Shock-Capturing Boussinesq Model. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 32, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Sun, J.; Song, G.; Wang, G.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z. A GPU accelerated Boussinesq-type model for coastal waves. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Lee, C.; Suh, K.D. Extended Boussinesq equations for rapidly varying topography. Ocean Eng. 2009, 36, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Shi, F.; Kirby, J.T.; Yu, F. FUNWAVE-GPU: Multiple-GPU acceleration of a Boussinesq-type wave model. J. Adv. Model Earth Sys. 2020, 12, e2019MS001957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkol, S.; Lynett, P. Celeris: A GPU-accelerated open source software with a Boussinesq-type wave solver for real-time interactive simulation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2017, 217, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Oh, C.; Yi, Y.; Kim, D.H. GPU-Accelerated Boussinesq Model Using Compute Unified Device Architecture FORTRAN. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 85, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the validation of models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, C.; Losada, M.A.; Medina, R.; Rubio, J. Solitary wave transmission through porous breakwaves. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Torremolinos, Spain, 29 January 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, J.L.; del Jesus, M.; Losada, I.J. Three-dimensional interaction of waves and porous coastal structures: Part II: Experimental validation. Coast. Eng. 2012, 64, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Case No. | Wave Type | H (m) | T (s) | h (m) | kh | H/h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Regular wave | 0.072 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 1.72 | 0.18 |
| R2 | Regular wave | 0.072 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 1.30 | 0.18 |
| R3 | Regular wave | 0.076 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 0.53 | 0.19 |
| S1 | Solitary wave | 0.046 | - | 0.4 | - | 0.12 |
| S2 | Solitary wave | 0.086 | - | 0.4 | - | 0.22 |
| Case | h (cm) | H/h | Structure Width (cm) | d50 (cm) | λ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | 30.0 | 0.06–0.26 | 20 | 1.43 | 0.44 |
| (b) | 30.2 | 0.06–0.23 | 20 | 2.43 | 0.44 |
| (c) | 30.0 | 0.07–0.27 | 40 | 1.43 | 0.44 |
| (d) | 31.7 | 0.06–0.24 | 40 | 2.43 | 0.44 |
| (e) | 30.1 | 0.07–0.33 | 20 | 3.15 | 0.42 |
| (f) | 30.1 | 0.07–0.32 | 40 | 3.15 | 0.42 |
| Gauge No. | x (m) | y (m) | Gauge No. | x (m) | y (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.0 | 7.0 | 9 | 22.0 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 15.0 | 1.0 | 10 | 21.5 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 19.5 | 1.0 | 11 | 23.0 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 19.5 | 3.0 | 12 | 23.5 | 4.0 |
| 5 | 20.0 | 4.0 | 13 | 25.0 | 2.0 |
| 6 | 21.0 | 4.5 | 14 | 22.5 | 7.0 |
| 7 | 21.5 | 3.5 | 15 | 19.5 | 7.5 |
| 8 | 22.5 | 2.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, K.; Huang, M.; Chen, G.; Wu, J.; Wu, H.; Jiang, T. Boussinesq Simulation of Coastal Wave Interaction with Bottom-Mounted Porous Structures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101367
Fang K, Huang M, Chen G, Wu J, Wu H, Jiang T. Boussinesq Simulation of Coastal Wave Interaction with Bottom-Mounted Porous Structures. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(10):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101367
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Kezhao, Minghan Huang, Guanglin Chen, Jinkong Wu, Hao Wu, and Tiantian Jiang. 2022. "Boussinesq Simulation of Coastal Wave Interaction with Bottom-Mounted Porous Structures" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 10: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101367
APA StyleFang, K., Huang, M., Chen, G., Wu, J., Wu, H., & Jiang, T. (2022). Boussinesq Simulation of Coastal Wave Interaction with Bottom-Mounted Porous Structures. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(10), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101367





