The Technical and Economic Feasibility of the CENTEC Floating Offshore Wind Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Technical Feasibility
2.2. Economic Feasibility
2.2.1. Economic Feasibility Parameters Analysed
- -
- Net Present Value (NPV).
- -
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR).
- -
- Discounted Pay-Back Period (DPBP).
- -
- Levelized Cost Of Energy (LCOE)
2.2.2. Net Present Value (NPV)
- -
- NPV > 0. The investment will generate earnings above the required return (r). This will imply that the acceptance of the project is recommended
- -
- NPV < 0. The investment produces returns below the required minimum return (r). It is not recommended to accept the project.
- -
- NPV = 0. The project does not add monetary value above the required profitability (r). The decision must be based on other criteria such as obtaining a better position in the market.
2.2.3. Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
- -
- IRR < k. The profitability obtained from the project is less than the minimum required, so the investment is not recommended.
- -
- IRR > k. The profitability of the project is above the minimum required, therefore, it is recommended to decide to invest.
- -
- IRR = k. The profitability is the same as that required, the same happens as in the case where the NPV = 0, the decision is conditioned by other factors
2.2.4. Discounted Pay-Back Period (DPBP)
- -
- DPBP <<< t. The initial outlay takes less time to recover than the life of the project (t). Accept project.
- -
- DPBP = t. The initial outlay takes to recover the same as the life of the project (t). Indifferent.
- -
- DPBP > t. The initial outlay takes longer to recover than the life of the project (t). Reject the project.
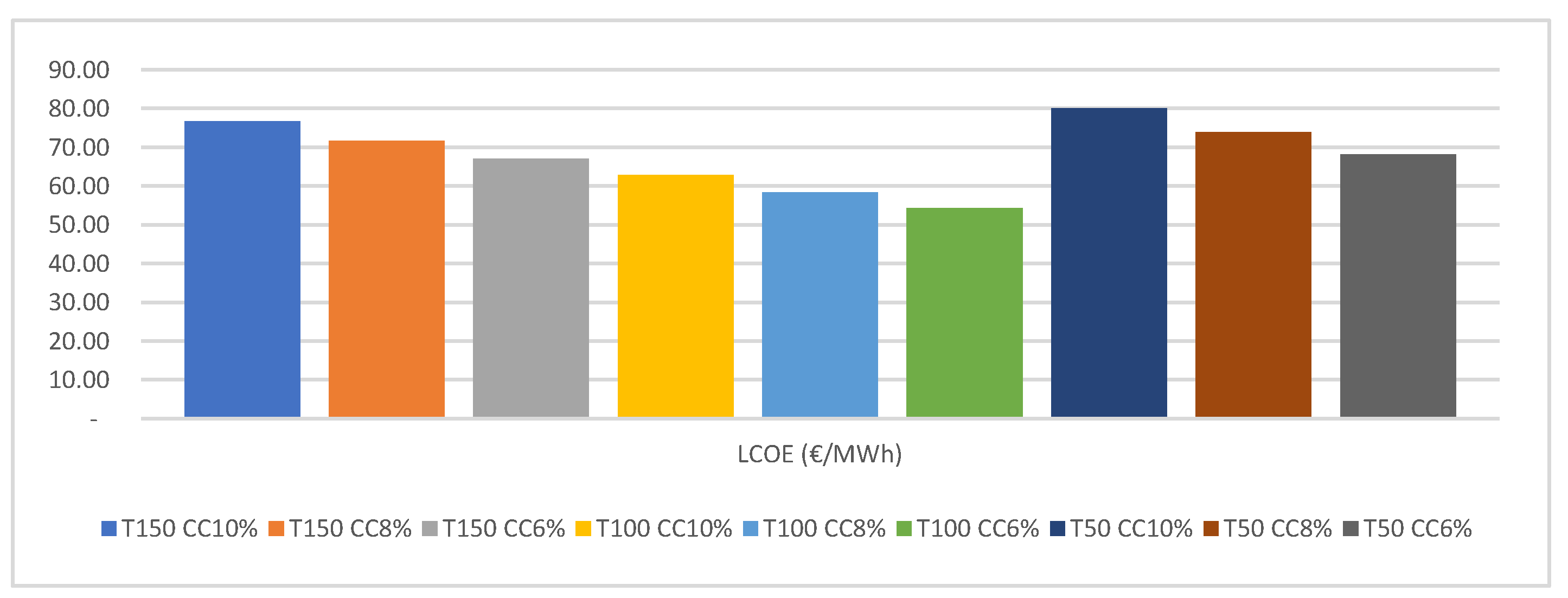
2.2.5. Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE)
2.2.6. Costs
- -
- C1: Conception and definition cost.
- -
- C2: Design and development cost.
- -
- C3: Manufacturing cost.
- -
- C4: Installation cost.
- -
- C5: Exploitation cost.
- -
- C6: Dismantling cost.
