Advances in Marine Self-Powered Vibration Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator
Abstract
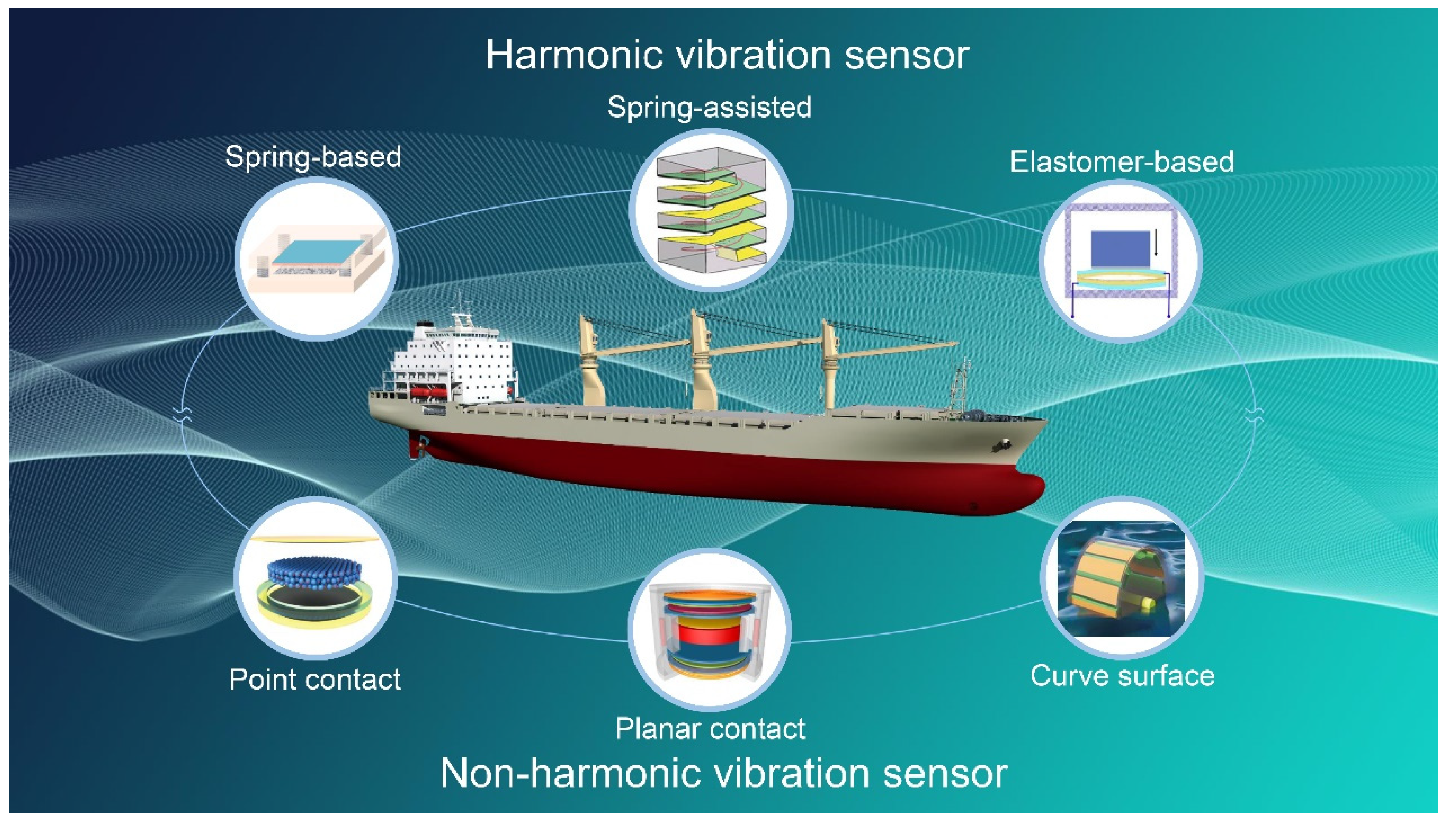
:1. Introduction
2. TENG-Based Harmonic Vibration Sensor
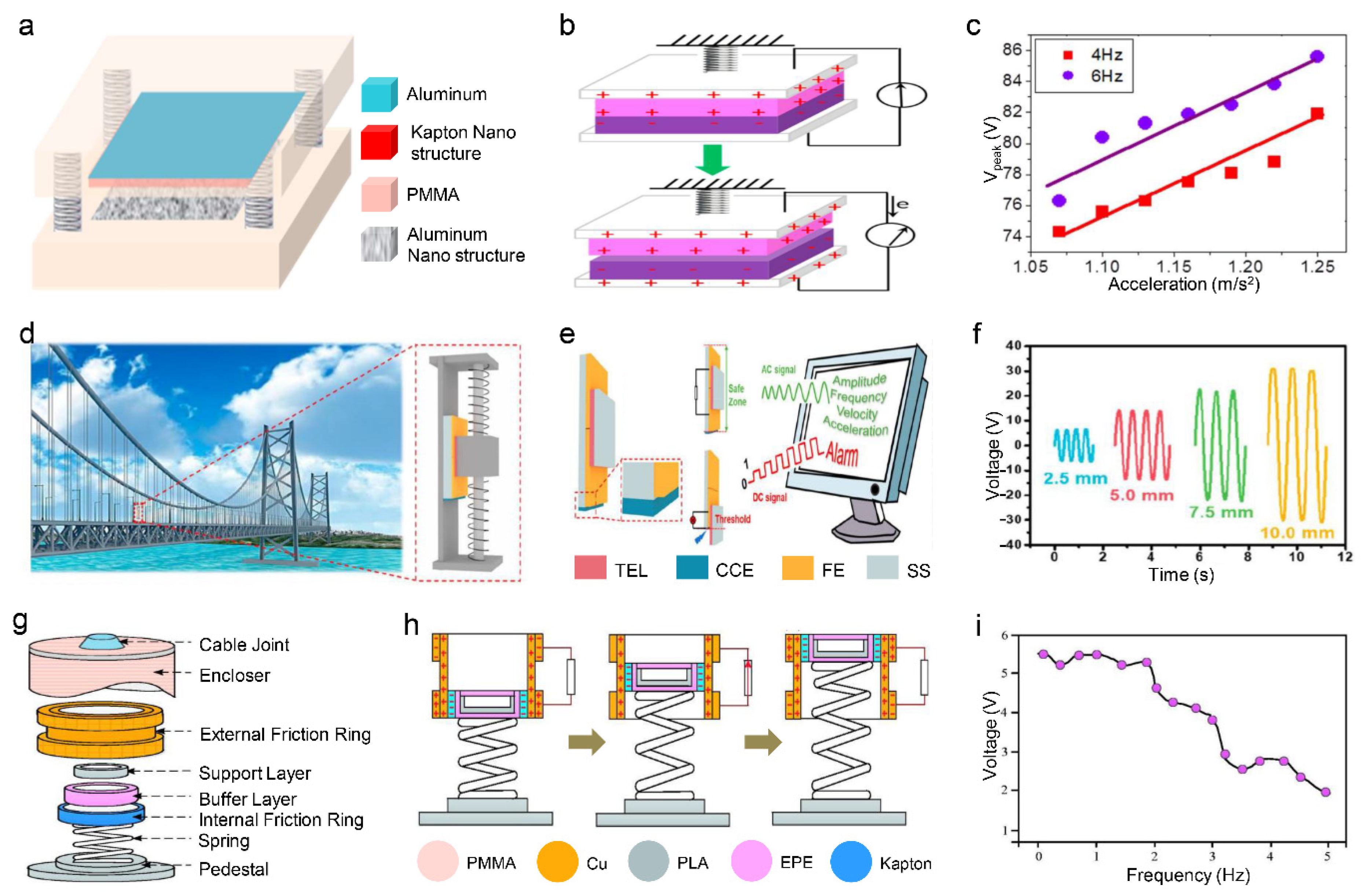
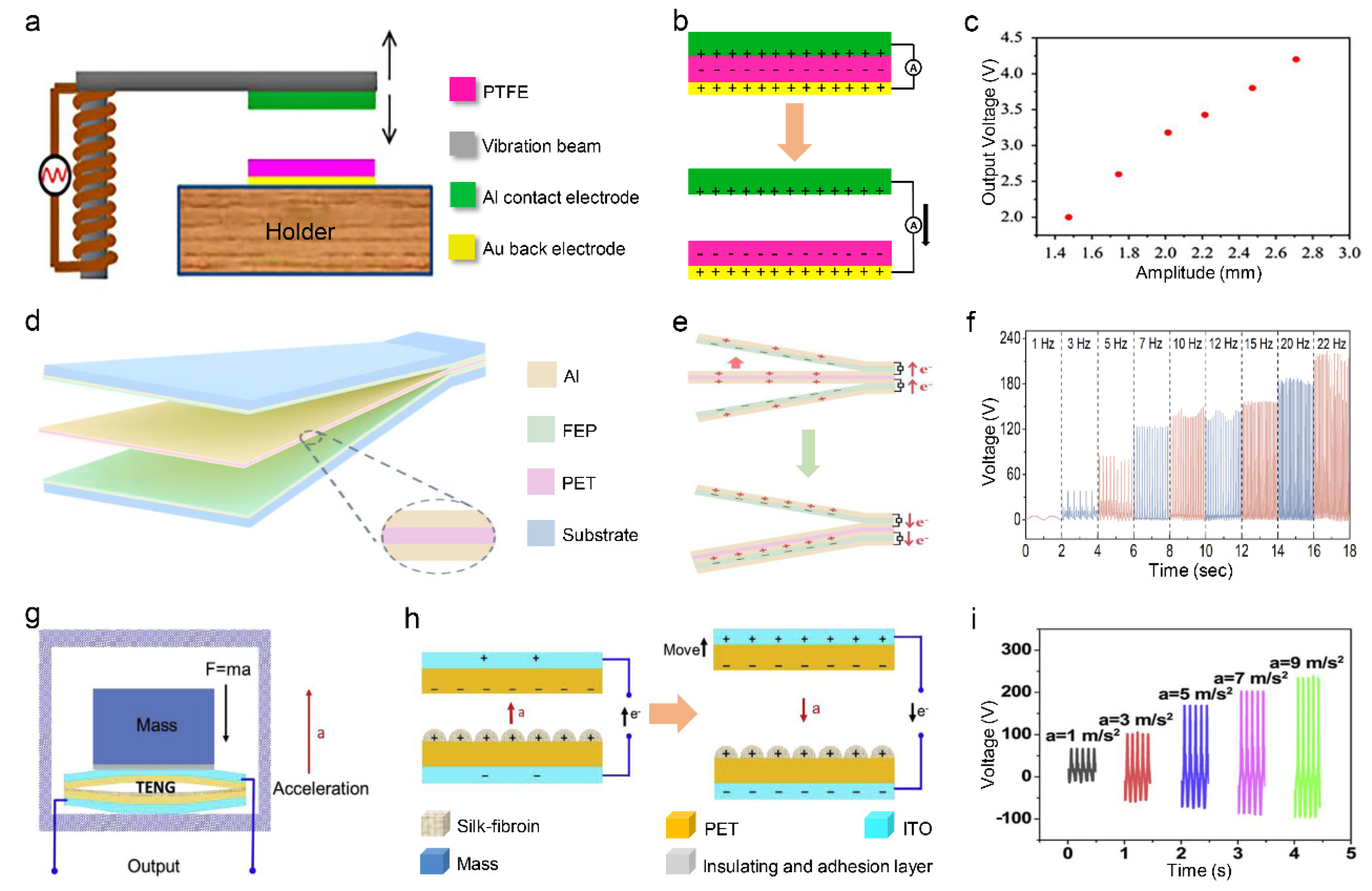
2.1. Spring-Based Vibration Sensor
2.2. Elastomer-Based Vibration Sensor
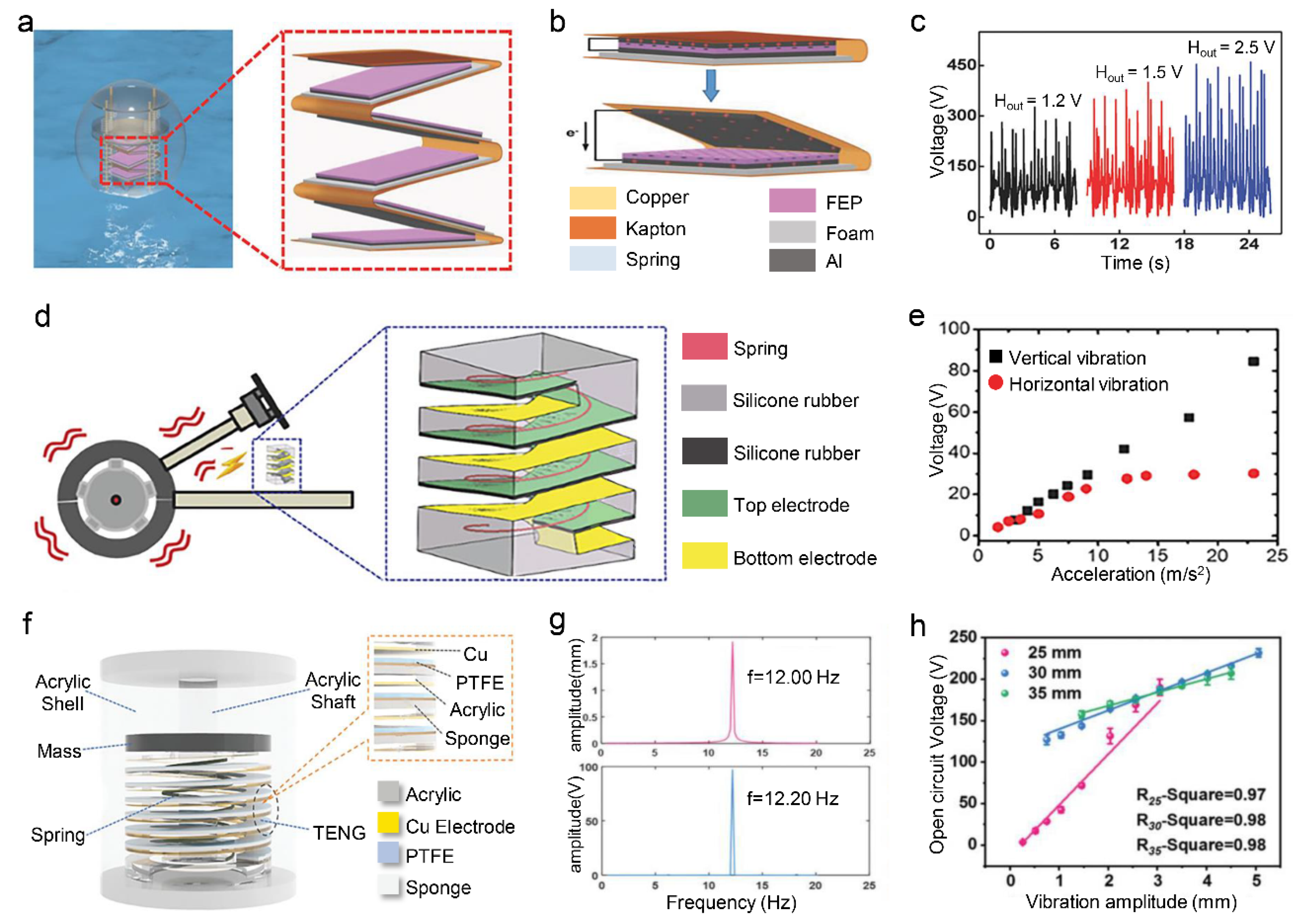
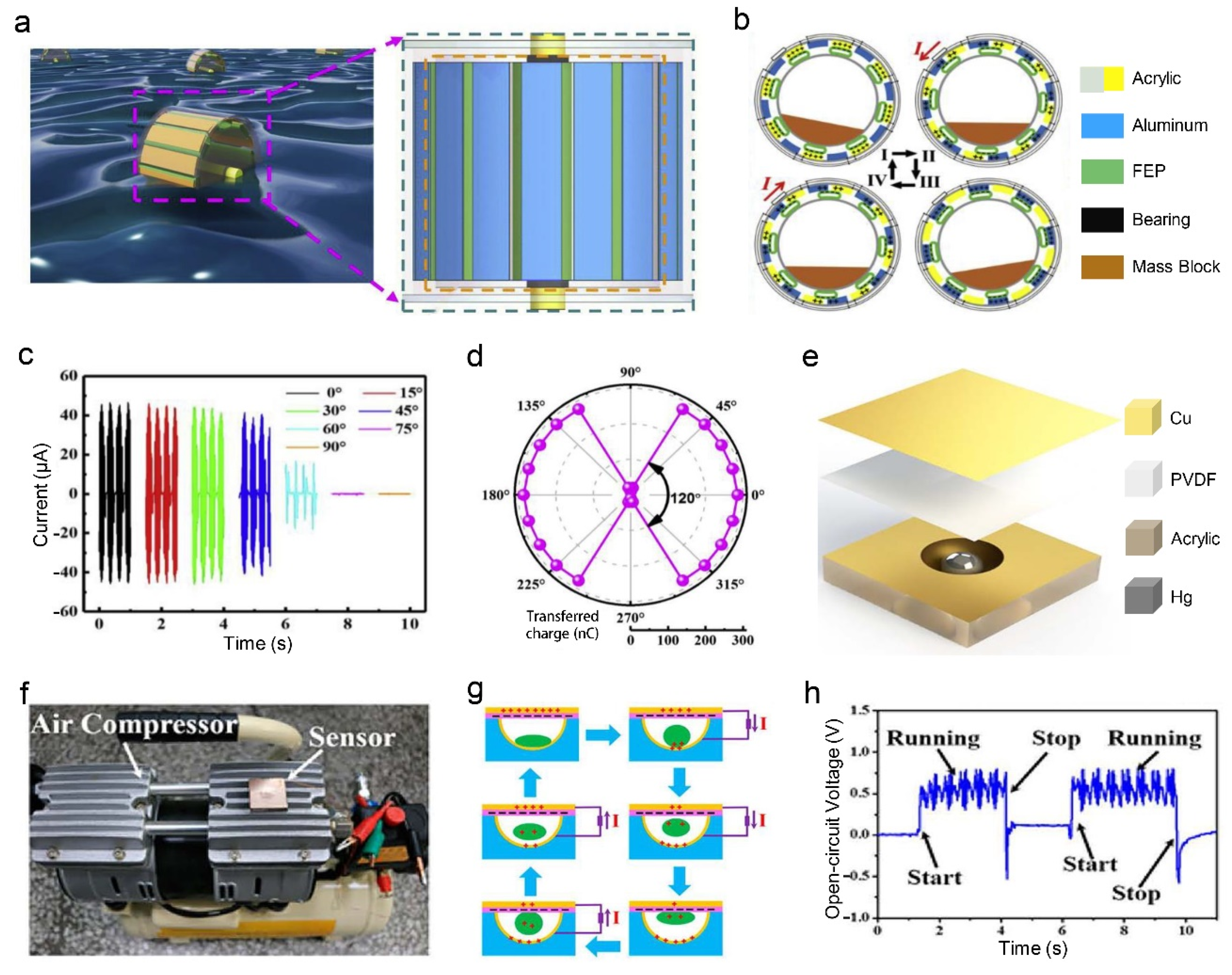
2.3. Spring-Assisted Vibration Sensor
3. TENG-Based Non-Harmonic Vibration Sensor
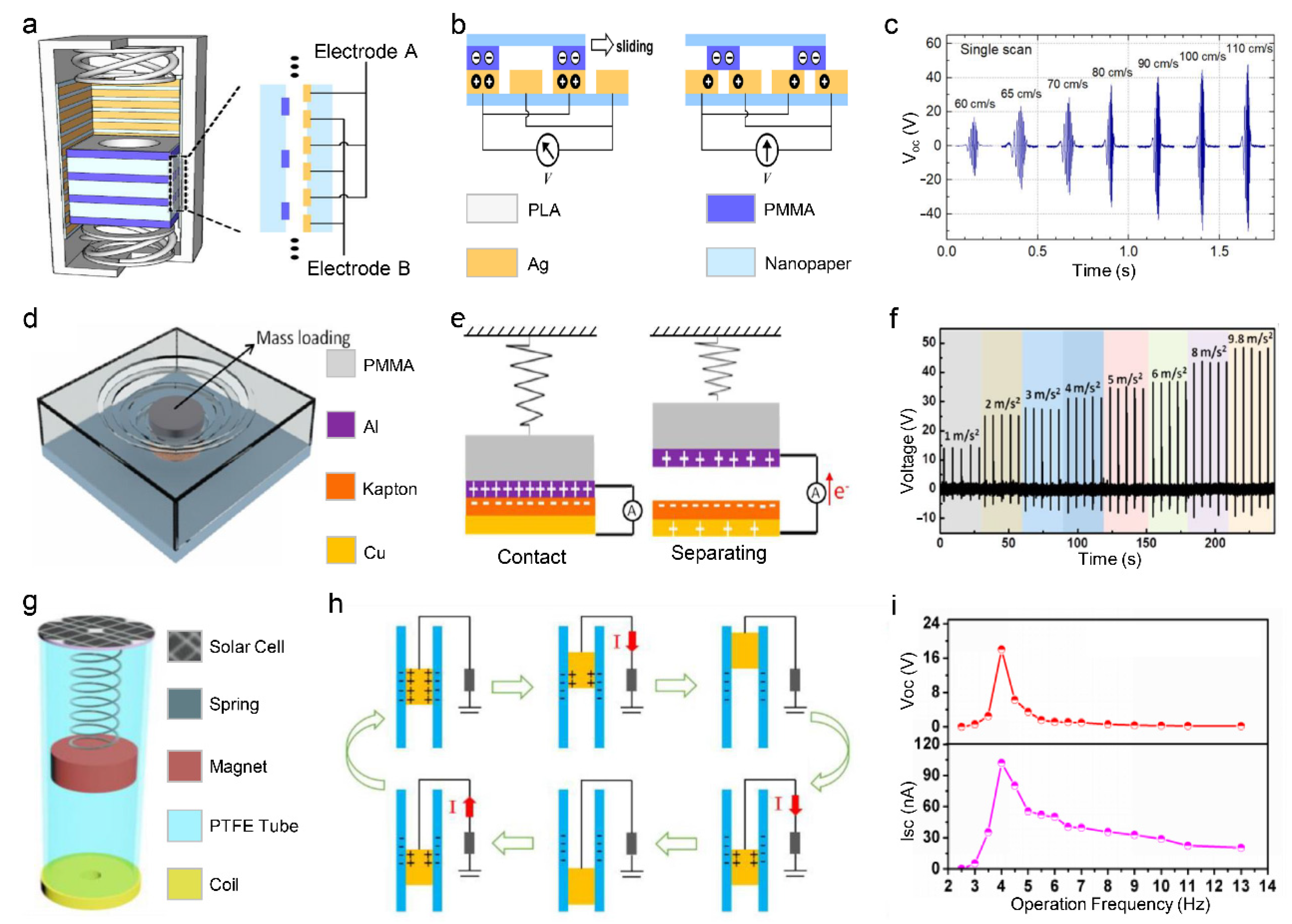
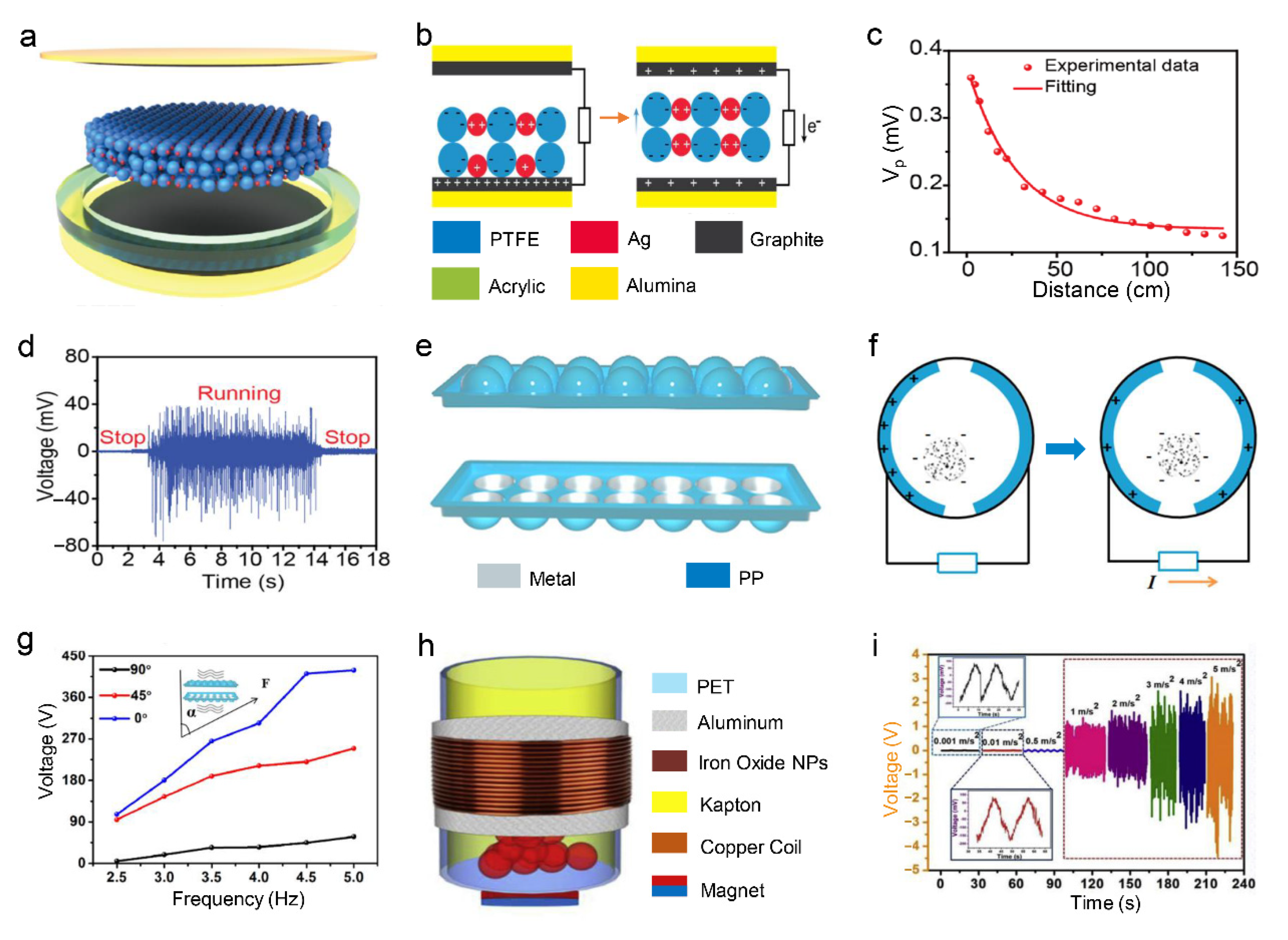
3.1. Point Contact Vibration Sensor
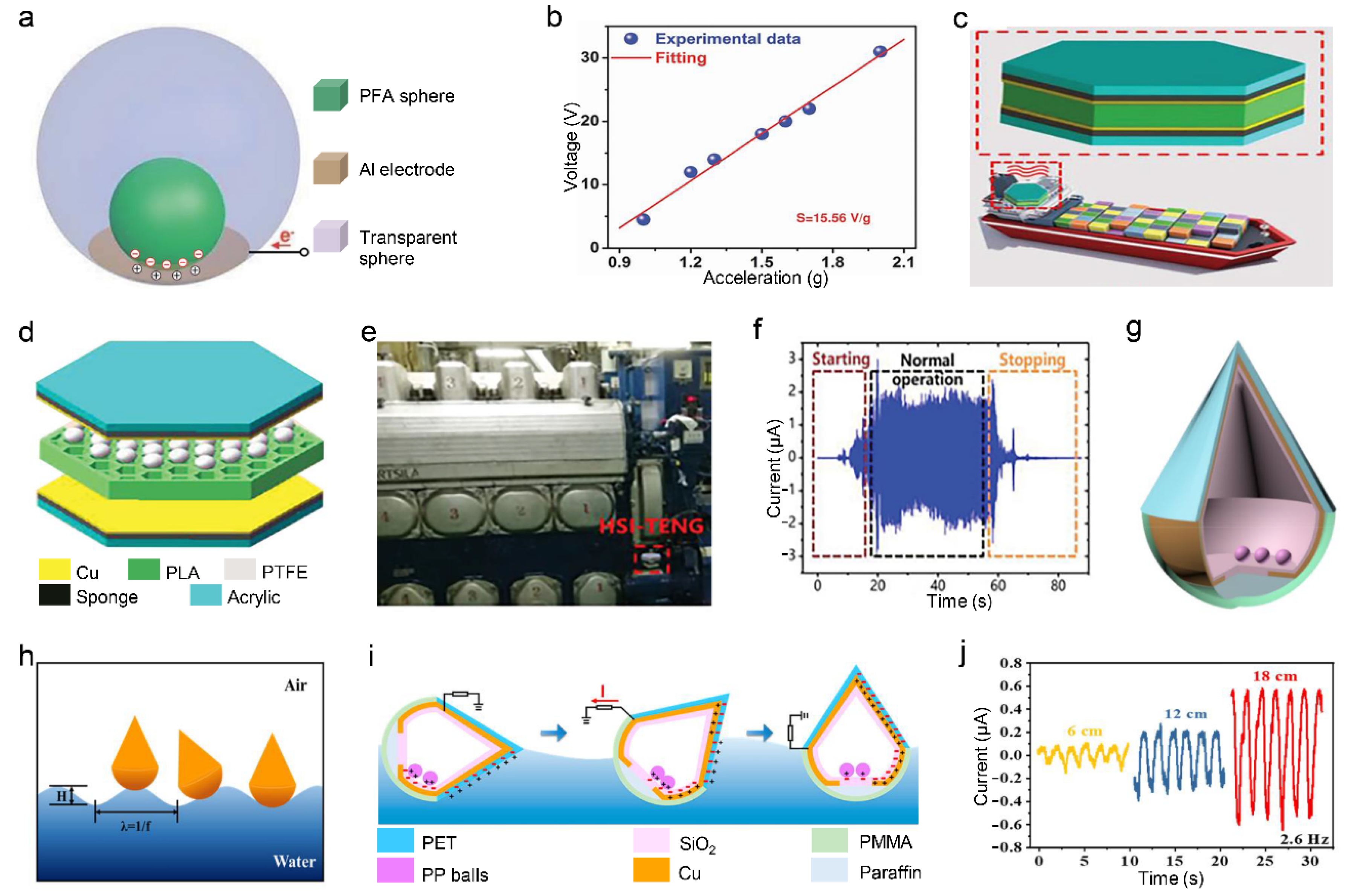
3.2. Planar Contact Vibration Sensor
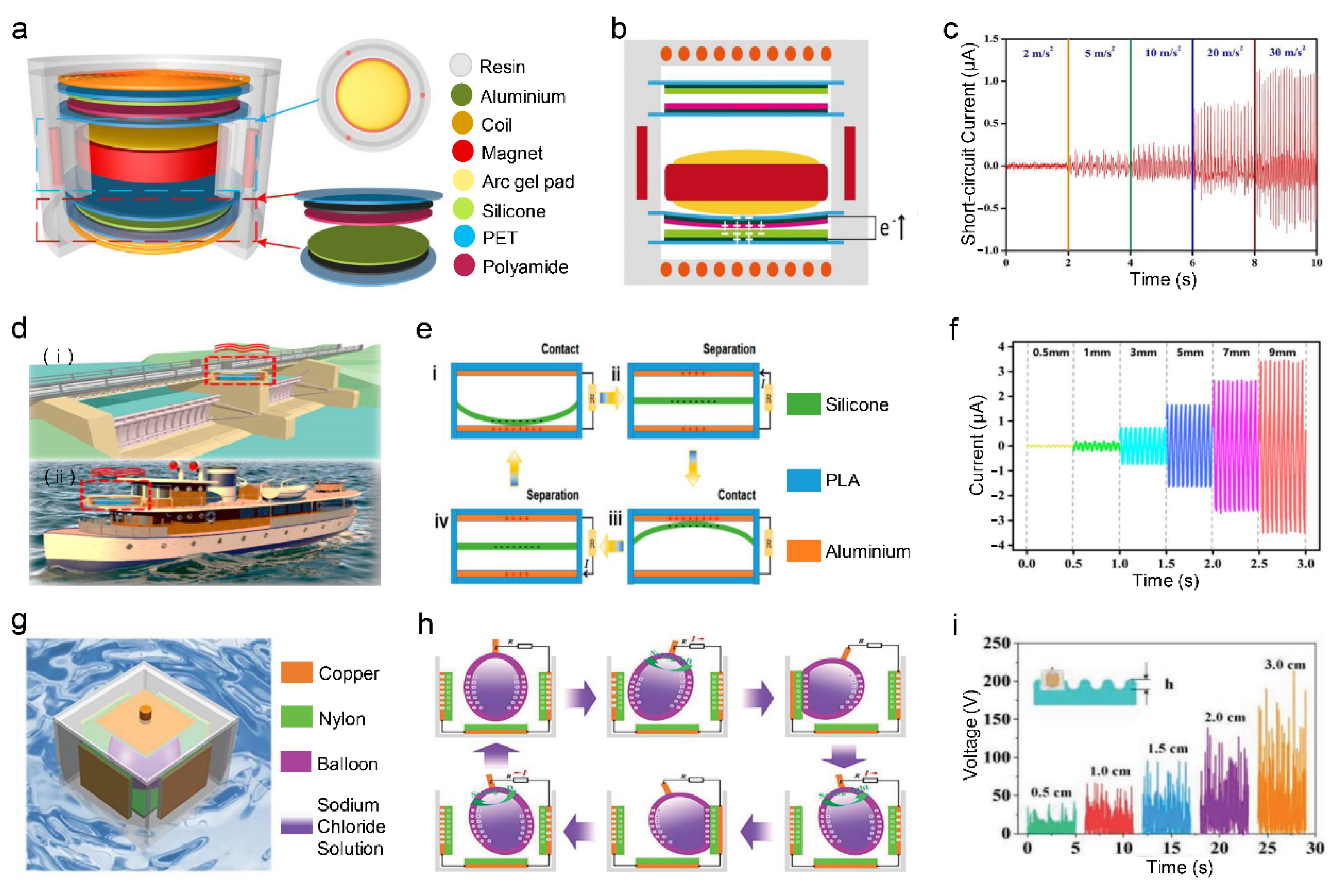
3.3. Curved Surface Contact Vibration Sensor
4. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, B. Research on Data Release and Location Monitoring Technology of Sensor Network Based on Internet of Things. J. Web Eng. 2021, 20, 689–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kumara, S.; Bukkapatnam, S.T.; Tsung, F. The internet of things for smart manufacturing: A review. IISE Trans. 2019, 51, 1190–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Entropy theory of distributed energy for internet of things. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.W.; Ginting, L.; Aziz, A.A.; Setiawan, D.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, S.I.; Kang, D.S.; Chung, M.Y.; Kim, D.I. Toward Realization of Long-Range Wireless-Powered Sensor Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.; Meng, K.; Lin, Z.; He, Q.; Sun, C.; Yang, J.; et al. Wireless self-powered sensor networks driven by triboelectric nanogenerator for in-situ real time survey of environmental monitoring. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, B.B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W.Q. Nanogenerator as new energy technology for self-powered intelligent transportation system. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, H.; Khajepour, A.; Khamesee, M.B.; Wang, Z.L. Embedded self-powered sensing systems for smart vehicles and intelligent transportation. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Chen, Z.; Papadimitriou, E.; Wu, C.; Van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M. Influence of environmental factors on human-like decision-making for intelligent ship. Ocean Eng. 2019, 186, 106060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Iop. Research on Digital, Networked and Intelligent Manufacturing of Modern Ship. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Information Science and Application Technology (CISAT), Dali, China, 17–19 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, X.; Liu, X. Design of Ship Intelligent Collision Prevention System Based on Computer Vision. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 97, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Gao, Y. A Study of the Marine Environment Monitoring Technology. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 107, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, W.; Wang, X.; IEEE. Marine Environment Monitoring Using Wireless Sensor Networks: A Systematic Review. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Shen, W.; Wang, X. Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks in Marine Environment Monitoring: A Survey. Sensors 2014, 14, 16932–16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, C.; Shu, Q. Research on marine environment monitoring based on Internet of things. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 219, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Du, Y.; Brett, P.M. Design of a Marine Environment Monitoring System Based on the Internet of Things. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 110, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Application of Wireless Sensor Network Based on ZigBee Technology in Marine Ecological Environment Monitoring. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 110, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-H. The Design and Development of Marine IT sensor Improving the Jitter Characteristic. J. Korean Inst. Illum. Electr. Install. Eng. 2020, 34, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, E.; Quiles, E.; Correcher, A.; Morant, F. Sensor Buoy System for Monitoring Renewable Marine Energy Resources. Sensors 2018, 18, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Dou, J.; Guo, Z.; Hu, K. Research of marine sensor web based on SOA and EDA. J. Ocean Univ. China 2015, 14, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, H.; Yu, W.; Huang, S.; Liao, J.; Yan, J.; Chen, C.-C. Features of Vibration of Ship Generator Caused by Coupling Effect of Load Fluctuation. Sens. Mater. 2021, 33, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L. Design of Vibration Signal Data Acquisition System for Ship Mechanical and Electrical Equipment. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 97, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.-Y.; Wei, F.; Li, J.-W.; Han, M.; Guan, D.