QTL Mapping and Fine Mapping of a Major Quantitative Trait Locus (qBS11) Conferring Resistance to Rice Brown Spot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Population Construction
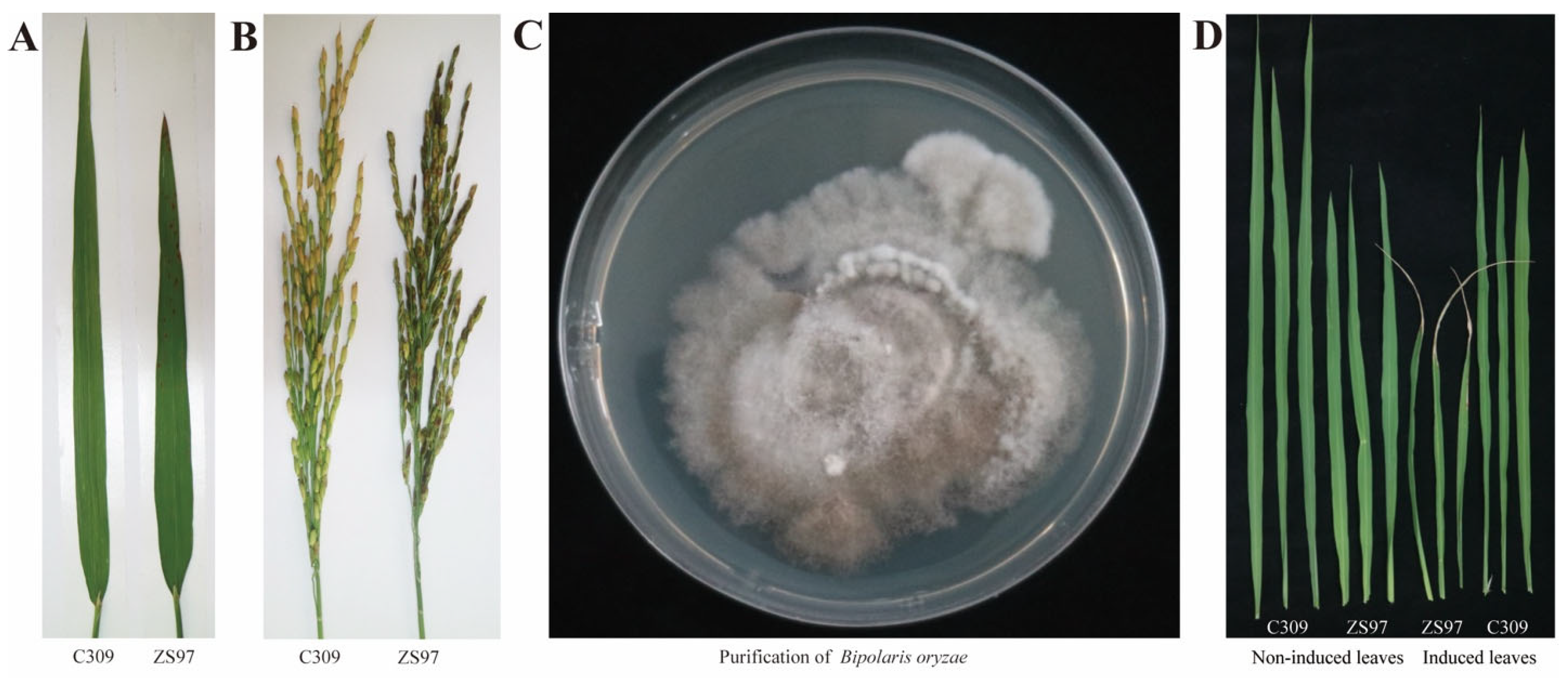
2.2. Pathogen Isolation and Verification
2.3. Pathogenicity Verification
2.4. Molecular Identification and Sequencing
2.5. Field Phenotyping of RIL Population and Backcross Population
2.6. Heritability Calculation
2.7. The DNA Library Construction, Sequencing, Genotyping and QTL Mapping
2.8. BSA-Seq Analysis
2.9. Fine Mapping
3. Results
3.1. Pathogen Confirmation and Phenotypic Distribution
3.2. Phenotypic Analysis of the RIL Population
3.3. Initial QTL Mapping of BS via GCIM
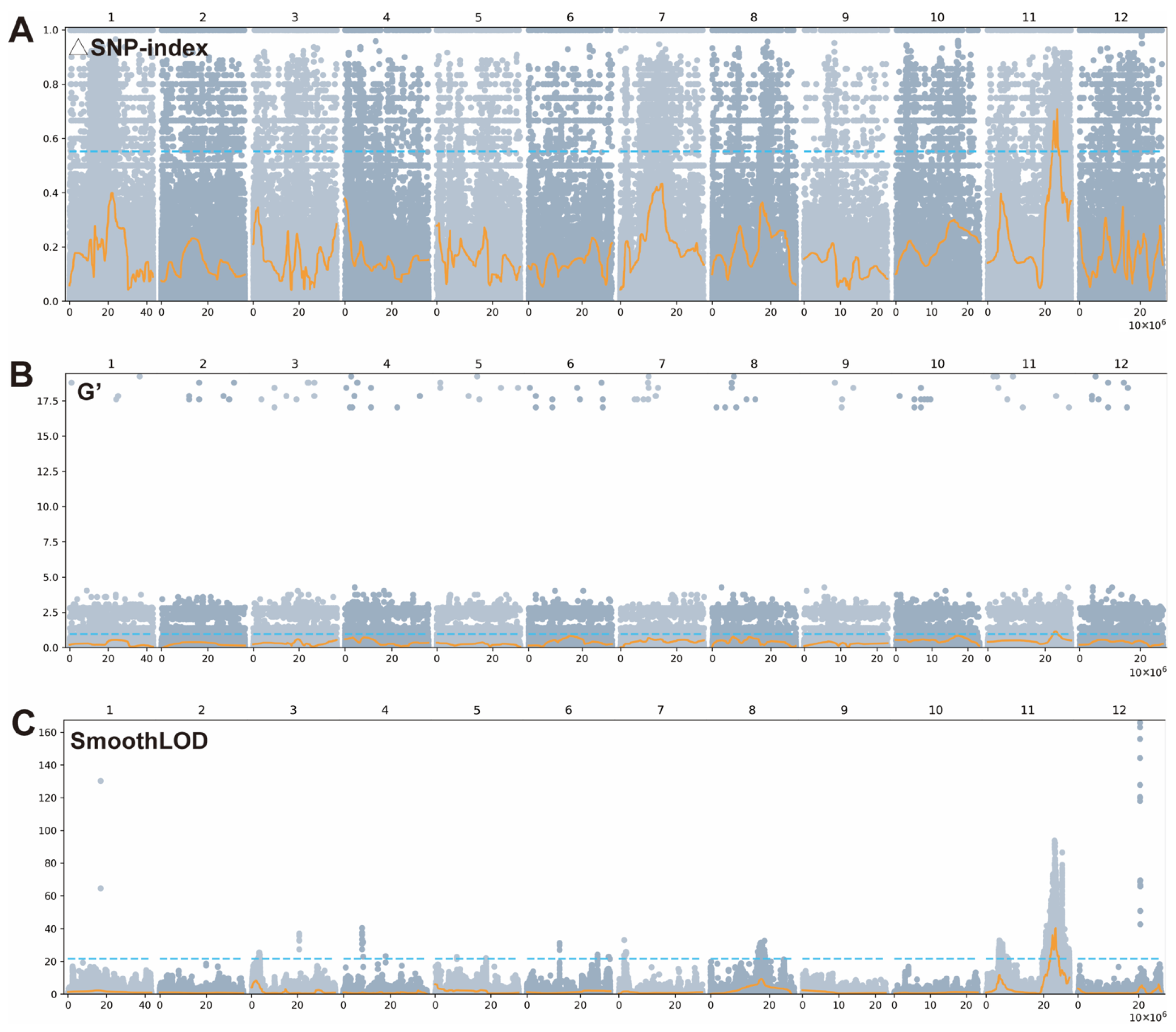
3.4. BSA-Seq for BS
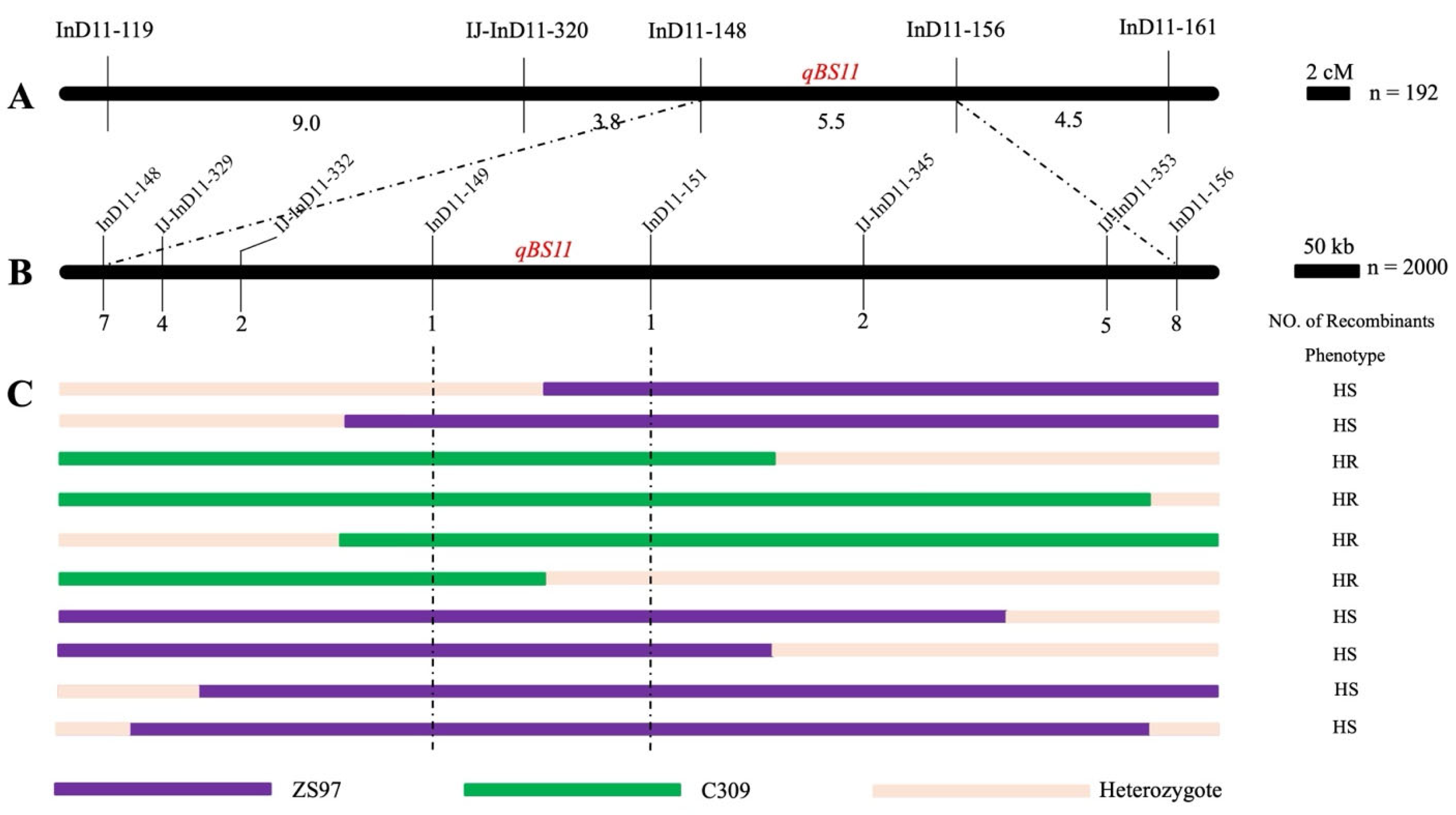
3.5. Fine Mapping of qBS11
3.6. Candidate Gene Analysis Within the qBS11 Fine-Mapped Interval
4. Discussion
4.1. The Critical Role of Genetic Resistance in Combating BS
4.2. Fine Mapping, Inheritance, and Molecular Identification of the Major Locus qBS11
4.3. Physical Co-Localization and Allelic Hypotheses
4.4. Molecular Breeding Prospects and Functional Analysis Outlook
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BS | brown spot |
| QTL | quantitative trait locus |
| RIL | recombinant inbred line |
| CIM | composite interval mapping |
| BSA-seq | bulked segregant analysis sequencing |
| MAS | marker-assisted selection |
| N | nitrogen |
| K | potassium |
| DH | doubled haploid |
| BILs | backcross inbred lines |
| GWAS | genome-wide association studies |
| ZS97 | Zhenshan 97 |
| HR-pool | high-resistant pool |
| HS-pool | highly susceptible pool |
| CSSLs | chromosome segment substitution lines |
| PDA | potato dextrose agar |
| ITS | internal transcribed spacer |
| HR | high resistance |
| MR | medium resistance |
| MS | medium susceptibility |
| S | susceptibility |
| HS | high susceptibility |
| LOD | logarithm of odds |
| H2 | broad-sense heritability |
| h2 | narrow-sense heritability |
| PVE | phenotypic variance |
| NBS-LRR | nucleotide-binding site–leucine-rich repeat |
| G × E | genotype-by-environment |
