Differential Molecular Interactions of Imidacloprid with Dissolved Organic Matter in Citrus Soils with Diverse Planting Ages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sample Collection
2.2. Soil Analysis
2.3. Extraction and Purification of Soil DOM
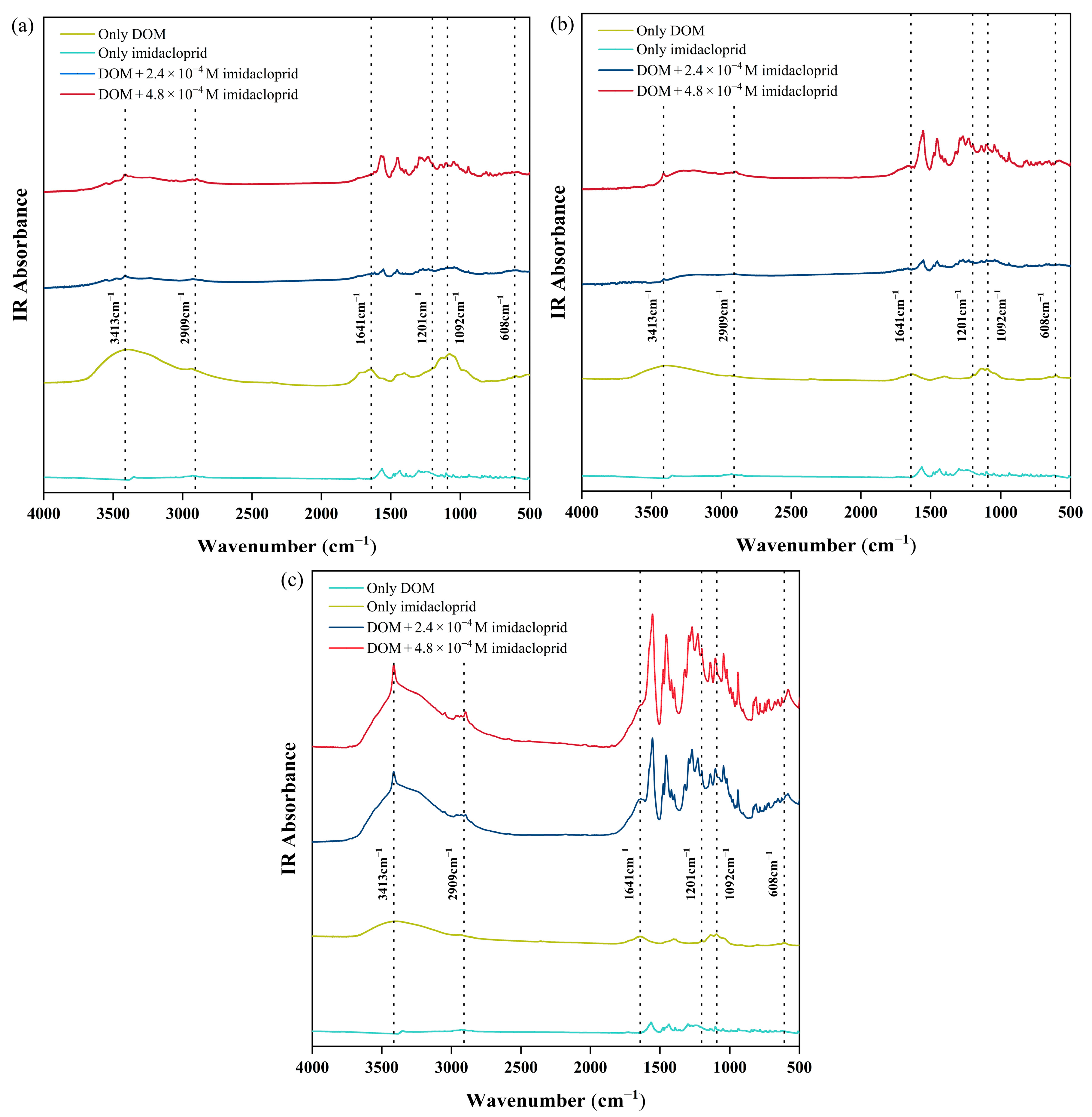
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements
2.5. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Scanning
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Changes in DOM Quality and Chemodiversity in Citrus Soils with Planting Years
3.1.1. Soil Quality and DOM Quantity
3.1.2. DOM Chemodiversity
3.2. Changes in DOM Functional Groups Before and After the Reaction with Imidacloprid
3.3. Complexation Behavior of DOM to Imidacloprid in Citrus Soils with Different Planting Years
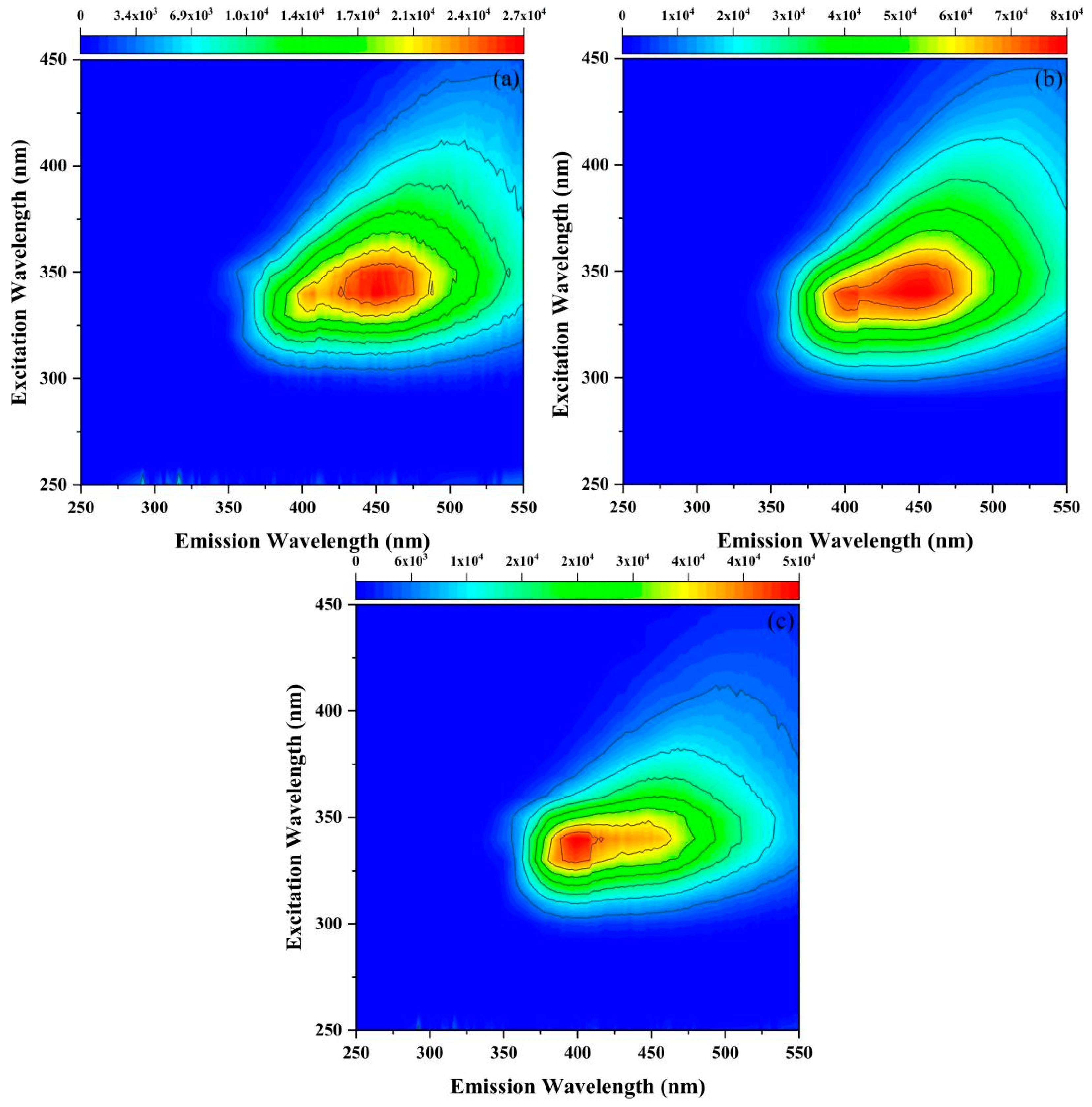
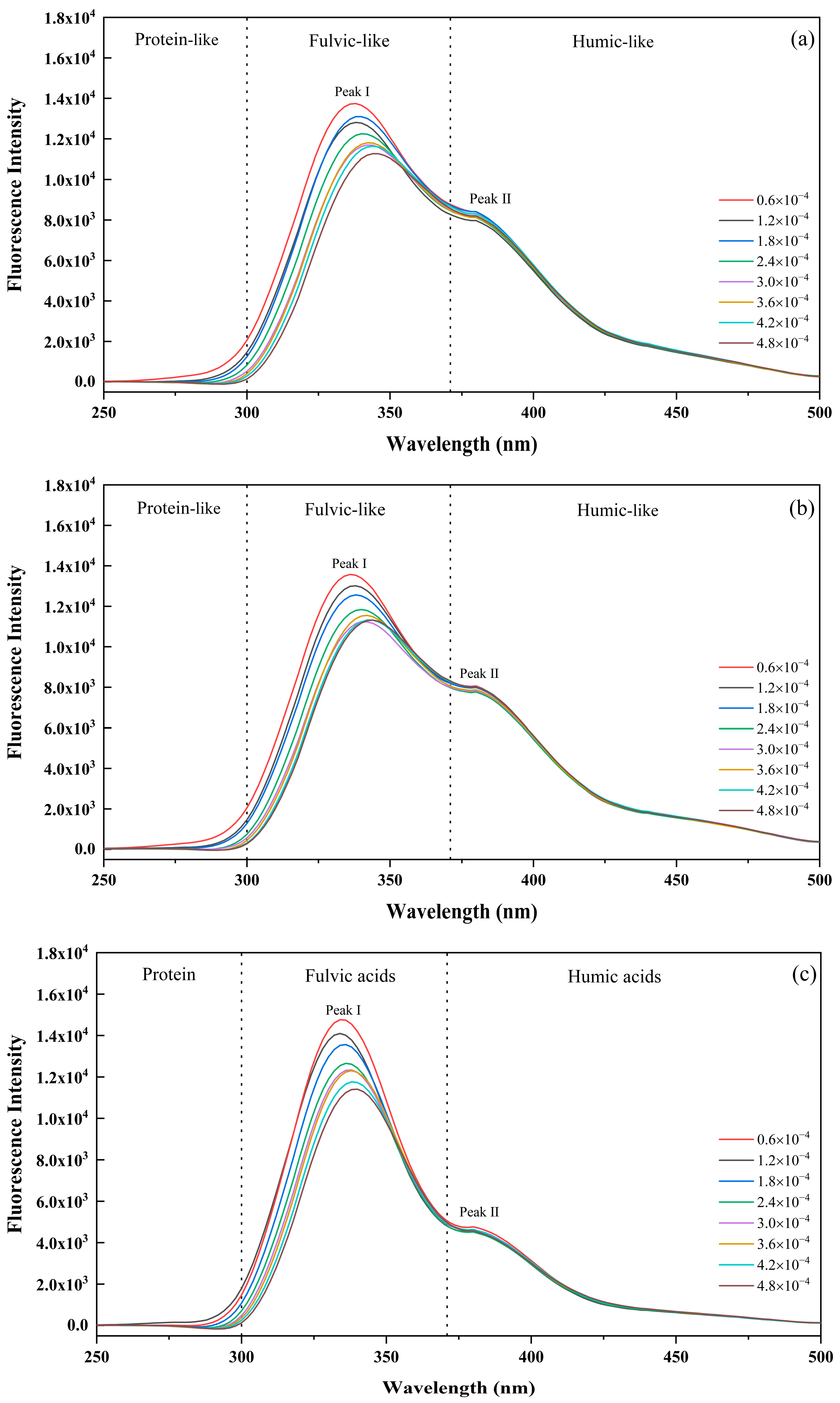
3.3.1. Fluorescence Quenching Behavior for Diverse DOM Fluorescent Components
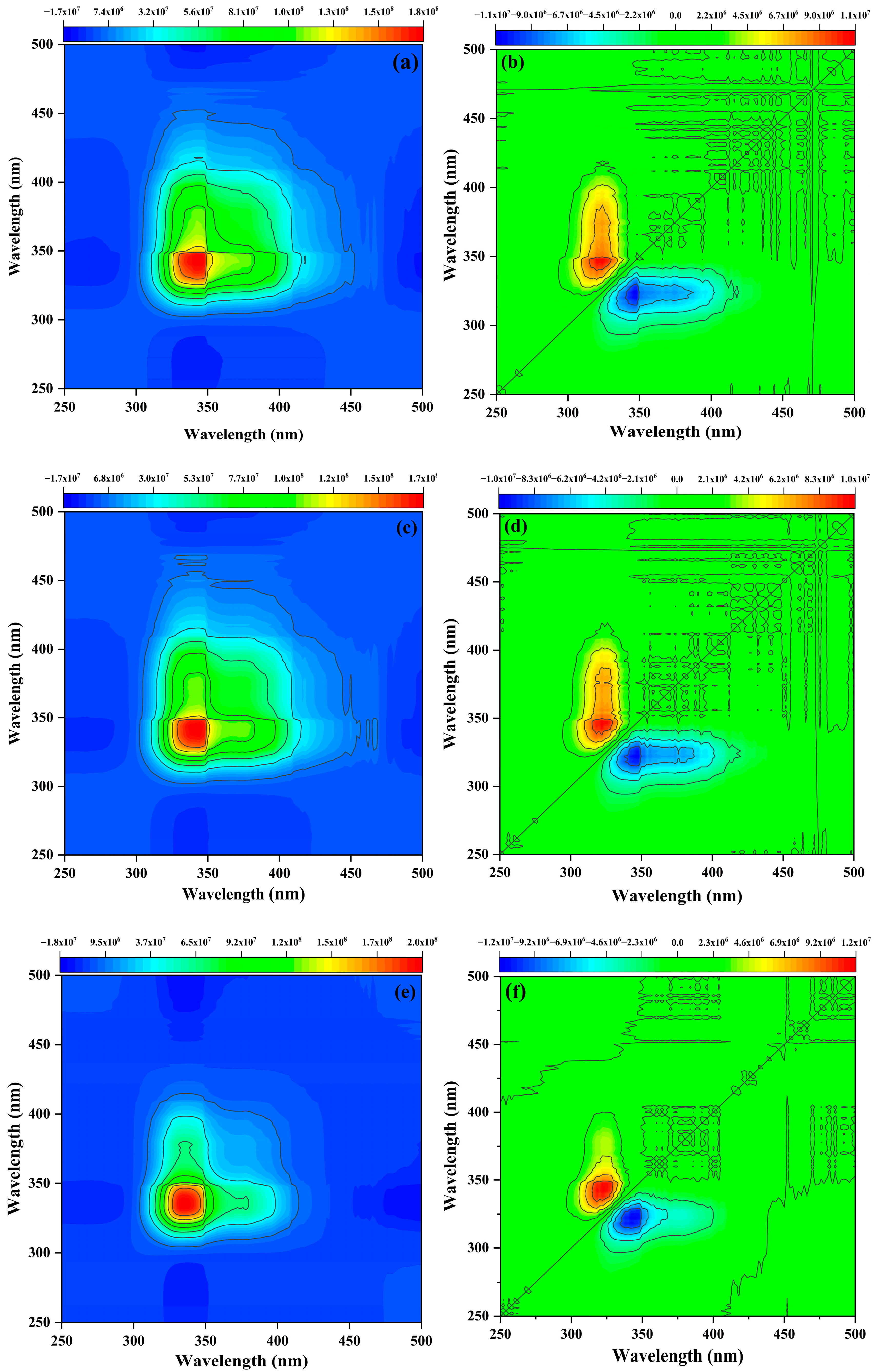
3.3.2. Sequential Changes in the Functional Groups of Citrus Soil DOM with the Addition Imidacloprid: Two-Dimensional Correlation Spectroscopy Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tu, A.; Xie, S.; Zheng, H.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Mo, M. Long-term effects of living grass mulching on soil and water conservation and fruit yield of citrus orchard in south China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 252, 106897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhan, T.; Zhang, S.; Cai, M.; Zhao, X. Soil applied Ca, Mg and B altered phyllosphere and rhizosphere bacterial microbiome and reduced Huanglongbing incidence in Gannan Navel Orange. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Alansary, N.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Insights into the Toxicity and Degradation Mechanisms of Imidacloprid via Physicochemical and Microbial Approaches. Toxics 2020, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X. UDP-Glycosyltransferases are involved in imidacloprid resistance in the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Lividae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 154, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Yu, S.X.; Zheng, J.Y.; Shi, Z.H. High-frequency monitoring of neonicotinoids dynamics in soil-water systems during hydrological processes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Lu, J.; Qiao, C.; Wang, C.; Pang, T.