-H.; IEEE. Vibration Monitoring System of Ships Using Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Tianjin, China, 3–6 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ramilli, R.; Crescentini, M.; Traverso, P.A.; IEEE. Sensors for Next-Generation Smart Batteries in Automotive: A Review. In Proceedings of the 1st IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Automotive (MetroAutomotive), Modena, Italy, 4–6 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Gye-choon, P. Battery Protection Method Using Gas Sensor Monitoring Device. Trans. Korean Hydrog. New Energy Soc. 2021, 32, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, K.-T.; Park, J.-H.; Bere, G.; Ochoa, J.J.; Kim, T. Convolutional Neural Network-Based False Battery Data Detection and Classification for Battery Energy Storage Systems. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 3108–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yi, C.; Li, Y. Battery-Friendly Packet Transmission Algorithms for Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3548–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Guo, J.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, Z. Recent Advances and Tendency in Fiber Bragg Grating-Based Vibration Sensor: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 12074–12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Bai, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jin, B. Pulse Coding in Distributed Optical Fiber Vibration Sensor: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 22371–22387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jin, B.; Bai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. Distributed Fiber-Optic Sensors for Vibration Detection. Sensors 2016, 16, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Xing, F.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Vibration sensor for the health monitoring of the large rotating machinery: Review and outlook. Sens. Rev. 2018, 38, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S. A review of analyses related to vibrations of rotating piezoelectric bodies and gyroscopes. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2005, 52, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devillez, A.; Dudzinski, D. Tool vibration detection with eddy current sensors in machining process and computation of stability lobes using fuzzy classifiers. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.Y.; Zhao, Z.X.; Baines, R.W. The research of inhomogeneity in eddy current sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 69, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Dong, Y.; Wu, X. Motion Induced Eddy Current Sensor for Non-Intrusive Vibration Measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, W.; Qi, S.; Jiang, J.; Hu, C.; Tao, J. Damping vibration analysis of a dual-axis precision force sensor based on passive eddy current. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 255001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Ji, Q. Vertical Vibration Conveyor Vibration Testing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Frontiers of Manufacturing Science and Measuring Technology (ICFMM2011), Chongqing, China, 23–24 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Cao, J.a.; Qiao, D. A Self-Powered Vibration Sensor with Wide Bandwidth. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Yahagi, T.; Abe, Y.; Murayama, H. Electromagnetic silicon MEMS resonator. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 2019, 206, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wen, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. A resonant electromagnetic vibration energy harvester for intelligent wireless sensor systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 17B509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegame, T.; Takagi, K.; Inoue, T.; Jikuya, I. Sensor-less parameter estimation of electromagnetic transducer and experimental verification. In Proceedings of the Conference on Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–12 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Fu, X.; Lin, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, C. Broadband vibration energy powered autonomous wireless frequency monitoring system based on triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhong, S.; Cao, J. Self-powered wireless sensor system for water monitoring based on low-frequency electromagnetic-pendulum energy harvester. Energy 2022, 251, 123883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tang, B.; Fu, H. Beacon Synchronization-Based Multi-Channel with Dynamic Time Slot Assignment Method of WSNs for Mechanical Vibration Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 13659–13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Li, X.; Chang, L.; Zang, Y.; IEEE. Application of Wireless Sensor Network in Vibration Signal Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechatronic Sciences, Electric Engineering and Computer (MEC), Shenyang, China, 20–22 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, K.-D.; Kim, J.-T.; Park, Y.-H. Long-Term Vibration Monitoring of Cable-Stayed Bridge Using Wireless Sensor Network. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2013, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Dong, X.; Li, X. Study on Machinery Vibration Data Acquisition Node Based on Wireless Sensor Network. