Optimization Design of Agrivoltaic Systems Based on Light Environment Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Light Environment Monitoring
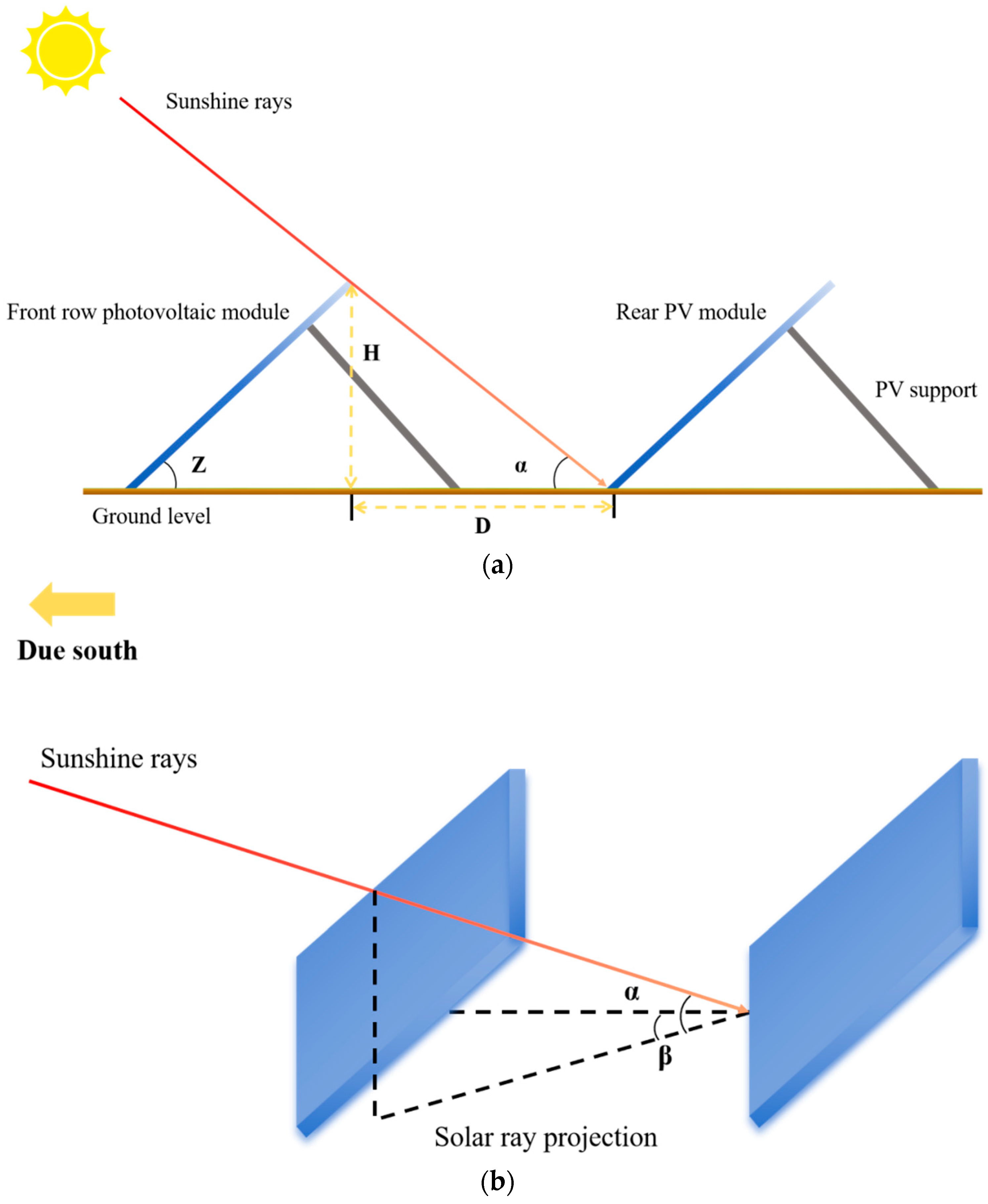
2.3. Three-Dimensional Model Construction
- is the local geographic latitude, 34.32°;
- δ is the solar declination angle, with a value of −23.5° on the winter solstice;
- ω is the solar hour angle, which is −45° at 9:00 a.m., 0° at solar noon, and increases by approximately 15° per hour (negative in the morning and positive in the afternoon);
- H represents the height difference between the highest point of the front-row PV module and the lowest point of the rear-row module, which varies with the installation tilt angle.
