Abstract
The results demonstrated that among the total 365 investigated samples, the proportion of samples detecting three target herbicides simultaneously, two herbicides, one herbicide, and none were 0.3%, 6.4%, 65.2%, and 23.2%, respectively. For samples with only one detected herbicide, the detection rates in Jiyuan, Luohe, Puyang, Luoyang, Xuchang, and Hebi were relatively high (ranging from 44% to 100%), whereas those in Sanmenxia, Nanyang, Xinxiang, and Kaifeng were relatively low (ranging from 6% to 20%). Regarding individual herbicides, the detection rates of mesosulfuron-methyl, quinclorac, halosulfuron-methyl, diflufenican, imazethapyr, pyroxasulfone, imazapic, fomesafen, and atrazine were 1.2%, 3.8%, 5.5%, 6.1%, 8.7%, 8.7%, 10.4%, 11.0%, and 33.9%, respectively. Based on these findings, the current reliance on long-acting effect herbicides for weed management in China’s agricultural management practices was systematically analyzed. Within the framework of agricultural sustainability, it is proposed that there is an urgent need to promote the concept of scientific herbicide use among farmers and that pesticide scientists must recognize the extreme importance of continuous innovation and the development of alternative herbicides with new mechanisms of action as a long-term strategic goal.
1. Introduction
Pesticides are the result of agricultural development and the crystallization of scientific and technological progress, playing an invaluable role in ensuring a sufficient supply of agricultural products (such as grains, vegetables, and fruits) for human consumption. They have become an indispensable tool of production in modern agricultural production practices. In recent decades, global agricultural production has undergone a significant restructuring from extensive traditional farming to technology-driven intensive agriculture, resulting in substantial transformations in the structure of the global pesticide industry. This industrial evolution has been driven by escalating demands for productivity optimization alongside mounting pressures for resource-efficient cultivation practices.
According to the statistical analysis conducted by S & P Global Commodity Insights Crop Science team (www.spglobal.com), the global sales of the crop pesticide market in 2022 reached USD 78.715 billion. Notably, herbicides accounted for a significant portion with a market share of USD 37.150 billion, which was nearly equivalent to the combined market shares of insecticides (USD 19.655 billion) and fungicides (USD 19.646 billion). This represents approximately 47.20% of the total agrochemical market share, indicating a steady growth trajectory expected for herbicides in the forthcoming years. According to Molan Digital Intelligence Research Center’s report (https://caifuhao.eastmoney.com/), China’s herbicides market size has achieved almost 30% of the global herbicides market size in 2023.
Undoubtedly, herbicides play an indispensable role in controlling weeds, reducing labor, and expanding agriculture in current agricultural production. However, concerns have been raised among experts in crop science, food safety, and environmental ecology, as well as the public, due to the extensive and frequent use of herbicides, particularly ones with long-lasting effects. These concerns arise from issues such as the development of weed resistance, the presence of pesticide residues in agricultural products, and contamination of ecological environments. According to the literature [1], only approximately 5% of sprayed herbicide quantities effectively reached target weeds to ensure optimal weed control efficacy. Meanwhile, around 95% of the herbicide enters soil, water, or air and interacts with non-target organisms, thus posing threats to farmland quality, crop health, agricultural product quality, and environmental safety.
The nine herbicides investigated in this study, including atrazine, imazethapyr, imazapic, mesosulfuron-methyl, halosulfuron-methyl, fomesafen, diflufenican, quinclorac, and pyroxasulfone, exhibited prolonged residual periods in field soil. The basic information regarding these herbicides is presented in Table 1. While their long-lasting effect in weed control was highly desirable in agricultural practices, the visible phytotoxicity resulting from soil residue remains a significant concern [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Furthermore, they were also suspected to exert substantial adverse effects on soil microorganisms [6,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18], contributing to the inevitable contamination of agricultural products by pesticide residue. The presence of these chemical residues in field soil has garnered significant attention and necessitates comprehensive analysis methods and performance indicators. A summary of the currently reported residue analysis methods and their corresponding performance parameters can be found in Table 2. However, to the best of our knowledge, no existing simultaneous determination method is available for assessing the aforementioned herbicide residues in field soil.

Table 1.
The basic information of nine representative long-lasting-effect herbicides.

Table 2.
Typical residue analysis methods of nine herbicides in soil in the literature.
