Interaction of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BV03 and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Physiology, Nutrition, and Yield
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Soil Characteristics
2.3. Experimental Design, Treatments, and Agronomic Management
2.4. Evaluations
2.4.1. Biometrics
2.4.2. Physiological Assessments
2.4.3. Photosynthetic Pigments
2.4.4. Leaf Nutritional Diagnosis
2.4.5. Plant Biomass and Yield
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
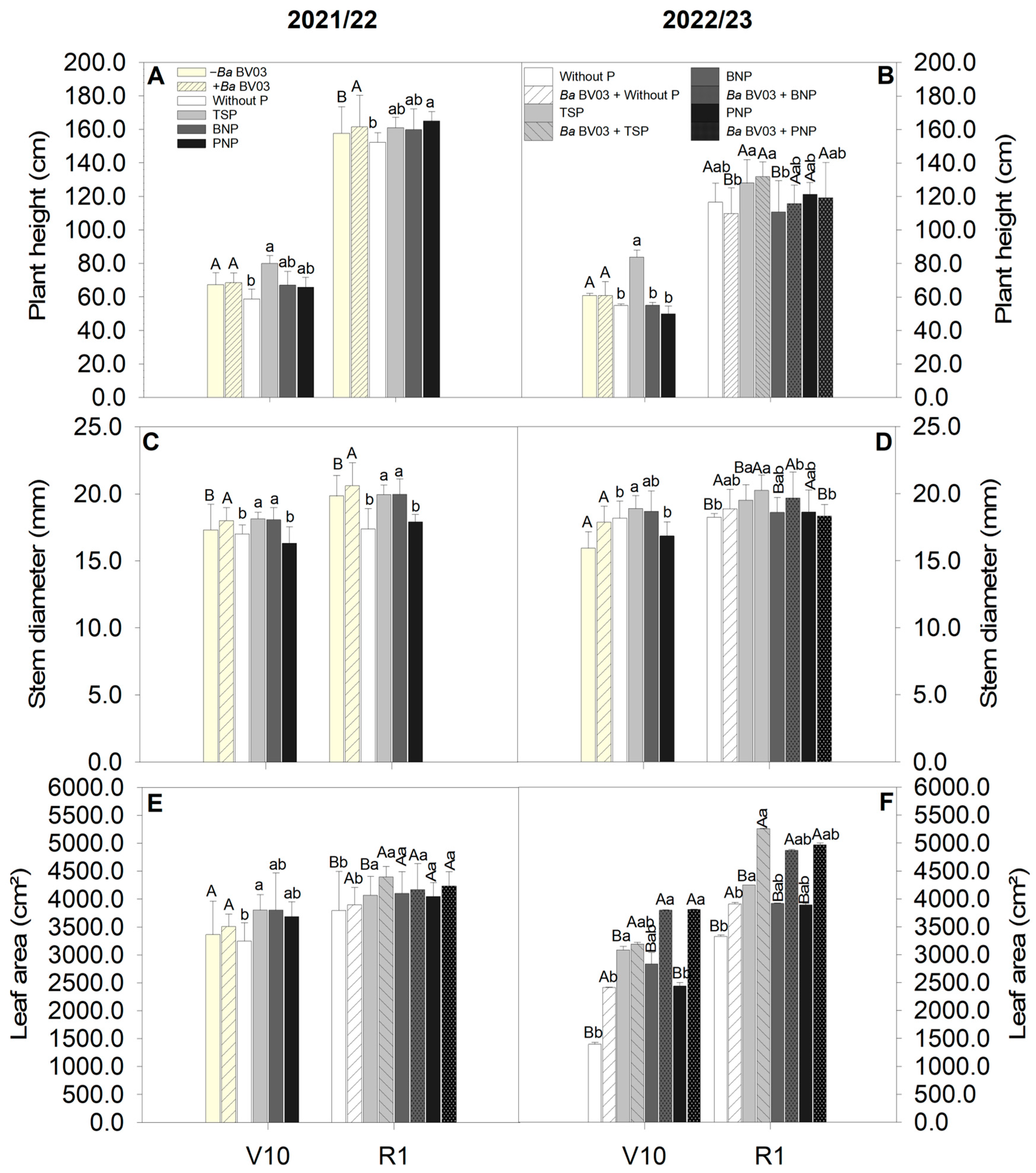
3.1. Impact of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Inoculation and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Morphological Parameters
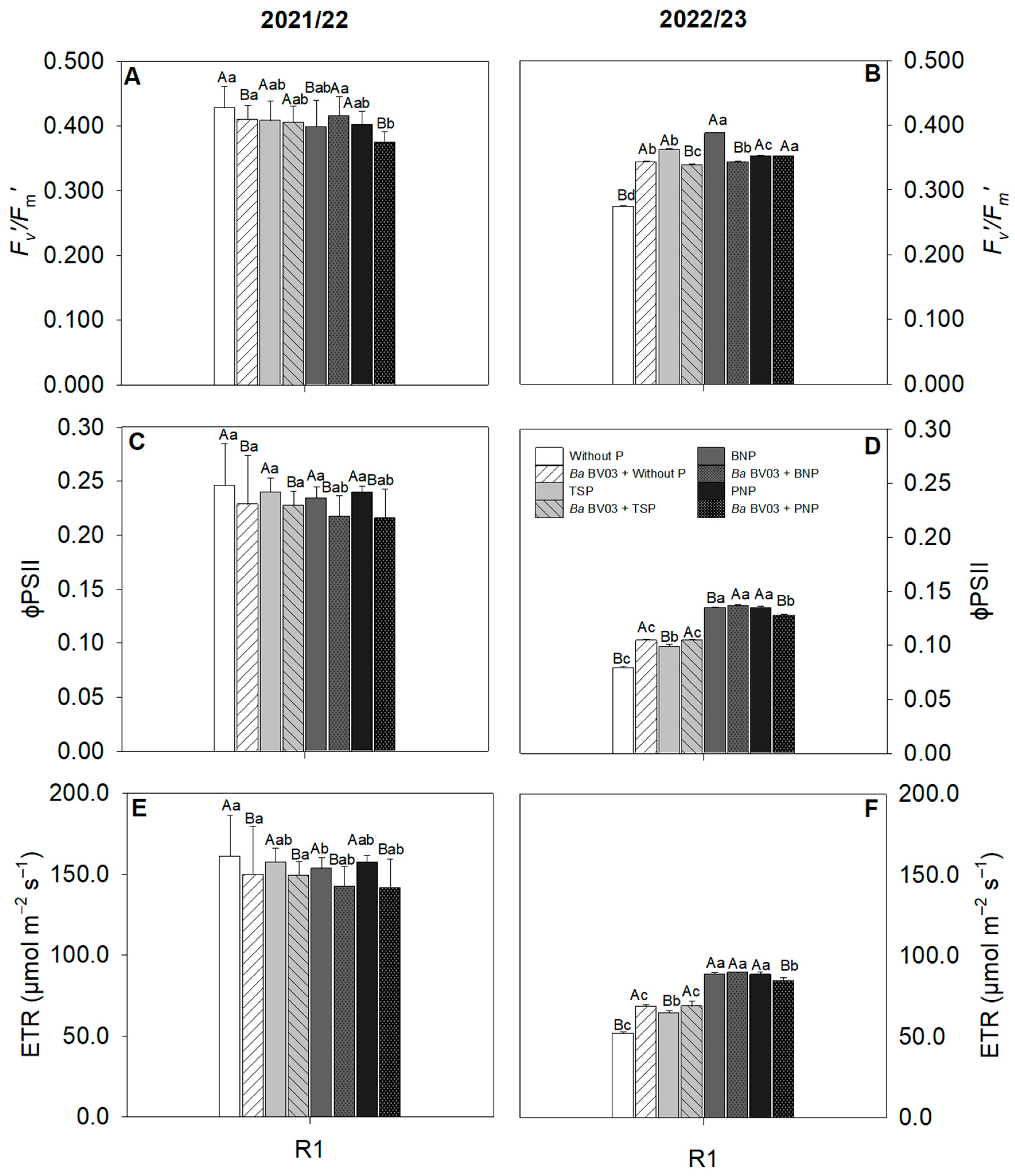
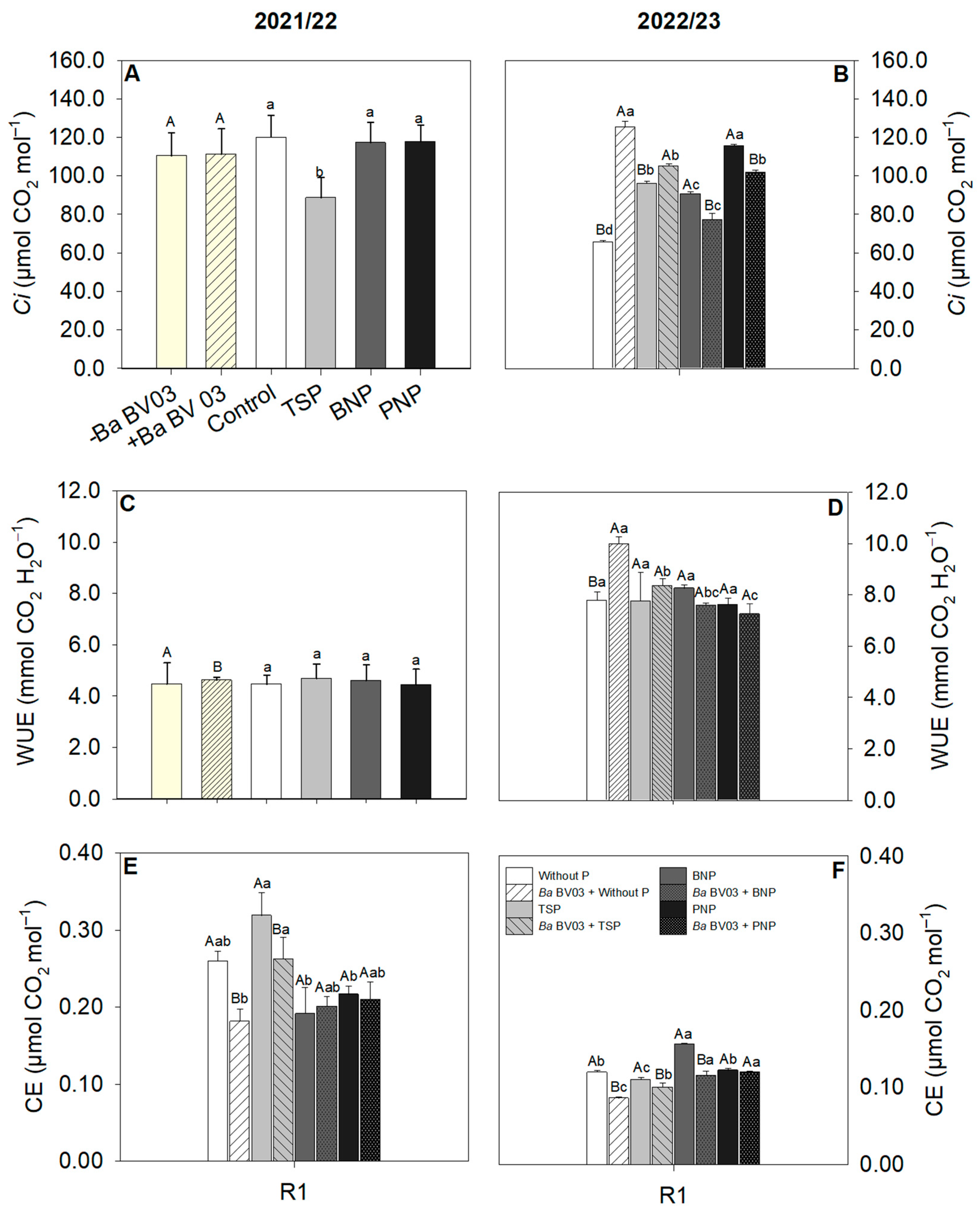
3.2. Impact of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Inoculation and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Physiology
3.3. Nutrient Content of Corn Leaves
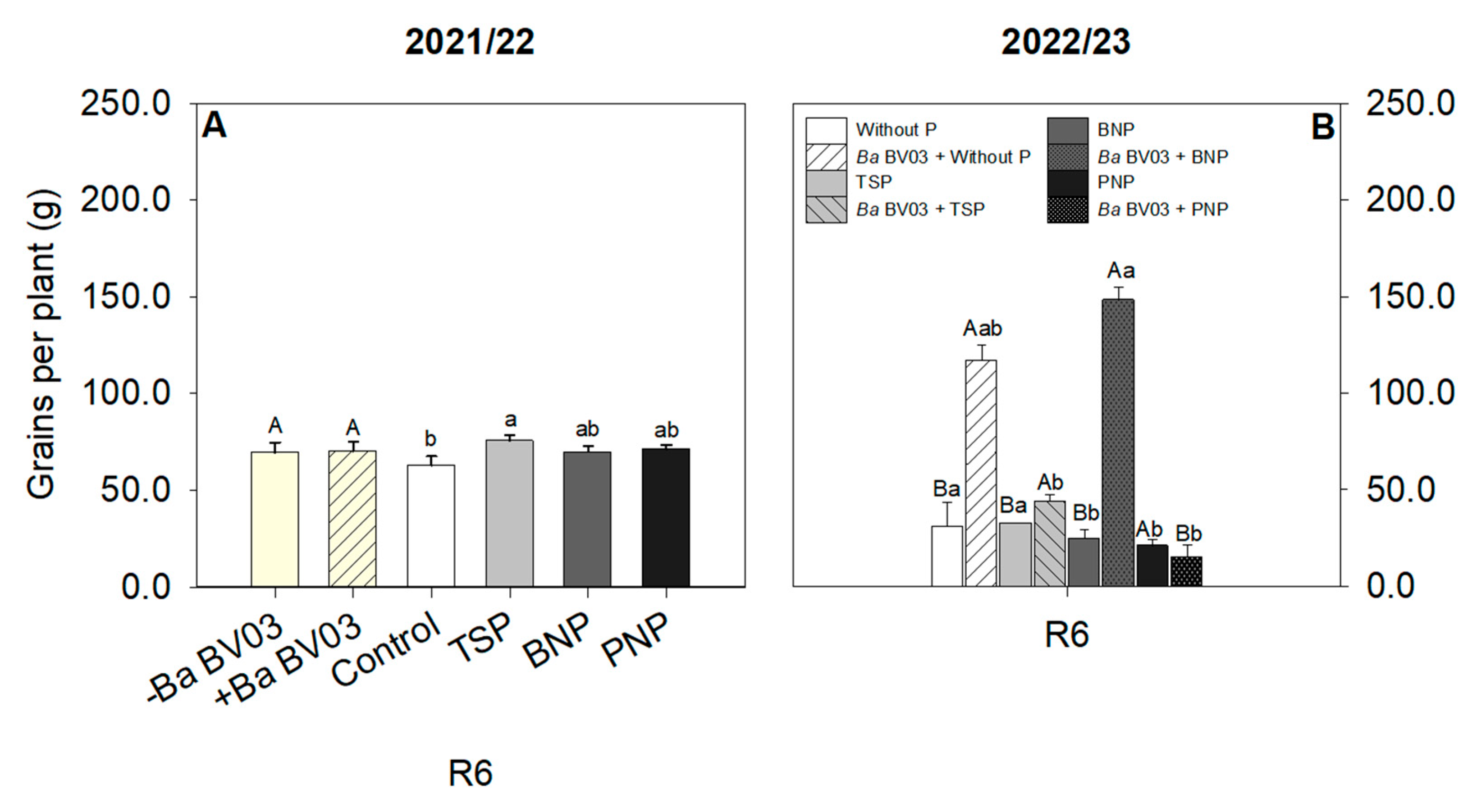
3.4. Impact of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Inoculation and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Biomass and Yield
3.5. Pearson’s Correlation Matrix and Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Growth and Development
4.2. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Inoculation and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Physiology
4.3. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Inoculation and Phosphorus Sources on Nutritional Status
4.4. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Inoculation and Phosphorus Sources on Plant Biomass and Yield of Corn
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations—FAO. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/visualize (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics—IBGE. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/explica/producao-agropecuaria/milho-em-grao/mt (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Conde-Barajas, E.; Negrete-Rodríguez, M.d.l.L.X.; Álvarez-Bernal, D.; Gámez-Vázquez, F.P.; Lastiri-Hernández, M.A.; Patiño-Galván, H.; Silva-Martínez, G.A.; Tristán-Flores, F.E.; Bedolla-Rivera, H.I. Maize cultivation and its relationship with soil quality: A focus on soil quality index methodologies. Land 2025, 14, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, P.; Li, W.; Schmidt, W. Omics’ approaches towards understanding plant phosphorus acquisition and use. In Annual Plant Reviews: Phosphorus Metabolism in Plants, 1st ed.; Plaxton, W.C., Lambers, H., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 8, pp. 65–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, J.; He, L.; Ma, K.; et al. Phosphorus solubilizing Bacillus altitudinis WR10 alleviates wheat phosphorus deficiency via remodeling root system architecture, enhancing phosphorus availability, and activating the ASA-GSH cycle. Plant Soil 2023, 492, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutardi, G.M.; Aziz, S.A.; Aswidinnoor, H.; Anda, M. Fertilizante inteligente: The improver-based NPK coating increased the yield and quality of rice in vertisol rice soil. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2025, 24, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Carmo, M. Why are unconventional materials answers to sustainable agriculture. MRS Energy Sustain. 2019, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Chretien, R.L.; Amaradasa, B.S.; He, Y.; Turner, A.; Lowman, S. Characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacterial endophytes and promotion of plant growth in vitro and in greenhouse. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelciu, C.E.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V.; Schlyter, P.; Stjernquist, I. Global phosphorus supply chain dynamics: Assessing regional impact to 2050. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantea, L.-E.; El-Sabeh, A.; Mihasan, M.; Stefan, M. Bacillus safensis P1.5S Exhibits Phosphorus-Solubilizing Activity Under Abiotic Stress. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Ahmad, M.; Raza, M.A.; Hilger, T.; Rasche, F. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacillus sp. Modulate Soil Exoenzyme Activities and Improve Wheat Growth. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garske, B.; Heyl, K.; Ekardt, F. How economic instruments address the sustainable use of nutrients: The example of phosphorus governance. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2025, 37, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, M.B.; Tiecher, T.; Fontoura, S.M.V.; Fink, J.; Bayer, C. Efficiency and availability of phosphorus in subtropical oxisols under no-tillage. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.F.K.; Alves, B.J.R.; Alonso, J.M.; Teixeira, P.C.; Benites, V.M. Characterization and agronomic efficiency of natural and recovered phosphates in tropical soil with corrected acidity. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2025, 49, e0240099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, C.P.; Klaic, R.; Bettiol, W.; Ribeiro, C.; Farinas, C.S. Bio-based composite granules with simultaneous biocontrol and phosphorus fertilization functions: Results of a laboratory-scale in vitro evaluation. Biotechnol. Prog. 2022, 38, e3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadiji, A.E.; Orozco-Mosqueda, M.d.C.; de los Santos-Villalobos, S.; Santoyo, G.; Babalola, O.O. Recent developments in the application of drought-adaptive rhizobacteria promoting plant growth for drought mitigation. Plants 2022, 11, 3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanveer, Y.; Yasmin, H.; Nosheen, A.; Farah, M.A.; Altaf, M.A. Synergizing Bacillus halotolerans, Pseudomonas sihuiensis and Bacillus atrophaeus with folic acid for enhanced drought resistance in wheat by metabolites and antioxidants. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patani, A.; Patel, M.; Islam, S.; Yadav, V.K.; Prajapati, D.; Yadav, A.N.; Sahoo, D.K.; Patel, A. Recent advances in Bacillus-mediated plant growth enhancement: A paradigm shift in redefining crop resilience. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Li, B.; Du, S. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: A good companion for heavy metal phytoremediation. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshegaihi, R.M.; Alatawi, A.; Alenezi, M.A. Ameliorative Effects of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on Cu Stress in Maize (Zea mays L.) with a Focus on Oxidative Damage, Antioxidant Responses, and Gene Expression. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 2437–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Pandey, S. ACC deaminase-producing bacteria with multifaceted plant growth-promoting traits relieve salinity stress in French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) plants. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Chauhan, P.S. ACC deaminase-producing rhizosphere competent Bacillus spp. mitigate salt stress and promote Zea mays growth by modulating ethylene metabolism. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif-Silini, H.; Silini, A.; Chenari Bouket, A.; Alenezi, F.N.; Luptakova, L.; Bouremani, N.; Belbahri, L. Tailoring Next Generation Plant Growth Promoting Microorganisms as Versatile Tools beyond Soil Desalinization: A Road Maptowards Field Application. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Misra, S.; Agarwal, R.; Kumar, S.; Chauhan, P.S. Endophytic Alkalotolerant Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Render Maize (Zea mays L.) Growth Under Alkaline Stress. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashajyothi, M.; Mahadevakumar, S.; Venkatesh, Y.N.; Sarma, P.V.S.R.N.; Danteswari, C.; Balamurugan, A.; Prakash, G.; Khandelwal, V.; Tarasatyavathi, C.; Podile, A.R.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus paralicheniformis associated with the pearl millet panicle reveals their antimicrobial potential against important plant pathogens. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Chakdar, H.; Anuroopa, N.; Bagyaraj, D.J. Bacillus species in soil as a natural resource for plant health and nutrition. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.A.; Santos, H.L.; Ferreira, L.S.; Nogueira, C.H.C.; Carnietto, M.R.A.; Santos, K.P.O. Interaction between Bacillus spp. and graphene oxide: Impacts on physiological and nutritional modulation for improving sugarcane drought resilience. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 228, 110299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Multifaceted applications of Bacillus probiotic species in aquaculture with special reference to Bacillus subtilis. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 862–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasakthi, S.; Usharani, G.; Saranraj, P. Biocontrol potential of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPR)-Pseudomonas fluorescens and Bacillus subtilis: A review. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 9, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, T.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W. Effects of the biocontrol agent Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SN16-1 on the rhizosphere bacterial community and tomato growth. J. Phytopathol. 2018, 166, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; González-Andrés, F. Bacillus as a source of phytohormones for use in agriculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 8629–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, S.; Ashajyothi, M.; Charishma, K.; Kumar, S.; Balamurugan, A.; Javed, M.; Karwa, S.; Ganesan, P.; Subramanian, S.; Gogoi, R.; et al. Improving defense against rice blast disease: Revealing the role of leaf endophytic firmicutes in antifungal antibiosis and induced systemic resistance. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 184, 106326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.; Tabassum, B.; Allah, A.E.F. Bacillus subtilis: A plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium that also impacts biotic stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlacher, A.; Cardinale, M.; Grosch, R.; Grube, M.; Berg, G. The impact of the pathogen Rhizoctonia solani and its beneficial counterpart Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on the microbiome of indigenous lettuce. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 21, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, P.; Macías-Benítez, S.; Revilla, E.; Tejada, M.; Parrado, J.; Castaño, A. Effect of subtilisin, a protease of Bacillus sp., on soil biochemical parameters and microbial biodiversity. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 101, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, I.; Bindschedler, S.; Junier, P. Firmicutes. In Beneficial Microbes in Agroecology; Amaresan, N., Kumar, M.S., Annapurna, K., Kumar, K., Sankaranarayanan, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 363–396. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Xing, Y.; Fu, X.; Ji, L.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, Q. Biochemical mechanisms of phytoextraction facilitated by Bacillus subtilis rhizospheric by alfalfa under cadmium stress—Microbial diversity and metabolomics analyses. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 112016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bini, D.; Mattos, B.B.; Figueiredo, J.E.F.; Marriel, I.E.; Santos, C.A.; Santos, F.C.; Oliveira-Paiva, C.A. Evaluation of parameters for the development of phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus inoculants. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Sharma, J.G.; Giri, B. Microbial inoculants improve growth in Zea mays L. under drought stress by up-regulating antioxidant, mineral acquisition, and ultrastructure modulations. Symbiosis 2023, 91, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.L.; Ferreira da Silva, G.; Carnietto, M.R.A.; Silva, G.F.D.; Fernandes, C.N.; Ferreira, L.S.; Silva, M.A. Improving sugarcane biomass and phosphorus fertilization through phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: A photosynthesis-based approach. Plants 2025, 14, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, J.; Torres, G.; Driver, E.; Figueiredo, B.; Raun, W.R. World phosphorus use efficiency in cereal crops. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.M.; Estrada-Bonilla, G.A.; Lopes, C.M.; Matteoli, F.P.; Cotta, S.R.; Feiler, H.P.