A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes that Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review and Discussion
2.1. The Need to Consider Context of Observations and Soil-Solution Dynamics
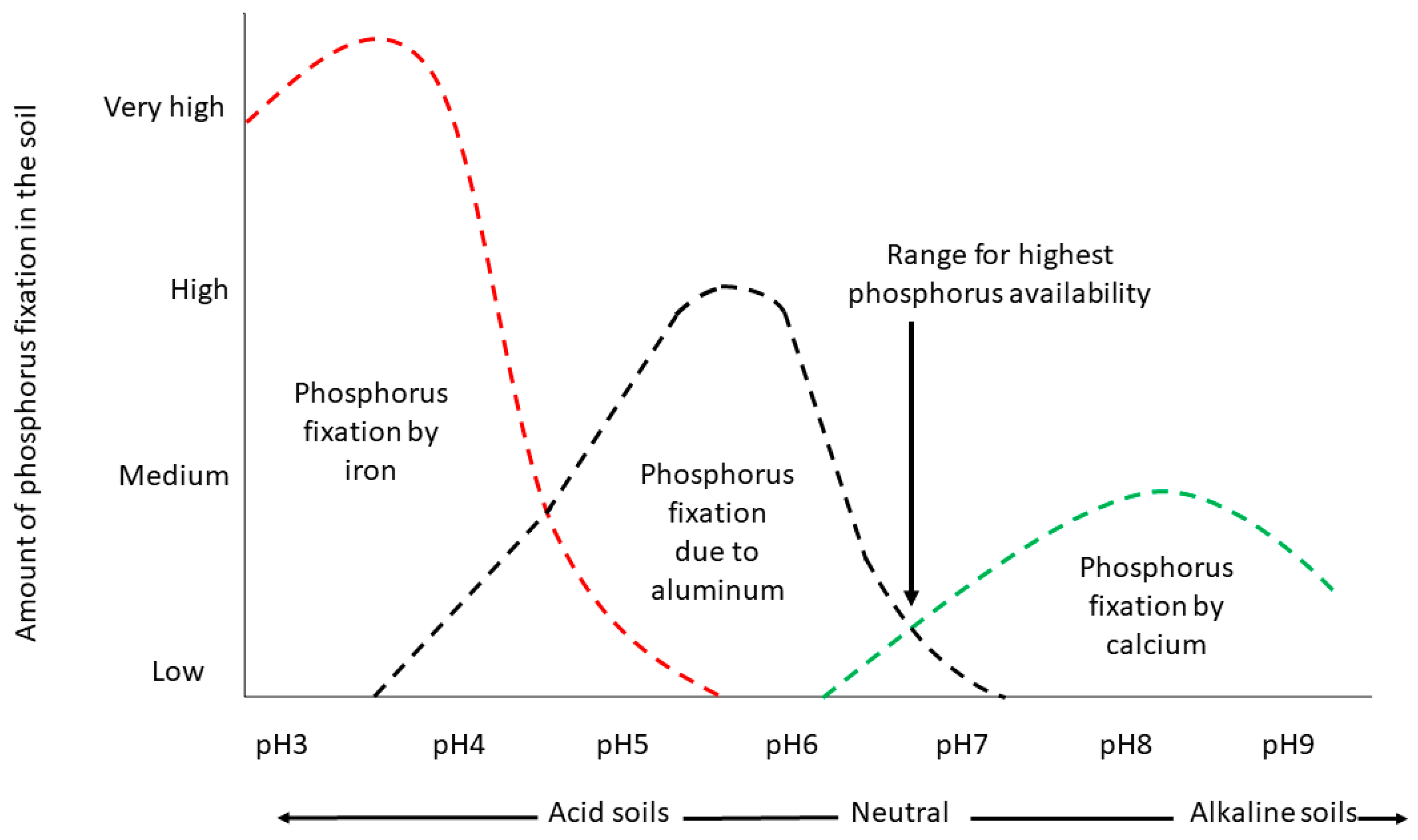
2.2. How Are Different Individual P Sorption Mechanisms Impacted by pH?
2.2.1. Anion Exchange
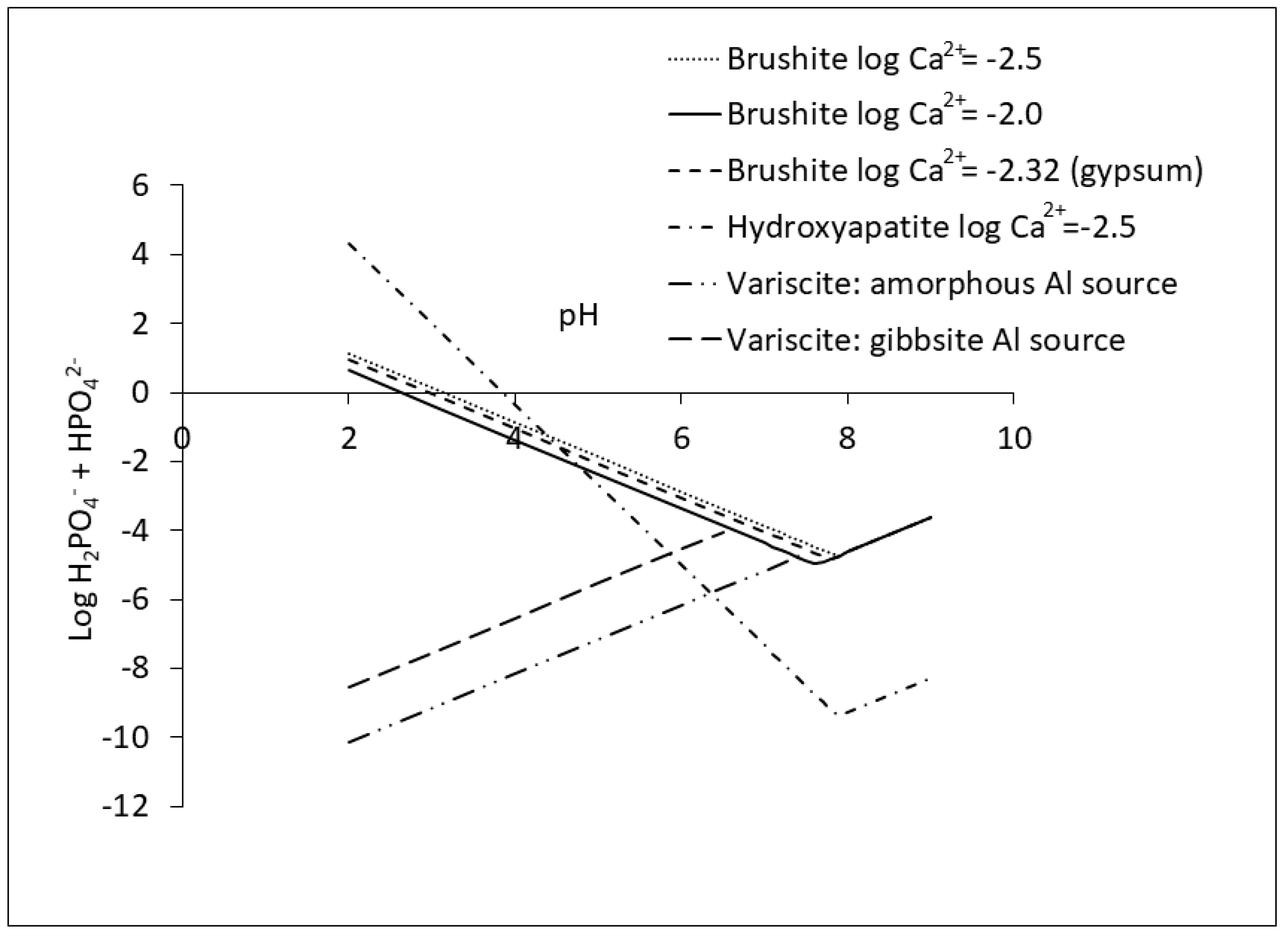
2.2.2. Precipitation of Ca Phosphates
2.2.3. Ligand Exchange (Adsorption) to Al and Fe Oxides/Hydroxides and Edges of Alumino-Silicate Minerals
2.2.4. Precipitation of Al and Fe Phosphates
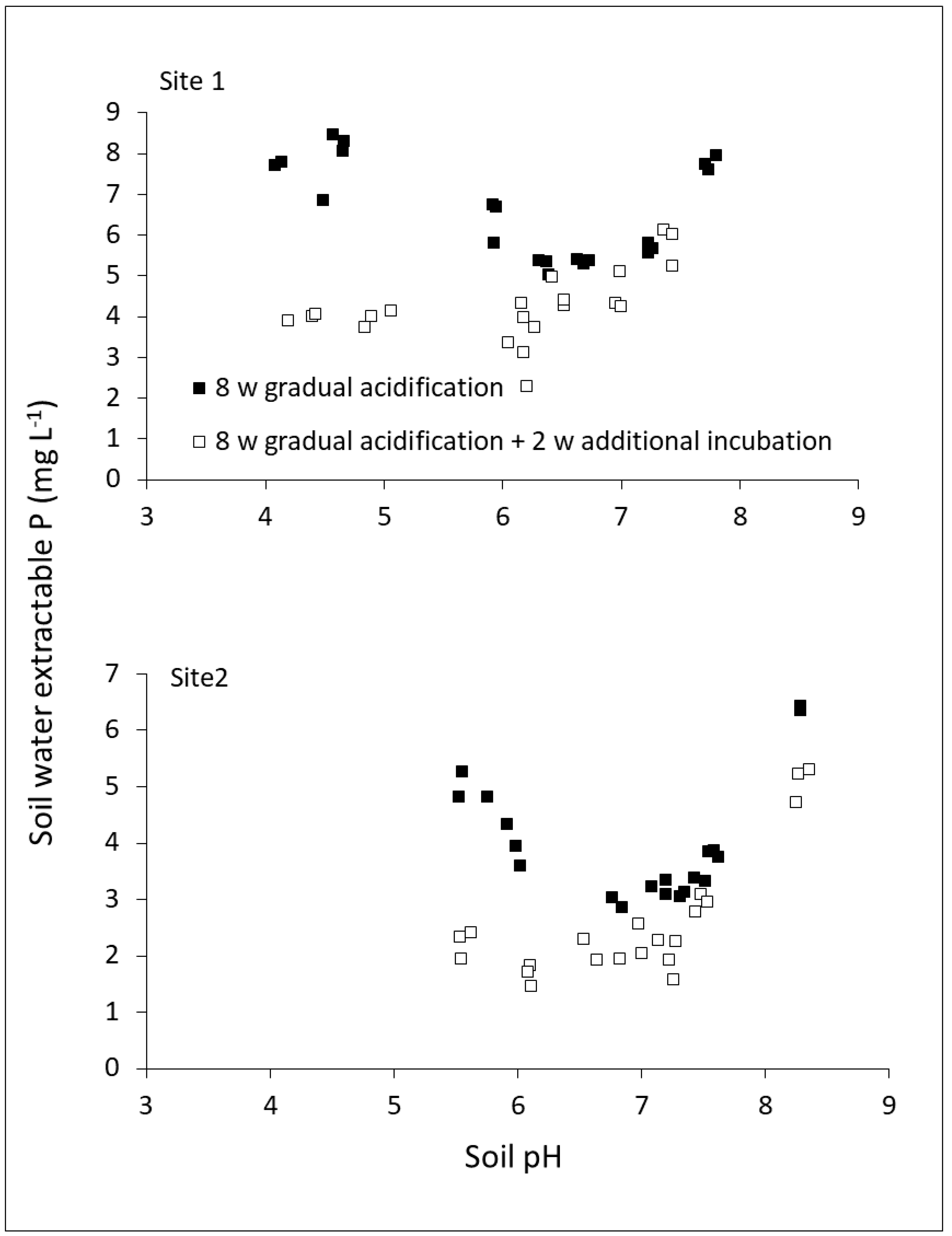
2.3. Dynamics among P Reactions in Soil
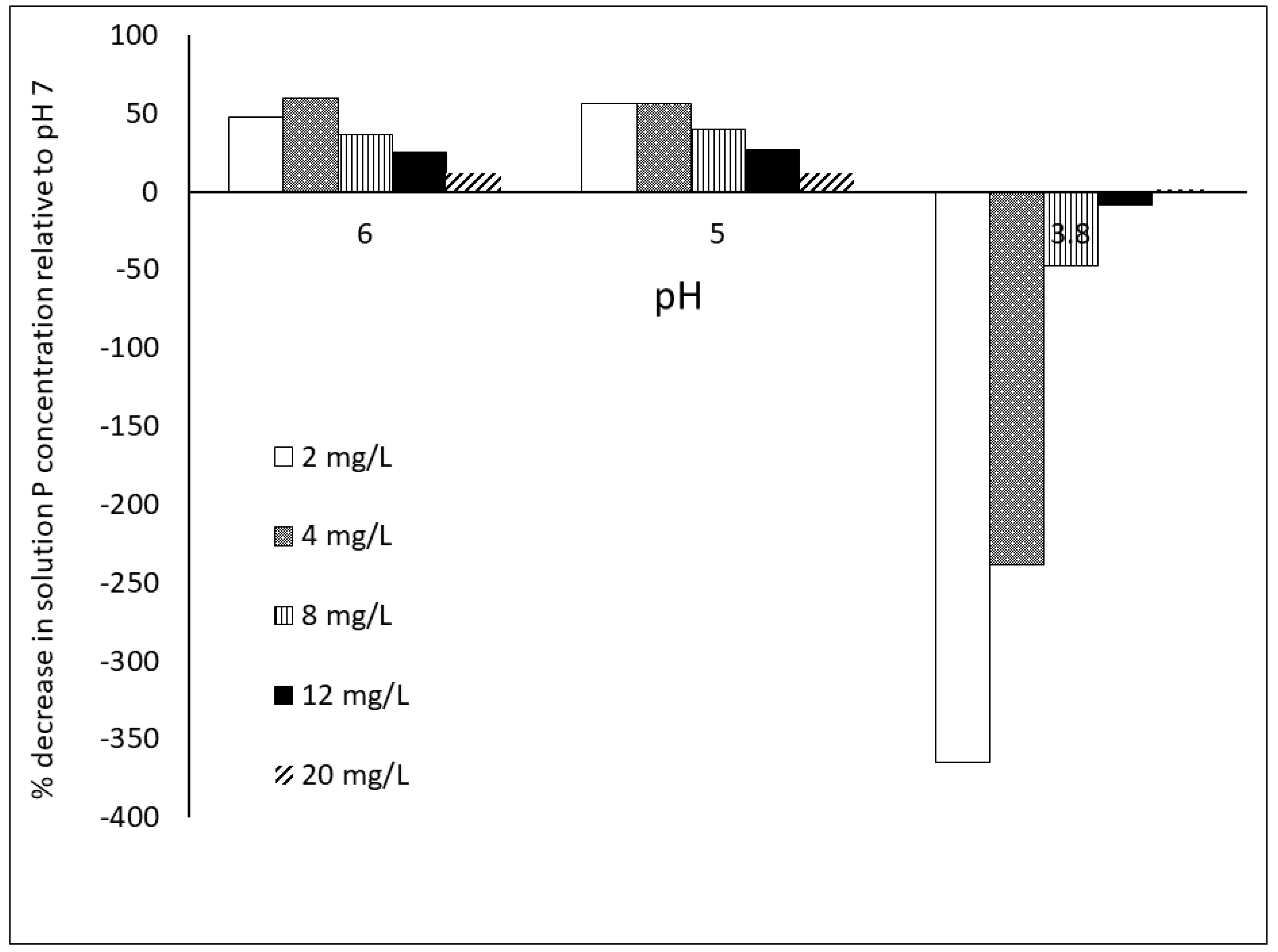
2.4. Impact of Methodology: Time of Equilibration and P Extraction Solution
2.5. Measuring P Uptake in Soil with Changing pH and the Interaction between Yield, Plant P Uptake, and Other Soil Properties Affected by pH
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CEC | cation exchange capacity |
| K | thermodynamic solubility constant |
| PZC | point of zero charge |
| AER | anion exchange resin |
| CER | cation exchange resin |
| d | days |
| w | weeks |
References
- Price, G. Australian Soil Fertility Manual; Fertilizer Industry Federation of Australia, Inc. & CSIRO: Collingwood, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, N.J. The effects of pH on phosphate uptake from the soil. Plant Soil 2017, 410, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasiri, S.L.; Olsen, S.R. Liming as Related to Solubility of P and Plant Growth in an Acid Tropical Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1973, 37, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, A.J.; Cook, R.L. The Effect of Soil Reaction on the Availability of Phosphorus for Alfalfa in Some Eastern Ontario Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1955, 19, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, D.F.; Loneragan, J.F. An effect of lime of residual phosphorus in soil. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1960, 11, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neller, J.R. Effect of Lime on Availability of Labeled Phosphorus of Phosphates in Rutlege Fine Sand and Marlboro and Carnegie Fine Sandy Loams. Soil Sci. 1953, 75, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensminger, L.E.; Pearson, R.W. Residual Effects of Various Phosphates as Measured by Yields, P32 Uptake, and Extractable Phosphorus. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1957, 21, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoop, G.J.; Brooks, C.R.; Blaser, R.E.; Thomas, G.W. Differential Responses of Grasses and Legumes to Liming and Phosphorus Fertilization. Agron. J. 1961, 53, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abruna, F.; Vicente-Chandler, J.; Pearson, R.W. Effects of Liming on Yields and Composition of Heavily Fertilized Grasses and on Soil Properties Under Humid Tropical Conditions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1964, 28, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, M.E.; Farina, M.P.W. Phosphorus interactions with other nutrients and lime in field cropping systems. In Advances in Soil Science; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 201–236. [Google Scholar]
- Curtin, D.; Syers, J.K. Lime-induced changes in indices of soil phosphate availability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, A.F. Inorganic soil phosphorus fractions of some Ontario soils as studied using isotopic exchange and solubility criteria. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1962, 42, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talibudeen, O. Isotopically exchangeable phosphorus in soils: Part II. Factors influencing the estimation of ‘labile’phosphorus. J. Soil Sci. 1957, 8, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrmann, R.P.; Peech, M. Effect of pH on Labile and Soluble Phosphate in Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1969, 33, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.; Barber, S.A. Effect of Ammonium and Nitrate Fertilization on Phosphorus Uptake as Related to Root-Induced pH Changes at the Root-Soil Interface. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1971, 35, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J.P.; Mwamila, L.B.; Kergoat, K. The pH dependence of phosphate sorption and desorption in Swedish agricultural soils. Geoderma 2012, 189, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, D.; Syers, J.K.; Smillie, G.W. The importance of exchangeable cations and resin-sink characteristics in the release of soil phosphorus. J. Soil Sci. 1987, 38, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, M.D.R.; Edwards, A.C.; Shand, C.A.; Cresser, M.S. Phosphorus fractions in soil solution: Influence of soil acidity and fertiliser additions. Plant Soil 1993, 148, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, P.H.; Rennie, D.A. Reactions of phosphate in aluminum systems.: I. adsorption of phosphate by X-ray amorphous” aluminum hydroxide”. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1962, 42, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, C.; Brennan, R.; Sarre, G.A. Effect of soil pH and crop sequence on the response of wheat (Triticum aestivum) to phosphorus fertiliser. Crop Pasture Sci. 2015, 66, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Tucher, S.; Hörndl, D.; Schmidhalter, U. Interaction of soil pH and phosphorus efficacy: Long-term effects of P fertilizer and lime applications on wheat, barley, and sugar beet. Ambio 2018, 47, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrmann, R.P.; Peech, M. Relative significance of labile and crystalline phosphates in soil. Soil Sci. 1969, 107, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.R.; Sinaj, S.; Condron, L.M.; Frossard, E.; Sherlock, R.R.; Davis, M.R. Characterization of phosphorus availability in selected New Zealand grassland soils. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2003, 65, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, J.; Vanderdeelen, J.; Hofman, G. Effect of soil properties on the kinetics of phosphate release. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1998, 29, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Rutter, E.B.; Arnall, D.B.; Camberato, J.; Williams, M.; Watkins, P. A discussion on mehlich-3 phosphorus extraction from the perspective of governing chemical reactions and phases: Impact of soil pH. Agriculture 2018, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.; Bryant, R. Incubation of dried and sieved soils can induce calcium phosphate precipitation/adsorption. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 37, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.T.; Guadalix, M.E.; Garcia-Gonzalez, M.T. Effect of pH and background electrolyte on P sorption by variable charge soils. Geoderma 1992, 54, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Jiang, J.; Cheng, C. Effect of Ionic Strength on Specific Adsorption of Ions by Variable Charge Soils: Experimental Testification on the Adsorption Model of Bowden et al. In Molecular Environmental Soil Science at the Interfaces in the Earth’s Critical Zone; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Bolan, N.S.; Syers, J.K.; Tillman, R.W. Ionic strength effects on surface charge and adsorption of phosphate and sulphate by soils. J. Soil Sci. 1986, 37, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darch, T.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Hawkins, J.M.B.; Haygarth, P.M.; Chadwick, D. A meta-analysis of organic and inorganic phosphorus in organic fertilizers, soils, and water: Implications for water quality. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2172–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vange, M.S.; Holmern, K.; Nissen, P.E.R. Multiphasic uptake of sulfate by barley roots I. Effects of analogues, phosphate, and pH. Physiol. Plant. 