3. Case Study
4. Results
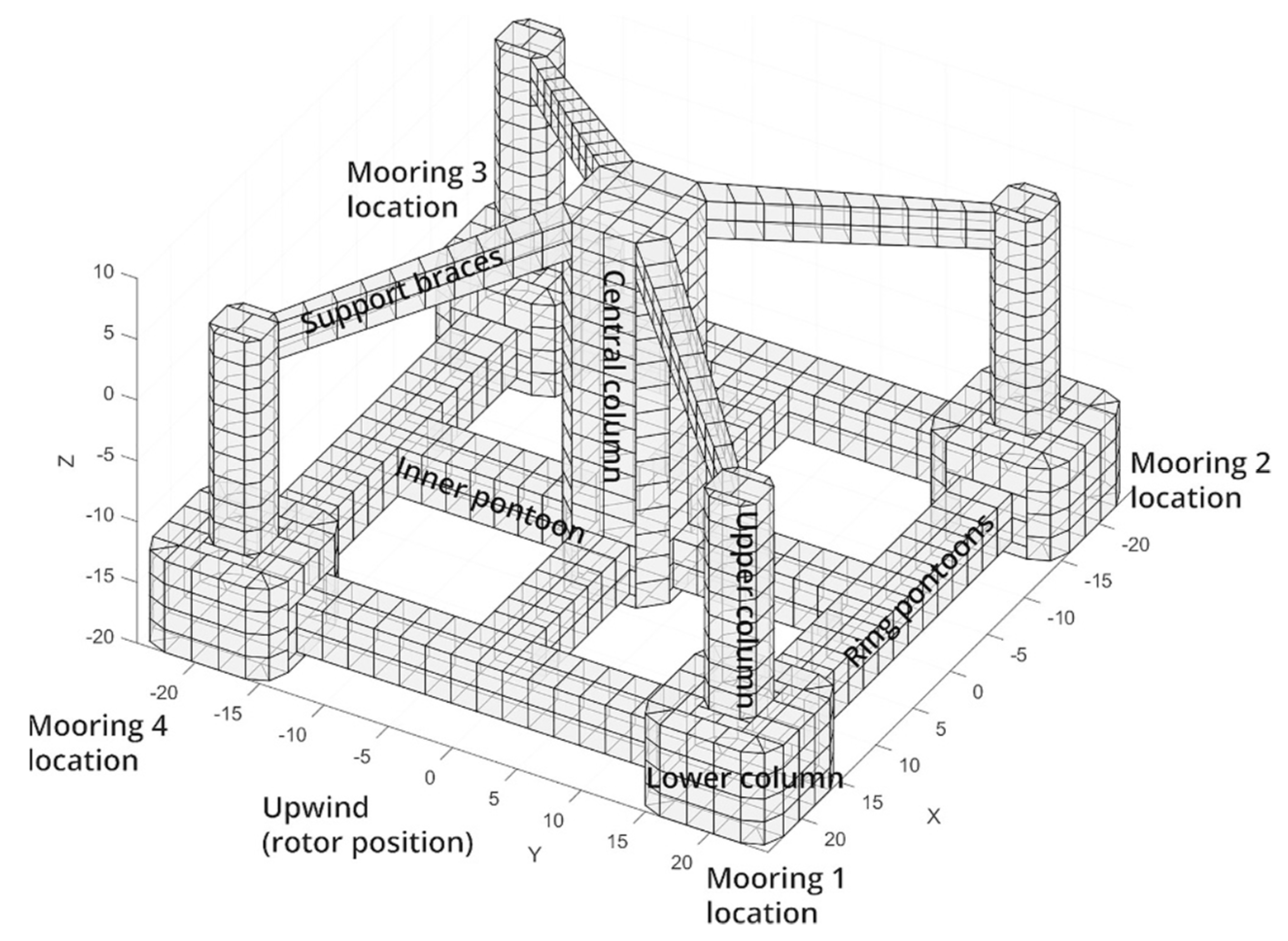
4.1. Technical Overview
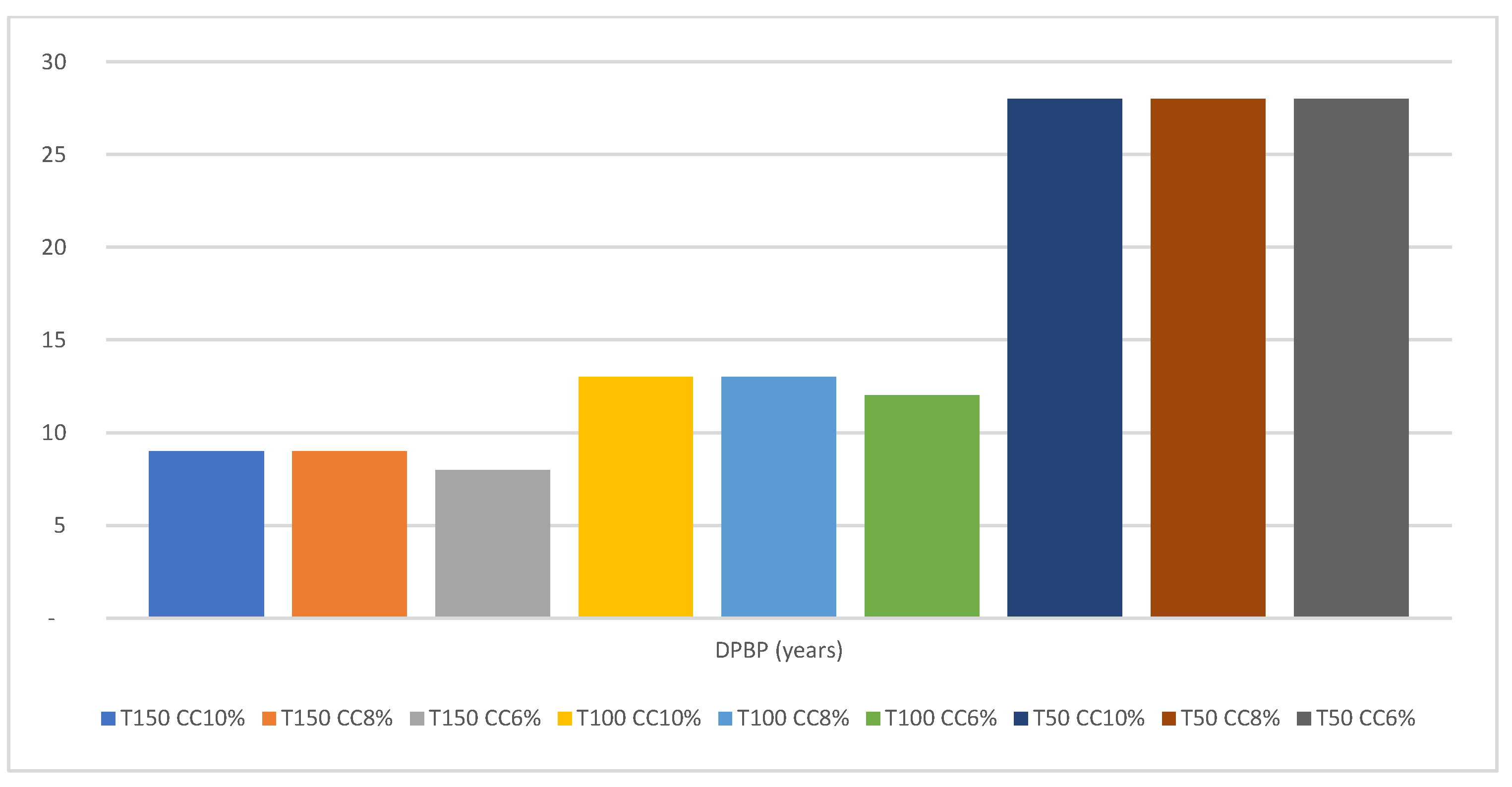
4.2. Economic Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WindEurope. Wind Europe Wind Energy in Europe 2020. Statistics and the Outlook for 2021–2025; WindEurope: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Negro, V.; López-Gutiérrez, J.S.; Esteban, M.D.; Alberdi, P.; Imaz, M.; Serraclara, J.M. Monopiles in Offshore Wind: Preliminary Estimate of Main Dimensions. Ocean Eng. 2017, 133, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gideon, R.A.; Bou-Zeid, E. Collocating Offshore Wind and Wave Generators to Reduce Power Output Variability: A Multi-Site Analysis. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeter, B.; Garbatov, Y.; Guedes Soares, C. Uncertainty Analysis of Soil-Pile Interactions of Monopile Offshore Wind Turbine Support Structures. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 82, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plodpradit, P.; Dinh, V.N.; Kim, K. Du Coupled Analysis of Offshore Wind Turbine Jacket Structures with Pile-Soil-Structure Interaction Using FAST v8 and X-SEA. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AREVA Technical Data the Evolution of the Proven Offshore M5000-135.5000. Available online: http://windturbine.co.kr/homepage/data/file/submenu4_1/622063319_JICPZj5z_AREVAwind_M5000_uk.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Yeter, B.; Garbatov, Y.; Guedes Soares, C. Fatigue Damage Assessment of Fixed Offshore Wind Turbine Tripod Support Structures. Eng. Struct. 2015, 101, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.D.; Couñago, B.; López-Gutiérrez, J.S.; Negro, V.; Vellisco, F. Gravity Based Support Structures for Offshore Wind Turbine Generators: Review of the Installation Process. Ocean Eng. 2015, 110, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Duan, L.; Wang, T.; Adcock, T.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Lin, Z.; et al. Foundations of Offshore Wind Turbines: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 104, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; González, J.A.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.I.; Park, K.C.; Han, S. Structural Topology Optimization of the Transition Piece for an Offshore Wind Turbine with Jacket Foundation. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermelli, C.; Roddier, D.; Aubault, A. WindFloat: A Floating Foundation for Offshore Wind Turbines—Part II: Hydrodynamics Analysis. In Proceedings of the Ocean Engineering; Ocean Renewable Energy, Ocean Space Utilization, Parts A and B., ASME, Honolulu, HI, USA, 31 May–5 June 2009; Volume 4, pp. 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Oguz, E.; Clelland, D.; Day, A.H.; Incecik, A.; López, J.A.; Sánchez, G.; Almeria, G.G. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a TLP Floating Offshore Wind Turbine. Ocean Eng. 2018, 147, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.M.M.; Begum, Z.A.; Yahya, S.; Lisar, S.; Motafakkerazad, R.; Cell, A.S.-P. Advances in Renewable Energy and Sustainable Systems; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 6312317269. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Santos, L.; Filgueira-Vizoso, A.; Carral-Couce, L.; Formoso, J.Á.F. Economic Feasibility of Floating Offshore Wind Farms. Energy 2016, 112, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Santos, L.; Filgueira-Vizoso, A.; Lamas-Galdo, I.; Carral-Couce, L. Methodology to Calculate the Installation Costs of Offshore Wind Farms Located in Deep Waters. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Santos, L.; deCastro, M.; Costoya, X.; Filgueira-Vizoso, A.; Lamas-Galdo, I.; Ribeiro, A.; Dias, J.M.; Gómez-Gesteira, M. Economic Feasibility of Floating Offshore Wind Farms Considering Near Future Wind Resources: Case Study of Iberian Coast and Bay of Biscay. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Ishihara, T. Upscaling and Levelized Cost of Energy for Offshore Wind Turbines Supported by Semi-Submersible Floating Platforms. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1356, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Santos, L.; Filgueira-Vizoso, A.; Piegari, L. Calculation of the Levelized Cost of Energy and the Internal Rate of Return Using GIS: The Case Study of a Floating Wave Energy Farm. In Proceedings of the ICCEP 2019—7th International Conference on Clean Electrical Power: Renewable Energy Resources Impact, Otranto, Italy, 2–4 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Santos, L.; Filgueira-Vizoso, A.; Lamas-Galdo, I.; Álvarez-Feal, C.; Carral-Couce, L. Influence of the Discount Rate in the Economic Analysis of a Floating Offshore Wind Farm in the Galician Region of the European Atlantic Area. In Proceedings of the Volume 10: Ocean Renewable Energy, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Madrid, Spain, 17–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cordal-Iglesias, D.; Filgueira-Vizoso, A.; Baita-Saavedra, E.; Graña-López, M.Á.; Castro-Santos, L. Framework for Development of an Economic Analysis Tool for Floating Concrete Offshore Wind Platforms. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueckerdt, F.; Hirth, L.; Luderer, G.; Edenhofer, O. System LCOE: What Are the Costs of Variable Renewables? Energy 2013, 63, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, B.; Foley, A.; Doran, J.; Littler, T. Levelised Cost of Energy, A Challenge for Offshore Wind. Renew. Energy 2020, 160, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawel, I. The Cost of Storage—How to Calculate the Levelized Cost of Stored Energy (LCOE) and Applications to Renewable Energy Generation. Energy Procedia 2014, 46, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Review: Costo Nivelado de La Energía (LCOE): Nuevo Enfoque Para El Análisis de Proyectos de Energía. Available online: https://repositorio.utdt.edu/handle/20.500.13098/11261 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Uzunoglu, E.; Guedes Soares, C. Hydrodynamic Design of a Free-Float Capable Tension Leg Platform for a 10 MW Wind Turbine. Ocean Eng. 2020, 197, 106888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Soler, J.; Uzunoglu, E.; Bulian, G.; Guedes Soares, C.; Souto-Iglesias, A. An Experimental Study on Transporting a Free-Float Capable Tension Leg Platform for a 10 MW Wind Turbine in Waves. Renew. Energy 2021, 179, 2158–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.N.; Jonkman, J.M.; Goupee, A.J.; Coulling, A.J.; Prowell, I.; Browning, J.; Masciola, M.D.; Molta, P. Summary of Conclusions and Recommendations Drawn from the DeepCWind Scaled Floating Offshore Wind System Test Campaign. In Proceedings of the ASME 2013 32nd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Nantes, France, 9–14 June 2013; p. V008T09A053. [Google Scholar]