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Does organomineral fertilizer combined with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in sugarcane modulate the microbial community and soil functions? Microb. Ecol. 2022, 84, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Ahmed, A. Phosphate solubilization potential of PSB: An advance approach to enhance phosphorous availability for phytostimulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 56174–56193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.H.M.; Luo, Y.W.J.; Luo, X. The role of proton excreted by Advenella kashmirensis DF12 during ammonium assimilation in phosphate solubilization. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.W.; Pletnyakov, P.; Haygarth, P.M. Phosphorus applications adjusted for optimal crop yields can help sustain global phosphorus reserves. Nat. Food 2024, 5, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illakwahhi, D.T.; Vegi, M.R.; Srivastava, B.B.L. Phosphorus’ future insecurity, the horror of depletion, and sustainability measures. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 9265–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Diksha; Sindhu, S.S.; Kumar, R. Harnessing phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms for mitigation of nutritional and environmental stresses, and sustainable crop production. Planta 2025, 95, 261. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, E.; Raza, A.; Yin, C. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens as an excellent agent for biofertilizer and biocontrol in agriculture: An overview of its mechanisms. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 259, 127016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Peng, J.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.-L.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Cui, L. Single-cell exploration of active phosphate-solubilizing bacteria across diverse soil matrices for sustainable phosphorus management. Nat. Food 2024, 5, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Dai, X.; Maitikadir, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hao, H.; Yan, C. Comparative genome analysis of endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MR4: A potential biocontrol agent isolated from wild medicinal plant root tissue. J. Appl. Genet. 2024, 65, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngalimat, M.S.; Yahaya, R.S.; Baharudin, M.M.A.; Yaminudin, S.M.; Karim, M.; Ahmad, S.A.; Sabri, S. A review on the biotechnological applications of the operational group Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.R.; Dal Pai, E.; Calça, M.V.C.; Raniero, M.R.; Dal Pai, A.; Sarnighausen, V.C.R.; Sánchez-Román, R.M. Atualização da normal climatológica e classificação climática de Köppen para o município de Botucatu-SP. Irriga 2023, 28, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, P.C.; Donagemma, G.K.; Fontana, A.; Teixeira, W.G. Manual of Soil Analysis Methods, 3rd ed.; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2017; p. 574. [Google Scholar]
- Raij, B.V.; Andrade, J.C.; Cantarella, H.; Quaggio, J.A. Análise Química Para Avaliação da Fertilidade de Solos Tropicais; IAC: Campinas, Brazil, 2001; pp. 5–39. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, A.P.; Cantarella, H.; Quaggio, J.A. Maize (Zea mays). In Recommendations for Fertilization and Liming for the State of São Paulo-B100, 3rd ed.; Cantarella, H., Quaggio, J.A., Mattos, D., Jr., Boaretto, R.M., van Raij, B., Eds.; Agronomic Institute of Campinas: Campinas, Brazil, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, I. Manejo de Pragas da Cultura do Milho; Cruz, J.C., Karam, D., Monteiro, M.A.R., Magalhães, P.C., Eds.; Embrapa Milho e Sorgo: Sete Lagoas, Brazil, 2008; pp. 303–362. [Google Scholar]
- Casela, C.R.; Ferreira, A.S.; Almeida Pinto, N.F.J. Doenças na Cultura do Milho; Cruz, J.C., Karam, D., Monteiro, M.A.R., Magalhães, P.C., Eds.; Embrapa Milho e Sorgo: Sete Lagoas, Brazil, 2008; pp. 215–256. [Google Scholar]