Henan Province is strategically located in the heartland of the Central Plains of China. The distinctive climatic conditions conducive to agricultural production have bestowed upon Henan Province its renowned title as the “Granary of the Central Plains”. As a prominent grain-producing region in China, Henan Province consistently maintains an annual wheat sowing area of approximately 5.6 million hectares, yielding around 35 million tons per year. The corn planting area remains consistently above 3.8 million hectares, resulting in an annual output of about 28 million tons. The rice planting area exhibits stable figures at 600,000 hectares annually and yields around 20 million tons each year. Soybean cultivation encompasses an average planting area of about 300,000 hectares annually, with an approximate yearly output of 4 million tons. In terms of both planting area and production volume, peanut cultivation in Henan Province holds the top position nationwide, with an annual planting area of approximately 1.3 million hectares and a total production volume reaching around 6 million tons (https://data.stats.gov.cn/). Furthermore, Henan Province plays a pivotal role as a prominent vegetable-producing region within China. In the Henan Province of China, the information regarding crop fields where the nine representative long-lasting-effect herbicides investigated by this research institute were applied is provided in Table S1 of the supporting information.
The nine representative long-lasting-effect herbicides mentioned above are widely used in the management of farmland weeds in Henan Province, China. This study aims to provide insight into the residual status and distribution characteristics of these herbicides in farmland soil in Henan Province by using a multi-residue analysis method specifically developed for them. Furthermore, it is essential to propose effective strategies to mitigate the potential adverse effects of these herbicides on the sustainable development of agriculture. Simultaneously, these results should establish a fundamental theoretical foundation for the implementation of pollution control measures targeting herbicide-induced contamination in farmlands.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
Analytical standards of imazethapyr (purity, 99.9%), imazapic (purity, 98.0%), mesosulfuron-methyl (purity, 98.3%), atrazine (purity, 99.0%), quinclorac (purity, 98.1%), halosulfuron-methyl (purity, 99.8%), pyroxasulfone (purity, 99.7%), and fomesafen (purity, 98.9%) were purchased from Alta Scientific Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China); the analytical standard of diflufenican (purity, 99.9%) was obtained from Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH (Augsburg, Germany). Formic acid, sodium chloride, and anhydrous magnesium sulfate (analytical grade) were supplied from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). HPLC-grade acetonitrile was purchased from Mreda Medical Technologies Inc. (Beijing, China). The sorbents of primary secondary amine (PSA, 40–60 μm) and octadecylsilane (C18, 50 μm particle size, 60 Å pore size) were supplied by Bonna-Agela Technologies Inc. (Tianjin, China). Ultrapure water was prepared using a Millipore-Q water purification system (Millipore Corporation, MA, USA).
2.2. Chromatography Analysis Conditions
The analytes were separated and analyzed using the Waters Acquity UPLC system (Waters Corporation, MA, USA), which consisted of a binary pump, vacuum degasser, and temperature controller for the column; vial autosampler; and eλ-PDA. For this purpose, a Cosmocore PBr column (2.1 × 150 mm, 2.6 μm) (Nacalai Tesque Inc. Kyoto, Japan) was utilized with the column oven temperature maintained at 35 °C. Instrument control, data acquisition, and processing were performed utilizing Waters Empower-3 LC software. The mobile phase comprised a acetonitrile (A)-10% volume fraction of acetonitrile in 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution (B).
The multi-channel detection capability of the PDA was fully utilized based on the ultraviolet absorption spectral characteristics of target analytes. Different detection wavelengths were configured for UPLC-PDA to screen residues of nine herbicides in soil samples from diverse regions.
2.3. Preparation of Analytic Sample
The instructions for preparation are as follows: Take 10 ± 0.1 g of homogenized and sieved soil sample in a 50 mL polypropylene centrifuge tube, and add 10 mL of deionized water along with 10 mL of sample extraction solution (containing 0.1% acetic acid in acetonitrile) and 2 g of sodium chloride. Vortex the mixture for three minutes, followed by ultrasonic extraction maintained at a temperature of 40 °C for five minutes; subsequently, centrifuge it at a speed of 4500 rpm for five minutes. Transfer the resulting supernatant extract (1.0 mL) into a pre-loaded materials-containing centrifuge tube (2 mL) consisting of anhydrous magnesium sulfate (100 mg), PSA (25 mg), and C18 (25 mg). Vortex the mixture again for one minute before subjecting it to another round of centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for five minutes. Finally, filter the supernatant through a syringe filter with the pore size set at 0.22 μm into an appropriate clean vial suitable for chromatographic analysis.
2.4. Analysis of Field Soil Samples
A total of 365 soil samples were systematically collected from 120 counties across 18 provincial-level cities (shown in Figure S1 in Supplementary Materials) in Henan Province, and standardized sampling was conducted using the grid sampling design with the BeiDou navigation and positioning system (BDNPS) between May and October 2023. The sampled areas encompassed a diverse range of crops, including wheat, corn, soybeans, peanuts, garlic, vegetables, orchards, and nursery plots.