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Frontiers of Manufacturing Science and Measuring Technology (ICFMM 2012), Xi’an, China, 12–13 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.G.; Guo, Y.B.; Jiang, C. Application for Vibration Monitoring of Aspheric Surface Machining Based on Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies-Large Mirrors and Telescopes, Dalian, China, 26–29 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Huang, Q. Rotational Speed Measurement Based on LC Wireless Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Jia, P.; Guan, X.; Xiong, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, C. Wireless Passive High-Temperature Sensor Readout System for Rotational-Speed Measurement. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 6656527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Jiang, R.; He, W.; He, J.; IEEE. Comparative Experiments of Optical Fiber Sensor and Piezoelectric Sensor based on Vibration Detection. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Conference on Frontiers of Sensors Technologies (ICFST), Shanghai, China, 6–9 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Jin, H.; Dai, L.; Shen, H. A biomimetic vibration sensor using a symmetric electrodes metal core piezoelectric fiber. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, Y.S.; Isaev, R.M.; Lubiviy, A.V.; Iop. Improvement of piezoelectric vibration sensors’ performance characteristics via optimization of details’ functional surfaces roughness. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Technologies in Business and Industry, Tomsk, Russia, 17–20 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, K.; Yi, H.; Tang, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, N.; Hu, L.; Fu, Y.; Miao, J.; Chang, H. Piezoelectric ZnO thin films for 2DOF MEMS vibrational energy harvesting. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 359, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, S.; Ji, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, S. A piezoelectric spring pendulum oscillator used for multi-directional and ultra-low frequency vibration energy harvesting. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Nishioka, T.; Nishiumi, T.; Noda, M. Vibration Modes of Piezoelectric Diaphragms for Ultrasonic Microsensors and Influence of Top Electrodes. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghisi, D.; Dalola, S.; Ferrari, M.; Ferrari, V. Ball-impact Piezoelectric Converter for Multi-degree-of-freedom Energy Harvesting from Broadband Low-frequency Vibrations in Autonomous Sensors. Procedia Eng. 2014, 87, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. New wave power. Nature 2017, 542, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology and self-powered sensors-Principles, problems and perspectives. Faraday Discuss. 2014, 176, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators as New Energy Technology for Self-Powered Systems and as Active Mechanical and Chemical Sensors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9533–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Nanosensors and Nanosystems. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Marty, F.; Xia, X.; Zi, Y.; Bourouina, T.; Galayko, D.; Basset, P. Employing a MEMS plasma switch for conditioning high-voltage kinetic energy harvesters. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Q.; Zi, Y.L.; Li, S.Y.; Chen, X.Y. High-voltage applications of the triboelectric nanogenerator-Opportunities brought by the unique energy technology. MRS Energy Sustain. 2020, 6, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, J.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Electrically Responsive Materials and Devices Directly Driven by the High Voltage of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, N.N.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, W.S.; Yang, Y. Transparent triboelectric nanogenerator-induced high voltage pulsed electric field for a self-powered handheld printer. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-J.; Song, W.-Z.; Li, C.-L.; Chen, T.; Zhang, D.-S.; Zhang, J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.-Z. High-voltage direct current triboelectric nanogenerator based on charge pump and air ionization for electrospinning. Nano Energy 2022, 101, 107599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Lei, W.; Gao, L.; Chen, X.; Tong, D.; Yuan, P.; Mu, X.; Yu, H. Regulating the high-voltage and high-impedance characteristics of triboelectric nanogenerator toward practical self-powered sensors. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Yang, H.; He, W.; Long, L.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Xi, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Ultra-stability high-voltage triboelectric nanogenerator designed by ternary dielectric triboelectrification with partial soft-contact and non-contact mode. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Iwamoto, M. Recent progress in the development of portable high voltage source based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Smart Mater. Med. 2020, 1, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Du, T.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, H.; et al. Highly-stretchable rope-like triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered monitoring in marine structures. Nano Energy 2022, 94, 106926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xu, M.; Xiao, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Recent progress in blue energy harvesting for powering distributed sensors in ocean. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, T.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, W.; Xu, M.; Tao, J.; Xie, G. A Triboelectric-Based Artificial Whisker for Reactive Obstacle Avoidance and Local Mapping. Research 2021, 2021, 9864967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Hu, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Du, T.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, T.; et al. A Triboelectric-Nanogenerator-Based Gas-Solid Two-Phase Flow Sensor for Pneumatic Conveying System Detecting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2001270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, C.; Du, T.; Xiao, X.; Song, L.; Pang, H.; et al. A robust and self-powered tilt sensor based on annular liquid-solid interfacing triboelectric nanogenerator for ship attitude sensing. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2021, 317, 112459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.K.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiao, X.; Pan, X.X.; Xu, M.Y.; Mi, J.C. A Self-Powered and Low Pressure Loss Gas Flowmeter Based on Fluid-Elastic Flutter Driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Sensors 2020, 20, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Yu, M.; Ma, Z.R.; Ouyang, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Niu, H.K.; Pan, X.X.; Xu, M.Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Self-Powered Distributed Water Level Sensors Based on Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Ship Draft Detecting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.L.; Ding, W.B.; Kien, P.T.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.X.; Wang, Z.L. A highly-sensitive wave sensor based on liquid-solid interfacing triboelectric nanogenerator for smart marine equipment. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. A hand-driven portable triboelectric nanogenerator using whirligig spinning dynamics. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, W.; Zhao, X.; Roustaei, M.; Hsiai, T.K.; Chen, J. Ambulatory Cardiovascular Monitoring Via a Machine-Learning-Assisted Textile Triboelectric Sensor. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2104178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X. Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors 2021, 21, 7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Salauddin, M.; Rasel, M.S. Nanogenerator for scavenging low frequency vibrations. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 053001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Parida, S.; Behera, R.K.; Roy, T. Vibration energy harvesting: A review. J. Adv. Dielectr. 2019, 9, 1930001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Closso, A.B.; Jin, C.; Tras, I.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.X. Vibration-Energy-Harvesting System: Transduction Mechanisms, Frequency Tuning Techniques, and Biomechanical Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Reviving Vibration Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensing by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Joule 2017, 1, 480–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Zhu, C.; Yu, H.; Song, L.; Pan, X.; Mi, J.; Lee, C.; et al. An underwater flag-like triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting ocean current energy under extremely low velocity condition. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Guo, H.; Hao, W.; Sheng, K.; An, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M. Research on dynamics of bouncing ball in triboelectric nanogenerator. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2021, 31, 085002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, E.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Mi, J.; Pan, X.; Xu, M. A novel humidity resisting and wind direction adapting flag-type triboelectric nanogenerator for wind energy harvesting and speed sensing. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, S.L.; Ding, W.B.; Cheng, J.; He, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.J.; Pan, X.X.; Wang, Z.L. An aeroelastic flutter based triboelectric nanogenerator as a self-powered active wind speed sensor in harsh environment. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2017, 15, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.F.; Xiao, X.; Xu, P.; Zhao, T.C.; Song, L.G.; Pan, X.X.; Mi, J.C.; Xu, M.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Dual-Tube Helmholtz Resonator-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Highly Efficient Harvesting of Acoustic Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Sun, M.; Yan, F.; Du, T.; Xi, Z.; Li, F.; Zhu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Sun, P.; et al. A High-Performance Flag-Type Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Scavenging Wind Energy toward Self-Powered IoTs. Materials 2022, 15, 3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Z.H.; Zhou, L.L.; Yin, X.; Li, X.Y.; Gao, Y.K.; Zhang, C.G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. A Fully Self-Powered Vibration Monitoring System Driven by Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.X.; Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Xu, L.; Shao, J.J.; Nie, J.H.; Bai, Y.