- Elings, A. Estimation of Leaf Area in Tropical Maize. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A.R. The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as weel as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavolta, E. Manual of Mineral Nutrition of Plants; Agronômica Ceres: São Paulo, Brazil, 2006; p. 631. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Malavolta, E.; Vitti, G.C.; Oliveira, S.A. Avaliação do Estado Nutricional das Plantas–Princípios e Aplicações, 2nd ed.; Associação Brasileira Para Pesquisa da Potassa e do Fosfato: Piracicaba, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, D.J.; Queiroz, A.D. Análise de Alimentos: Métodos Químicos e Biológicos, 3rd ed.; Universidade Federal de Viçosa: Viçosa, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Supply. Rules for Seed Analysis; Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Supply: Brasília, Brazil, 2009; 395p. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team. 2021. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Ferreira, E.; Cavalcanti, P.; Nogueira, D. ExpDes: An R Package for ANOVA and Experimental Projects. Appl. Math. 2014, 5, 2952–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.C.; Maldonado Júnior, W. AgroEstat Version 1.0.—System for Statistical Analysis of Agronomic Trials; São Paulo State University: Jaboticabal, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sigmaplot, version 14; Systat Software Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2017.
- Iqbal, A.; Zhang, D.Q.; Xiling, W.; Wang, X.; Song, M. Integrative physiological, transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the involvement of carbon and flavonoid biosynthesis in low phosphorus tolerance in cotton. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 196, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquino, A.C.B.; Mendes, L.W.; Pellegrinetti, T.A.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Microbial communities in the rhizosphere of tropical soils cultivated with corn as a function of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025, 56, 1949–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.J.R.; Silva, A.P.R.; Sandim, A.D.S.; Deus, A.C.F.; Antonangelo, J.A.; Büll, L.T. Evaluation of the agronomic efficiency of alternative sources of phosphorus applied in Brazilian tropical soils. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezquita-Aviles, C.; Coronel-Acosta, C.B.; Santos-Villalobos, S.; Santoyo, G.; Parra-Cota, F.I. Characterization of native plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) and their effect on the development of maize (Zea mays L.). Biotecnia 2022, 24, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.P.; Soares, P.P.S.; Correia, A.J.; França, R.S.; Miguel, D.L.; Nóbrega, R.S.A.; Leal, P.L. Humic substances and plant growth-promoting bacteria enhance corn (Zea mays L.) development. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 166, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarezi, J.A.; Aniceto, R.M.; Carvalho-Estrada, P.A.; Tschoeke, B.A.; Andrade, P.A.; Lopes, B.M.; Batista, B.D.; Bonatelli, M.L.; Jussie, E.O.; Azevedo, J.L.; et al. Effects of inoculation with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria from the Brazilian Amazon on the bacterial community associated with maize in field. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.C.; Reis, D.P.; Gomes, E.A.; Ladeira, D.A.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Melo, I.G.; de Souza, F.F.; Mattos, B.B.; Campos, C.N.; de Oliveira-Paiva, C.A. Influence of phosphorus-solubilizing microorganisms and phosphate additives on pearl millet growth and nutrient use efficiency in different types of soils. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 16, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira-Paiva, C.A.; Marriel, I.E.; Gomes, E.A.; Cota, L.V.; Santos, F.C.; Sousa, S.M.; Lana, U.G.P.; Oliveira, M.C.; Mattos, B.B.; Alves, V.M.C.; et al. Recomendação Agronômica de Cepas de Bacillus subtilis (CNPMS B2084) e Bacillus megaterium (CNPMS B119) na Cultura do Milho; Embrapa Milho e Sorgo. Circular Técnica. 260; Embrapa: Sete Lagoas, Brazil, 2020; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, S.M.; Oliveira, C.A.; Andrade, D.L.; Carvalho, C.G.; Ribeiro, V.P.; Pastina, M.M.; Marriel, I.E.; Lana, U.G.P.; Gomes, E.A. Tropical Bacillus strains inoculation enhances maize root surface area, dry weight, nutrient uptake and grain yield. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.; Kaleem, A.M.; Sultan, T. Isolation of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria from Maize Rhizosphere and Their Potential for Rock Phosphate Solubilization–Mineralization and Plant Growth Promotion. Geomicrobiol. J. 2017, 34, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, U.C.; Medeiros, J.D.; Leite, L.R.; Morais, D.K.; Cuadros-Orellana, S.; Oliveira, C.A.; Lana, U.G.P.; Gomes, E.A.; Santos, V.L. Long-term rock phosphate fertilization affects the microbial communities of the corn rhizosphere. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.B.; França, C.C.R.; e Sá, J.M.; Costa, R.Q.; Barbosa, G.M.; Nunes, H.B. Crescimento de milho em função da aplicação de fertilizantes fosfatados associados a bactérias solubilizadoras de fósforo. Rev. Soc. Ambiente 2023, 4, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, V.P.; de Marriel, I.E.; Sousa, S.M.; Lana, U.G.P.; Mattos, B.B.; Oliveira, C.A.; Gomes, E.A. Endophytic strains of Bacillus increase pearl millet growth and nutrient uptake under low P. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mattos, B.B.; Marriel, I.E.; de Sousa, S.M.; Lana, U.G.P.; Schaffert, R.E.; Gomes, E.A.; Oliveira, C.A. Response of sorghum genotypes to inoculation with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Braz. J. Maize Sorghum 2020, 19, e1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, R.A.; Costa, E.M.; Michel, D.C.; Leite, A.A.; Oliveira-Longatti, S.M.; Lima, W.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Moreira, F.M.S. Genomic insights into organic acid production and plant growth promotion by different species of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinci, G.; Cozzolino, V.; Mazzei, P.; Monda, H.; Savy, D.; Drosos, M.; Piccolo, A. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and different phosphorus sources on maize plants as revealed by NMR and GC-MS based metabolomics. Veg. Soil 2018, 429, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaj, M.A.; Roosta, H.R. Evaluation of Nutrient Uptake and Flowering of Gerbera in Response of Various Growing Media. World. J. Environ. Biosci. 2019, 8, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ruban, A.V.; Wilson, S. The mechanism of non-photochemical quenching in plants: Localization and driving forces. Plant Cell. Physiol. 2021, 62, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiz, L.; Zeiger, E.; Moller, I.; Murphy, A. Fundamentals of Plant Physiology; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.J.; Fan, D.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Xu, C.Y.; Xia, X.L.; Chow, W.S. The protective role of non-photochemical quenching in PSII photo-susceptibility: A case study in the field. Plant Cell. Physiol. 2023, 64, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, K.; Johnson, G.N. Chlorophyll fluorescence—A practical guide. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.R. Chlorophyll fluorescence: A probe of photosynthesis in vivo. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmig-Adams, B.; Adams, W.W., III. Photoprotection in an ecological context: The remarkable complexity of thermal energy dissipation. New Phytol. 2006, 172, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivay, Y.S.; Prasanna, R.; Mandi, S.; Kanchan, A.; Simranjit, K.; Nayak, S.; Baral, K.; Sirohi, M.P.; Nain, L. Inoculation of cyanobacteria increases the efficiency of nutrient use and the grain quality of basmati rice in the rice intensification system. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, K.; Song, W.; Zhong, N.; Wu, Y.; Fu, X. Improving Crop Nitrogen Use Efficiency Toward Sustainable Green Revolution. Annu. Ver. Plant Bio. 2022, 73, 523–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga-Freitas, R.; Blouin, M. A review of the effects of soil organisms on plant hormone signalling pathways. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 114, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flexas, J.; Ribas-Carbó, M.; Diaz-Espejo, A.; Galmés, J.; Medrano, H. Conductance of the mesophyll to CO2: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Plant Cell Environ. 