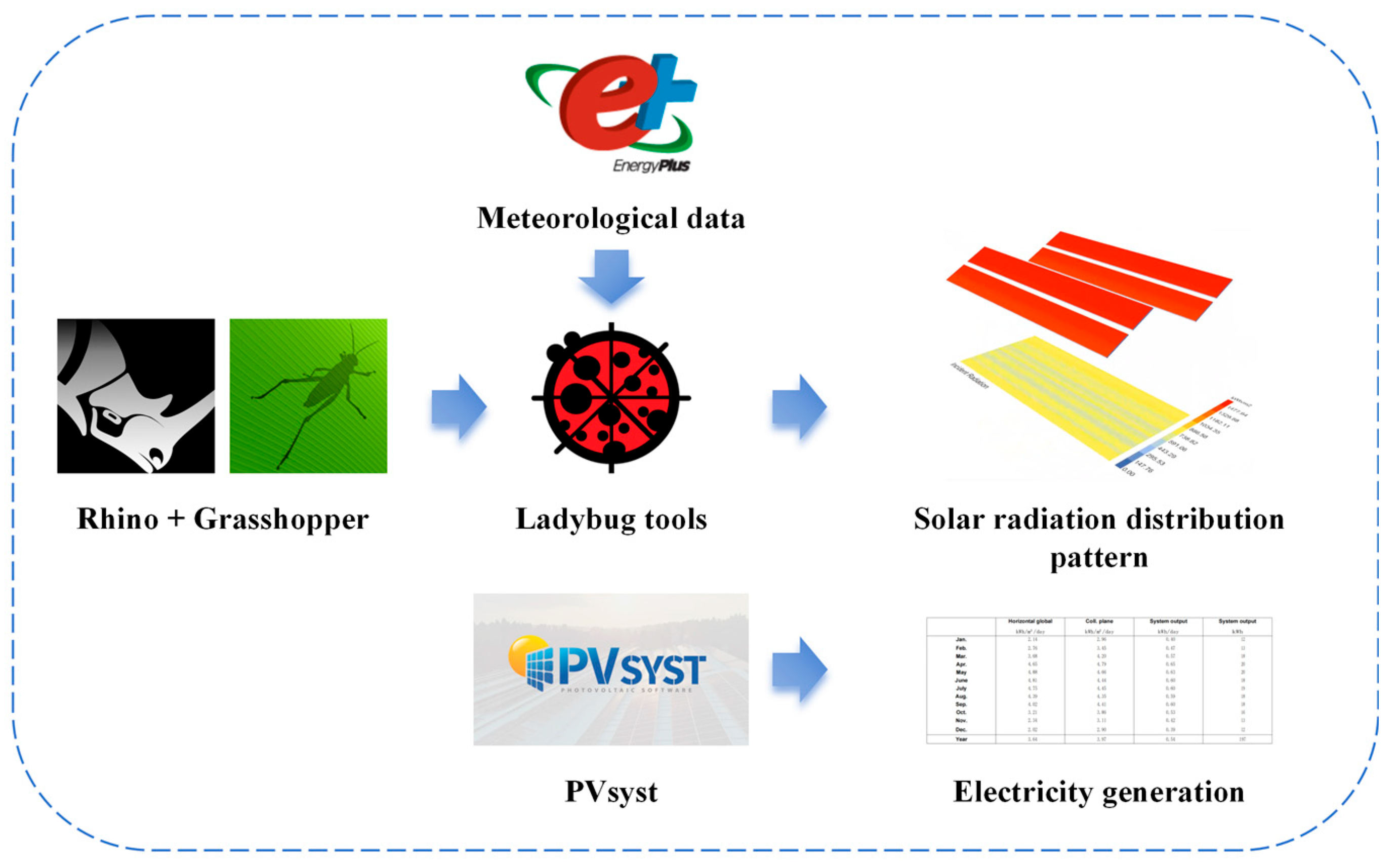
2.4. Light Environment Simulation Software
2.5. Meteorological Data and Simulation Grid Setup
2.6. Power Generation Simulation
2.7. Light Environment Evaluation Indicators
- μ is the mean value;
- σ is the standard deviation;
- n is the number of discretized grid cells within the calculation domain;
- represents the PAR at the i-th grid point (kWh·m−2);
- denotes the average PAR over all grid points (kWh·m−2).
3. Results
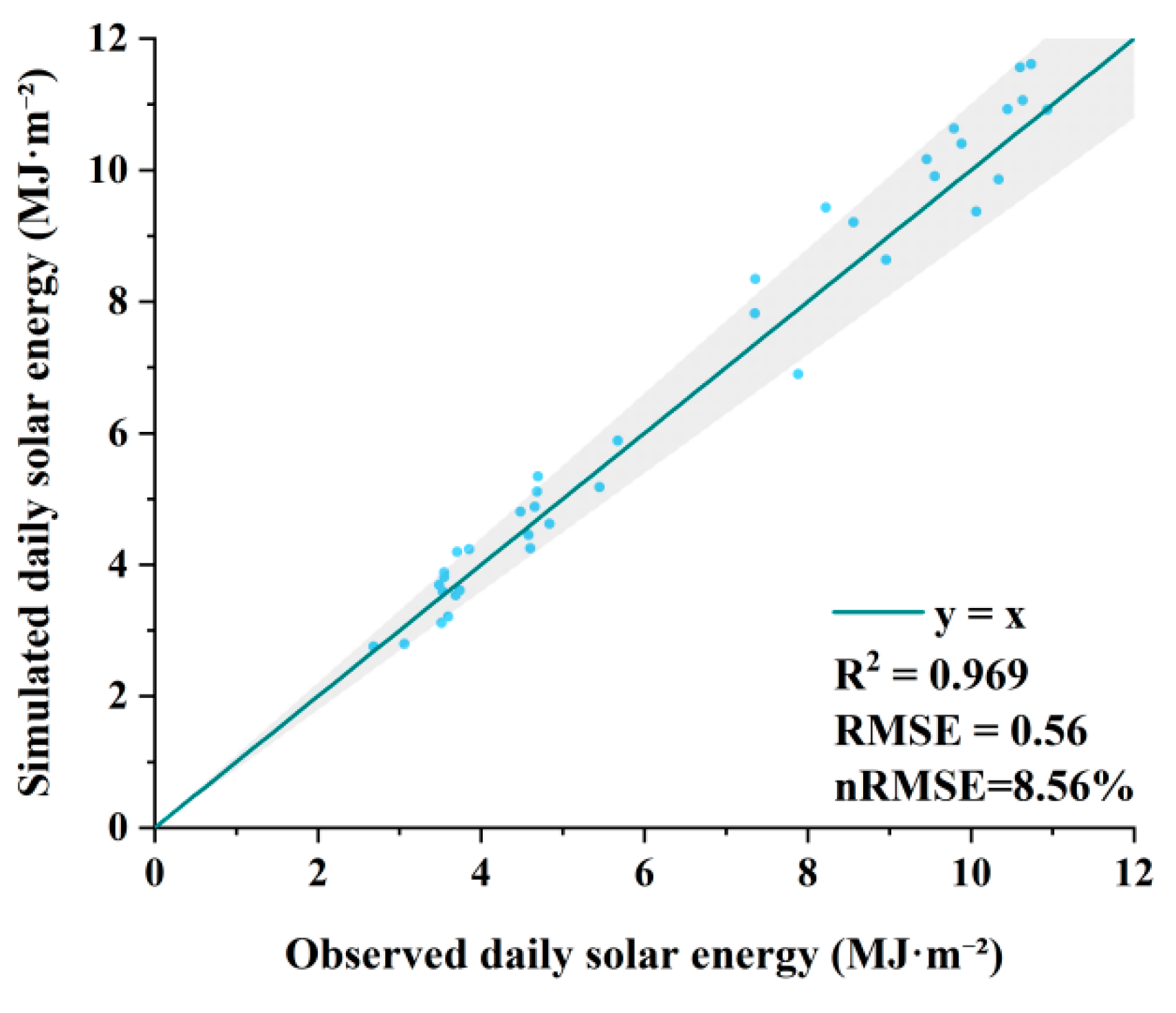
3.1. Model Validation
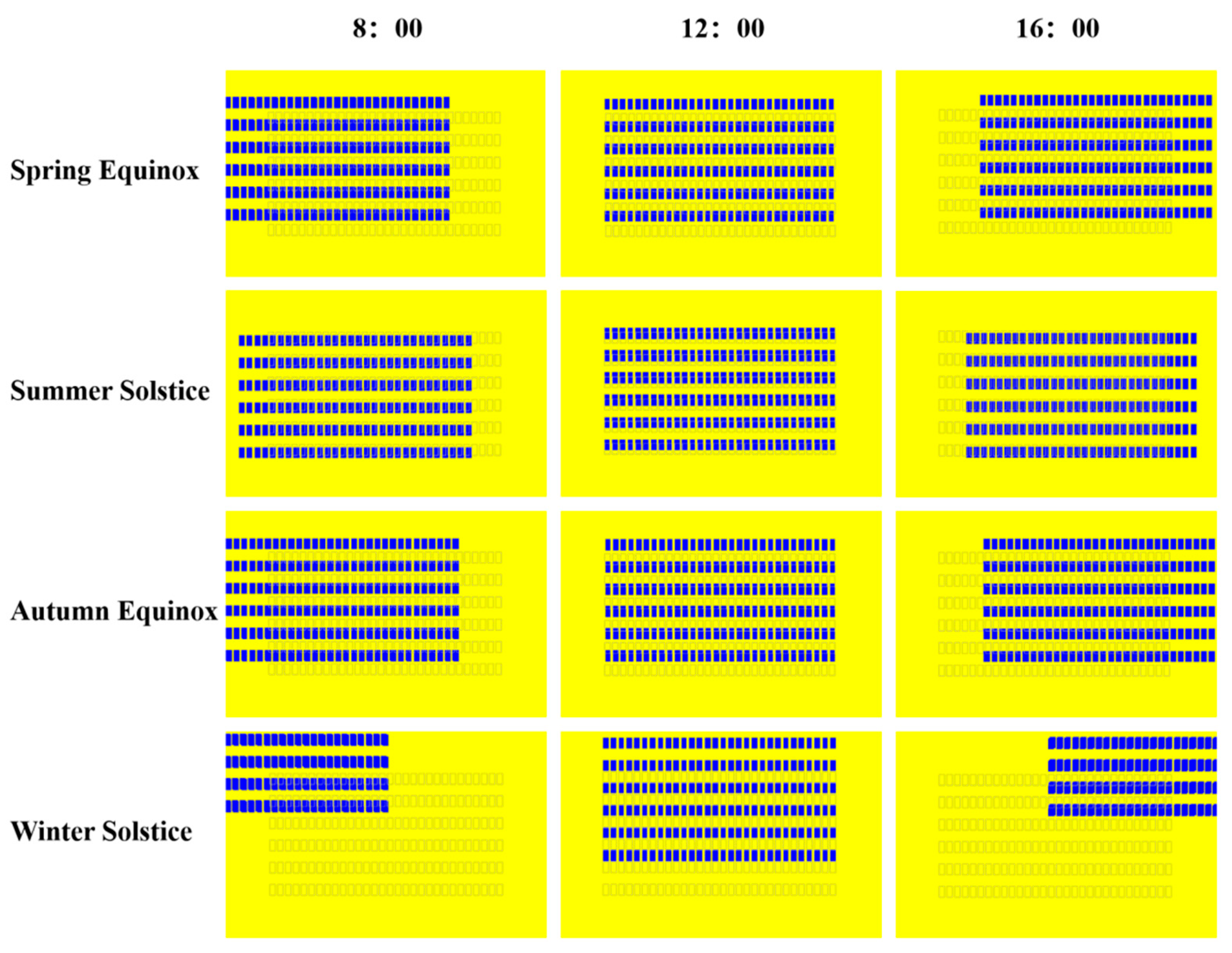
3.2. Typical Daily Solar Shadow Distribution
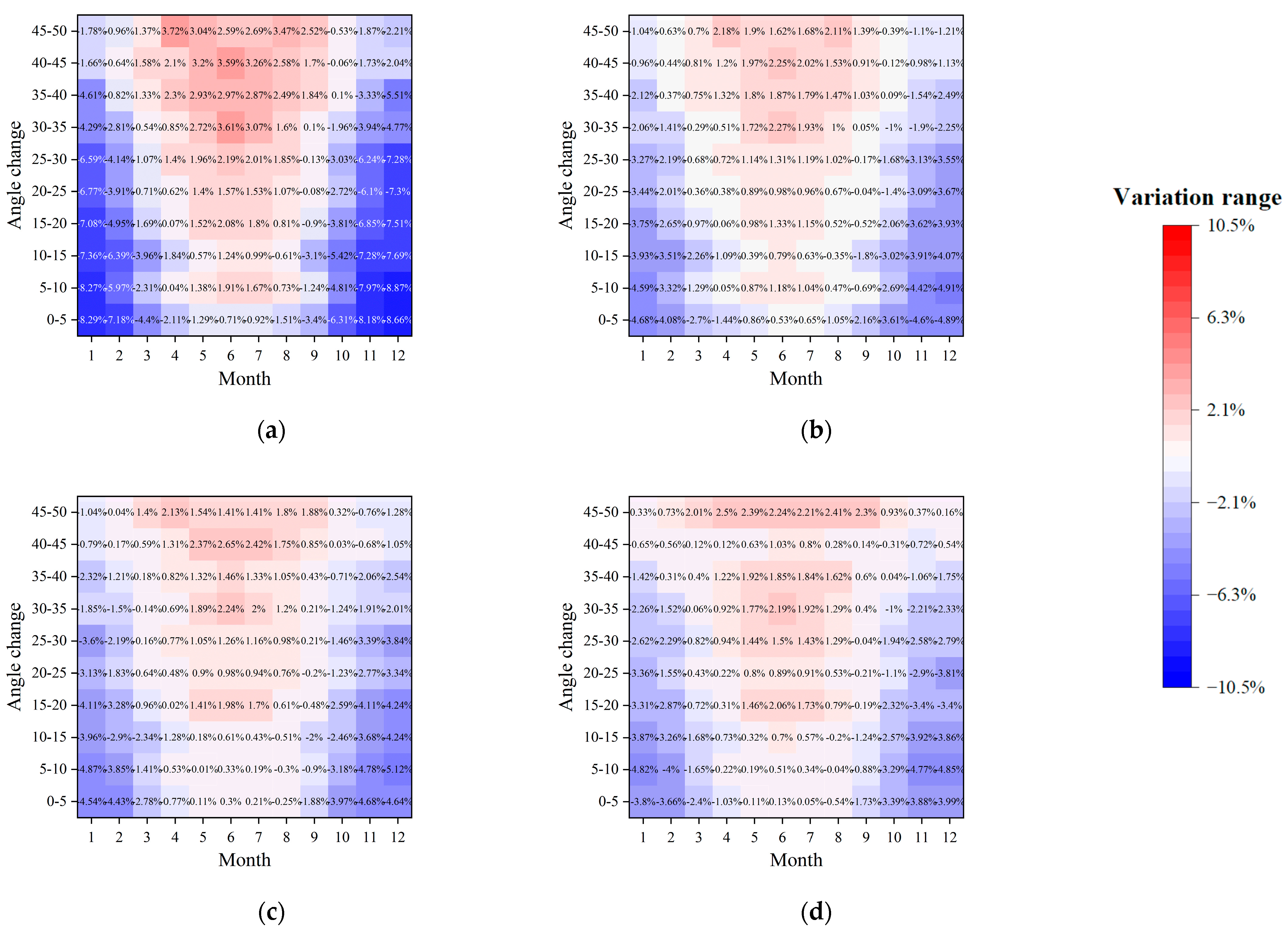
3.3. Impact of Tilt Angle Variation on Internal DLI Under Different Configurations
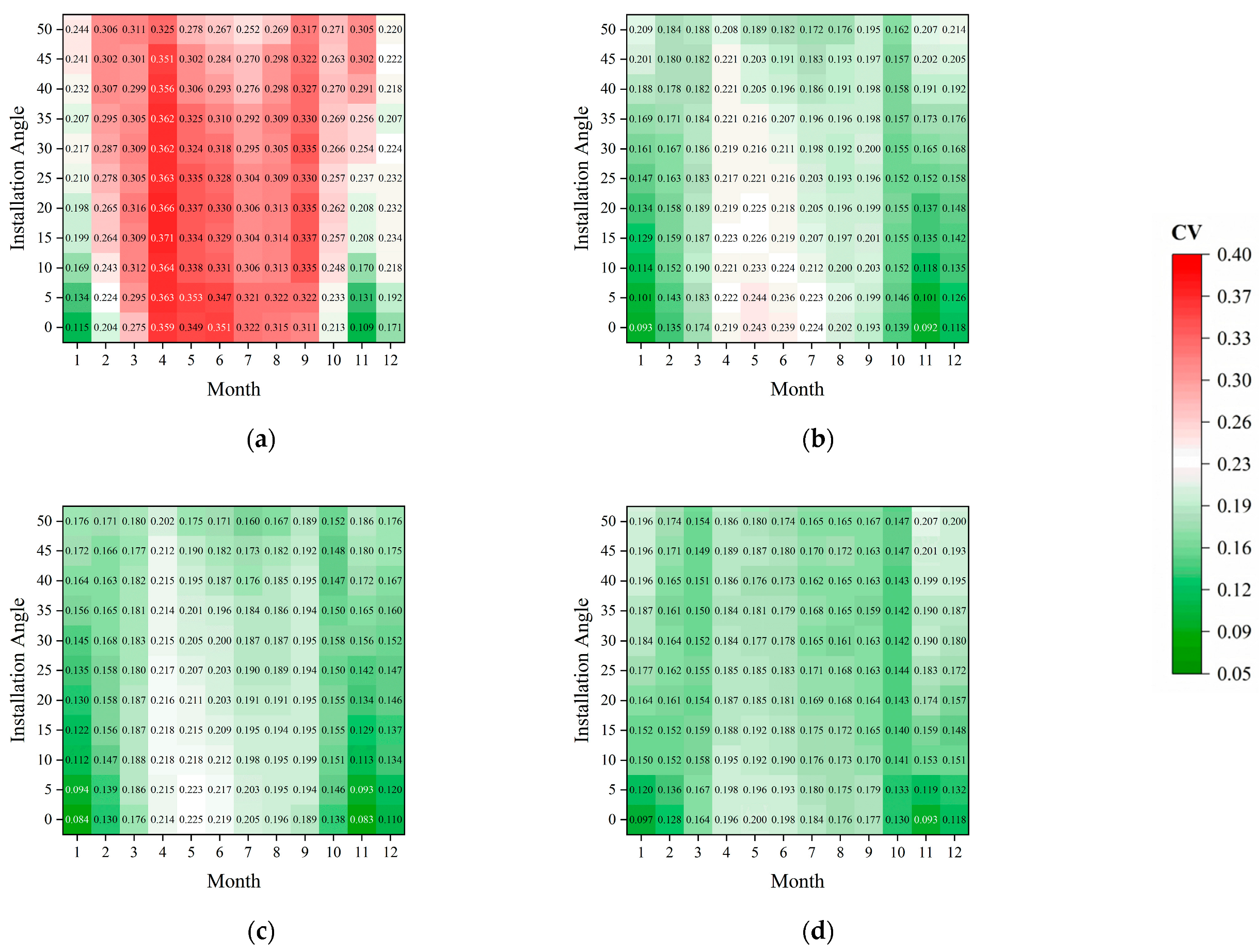
3.4. Impact of Tilt Angle Variation on Light Uniformity Under Different Configurations
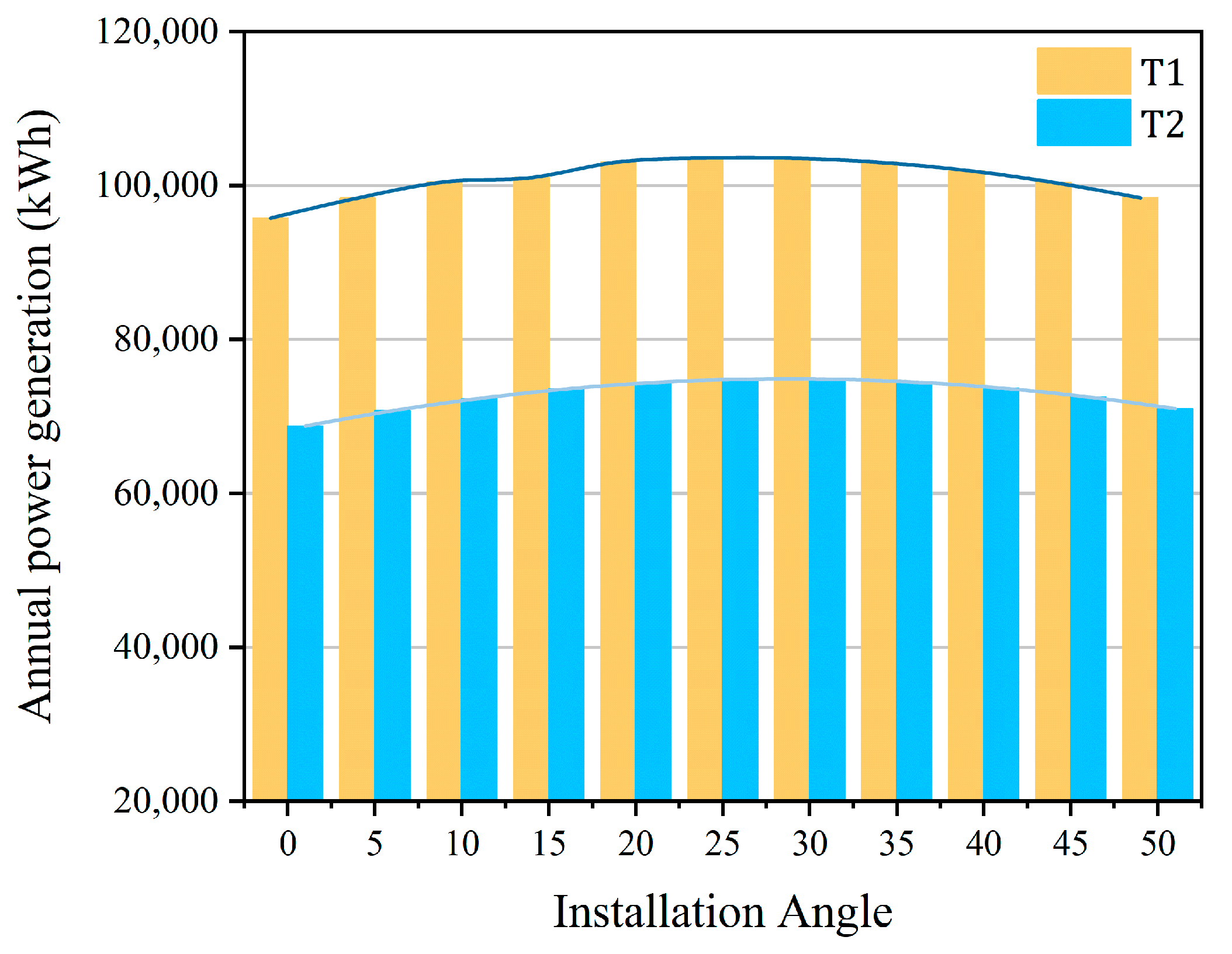
3.5. Annual Energy Yield of Different PV Module Layouts and Installation Tilt Angles
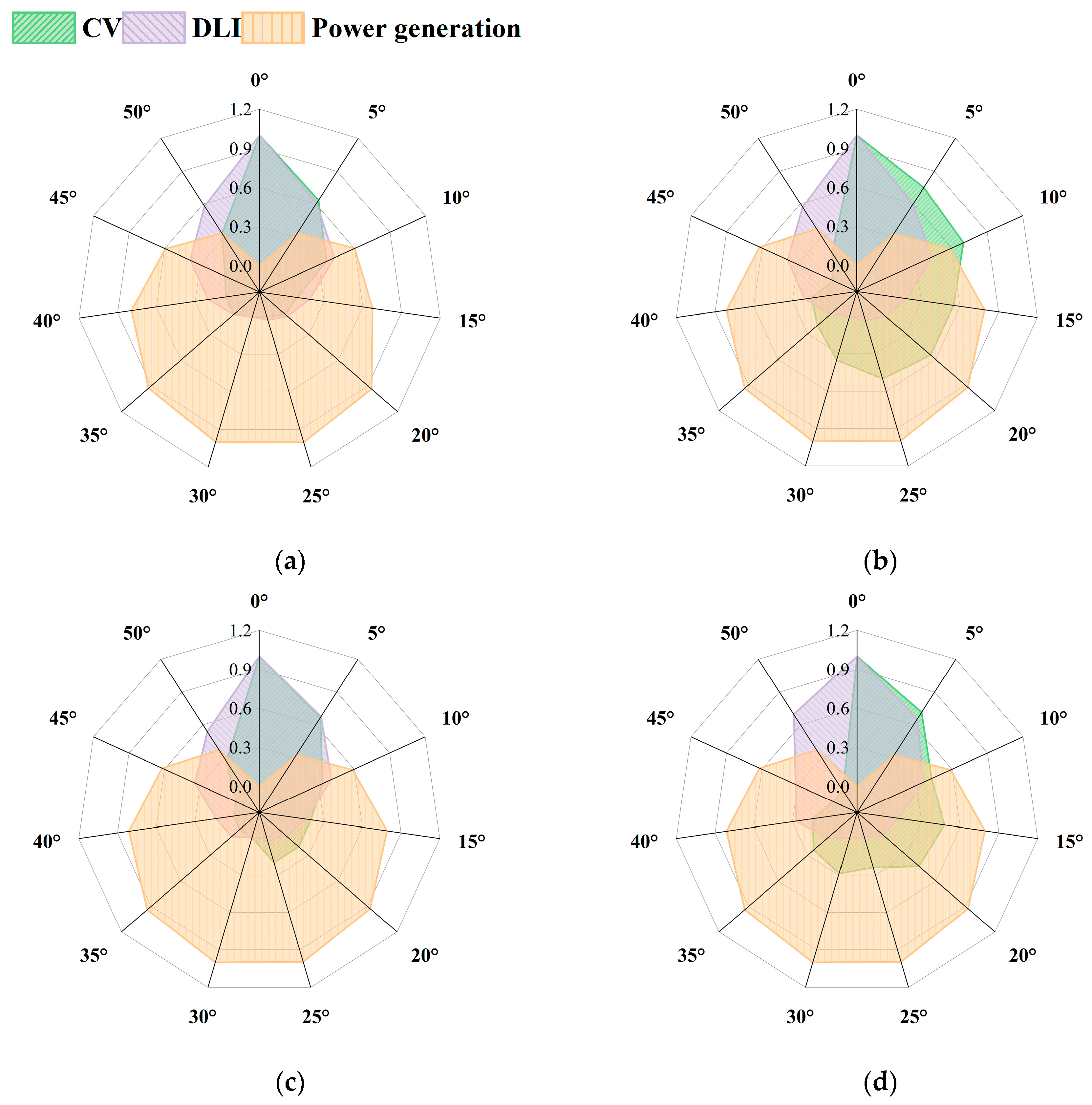
3.6. Comprehensive Evaluation of Light Environment and Power Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Structural Parameters on Seasonal Light Environment Distribution and the Agro-Energy Trade-Off
4.2. Reliability of the Simulation Framework and Its Potential for Regional Application
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emblemsvåg, J. Wind Energy Is Not Sustainable When Balanced by Fossil Energy. Appl. Energy 2022, 305, 117748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londoño-Pulgarin, D.; Cardona-Montoya, G.; Restrepo, J.C.; Muñoz-Leiva, F. Fossil or Bioenergy? Global Fuel Market Trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, A. Scaling up Renewables without Phasing down Fossil Fuels? Rethinking the Role of Financial Globalization. Energy Policy 2025, 204, 114654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renewables 2024—Analysis. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2024 (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- World Energy Outlook 2024—Analysis. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2024 (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Krozer, Y.; Bykuc, S.; Coenen, F. Growth of Renewable Energy: A Review of Drivers from the Economic Perspective. Energies 2025, 18, 5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H. Autonomous Decentralized Cooperative Control DC Microgrid Deployed in Residential Areas. Energies 2025, 18, 5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A. Nexus between Agriculture and Photovoltaics (Agrivoltaics, Agriphotovoltaics) for Sustainable Development Goal: A Review. Sol. Energy 2023, 266, 112146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edouard, S.; Combes, D.; Van Iseghem, M.; Tin, M.N.W.; Escobar-Gutiérrez, A.J. Increasing Land Productivity with Agriphotovoltaics: Application to an Alfalfa Field. Appl. Energy 2023, 329, 120207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junedi, M.M.; Ludin, N.A.; Hamid, N.H.; Kathleen, P.R.; Hasila, J.; Ahmad Affandi, N.A. Environmental and Economic Performance Assessment of Integrated Conventional Solar Photovoltaic and Agrophotovoltaic Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Omer, A.A.A.; Li, M. Agrivoltaic: Challenge and Progress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, H.; Pearce, J.M. The Potential of Agrivoltaic Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Park, S.M.; Park, A.R.; Lee, O.C.; Nam, G.; Ra, I.-H. Application of Photovoltaic Systems for Agriculture: A Study on the Relationship between Power Generation and Farming for the Improvement of Photovoltaic Applications in Agriculture. Energies 2020, 13, 4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelczar, S. An Overview of Open Field Agrivoltaic Systems: A Comprehensive Description of Combination of Agricultural and Energy Production. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2025, 80, 104369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Abaker Omer, A.; Li, M.; Zhang, F.; Hassaan, M.M.E.; El Kolaly, W.; Zhang, X.; Lan, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, W. Impacts of Agrivoltaic Systems on Microclimate, Water Use Efficiency, and Crop Yield: A Systematic Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 221, 115930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainelli, R.; Santoni, M.; Maienza, A.; Remelli, S.; Menta, C.; Zanotti, D.; Ghidesi, G.; Dal Prà, A. Weed and Grassland Community Structure, Biomass and Forage Value Across Crop Types and Light Conditions in an Organic Agrivoltaic System. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Yin, J.; Chen, H.; Peng, Y.; Tan, J.; Wei, M. Agrivoltaics Development Progresses: From the Perspective of Photovoltaic Impact on Crops, Soil Ecology and Climate. Environ. Res. 2025, 266, 120540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.W.C.; Soh, C.B.; Devihosur, S.C.; Tay, R.H.S.; Jusuf, S.K. Effects of Agrivoltaic Systems on the Surrounding Rooftop Microclimate. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Abaker Omer, A.; Liu, W.; Li, M.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Osman Hamid Mohammed, S.; Fan, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, F.; et al. Water Evaporation Reduction by the Agrivoltaic Systems Development. Sol. Energy 2022, 247, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, T.; Lu, W. Comparison of Ray Tracing Software Performance Based on Light Intensity for Spinach Growth. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baligar, V.C.; Elson, M.K.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Paiva, A.d.Q.; Almeida, A.-A.F.; Ahnert, D. Impact of Ambient and Elevated [CO2] in Low Light Levels on Growth, Physiology and Nutrient Uptake of Tropical Perennial Legume Cover Crops. Plants 2021, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X. Agrivoltaics with Semitransparent Panels Can Maintain Yield and Quality in Soybean Production. Sol. Energy 2024, 282, 112978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-agele, H.A.; Proctor, K.; Murthy, G.; Higgins, C. A Case Study of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicon var. Legend) Production and Water Productivity in Agrivoltaic Systems. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, Ö.; Kuzyaka, D.; Özden, T. Agrivoltaic System Design for Sugar Beets and Wheat in Central Anatolia. Renew. Energy 2025, 245, 122800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarelli, A.; Mazzeo, A.; Alhajj Ali, S.; Ferrara, G. Shading Enhanced Microclimate Variability, Photomorphogenesis and Yield Components in a Grapevine Agrivoltaic System in Semi-Arid Mediterranean Conditions in Puglia Region, Southeastern Italy. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 350, 114311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnayem, N.; Magadley, E.; Haj-Yahya, A.; Masalha, S.; Kabha, R.; Abasi, A.; Barhom, H.; Matar, M.; Attrash, M.; Yehia, I. Examining the Effect of Different Photovoltaic Modules on Cucumber Crops in a Greenhouse Agrivoltaic System: A Case Study. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 241, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asa’a, S.-N.; Bizinoto Ferreira Bosco, G.; Kyranaki, N.; van der Heide, A.; Sivaramakrishnan Radhakrishnan, H.; Poortmans, J.; Daenen, M. Assessing the Light Scattering Properties of C-Si PV Module Materials for Agrivoltaics: Towards More Homogeneous Light Distribution in Crop Canopies. Sol. Energy 2024, 276, 112690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, U.; Pearce, J.M. Experimental Impacts of Transparency on Strawberry Agrivoltaics Using Thin Film Photovoltaic Modules under Low Light Conditions. Sol. Energy 2025, 290, 113375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayibo, K.S.; Pearce, J.M. Vertical Free-Swinging Photovoltaic Racking Energy Modeling: A Novel Approach to Agrivoltaics. Renew. Energy 2023, 218, 119343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, U.; Vandewetering, N.; Pearce, J.M. Solar Photovoltaic Wood Racking Mechanical Design for Trellis-Based Agrivoltaics. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukač, N.; Špelič, D.; Štumberger, G.; Žalik, B. Optimisation for Large-Scale Photovoltaic Arrays’ Placement Based on Light Detection And Ranging Data. Appl. Energy 2020, 263, 114592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Ö.E.; Bretzel, T.; Gfüllner, L.; Gorjian, S.; Katircioglu, Y.; Dur, B.; Trommsdorff, M. Design, Simulation, and Experimental Evaluation of an Agrivoltaic Greenhouse in Turkey. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 105278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.H.; Imran, H.; Younas, R.; Butt, N.Z. The Optimization of Vertical Bifacial Photovoltaic Farms for Efficient Agrivoltaic Systems. Sol. Energy 2021, 230, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, H.R.; Sargent, K.; Penney, J.; Schmitz, T. Path Programming in Rhino 7 for Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Manuf. Lett. 2025, 44, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50797—2012; Design Code for Photovoltaic Power Stations. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Freitas, J.d.S.; Cronemberger, J.; Soares, R.M.; Amorim, C.N.D. Modeling and Assessing BIPV Envelopes Using Parametric Rhinoceros Plugins Grasshopper and Ladybug. Renew. Energy 2020, 160, 1468–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Sánchez, C.; Giannelli, D.; Agugiaro, G.; Stoter, J. Comparative Analysis of Geospatial Tools for Solar Simulation. Trans. GIS 2025, 29, e13296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, S.; Guo, S.; Ma, M.; Feng, S.; Bao, L. Benchmarking Urban Local Weather with Long-Term Monitoring Compared with Weather Datasets from Climate Station and EnergyPlus Weather (EPW) Data. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 6501–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Severin, S.N. Continuous Light Can Promote Growth of Baby Greens over Diurnal Light under a High Daily Light Integral. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 220, 105695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yue, Z.; Ma, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Meng, X.; Kribus, A.; Vitoshkin, H.; et al. Agricultural Friendly Single-Axis Dynamic Agrivoltaics: Simulations, Experiments and a Large-Scale Application for Chinese Solar Greenhouses. Appl. Energy 2024, 374, 123891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, R.; van der Meer, M.; de Visser, P.H.B.; Heuvelink, E.; Marcelis, L.F.M. Consequences of Intra-Canopy and Top LED Lighting for Uniformity of Light Distribution in a Tomato Crop. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1012529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmott, C.J. Some Comments on the Evaluation of Model Performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 636, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhlamini, M.M.; Brent, A.C. The Impact of Fixed-Tilt PV Arrays on Vegetation Growth Through Ground Sunlight Distribution at a Solar Farm in Aotearoa New Zealand. Energies 2025, 18, 5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddoura, T.O.; Ramli, M.A.M.; Al-Turki, Y.A. On the Estimation of the Optimum Tilt Angle of PV Panel in Saudi Arabia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, M.; Yano, A.; Solinas, S.; Deligios, P.A.; Tiloca, M.T.; Cossu, A.; Ledda, L. Agricultural Sustainability Estimation of the European Photovoltaic Greenhouses. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 118, 126074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ge, Z.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; Lin, Y. Study on the Optimum Tilted Angle of Solar Panels in Hainan Tropical Photovoltaic Facility Agricultural System. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 61, 012073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apriani, S.; Mangkuto, R.A.; Saputro, A.G.; Chow, E.C. Performance Prediction and Optimisation of Even-Lighting Agrivoltaic Systems with Semi-Transparent PV Module in the Tropical Region. Sol. Energy 2024, 283, 113013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubleday, K.; Oleskewicz, K.; Ovaitt, S.; Hickey, T.; Herbert, S.J.; Macknick, J. Impacts of Year-to-Year Weather Variability and Inter-Panel Spacing on Agrivoltaic Crop Yields in Massachusetts. Agrofor. Syst. 2025, 99, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willockx, B.; Lavaert, C.; Cappelle, J. Geospatial Assessment of Elevated Agrivoltaics on Arable Land in Europe to Highlight the Implications on Design, Land Use and Economic Level. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 8736–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gong, J.; Yang, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Xu, G.; Wu, C.; Bao, E. Evaluating the Contribution of Decreasing Heights of Photovoltaic Panels on Light Environment and Agricultural Production in Agrivoltaic Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 495, 145091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, R.; Aneli, S.; Gagliano, A.; Tina, G.M. Optimal Photovoltaic Array Layout of Agrivoltaic Systems Based on Vertical Bifacial Photovoltaic Modules. Sol. RRL 2024, 8, 2300505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.N.; Ghosh, A. Evaluating Tracking Bifacial Solar PV Based Agrivoltaics System across the UK. Sol. Energy 2024, 284, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Xu, G.; Wu, C.; Bao, E. Open-Field Agrivoltaic System Impacts on Photothermal Environment and Light Environment Simulation Analysis in Eastern China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Technical Parameters | Unit | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Peak power | Wp | 330 |