| CC | coiled-coil |
References
- Barnwal, M.K.; Kotasthane, A.; Magculia, N.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Savary, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, H.B.; Singh, U.; Sparks, A.; Variar, M. A review on crop losses, epidemiology and disease management of rice brown spot to identify research priorities and knowledge gaps. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 136, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.; Sharma, R.; Hunjan, M.S.; Sharma, V.K.; Sharma, P.; Chauhan, S.K. Microstructural and metabolic variations induced by Bipolaris oryzae inciting brown spot disease of rice. Cereal Res. Commun. 2023, 51, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, B.; Arshad, H.M.I.; Atiq, M.; Yousaf, S.; Saleem, K.; Arshad, A. Biochemical profiling of resistant phenotypes against bipolaris oryzae causing brown spot disease in rice. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 675895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunder, S.; Singh, R.; Agarwal, R. Brown spot of rice: An overview. Indian Phytopathol. 2014, 67, 201–215. [Google Scholar]
- Kaboré, K.H.; Kassankogno, A.I.; Tharreau, D. Brown spot of rice: Worldwide disease impact, phenotypic and genetic diversity of the causal pathogen Bipolaris oryzae, and management of the disease. Plant Pathol. 2025, 74, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Tang, J.R.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.K. First report of Bipolaris oryzae causing leaf spot on cultivated wild rice (Oryza rufipogon) in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M Bekheet, S.M.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Aboshosha, S.S.; Saleh, M.M.; M Shams, A.H. Pathogenicity evaluation of Bipolaris oryzae isolates on Egyptian rice cultivars. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 2021, 42, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabore, K.H.; Kassankogno, A.I.; Adreit, H.; Milazzo, J.; Guillou, S.; Blondin, L.; Chopin, L.; Ravel, S.; Charriat, F.; Barro, M. Genetic diversity and structure of Bipolaris oryzae and Exserohilum rostratum populations causing brown spot of rice in Burkina Faso based on genotyping-by-sequencing. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1022348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, A.; Castell-Miller, C.; Javan-Nikkhah, M.; Naghavi, M.R.; Dehkaei, F.P.; Leng, Y.; Puri, K.; Zhong, S. Population structure, genetic diversity, and sexual state of the rice brown spot pathogen Bipolaris oryzae from three Asian countries. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.P.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Silveira, P.R.; Andrade, C.C.L.; Baroni, J.C.P.; Paye, H.S.; Loureiro Junior, J.E. Rice resistance to brown spot mediated by nitrogen and potassium. J. Phytopathol. 2010, 158, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nargave, S.; Gehlot, J.; Buri, R.; Jakhar, M.; Damor, J.S.; Jain, S. Biological and chemical management strategy to control brown spot disease in rice caused by Bipolaris oryzae. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2023, 35, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balgude, Y.S.; Gaikwad, A.P.; Tirmali, A.M. Integrated management of sheath rot and brown spot of paddy. IJCS 2020, 8, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, A.A.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Datnoff, L.E. Silicon control of soil-borne and seed-borne diseases. In Silicon and Plant Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ota, Y.; Seta, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Ohno, T.; Mizobuchi, R.; Sato, H. Identification of QTLs for rice brown spot resistance in backcross inbred lines derived from a cross between Koshihikari and CH45. Breed. Sci. 2017, 67, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katara, J.; Sonah, H.; Deshmukh, R.; Chaurasia, R.; Kotasthane, A. Molecular analysis of QTLs associated with resistance to brown spot in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2010, 70, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ota, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Honda, Y.; Ohashi, S.; Nakamura, D.; Mizobuchi, R.; Sato, H. Identification of QTLs for brown spot resistance in rice. Breed. Sci. 2025, 75, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.