The Impact of Environmental Regulation and Cognition of Manure Treatment on the Resource Utilization Behaviors of Swine Farmers
Abstract
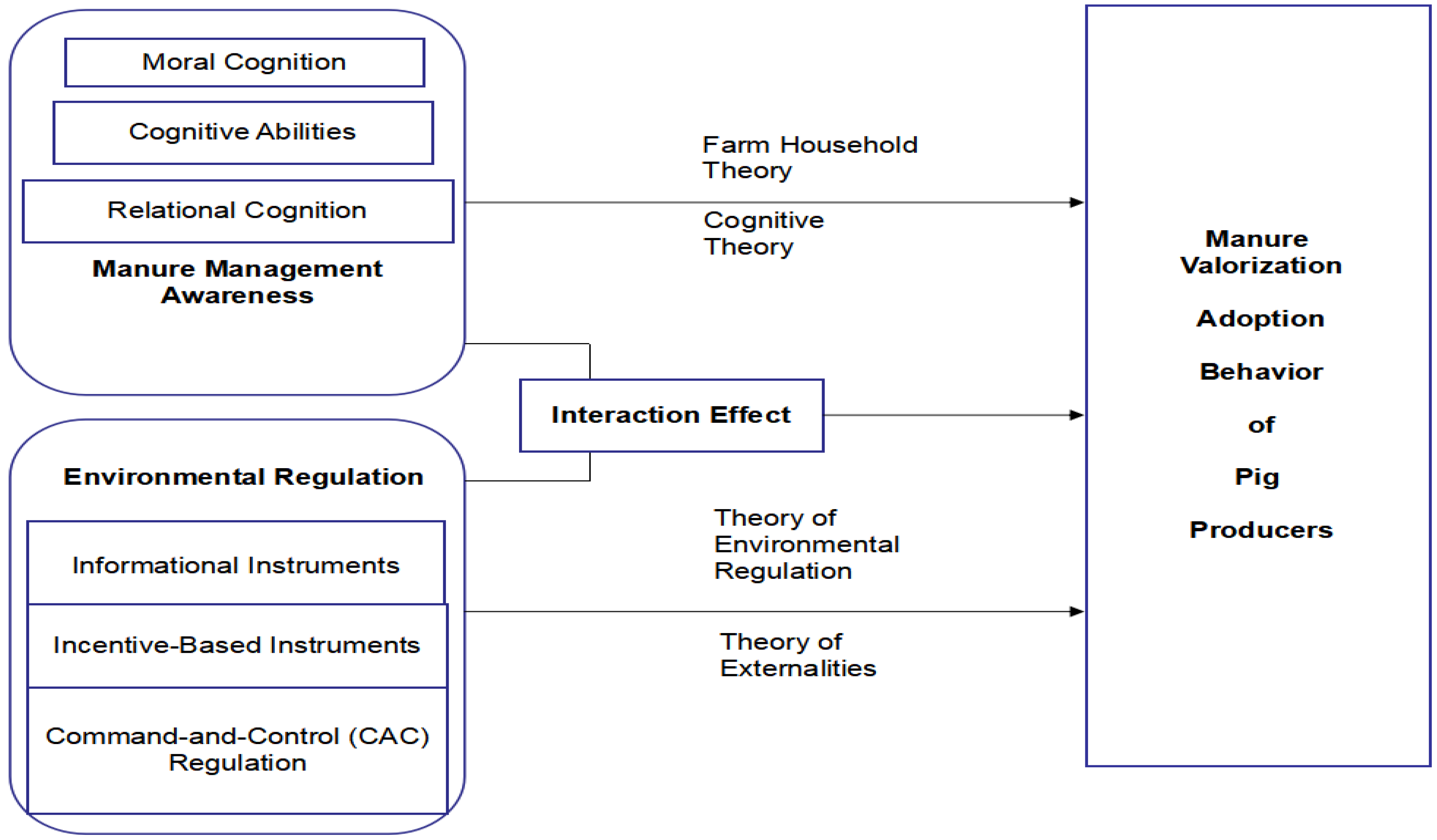
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Analysis
2.1. The Impact of Farmers’ Cognition of Manure Treatment on the Resource Utilization of Swine Manure Behavior
2.2. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on the Behavior of Farmers Toward Resource Utilization of Swine Manure
2.3. The Interactive Effects of Cognition of Manure Treatment and Environmental Regulation on Farmers’ Behavior Regarding the Resource Utilization of Swine Manure
3. Data, Variables, and Models
3.1. Data Source
3.2. Basic Characteristics of Sampled Farmers
3.3. Variable Definitions
3.3.1. Dependent Variable
3.3.2. Independent Variables
3.3.3. Control Variables and Instrumental Variables
3.4. Model Specification
3.4.1. Factor Analysis Method
3.4.2. Ordered Probit Model
4. Results
4.1. Benchmark Regression Analysis
4.2. Endogeneity Correction
4.3. Analysis of Interaction Effects
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
- (1)
- Analysis of Resource Utilization Behavior by Farmers with Different Farming Scales
- (1)
- Analysis of resource utilization behaviors among different generations of farmers
4.5. Robustness Check
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, K.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Li, J.Q. Effect of digital economy on large-scale pig farming: An empirical study from China. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 2238985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W. Does scaling up pig farming promote carbon neutrality among pig farmers? Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 9027–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council; Division on Earth; Committee on Nutrient Requirements of Swine. Nutrient Requirements of Swine; National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Li, J.Q. Except for environmental protection, promoting income: An analysis of the role of outsourcing livestock manure on promoting farmers’ incomes. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.A. Environmental Economics and Natural Resource Management; Routledge: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, T.T.; Massey, R.; McCann, L.; Canter, T.; Omura, S.; Willett, C.; Roach, A.; Key, N.; Dodson, L. Increasing the Value of Animal Manure for Farmers; Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Zheng, X.; Long, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, J.Q. Environmental regulation, rural residents’ health investment, and agricultural eco-efficiency: An empirical analysis based on 31 Chinese provinces. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.T.; Xiao, Y.N.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhao, S. How does central-local interaction affect local environmental governance? Insights from the transformation of central environmental protection inspection in China. Environ. Res. 2024, 243, 117668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankiw, N.G. Principles of Economics; Cengage Learning: Independence, KY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.R.; Wang, C.; Yang, R.J.; Sun, M.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, X.H. Research on the progress of agricultural non-point source pollution management in China: A review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Q.; Liu, Z.Z.; Ai, J.; Chen, Z.J. Effect of pig breeding scale on manure resource utilization-The moderating effect based on technology cognition. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0314410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, P.H.; Bi, W.T.; Qi, Q.; Xie, F.J. Contract farming and pro-environmental behavior: Insights from beef cattle farmers. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1590726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Tao, J.Y. An analysis of farmers’ resource disposal methods for livestock and poultry waste and their determinants. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 18, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.D.; Li, J.G.; Tang, Y.Q.; Pan, P.Y.; Xu, L. Human factors and their acting pathway influencing livestock and poultry farmers’ willingness to environmental management in coastal areas: A model of bayesian network. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, M. Relationship between livestock pollution and the environmental behaviour of farmers: A case study of Xiantao, China. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2018, 17, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.M.; Luo, S.L.; Xie, H.L.; Li, X.B. Intergenerational differences and influencing factors of farmers’ terrace abandonment behavior: Based on a questionnaire survey of 2382 rural households in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 35, 315–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Xu, X.Y.; Liu, L.L. Attribution and causal mechanism of farmers’ willingness to prevent pollution from livestock and poultry breeding in coastal areas. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 7193–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapa Tankosić, J.; Ignjatijević, S.; Lekić, N.; Kljajić, N.; Ivaniš, M.; Andžić, S.; Ristić, D. The role of environmental attitudes and risk for adoption with respect to farmers’ participation in the agri-environmental practices. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Cheng, P.; Yang, F. Study on the impact of digital transformation on green competitive advantage: The role of green innovation and government regulation. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, X. Can social learning promote farmers’ green breeding behavior? regulatory effect based on environmental regulation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garske, B.; Stubenrauch, J.; Ekardt, F. Sustainable phosphorus management in European agricultural and environmental law. Rev. Eur. Comp. Int. Environ. Law 2020, 29, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Kuang, Y.J.; Li, C.; Sun, M.X.; Zhang, L.X.; Chang, D.H. Waste pesticide bottles disposal in rural China: Policy constraints and smallholder farmers’ behavior. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.X.; Ren, Y.X.; Luning, P.A. Factors influencing Chinese farmers’ proper pesticide application in agricultural products—A review. Food Control 2021, 122, 107788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.L.; Chen, J.H.; Liang, X.; Li, D.H.; Chen, K. Government regulations, benefit perceptions, and safe production behaviors of family farms—A survey based on Jiangxi Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.J.; Liang, X.M.; Xue, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xue, Y.J. Can government regulation weak the gap between green production intention and behavior? Based on the perspective of farmers’ perceptions. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willy, D.K.; Holm-Müller, K. Social influence and collective action effects on farm level soil conservation effort in rural Kenya. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 90, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.M.; Chen, T.L.; Xie, Y.H. Influencing factors of farmers’ participation in agricultural waste resource utilization. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2024, 44, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.Z.; Baylis, K.; Kozak, R.; Bull, G. Farmers’ risk preferences and pesticide use decisions: Evidence from field experiments in China. Agric. Econ. 2016, 47, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Y.; Muminov, M.A.; Wu, G.L.; Liang, X.T.; Li, C.H.; Meng, J.; Li, L.J.; Cheng, D.; Song, Y.J.; Gu, X.; et al. Large reductions in pesticides made possible by use of an insect-trapping lamp: A case study in a winter wheat-summer maize rotation system. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xu, J.P.; Cao, H.M.; Wang, F.F.; Yan, Z.Y.; Muhammad, T. The impact of environmental regulation and economic expectations on crop-livestock integration among hog farmers: A field study from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 39514–39532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, P. Trustworthiness and competitive altruism can also solve the “tragedy of the commons”. Evol. Hum. Behav. 2004, 25, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Dan, W.; Ge, D.M.; Zhao, X.H.; Wang, Y.H. The impact of environmental regulations and government subsidies and their policy mix on clean technology innovation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 27, 1987–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.Y.; Huang, S.Z. The effect of environmental regulation and green subsidies on agricultural low-carbon production behavior: A survey of new agricultural management entities in Guangdong Province. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.H.; Zou, W. The effect of farmer’s cognition on the inconsistency between behavior and intention in manure application. Sage Open 2024, 14, 21582440241286583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jijue, W.; Xiang, J.L.; Yi, X.; Dai, X.W.; Tang, C.M.; Liu, Y.Y. Market participation and farmers’ adoption of green control techniques: Evidence from China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, L.; Behera, B.; Sethi, N. Do green finance, green technology innovation, and institutional quality help achieve environmental sustainability? Evidence from the developing economies. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 2709–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; He, K.; Zhang, J.B. How Do Environmental Regulations Affect Farmers’ Decision-making of Utilizing Livestock and Poultry Manure as Resources? From the Perspective of Perceptions of Large-scale Pig Farmers. China Rural Surv. 2021, 6, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.M.; Qian, Y.W.; Kaner, J. A study on smart home use intention of elderly consumers based on technology acceptance models. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Category | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | Variable | Category | Sample Size | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 424 | 83.3 | Party Membership | Yes | 115 | 22.59 |
| Female | 85 | 16.7 | No | 394 | 77.41 | ||
| Age/Years | ≤45 | 111 | 21.81 | Green Revenue Cognition | Disagree | 19 | 3.37 |
| 45~60 | 360 | 70.73 | Neutral | 53 | 10.41 | ||
| >60 | 38 | 7.74 | Agree | 437 | 85.85 | ||
| Education/Years | ≤9 | 361 | 70.92 | Risk Preference | High Risk | 103 | 20.24 |
| 9~13 | 96 | 18.86 | Moderate Risk | 109 | 21.41 | ||
| ≥13 | 52 | 10.22 | Low Risk | 297 | 58.35 |
| Dimension | Variable Definition and Values | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capability Cognition | Resource utilization of swine manure reflects my environmental responsibility and ability: 1 = strongly disagree; 2 = disagree somewhat; 3 = neutral; 4 = agree somewhat; 5 = strongly agree | 4.202 | 1.117 |