| Open circuit voltage (Voc) | V | 47.1 |
| Short circuit current (Isc) | A | 8.99 |
| Peak voltage (Vmppt) | V | 38 |
| Peak current (Imppt) | A | 8.68 |
| Dimensions | mm | 1956 × 992 × 45 |
| Scheme ID | Layout | No. of Modules (pcs) | GCR (%) | 3D Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | Single-row vertical layout with zero spacing between adjacent modules | 252 | 48.5 | 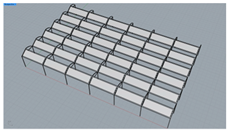 |
| T2 | Single-row vertical layout with 0.4 m spacing between adjacent modules | 180 | 34.6 |  |
| T3 | Double-row horizontal layout with 0 m vertical spacing and 0.8 m horizontal spacing between modules | 180 | 34.6 | 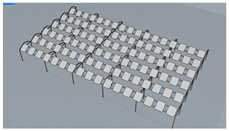 |
| T4 | Double-row horizontal layout with 0.2 m vertical spacing and 0.8 m horizontal spacing between modules | 180 | 34.6 | 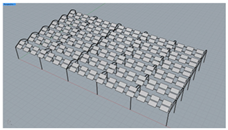 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, H.; Tao, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Bao, E.; Cao, K. Optimization Design of Agrivoltaic Systems Based on Light Environment Simulation. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232437
Ding H, Tao S, Zhang L, Li Y, Wu X, Zhang J, Guo J, Bao E, Cao K. Optimization Design of Agrivoltaic Systems Based on Light Environment Simulation. Agriculture. 2025; 15(23):2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232437
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Hangwei, Shida Tao, Long Zhang, Yueyue Li, Xue Wu, Jinxin Zhang, Jiguang Guo, Encai Bao, and Kai Cao. 2025. "Optimization Design of Agrivoltaic Systems Based on Light Environment Simulation" Agriculture 15, no. 23: 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232437
APA StyleDing, H., Tao, S., Zhang, L., Li, Y., Wu, X., Zhang, J., Guo, J., Bao, E., & Cao, K. (2025). Optimization Design of Agrivoltaic Systems Based on Light Environment Simulation. Agriculture, 15(23), 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232437







