Heavy Metal Source Apportionment, Environmental Capacity, and Health Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils of a Rice-Growing Watershed in Eastern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
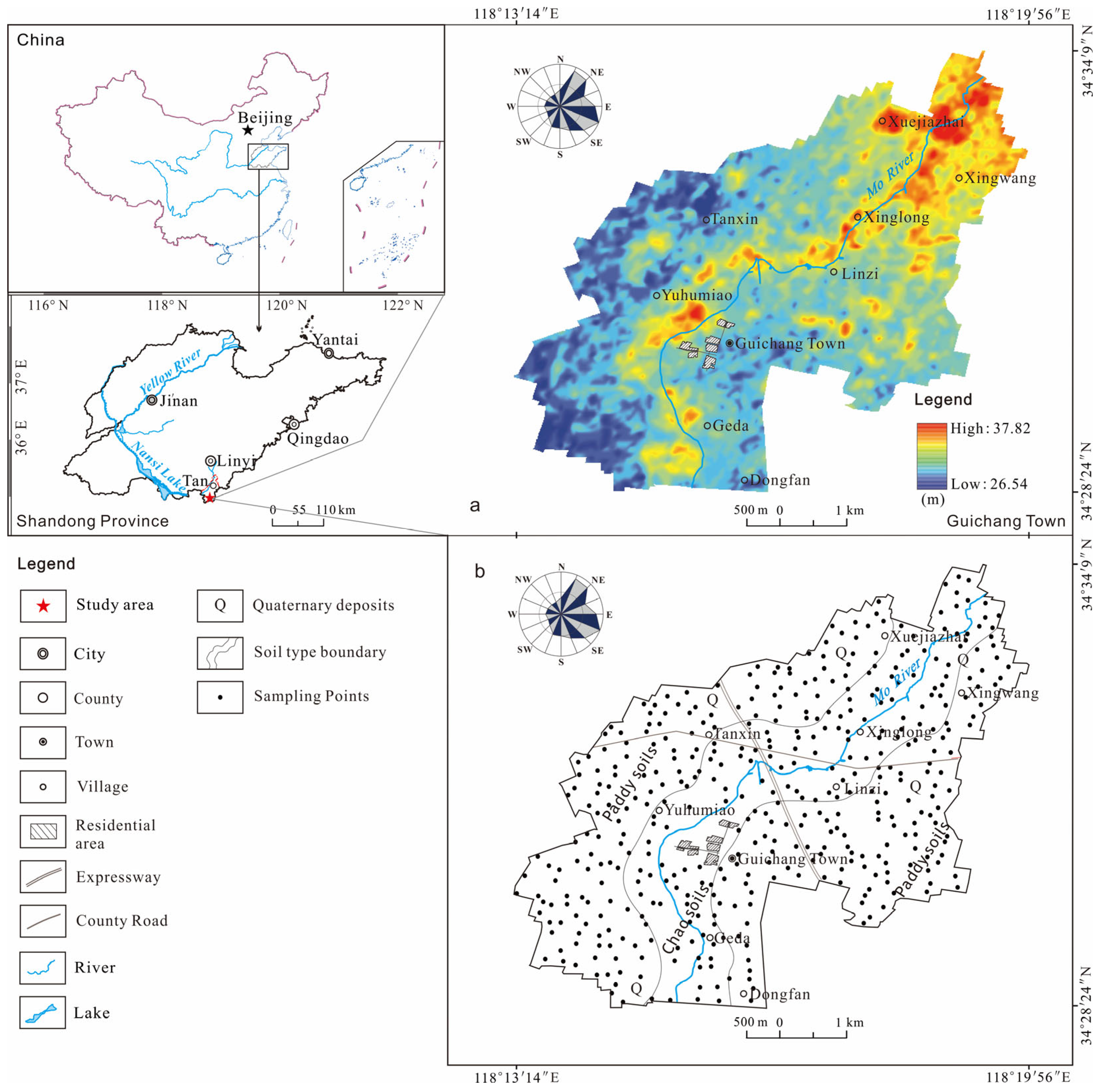
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Evaluation Method
2.3.1. Enrichment Factor Method
2.3.2. Positive Matrix Factorization
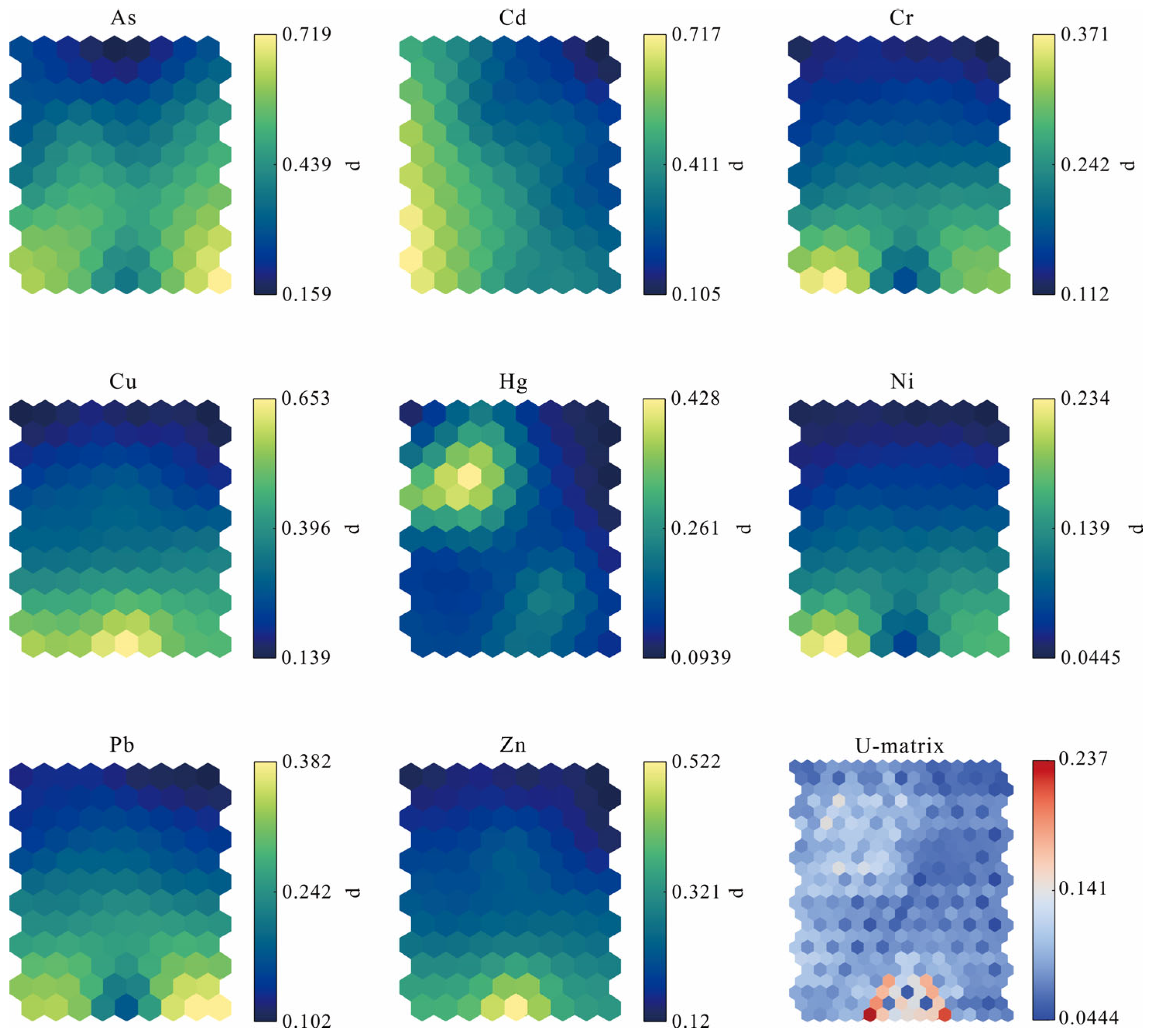
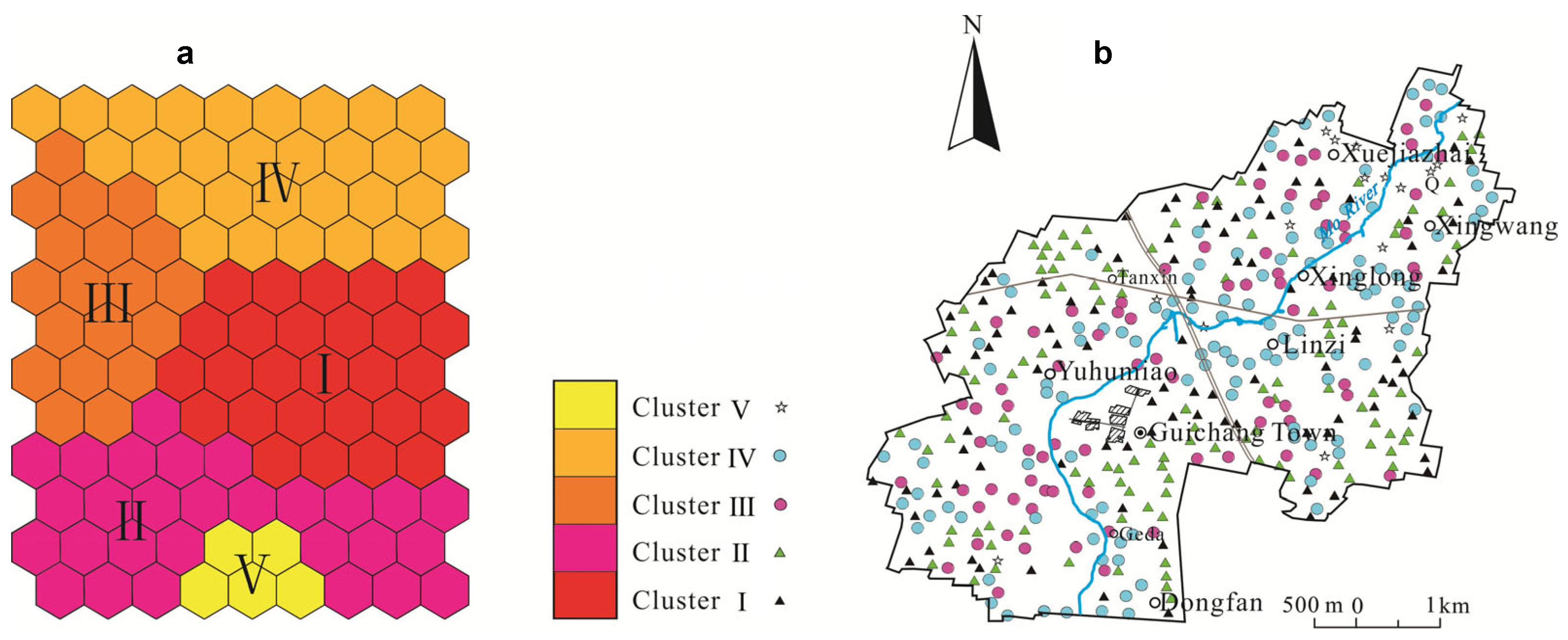
2.3.3. Self-Organizing Map
2.3.4. Soil Environmental Capacity
- Soil heavy metal static environmental capacity
- 2.
- Improved comprehensive Environmental Capacity Index
2.3.5. Health Risk Assessment
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Heavy Metal Concentration and Spatial Distribution Characteristics
3.2. Heavy Metal Source Apportionment
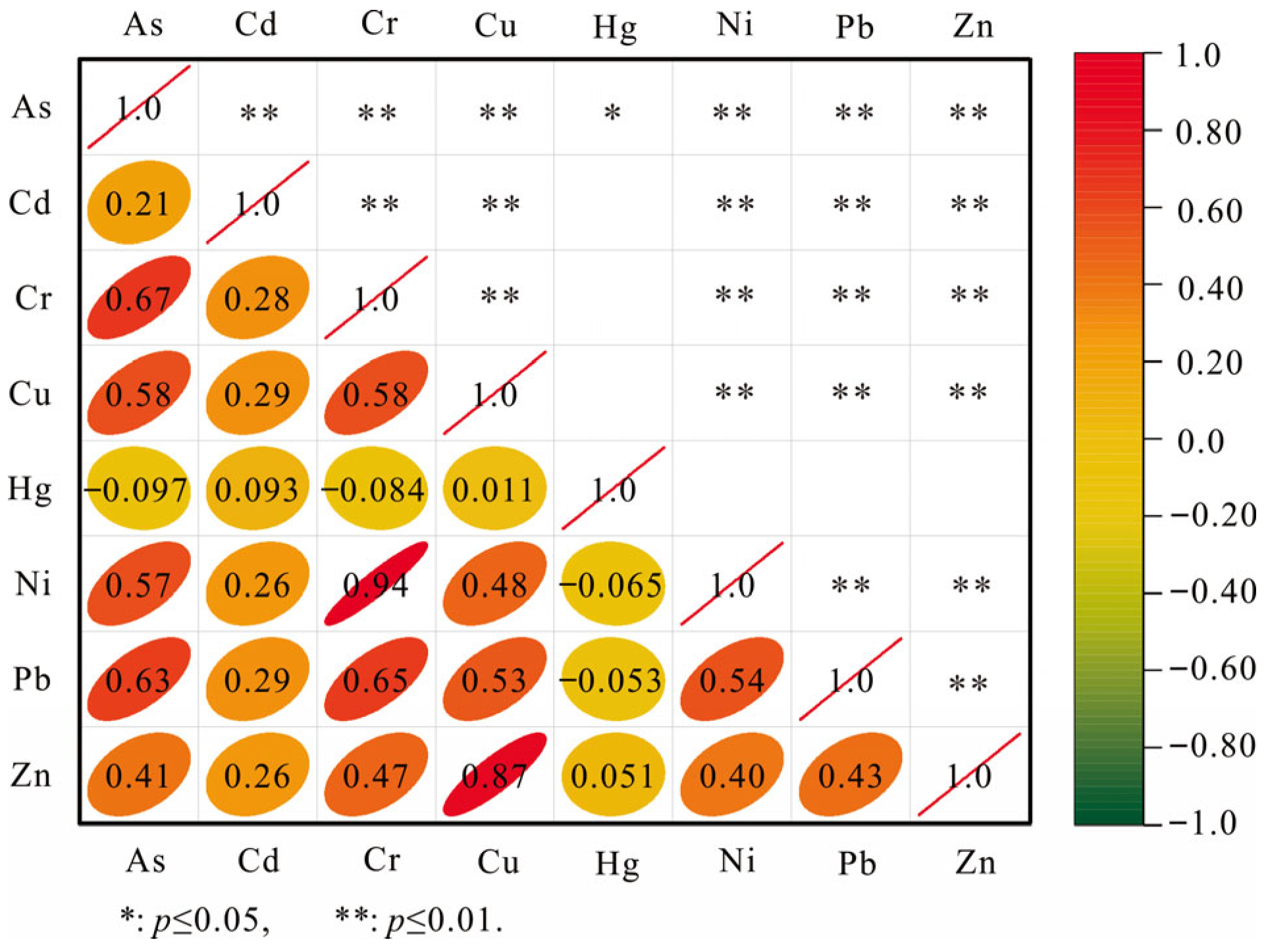
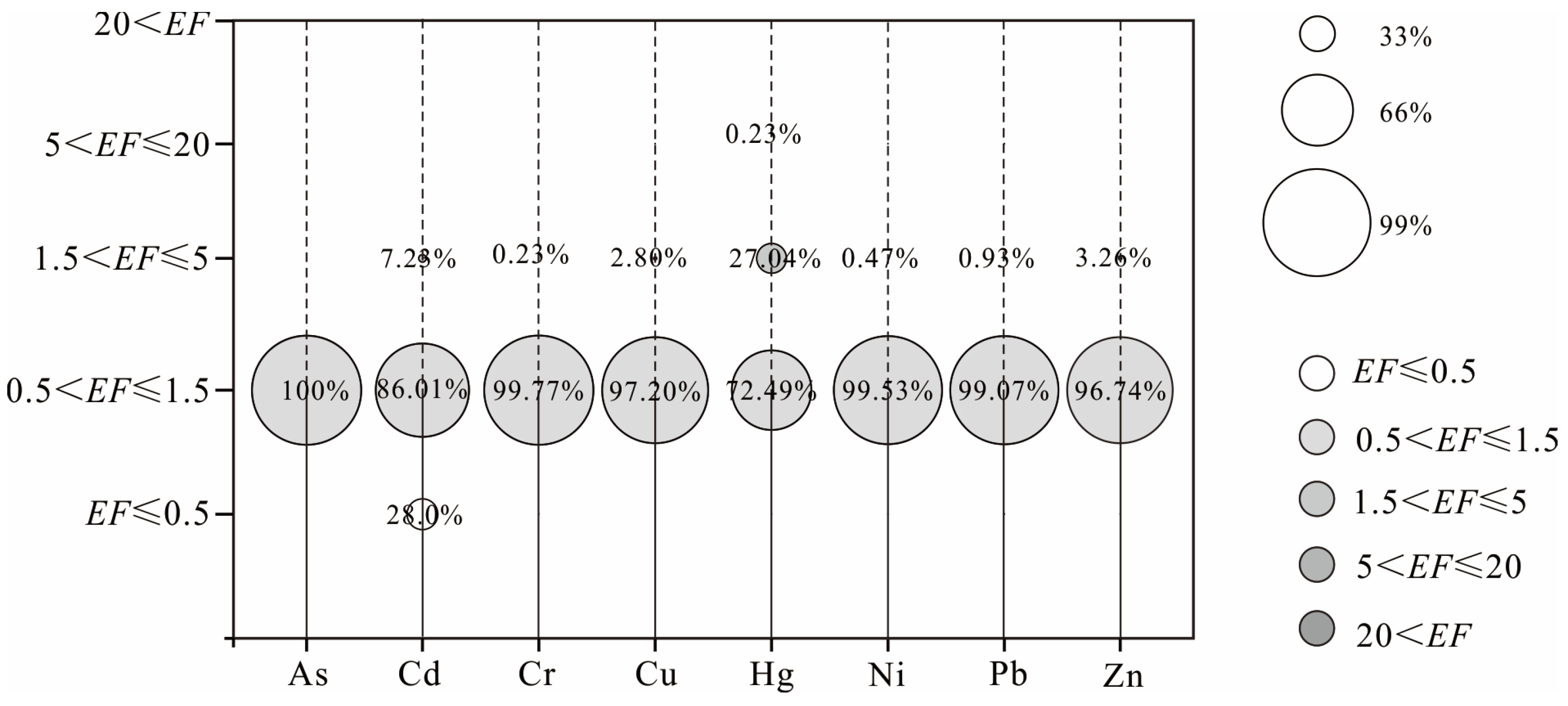
3.2.1. Enrichment Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Soil
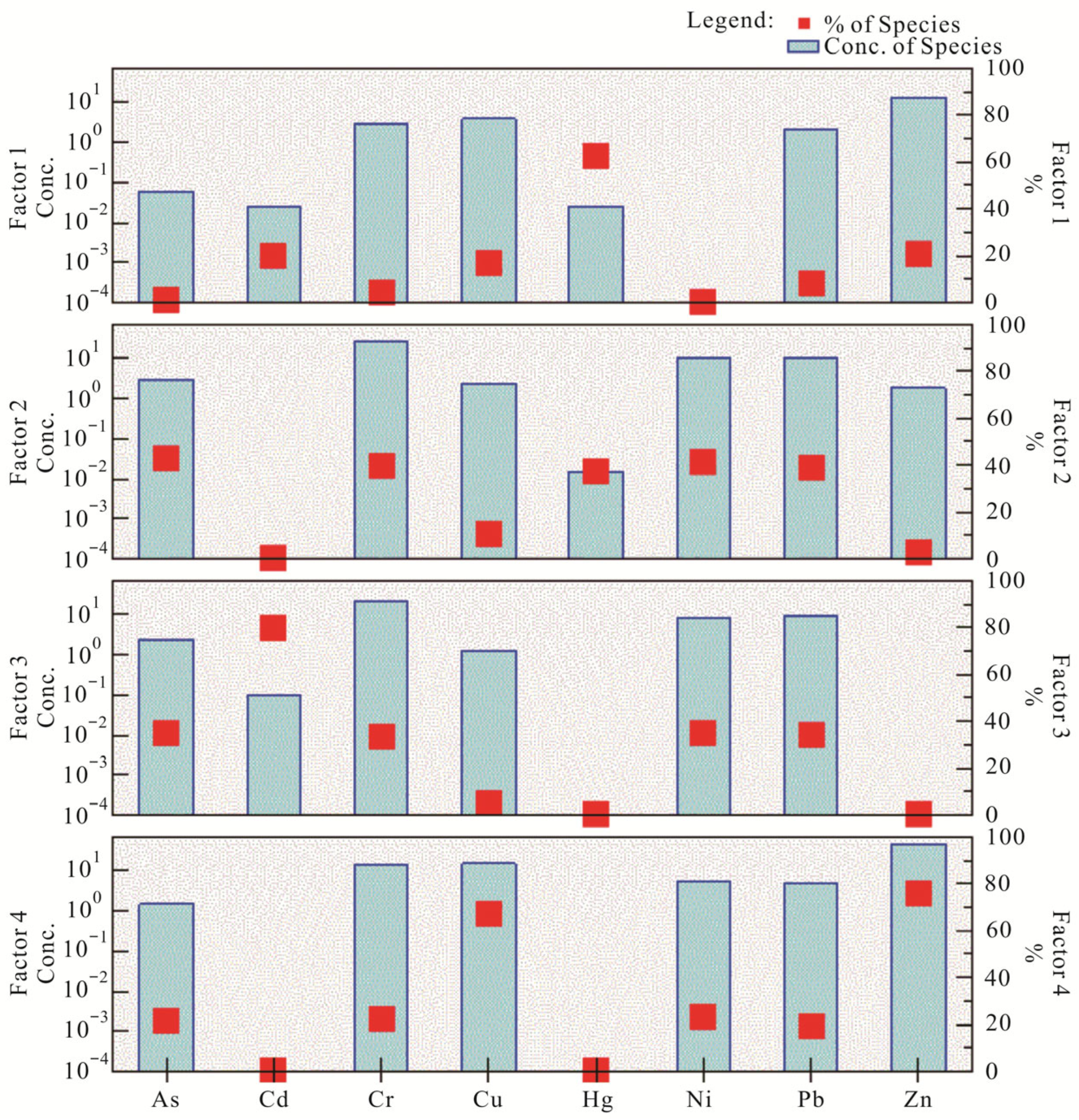
3.2.2. Positive Matrix Factorization Analysis
3.2.3. Self-Organizing Map Analysis
3.3. Environmental Capacity of Soil Heavy Metals
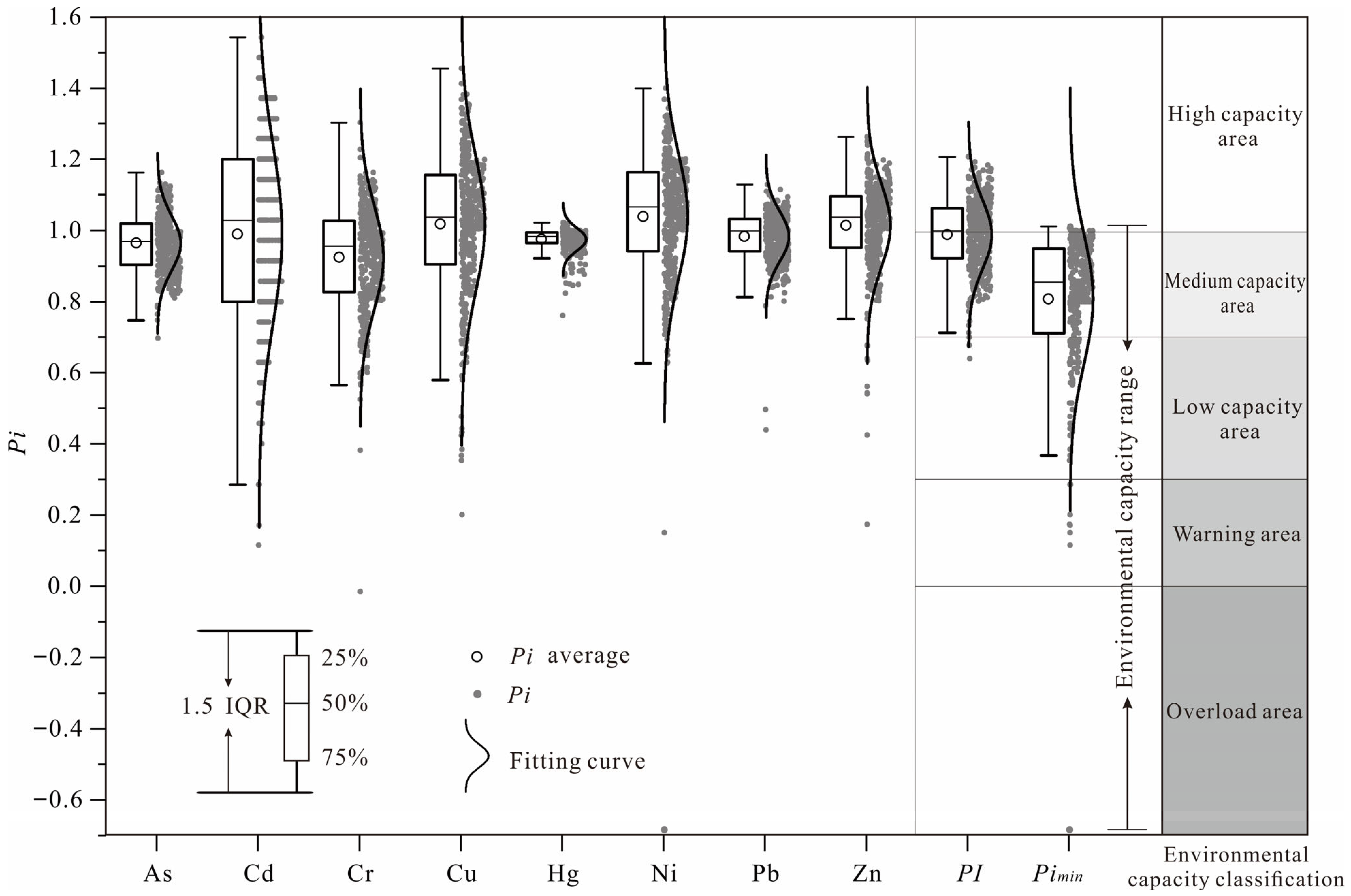
3.3.1. Static Environmental Capacity of Heavy Metals
3.3.2. Evaluation of Soil Environmental Capacity
3.4. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals
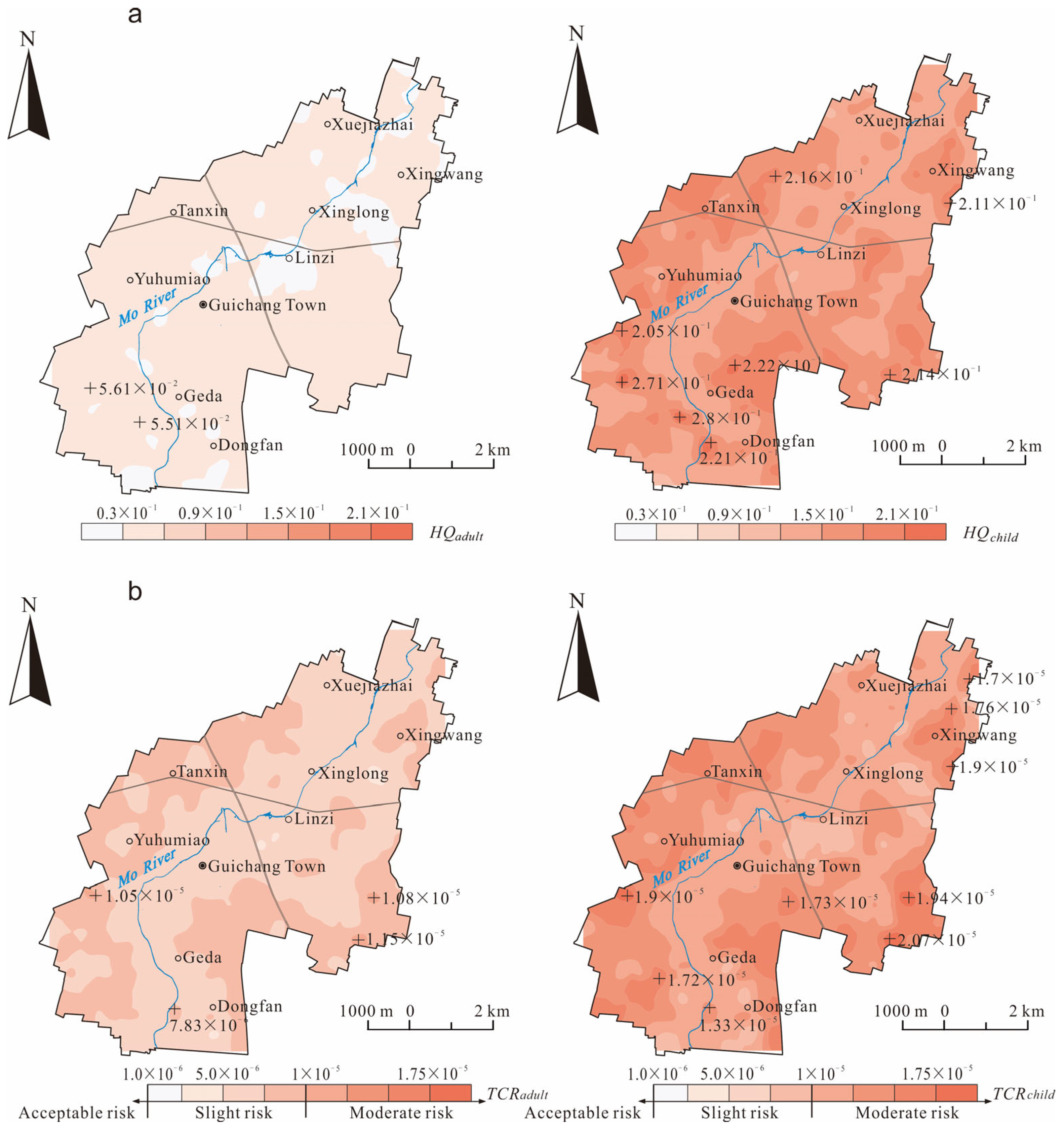
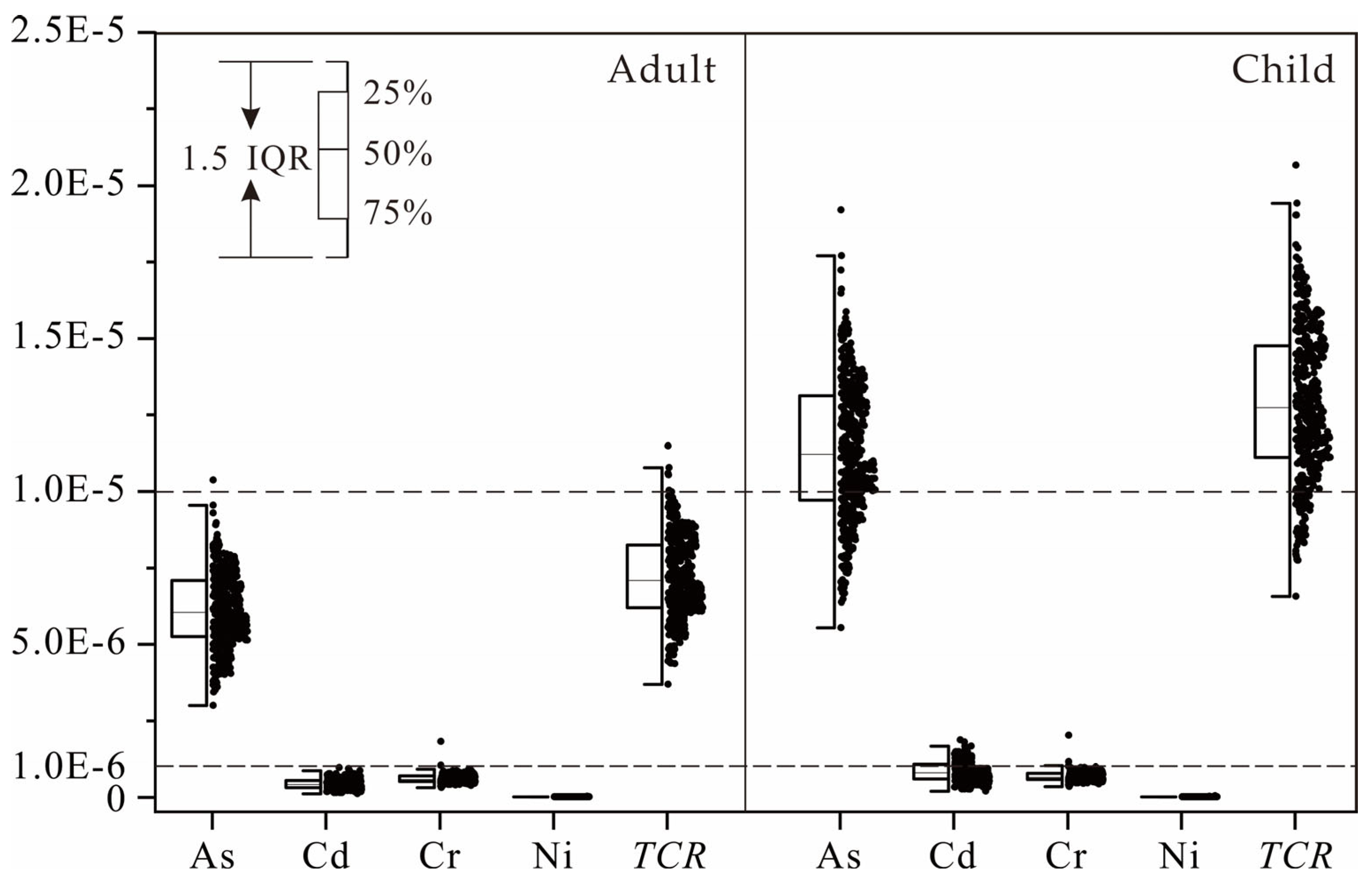
3.4.1. Heavy Metal Exposure Assessment
3.4.2. Health Risk Characterization and Spatial Distribution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture: Systems at Breaking Point (SOLAW 2021); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Global Assessment of Soil Pollution: Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): Gigiri Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhair, K.S.; Ashraf, M.A. Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.J.; Wang, X.Q. Distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the floodplain soils of the karst area of Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, K.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z. A study on soil priority management of toxic and hazardous substances for development land. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 18, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.X.; Su, L.M.; Wang, Y.H. Sources appointment of heavy metals in cultivated soils of Lanzhou based on PMF models. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 3919–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.Y.; Jia, X.Y.; Wang, L.W.; Steve, P.M.; Zhu, Y.G.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.J.; Michael, S.B.; O’Connor, D.; Jerime, N. Global soil pollution by toxic metals threatens agriculture and human health. Science 2025, 388, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.L.; Zuo, F.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, C.D.; Chi, X.X.; Zhang, D.J. Determination of geographical origin of Wuchang Rice with the geographical indicator by multielement analysis. J. Food Qual. 2019, 1, 8396865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Song, X.J.; Cao, D.M.; Zhang, D.J.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, C. Distribution and health risk evaluation of heavy metal lead in the main production area of rice in Heilongjiang Province. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, e000623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.L.; Li, Q.; Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Ji, H.; Pang, C.; Wan, M. Characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution and its ecological risk assessment in South Jining District using methods of enrichment factor and index of geoaccumulation. Rock Miner. Anal. 2015, 34, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wan, F.; Fan, H.; Kang, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, J. Spatial distribution, source apportionment, and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in Jianghugongmi Producing Area, Shandong Province. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4199–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahim, G.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Wang, Z.H.; Lu, S.H.; Jiang, S.J.; Mu, D.H.; Shu, Y.H. Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify source of anthropogenic impacts on metallic elements in sediments from the mid Guangdong coasts, China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Heavy metal pollution of the sediments of Neckars and its tributary: A stocktaking. Chem. Ztg. 1979, 105, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, C.; Caritat, P. Intrinsic flaws of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 5084–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Pandita, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.; Cerda, A. A review of ecological risk assessment and associated health risks with heavy metals in sediment from India. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 35, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Ye, X.; Feng, H.; Jing, Y.; Yu, X.; Liang, R.; Gao, C.; Chen, W. Heavy metal contamination in western Xiamen Bay sediments and its vicinity, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.P.; Xie, X.M.; Tang, Z.H. Study on soil heavy metal environmental capacity in Shantou City based on source analysis. Earth Sci. Front. 2024, 31, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-research/epa-positive-matrix-factorization-50-fundamentals-and-user-guide (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Kohonen, T. The self-organizing map. Neurocomputing 1998, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohonen, T.; Oja, E.; Simula, O.; Visa, A.; Kangas, J. Engineering applications of the self-organizing map. Proc. IEEE 1996, 84, 1358–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesanto, J.; Alhoniemi, E. Clustering of the self-organizing map. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2000, 11, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigdeli, A.; Maghsoudi, A.; Ghezelbash, R. Application of self-organizing map (SOM) and K-means clustering algorithms forportraying geochemical anomaly patterns in Moalleman district, NE lran. J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 233, 106923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Hu, G.; Yu, R.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Y. Self-organizing map (SOM) and positive matrix factorization (PMF) Models for source apportionment of metals in sediments of a wetland park. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 5070–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z. Assessment of soil environmental capacity for heavy metals in Shantou City, Guangdong Province, China: Source analysis and enrichment evaluation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.C.; Wang, W.Y.; Pan, J.J.; Lu, H.D.; Liao, Q.L. Research of heavy metal environmental capacity in Lishui District, Nanjing. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 45, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Pan, Y.; Peng, H.; Zeng, M.; Huang, C. Time-space simulation, health risk warning and policy recommendations of environmental capacity for heavy metals in the Pearl River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wei, W.; Song, Y.; Pan, Y. Evaluation and prediction of environmental capacities of heavy metals in the surface sediments of lakes in Huoqiu County. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 6106–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Ding, L.; Xie, S.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, J.; Peng, H. Spatiotemporal simulation, early warning, and policy recommendations of the soil heavy metal environmental capacity of the agricultural land in a typical industrial city in China: Case of Zhongshan City. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, W.; Wan, W.; Gou, S.; Luo, L. Assessing soil environmental capacity on different land uses in a suburban area of Chengdu, China. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2019, 45, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, B.; Xu, D.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M. Hydrodynamic impact on trace metals in sediments in the cascade reservoirs, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yun, X.Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J. Distribution and ecological assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the East Lake, China. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China; State Administration for Market Regulation. Soil Environmental Quality—Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB 15618-2018); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Yu, L.; Zhang, F.; Zang, K.; He, L.; Wan, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z. Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in cultivated land based on soil geochemical zoning: Yishui County, North China case study. Water 2021, 13, 3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, X.; Ren, W.; Dai, J. Background values of soil geochemistry in Shandong Province. Shandong Land Resour. 2018, 34, 39–43, CNKI:SUN:SDDI.0.2019-01-008. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; He, K.; Sun, Z.; Chen, G.; Cheng, H. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in the agricultural soils of an industrializing region and associated model uncertainty. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M.; Gündüz, K.; Sünbül, M.R. Pollution status, potential sources and health risk assessment of arsenic and trace metals in agricultural soils: A case study in Malatya province, Turkey. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. Chinese Population Exposure Parameter Manual. Adult Volume; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. Chinese Population Exposure Parameters Handbook (Children Volume: 6–17 Years Old); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- US EPA. Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Liu, Y.; He, Z.H.; Niu, X.K.; Zhang, D.; Pan, B. Health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in a small watershed of a mining area in Yunnan. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment) Final; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Duan, X.L. Exposure Factors Handbook of Chinese Population; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Alharthy, R.D.; Zubair, M.; Ahmed, M.; Rafique, S. Toxic and heavy metals contamination assessment in soil and water to evaluate human health risk. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Exposure Factors Handbook; National Center for Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/about-exposure-factors-handbook (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Li, Y.W.; Wang, J.; Ju, T.Z.; Wang, L.N.; Zhang, S.N.; Zha, X.H. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and human health risk assessment in soils from different functional areas of Baiyin, Gansu, China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Yin, R.S.; Zhang, H.; Yao, L. Bioaccumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Soil-Rice System in a Typical Seleniferous Area in Central China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, T.N.; Wu, X.; Shi, H.D.; Gao, F.; Li, X.Z.; Wang, Y.; Luan, T.; Fan, P. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of arable land soil in Haigou small watershed. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 8, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xia, T.; Jia, X. Spatial variation and pollution risk assessment of heavy metals in industrial soil based on geochemical data and GIS-A case of an iron and steel plant in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 104, 6826–6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Dai, J.; Yu, C.; Ren, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Cao, H.; Zeng, X.; Ren, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Soil geochemistry Reference value of 17 cities in Shandong Province. Shandong Land Resour. 2019, 35, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Q.H.; Yan, M.C. Handbook of Elemental Abundance for Applied Geochemistry; Geological Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Q.H.; Ma, S.M. Comparison between chemical composition of bedrocks in the upper reaches and that of alluvial plain soils in the lower reaches of a drainage area. Geol. Bull. China 2008, 27, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H. Soil Chemistry; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zong, K. Trace Element Geochemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.H.; Wang, Q.C.; Lu, X. Distribution and speciation of mercury in the peat bog of Xiaoxing’an mountain, Northeastern China. Env. Pollut. 2003, 124, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonokhuu, S.; Batbold, C.; Chuluunpurev, B. Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil of major cities in Mongolia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Xu, Z.; Bao, P.; He, M.; Dou, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and source of arsenic and heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunde, Southeast China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 148, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.J.; Parker, D.R.; Clarke, J.M. Metals and Micronutrients—Food Safety Issues. Field Crops Res. 1999, 60, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; He, J.; Luo, L. Spatial distribution characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in vineyard soil at east piedmont of Helan Mountains. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 34, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Z.G.; Cheng, K.; Qu, Y.P.; Chai, F.H.; Hao, J.M. Trend and characteristics of atmospheric emissions of Hg, As, and Se from coal combustion in China, 1980–2007. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11905–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, P.A.; Hintelman, H.; Lobos, G.; Bravo, M.A. Mercury and Methylmercury Levels in Soils Associated with Coal-Fired Power Plants in Central-Northern Chile. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T. Mercury Pollution in Soil Environment: Current Status and Its Influencing Factors. Earth Environ. 2022, 50, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.G.; Peng, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Ma, H.H.; Xu, R.T.; Cheng, X.M.; Hou, Z.L.; Chen, Z.; Li, K.; Cheng, H.X. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals at township scale in the high background of heavy metals, Southwestern, China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4197–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanos, N.; Rodríguez Martín, J.A. Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in soils: Spatial variability in the Duero River basin (Spain). Geoderma 2012, 189–190, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Lei, H. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.M.; Xu, F.; Wang, Q.G.; Shen, Z. Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.P.; Tu, Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Yang, Z. Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H. Forms, contents and distribution of Cu, Zn in some orchard soils in Shandong Province. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2002, 18, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z. Spatiotemporal variability and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a industrially developed city. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Xu, X. Quantitative evaluation of human health risk of heavy metals in soils based on positive matrix factorization model and geo-statistics. Environ. Sci 2020, 41, 5114–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, C.P.; Deng, J.; Kang, P.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y. Ecological health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in eastern Yinan County, Shandong Province. Geol. China 2022, 49, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, B.C.; Chen, L.; Yuan, X.X.; Shao, M.J.; Dong, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.C. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Honeysuckle and Soil From the Main Producing Area in China. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2021, 35, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, R.Q.; Li, Y.P.; Li, Y.; Duan, G.; Gao, X. Characteristics and Potential Ecologic al Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Garlic Producing Areas of Jinxiang. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Factors | Description | Unit | Values | Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Child | |||||