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Pang, R.; Xie, H. Dissipation behavior and risk assessment of imidacloprid and its metabolites in apple from field to products. Chemosphere 2024, 359, 142309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.H.; Li, X.; Wang, H.X.; Liu, Y.J.; Shi, Z.H.; Wang, L. Soil erosion-related transport of neonicotinoids in new citrus orchards. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 290, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Hu, T.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Duan, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Q. Dynamics in imidacloprid sorption related to changes of soil organic matter content and quality along a 20-year cultivation chronosequence of citrus orchards. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi, M. Time-dependent sorption of imidacloprid in two different soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellerman, A.M.; Dittmar, T.; Kothawala, D.N.; Tranvik, L.J. Chemodiversity of dissolved organic matter in lakes driven by climate and hydrology. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.; Lu, Q.; Yu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, S. Electron transfer capacity of soil dissolved organic matter and its potential impact on soil respiration. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Q.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of spectral responses of dissolved organic matter (DOM) for atrazine binding during the sorption process onto black soil. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Cui, Z.; Bai, Y.; Ding, D.; Hu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, L.; Qu, K.; Su, R. Optical characteristic of dissolved organic matter polar fractions by spectrum technologies and the relationship with indirect photodegradation of ofloxacin. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ren, C.; Wu, C.; Li, Y.; Deng, X.; Li, Q. Mechanisms by which different polar fractions of dissolved organic matter affect sorption of the herbicide MCPA in ferralsol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Duan, Y.; Cai, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y. Changes in the characteristics of soil dissolved organic matter over time since inter-planting with white clover (Trifolium repens L.) in apple orchards on the Loess Plateau in China. Plant Soil 2022, 499, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Heal, K.; Wang, S.; Cao, S.; Zhou, C. Chemodiversity of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter and Its Association with Soil Microbial Communities Along a Chronosequence of Chinese Fir Monoculture Plantations. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 729344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Xue, B.; Ndzana, G.M.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, B.; Gao, R.; Ma, K.; Du, L.; An, H.; et al. Variations in the quantity and chemical composition of soil dissolved organic matter along a chronosequence of wolfberry plantations in an arid area of Northwest China. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, H.; Tuo, D.; Wang, C.; Fu, B.; Lv, Y.; Liu, G. Land use change and stand age regulate soil respiration by influencing soil substrate supply and microbial community. Geoderma 2020, 359, 113991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.P.; Ding, Y.D.; Li, S.L.; Sun, X.X.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, R. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry controls interspecific patterns of leaf litter-derived dissolved organic matter biodegradation in subtropical plantations of China. Ifor. Biogeosci. For. 2021, 14, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriuso, E.; Andrades, M.-S.; Benoit, P.; Houot, S. Pesticide desorption from soils facilitated by dissolved organic matter coming from composts: Experimental data and modelling approach. Biogeochemistry 2010, 106, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Céspedes, F.; Fernández-Pérez, M.; Villafranca-Sánchez, M.; González-Pradas, E. Cosorption study of organic pollutants and dissolved organic matter in a soil. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, F.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Na, R.; Li, Q.X. Interactions between Imidacloprid and Thiamethoxam and Dissolved Organic Matter Characterized by Two-Dimensional Correlation Spectroscopy Analysis, Molecular Modeling, and Density Functional Theory Calculations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Teng, C.