Optimal Water Allocation Considering Water Diversion Projects in an Agricultural Irrigation District
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
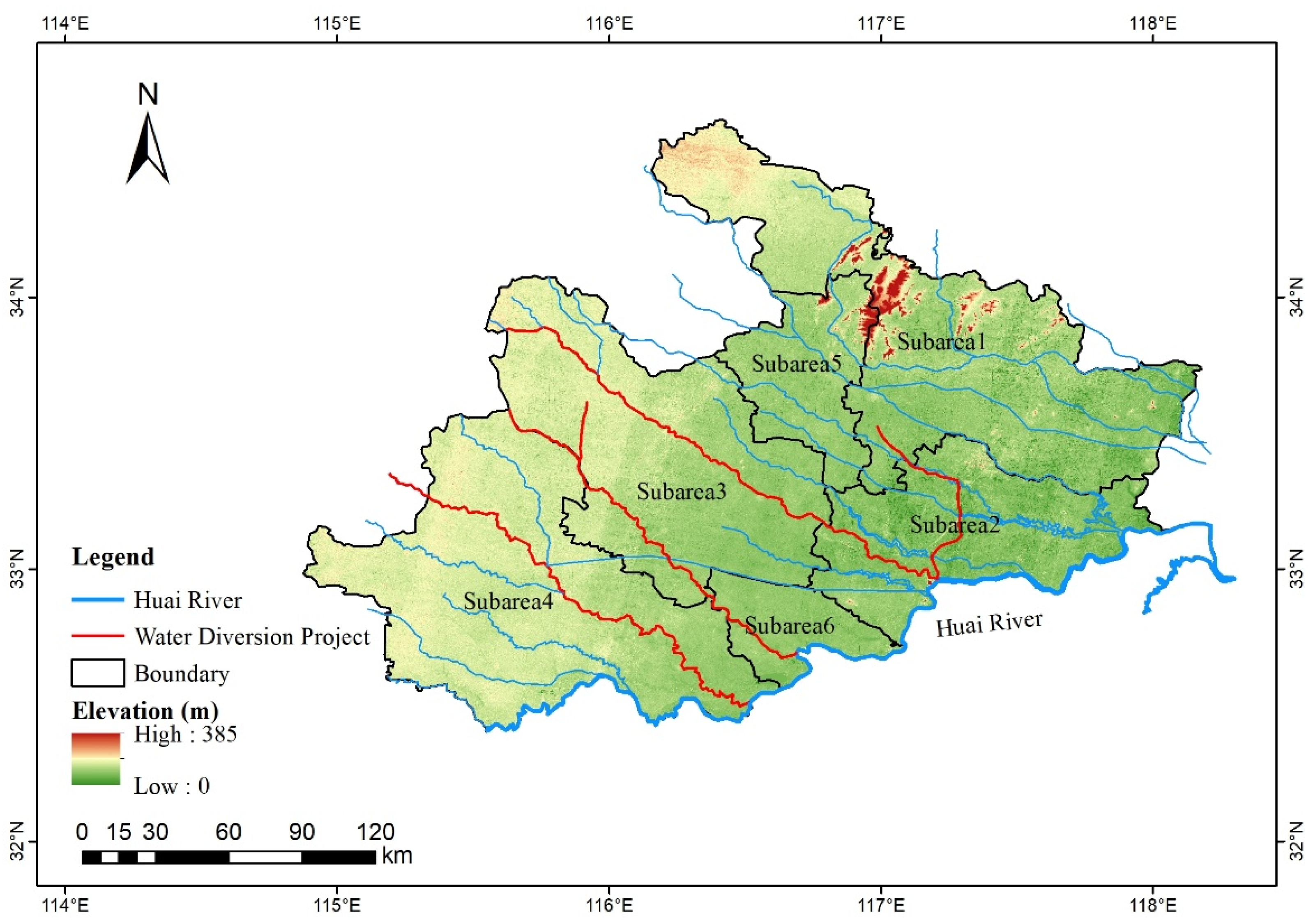
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. Water Diversion Capacity and Related Ecological Water Table
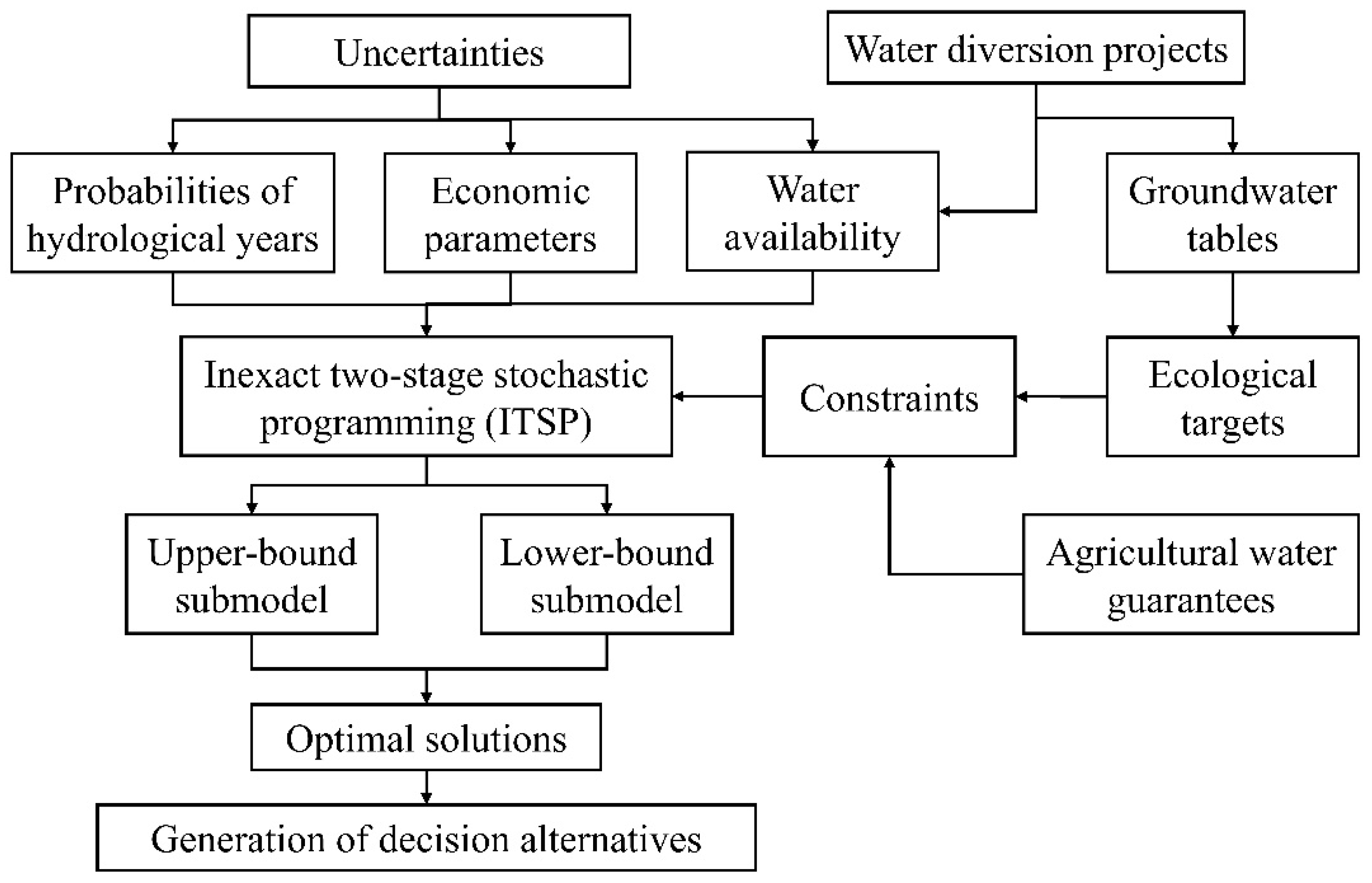
2.3. Two-Stage Stochastic Programming
2.4. The Water Resource Optimization Allocation Model in the Huaibei Agricultural Irrigation District
2.5. Water Supply–Demand in the Agricultural Irrigation District
3. Results and Discussion
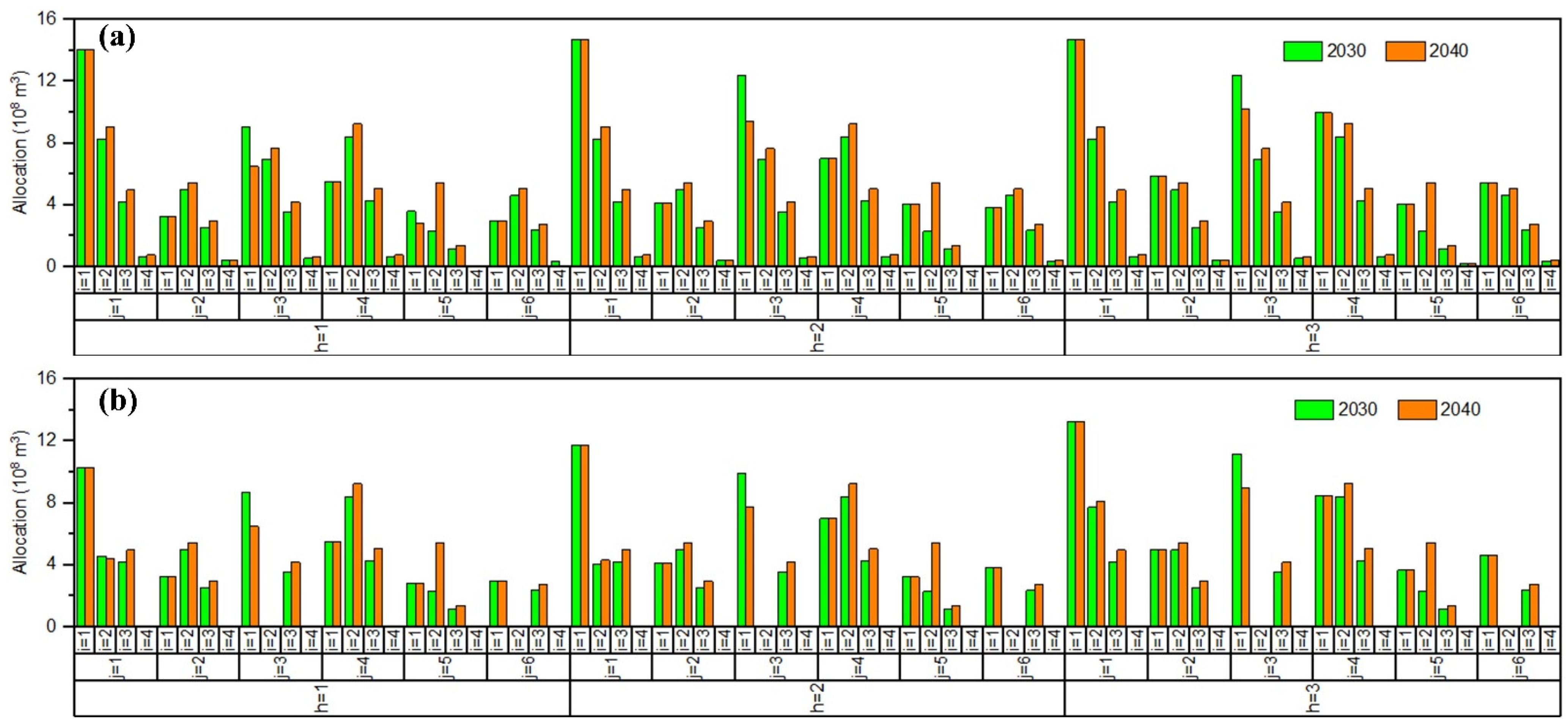
3.1. Initial Water Allocation
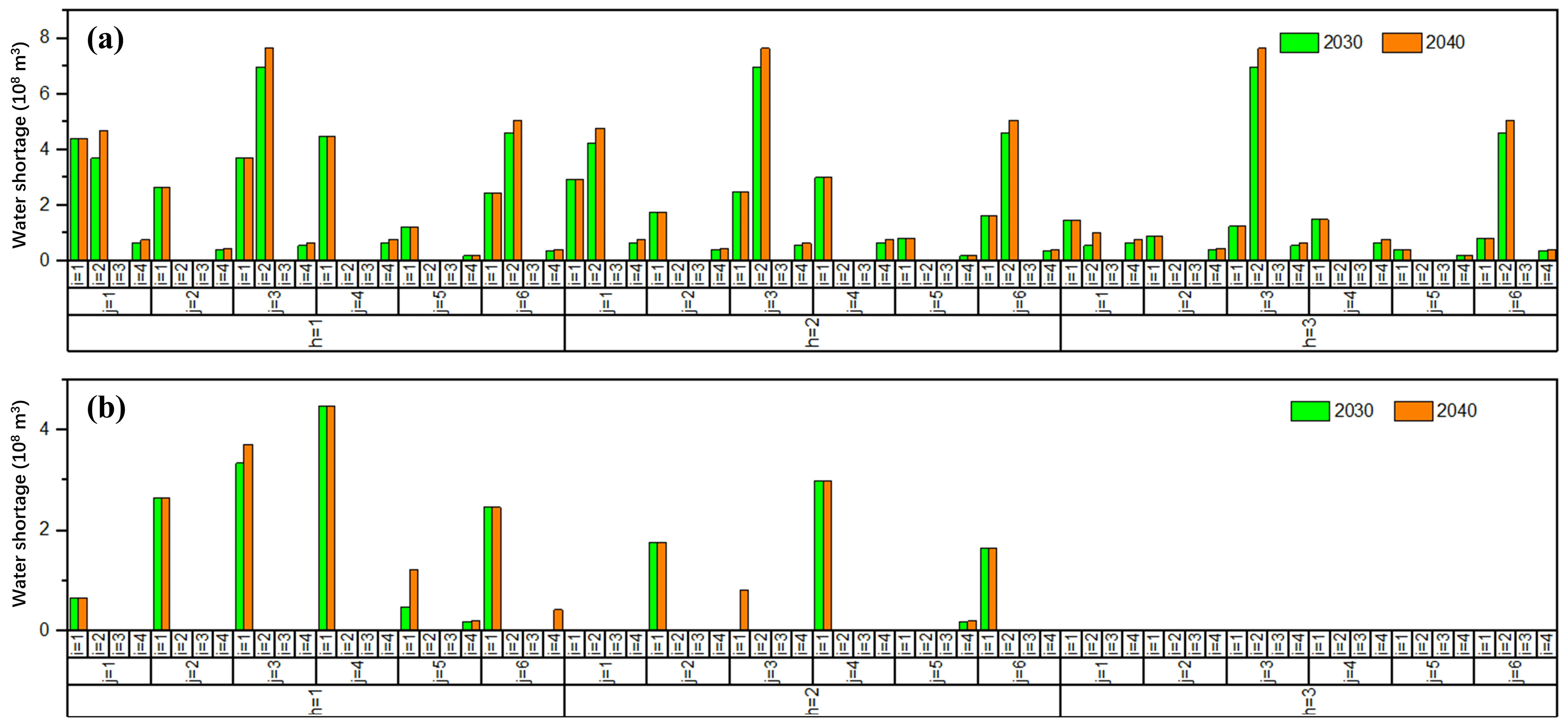
3.2. Water Deficit Amounts
3.3. Water Allocation Strategies
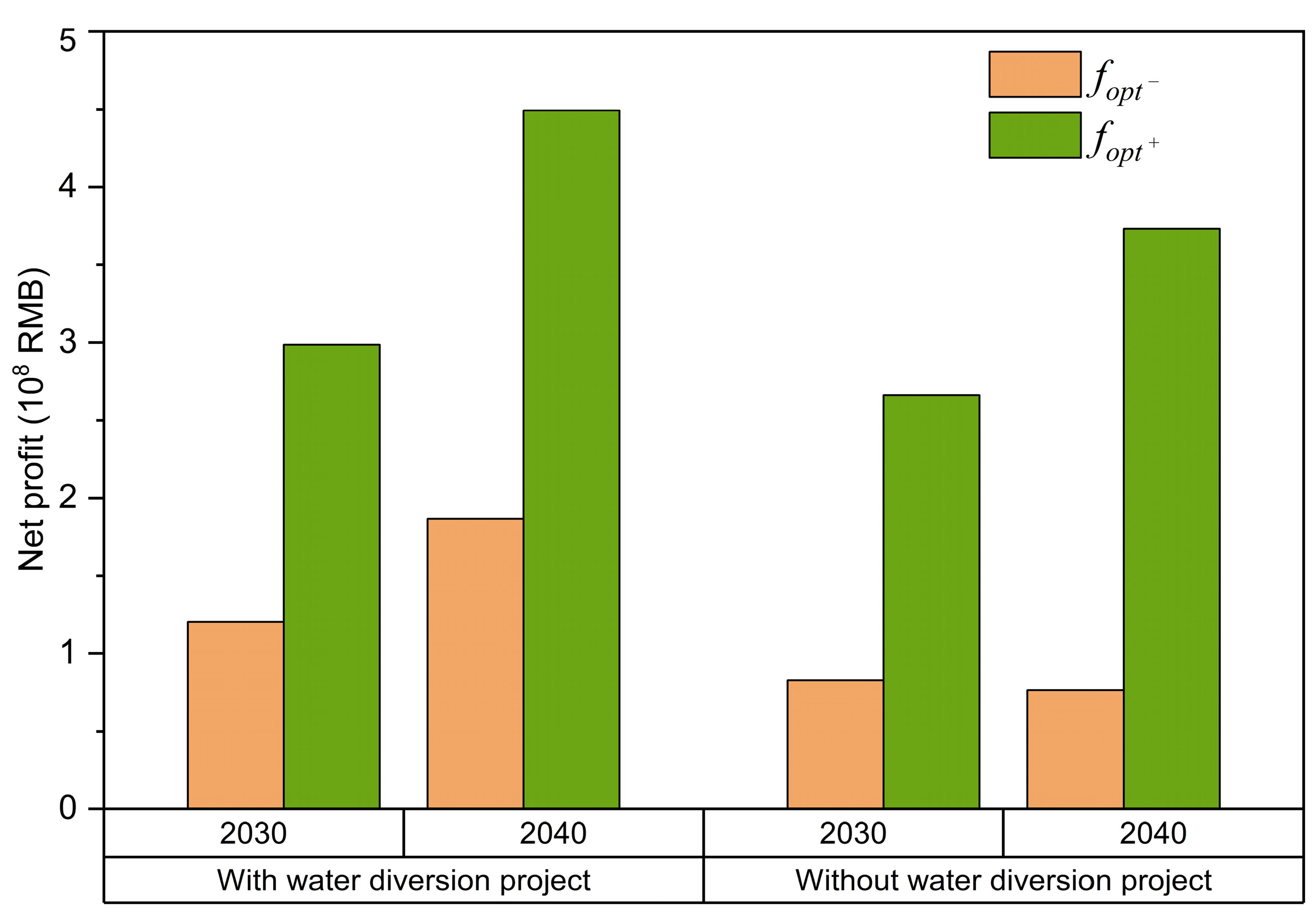
3.4. Economic Benefit Comparison
3.5. Limitations and Future Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shu, R.; Cao, X.C.; Wu, M.Y. Clarifying Regional Water Scarcity in Agriculture based on the Theory of Blue, Green and Grey Water Footprints. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 1101–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warziniack, T.; Brown, T.C. The importance of municipal and agricultural demands in future water shortages in the United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 084036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Liu, D.; Li, T. Efficient irrigation water allocation and its impact on agricultural sustainability and water scarcity under uncertainty. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.C.; Zhao, T.Q.; Wu, Z.H.; Zhang, F.; Yan, J.; Lu, N.J. Promoting ecological sustainability in the arid farming-pastoral ecotone through optimal water allocation. J. Hydrol. 2025, 652, 132609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.T.; Wu, Q.S.; Yu, L.; Li, Y.P.; Fan, Y.R. Optimization of uncertain agricultural management considering the framework of water, energy and food. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 253, 106907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, T.; Cui, S.; Liu, D.; Lu, X. Agricultural Multi-Water Source Allocation Model Based on Interval Two-Stage Stochastic Robust Programming under Uncertainty. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karandish, F.; Hogeboom, R.J.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Physical versus virtual water transfers to overcome local water shortages: A comparative analysis of impacts. Adv. Water Resour. 2021, 147, 103811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, S.; Feng, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Ding, J. A Review of the Eco-Environmental Impacts of the South-to-North Water Diversion: Implications for Interbasin Water Transfers. Engineering 2023, 30, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Che, L.; Wang, Z. Where are the critical points of water transfer impact on grain production from the middle route of the south-to-north water diversion project? J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, B.