| Moral Cognition | Direct discharge of swine manure causes feelings of guilt and remorse: 1 = strongly disagree; 2 = disagree somewhat; 3 = neutral; 4 = agree somewhat; 5 = strongly agree | 4.393 | 0.961 |
| Relational Cognition | Direct discharge of swine manure impacts my reputation among neighbors: 1 = strongly disagree; 2 = disagree somewhat; 3 = neutral; 4 = agree somewhat; 5 = strongly agree | 4.462 | 0.794 |
| Constraint Regulation | Government supervision and punishment for swine manure management: 1 = very lenient; 2 = somewhat lenient; 3 = neutral; 4 = fairly strict; 5 = very strict | 3.754 | 1.118 |
| Guidance Regulation | Government training intensity on resource utilization of swine manure: 1 = none; 2 = low; 3 = moderate; 4 = high; 5 = very high | 3.190 | 1.263 |
| Incentive Regulation | Government rewards and subsidies for on-site manure resource utilization: 1 = very low; 2 = low; 3 = moderate; 4 = high; 5 = very high | 3.248 | 1.451 |
| Variable | Variable Definition and Coding | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Utilization Behavior | Number of resource utilization behaviors by farmers: 1 = none; 2 = one type; 3 = two types; 4 = three types | 2.275 | 0.473 |
| Manure Treatment Cognition | Calculated based on factor scores | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Environmental Regulation | Calculated based on factor scores | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Age | Actual age in years | 50.650 | 8.399 |
| Years of Education | Number of years of education | 9.024 | 3.237 |
| Risk Preference | Preferred investment type: 1 = high risk; 2 = moderate risk; 3 = low risk | 2.010 | 0.645 |
| Communist Party Membership | Whether a member of the Communist Party: Yes = 1; No = 0 | 0.226 | 0.419 |
| Number of Family Members | Number of people in the household | 5.002 | 1.643 |
| Cadre Household Status | Whether the household includes a cadre: Yes = 1; No = 0 | 0.194 | 0.578 |
| Number of People Engaged in Swine Farming | Number of people in the household engaged in swine farming | 1.833 | 0.940 |
| Years Engaged in Swine Farming | Number of years engaged in swine farming | 13.569 | 9.592 |
| Proportion of Farming Income | Proportion of farming income to total family income (%) | 65.614 | 27.848 |
| Cognition of Green Revenue | Perception of increased income through manure resource utilization: 1 = strongly disagree; 2 = disagree; 3 = neutral; 4 = agree; 5 = strongly agree | 4.234 | 0.834 |
| Variable | Oprobit Model | Oprobit Model (Marginal Effect/%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | |
| Manure Treatment Cognition | 0.148 ** (0.064) | −0.237 (0.002) | −4.389 ** (0.019) | 4.366 ** (0.019) | 0.259 (0.002) | |
| Environmental Regulation | 0.239 *** (0.062) | −0.381 * (0.002) | −7.069 *** (0.018) | 7.032 *** (0.017) | 0.418 * (0.002) | |
| Capability Cognition | 0.137 ** (0.067) | |||||
| Moral Cognition | 0.141 * (0.082) | |||||
| Relational Cognition | −0.096 (0.098) | |||||
| Constraint Regulation | −0.036 (0.067) | |||||
| Guidance Regulation | 0.136 ** (0.063) | |||||
| Incentive Regulation | 0.106 ** (0.050) | |||||
| Age | 0.001 (0.008) | 0.002 (0.008) | −0.002 (0.000) | −0.045 (0.002) | 0.045 (0.002) | 0.003 (0.000) |
| Education Years | 0.052 ** (0.021) | 0.056 *** (0.021) | −0.089 (0.001) | −1.648 *** (0.006) | 1.639 *** (0.006) | 0.097 (0.001) |
| Risk Preference | 0.107 (0.093) | 0.102 (0.093) | −0.163 (0.002) | −3.028 (0.027) | 3.012 (0.027) | 0.179 (0.002) |
| Party Membership | −0.162 (0.153) | −0.177 (0.152) | 0.282 (0.003) | 5.235 (0.045) | −5.208 (0.045) | −0.309 (0.003) |
| Household Members | −0.071 * (0.037) | −0.068 * (0.037) | 0.108 (0.001) | 2.003 * (0.011) | −1.992 * (0.011) | −0.118 (0.001) |