- Kibbee, S.; Chianis, J.; Davies, K.; Sarwono, B. A Mini-Platform for Deepwater—the SeaStar TLP. In Proceedings of the 4th Offshore Symposium on Tension Leg Platform Technology, Houston, TX, USA, 24–25 February 1995; The Society of Naval Architects and Marine Engineers: Houston, TX, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sclavounos, P.D.; Tracy, C.; Lee, S. Floating Offshore Wind Turbines: Responses in a Seastate, Pareto Optimal Designs and Economic Assessment. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, Estoril, Portugal, 15–20 June 2007; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.D.; Aggarwal, R. The Tension Leg Platform Technology—Historical and Recent Developments. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 29–31 October 2013; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Roddier, D.; Cermelli, C.; Aubault, A.; Weinstein, A. WindFloat: A Floating Foundation for Offshore Wind Turbines. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2010, 2, 033104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Koo, B.J.; Samsung Heavy Industries Co. Ltd; Clauss, G.; Berlin, T.U. Automated Design of a Tension Leg Platform with Minimized Tendon Fatigue Damage and Its Verification by a Fully Coupled Analysis. Ship Technol. Res. 2007, 54, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatish, T.S. Modular Wind Energy Systems. In Modular Systems for Energy and Fuel Recovery and Conversion; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 371–409. ISBN 978-0-367-23512-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zavvar, E.; Chen, B.Q.; Uzunoglu, E.; Guedes Soares, C. Stress Distribution on the CENTEC-TLP in Still Water and Rated Wind Speed. In Trends in Maritime Technology and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- DNVGL-ST-0119; Floating Wind Turbine Structures. DNV-GL: Bærum, Norway, 2018.
- Vittori, F.; Pires, O.; Azcona, J.; Uzunoglu, E.; Guedes Soares, C.; Zamora Rodríguez, R.; Souto-Iglesias, A. Hybrid Scaled Testing of a 10MW TLP Floating Wind Turbine Using the SiL Method to Integrate the Rotor Thrust and Moments. In Developments in Renewable Energies Offshore; Guedes Soares, C., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2021; pp. 417–423. ISBN 9780367681319. [Google Scholar]
- Uzunoglu, E.; Soares, C.G. An Integrated Design Approach for a Self-Float Capable Tension Leg Platform for Wind Energy. In Developments in Maritime Technology and Engineering; Guedes Soares, C., Santos, T.A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2021; pp. 673–682. ISBN 9780367773779. [Google Scholar]
- Short, W.; Packey, D.; Holt, T. A Manual for the Economic Evaluation of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Technologies; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Santos, L.; Martins, E.; Guedes Soares, C. Cost Assessment Methodology for Hybrid Floating Offshore Renewable Energy Platforms. Renew. Energy 2016, 97, 866–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Santos, L.; Silva, D.; Bento, A.R.; Salvação, N.; Guedes Soares, C. Economic Feasibility of Floating Offshore Wind Farms in Portugal. Ocean Eng. 2020, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Santos, L.; Diaz-Casas, V. Economic Influence of Location in Floating Offshore Wind Farms. Ocean Eng. 2015, 107, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Santos, L.; Bento, A.R.; Silva, D.; Salvação, N.; Guedes Soares, C. Economic Feasibility of Floating Offshore Wind Farms in the North of Spain. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.; Vasilakos, N. The Economics of Offshore Wind. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenar-Santos, A.; Campíñez-Romero, S.; Pérez-Molina, C.; Mur-Pérez, F. Repowering: An Actual Possibility for Wind Energy in Spain in a New Scenario without Feed-in-Tariffs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvação, N.; Guedes Soares, C. Wind Resource Assessment Offshore the Atlantic Iberian Coast with the WRF Model. Energy 2018, 145, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvação, N.; Bernardino, M.; Guedes Soares, C. Assessing Mesoscale Wind Simulations in Different Environments. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 71, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.M.; Guedes Soares, C. Spatial Distribution of Offshore Wind Statistics on the Coast of Portugal Using Regional Frequency Analysis. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.M.; Guedes Soares, C. Assessment of Three Wind Reanalyses in the North Atlantic Ocean. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2017, 10, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
