Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Promote Alfalfa Yield by Regulating Root Development, Osmoregulatory Substances and Improve Soil Physicochemical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Field Management
2.3. Sampling and Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
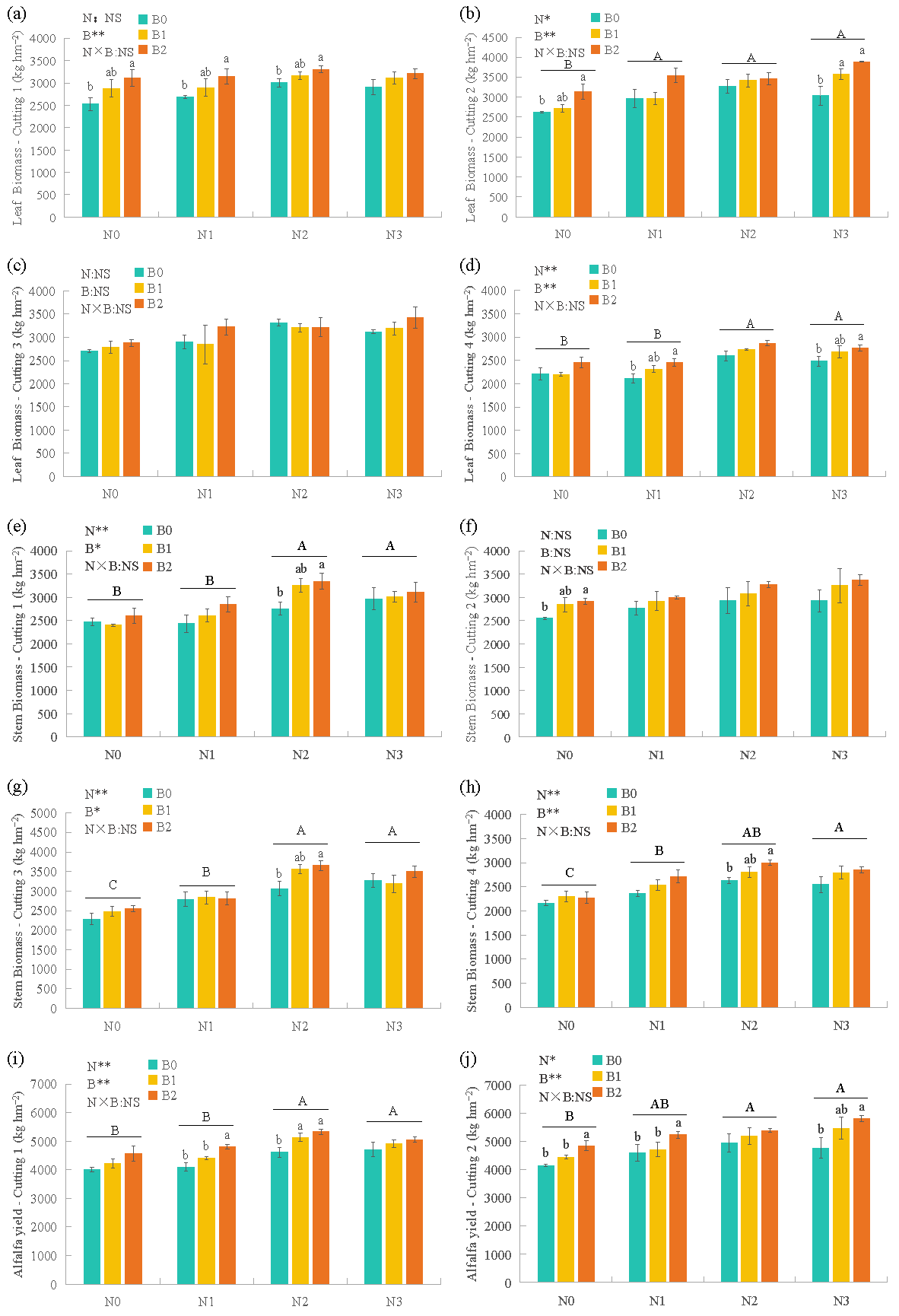
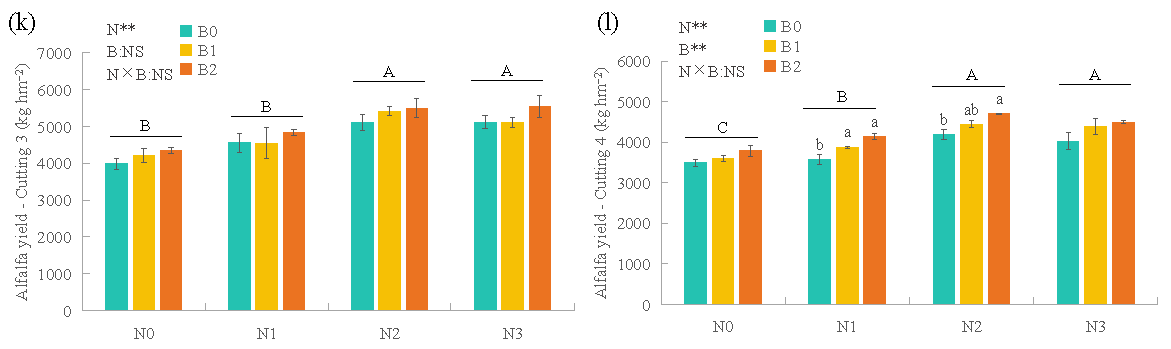
3.1. Alfalfa Yield and Allocation
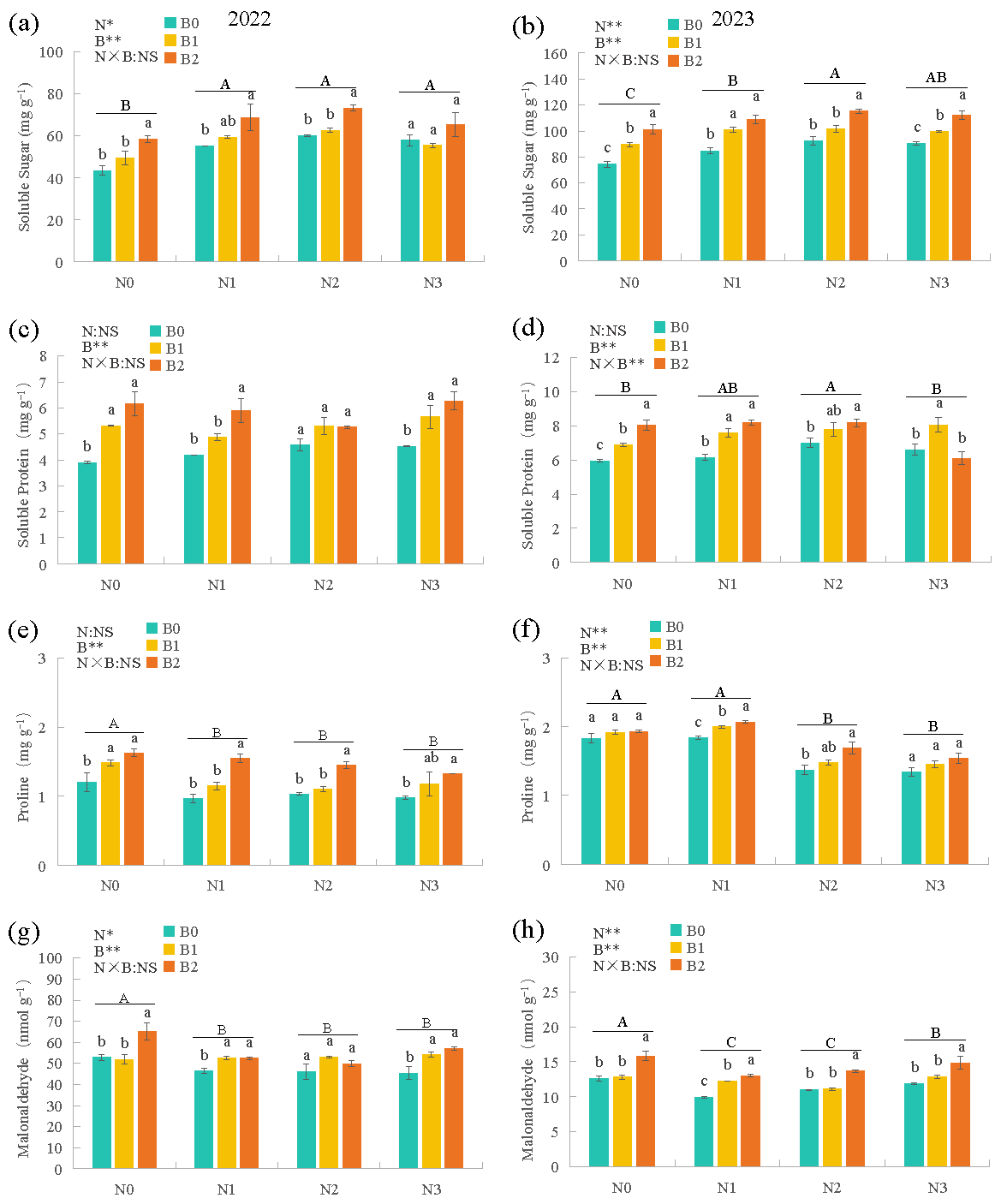
3.2. Alfalfa Quality
3.3. Root Traits
3.4. Root Osmoregulatory Substances
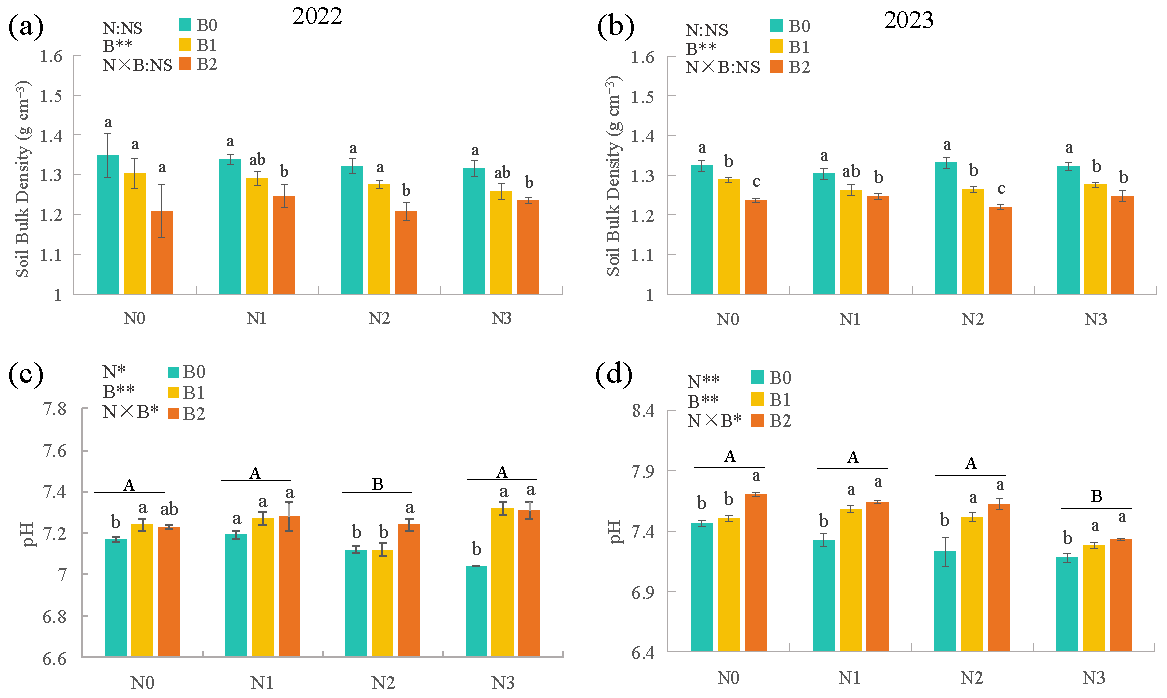
3.5. Soil Physicochemical Properties
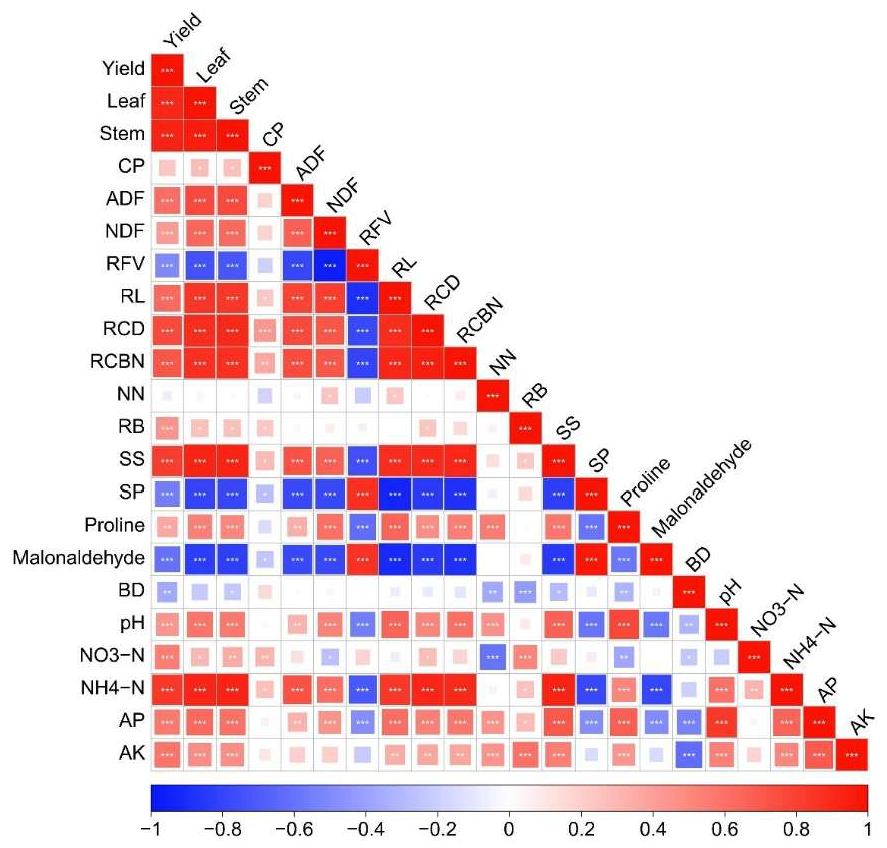
3.6. Correlation Among Yields, Alfalfa Quality, Root Traits, Root Osmoregulatory Substances, and Soil Physicochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Biochar and N on Root Morphology of Alfalfa
4.2. Effects of Biochar and N on Soil Physicochemical Properties
4.3. Effects of Biochar and N on Alfalfa Yield
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valin, H.; Havlík, P.; Mosnier, A.; Herrero, M.; Schmid, E.; Obersteiner, M. Agricultural productivity and greenhouse gas emissions: Trade-offs or synergies between mitigation and food security? Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 035019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cai, A.; Wu, D.; Liang, G.; Xiao, J.; Xu, M.; Colinet, G.; Zhang, W. Effects of biochar application on crop productivity, soil carbon sequestration, and global warming potential controlled by biochar C:N ratio and soil pH: A global meta-analysis. Soil. Till. Res. 2021, 213, 105125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. Achieving food security in China: Past three decades and beyond. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2010, 2, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Xing, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.F.; Dou, Z.X.; He, P.; Ju, X.T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y. The effects of biochar addition on soil physicochemical properties: A review. Catena 2021, 202, 105284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lewis, S.; Heal, K.V.; Lin, Q.; Sohi, S.P. Biochar engineering and ageing influence the spatiotemporal dynamics of soil pH in the charosphere. Geoderma 2021, 386, 114919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.S.; Vijay, V.K.; Chandra, R.; Kumar, H. Production and characterization of biochar produced from slow pyrolysis of pigeon pea stalk and bamboo. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 3, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, I.; Xu, C.-Y.; Wallace, H.M.; Joseph, S.; Pace, B.; Bai, S.H. Short-term dynamics of carbon and nitrogen using compost, compost-biochar mixture and organo-mineral biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11267–11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, F.