Identification and Expression Analysis of Two allene oxide cyclase (AOC) Genes in Watermelon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Sequence Analysis of the AOC Genes in Watermelon
2.2. Alignment of Amino Acid Sequences and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Expression Pattern Analysis of the AOC Genes in Different Tissues
2.4. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.5. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR of the AOC Genes in Watermelon
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification and Sequence Analysis of the AOC Genes in Watermelon
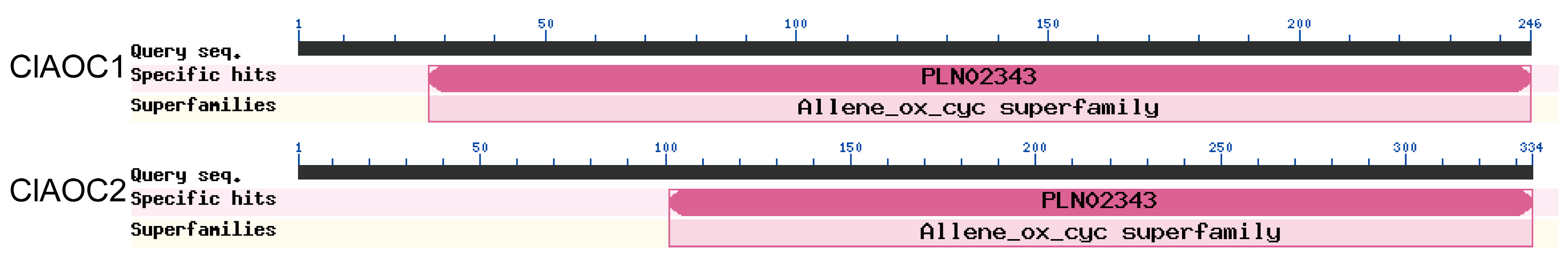
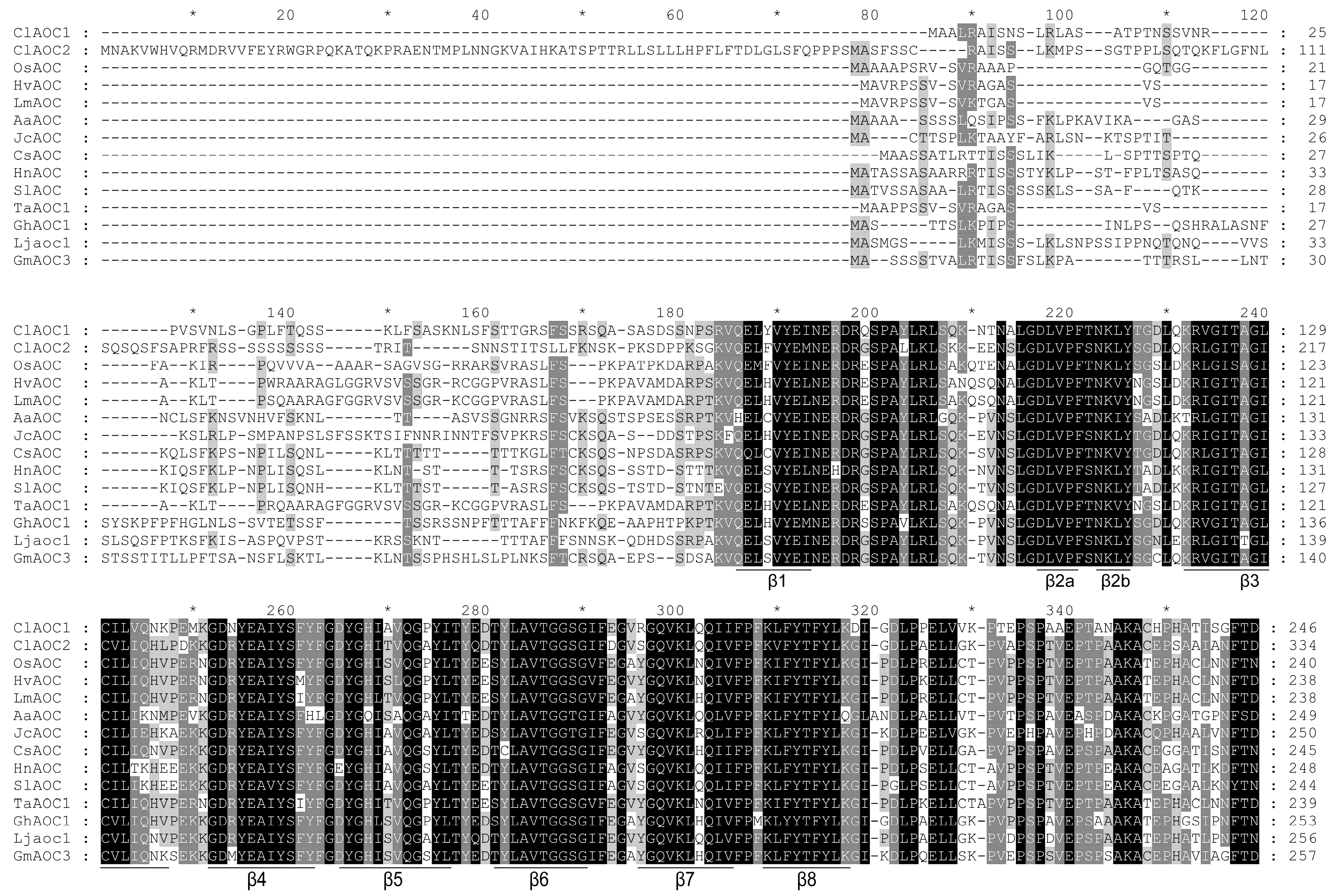
3.2. Characterization of ClAOC1 and ClAOC2
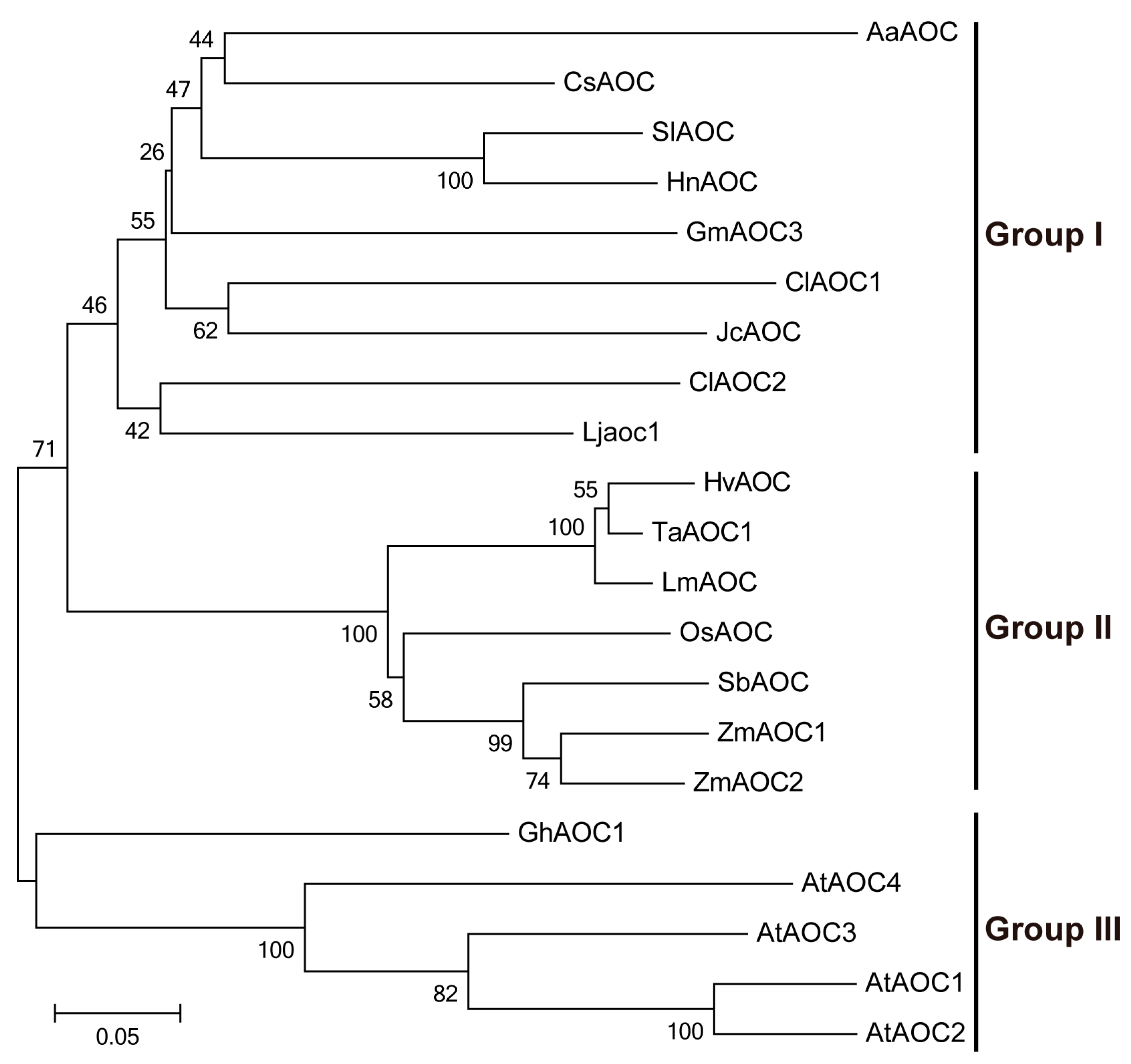
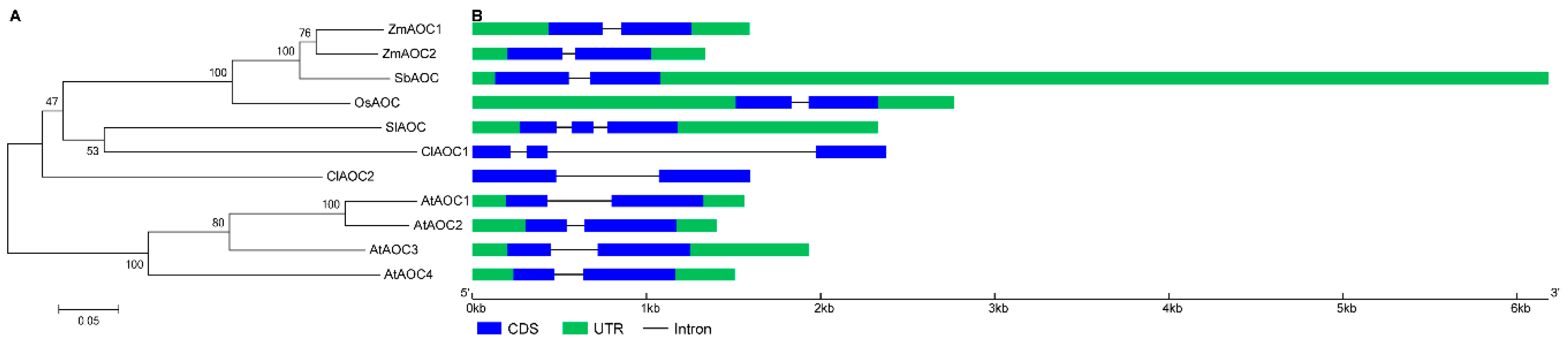
3.3. Phylogenetic and Structural Analyses of AOC Genes from Different Plant Species
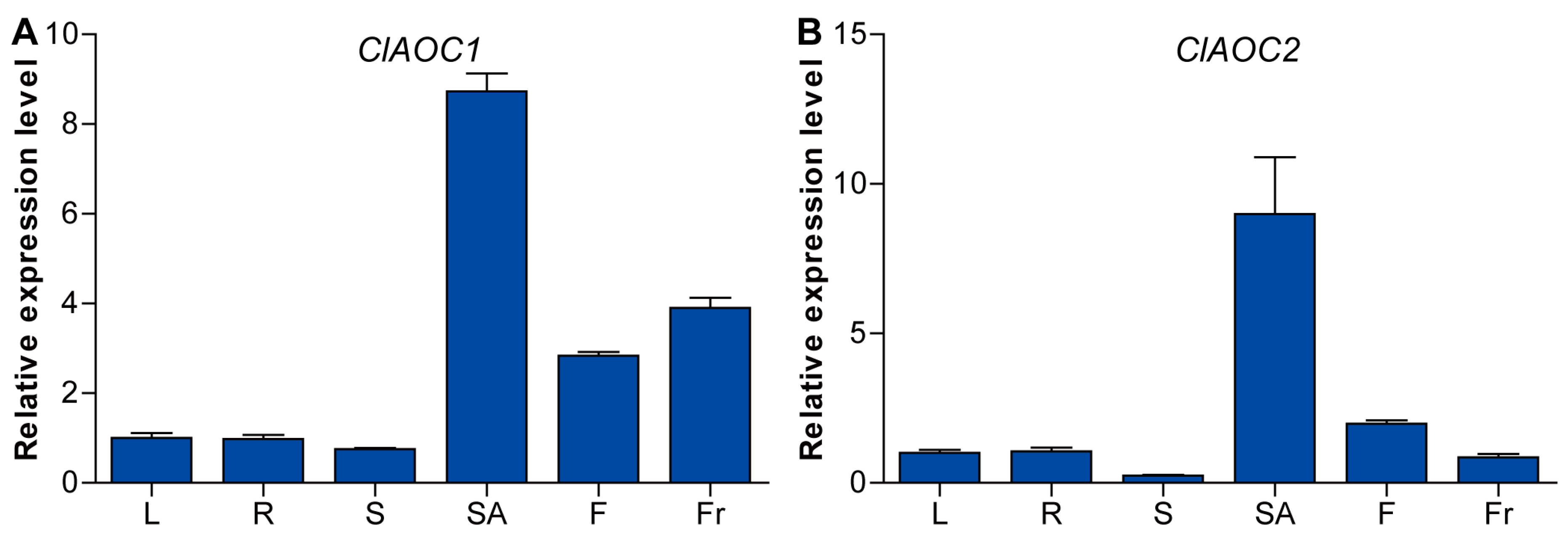
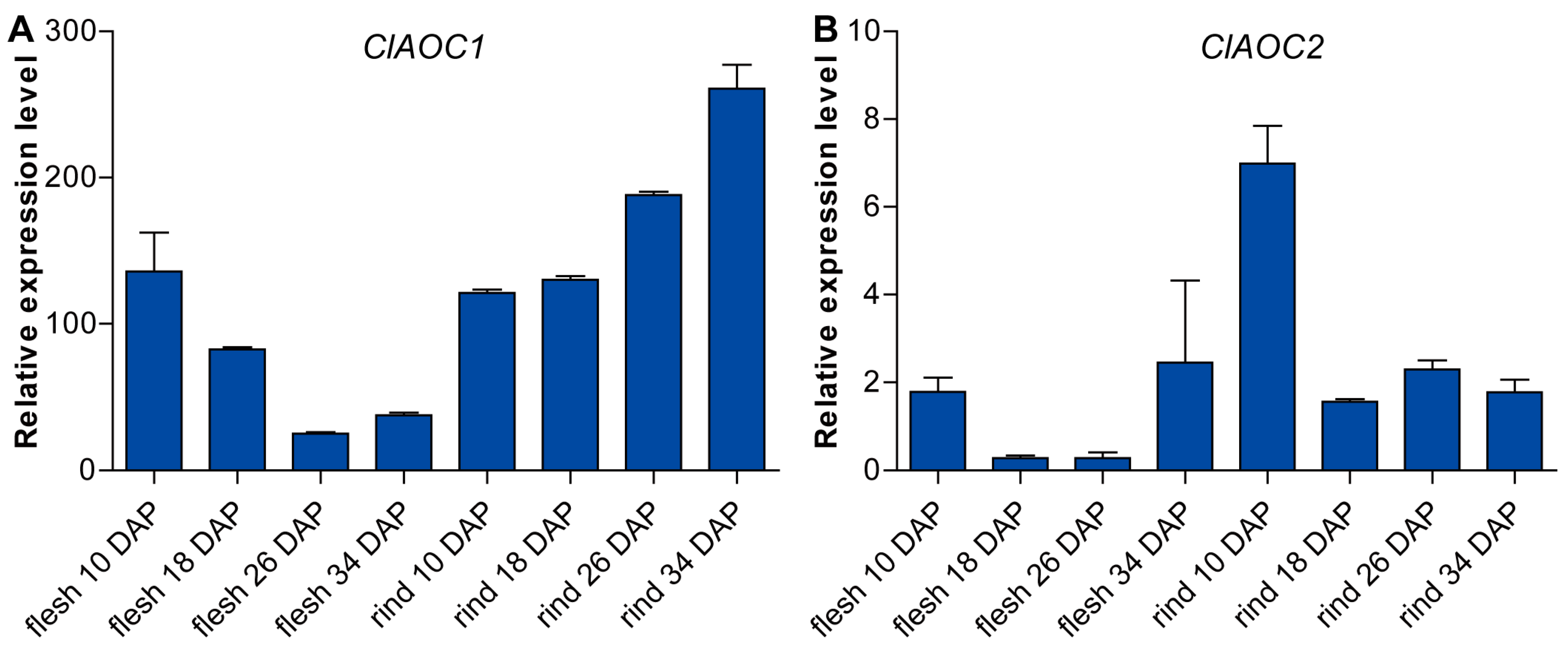
3.4. Expression Patterns of ClAOC1 and ClAOC2 in Different Tissues
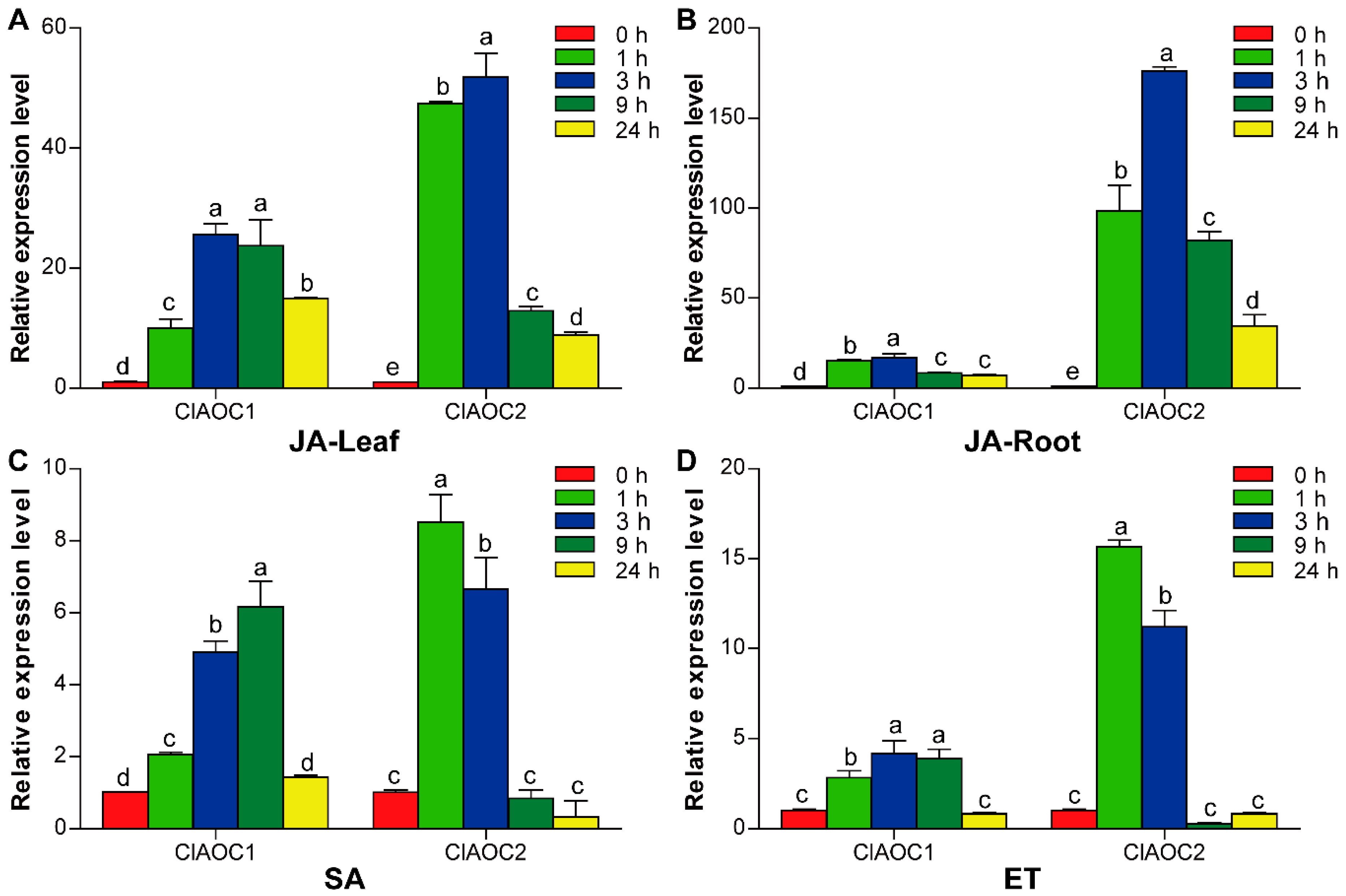
3.5. Expression Patterns of ClAOC1 and ClAOC2 in Response to Hormones
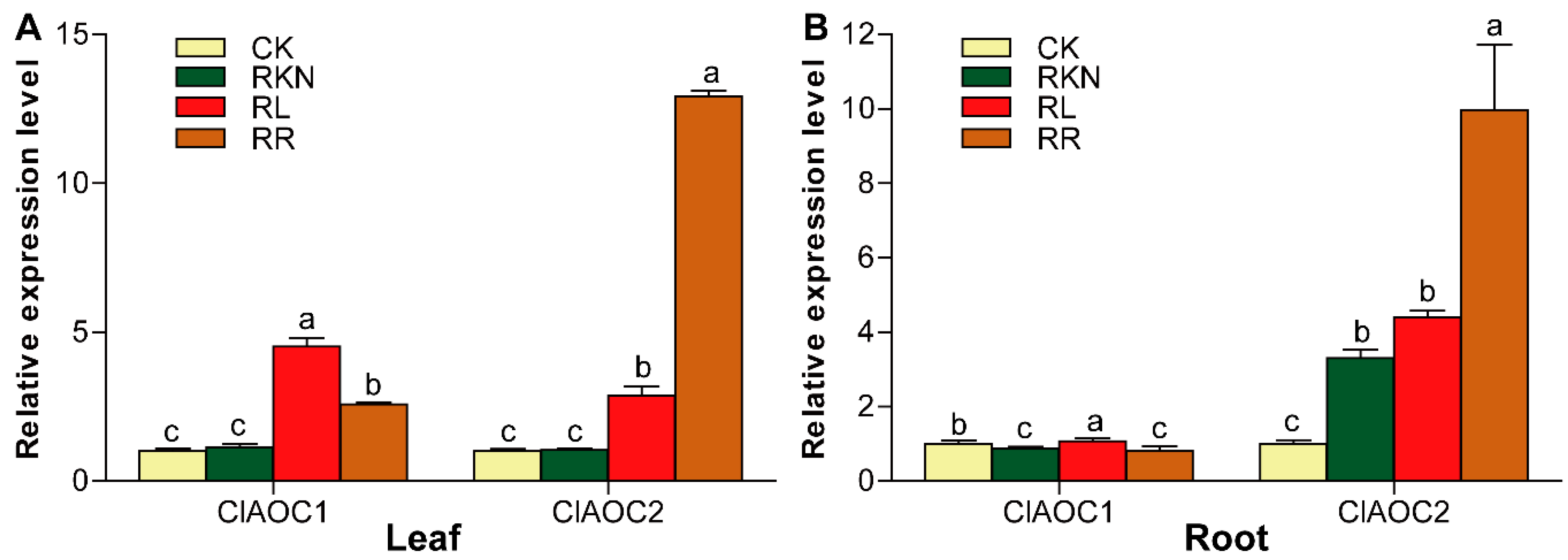
3.6. Expression Patterns of ClAOC1 and ClAOC2 in Response to Root-Knot Nematode Infection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyons, R.; Manners, J.M.; Kazan, K. Jasmonate biosynthesis and signaling in monocots: A comparative overview. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Per, T.S.; Khan, M.I.R.; Anjum, N.A.; Masood, A.; Hussain, S.J.; Khan, N.A. Jasmonates in plants under abiotic stresses: Crosstalk with other phytohormones matters. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 145, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpe, M.; Feussner, I. Formation of oxylipins by CYP74 enzymes. Phytochem. Rev. 2006, 5, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberg, M.; Fahlstadius, P. Allene oxide cyclase: A new enzyme in plant lipid metabolism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 276, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Jiang, W.; Pan, Q.; Lv, Z.; Yan, T.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Qian, H.; et al. Overexpression of allene oxide cyclase improves the biosynthesis of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.; Stenzel, I.; Hause, B.; Maucher, H.; Hamberg, M.; Grimm, R.; Ganal, M.; Wasternack, C. Molecular cloning of allene oxide cyclase: The enzyme establishing the stereochemistry of octadecanoids and jasmonates. J. Boil. Chem. 2000, 275, 19132–19138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, D.; Yu, D. Sequence and expression divergence of the AOC gene family in soybean: Insights into functional diversity for stress responses. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Xin, Q. Improvement of copper tolerance of Arabidopsis by transgenic expression of an allene oxide cyclase gene, GhAOC1, in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Crop J. 2015, 3, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, I.; Hause, B.; Miersch, O.; Kurz, T.; Maucher, H.; Weichert, H.; Ziegler, J.; Feussner, I.; Wasternack, C. Jasmonate biosynthesis and the allene oxide cyclase family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Boil. 2003, 51, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdyb, A.; Salgado, M.G.; Demchenko, K.N.; Brenner, W.G.; Płaszczyca, M.; Stumpe, M.; Herrfurth, C.; Feussner, I.; Pawlowski, K. Allene oxide synthase, allene oxide cyclase and jasmonic acid levels in Lotus japonicus nodules. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.; Brodhun, F.; Sauer, K.; Herrfurth, C.; Hamberg, M.; Brinkmann, J.; Scholz, J.; Dickmanns, A.; Feussner, I.; Ficner, R. Crystal structures of Physcomitrella patens AOC1 and AOC2: Insights into the enzyme mechanism and differences in substrate specificity. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemann, M.; Haga, K.; Shimizu, T.; Okada, K.; Ando, S.; Mochizuki, S.; Nishizawa, Y.; Yamanouchi, U.; Nick, P.; Yano, M.; et al. Identification of rice Allene Oxide Cyclase mutants and the function of jasmonate for defence against Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant J. 2013, 74, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maucher, H.; Stenzel, I.; Miersch, O.; Stein, N.; Prasad, M.; Zierold, U.; Schweizer, P.; Dorer, C.; Hause, B.; Wasternack, C. The allene oxide cyclase of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.)—cloning and organ-specific expression. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, Y.; Liao, Z.; Jiang, K.; Huang, B.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, H.; Sun, X.; Tang, K. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of a jasmonate biosynthetic pathway gene encoding allene oxide cyclase from Camptotheca acuminata. Biosci. Rep. 2008, 28, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, I.; Otto, M.; Delker, C.; Kirmse, N.; Schmidt, D.; Miersch, O.; Hause, B.; Wasternack, C. ALLENE OXIDE CYCLASE (AOC) gene family members of Arabidopsis thaliana: Tissue- and organ-specific promoter activities and in vivo heteromerization. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 6125–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayenkov, S.; Mrosk, C.; Stenzel, I.; Strack, D.; Hause, B. Suppression of allene oxide cyclase in hairy roots of Medicago truncatula reduces jasmonate levels and the degree of Mycorrhization with Glomus intraradices. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhang, N.; Ai, X.; Wang, M.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, L.; Xia, G. A wheat allene oxide cyclase gene enhances salinity tolerance via jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Yu, D. Soybean GmAOC3 promotes plant resistance to the common cutworm by increasing the expression of genes involved in resistance and volatile substance emission in transgenic tobaccos. J. Plant Boil. 2015, 58, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazman, M.; Hause, B.; Eiche, E.; Nick, P.; Riemann, M. Increased tolerance to salt stress in OPDA-deficient rice ALLENE OXIDE CYCLASE mutants is linked to an increased ROS-scavenging activity. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3339–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.M.; Li, H.C.; Zhou, S.R.; Xue, H.W.; Miao, X.X. Cis-12-oxo-phytodienoic acid stimulates rice defense response to a piercing-sucking insect. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, H. Cloning and characterization of peanut allene oxide cyclase gene involved in salt-stressed responses. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ge, X. The CfAOS and CfAOC genes related to flower fragrance biosynthesis in Cymbidium faberi could confer drought tolerance to transgenic tomatoes. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 20, 883–892. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.X.; Wu, C.; Ahammed, G.J.