Upon arrival at the laboratory, farmland soil samples collected from various locations were meticulously removed of gravel and plant remains. Subsequently, these samples underwent sieving through a 2 mm sieve size before being divided into sub-samples weighing approximately 200 g each. The refined soil samples were then transferred into polyethylene self-sealing bags, appropriately labeled, and stored at −20 ± 1 °C for freezing preservation. During the analysis process, the analytical samples were prepared following the sample preparation procedure outlined in Section 2.3, followed by analyzing the residue levels of nine herbicides in soil samples using the chromatographic conditions described in Section 2.2.
The chromatographic analysis results of 9 herbicides in the investigated soil samples were processed by Waters Empower-3 LC software to obtain the residue detection data. Then, the residue detection data of the target analytes in the samples from different regions were analyzed by Microsoft Excel 2003 software and plotted as intuitive distribution pattern column charts.
3. Results
3.1. Optimized Chromatographic Conditions
A mobile phase flow rate of 0.3 mL/min was employed, and a gradient elution procedure was utilized as follows: initially, the system contained 15% B for 4.5 min; subsequently, the concentration of B increased to 40% within 6.0 min; further elevation to 60% B occurred over a period of 10.0 min; achieving a final concentration of 95% B and maintaining it for 3.0 min before returning to the initial conditions (15% B).
Based on a comprehensive analysis of standard chromatograms and ultraviolet spectra (210 nm to 400 nm) of nine herbicides, considering both detection sensitivity and interference from the soil sample matrix, different detection wavelengths were selected using UPLC-PDA for quantitative analysis of residual levels of these nine herbicides in soil samples collected from diverse regions. Specifically, the ultraviolet detection wavelength was set at 220 nm for quinclorac, atrazine, and pyroxasulfone; 235 nm for mesosulfuron-methyl; 254 nm for imazethapyr and imazapic; and 290 nm for fomesafen and diflufenican. The standard chromatograms of the nine target analytes under the optimized chromatographic conditions are shown in Figure 1. Details regarding the optimization process for wavelength detection can be found in Supplementary Materials (Figure S2).
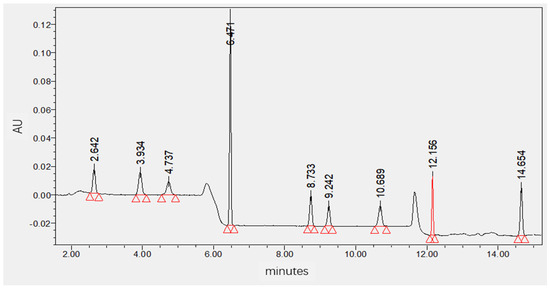
Figure 1.
Chromatographic separation of nine target analytes under the optimized conditions (imazapic Rt = 2.642 min, imazethapyr Rt = 3.934 min, quinclorac Rt = 4.737 mins, atrazine Rt = 6.471 min, mesosulfuron −methyl Rt = 8.733 min, pyroxasulfone Rt = 9.242 min, fomesafen Rt = 10.689 min, halosulfuron −methyl Rt = 12.156 min, and diflufenican Rt = 14.654 min).
3.2. Method Validation
According to the method validation guideline (CAC/GL 90-2017, http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/11/51256.html, 22 February 2025), the optimized method was evaluated for linearity, spiked fortified recoveries, relative standard deviations (RSDs), and sensitivity.
3.2.1. Linearity
The linearity was assessed by determining the correlation coefficient (R2) of determination for the seven-point calibration curves, which were obtained by diluting mixed standard solutions of nine target herbicides with acetonitrile extract from blank soil samples. The concentrations of the mixed matrix standard solvents ranged from 0.01 mg/L to 10.0 mg/L for soil, including concentrations of 0.01 mg/L, 0.05 mg/L, 0.1 mg/L, 0.5 mg/L, 1 mg/L, 5 mg/L, and 10.0 mg/L. Linear regression analysis was performed to establish quantitative calibration equations between the mass concentration of these analytes and their corresponding chromatographic response values. The obtained linear responses and the quantitative calibration equations were presented in Supplementary Materials (Figure S3), demonstrating favorable linearity for all nine target herbicides within the tested range of mass concentrations under optimized chromatographic conditions. Results revealed a linear detection range from 0.05 mg/L to 10 mg/L for mesosulfuron-methyl, while the remaining eight herbicides exhibited a detection range of 0.01 mg/L to 10 mg/L.