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: An Introduction. Sci. Tec. 2009, 25, 15801–15811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, A.; Rengel, Z. Long-term biochar application promotes rice productivity by regulating root dynamic development and reducing nitrogen leaching. GCB Bioenergy 2020, 13, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayogo, C.; Jones, J.E.; Baeyens, J.; Bending, G.D. Impact of biochar on mineralisation of C and N from soil and willow litter and its relationship with microbial community biomass and structure. Biol. Fert. Soils 2013, 50, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Cowie, A.L.; Van Zwieten, L.; Bolan, N.; Budai, A.; Buss, W.; Cayuela, M.L.; Graber, E.R.; Ippolito, J.A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. How biochar works, and when it doesn’t: A review of mechanisms controlling soil and plant responses to biochar. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 1731–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Tong, C.; Hu, K.; Zhou, B.; Xing, S.; Mao, Y. Biochar-fertilizer interaction modifies N-sorption, enzyme activities and microbial functional abundance regulating nitrogen retention in rhizosphere soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaran, U.; Sandhu, S.S.; Qiu, Y.; Kumar, S.; Gonzalez Hernandez, J.L. Biochar and manure addition influenced soil microbial community structure and enzymatic activities at eroded and depositional landscape positions. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2019, 31, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast-Miller, M.T.; Duvall, M.; Sohi, S.P. Localisation of nitrate in the rhizosphere of biochar-amended soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Shi, F.; Zhang, B.; Li, K.; Chang, W.; Fan, X.; Dai, C.; Song, F. Rhizophagus irregularisand biochar can synergistically improve the physiological characteristics of saline-alkali resistance of switchgrass. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Duan, H.; Guo, Y. Effects of biochar application on root traits: A meta-analysis. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, L.A.; Harpole, W.S. Biochar and its effects on plant productivity and nutrient cycling: A meta-analysis. GCB Bioenergy 2012, 5, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, D.; Rondón, M.; Laossi, K.-R.; Hoyos, V.; Lavelle, P.; Cruz de Carvalho, M.H.; Barot, S. Contrasted effect of biochar and earthworms on rice growth and resource allocation in different soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yang, L.; Qin, H.; Jiang, L.; Zou, Y. Quantifying the effect of biochar amendment on soil quality and crop productivity in Chinese rice paddies. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 154, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Ali, A.; Umair, M.; Munsif, F.; Ayub, G. Effect of biochar, FYM and mineral nitrogen alone and in combination on yield and yield components of maize. Sarhad J. Agric. 2012, 28, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Improving China’s alfalfa industry development: An economic analysis. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2020, 13, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Jia, Z.; Wang, J. The analysis of current situation and development prospect of alfalfa industry at home and abroad. Pratacultural Sci. 2005, 22, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Y.; López, I.F.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Q. Optimizing nitrogen and phosphorus application to improve soil organic carbon and alfalfa hay yield in alfalfa fields. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1276580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanger, T.F.; Lauer, J.G. Corn Grain Yield Response to Crop Rotation and Nitrogen over 35 Years. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharably, A.; Benes, S. Alfalfa Biomass Yield and Nitrogen Fixation in Response to Applied Mineral Nitrogen Under Saline Soil Conditions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil. Sci. 2021, 21, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhuo, Y.; Guo, H.; Yan, H.; Yan, X. Responses of Alfalfa Growth and Nitrogen Utilization to Foliar Fertilization with Different Urea Concentrations. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 49, 5507–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Xing, G. Impacts of Pollution Growth and Economic Development on the Nitrogen Cycle in Asian. Sci. China Ser. C. 2006, 48, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Lu, C. Biochar combined with nitrogen fertilizer affects soil properties and wheat yield in medium-low-yield farmland. Soil Use Manag. 2021, 38, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Huang, F.; Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Plastic film mulching and biochar amendment enhance maize yield and nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency by reducing gaseous nitrogen losses. Field Crop. Res. 2022, 289, 108714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Chi, D.; Xia, G.; Arthur, E. Mulched drip irrigation and maize straw biochar increase peanut yield by regulating soil nitrogen, photosynthesis and root in arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaufmann, E.; Schmid, H.; Hülsbergen, K.-J. Effects of biochar in combination with cattle slurry and mineral nitrogen on crop yield and nitrogen use efficiency in a three-year field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 156, 127168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Sun, Q.; Ren, Z.; Xia, N.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, W. Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper. Open Life Sci. 2024, 19, 20220882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laird, D.; Fleming, P.; Wang, B.Q.; Horton, R.; Karlen, D. Biochar impact on nutrient leaching from a Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 2010, 158, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, V.; Hussain, N.; Husk, B.R.; Whalen, J.K. Biochar induced soil stability influences phosphorus retention in a temperate agricultural soil. Geoderma 2019, 351, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, P.; Ma, Z.; Chang, S. Biochar increase soil microbial biomass with changes in extra and intracellular enzyme activities: A global meta-analysis. Biochar 2020, 2, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, M.; Villar, R. Changes in root traits explain the variability of biochar effects on fruit production in eight agronomic species. Org. Agric. 