-Y.; Qian, C.; Yu, H.-Q. Characterizing Properties and Environmental Behaviors of Dissolved Organic Matter Using Two-Dimensional Correlation Spectroscopic Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4683–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Pan, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, B. Effects of heat treatment on fluorescence properties of humic substances from sandy soil in arid land and their Hg(II) binding behaviors. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 66, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.J.; Schlenger, P.; García-Valverde, M. A comprehensive structural evaluation of humic substances using several fluorescence techniques before and after ozonation. Part I: Structural characterization of humic substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y. Insight into removals of PARAFAC components from dissolved and particulate organic matter in wastewater treatment process by two-dimensional correlation and structure equation modeling. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Hu, G.; Wang, H.; Bai, E.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhuge, Y. 35 years of manure and chemical fertilizer application alters soil microbial community composition in a Fluvo-aquic soil in Northern China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 82, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, D.; Schumacher, T.; Doolittle, J. Long-term cultivation impacts on selected soil properties in the northern Great Plains. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 81, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Chen, S.; Zhao, W.; Song, S. Response of soil inorganic nitrogen dynamics to planting age and vegetation type in artificial sand-fixing land. Ecosphere 2024, 15, e4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Jing, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Sui, Y.; Sun, B.; Liang, Y. Microbial metabolism and necromass mediated fertilization effect on soil organic carbon after long-term community incubation in different climates. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Berhe, A.A.; Xiao, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Peng, H.; Zeng, G. Characterizing dissolved organic matter in eroded sediments from a loess hilly catchment using fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC and UV–Visible absorption: Insights from source identification and carbon cycling. Geoderma 2019, 334, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Han, C.; Gao, L.; Wu, H.; Li, M. A new view into three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy for dissolved organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario-Ortiz, F.L.; Korak, J.A. Oversimplification of Dissolved Organic Matter Fluorescence Analysis: Potential Pitfalls of Current Methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohinuzzaman, M.; Yuan, J.; Yang, X.; Senesi, N.; Li, S.-L.; Ellam, R.M.; Mostofa, K.M.G.; Liu, C.-Q. Insights into solubility of soil humic substances and their fluorescence characterisation in three characteristic soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebecca, S.; Garrison, S. Molecular structure in soil humic substances: The new view. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9009–9015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korak, J.A.; Dotson, A.D.; Summers, R.S.; Rosario-Ortiz, F.L. Critical analysis of commonly used fluorescence metrics to characterize dissolved organic matter. Water Res. 2014, 49, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ren, C.; Jiang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, C. Characteristic of dissolved organic matter polar fractions with variable sources by spectrum technologies: Chemical properties and interaction with phenoxy herbicide. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ren, D.; Li, Q.; Zhu, A.; Song, Y.; Yin, W.; Wu, C. Molecular linkages between chemodiversity and MCPA complexation behavior of dissolved organic matter in paddy soil: Effects of land conversion. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.M.; Abdel-Aty, B.; El-Sayed, W.; Mariy, F.M.; Hegazy, G.M.; Mohamed, R.A.; Zoghly, H.M. Imidacloprid effects on acetylcholinesterase and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in Apis mellifera. Experimental and molecular modeling approaches. Chemosphere 2024, 356, 141899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Song, F.; Zhang, J.; Tian, S.; Huang, N.; Xing, B.; Bai, Y. Experimental and modeling study of proton and copper binding properties