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Lu, F. Research on Scale Demonstration Technology of Inter Basin Water Transfer Project in Agricultural Irrigation. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 5243–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Xu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhong, P.-a.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Tan, J. Multiobjective risk-based optimization for real-time interbasin water diversion under decomposed chance-constrained total water use. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 58, 102252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingsanchali, T.; Boonyasirikul, T. Stochastic dynamic programming with risk consideration for transbasin diversion system. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2006, 132, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, R.; Pudeh, H.T.; Yonesi, H.A.; Haghiabi, A.H. Dynamic programming model for hydraulics and water resources simulating and optimizing water transfer system (a case study in Iran). J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua. 2017, 66, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, P.; Yang, G.Q.; Fang, S.Q. IB-ICCMSP: An Integrated Irrigation Water Optimal Allocation and Planning Model Based on Inventory Theory under Uncertainty. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, K.; Dong, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, B.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y. Leakage and evapotranspiration act as two major water losses for the largest lake on North China Plain during water diversion period. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ma, R.; Ma, T.; Sun, Z. Modeling the effects of water diversion projects on surface water and groundwater interactions in the central Yangtze River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.-M. Influence of south-to-north water diversion on major cones of depression in North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3845–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, C.; Huo, Z. Efficient and equitable irrigation management: A fuzzy multi-objective optimization model integrating water movement processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, H.; Farid, M.A.; He, X.L.; Heng, T.; Hermansen, C.; de Jonge, L.W.; Li, F.D.; Gao, Y.L.; Tian, L.J.; et al. Metaheuristic optimization of water resources: A case study of the Manas River irrigation district. J. Hydrol. 2024, 639, 131640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Hao, X.M.; Zhou, H.P.; Ding, R.S. An integrated strategy for improving water use efficiency by understanding physiological mechanisms of crops responding to water deficit: Present and prospect. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-p.; Fu, B.-j.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.