1974, 31, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentenac, H.; Grignon, C. Effect of pH on orthophosphate uptake by corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1985, 77, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N. Phosphorus solubility and release kinetics as a function of soil test P concentration. Geoderma 2003, 112, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, N.T.; Thorup, J.T.; Jackson, W.A. Phosphate-sorption Reactions That Involve Exchangeable A1. Soil Sci. 1960, 90, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.S.; Melo, L.C.A.; Vergütz, L.; Rodríguez-Vila, A.; Covelo, E.F.; Fernandes, A.R. Adsorption and desorption kinetics and phosphorus hysteresis in highly weathered soil by stirred flow chamber experiments. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 162, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.W.; Condron, L.M.; Mahieu, N.; Brookes, P.C.; Poulton, P.R.; Sharpley, A.N. Analysis of potentially mobile phosphorus in arable soils using solid state nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, S.; Sims, J.T.; Sparks, D.L. How accurate is the assessment of phosphorus pools in poultry litter by sequential extraction? J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prietzel, J.; Dümig, A.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Klysubun, W. Synchrotron-based P K-edge XANES spectroscopy reveals rapid changes of phosphorus speciation in the topsoil of two glacier foreland chronosequences. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 108, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchemin, S.; Hesterberg, D.; Chou, J.; Beauchemin, M.; Simard, R.R.; Sayers, D.E. Speciation of phosphorus in phosphorus-enriched agricultural soils using X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy and chemical fractionation. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Solomon, D.; Hyland, C.; Ketterings, Q.M.; Lehmann, J. Phosphorus speciation in manure and manure-amended soils using XANES spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7485–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ler, A.; Stanforth, R. Evidence for surface precipitation of phosphate on goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2694–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kirkpatrick, R.J. An investigation of phosphate adsorbed on aluminium oxyhydroxide and oxide phases by nuclear magnetic resonance. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 55, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittrick, J.A.; Jackson, M.L. Rate of Phosphate Reaction with Soil Minerals and Electron Microscope Observations on the Reaction Mechanism. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1955, 19, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Ellis, A.S. Testing a mechanistic model. V. The points of zero salt effect for phosphate retention, for zinc retention and for acid/alkali titration of a soil. J. Soil Sci. 1986, 37, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Debnath, A. Effect of phosphate status on the sorption and desorption properties of some soils of northern India. Plant Soil 2014, 378, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, R.; Brümmer, G.W.; Barrow, N.J. Effects of crystallinity of goethite: II. Rates of sorption and desorption of phosphate. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1997, 48, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L. Chemical Equilibria in Soils; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979; ISBN 0471027049. [Google Scholar]
- Essington, M.E. Soil and Water Chemistry: An Integrative Approach, 2nd ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2015; ISBN 9781466573154. [Google Scholar]
- Haseman, J.F.; Brown, E.H.; Whitt, C.D. Some reactions of phosphate with clays and hydrous oxides of iron and aluminum. Soil Sci. 1950, 70, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, E.O. Reactions of Phosphate in Soils: Recent Research by TVA; Fertiliser Society: Colchester, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, W.L.; Stephenson, H.F. Nature of the Reactions of Monocalcium Phosphate Monohydrate in Soils: II. Dissolution and Precipitation Reactions Involving Iron, Aluminum, Manganese, and Calcium. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1959, 23, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L.; Lehr, J.R.; Stephenson, H.F. Nature of the Reactions of Monocalcium Phosphate Monohydrate in Soils: III. Studies with Metastable Triple-Point Solution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1959, 23, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, A.K.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Hesterberg, D. Phosphorus speciation of clay fractions from long-term fertility experiments in Sweden. Geoderma 2015, 241, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Sanders, R.L.; Xu, C.; Li, J.; Myneni, S.C.B. Phosphorus speciation and transformation in long-term fertilized soil: Evidence from chemical fractionation and P K-edge XANES spectroscopy. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2017, 107, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, M.B. Environmental Soil Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zelazny, L.W.; He, L.; Vanwormhoudt, A.N. Charge analysis of soils and anion exchange. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3—Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., et al., Eds.; SSSA, ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 1231–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L. Environmental Soil Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; ISBN 0080494803. [Google Scholar]