2019, 9, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, D.; Shen, X.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Lan, T.; Wang, W.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y. Effects of biochar, compost and straw input on root exudation of maize (Zea mays L.): From function to morphology. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 297, 106952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, E.W.; Petersen, C.T.; Hansen, E.; Holm, J.K.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H. Biochar amendment to coarse sandy subsoil improves root growth and increases water retention. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.F.; Chen, D.X.; Zheng, Y.M.; Wang, C.B.; Sun, X.W.; Li, X.D.; Wang, X.X.; Shi, C.R.; Feng, H.; Yu, T.Y. Supply characteristics of different nitrogen sources and nitrogen use efficiency of peanut. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2016, 38, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Etesami, H. Bacterial mediated alleviation of heavy metal stress and decreased accumulation of metals in plant tissues: Mecha nisms and future prospects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, M.; Monaco, T.; Wang, D. Soil extracellular enzyme activities and the abundance of nitrogen-cycling functional genes responded more to N addition than P addition in an Inner Mongolian meadow steppe. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 759, 143541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmanov, R.Z.; Babaeva, M.A.; Osipova, S.V. Influence of salted environment on fodder herbs efficiency of pasturable phytocoenoses of the north-western Caspian lowland. South Russ.-Ecol. Dev. 2013, 4, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z. Feed Analysis and Feed Quality Testing Technology; China Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 23–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.X.; Liu, X.J.; Hao, F.; Fan, J.J.; Feng, B.Z.; Qi, P. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus regulation on alfalfa nitrogen accumulation and the nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients of soil. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2016, 24, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Mu, L.; Xu, R.; Yang, H. Effect of regulated deficit irrigation on alfalfa performance under two irrigation systems in the inland arid area of midwestern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, M.; Yang, L.; Han, M. Platycodon grandiflorus subjected to full- and restricted-water regimes show differential biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2023, 45, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Yu, X.; Xu, C.