-b.; Zhao, M.M.; Ma, J.-f.; Wu, J.-H.; Xu, C.; Liu, W.-g.; Wang, H. Sustainable development in the Yellow River Basin: Issues and strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.A.; Getahun, B.A. Assessment of water resource and forecasting water demand using WEAP model in Beles river, Abbay river basin, Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KhazaiPoul, A.; Moridi, A.; Yazdi, J. Multi-Objective Optimization for Interactive Reservoir-Irrigation Planning Considering Environmental Issues by Using Parallel Processes Technique. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 5137–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringler, C.; Huy, N.V.; Msangi, S. Water allocation policy modeling for the Dong Nai River Basin: An integrated perspective. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 1465–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Waseem, M.; Wahab, H.; Khan, A.Q.; Jehan, Z.; Ahmad, I.; Leta, M.K. Assessing water demand and supply in the Upper Indus Basin using integrated hydrological modeling under varied socioeconomic scenarios. Appl. Water Sci. 2025, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buri, E.S.; Keesara, V.R.; Loukika, K.N.; Sridhar, V.; Dzwairo, B.; Montenegro, S. Climate-adaptive optimal water resources management: A multi-sectoral approach for the Munneru river basin, India. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 374, 124014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Duan, W.; Chen, Y.; Dukhovny, V.A.; Sorokin, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Comprehensive evaluation and sustainable development of water-energy-food-ecology systems in Central Asia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, U.; Harboe, R. Deterministic and stochastic optimization of a reservoir system. Water Int. 2007, 32, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Y.S.; Pflug, G.C. Stochastic vs deterministic programming in water management: The value of flexibility. Ann. Oper. Res. 2014, 223, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, D.; Peng, Q.; Jin, T. Water Quality by Spectral Proper Orthogonal Decomposition and Deep Learning Algorithms. Sustainability 2025, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qu, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhou, F.; Wu, Q. Joint Training and Resource Allocation Optimization for Federated Learning in UAV Swarm. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 2272–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.H. A hybrid inexact-stochastic water management model. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 107, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.H.; Loucks, D.P. An inexact two-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management under uncertainty. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2000, 17, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Lev, B. Optimal river basin water resources allocation considering multiple water sources joint scheduling: A bi-level multi-objective programming with copula-based interval-bistochastic information. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 194, 110388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Wei, J.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Ye, S. Evolution and prediction of drought-flood abrupt alternation events in Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Editorial Committee of “Anhui Statistical Yearbook”. Anhui Statistical Yearbook 2024; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2024. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Department of Water Resources of Anhui Province, Anhui Province Water Resources Bulletin. 1999–2024. Available online: https://slt.ah.gov.cn/public/column/21731?type=4&catId=32715131&action=list (accessed on 19 April 2025). (In Chinese)
- Chen, S.; Huang, B.; Yuan, F.; Berndtsson, R.; Qiu, J.; Chen, X.; Hao, Z. Spatiotemporal Changes in Precipitation and Temperature in the Huaibei Plain and the Relation between Local Precipitation and Global Teleconnection Patterns. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2019, 24, 05019019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Horton, R.; Lu, H.; Wang, Z.; Su, J.; Cui, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J.; et al. Effect of climate change on the contribution of groundwater to the root zone of winter wheat in the Huaibei Plain of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 240, 106292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.D.; Zhang, H.R.; Xu, J.J.; Yang, F. Scalar configuration, power strategies and water governance: Insights from the politics of the Yangtze-to-Huai Water Transfer Project. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2022, 38, 658–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Ecological Compensation Standard and Distribution of Water Diversion in the Project of Leading Water from Changjiang to Huaihe River in Anhui Province. J. Bengbu Univ. 2022, 11, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Zhang, L.; Ji, Y.; Sun, J.; Shen, D.; Wang, C. Research on annual water dispatch model of Yangtze -to-Huaihe River Water Diversion. Yangtze River 2021, 52, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of “Anhui Statistical Yearbook”. Anhui Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1999–2024. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yang, G.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Chang, C.; Du, J.; Gao, D. A spatial-temporal optimal allocation method of irrigation water resources considering groundwater level. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 275, 108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Xu, X.; Engel, B.; Huang, G. Growth responses of crops and natural vegetation to irrigation and water table changes in an agro-ecosystem of Hetao, upper Yellow River basin: Scenario analysis on maize, sunflower, watermelon and tamarisk. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 199, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.K.; Yang, Y.G.; Yang, Y.M.; Chen, S.Y.; Hu, Q.L.; Liu, X.J.; Gao, F. HYDRUS Simulation of Sustainable Brackish Water Irrigation in a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain. Water 2017, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Tian, L.; Li, X.; He, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Xue, L.; Li, P. Numerical assessment of the effect of water-saving irrigation on the water cycle at the Manas River Basin oasis, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; He, X.; Ma, M.; Lu, C. Research on the restoration target of healthy depth to water table in Haihe Plain. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2022, 53, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y. Effects of Different Groundwater Burial Depths on Crop Growth and Yield in Huaibei Plain. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 23, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Schuetze, N. Assessing crop yield and water balance in crop rotation irrigation systems: Exploring sensitivity to soil hydraulic characteristics and initial moisture conditions in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 300, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, R.W.; Rivera, J.F.; Shahidehpour, S.M. Dynamic programming two-stage algorithm for long-term hydrothermal scheduling of multireservoir systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1998, 13, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Li, J.B.; Huang, G.H.; Li, H.L. A simulation-based interval two-stage stochastic model for agricultural nonpoint source pollution control through land retirement. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 361, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, M.; Chen, X. A Preliminary Study on the Exploitation Potential and Management of Groundwater Resources in the Huaibei Region of Anhui Province. Gov. Huai River 2011, 8, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, T.C.; Steduto, P.; Fereres, E. A systematic and quantitative approach to improve water use efficiency in agriculture. Irrig. Sci. 2007, 25, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.; Cao, Y.; Gu, Y. Causes and management measures of groundwater overexploitation in Huaihe River Basin and Shandong Peninsula. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2024, 44, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Yue, Y.; Wang, F. The spatial-temporal coupling pattern of grain yield and fertilization in the North China plain. Agric. Syst. 2022, 196, 103330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z. Physical limitations and challenges to Grain Security in China. Food Secur. 2014, 6, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, L.; Liu, P.; Hailu, A. Relationships between regional economic sectors and water use in a water-scarce area in China: A quantitative analysis. J. Hydrol. 