onto fulvic acid fractions using spectroscopic techniques combined with two-dimensional correlation analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Xu, W.; Yu, H.; Gao, H.; Gao, X.; Zhu, N. Insight into temporal–spatial variations of DOM fractions and tracing potential factors in a brackish-water lake using second derivative synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy and canonical correlation analysis. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Ma, F.; Gu, Q. Complexation of humic acid with Fe ions upon persulfate/ferrous oxidation: Further insight from spectral analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xi, B.; Wei, Z.; Guo, X.; Li, M.; An, D.; Liu, H. Spectroscopic characterization of water extractable organic matter during composting of municipal solid waste. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, K.; Yu, X.; Xu, Y.; Ye, H.; Bai, M.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Fulvic acid more facilitated the soil electron transfer than humic acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.-L.; He, J.-Z.; Blaney, L.; Zhou, D.-M. Roxarsone binding to soil-derived dissolved organic matter: Insights from multi-spectroscopic techniques. Chemosphere 2016, 155, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Wu, X.; Chen, P.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Xue, J.; Wang, Y. New insights into the interactions between humic acid and three neonicotinoid pesticides, with multiple spectroscopy technologies, two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy analysis and density functional theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, S.; Pang, C.; Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Zhang, C. Highly selective fluorescence probe for imidacloprid measurement based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, I. Two-dimensional infrared (2D IR) spectroscopy: Theory and applications. Appl. Spectrosc. 1990, 44, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, I. Modified two-dimensional correlation spectra for streamlined determination of sequential order of intensity variations. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1124, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, P.; Ma, Y. Interaction and coexistence characteristics of dissolved organic matter and toxic metals with per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in landfill leachate. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Zheng, Z.; Zhu, R. Long-term tea plantation effects on composition and stabilization of soil organic matter in Southwest China. Catena 2021, 199, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cultivation Ages | pH | TN/g·kg−1 | TP/g·kg−1 | AK/mg·kg−1 | SOM/g·kg−1 | DOC/mg·L−1 | Mechanical Composition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay/% <0.002 mm | Silt/% 0.002~0.050 mm | Sand/% >0.050 mm | |||||||
| 10a | 4.83 ± 0.12 | 1.25 ± 0.15 | 0.78 ± 0.61 | 341.38 ± 167.34 | 12.48 ± 1.48 | 20.23 ± 0.41 | 28.87 ± 1.37 | 42.70 ± 2.98 | 28.44 ± 1.60 |
| 30a | 4.68 ± 0.71 | 1.60 ± 0.25 | 0.98 ± 0.16 | 545.64 ± 56.43 | 15.94 ± 2.52 | 22.06 ± 0.52 | 42.33 ± 2.85 | 38.85 ± 0.04 | 18.83 ± 2.81 |
| 50a | 4.08 ± 0.23 | 2.97 ± 0.45 | 3.07 ± 0.21 | 507.48 ± 49.20 | 29.68 ± 4.50 | 26.47 ± 0.97 | 41.98 ± 2.35 | 41.79 ± 0.59 | 16.24 ± 1.77 |
| Cultivation Ages | System | Peaks | Peaks Position Ex/Em (nm/nm) | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10a | Only DOM | Peak A | 250/448 | 37,817 |
| Peak B | 325/394 | 86,500 | ||
| DOM−imidacloprid | Peak A | |||
| Peak B | 340/400 | 48,023 | ||
| 30a | Only DOM | Peak A | 250/454 | 53,966 |
| Peak B | 325/398 | 55,556 | ||
| DOM−imidacloprid | Peak A | |||
| Peak B | 340/450 | 30,733 | ||
| 50a | Only DOM | Peak A | 250/462 | 38,495 |
| Peak B | 325/404 | 36,791 | ||
| Peak C | 330/448 | 38,708 | ||
| DOM−imidacloprid | Peak A | |||
| Peak B | ||||
| Peak C | 340/448 | 27,323 |
| Cultivation Ages | IC (mol/L) | PLR (%) | FLR (%) | HLR (%) | FLR/HLR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10a | 0.6 × 10−4 | 0.04 | 0.74 | 0.22 | 3.36 |
| 1.2 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.74 | 0.24 | 3.08 | |
| 1.8 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.73 | 0.25 | 2.92 | |
| 2.4 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.72 | 0.26 | 2.77 | |
| 3.0 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.71 | 0.27 | 2.63 | |
| 3.6 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.71 | 0.27 | 2.63 | |
| 4.2 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 0.28 | 2.50 | |
| 4.8 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.69 | 0.29 | 2.38 | |