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Z.L. Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Spring-Assisted Multilayered Structure for Efficient Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, J.; Adams, K.; Lee, S.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Vibration Energy in Full Space and as Self-Powered Acceleration Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Built on Suspended 3D Spiral Structure as Vibration and Positioning Sensor and Wave Energy Harvester. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10424–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wang, S.Y.; Ouyang, H.; Chen, P.F.; Song, L.G.; Yuan, H.C.; Ji, Y.L.; Wang, P.H.; Li, Z.; et al. Honeycomb Structure Inspired Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Highly Effective Vibration Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Engine Condition Monitoring. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Y.; Wang, P.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, S.L.; Wang, A.C.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, Z.J.; Pan, X.X.; Wang, Z.L. A Soft and Robust Spring Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Arbitrary Directional Vibration Energy and Self-Powered Vibration Sensing. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xu, R.; Lin, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. A Cantilever Beam-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator as a Drill Pipe Transverse Vibration Energy Harvester Powering Intelligent Exploitation System. Sensors 2022, 22, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, C. Self-Powered Downhole Drilling Tools Vibration Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, W.; He, H.; Shuo, Y.; Chenxing, F. Research on the self-powered downhole vibration sensor based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2021, 235, 6427–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Gu, J.C.; Chen, C.M. The effect of harmonic torque to torsional vibration of induction machines. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 1999, 22, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, T. Harmonic vibration synchronization phenomenon analysis of dual excitation rotors nonlinear vibration system. J. Vibroeng. 2014, 16, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar]
- Seolab, M.; Han, J.; Moon, D.; Yoon, K.; Hwang, C.; Meyyappan, M. All-printed triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.J.; Wei, G.W.; Li, X.H.; Qin, Y.; Xu, D.D.; Tang, W.; Yin, H.J.; Wei, X.K.; Jia, L.M. Self-powered triboelectric nano vibration accelerometer based wireless sensor system for railway state health monitoring. Nano Energy 2017, 34, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Liu, G.; Gao, Y.; Bu, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, C. Frequency Band Characteristics of a Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Ultra-Wide-Band Vibrational Energy Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 26084–26092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; He, X.; Ding, W.B.; Hu, Y.S.; Yang, D.C.; Lu, S.; Wu, C.S.; Zou, H.Y.; Liu, R.Y.; Lu, C.H.; et al. A Self-Powered Dynamic Displacement Monitoring System Based on Triboelectric Accelerometer. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhanga, Z.; Yan, X.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lu, S.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y. Functional triboelectric generator as self-powered vibration sensor with contact mode and non-contact mode. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.R.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, N.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.K.; Zhao, L.B.; Yang, W.H.; Dong, L.X.; Che, L.F.; Wang, G.F.; et al. A self-powered and high sensitivity acceleration sensor with V-Q-a model based on triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Cui, C.; Bao, J.Z.; Zhu, Y.B.; Xia, J.; Wen, S.M.; Wu, H.A.; Yu, S.H. A Highly Compressible and Stretchable Carbon Spring for Smart Vibration and Magnetism Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C. Vibrational Triboelectric Nanogenerator-based Multi-node Self-powered Sensor Network for Machine Fault Detection. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020, 25, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Kang, S.; Wei, X.; Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Yang, L.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.L. Multi-Parameter Optimized Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based Self-Powered Sensor Network for Broadband Aeolian Vibration Online-Monitoring of Transmission Lines. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Fan, X.; Zhao, D.; Cui, M.; Han, B.; Hou, X.; Chou, X. A high-efficient triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator for vibration energy harvesting and wireless monitoring. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 65, 142401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, W.Q.; Jing, Q.S.; Bai, P.; Yang, Y.; Hou, T.C.; Wang, Z.L. Harmonic-Resonator-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator as a Sustainable Power Source and a Self-Powered Active Vibration Sensor. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6094–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Quantitative Measurements of Vibration Amplitude Using a Contact-Mode Freestanding Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12004–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.Q.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.S.; Yang, J.; Wen, X.N.; Su, Y.J.; Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Wang, Z.L. 3D Stack Integrated Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Vibration Energy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4090–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, J.; Ouyang, H.; Chang, Y.; Xu, D. A dual quasi-zero-stiffness sliding-mode triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting ultralow-low frequency vibration energy. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 151, 107368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y. Hybrid electromagnetic–triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting vibration energy. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 3272–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.K.; Li, X.H.; Chen, M.X.; Han, C.B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators as a Self-Powered 3D Acceleration Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19076–19082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Liu, R.Y.; Wang, J.; Zi, Y.L.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. A spring-based resonance coupling for hugely enhancing the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting low-frequency vibration energy. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.; Khan, S.A.; Jin, L.; Yan, Z.; Huang, L.; Pan, T.; Yang, W.; et al. Hybrid nanogenerators for low frequency vibration energy harvesting and self-powered wireless locating. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 015510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Yu, X.; Cheng, T.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.L. Double-spring-piece structured triboelectric sensor for broadband vibration monitoring and warning. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 166, 108429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, H.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zou, C.; Wang, Z.L. Elastic-Beam Triboelectric Nanogenerator for High-Performance Multifunctional Applications: Sensitive Scale, Acceleration/Force/Vibration Sensor, and Intelligent Keyboard. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1802159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Liang, X.; Yang, R. Trapezoidal Cantilever-Structure Triboelectric Nanogenerator Integrated with a Power Management Module for Low-Frequency Vibration Energy Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 5497–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, H.; Yang, S.; Wen, G. Pagoda-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator with High Reliability for Harvesting Vibration Energy and Measuring Vibration Frequency in Downhole. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13999–14006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Q.; Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Wen, X.N.; Bai, P.; Su, Y.J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting vibration energy by a triple-cantilever based triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafari, A.; Sodano, H.A. Surface morphology effects in a vibration based triboelectric energy harvester. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 015029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, S.; Yi, F.; Yin, Y.; Hao, C.; Dai, K.; Zhang, Y.; You, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Ambient Vibration Energy over a Wide Frequency Range for Self-Powered Electronics. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Su, X.; Quan, L.; Jiang, J.; Dong, B.; Wei, G. Sponge-Supported Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting from Rail Vibration. J. Energy Eng. 2021, 147, 04021006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Sun, C.; Liu, W.; Fan, E.; Zhang, G.; Tan, X.; Shen, Z.; Qiu, J.; Yang, J. A self-powered and high-frequency vibration sensor with layer-powder-layer structure for structural health monitoring. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, X. Sugar-based triboelectric nanogenerators for effectively harvesting vibration energy and sugar quality assessment. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekananthan, V.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Alluri, N.R.; Purusothaman, Y.; Khandelwal, G.; Pandey, R.; Kim, S.-J. Fe2O3 magnetic particles derived triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid generator for zero-power consuming seismic detection. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jin, I.K.; Choi, Y.K. Ferromagnetic nanoparticle-embedded hybrid nanogenerator for harvesting omnidirectional vibration energy. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12276–12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-N.; Chang, C.-K.; Yang, C.-S.; Su, C.-W.; Leu, C.-M.; Chu, Y.-H.; Sha, P.-W.; Wu, J.M. Ultrasensitivity of self-powered wireless triboelectric vibration sensor for operating in underwater environment based on surface functionalization of rice husks. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.G.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhang, Z.C.; Yu, Y.; Luo, J.K.; Dong, S.R. A novel rhombic-shaped paper-based triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting energy from environmental vibration. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2020, 302, 111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Lee, C.; Luo, G.; Mao, Q.; Yang, P.; Lin, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Self-sustained autonomous wireless sensing based on a hybridized TENG and PEG vibration mechanism. Nano Energy 2020, 80, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Dong, F.; Xu, R.; Zou, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X.; Xi, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; et al. A Drill Pipe-Embedded Vibration Energy Harvester and Self-Powered Sensor Based on Annular Type Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Measurement while Drilling System. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 2200003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, J.; Wen, T.; Zhai, C.; Han, J.; Mu, J.; Jia, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Chou, X.; et al. Magnetically levitated-triboelectric nanogenerator as a self-powered vibration monitoring sensor. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Huang, M.; Dai, R.; An, Y.; Chen, C.; Nie, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, W. Using non-contact eccentric nanogenerator to collect energy continuously under periodic vibration. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Cho, S.; Yun, Y.; La, M.; Park, S.J.; Choi, D. A highly sensitive magnetic configuration-based triboelectric nanogenerator for multidirectional vibration energy harvesting and self-powered environmental monitoring. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 18262–18274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.F.; Huang, M.J.; Shi, Q.F.; Liu, H.C.; Sun, L.N.; Lee, C. A rotational pendulum based electromagnetic/triboelectric hybrid-generator for ultra-low-frequency vibrations aiming at human motion and blue energy applications. Nano Energy 2019, 63, 103871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.D.; Tang, W.; He, C.; Deng, C.R.; Yang, L.J.; Zhu, L.P.; Chen, J.; Shao, J.J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.L. Water wave energy harvesting and self-powered liquid-surface fluctuation sensing based on bionic-jellyfish triboelectric nanogenerator. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Yan, X.; Liao, X.; Cao, S.; Lu, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y. Integrated active sensor system for real time vibration monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zeng, Q.; Shao, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Tian, H.; Liu, G.; Nie, B.; Luo, Y. Channel-Crack-Designed Suspended Sensing Membrane as a Fully Flexible Vibration Sensor with High Sensitivity and Dynamic Range. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 34637–34647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Ge, B.; Mtui, A.E.; Zhao, C.; Dong, F.; Zou, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, P.; Xu, M. A Robust Silicone Rubber Strip-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Vibration Energy Harvesting and Multi-Functional Self-Powered Sensing. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, K.; Fu, J.; Xu, Z. Multiple-Frequency High-Output Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on a Water Balloon for All-Weather Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, N.; Yao, T.; Lv, D.; Cao, G. Self-Powered Multifunctional Triboelectric Sensor Based on PTFE/PU for Linear, Rotary, and Vibration Motion Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Fan, X.; Mu, J.; Wang, C.; Qian, J.; Li, X.; Hou, X.; Geng, W.; Wang, X.; Chou, X. 3D full-space triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator for high-efficient mechanical energy harvesting in vibration system. Energy 2020, 194, 116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.K.; Chen, S.E.; Chu, Y.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, C.Y. Matryoshka-inspired hierarchically structured triboelectric nanogenerators for wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, H.; Li, R.; Fan, C.X. Research on the Potential of Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Collecting Vibration Energy and Measuring Vibration. Sensors 2020, 20, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Zuo, X.; Dong, F.; Li, S.; Mtui, A.E.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; et al. A Self-Powered and Highly Accurate Vibration Sensor Based on Bouncing-Ball Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Intelligent Ship Machinery Monitoring. Micromachines 2021, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Gao, F.; Zhao, B.; Kang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y. Tumbler-shaped hybrid triboelectric nanogenerators for amphibious self-powered environmental monitoring. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, P.S.