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wan, C.; Chen, J. Red light-induced systemic resistance against root-knot nematode is mediated by a coordinated regulation of salicylic acid, jasmonic acid and redox signaling in watermelon. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.X.; Wang, M.M.; Ren, Y.; Onac, E.; Zhou, G.; Peng, S.; Xia, X.J.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q. Light-induced systemic resistance in tomato plants against root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, K.; Kyndt, T.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Höfte, M.; Gheysen, G. The jasmonate pathway is a key player in systemically induced defense against root knot nematodes in rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, X.; Lei, H.; Fan, J.; Yang, R.; Li, Z.; Hu, C.; Li, M.; Zhao, F.; Wang, S. Transcriptional evidence for cross talk between JA and ET or SA during root-knot nematode invasion in tomato. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naor, N.; Gurung, F.B.; Ozalvo, R.; Bucki, P.; Sanadhya, P.; Miyara, S.B. Tight regulation of allene oxide synthase (AOS) and allene oxide cyclase-3 (AOC3) promote Arabidopsis susceptibility to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne javanica. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 150, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ge, L.; Li, G.; He, P.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S. In silico identification and expression analysis of Rare Cold Inducible 2 (RCI2) gene family in cucumber. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Salse, J.; Lucas, W.J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. The draft genome of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) and resequencing of 20 diverse accessions. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Yang, Y. Identification and characterization of the glutathione peroxidase (GPX) gene family in watermelon and its expression under various abiotic stresses. Agronomy 2018, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Liao, Z.; Pi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Hou, R.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Tang, K. Molecular cloning and expression profile of a jasmonate biosynthetic pathway gene for allene oxide cyclase from Hyoscyamus niger. Mol. Boil. 2008, 42, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, W.; Gao, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Tang, L.; Jia, Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a jasmonate biosynthetic pathway gene for allene oxide cyclase from Jatropha curcas. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 32, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lin, X.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, S.; Tang, K. Characterization of the jasmonate biosynthetic gene allene oxide cyclase in Artemisia annua L., source of the antimalarial drug artemisinin. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 29, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habora, M.E.E.; Eltayeb, A.E.; Oka, M.; Tsujimoto, H.; Tanaka, K. Cloning of allene oxide cyclase gene from Leymus mollis and analysis of its expression in wheat–Leymus chromosome addition lines. Breed. Sci. 2013, 63, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.X.; Ma, Q.P.; Han, B.Y.; Li, X.H. Molecular cloning and expression of a jasmonate biosynthetic gene allene oxide cyclase from Camellia sinensis. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2016, 96, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, E.; Zerbe, P.; Schaller, F. The crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana allene oxide cyclase: Insights into the oxylipin cyclization reaction. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3201–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.C.; Chen, J.F.; Xiao, Y.; Di, P.; Xuan, H.J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.S. Overexpression of allene oxide cyclase promoted tanshinone/phenolic acid production in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Medina, A.; Fernandez, I.; Lok, G.B.; Pozo, M.J.; Pieterse, C.M.; Van Wees, S.C. Shifting from priming of salicylic acid- to jasmonic acid-regulated defences by Trichoderma protects tomato against the root knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrudo, I.; Keller, M.M.; Cargnel, M.D.; Demkura, P.V.; De Wit, M.; Patitucci, M.S.; Pierik, R.; Pieterse, C.M.; Ballaré, C.L. Low red/far-red ratios reduce Arabidopsis resistance to Botrytis cinerea and jasmonate responses via a COI1-JAZ10-dependent, salicylic acid-independent mechanism. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 2042–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazan, K.; Manners, J.M. The interplay between light and jasmonate signalling during defence and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4087–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, M.R.; Ferrieri, A.P.; Herth, M.M.; Ferrieri, R.A. 11C-imaging: Methyl jasmonate moves in both phloem and xylem, promotes transport of jasmonate, and of photoassimilate even after proton transport is decoupled. Planta 