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Pan, T. Effects of yak and Tibetan sheep trampling on soil properties in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 144, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Pinzon, P.A.; Prommer, J.; Sedlacek, C.J.; Sandén, T.; Spiegel, H.; Pjevac, P.; Fuchslueger, L.; Giguere, A.T. Inhibition profile of three biological nitrification inhibitors and their response to soil pH modification in two contrasting soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2024, 100, fiae072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Chen, C.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, G. Response of Soil Fungal Community in Coastal Saline Soil to Short-Term Water Management Combined with Bio-Organic Fertilizer. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; He, B.; Dong, B.; Zhang, G. Film mulched ridge–furrow tillage improves the quality and fertility of dryland agricultural soil by enhancing soil organic carbon and nutrient stratification. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 292, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zheng, G.; Tao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chu, G.; Xu, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Effect of Soil Texture on Soil Nutrient Status and Rice Nutrient Absorption in Paddy Soils. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Yi, Q.; Liang, B.; Xu, J.; Wu, W. Biochar drives microbially-mediated rice production by increasing soil carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Cabrera, J.; Leon, R.G.; Erickson, J.E.; Silveira, M.L.; Rowland, D.L.; Morgan, K.T. Biochar Changes Shoot Growth and Root Distribution of Soybean during Early Vegetative Stages. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Kong, L.; Xie, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Ao, X. Effects of biochar on seedling root growth of soybeans. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 78, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, W.; Xiu, L.; Sun, Y.; Gu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Soybean Yield Response of Biochar-Regulated Soil Properties and Root Growth Strategy. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Liu, R.; Kuang, X.; Chen, H.; Tian, J.; Cai, C. Nitrogen fertilizer reduction combined with biochar application maintain the yield and nitrogen supply of rice but improve the nitrogen use efficiency. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorter, H.; Niklas, K.J.; Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J.; Poot, P.; Mommer, L. Biomass allocation to leaves, stems and roots: Meta-analyses of interspecific variation and environmental control. New Phytol. 2011, 193, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ci, D.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xu, M.; He, K. Effect of Reducing Nitrogen Fertilization and Adding Organic Fertilizer on Net Photosynthetic Rate, Root Nodules and Yield in Peanut. Plants 2023, 12, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.M.; Wang, C.X.; Liu, Q.M.; Wu, Z.F.; Wang, C.B.; Sun, X.S.; Zheng, Y.P. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer regulation on root growth and nodulating ability of peanut. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2017, 31, 2418–2425. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Xu, F.X.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.C.; Guo, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Ming, J. Effect of reduced nitrogen application on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of hybrid mid-season rice under two yield levels. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2020, 1, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.M.; Sun, X.S.; Wang, C.B.; Zheng, Y.P. Differences in nitrogen utilization characteristics of different peanut genotypes in high fertility soils. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3977–3986. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.F.; Han, X.Z. Effects of long-term fertilization on root phenotype and nodulation of soybean. Soybean Sci. 2011, 30, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.E. Study on the Rules of Alfalfa Crown Bud Developing into Shoot and Its Winter Hardiness in the State of Dormancy. Ph.D. Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Phares, C.; Amoakwah, E.; Danquah, A.; Akaba, S.; Frimpong, K.; Mensah, T. Improved soil physicochemical, biological properties and net income following the application of inorganic NPK fertilizer and biochar for maize production. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 42, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammal, A.; Seutra, K.; Evans, D.; Adutwum, A. A comprehensive review of the effects of biochar on soil physicochemical properties and crop productivity. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2022, 4, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lin, X.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Fan, S. Interactions between flue gas desulfurization gypsum and biochar on water infiltration characteristics and physicochemical properties of saline-alkaline soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra-Mendoza, K.; Horn, R. Effect of biochar addition on hydraulic functions of two textural soils. Geoderma 2018, 326, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Singh, A.; Khare, P.; Chanda, D.; Mishra, D.; Shanker, K.; Karak, T. Toxicity assessment of Bacopa monnieri L. grown in biochar amended extremely acidic coal mine spoils. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, A.; Jiménez, E.M.; Puschenreiter, M.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Switzer, C. Effects of biochar amendment on root traits and contaminant availability of maize plants in a copper and arsenic impacted soil. Plant Soil. 2014, 379, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Tiwari, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, J.S. The effect of rice husk biochar on soil nutrient status, microbial biomass and paddy productivity of nutrient poor agriculture soils. Catena 2018, 171, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abujabhah, I.S.; Bound, S.A.; Doyle, R.; Bowman, J.P. Effects of biochar and compost amendments on soil physico-chemical properties and the total community within a temperate agricultural soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 98, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatav, H.; Jayant, H.