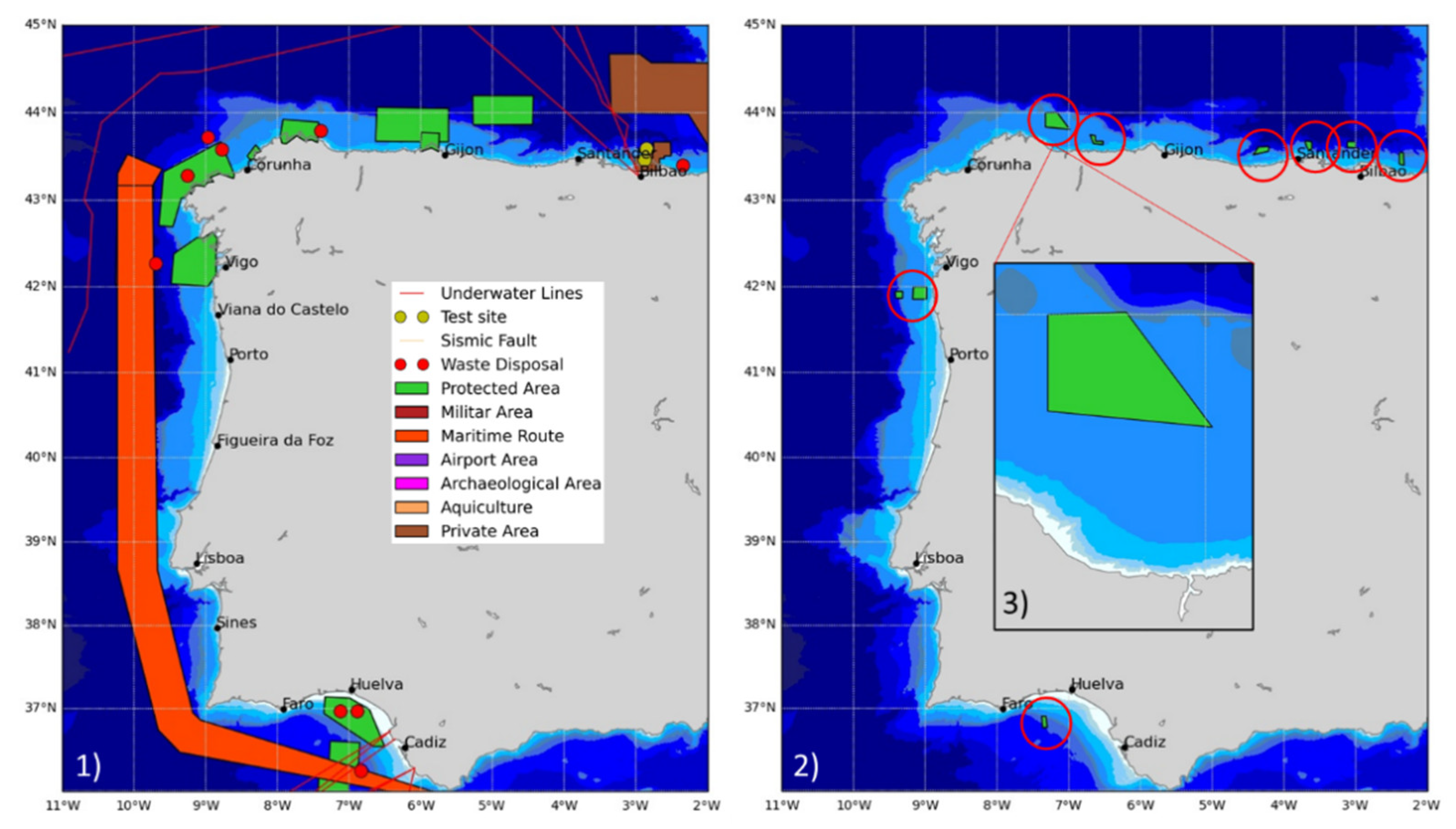
- Díaz, H.; Guedes Soares, C. An Integrated GIS Approach for Site Selection of Floating Offshore Wind Farms in the Atlantic Continental European Coastline. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, H.; Guedes Soares, C. A Multi-Criteria Approach to Evaluate Floating Offshore Wind Farms Siting in the Canary Islands (Spain). Energies 2021, 14, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, H.; Guedes Soares, C. A Novel Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Model to Evaluate Floating Wind Farm Locations. Renew. Energy 2021, 185, 431–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, H.; Palos Teixeira, A.; Guedes Soares, C. Application of Fuzzy and Monte Carlo Analytic Hierarchy Processes for Ranking Floating Wind Farm Locations. Ocean Eng. 2022, 245, 110453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokicki, T.; Bórawski, P.; Gradziuk, B.; Gradziuk, P.; Mrówczyńska-Kamińska, A.; Kozak, J.; Guzal-Dec, D.J.; Wojtczuk, K. Differentiation and Changes of Household Electricity Prices in EU Countries. Energies 2021, 14, 6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baita-Saavedra, E.; Cordal-Iglesias, D.; Filgueira-Vizoso, A.; Morató, À.; Lamas-Galdo, I.; Álvarez-Feal, C.; Carral, L.; Castro-Santos, L. An Economic Analysis of An Innovative Floating Offshore Wind Platform Built with Concrete: The SATH® Platform. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunoglu, E.; Guedes Soares, C. Response Dynamics of a Free-Float Capable Tension Leg Platform for a 10 MW Wind Turbine at the Northern Iberian Peninsula. In Developments in Renewable Energies Offshore; Guedes Soares, C., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2021; pp. 408–416. ISBN 9780367681319. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.T.; Kim, D.H. The Platform Pitching Motion of Floating Offshore Wind Turbine: A Preliminary Unsteady Aerodynamic Analysis. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2015, 142, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, A.; Angus, A.; Brennan, F. Stochastic Prediction of Offshore Wind Farm LCOE through an Integrated Cost Model. Energy Procedia 2017, 107, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, M.; Sandborn, P.; Goudarzi, N. A Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) Model for Wind Farms That Include Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). Renew. Energy 2018, 122, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
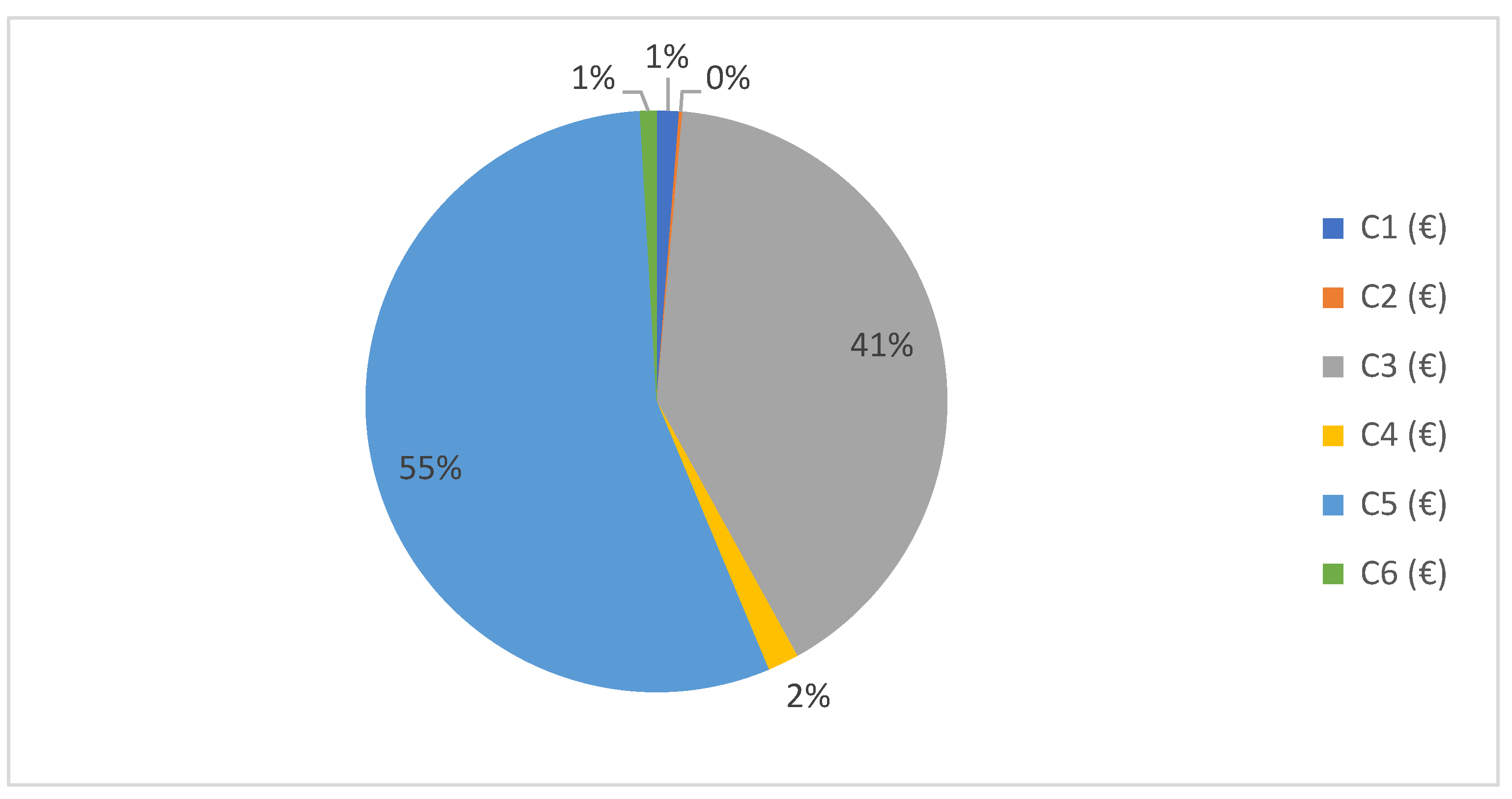

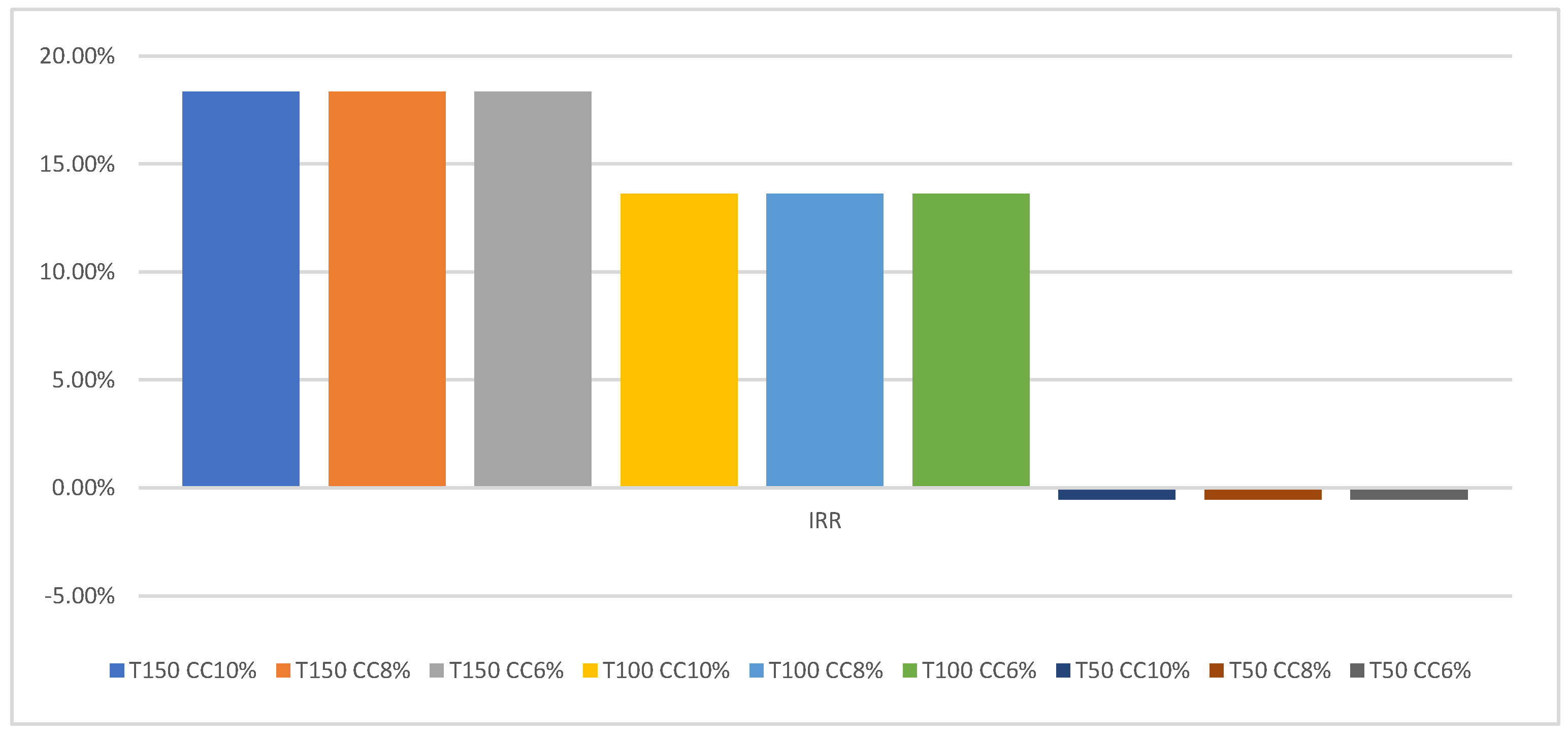
| Variable | Concept | Units |
|---|---|---|
| EPCIC | EPCIC stands for Engineering, Procurement, Construction, Installation & Commissioning (contract) | % |
| OffshoreSiteR | Offshore site renting | € |
| Nplatforms | Number of floating platforms | platforms |
| Cemet | Meteorological structure cost | € |
| Csmet | Meteorological sensors cost | € |
| Csamet | Auxiliary meteorological systems cost | € |
| EvaluationReportCost | Evaluation report cost | €/MW |
| TurbineP | Power of the wind turbine | MW |