2014, 515, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Yue, X.; Miao, L.; Lu, F. Identification of key sectors of water resource utilization in China from the perspective of water footprint. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floerke, M.; Kynast, E.; Baerlund, I.; Eisner, S.; Wimmer, F.; Alcamo, J. Domestic and industrial water uses of the past 60 years as a mirror of socio-economic development: A global simulation study. Glob. Environ. Change-Hum. Policy Dimens. 2013, 23, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H. Assessment of the Socio-Economic Impact of a Water Diversion Project for a Water-Receiving Area. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Ni, Z.; Yu, E. Quenching thirst, easing debt: Improvement in water resource endowment alleviates local government debt risk. China Econ. Rev. 2024, 88, 102302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wei, J.; Jiang, S.; Pei, H. Shift of phytoplankton assemblages in a temperate lake located on the eastern route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Qin, J.; He, X.H.; Zho, M.D. Eco-water diversion project is not a simply measure to improve the ecological environment. Glob. Nest J. 2022, 24, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Hou, S.; Yao, L.; Li, C. Integrated waste load allocation for river water pollution control under uncertainty: A case study of Tuojiang River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17741–17759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.F.; Li, T.X.; Liu, D.; Fu, Q.; Hou, R.J.; Li, Q.L.; Ji, Y.; Cui, S.; Li, M. How soil texture, channel shape and cross-sectional area affect moisture dynamics and water loss in irrigation channels. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, K.P.; Schultz, B.; Depeweg, H. Modelling of an irrigation scheme with sediment-laden water for improved water management: A Case Study of Sunsari Morang Irrigation Scheme, Nepal. Irrig. Drain. 2013, 62, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, F.A. Financing Irrigation Water Management and Infrastructure: A Review. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2010, 26, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
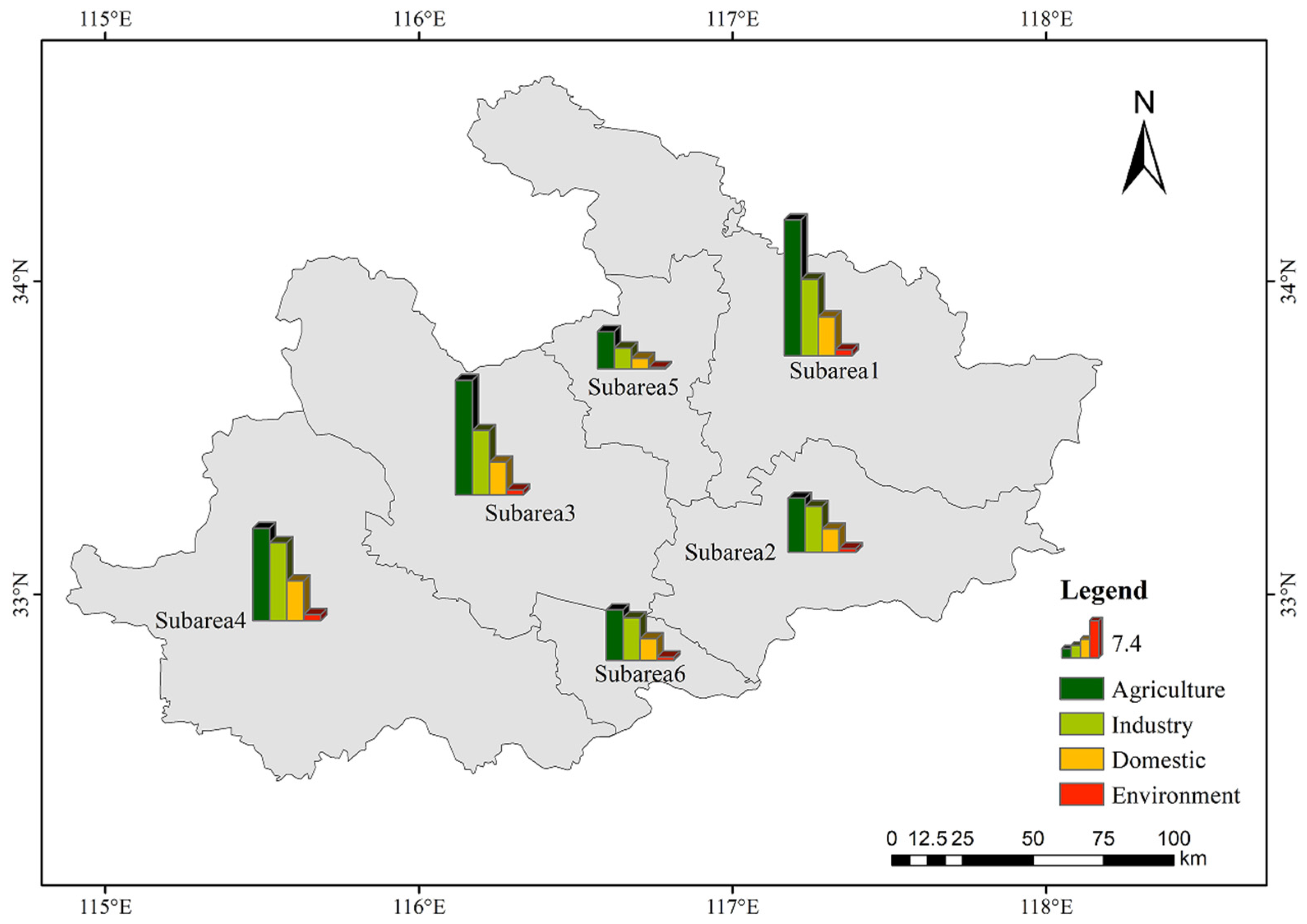
| Area (103 km2) | Population (106) | GDP (109 CNY) | IVA (109 CNY) | AVA (109 CNY) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subarea1 | 9.9 | 5.3 | 229.1 | 50.0 | 40.1 |
| Subarea2 | 5.3 | 3.2 | 211.6 | 54.8 | 29.1 |
| Subarea3 | 8.4 | 4.9 | 221.6 | 56.1 | 29.7 |
| Subarea4 | 9.8 | 8.1 | 332.4 | 94.5 | 48.6 |
| Subarea5 | 2.7 | 1.9 | 136.6 | 53.0 | 9.3 |
| Subarea6 | 1.6 | 3.0 | 160.1 | 57.8 | 15.7 |
| Total | 37.6 | 26.4 | 1291.4 | 366.1 | 172.5 |
| The Year of 2030 | The Year of 2040 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Year | Normal Year | Wet Year | Dry Year | Normal Year | Wet Year | |
| Subarea1 | [6.09, 9.13] | [4.46, 6.68] | [2.54, 3.80] | [6.58, 9.86] | [5.05, 7.57] | [3.15, 4.73] |