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, V.; Chattopadhya, A.; Dhawal, S.; Singh, Y. Role of Biochar: In agriculture sector its implication and perspective. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2017, 5, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, M.R.; Bakker, C.; Motior, M.R. Evaluation of wood biochar and compost soil amendment on cabbage yield and quality. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2019, 99, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, T.; Condron, L.; Kammann, C.; Müller, C. A review of biochar and soil nitrogen dynamics. Agronomy 2013, 3, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uroić Štefanko, A.; Leszczynska, D. Impact of Biomass Source and Pyrolysis Parameters on Physicochemical Properties of Biochar Manufactured for Innovative Applications. Front. Energy. Res. 2020, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, É.M.G.; Reis, M.M.; Frazão, L.A.; da Mata Terra, L.E.; Lopes, E.F.; dos Santos, M.M.; Fernandes, L.A. Biochar increases enzyme activity and total microbial quality of soil grown with sugarcane. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Fan, M.; Wu, Y.; Shangguan, Z. Interactions between biochar and nitrogen impact soil carbon mineralization and the microbial community. Soil. Till. Res. 2020, 196, 104437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.J.; Duprè, C.; Dorland, E. The impact of nitrogen deposition on acid grasslands in the Atlantic region of Europe. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agegnehu, G.; Nelson, P.N.; Bird, M.I. Crop yield, plant nutrient uptake and soil physicochemical properties under organic soil amendments and nitrogen fertilization on Nitisols. Soil. Till. Res. 2016, 160, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Wu, L.; Ding, X. Combined organic amendments and mineral fertilizer application increase rice yield by improving soil structure, P availability and root growth in saline-alkaline soil. Soil Till. Res. 2021, 212, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


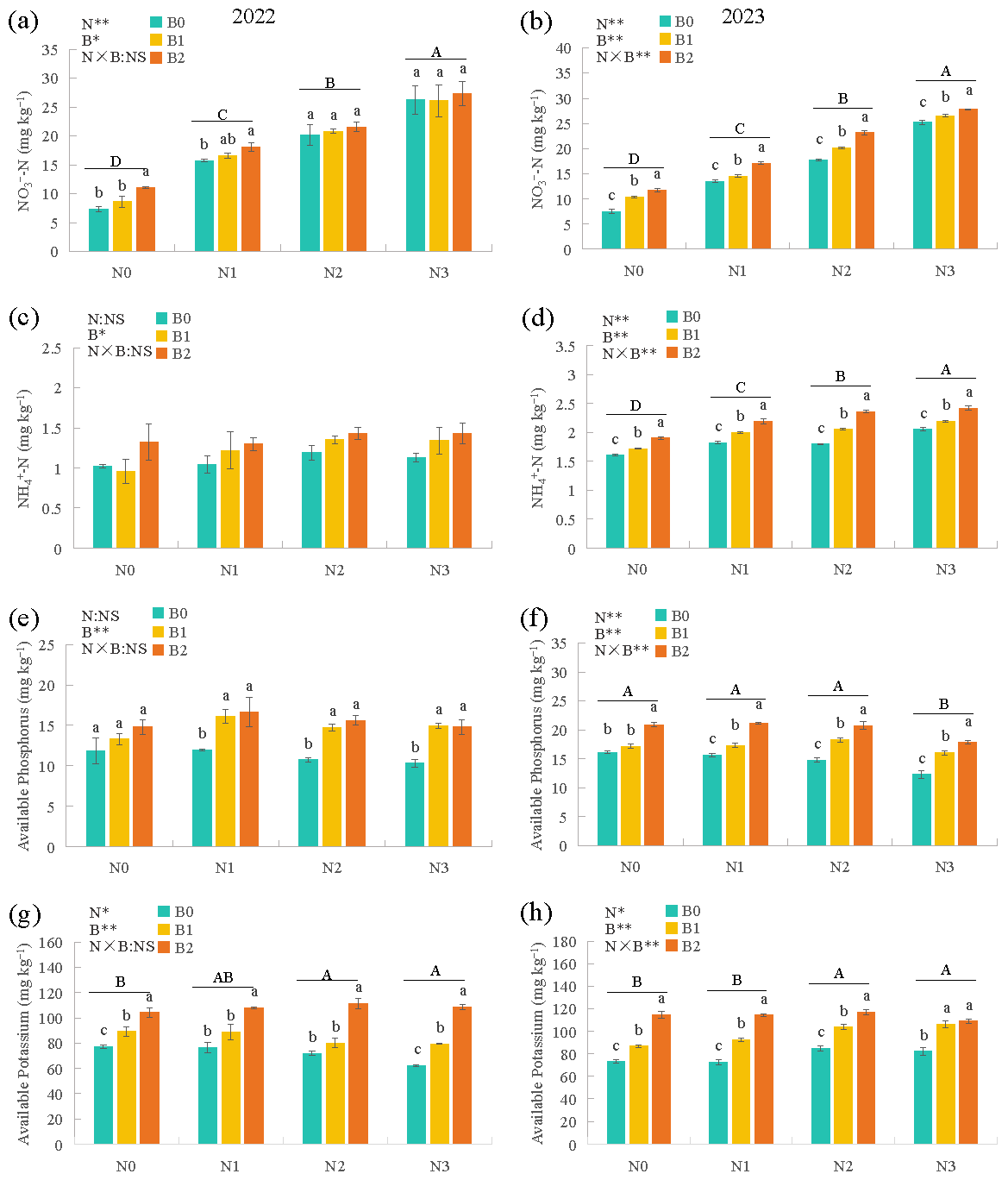
| Year | Treatments | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | B0 | 22.7 ± 0.3 Aab | 23.3 ± 0.3 Aa | 21.7 ± 0.3 Ab | 22.0 ± 0.6 Aab |
| B1 | 21.7 ± 0.3 ABa | 22.0 ± 0.1 Aa | 21.7 ± 0.3 Aa | 21.3 ± 0.7 Aa | |
| B2 | 20.7 ± 0.3 Ba | 22.0 ± 0.6 Aa | 20.7 ± 0.3 Aa | 22.0 ± 0.6 Aa | |
| N * | B ** | N × B ** | |||
| 2023 | B0 | 20.3 ± 0.3 Ac | 21.7 ± 0.3 Bb | 23.0 ± 0.1 Aa | 23.0 ± 0.1 Aa |
| B1 | 21.0 ± 0.6 Ab | 21.7 ± 0.3 Bab | 22.7 ± 0.3 Aa | 22.7 ± 0.3 Aa | |
| B2 | 21.3 ± 0.7 Ab | 23.0 ± 0.1 Aa | 23.0 ± 0.1 Aa | 23.0 ± 0.1 Aa | |
| N ** | B ** | N × B:NS |