| GeophysicalDailyCost | Geophysical campaign cost (bathymetry, sub bottom profiler, garbage, wreck detections, etc.) | €/day |
| GeophysicalDays | Duration of the geophysical campaign | days |
| GeotechnicalDailyCost | Geotechnical campaign cost (CPT: cone penetration tests) | €/day |
| GeotechnicalDays | Duration of the geotechnical campaign | days |
| Cinsurance | Insurances coefficient | €/MW |
| TravellingCosts | Travelling costs of the preparation of the project | - |
| Staff | Number of staff of the project enterprise | staff |
| AverageCostY | Staff average cost per year | €/year |
| Years0 | Number of years until year 0 | years |
| OfficeRentingM | Office renting per month | €/month |
| RatioWTGPriceCosts | Ratio between wind turbine generator price and its costs | - |
| Nplatforms | Number of floating platforms | platforms |
| FEED | Drafting Costs | € |
| DetailDesignCosts | Detailed design costs | € |
| TankTestingInplace | Tank testing-inplace cost (based on other similar projects) | € |
| TankTestingTransport | Tank testing-transport cost (based on other similar projects) | € |
| PreliminaryWorksYardCosts | Preliminary works at yard Costs | € |
| OneDrydockCost | One dry dock costs | € |
| Ndrydocks | Number of drydocks | docks |
| C3241 | Renting on harbour area cost for foundations | € |
| C3242 | Renting on harbour area cost for generator | € |
| C3243 | Renting on harbour area cost for office | € |
| C3244 | Renting on wet harbour area cost | € |
| PreparingSeabedCost | Cost of preparing the seabed for one unit | € |
| TotalMaterialCostPlatform | Total cost of the materials of the platforms considering scale economy | € |
| CraneDrydockConstructionCostYT | Crane dry dock construction cost | € |
| CraneDrydockSupportCostYT | Crane dry dock support cost | € |
| HarbourInternalTowingYears | Number of years neccesary for the harbour internal towings | years |
| TugMobDemobCost | Cost of mob or demob the tug | € |
| BollarPullTugDR | Daily rate associated with a bollard pull tug (65 tonnes) | €/day |
| NDiversPlat | Number of divers per platform | divers |
| DiverDailyCost | Daily cost associated with one diver | €/day |
| DiverDaysIntervention | Days that the diver need for each intervention | days |
| NAccessesPlat | Number of accesses per platform | - |
| PlatformAccessCost | Platform access cost (1 unit) | €/platform |
| NInternalsTower | Number of internals per tower | - |
| TowerInternalsCost | Tower internals cost (1 unit) | €/platform |
| NJTubesPlat | Number of J-tubes per platform | j-tubes |
| JTubeCost | J-tube cost (per unit) | €/j-tube |
| ReductionFactorBallast | Reduction factor (economy of scale) for the ballast system | - |
| TotalBallastCostPlat | Total Ballast Cost platform | € |
| NSetsCommunicationPlat | Number of sets (communication system) per platform | - |
| ReductionFactorCommunication | Cost of 1 communication system | € |
| CommunicationSystemCost1 | Reduction factor (economy of scale) for the communication system | - |
| NSetsLightingPlat | Number of sets (lighting system) per platform | - |
| LightingSystemCost1 | Cost of 1 lighting system | € |
| ReductionFactorLighting | Reduction factor (economy of scale) for the lighting system | - |
| PlatformMonitoringCost | Platform monitoring cost (inclinometer and others) (1 platform) | €/platform |
| StructuralMonitoringCost | Structural monitoring cost | € |
| C33+ C34 | Mooring and anchoring manufacturing cost | € |
| C351 | Electric cable manufacturing cost | € |
| C352 | Substation manufacturing cost | € |
| C411 | Cost of installation of turbines at port | € |
| C412 | Cost of the transport of the turbines | € |
| C413 | Cost of installation of turbines offshore | € |