| C | Heavy metal concentration in topsoil | mg·kg−1 | – | – | This study | |
| IngR | Ingestion rate | mg·d−1 | 100 | 200 | [41,42] | |
| InhR | Inhalation rate | m3·d−1 | 7.5 | 15 | [41,42] | |
| EF | Exposure frequency | d·a−1 | 350 | 350 | [43,44] | |
| ED | Exposure duration | a | 24 | 6 | [41,42] | |
| CF | Conversion factor | kg·mg−1 | 1 × 10−6 | 1 × 10−6 | [42,45] | |
| SA | Exposed skin area | cm2 | 5700 | 2800 | [41,42] | |
| AF | Skin adherence factor | mg·cm−2·d−1 | 0.07 | 0.2 | [41,42] | |
| ABS | Dermal absorption factor | unitless | 0.01 | 0.01 | [45] | |
| PEF | Particle emission factor | m3·kg−1 | 1.36 × 10−9 | 1.36 × 10−9 | [41,42] | |
| BW | Average body weight | kg | 62.5 | 16 | [42,43] | |
| AT | Average time | non-carcinogens | d | ED × 365 | [39,40,46] | |
| carcinogens | d | 70 × 365 | ||||
| RfD | Source | SF | Source | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingestion | Dermal | Inhalation | Ingestion | Dermal | Inhalation | |||
| As | 3.00 × 10−4 | 1.23 × 10−4 | 3.00 × 10−4 | [42,46] | 1.50 | 1.50 | 4.30 × 10−3 | [47] |
| Cd | 1.00 × 10−4 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 1.00 × 10−4 | [45] | 6.10 | 6.10 | 1.80 × 10−3 | [47] |
| Cu | 4.00 × 10−2 | 1.20 × 10−2 | 4.02 × 10−2 | [45] | – | – | – | – |
| Cr | 3.00 × 10−3 | 6.00 × 10−5 | 2.86 × 10−5 | [42,46] | – | – | 42.00 | [47] |
| Hg | 3.00 × 10−4 | 2.10 × 10−5 | 3.00 × 10−4 | [42,46] | – | – | – | – |
| Ni | 2.00 × 10−2 | 5.40 × 10−3 | 2.06 × 10−2 | [42] | – | – | 8.40 × 10−1 | [47] |
| Pb | 3.50 × 10−3 | 5.25 × 10−4 | 3.25 × 10−3 | [45] | – | – | – | – |
| Zn | 3.00 × 10−1 | 6.00 × 10−2 | 3.00 × 10−1 | [42] | – | – | – | – |
| pH | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 4.82 | 3.50 | 0.030 | 34.19 | 11.71 | 0.017 | 11.58 | 17.85 | 26.93 |
| Maximum | 7.78 | 12.12 | 0.280 | 202.06 | 47.30 | 0.141 | 149.73 | 61.98 | 176.51 |
| Mean | 6.21 ± 0.02 | 7.16 ± 0.07 | 0.127 ± 0.002 | 68.21 ± 0.70 | 23.13 ± 0.28 | 0.040 ± 0.001 | 25.52 ± 0.45 | 27.15 ± 0.22 | 62.44 ± 0.83 |
| S.D. | 0.40 | 1.44 | 0.04 | 14.53 | 5.72 | 0.02 | 9.24 | 4.61 | 17.17 |
| CV (%) | 6.5 | 20.2 | 34.9 | 21.3 | 24.7 | 38.7 | 36.2 | 17.0 | 27.5 |
| SEQRCS (1) | pH ≤ 5.5 | 30.00 | 0.300 | 150.00 | 50.00 | 0.500 | 60.00 | 70.00 | 200.00 |
| 5.5 < pH ≤ 6.5 | 30.00 | 0.300 | 150.00 | 50.00 | 0.500 | 70.00 | 90.00 | 200.00 | |
| 6.5 < pH ≤ 7.5 | 30.00 | 0.300 | 200.00 | 100.00 | 0.600 | 100.00 | 120.00 | 250.00 | |
| SD topsoil (2) | 7.32 | 8.60 | 0.132 | 62.00 | 22.60 | 0.031 | 27.10 | 23.60 | 63.30 |
| SD baseline value (3) | 8.01 | 8.70 | 0.092 | 62.60 | 21.30 | 0.016 | 27.90 | 21.40 | 58.60 |
| China topsoil (4) | 6.70 | 11.20 | 0.100 | 61.00 | 23.00 | 0.030 | 26.90 | 26.00 | 74.20 |
| Metal | Partial Correlation Coefficient | p-Value | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | As | −0.152 | 0.002 | ** |
| Cd | −0.218 | <0.001 | *** | |
| Cr | 0.084 | 0.089 | n.s. | |
| Cu | −0.134 | 0.006 | ** | |
| Hg | −0.181 | <0.001 | *** | |
| Ni | 0.096 | 0.051 | n.s. | |
| Pb | −0.123 | 0.012 | * | |
| Zn | −0.141 | 0.004 | ** |
| As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Csp | Minimum | 28.98 | 0.04 | −4.64 | 11.88 | 0.81 | −111.89 | 63.05 | 52.85 |
| Maximum | 48.38 | 0.61 | 360.18 | 198.45 | 1.31 | 194.85 | 226.46 | 501.91 | |
| Mean | 40.14 | 0.39 | 207.47 | 83.37 | 1.08 | 113.10 | 153.69 | 332.43 | |
| S.D. | 3.25 | 0.10 | 58.33 | 47.25 | 0.10 | 34.49 | 31.80 | 59.69 | |