| Year | Treatments | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | B0 | 23.0 ± 0.1 Aa | 23.3 ± 0.3 Aa | 23.7 ± 0.3 Aa | 23.3 ± 0.3 Aa |
| B1 | 23.3 ± 0.3 Aa | 23.0 ± 0.1 Aa | 22.7 ± 0.3 Aab | 22.0 ± 0.1 Bb | |
| B2 | 23.7 ± 0.3 Aa | 22.7 ± 0.9 Aa | 23.7 ± 0.9 Aa | 22.7 ± 0.3 ABa | |
| N:NS | B:NS | N × B:NS | |||
| 2023 | B0 | 26.0 ± 0.6 Aa | 25.7 ± 0.3 Aa | 26.0 ± 0.1 Aa | 26.3 ± 0.7 Aa |
| B1 | 25.0 ± 0.1 Ab | 24.7 ± 0.9 Ab | 26.0 ± 0.6 Aab | 27.3 ± 0.3 Aa | |
| B2 | 24.7 ± 0.3 Ab | 24.3 ± 0.7 Ab | 26.3 ± 0.3 Aa | 27.0 ± 0.6 Aa | |
| N ** | B:NS | N × B:NS |
| Year | Treatments | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | B0 | 37.3 ± 0.7 Aab | 38.0 ± 0.6 Aa | 35.7 ± 0.9 Ab | 36.0 ± 0.1 Aab |
| B1 | 38.0 ± 0.6 Aa | 37.0 ± 0.6 Aa | 34.7 ± 0.7 Aa | 35.3 ± 1.8 Aa | |
| B2 | 39.0 ± 0.6 Aa | 38.1 ± 0.6 Aab | 36.0 ± 0.6 Ab | 35.2 ± 0.2 Ac | |
| N * | B:NS | N × B:NS | |||
| 2023 | B0 | 40.1 ± 0.1 Ab | 43.0 ± 0.6 Aa | 42.3 ± 0.3 Aa | 40.3 ± 0.7 Ab |
| B1 | 39.8 ± 0.1 Ab | 42.7 ± 0.3 Aa | 43.0 ± 0.6 Aa | 40.1 ± 0.6 Ab | |
| B2 | 40.7 ± 0.3 Aa | 40.3 ± 0.9 Ba | 40.0 ± 0.6 Ba | 39.3 ± 0.7 Aa | |
| N * | B ** | N × B * |
| Year | Treatments | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | B0 | 193.1 ± 3.1 Aa | 184.7 ± 6.3 Aa | 203.7 ± 8.7 Aa | 195.3 ± 2.3 Aa |
| B1 | 185.7 ± 3.5 ABa | 193.7 ± 6.1 Aa | 209.0 ± 3.1 Aa | 207.0 ± 11.9 Aa | |
| B2 | 178.7 ± 2.2 Bb | 189.3 ± 4.5 Ab | 192.0 ± 6.5 Ab | 207.1 ± 1.5 Aa | |
| N * | B:NS | N × B:NS | |||
| 2023 | B0 | 160.7 ± 1.3 Aa | 150.1 ± 2.6 Bb | 150.3 ± 0.3 Bb | 158.3 ± 3.8 Aa |
| B1 | 160.3 ± 0.3 Aab | 153.3 ± 1.8 ABbc | 148.7 ± 2.9 Bc | 161.3 ± 2.9 Aa | |
| B2 | 160.7 ± 1.5 Aa | 160.7 ± 2.3 Aa | 158.7 ± 2.4 Aa | 161.7 ± 2.9 Aa | |
| N * | B ** | N × B:NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Yu, X. Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Promote Alfalfa Yield by Regulating Root Development, Osmoregulatory Substances and Improve Soil Physicochemical Properties. Agriculture 2025, 15, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15030239
Chai J, Yang H, Chen Z, Li W, Li D, Yu X. Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Promote Alfalfa Yield by Regulating Root Development, Osmoregulatory Substances and Improve Soil Physicochemical Properties. Agriculture. 2025; 15(3):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15030239
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Jinlong, Hang Yang, Zhen Chen, Weifang Li, Dongqing Li, and Xiaojun Yu. 2025. "Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Promote Alfalfa Yield by Regulating Root Development, Osmoregulatory Substances and Improve Soil Physicochemical Properties" Agriculture 15, no. 3: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15030239
APA StyleChai, J., Yang, H., Chen, Z., Li, W., Li, D., & Yu, X. (2025). Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Promote Alfalfa Yield by Regulating Root Development, Osmoregulatory Substances and Improve Soil Physicochemical Properties. Agriculture, 15(3), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15030239