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Y.M.; Wei, X.X.; Guo, Y.C.; Shi, S.W.; Liao, Y.L.; Cheng, J.; Wang, P.H. High-performance cylindrical pendulum shaped triboelectric nanogenerators driven by water wave energy for full-automatic and self-powered wireless hydrological monitoring system. Nano Energy 2020, 74, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Deng, W.; Jin, L.; Chun, F.; Pan, H.; Gu, B.; Zhang, H.; Lv, Z.; Yang, W.; et al. Self-Powered Acceleration Sensor Based on Liquid Metal Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Vibration Monitoring. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7440–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhao, Z.; Jiao, C.; Ye, J.; Zhao, S.; Ma, M.; Zhong, X. A Liquid-Metal-Based Freestanding Triboelectric Generator for Low-Frequency and Multidirectional Vibration. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 692273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, K.; Chen, J. Advances in Nanostructures for High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zou, Y.; Nashalian, A.; Chen, J. Leverage Surface Chemistry for High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 57732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Deng, W.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Engineering Materials at the Nanoscale for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, G.; Nashalian, A.; Chen, J. Advances in self-powered chemical sensing via a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 2065–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.Q.; Luo, H.S.; Gao, D.C.; Zhou, X.R.; Cui, P.; Thangavel, G.; Parida, K.; Lee, P.S. Self-restoring, waterproof, tunable microstructural shape memory triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered water temperature sensor. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Miao, L.M.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.T.; Song, Y.; Su, Z.M.; Zhang, H.X. Waterproof and stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 203902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Che, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X. Toward large-scale fabrication of triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) with silk-fibroin patches film via spray-coating process. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gao, Y.; Xu, S.; Bu, T.; Xie, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhou, H.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, C. One-stop fabrication of triboelectric nanogenerator based on 3D printing. Ecomat 2021, 3, e12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.M.; Yang, J.; Li, X.S.; Wu, Y.F.; Wei, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, J. Large-Scale and Washable Smart Textiles Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator Arrays for Self-Powered Sleeping Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.-L. Intelligent Sensing for Internet of Things Systems. J. Internet Technol. 2022, 23, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
| Sensor Type | Structure Characteristic | Triboelectric Materials | Acceleration (m/s2) | Amplitude (mm) | Velocity (m/s) | Frequency (Hz) | Sensitivity | Durability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harmonic vibration | Spring-assisted | Silicone rubber and carbon nanofiber | 0~23 | / | / | 0~30 | / | 30,000 | [95] |
| Spring-assisted | PTFE and Cu | / | 0.7~5 | / | 5~50 | / | 500,000 | [109] | |
| Spring-based | Kapton and Al | 1.07~1.25 | / | / | / | / | / | [102] | |
| Spring-based | PMMA and Ag | / | 1~6 | 0.6~1.1 | 30~60 | / | / | [101] | |
| Spring-based | FE and TEL | / | 0~40 | / | 0.5~2 | / | 10,000 | [90] | |
| Elastomer-based | FEP-Al | / | / | / | 1~22 | / | 200,000 | [121] | |
| Elastomer-based | Silk-fibroin and PET | 1~11 | / | / | / | 20.4 V/(m/s2) | 108,000 | [106] | |
| Non-harmonic vibration | Point contact | PTTEE and Ag | / | / | / | 3~133 K | 0.22 V/m/s | / | [127] |
| Point contact | Ni and sugar | / | 50~100 | / | 2.5~5.0 | / | 2000 | [128] | |
| Curve contact | Cu and Hg and PVDF | 0~60 | / | / | / | 0.26 V s/m2 | 200,000 | [151] | |
| Curve contact | PTFE and Cu | / | 1~4.5 | / | 10~60 | / | 2000 | [94] | |
| Curve contact | PP and SiO2 | / | 60~180 | 0~10 | 0.7~1.2 | / | / | [149] | |
| Planar contact | Polyamide and Silicone | 0–30 | 0~7.5 | / | / | / | 6000 | [135] | |
| Planar contact | PVC and nylon | / | 40~120 | / | 0.5~2.5 | / | 1500 | [143] | |
| Planar contact | Silicone rubber and Aluminum | 0.5~319.8 | 0.5~9 | / | 5~90 | 94.95 W/m3 | / | [142] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Y.; Sun, M.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Du, T.; Sun, P.; Xu, M. Advances in Marine Self-Powered Vibration Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101348
Zou Y, Sun M, Xu W, Zhao X, Du T, Sun P, Xu M. Advances in Marine Self-Powered Vibration Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(10):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101348
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Yongjiu, Minzheng Sun, Weipeng Xu, Xin Zhao, Taili Du, Peiting Sun, and Minyi Xu. 2022. "Advances in Marine Self-Powered Vibration Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 10: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101348
APA StyleZou, Y., Sun, M., Xu, W., Zhao, X., Du, T., Sun, P., & Xu, M. (2022). Advances in Marine Self-Powered Vibration Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(10), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101348