3.2.2. Accuracy, Precision, and Sensitivity
To evaluate the accuracy and precision of the methodology, recovery tests were performed on campus soil samples that had been confirmed to be free of the target analytes at three different levels (0.1 mg/kg, 0.5 mg/kg, and 1 mg/kg). The results obtained from these tests were used to determine both the recoveries and RSDs between detection values of three parallel treatments at each spiked level. Additionally, the LOQ for the analysis method was determined by calculating the detection sensitivities based on test results from nine herbicides spiked at a mass concentration of 0.1 mg/kg in blank soil samples with a signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of 10:1.
The recoveries of all nine analytes ranged from 76% to 100%, with corresponding RSDs all being less than 7%, as observed in the results presented in Table 3. The calculated LOQs for imazapic, imazethapyr, and quinclorac in soil were determined to be at a level of accuracy up to or equaling that which is required by an LOQ (0.016 mg/kg), while those for halosulfuron-methyl and diflufenican were established slightly higher at a level still within LOQs (0.026 mg/kg). Both atrazine and mesosulfuron-methyl exhibited LOQ values also within acceptable standards (0.017 mg/kg), whereas pyroxasulfone and fomesafen demonstrated LOQs of 0.031 mg/kg each. These findings underscore the precision, sensitivity, and robustness of the employed analytical sample preparation method.

Table 3.
The recoveries (%) and RSD (%) of nine herbicides at different spiked levels in soil.
3.3. Residual Detection Results of Nine Herbicides in Field Soil
To ensure the credibility of the detection results for the nine herbicides investigated in the collected soil samples, it is necessary to employ a grid sampling design to determine the sampling locations while minimizing the inclusion of industrial areas, towns, villages, ponds, and breeding farms. A total of 365 field soil samples were collected from various vegetable fields (including cabbage, cowpea, carrot, chili pepper, pumpkin, scallion, garlic, and potato), resulting in 28 samples. Furthermore, wheat fields contributed 63 samples; corn fields contributed 150; peanut fields contributed 64; soybean fields contributed 35; rice and sesame fields each provided 7 samples; and tea gardens accounted for 3 samples. The remaining soil samples (totaling 15) were obtained from cotton fields as well as those associated with sweet potato cultivation, along with orchards and nurseries.