| Subarea2 | [3.65, 5.47] | [2.67, 4.00] | [1.52, 2.28] | [3.94, 5.90] | [3.02, 4.54] | [1.89, 2.83] |
| Subarea3 | [5.13, 7.69] | [3.75, 5.63] | [2.14, 3.20] | [5.54, 8.30] | [4.26, 6.38] | [2.66, 3.98] |
| Subarea4 | [6.20, 9.30] | [4.54, 6.80] | [2.58, 3.88] | [6.69, 10.03] | [5.14, 7.70] | [3.22, 4.82] |
| Subarea5 | [1.68, 2.52] | [1.23, 1.85] | [0.70, 1.06] | [1.82, 2.72] | [1.39, 2.09] | [0.87, 1.31] |
| Subarea6 | [3.39, 5.09] | [2.48, 3.72] | [1.42, 2.12] | [3.66, 5.48] | [2.81, 4.21] | [1.76, 2.64] |
| Depth (m) | Water Deficit (×108 m3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Year | Normal Year | Wet Year | |
| 2 | 29.40 | 21.43 | 11.93 |
| 4 | 0.66 | 0 | 0 |
| Available Surface Water | Available Groundwater | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry year | Subarea1 | [2.38, 2.86] | [1.17, 1.41] |
| (h = 1) | Subarea2 | [7.28, 8.72] | [3.59, 4.3] |
| Subarea3 | [8.64, 10.35] | [4.26, 5.1] | |
| Subarea4 | [4.61, 5.52] | [2.27, 2.72] | |
| Subarea5 | [8.5, 10.19] | [4.19, 5.02] | |
| Subarea6 | [1.36, 1.62] | [0.67, 0.8] | |
| Normal year | Subarea1 | [3.01, 3.74] | [1.48, 1.84] |
| (h = 2) | Subarea2 | [9.19, 11.43] | [4.53, 5.63] |
| Subarea3 | [10.9, 13.57] | [5.37, 6.68] | |
| Subarea4 | [5.81, 7.23] | [2.86, 3.56] | |
| Subarea5 | [10.73, 13.35] | [5.28, 6.57] | |
| Subarea6 | [1.71, 2.13] | [0.84, 1.05] | |
| Wet year | Subarea1 | [3.89, 5.03] | [1.92, 2.48] |
| (h = 3) | Subarea2 | [11.89, 15.36] | [5.86, 7.57] |
| Subarea3 | [14.11, 18.24] | [6.95, 8.98] | |
| Subarea4 | [7.52, 9.72] | [3.71, 4.79] | |
| Subarea5 | [13.88, 17.94] | [6.84, 8.83] | |
| Subarea6 | [2.21, 2.86] | [1.09, 1.41] |
| Period | Sub-Irrigation Area | Agriculture | Industry | Domestic | Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2030 | Subarea1 | [9.81, 14.71] | [5.52, 8.28] | [2.82, 4.22] | [0.43, 0.65] |
| Subarea2 | [5.87, 8.81] | [3.30, 4.96] | [1.69, 2.53] | [0.26, 0.40] | |
| Subarea3 | [8.26, 12.40] | [4.65, 6.97] | [2.38, 3.56] | [0.37, 0.55] | |
| Subarea4 | [9.98, 14.98] | [5.62, 8.42] | [2.86, 4.30] | [0.44, 0.66] | |
| Subarea5 | [2.70, 4.06] | [1.52, 2.28] | [0.78, 1.16] | [0.12, 0.18] | |
| Subarea6 | [5.46, 8.20] | [3.07, 4.61] | [1.57, 2.35] | [0.24, 0.36] | |
| 2040 | Subarea1 | [9.81, 14.71] | [6.06, 9.08] | [3.30, 4.96] | [0.50, 0.76] |
| Subarea2 | [5.87, 8.81] | [3.62, 5.44] | [1.98, 2.96] | [0.30, 0.46] | |
| Subarea3 | [8.26, 12.40] | [5.10, 7.64] | [2.78, 4.18] | [0.42, 0.64] | |
| Subarea4 | [9.98, 14.98] | [6.16, 9.24] | [3.36, 5.04] | [0.51, 0.77] | |
| Subarea5 | [2.70, 4.06] | [3.62, 5.44] | [0.91, 1.37] | [0.14, 0.20] | |
| Subarea6 | [5.46, 8.20] | [3.37, 5.05] | [1.84, 2.76] | [0.28, 0.42] |
| Period | Subarea | Coefficient | Agriculture (i = 1) | Industry (i = 2) | Domestic (i = 3) | Environment (i = 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2030 | j = 1 | [58.98, 88.46] | [236.78, 355.18] | [416.89, 625.33] | [98.61, 147.91] | |