| CV/% | 8.10 | 25.58 | 28.11 | 56.67 | 9.03 | 30.50 | 20.69 | 17.95 | |
| Css | pH ≤ 5.5 | 41.63 | 0.39 | 200.03 | 59.18 | 1.06 | 73.58 | 98.78 | 304.88 |
| 5.5 < pH ≤ 6.5 | 41.63 | 0.39 | 200.03 | 59.18 | 1.06 | 96.08 | 143.78 | 417.38 | |
| 6.5 < pH ≤ 7.5 | 41.63 | 0.39 | 312.53 | 171.68 | 1.29 | 163.58 | 211.28 | 417.38 | |
| As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental capacity level | High Capacity | 156 | 219 | 145 | 260 | 73 | 276 | 208 | 265 |
| Moderate Capacity | 270 | 146 | 247 | 142 | 354 | 143 | 217 | 152 | |
| Low Capacity | 1 | 57 | 34 | 24 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 9 | |
| Alert Level | 0 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Overloaded Level | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Range of Pi | 0.70~1.16 | 0.11~1.54 | −0.01~1.30 | 0.20~1.46 | 0.76~1.02 | −0.68~1.39 | 0.43~1.13 | 0.17~1.26 | |
| Proportion/% | High Capacity | 36.5 | 51.3 | 34.0 | 60.9 | 17.1 | 64.6 | 48.7 | 62.1 |
| Moderate Capacity | 63.2 | 34.2 | 57.8 | 33.3 | 82.9 | 33.5 | 50.8 | 35.6 | |
| Low Capacity | 0.2 | 13.3 | 8.0 | 5.6 | 0 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 2.1 | |
| Alert Level | 0 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.2 | |
| Overloaded Level | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Adult | Child | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADDing | ADDder | ADDinh | ADDing | ADDder | ADDinh | |
| As | 3.93 × 10−6 | 1.57 × 10−7 | 5.26 × 10−10 | 7.35 × 10−6 | 2.06 × 10−7 | 2.35 × 10−10 |
| Cd | 6.96 × 10−8 | 2.78 × 10−9 | 9.31 × 10−12 | 1.36 × 10−7 | 3.81 × 10−9 | 4.35 × 10−12 |
| Cu | 3.70 × 10−5 | 1.48 × 10−6 | 4.95 × 10−9 | 2.89 × 10−4 | 8.10 × 10−6 | 9.25 × 10−9 |
| Cr | 1.09 × 10−4 | 4.35 × 10−6 | 1.46 × 10−8 | 5.12 × 10−4 | 1.43 × 10−5 | 1.64 × 10−8 |
| Hg | 6.39 × 10−8 | 2.55 × 10−9 | 8.55 × 10−12 | 4.99 × 10−7 | 1.40 × 10−8 | 1.60 × 10−11 |
| Ni | 4.08 × 10−5 | 1.63 × 10−6 | 5.46 × 10−9 | 3.19 × 10−4 | 8.93 × 10−6 | 1.02 × 10−8 |
| Pb | 4.34 × 10−5 | 1.73 × 10−6 | 5.81 × 10−9 | 3.39 × 10−4 | 9.50 × 10−6 | 1.09 × 10−8 |
| Zn | 9.99 × 10−5 | 3.99 × 10−6 | 1.34 × 10−8 | 7.81 × 10−4 | 2.19 × 10−5 | 2.50 × 10−8 |
| HQ-non-canc. | As | Cd | Cu | Cr | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | HI | Proportion of HQ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Minimum | 2.43 × 10−2 | 2.15 × 10−3 | 2.14 × 10−3 | 2.24 × 10−4 | 1.18 × 10−3 | 1.38 × 10−2 | 3.59 × 10−2 | 1.13 × 10−3 | 5.61 × 10−2 | 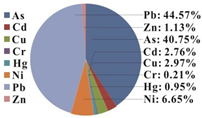 |
| Maximum | 7.02 × 10−3 | 2.30 × 10−4 | 5.31 × 10−4 | 3.79 × 10−5 | 1.46 × 10−4 | 1.06 × 10−3 | 1.03 × 10−2 | 1.72 × 10−4 | 2.24 × 10−2 | ||
| Mean | 1.44 × 10−2 | 9.74 × 10−4 | 1.05 × 10−3 | 7.57 × 10−5 | 3.35 × 10−4 | 2.34 × 10−3 | 1.57 × 10−2 | 3.99 × 10−4 | 3.53 × 10−2 | ||
| S.D. | 2.90 × 10−3 | 3.40 × 10−4 | 2.59 × 10−4 | 1.61 × 10−5 | 1.29 × 10−4 | 8.49 × 10−4 | 2.67 × 10−3 | 1.10 × 10−4 | 5.93 × 10−3 | ||
| Amount (>1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Child | Minimum | 4.43 × 10−2 | 3.84 × 10−3 | 1.62 × 10−2 | 1.04 × 10−3 | 8.22 × 10−3 | 1.03 × 10−1 | 2.22 × 10−1 | 8.38 × 10−3 | 2.80 × 10−1 | 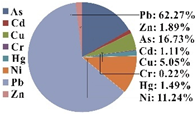 |
| Maximum | 1.28 × 10−2 | 4.11 × 10−4 | 4.00 × 10−3 | 1.76 × 10−4 | 1.02 × 10−3 | 7.99 × 10−3 | 6.43 × 10−2 | 1.28 × 10−3 | 1.02 × 10−1 | ||