-Y.; Lee, G.-H.; Zeng, Y.; Lee, A.-R.; Park, S.-Y.; Jang, S.-G.; Cho, L.-H.; Kim, S.T.; Lee, J.; Kwon, S.-W. Genome-wide identification and functional characterization of brown spot resistance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 14089–14098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, O.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Haeck, A.; Demeestere, K.; Höfte, M. The energy sensor OsSnRK1a confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.-Y.; Zeng, Y.; Lee, A.-R.; Kim, B.; Lee, D.; Kim, S.-T.; Kwon, S.-W. OsFBN6 enhances brown spot disease resistance in rice. Plants 2024, 13, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Gan, P.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Hu, W. Identification of QTLs for internode length and diameter associated with lodging resistance in rice. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Dunwell, J.M.; Zhang, Y. QTL. gCIMapping. GUI v2. 0: An R software for detecting small-effect and linked QTLs for quantitative traits in bi-parental segregation populations. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. WIREs Comp. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, Y.; de la Bastide, M.; Hamilton, J.P.; Kanamori, H.; McCombie, W.R.; Ouyang, S.; Schwartz, D.C.; Tanaka, T.; Wu, J.; Zhou, S. Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Subgroup, G.P.D.P. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Shi, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Li, L. DeepBSA: A deep-learning algorithm improves bulked segregant analysis for dissecting complex traits. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhou, T.; Wang, P.; Wang, B.; Song, J.; Han, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, K.; Xing, Y. Development of whole-genome agarose-resolvable LInDel markers in rice. Rice 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, S.E.; Daly, M.J.; Lander, E.S. Constructing genetic linkage maps with MAPMAKER/EXP Version 3.0: A tutorial and reference manual. In A Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Technical Report; Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993; Volume 3, pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J. 2015, 3, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsman, G.; Modliszewski, J.L.; Valdes, M.; Benfey, P.N. A SIMPLE pipeline for mapping point mutations. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ota, Y.; Yamakawa, T.; Ohno, T.; Seta, S.; Honda, Y.; Mizobuchi, R.; Sato, H. Breeding and characterization of the world’s first practical rice variety with resistance to brown spot (Bipolaris oryzae) bred using marker-assisted selection. Breed. Sci. 2021, 71, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, C.R. Inheritance in Rice of Reaction to Helminthosporium oryzae and Cercospora oryzae; United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Balal, M.; Omar, R.; El-Khadem, M.; Aidy, I. Inheritance of resistance to the brown spot disease of rice, Cochliobolus miyabeanus. Agric. Res. Rev. 1979, 57, 119–133. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, R.; Ritu Bala, R.B.; Kuldeep Singh, K.S. Genetic characterization of resistance to brown leaf spot caused by Drechslera oryzae in some wild rice (Oryza sativa) lines. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 76, 705–707. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Xu, Y.; He, Y. Pyramiding of Xa7 and Xa21 for the improvement of disease resistance to bacterial blight in hybrid rice. Plant Breed. 2006, 125, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulbah, Q.S.; Shimelis, H.A.; Laing, M.D. Combining ability and gene action of three components of horizontal resistance against rice blast. Euphytica 2015, 206, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.d.; Sanchez, P.; Fernandez-Delmond, I.; Grant, M. Expression profiling of the host response to bacterial infection: The transition from basal to induced defence responses in RPM1-mediated resistance. Plant J. 2003, 33, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chung, E.