| [94.36, 141.54] | [378.86, 568.28] | [667.02, 1000.54] | [157.78, 236.66] | |||
| j = 2 | [22.72, 34.08] | [316.22, 474.32] | [676.85, 1015.27] | [60.26, 90.40] | ||
| [36.35, 54.53] | [505.94, 758.92] | [1082.96, 1624.44] | [96.42, 144.64] | |||
| j = 3 | [34.58, 51.88] | [230.31, 345.47] | [467.70, 701.56] | [84.02, 126.02] | ||
| [55.34, 83.00] | [368.5, 552.74] | [748.33, 1122.49] | [134.42, 201.64] | |||
| j = 4 | [29.48, 44.22] | [262.41, 393.61] | [553.16, 829.74] | [100.44, 150.66] | ||
| [47.17, 70.75] | [419.86, 629.78] | [885.06, 1327.58] | [160.70, 241.06] | |||
| j = 5 | [39.63, 59.45] | [283.47, 425.21] | [815.68, 1223.52] | [27.37, 41.05] | ||
| [63.41, 95.11] | [453.55, 680.33] | [1305.09, 1957.63] | [43.79, 65.69] | |||
| j = 6 | [9.82, 14.74] | [61.26, 91.88] | [464.94, 697.42] | [54.82, 82.22] | ||
| [15.72, 23.58] | [98.00, 147.01] | [743.91, 1115.87] | [87.70, 131.56] | |||
| 2040 | j = 1 | [76.67, 115.00] | [307.82, 461.72] | [541.95, 812.93] | [128.19, 192.29] | |
| [122.67, 184.00] | [492.50, 738.76] | [867.12, 1300.68] | [205.10, 307.66] | |||
| j = 2 | [29.54, 44.30] | [411.08, 616.62] | [879.90, 1319.86] | [78.34, 117.52] | ||
| [47.26, 70.88] | [657.73, 986.59] | [1407.85, 2111.77] | [125.35, 188.03] | |||
| j = 3 | [44.96, 67.44] | [299.41, 449.11] | [608.02, 912.02] | [109.22, 163.84] | ||
| [71.94, 107.9] | [479.06, 718.58] | [972.82, 1459.24] | [174.76, 262.14] | |||
| j = 4 | [38.33, 57.49] | [341.13, 511.69] | [719.11, 1078.67] | [130.58, 195.86] | ||
| [61.33, 91.99] | [545.81, 818.71] | [1150.58, 1725.86] | [208.92, 313.38] | |||
| j = 5 | [51.52, 77.28] | [368.51, 552.77] | [1060.38, 1590.58] | [35.58, 53.36] | ||
| [82.43, 123.65] | [589.62, 884.42] | [1696.62, 2544.92] | [56.92, 85.38] | |||
| j = 6 | [12.77, 19.15] | [79.63, 119.45] | [604.42, 906.64] | [71.26, 106.9] | ||
| [20.43, 30.65] | [127.41, 191.11] | [967.08, 1450.62] | [114.03, 171.05] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Dai, S.; Tian, L.; Ni, Z.; Lu, S.; Yao, Y. Optimal Water Allocation Considering Water Diversion Projects in an Agricultural Irrigation District. Agriculture 2025, 15, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090949
Sun L, Dai S, Tian L, Ni Z, Lu S, Yao Y. Optimal Water Allocation Considering Water Diversion Projects in an Agricultural Irrigation District. Agriculture. 2025; 15(9):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090949
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Lian, Suyan Dai, Liuyan Tian, Zichen Ni, Siyuan Lu, and Youru Yao. 2025. "Optimal Water Allocation Considering Water Diversion Projects in an Agricultural Irrigation District" Agriculture 15, no. 9: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090949
APA StyleSun, L., Dai, S., Tian, L., Ni, Z., Lu, S., & Yao, Y. (2025). Optimal Water Allocation Considering Water Diversion Projects in an Agricultural Irrigation District. Agriculture, 15(9), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090949