| C42 | Cost of installing the floating TLP platforms | € |
| Cabarge | Cost of installing mooring and anchoring of a barge per day | €/day |
| Catug | Cost of installing mooring and anchoring of a tug per day | €/day |
| CaaMOD | Cost of labour per day for installing mooring and anchoring | €/day |
| Caapumpsanddivers | Cost of divers | €/day |
| Nanchoring | Number of anchors | anchors |
| Tinstbarge | Time of installing mooring and anchoring | Anchors/day |
| BurialCableCost1Plat | Cost associated with the burial cable intertidal area for 1 platform | €/platform |
| HDDCost1Plat | Cost associated with the HDD horizontal drilling for 1 platform | €/platform |
| DynamicCableInstallationCost1Plat | Cost associated with the dynamic cable installation for 1 platform | €/platform |
| ExportCableInstallationCost | Export cable installation cost | € |
| CableMechanicalProtectionCost | Cable mechanical protection cost | € |
| CableBurialIntertidalAreaCost | Cable burial (intertidal area) cost | € |
| InterarrayCableCommissioningCost | Interarray cable commissioning cost | € |
| ExportCableCommissioningCost | Export cable commisioning cost | € |
| C51 | Cost of assurance | € |
| C521 | Data acquisition (SCADA) cost | € |
| C522 | SAP & Maritime coordination costs | € |
| C523 | Meteorological prediction cost | € |
| C524 | Administration cost | € |
| C531 | Turbine maintenance cost | € |
| C532 | Export cable and grid connection maintenance | € |
| C533 | Interarray cable survey and repairs cost | € |
| C534 | Substructure maintenance | € |
| Nfarm | Number of years of life-cycle of the farm | Years |
| C54year | Onshore logistics costs per year | €/year |
| C551year | Workboats costs per year | €/year |
| C552year | Helicopter costs per year | €/year |
| C553year | Crane barge service costs per year | €/year |
| C554year | Offshore accommodation (if any) cost | €/year |
| PDturbine | Percentage of dismantling turbine and platform | - |
| PDmooring | Percentage of dismantling mooring | - |
| PDcable | Percentage of dismantling cable | - |
| PDsubstation | Percentage of dismantling substation | - |
| Item | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Water depth | 150 | m/s |
| Wave conditions | 2.15 | m |
| Marine currents | 0.51 | m/s |
| Distance to local electrical grid | 18.60 | km |
| Distance from coastal facilities | 89.50 | km |
| Distance from shore | 17.61 | km |
| Distance from maritime routes | 1.50 | km |
| Distance from protected areas | 10.92 | km |
| Area of the territory | 405 | km2 |
| Wind farm capacity | 880 | MW |
| Number of 10 MW turbines | 88 | - |
| Variable | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| EPCIC | 0 | % |
| OffshoreSiteR | 100,000 | € |
| Nplatforms | 88 | platforms |
| Cemet | 2,338,480 | € |
| Csmet | 467,696 | € |
| Csamet | 116,924 | € |
| EvaluationReportCost | 2500 | €/MW |
| TurbineP | 10 | MW |
| GeophysicalDailyCost | 15,000 | €/day |
| GeophysicalDays | 2 | days |
| GeotechnicalDailyCost | 35,000 | €/day |
| GeotechnicalDays | 3 | days |
| Cinsurance | 33,877.2 | €/MW |
| TravellingCosts | 0.15 | - |
| Staff | 15 | staff |
| AverageCostY | 65,000 | €/year |
| Years0 | 7 | years |
| OfficeRentingM | 4000 | €/month |
| RatioWTGPriceCosts | - | - |
| Nplatforms | 88 | platforms |
| FEED | 3,877,520 | € |
| DetailDesignCosts | 5,028,000 | € |
| TankTestingInplace | 125,000 | € |
| TankTestingTransport | 75,000 | € |
| PreliminaryWorksYardCosts | 5,000,000 | € |
| OneDrydockCost | 3,550,000 | € |
| Ndrydocks | 1 | docks |
| C3241 | 17,104,140.9 | € |
| C3242 | 82,125 | € |
| C3243 | 54,750 | € |
| C3244 | 862,312.5 | € |
| PreparingSeabedCost | 200,000 | € |
| TotalMaterialCostPlatform | 312,052,35 | € |