| Mean | 2.62 × 10−2 | 1.74 × 10−3 | 7.90 × 10−3 | 3.51 × 10−4 | 2.33 × 10−3 | 1.76 × 10−2 | 9.75 × 10−2 | 2.97 × 10−3 | 1.57 × 10−1 | ||
| S.D. | 5.29 × 10−3 | 6.07 × 10−4 | 1.95 × 10−3 | 7.47 × 10−5 | 9.02 × 10−4 | 6.38 × 10−3 | 1.65 × 10−2 | 8.16 × 10−4 | 2.64 × 10−2 | ||
| Amount (>1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| CR-canc. | As | Cd | CR | TCR | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RfDing | RfDdermal | RfDinh | RfDHQing | RfDdermal | RfDinh | As | Cd | Cr (RfDinh) | Ni (RfDinh) | |||
| Adult | Maximum | 9.97 × 10−6 | 3.98 × 10−7 | 3.83 × 10−12 | 9.37 × 10−7 | 3.74 × 10−8 | 3.70 × 10−14 | 1.04 × 10−5 | 9.74 × 10−7 | 1.82 × 10−6 | 2.69 × 10−8 | 1.15 × 10−5 |
| Minimum | 2.88 × 10−6 | 1.15 × 10−7 | 1.10 × 10−12 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 4.01 × 10−9 | 3.96 × 10−15 | 2.99 × 10−6 | 1.04 × 10−7 | 3.07 × 10−7 | 2.08 × 10−9 | 3.70 × 10−6 | |
| Mean | 5.89 × 10−6 | 2.35 × 10−7 | 2.26 × 10−12 | 4.24 × 10−7 | 1.69 × 10−9 | 1.68 × 10−14 | 6.13 × 10−6 | 4.41 × 10−7 | 6.13 × 10−7 | 4.59 × 10−9 | 7.18 × 10−6 | |
| S.D. | 1.19 × 10−6 | 4.74 × 10−8 | 4.56 × 10−13 | 1.48 × 10−7 | 5.91 × 10−9 | 5.85 × 10−15 | 1.24 × 10−6 | 1.54 × 10−7 | 1.31 × 10−7 | 1.66 × 10−9 | 1.37 × 10−6 | |
| Amount (>10−4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Child | Maximum | 1.87 × 10−5 | 5.23 × 10−7 | 1.71 × 10−12 | 1.83 × 10−6 | 5.12 × 10−8 | 1.73 × 10−14 | 1.92 × 10−5 | 1.88 × 10−6 | 2.04 × 10−6 | 5.03 × 10−8 | 2.07 × 10−5 |
| Minimum | 5.39 × 10−6 | 1.51 × 10−7 | 4.95 × 10−13 | 1.96 × 10−7 | 5.49 × 10−9 | 1.85 × 10−15 | 5.54 × 10−6 | 2.02 × 10−7 | 3.44 × 10−7 | 3.89 × 10−9 | 6.56 × 10−6 | |
| Mean | 1.10 × 10−5 | 3.09 × 10−7 | 1.01 × 10−12 | 8.29 × 10−7 | 2.32 × 10−8 | 7.82 × 10−15 | 1.13 × 10−5 | 8.52 × 10−7 | 6.87 × 10−7 | 8.57 × 10−9 | 1.29 × 10−5 | |
| S.D. | 2.23 × 10−6 | 6.23 × 10−8 | 2.04 × 10−13 | 2.89 × 10−7 | 8.11 × 10−9 | 2.73 × 10−15 | 2.29 × 10−6 | 2.98 × 10−7 | 1.46 × 10−7 | 3.10 × 10−9 | 2.47 × 10−6 | |
| Amount (>10−4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Chu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Z. Heavy Metal Source Apportionment, Environmental Capacity, and Health Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils of a Rice-Growing Watershed in Eastern China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212275
Yu L, Chu Y, Zhou Z, Zhang J, Li S, Li H, Zhang Z, Zhang F, Shi Z. Heavy Metal Source Apportionment, Environmental Capacity, and Health Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils of a Rice-Growing Watershed in Eastern China. Agriculture. 2025; 15(21):2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212275
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Linsong, Yanling Chu, Zhaoyu Zhou, Jingyi Zhang, Shiyong Li, Huayong Li, Zhigao Zhang, Fugui Zhang, and Zeming Shi. 2025. "Heavy Metal Source Apportionment, Environmental Capacity, and Health Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils of a Rice-Growing Watershed in Eastern China" Agriculture 15, no. 21: 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212275
APA StyleYu, L., Chu, Y., Zhou, Z., Zhang, J., Li, S., Li, H., Zhang, Z., Zhang, F., & Shi, Z. (2025). Heavy Metal Source Apportionment, Environmental Capacity, and Health Risk Assessment in Agricultural Soils of a Rice-Growing Watershed in Eastern China. Agriculture, 15(21), 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212275