The distribution pattern and detection ratios of herbicides across different regions are visually depicted in Figure 2. From an alternative perspective, out of the total 365 soil samples collected from agricultural fields using the grid sampling design, only a mere 0.3% exhibited simultaneous detection of three target herbicides out of the nine herbicides under investigation. Meanwhile, the detection ratio for two herbicides was found to be 6.4%, and it was observed that one herbicide alone had a detection ratio of 65.2%.
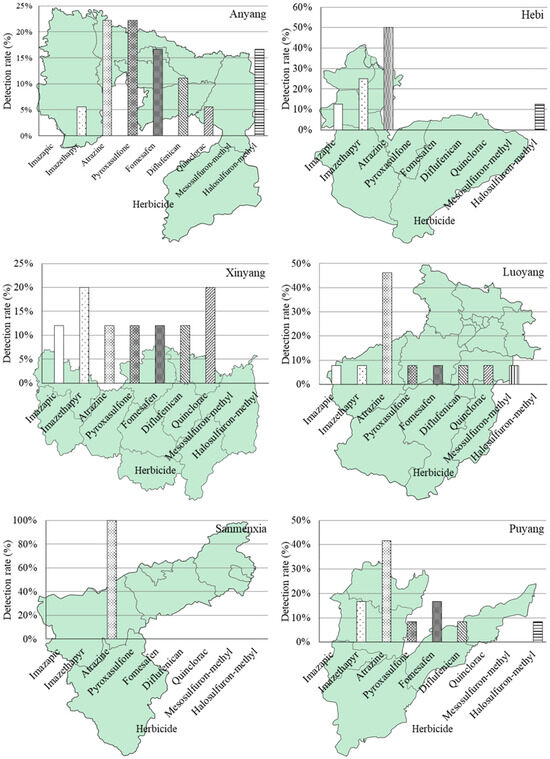
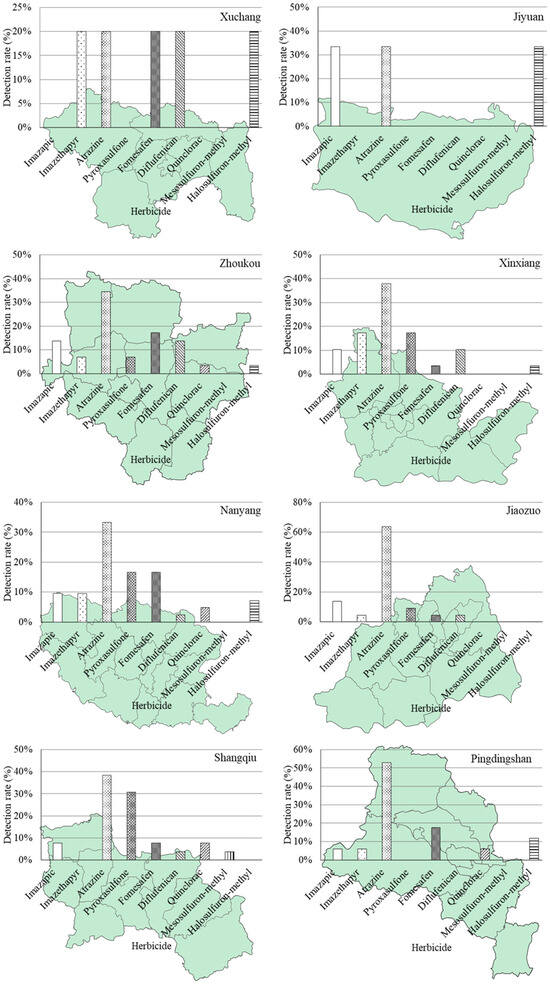
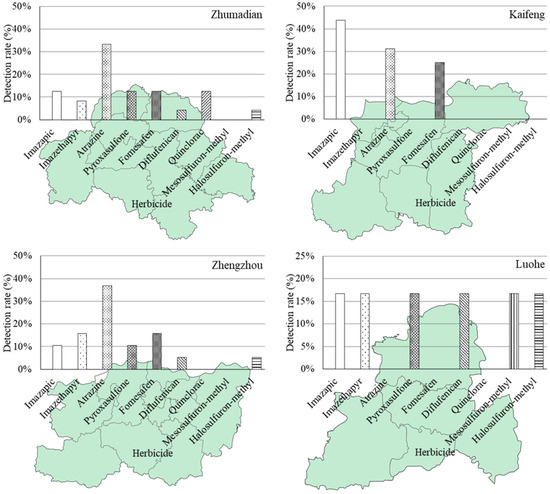
Figure 2.
Distribution pattern and detection rate of nine investigated herbicides in eighteen major agricultural producing areas (prefecture-level cities) in Henan Province of China.
The non-detection ratio for any herbicide accounted for 23.2%. In terms of detecting a specific herbicide, relatively high detection ratios were observed in Jiyuan (100%), Luohe (86%), Puyang (58%), Luoyang (50%), and Xuchang (50%) regions. However, it should be noted that Jiyuan is located in a major industrial area with limited agricultural land, comprising only 32,000 hectares of cultivated land. Therefore, the representativeness of the two samples considered from Jiyuan may be compromised. On the contrary, Sanmenxia, Nanyang, and Xinxiang regions all demonstrate detection frequencies below 20%. Furthermore, for the entire Henan province situation depicted in Figure 3, individual herbicides’ detection ratios were as follows: mesosulfuron-methyl was detected at 0.8%, quinclorac at 4.4%, halosulfuron-methyl at 4.7%, diflufenican at 5.8%, imazethapyr at 8.5%, pyroxasulfone at 10.7%, imazapic at 9.9%, fomesafen at 10.7%, and atrazine at 32.1%.
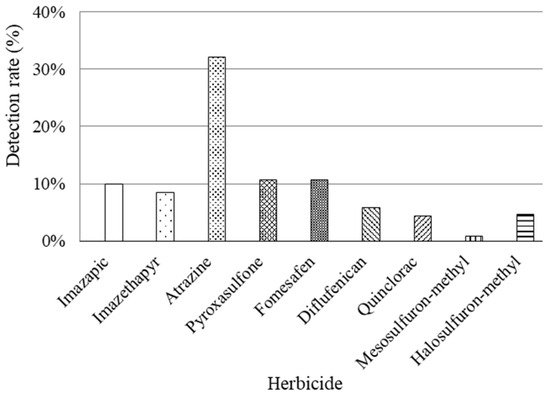
Figure 3.
Detection rate of nine investigated herbicides in Henan Province of China.
It is noteworthy that none of the twenty-eight soil samples collected from vegetable fields showed detectable residues of the target herbicides. This observed outcome could be due to either the detection results being below the limit of detection or no application of herbicides for weed management during vegetable cultivation.