| CraneDrydockConstructionCostYT | 2,940,000 | € |
| CraneDrydockSupportCostYT | 1,900,000 | € |
| HarbourInternalTowingYears | 2 | years |
| TugMobDemobCost | 3000 | € |
| BollarPullTugDR | 18,000 | €/day |
| NDiversPlat | 2 | divers |
| DiverDailyCost | 1500 | €/day |
| DiverDaysIntervention | 2 | days |
| NAccessesPlat | 1 | - |
| PlatformAccessCost | 175,000 | €/platform |
| NInternalsTower | 1 | - |
| TowerInternalsCost | 125,000 | €/platform |
| NJTubesPlat | 1 | j-tubes |
| JTubeCost | 40,000 | €/j-tube |
| ReductionFactorBallast | 0.8 | - |
| TotalBallastCostPlat | 0 | € |
| N_SetsCommunicationPlat | 1 | - |
| ReductionFactorCommunication | 75,000 | € |
| CommunicationSystemCost1 | 0.8 | - |
| NSetsLightingPlat | 1 | - |
| LightingSystemCost1 | 20,000 | € |
| ReductionFactorLighting | 0.8 | - |
| PlatformMonitoringCost | 20.000 | €/platform |
| StructuralMonitoringCost | 90.000 | € |
| C33 + C34 | 268,712,67 | € |
| C351 | 60,901,417 | € |
| C352 | 15,000.000 | € |
| C411 | 132,285 | € |
| C412 | 7,002,858.21 | € |
| C413 | 14,744,889 | € |
| C42 | 12,414,616 | € |
| Cabarge | 7500 | €/day |
| Catug | 22,502 | €/day |
| CaaMOD | 5656 | €/day |
| Caapumpsanddivers | 0 | €/day |
| Nanchoring | 1056 | anchors |
| Tinstbarge | 3 | Anchors/day |
| BurialCableCost1Plat | 25,000 | €/platform |
| HDDCost1Plat | 0 | €/platform |
| DynamicCableInstallationCost1Plat | 100,000 | €/platform |
| ExportCableInstallationCost | 8,000,000 | € |
| CableMechanicalProtectionCost | 80,000 | € |
| CableBurialIntertidalAreaCost | 1,000,000 | € |
| InterarrayCableCommissioningCost | 100,000 | € |
| ExportCableCommissioningCost | 100,000 | € |
| C51 | 22,618,239 | € |
| C521 | 6,750,000 | € |
| C522 | 33,000,000 | € |
| C523 | 3,575,000 | € |
| C524 | 19,250,000 | € |
| C531 | 630,300 | € |
| C532 | 16,654,000 | € |
| C533 | 19,250,000 | € |
| C534 | 115,500,000 | € |
| Nfarm | 25 | Years |
| C54year | 1,210,000 | €/year |
| C551year | 5,500,000 | €/year |
| C552year | 4,950,000 | €/year |
| C553year | 17,600,000 | €/year |
| C554year | 33,000,000 | €/year |
| PDturbine | 70% | - |
| PDmooring | 90% | - |
| PDcable | 10% | - |
| PDsubstation | 90% | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filgueira-Vizoso, A.; Castro-Santos, L.; Iglesias, D.C.; Puime-Guillén, F.; Lamas-Galdo, I.; García-Diez, A.I.; Uzunoglu, E.; Díaz, H.; Soares, C.G. The Technical and Economic Feasibility of the CENTEC Floating Offshore Wind Platform. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101344
Filgueira-Vizoso A, Castro-Santos L, Iglesias DC, Puime-Guillén F, Lamas-Galdo I, García-Diez AI, Uzunoglu E, Díaz H, Soares CG. The Technical and Economic Feasibility of the CENTEC Floating Offshore Wind Platform. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(10):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101344
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilgueira-Vizoso, Almudena, Laura Castro-Santos, David Cordal Iglesias, Félix Puime-Guillén, Isabel Lamas-Galdo, Ana Isabel García-Diez, Emre Uzunoglu, Hugo Díaz, and C. Guedes Soares. 2022. "The Technical and Economic Feasibility of the CENTEC Floating Offshore Wind Platform" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 10: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101344
APA StyleFilgueira-Vizoso, A., Castro-Santos, L., Iglesias, D. C., Puime-Guillén, F., Lamas-Galdo, I., García-Diez, A. I., Uzunoglu, E., Díaz, H., & Soares, C. G. (2022). The Technical and Economic Feasibility of the CENTEC Floating Offshore Wind Platform. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(10), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101344