-H.; Eitas, T.K.; Dangl, J.L. Plant intracellular innate immune receptor Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola 1 (RPM1) is activated at, and functions on, the plasma membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7619–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Guo, D.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, X. Functions of RPM1-interacting protein 4 in plant immunity. Planta 2021, 253, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, D.; Holt, B.F.; Wiig, A.; Dangl, J.L. RIN4 interacts with Pseudomonas syringae type III effector molecules and is required for RPM1-mediated resistance in Arabidopsis. Cell 2002, 108, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z. Overexpression of Arabidopsis nucleotide-binding and leucine-rich repeat genes RPS2 and RPM1 (D505V) confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Ando, I.; Hirabayashi, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Arase, S.; Kihara, J.; Kato, H.; Imbe, T.; Nemoto, H. QTL analysis of brown spot resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed. Sci. 2008, 58, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, S.C.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ramlee, S.I.; Ismail, S.I.; Oladosu, Y.; Okporie, E.; Onyishi, G.; Utobo, E.; Ekwu, L.; Swaray, S. Marker-assisted selection and gene pyramiding for resistance to bacterial leaf blight disease of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajiwala, K.S.; Burley, S.K. Winged helix proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000, 10, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, E.; Clark, K.L.; Burley, S.K.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/fork head or “winged helix” proteins: A family of transcription factors of diverse biologic function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10421–10423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, M.P.; Hubl, S.T.; Harrison, C.J.; Littlefield, O.; Hardy, J.A.; Nelson, H.C. The wing in yeast heat shock transcription factor (HSF) DNA-binding domain is required for full activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Smith, C.L.; DeRyckere, D.; DeAngelis, K.; Martin, G.S.; Berger, J.M. Structure and function of Cdc6/Cdc18: Implications for origin recognition and checkpoint control. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Miyata, T.; Tsuchiya, D.; Oyama, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Shinagawa, H.; Ariyoshi, M.; Mayanagi, K. Crystal structure of the RuvA-RuvB complex: A structural basis for the Holliday junction migrating motor machinery. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wah, D.A.; Hirsch, J.A.; Dorner, L.F.; Schildkraut, I.; Aggarwal, A.K. Structure of the multimodular endonuclease Fok I bound to DNA. Nature 1997, 388, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
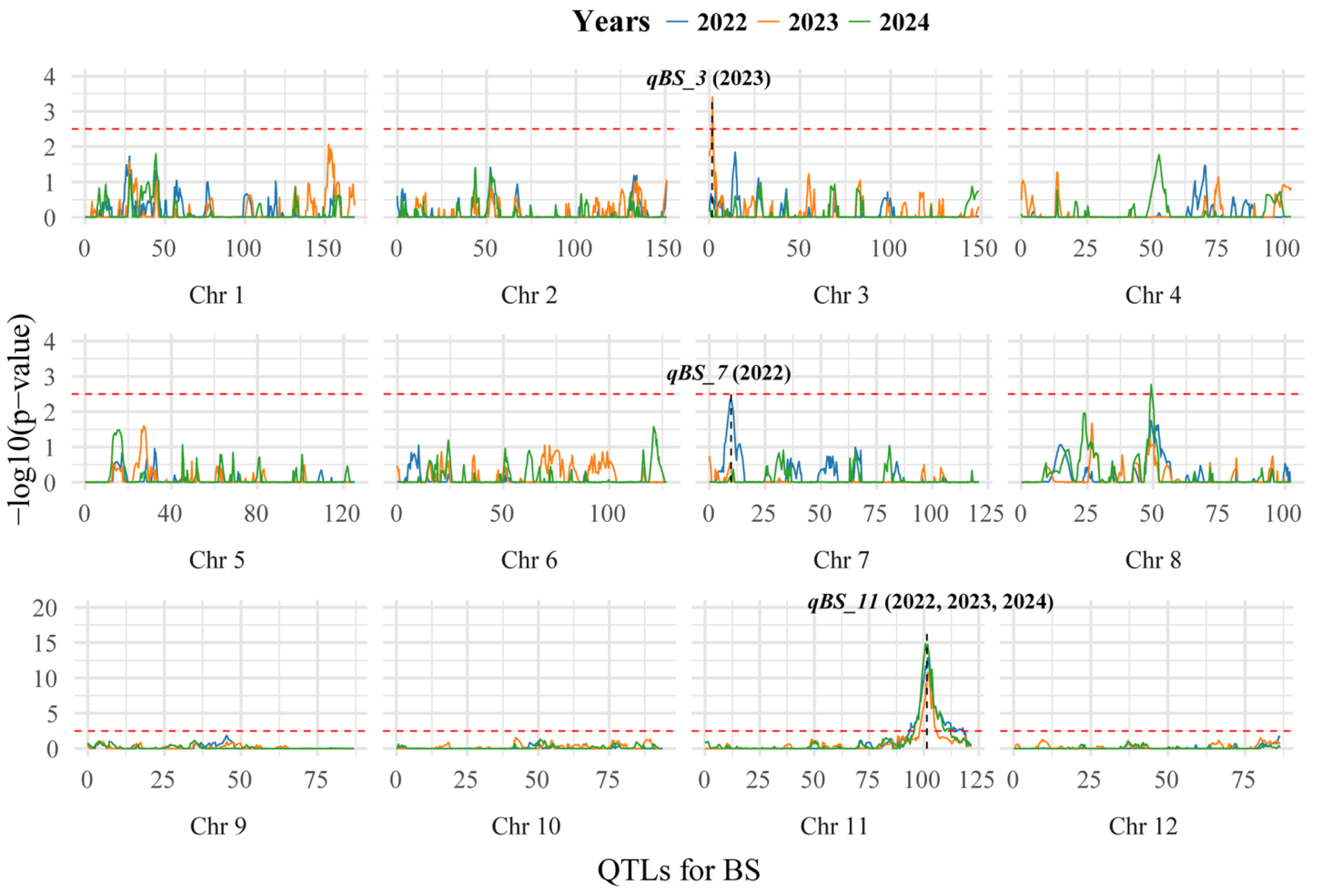
| QTLs | Years | Chr | Position (cM) | Additive Effect | LOD | Peak_Marker | PVE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qBS3 | 2023 | 3 | 1.69 | 0.46 | 4.49 | 866,776 | 5.1 |
| qBS7 | 2022 | 7 | 9.74 | −0.38 | 2.61 | 1,855,566 | 3.6 |
| qBS11 | 2022 | 11 | 101.69 | −1.19 | 20.35 | 23,925,783 | 36.0 |
| 2023 | 11 | 101.69 | −1.40 | 30.03 | 23,925,783 | 47.7 | |
| 2024 | 11 | 100.71 | −1.34 | 29.80 | 23,793,621 | 47.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Hu, W. QTL Mapping and Fine Mapping of a Major Quantitative Trait Locus (qBS11) Conferring Resistance to Rice Brown Spot. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232417
Lin Q, Zhou Y, Lin Y, Xie Z, Hu W. QTL Mapping and Fine Mapping of a Major Quantitative Trait Locus (qBS11) Conferring Resistance to Rice Brown Spot. Agriculture. 2025; 15(23):2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232417
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Qiuyun, Yujie Zhou, Yuehui Lin, Zhenyu Xie, and Wei Hu. 2025. "QTL Mapping and Fine Mapping of a Major Quantitative Trait Locus (qBS11) Conferring Resistance to Rice Brown Spot" Agriculture 15, no. 23: 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232417
APA StyleLin, Q., Zhou, Y., Lin, Y., Xie, Z., & Hu, W. (2025). QTL Mapping and Fine Mapping of a Major Quantitative Trait Locus (qBS11) Conferring Resistance to Rice Brown Spot. Agriculture, 15(23), 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232417