4. Discussion
The objective of investigating soil herbicide contamination is to quantify the level of herbicide pollution in agricultural soils and analyze their spatial distribution. During this process, it is crucial to carefully allocate sampling points for accurate and scientifically valid survey results. The uncertainty arising from the sampling location contributes approximately 50% to the overall uncertainty in estimating pollutant content [44]. However, by effectively designing a sampling scheme based on both historical background regarding pesticide application and the geographical environment specific to the survey area [45,46], we can significantly improve accuracy during investigations of soil pollution. In this study, a grid sampling method based on the BDNPS was employed to investigate the provincial-scale geographical distribution of residues from nine typical long-lasting-effect herbicides in soil samples collected from Henan Province, which is a prominent agricultural region in China. The successful analytical method developed for these herbicides in soil samples was leveraged.
Considering both a large sample size (a total of 365 samples) and a wide distribution range for soil sampling sites (covering an area of 167,000 square kilometers), as well as an extended duration for sampling (lasting for six months), it becomes evident that despite classifying these nine target herbicides under investigation as pesticides with long-lasting residual properties, there is potential for detected residues to originate from either recent crop applications or remnants in previous crop fields. Furthermore, herbicide application timings often vary among different regions even when considering current crops. Therefore, discussing absolute residue values regarding these investigated herbicides lacks significance within this scope; instead, all results exceeding LOQ were included in our analysis process.
Based on the comprehensive survey results, it is evident that weed management practices in diverse crop fields across China’s primarily agricultural regions predominantly rely on conventional herbicides like atrazine, imazethapyr, imazapic, fomesafen, quinclorac, and mesosulfuron-methyl. However, in recent years, there has been a gradual adoption of newly developed advanced herbicides such as pyroxasulfone, halosulfuron-methyl, and diflufenican. This phenomenon can be attributed to the entrenched practice of herbicide usage in local areas and the provision of high-quality professional training aimed at enhancing knowledge related to plant protection during China’s intensive agricultural development process.
In the survey results, several phenomena were also observed. For instance, samples from multiple sampling points revealed residues of herbicides unsuitable for this season’s crop fields. These residues could be attributed to the remnants left by previous crops or even traced back to earlier years’ applications of herbicides in the fields. This occurrence is undoubtedly linked to the long-lasting-effect nature of the investigated herbicides but is further facilitated by their long-term, continuous, and high-dose application. The survey results also reveal a noteworthy situation: the relatively simple cropping system (primarily consisting of wheat–corn and wheat–soybean/peanut rotation) in Henan Province of China predominantly relies on traditional herbicide varieties, which may serve as the fundamental reason behind the rapid development of weed resistance in various regions of Henan Province in recent years.
Due to the influence of multiple factors, the deeply entrenched cultivation system has exhibited remarkable resistance to change. Therefore, there is an urgent need to enhance farmers’ selection and application techniques for herbicides, including rational blending, timely replacement, and strict adherence to label instructions. Additionally, it is crucial for pesticide scientists to continuously innovate and develop alternative herbicide varieties with novel mechanisms as a long-term objective.
Meanwhile, in order to align with the sustainable development goals of modern agriculture, it is imperative to give due attention to the survey results and systematic analysis presented in this article as a significant source of inspiration for weed management in other regions.