| 30a | 0.6 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.61 | 0.37 | 1.65 |
| 1.2 × 10−4 | 0.01 | 0.60 | 0.39 | 1.54 | |
| 1.8 × 10−4 | 0.01 | 0.59 | 0.40 | 1.48 | |
| 2.4 × 10−4 | 0.01 | 0.58 | 0.41 | 1.41 | |
| 3.0 × 10−4 | 0.01 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 1.33 | |
| 3.6 × 10−4 | 0.01 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 1.33 | |
| 4.2 × 10−4 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 0.44 | 1.25 | |
| 4.8 × 10−4 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 0.44 | 1.25 | |
| 50a | 0.6 × 10−4 | 0.03 | 0.61 | 0.36 | 1.69 |
| 1.2 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.61 | 0.37 | 1.65 | |
| 1.8 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.60 | 0.38 | 1.58 | |
| 2.4 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.59 | 0.39 | 1.51 | |
| 3.0 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.57 | 0.41 | 1.39 | |
| 3.6 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.57 | 0.41 | 1.39 | |
| 4.2 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 1.33 | |
| 4.8 × 10−4 | 0.03 | 0.55 | 0.42 | 1.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, K.; Li, D.; Zheng, T. Differential Molecular Interactions of Imidacloprid with Dissolved Organic Matter in Citrus Soils with Diverse Planting Ages. Agriculture 2025, 15, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090997
Chen J, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Jiang K, Li D, Zheng T. Differential Molecular Interactions of Imidacloprid with Dissolved Organic Matter in Citrus Soils with Diverse Planting Ages. Agriculture. 2025; 15(9):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090997
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Junquan, Yawen Zhang, Yanqi Guo, Kai Jiang, Duo Li, and Taihui Zheng. 2025. "Differential Molecular Interactions of Imidacloprid with Dissolved Organic Matter in Citrus Soils with Diverse Planting Ages" Agriculture 15, no. 9: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090997
APA StyleChen, J., Zhang, Y., Guo, Y., Jiang, K., Li, D., & Zheng, T. (2025). Differential Molecular Interactions of Imidacloprid with Dissolved Organic Matter in Citrus Soils with Diverse Planting Ages. Agriculture, 15(9), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090997