- Hingston, F.J. A review of anion adsorption. In Adsorption Inorganic Solid Liquids Interfaces; Ann Arbor Science: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1981; pp. 51–90. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.M.; Zelazny, L.W.; Martens, D.C.; Baligar, V.C.; Ritchey, K.D. Ionic strength effects on sulfate and phosphate adsorption on γ-alumina and kaolinite: Triple-layer model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Warren, J.G. Investigating phosphorus sorption onto kaolinite using isothermal titration calorimetry. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Zhang, H. Isothermal titration calorimetry as an indicator of phosphorus sorption behavior. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J. A mechanistic model for describing the sorption and desorption of phosphate by soil. J. Soil Sci. 1983, 34, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, E.C.; Soper, R.J.; Racz, G.J. Reactions of phosphate fertilizers in soils. In Role of Phosphorus in Agriculture; Khasawneh, F.E., et al., Eds.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1980; pp. 263–310. [Google Scholar]
- Kittrick, J.A.; Jackson, M.L. Electron-microscope observations of the reaction of phosphate with minerals, leading to a unified theory of phosphate fixation in soils. J. Soil Sci. 1956, 7, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riemsdijk, W.H.; Lyklema, J. Reaction of phosphate with gibbsite (Al (OH) 3) beyond the adsorption maximum. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 76, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.R.; Butler, J.N.; Stumm, W. Kinetic study of phosphate reaction with aluminum oxide and kaolinite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1973, 7, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L.; Frazier, A.W.; Stephenson, H.F. Identification of reaction products from phosphate fertilizers in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1962, 26, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philen, O.D.; Lehr, J.R. Reactions of Ammonium Polyphosphates with Soil Minerals. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1967, 31, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, I.; Hughes, J.D.; Philen, O.D. Reactions of Triammonium Pyrophosphate with Soils and Soil Minerals. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1969, 33, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, P.F.; Black, C.A. Phosphate-Induced Decomposition of Kaolinite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1948, 12, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robarge, W.P.; Corey, R.B. Adsorption of phosphate by hydroxy-aluminum species on a cation exchange resin. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1979, 43, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.H.; Rennie, D.A. Reactions of phosphate in aluminum systems: II. Precipitation of phosphate by exchangeable aluminum on a cation exchange resin. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1962, 42, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Woodruff, J.R.; Kamprath, E.J. Phosphorus Adsorption Maximum as Measured by the Langmuir Isotherm and Its Relationship to Phosphorus Availability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1965, 29, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Bryant, R.B. Phosphorus solubility in response to acidification of dairy manure amended soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devau, N.; Hinsinger, P.; Le Cadre, E.; Colomb, B.; Gérard, F. Fertilization and pH effects on processes and mechanisms controlling dissolved inorganic phosphorus in soils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 2980–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsinger, P.; Herrmann, L.; Lesueur, D.; Robin, A.; Trap, J.; Waithaisong, K.; Plassard, C. Impact of roots, microorganisms and microfauna on the fate of soil phosphorus in the rhizosphere. Annu. Plant Rev. Online 2018, 48, 377–407. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, J.D.; Brown, D.S.; Novo-Gradac, K.J. MINTEQA2/PRODEFA2, A Geochemical Assessment Model for Environmental Systems: Version 3.0 User’s Manual; Environmental Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1991.
- Racz, G.J.; Soper, R.J. Solubility of dimagnesium phosphate trihydrate and trimagnesium phosphate. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1968, 48, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fuhrman, J.K.; Zhang, H.; Schroder, J.L.; Davis, R.L.; Payton, M.E. Water-Soluble Phosphorus as Affected by Soil to Extractant Ratios, Extraction Times, and Electrolyte. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 36, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, A.K.; Ulén, B.; Berzina, L.; Iital, A.; Janssons, V.; Sileika, A.S.; Toomsoo, A. Phosphorus in agricultural soils around the Baltic Sea–comparison of laboratory methods as indices for phosphorus leaching to waters. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryden, J.C.; Syers, J.K. Rationalization of ionic strength and cation effects on phosphate sorption by soils. J. Soil Sci. 1975, 26, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryden, J.C.; Syers, J.K. Calcium Retention in Response to Phosphate Sorption by Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1976, 40, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3; Chemical Methods; SSSA Book Series 5; Sparks, D.L., et al., Eds.; SSSA, ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 869–919. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, N.J. Further investigations on the use of lime on established pastures. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1965, 5, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, A.; Rosolem, C.A.; He, Z. Non-labile phosphorus acquisition by Brachiaria. J. Plant Nutr. 2016, 39, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Almeida, D.S.; Penn, C.J.; Rosolem, C.A. Assessment of phosphorus availability in soil cultivated with ruzigrass. Geoderma 2018, 312, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, M.; Watanabe, T.; Tadano, T. Beneficial effect of aluminum on growth of plants adapted to low pH soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1997, 43, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-H.; Barber, S.A. Soil pH and phosphorus and potassium uptake by maize evaluated with an uptake model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Mollier, A.; Morel, C.; Vives, A.; Prud’homme, L.; Pellerin, S. Relative contribution of seed phosphorus reserves and exogenous phosphorus uptake to maize (Zea mays L.) nutrition during early growth stages. Plant Soil 2011, 346, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J.; Veneklaas, E.J. Nature and nurture: The importance of seed phosphorus content. Plant Soil 2012, 357, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes that Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9060120
Penn CJ, Camberato JJ. A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes that Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants. Agriculture. 2019; 9(6):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9060120
Chicago/Turabian StylePenn, Chad J., and James J. Camberato. 2019. "A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes that Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants" Agriculture 9, no. 6: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9060120
APA StylePenn, C. J., & Camberato, J. J. (2019). A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes that Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants. Agriculture, 9(6), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9060120