Although the investigation results obtained in this study are relatively comprehensive, the influence of key soil enzyme activities that are closely associated with assessing the soil pollution status has not yet been addressed. Additionally, even without considering climatic factors, differences exist in the degradation patterns of pesticides in soils with varying textures. It appears inappropriate to evaluate the residual risks of these herbicides solely based on the findings of this investigation as a uniform benchmark. Moreover, there remains a significant gap in long-term dynamic monitoring data regarding the residues of related herbicides in farmland soil. All these aspects require further attention and improvement in subsequent studies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture15090996/s1, Figure S1: Map of Henan Province, China; Figure S2: Ultraviolet spectrum of nine herbicides; Figure S3: Linear detection ranges of nine herbicides: Table S1: Source information of the 365 investigated soil samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition, G.L.; investigation, visualization, and original draft preparation, Y.Y.; investigation, visualization, and original draft preparation, S.W.; validation and writing—review and editing, D.L.; resources and data curation, R.L.; resources, Y.Z.; formal analysis, validation, and funding acquisition, Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Research and Development Special Project of Henan Province, China, grant number 221111112300 and 241111320100.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not involving humans or animals.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its additional files.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Bajeeb Allah from the University of Qatar for his kind help in the language review of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Miller, G.T. Sustaining the Earth, 6th ed.; Thompson Learning Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Dubelman, A.M.; Solsten, T.R.; Fujiwara, H.; Akbar, M.; Mehrsheikh, A. Metabolism of halosulfuron-methyl by corn and wheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2314–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.J.; Neal, J.C.; Ditomaso, J.M. Mechanism of action and selectivity of quinclorac in grass roots. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 1997, 57, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, J.R.; Esau, R.; Boswall, A.L. Effects of quinclorac on following rotational crops. Weed Technol. 1999, 13, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, K.; Kwiatkowski, J. The mechanism of quinclorac selectivity in grasses. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2000, 66, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Baćmaga, M.; Borowik, A.; Kucharski, J.; Tomkiel, M.; Wyszkowska, J. Microbial and enzymatic activity of soil contaminated with a mixture of diflufenican + mesosulfuron-methyl + iodosulfuron-methyl-sodium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2015, 22, 643–656. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, W.P. Enantioselectivity in the phytotoxicity of herbicide imazethapyr. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Shao, T.J.; Min, H.; Lu, Z.M.; Xu, X.Y. Stress response of Burkholderia cepacia WZ1 exposed to quinclorac and the biodegradation of quinclorac. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Ye, F. Applications of imidazolinone herbicide and its degradation. Plant Protec. 2009, 35, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tejada, M. Evolution of soil biological properties after addition of glyphosate, diflufenican and glyphosate + diflufenican herbicides. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.P.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.G.; Dong, F.S.; Kong, Z.Q.; Sheng, Y.; Zheng, Y.Q. Impact of imazethapyr on the microbial community structure in agricultural soils. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 800–806. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, A.L.; Cui, Y.; Feng, L.; Wu, D.D. Effect of quinclorac on soil microbial community structure under culture conditions. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2015, 35, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kewat, M.L.; Sondhia, S. Studies on the effect of day time application of herbicide mesosulfuron-methyl on soil microbial communities of wheat rhizosphere. J. Environ. Biol. 2018, 39, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, P.Q.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.S.; Liu, X.G.; Zheng, Y.Q. Impact of fomesafen on the soil microbial communities in soybean fields in Northeastern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.H.; Yao, X.F.; Li, X.X.; Zhu, L.S.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, J. Responses of soil microbial community to herbicide atrazine contamination. Water Air Soil Poll. 2023, 234, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakar, K.; Medina, S.; Ziadna, H.; Igbaria, K.; Achdari, G.; Lati, R.; Zarecki, R.; Ronen, Z.; Dovrat, G.; Eizenberg, H. Comparative study of bacterial community dynamics in different soils following application of the herbicide atrazine. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Men, J.N.; Zheng, T.; Ma, Y.L.; Li, W.S.; Cernava, T.; Bai, L.Y.; Jin, D.C. Impact of pyroxasulfone on sugarcane rhizosphere microbiome and functioning during field degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.C.; Zhu, Y.F.; Chen, H. Chiral herbicide imazethapyr influences plant-soil feedback on nitrogen metabolism by shaping rhizosphere microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2024, 31, 18625–18635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, L.N.; Pasztor, Z. Environmental distribution of acetochlor, atrazine, chlorpyrifos, and propisochlor under field conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3859–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnac, T.; Bristeau, S.; Jeannot, R.; Mouvet, C.; Baran, N. Determination of chloroacetanilides, triazines and phenylureas and some of their metabolites in soils by pressurised liquid extraction, GC-MS/MS, LC-MS and LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1067, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Q.