2008, 31, 602–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Sale, P.; Wood, J.L.; Reddy, P.; Franks, A.E.; Clark, G.; Jin, J.; Rochfort, S.; Hunt, J.; Tang, C. Organic amendments increase the transpiration efficiency of corn plants through changes in soil microbial abundance and leaf hormones. Plant Soil 2024, 497, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Geng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Optimized phosphorus application increases canopy photothermal responses, phosphorus accumulation, and yield in summer maize. Agronomy 2025, 15, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M.A.; Mustafa, A.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Curá, J.A. Insights into the interactions between roots, rhizosphere, and rhizobacteria to improve plant growth and tolerance to abiotic stresses: A review. Cells 2021, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, Z.; Shan, X.; Li, C.; Tang, X.; Chi, M.; Feng, H. Physiological properties and chlorophyll biosynthesis in a Pak-choi (Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis) yellow leaf mutant, pylm. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Das, S.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: Mechanism and their role in phosphate solubilization and uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Luo, Y.; Wei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, W.; Sheng, H.; An, L. Screening of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) from the rhizosphere and soil of Caragana microphylla in different habitats and their effects on the growth of Arabidopsis seedlings. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, C.B.; Tomás, M.S.J.; Viruel, E.; Ferrero, M.A.; Lucca, M.E. Development of low-cost formulations of plant growth-promoting bacteria for use as inoculants in beneficial agricultural technologies. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 219, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral Leite, A.; Souza Cardoso, A.A.; Almeida Leite, R.; Oliveira-Longatti, S.M.; Filho, J.F.L.; Souza Moreira, F.M.; Melo, L.C.A. Selected bacterial strains increase the availability of phosphorus from biochar-based phosphate fertilizer. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Ahmed, A. Phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria as a sustainable management strategy in agrobiology. In Sustainable Management of Natural Resources; Suratman, M.N., Azlin Ariff, R.E., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Severo, H.C.; Arauco, A.M.d.S.; Nunes, R.W.F.; Monteiro, G.N.; Duarte, M.H.F.; Silva, A.P.d.M.; Ferreira, A.C.; Luz, M.R.; Miranda, R.S.; Araújo, A.S.F.; et al. The co-inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Bacillus subtilis improves morphological characteristics, growth and nutrient uptake in maize under limited phosphorus availability. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.V.; Triveni, S.; Reddy, R.S.; Sathyanarayana, J. Screening of corn rhizoperic phosphate solubilizing isolates for plant growth-promoting traits. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci 2017, 6, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomfim, C.S.G.; Silva, V.B.; Cursino, L.H.S.; Mattos, W.S.; Santos, J.C.S.S.; Souza, L.S.B.; Dantas, B.F.; Freitas, A.D.S.; Fernandes-Júnior, P.I. Endophytic bacteria that naturally inhabit commercial corn seeds occupy different niches and are efficient plant growth promoters. Symbiosis 2020, 81, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, R.C.; Cavalcanti, M.I.P.; Correia, A.J.; Escobar, I.E.C.; Freitas, A.D.S.; Nóbrega, R.S.A.; Fernandes-Júnior, P.I. Bacteria associated with corn from the Brazilian semi-arid region boost plant growth and grain yield. Symbiosis 2021, 83, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilyera, N.; Hummel, C.; Daudin, G.; Santangeli, M.; Zhang, X.; Santner, J.; Lippold, E.; Schlüter, S.; Bertrand, I.; Wenzel, W.; et al. Co-localised phosphorus mobilization processes in the rhizosphere of field-grown maize jointly contribute to plant nutrition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 165, 108497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, K.R.; Keyes, S.D.; Masum, S.; Roose, T. Image-based modelling of nutrient movement in and around the rhizosphere. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Koebernick, N.; Duncan, S.; Fletcher, D.M.; Scotson, C.; Boghi, A.; Marin, M.; Bengough, A.G.; George, T.S.; Brown, L.K.; et al. Significance of root hairs at the field scale–modelling root water and phosphorus uptake under different field conditions. Plant Soil 2019, 447, 281–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Alikhani, H.A. Fungi and bacteria that promote the growth of halotolerant plants as an alternative strategy to improve nutrient availability for plants grown under salt stress. In Agriculture in Saline Soil by Halotolerant Microorganisms; Kumar, M., Etesami, H., Kumar, V., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 103–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ercole, T.G.; Savi, D.C.; Adamoski, D.; Kava, V.M.; Hungria, M.; Galli-Terasawa, L.V. Diversity of maize rhizobacteria (Zea mays L.) with the potential to promote plant growth. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1807–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnietto, M.R.A.; Santos, H.L.; Ferreira, L.S.; Silva, G.F.; Silva, M.A. Soil texture affects the efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis in the physiological and biochemical modulation of sugarcane tolerance to water deficit. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 225, 109997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataeva, Y.V.; Pokhilenko, V.D.; Dunaitsev, I.A.; Tekutov, A.R.; Kalmantaev, T.A. Prospects for application of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens in biocontrol, metabolic engineering, and protein expression. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2025, 61, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, S.K.; Ilyas, T.; Shahid, M.; Malviya, D.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.; Johri, P.; Singh, U.B.; Singh, H.V. Bacillus spp.: Nature’s gift to agriculture and humankind. In Applications of Bacillus and Bacillus Derived Genera in Agriculture, Biotechnology and Beyond; Mageshwaran, V., Singh, U.B., Saxena, A.K., Singh, H.B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; Volume 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Treatments | Planting Fertilization | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021/22 | 2022/23 | 2021/22 | 2022/23 | 2021/22 | 2022/23 | |
| P2O5 | N | KCl | ||||
| Without P | – | 90 kg ha−1 (0.7 g pot−1) | 120 kg ha−1 (1.4 g pot−1) | 70 kg ha−1 (1.0 g pot−1) | 100 kg ha−1 (0.874 g pot−1) | |
| Ba + Without P | ||||||
| TSP | 70 kg ha−1 | 120 kg ha−1 | ||||
| Ba + TSP | (1.8 g pot−1) | (3.0 g pot−1) | ||||
| BNP | 70 kg ha−1 | 120 kg ha−1 | ||||
| Ba + BNP | (3.0 g pot−1) | (5.04 g pot−1) | ||||
| PNP | 70 kg ha−1 | 120 kg ha−1 | ||||
| Ba + PNP | (6.3 g pot−1) | (10.5 g pot−1) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Ferreira, L.d.S.; Luiz Santos, H.; Silva, G.F.d.; Carnietto, M.R.A.; Nogueira, C.H.d.C.; de Almeida Silva, M. Interaction of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BV03 and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Physiology, Nutrition, and Yield. Agriculture 2026, 16, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010044
Ferreira LdS, Luiz Santos H, Silva GFd, Carnietto MRA, Nogueira CHdC, de Almeida Silva M. Interaction of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BV03 and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Physiology, Nutrition, and Yield. Agriculture. 2026; 16(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Lusiane de Sousa, Hariane Luiz Santos, Gustavo Ferreira da Silva, Melina Rodrigues Alves Carnietto, Carlos Henrique de Castro Nogueira, and Marcelo de Almeida Silva. 2026. "Interaction of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BV03 and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Physiology, Nutrition, and Yield" Agriculture 16, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010044
APA StyleFerreira, L. d. S., Luiz Santos, H., Silva, G. F. d., Carnietto, M. R. A., Nogueira, C. H. d. C., & de Almeida Silva, M. (2026). Interaction of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BV03 and Phosphorus Sources on Corn Physiology, Nutrition, and Yield. Agriculture, 16(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010044