2007, 226, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacombe, B.; Achard, P. Long-distance transport of phytohormones through the plant vascular system. Curr. Opin. Plant Boil. 2016, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, M.; Ton, J. Long-distance signalling in plant defence. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Gene ID | Genomic Position | gDNA (bp) | ORF (bp) | Length (aa) | pI | MW (kDa) | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClAOC1 | Cla016453 | Chr11: 21540468 .. 21542845 (+) | 2378 | 741 | 246 | 8.74 | 28.86 | −0.268 |
| ClAOC2 | Cla003512 | Chr3: 13175215 .. 13176809 (+) | 1595 | 1005 | 334 | 9.62 | 36.67 | −0.309 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Guang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Identification and Expression Analysis of Two allene oxide cyclase (AOC) Genes in Watermelon. Agriculture 2019, 9, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9100225
Li J, Guang Y, Yang Y, Zhou Y. Identification and Expression Analysis of Two allene oxide cyclase (AOC) Genes in Watermelon. Agriculture. 2019; 9(10):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9100225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jingwen, Yelan Guang, Youxin Yang, and Yong Zhou. 2019. "Identification and Expression Analysis of Two allene oxide cyclase (AOC) Genes in Watermelon" Agriculture 9, no. 10: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9100225
APA StyleLi, J., Guang, Y., Yang, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2019). Identification and Expression Analysis of Two allene oxide cyclase (AOC) Genes in Watermelon. Agriculture, 9(10), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9100225