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.S.; Liu, X.G.; Zheng, Y.Q. Simultaneous determination of nicosulfuron, atrazine and fluroxypyr in soil and corn by ultraperformance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2012, 14, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bzour, M.; Zuki, F.M.; Mispan, M.S.; Jodeh, S.; Abdel-Latif, M. Determination of the leaching potential and residues activity of imidazolinone herbicide in clear field rice soil using high-performance liquid chromatography. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2019, 103, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.S.; Su, S.Q.; Wu, Y.Q.; Han, X.J. Trace residue analysis of the herbicide imazethapyr in soil by gas chromatography-nitrogen/phosphorous detector. J. Northeast Agr. Unive. 1997, 4, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Stout, S.J.; Dacunha, A.R.; Allardice, D.G. Microwave-assisted extraction coupled with gas chromatography/electron capture negative chemical ionization mass spectrometry for the simplified determination of imidazolinone herbicides in soil at the ppb level. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaifuddin, S.N.M.; Hussain, H.; Hassan, H.F. Optimization of extraction and detection method for imazapyr and imazapic residues in water, soil and fish tissue samples using high performance liquid chromatography. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assalin, M.R.; Queiroz, S.C.N.; Ferracini, V.L.; Oliveira, T.; Vilhena, E.; Mattos, M.L.T. A method for determination of imazapic and imazethapyr residues in soil using an ultrasonic assisted extraction and LC-MS/MS. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2014, 93, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmerich, M.; Bernardi, G.; Adaime, M.B.; Zanella, R.; Prestes, O.D. A simple and efficient method for imidazolinone herbicides determination in soil by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1412, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Kaur, P. Comparison of extraction procedures for the determination of mesosulfuron methyl and iodosulfuron methyl sodium from soil and wheat using response surface modelling. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 10645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Yang, G.L.; Zheng, Z.S.; Chen, Y.D.; Wang, L.; Qian, X. Study on the residue dynamics of mesosulfuron-methyl in wheat and soil. J Agric Univ Hebei 2009, 32, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, R.; Duhan, A.; Punia, S.S.; Yadav, D.B. Degradation dynamics of halosulfuron-methyl in two textured soils. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2019, 102, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Shan, Z.J.; Shi, L.L.; Song, N.H.; Xu, J. Degradation and adsorption characteristics of three sulfonylurea herbicides in different soils. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2012, 32, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekharam, C.; Ramesh, A. Adsorption and degradation of herbicide halosulfuron-methyl in Indian soils. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, A.; Queiroz, M.E.; Neves, A.A.; de Assis, R.C.; dos Soares, C.E.S.; da Silva D’Antonino, L.; de Oliveira, A.F.; Bellato, C.R. Mobility and persistence of the herbicide fomesafen in soils cultivated with bean plants using SLE/LTP and HPLC/DAD. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 3457–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.N.; Gioia, F.D.; Hwang, J.I.; Hong, J.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Zhao, X.; Pisani, C.; Rosskopf, E.; Wilson, P.C. Dissipation of fomesafen in fumigated, anaerobic soil disinfestation-treated, and organic-mended soil in Florida tomato production systems. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.J.; Han, Y.J.; Jiang, L.X.; Tao, B. Study on bioassay method of fomesafen. J. Northeast Agr. Univ. 2011, 42, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Wu, J.J.X.; Han, L.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, W.; Guo, H.C.; We, H. Nanozyme sensor arrays based on heteroatom-doped graphene for detecting pesticides. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7444–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.Q.; Chen, L.; An, Z.X.; Wang, Y.S.; Yang, D.C.; Wang, Z.Z.; Kang, J.; Barnych, B.; Hammock, B.D.; Huo, J.Q.; et al. Development of an immunoassay based on a specific antibody for the detection of diphenyl ether herbicide fomesafen. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouchaud, J.; Neus, O.; Bulcke, R.; Bulcke, O.N.R.; Cools, K.; Eelen, H.; Dekkers, T. Soil dissipation of diuron, chlorotoluron, simazine, propyzamide, and diflufenican herbicides after repeated applications in fruit tree orchards. Arch. Environ. Con. Tox. 2000, 39, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Shi, Y. Determination of residue of diflufenican in wheat and soil by ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Li, L.C.; Zhong, Q.Z.; Zhang, G.B.; Feng, X.J.; Deng, S.Q.; Wan, S.Q. Determination of herbicides in soil by dispersive solid-phase extraction, dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction, and high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 2871–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Z.; Zeng, W.A.; Zhao, S.Y.; Cai, Z.M.; Zhou, Q.M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, Z.D.; Ou, X.M. Determination of quinclorac residues in tobacco and soil using HPLC coupled to photodiode array detector. Acta Tabacaria Sin. 2013, 19, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Ward, P.; Piggin, C.; Bong, S.H.; Nambiar, S.; Trengove, R.D.; Flower, K. A bioassay for prosulfocarb, pyroxasulfone and trifluralin detection and quantification in soil and crop residue. Crop Pasture Sci. 2018, 69, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, E.P.; Shaner, D.L.; Westra, P.H.; Chapman, P.L. Dissipation and leaching of pyroxasulfone and S-metolachlor. Weed Technol. 2014, 28, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyraki, A.; Ramsey, M.H.; Potts, P.J. Evaluation of portable X-ray fluorescence instrumentation for in situ measurements of lead on contaminated land. Analyst 1997, 122, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.; Lark, R.M. Field Sampling for Environmental Science and Management; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2012; pp. 162–200. [Google Scholar]
- Muntau, H.; Rehnert, A.; Desaules, A.; Wagner, G.; Quevauviller, P. Analytical aspects of the CEEM soil project. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 264, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).