| Cadre Household | 0.113 (0.099) | 0.117 (0.099) | −0.187 (0.002) | −3.461 (0.029) | 3.443 (0.029) | 0.205 (0.002) |
| Engagement in Swine Farming | −0.008 (0.067) | −0.007 (0.067) | 0.011 (0.001) | 0.208 (0.020) | −0.207 (0.020) | −0.012 (0.001) |
| Farming Years | 0.009 (0.007) | 0.009 (0.007) | −0.014 (0.000) | −0.260 (0.002) | 0.259 (0.002) | 0.015 (0.000) |
| Farming Income Proportion | 0.002 (0.002) | 0.002 (0.002) | −0.004 (0.000) | −0.068 (0.001) | 0.068 (0.001) | 0.004 (0.000) |
| Green Revenue Cognition | −0.017 (0.073) | 0.016 (0.001) | 0.290 (0.021) | −0.289 (0.021) | −0.017 (0.001) | 0.016 (0.001) |
| LR chi2 | 48.31 ** | 40.21 *** | ||||
| Pseudo R2 | 0.074 ** | 0.062 *** | ||||
| Variable | IV-Oprobit | |
|---|---|---|
| First Stage | Second Stage | |
| Number of Visits | 0.165 *** (0.055) | |
| Manure Treatment Cognition | 0.817 *** (0.192) | |
| Controlled Variables | Controlled | |
| atanhrho_12 | −0.863 ** | |
| Variable | Oprobit | |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Standard Error | |
| Moral Cognition × Constraint Regulation | −0.246 *** | 0.106 |
| Capability Cognition × Guidance Regulation | 0.189 * | 0.065 |
| Control Variables | Controlled | |
| Pseudo R2 | 0.089 | |
| LR chi2 | 58.27 *** | |
| Variable | Large-Scale Farmers | Small-Scale Farmers | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Standard Error | Coefficient | Standard Error | |
| Capability-oriented Cognition | 0.197 | 0.135 | 0.157 *** | 0.061 |
| Moral Cognition | 0.284 ** | 0.135 | 0.096 | 0.091 |
| Relational Cognition | −0.150 | 0.278 | −0.066 | 0.123 |
| Constraint Regulation | 0.007 | 0.126 | −0.051 | 0.071 |
| Guidance Regulation | 0.024 | 0.114 | 0.181 *** | 0.068 |
| Incentive Regulation | 0.065 | 0.112 | 0.108 * | 0.055 |
| Control Variables | Controlled | Controlled | ||
| Pseudo R2 | 0.0765 | 0.0955 | ||
| Sample Size | 104 | 405 | ||
| Variable | Young and Middle-Aged Farmers | Older Generation Farmers | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Standard Error | Coefficient | Standard Error | |
| Capability Cognition | 0.177 * | 0.093 | 0.096 | 0.104 |
| Moral Cognition | 0.103 | 0.117 | 0.157 | 0.123 |
| Relational Cognition | −0.172 | 0.148 | −0.016 | 0.138 |
| Constraint Regulation | −0.123 | 0.105 | 0.052 | 0.092 |
| Guidance Regulation | 0.094 | 0.092 | −0.182 ** | 0.090 |
| Incentive Regulation | 0.167 ** | 0.072 | 0.069 | 0.074 |
| Control Variables | Controlled | Controlled | ||
| Pseudo R2 | 0.068 | 0.203 | ||
| Sample Size | 248 | 261 | ||
| Variable | Model 7 | Model 8 | Model 9 | Model 10 | Model 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manure Treatment Cognition | 0.045 ** | 0.264 ** | 0.148 ** | 0.150 ** | 0.150 ** |
| (0.021) | (0.123) | (0.064) | (0.064) | (0.064) | |
| Environmental Regulation | 0.082 *** | 0.465 *** | 0.240 *** | 0.243 *** | 0.245 *** |
| (0.021) | (0.112) | (0.062) | (0.062) | (0.062) | |
| Control Variables | Controlled | Controlled | Controlled | Controlled | Controlled |
| R2 | 0.0762 | 0.0669 | 0.0644 | 0.062 | 0.065 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, H. The Impact of Environmental Regulation and Cognition of Manure Treatment on the Resource Utilization Behaviors of Swine Farmers. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202131
Li J, Liu H, Zheng X, Liu W, Wang H. The Impact of Environmental Regulation and Cognition of Manure Treatment on the Resource Utilization Behaviors of Swine Farmers. Agriculture. 2025; 15(20):2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202131
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jianqiang, Hongming Liu, Xingqiang Zheng, Wenjie Liu, and Huan Wang. 2025. "The Impact of Environmental Regulation and Cognition of Manure Treatment on the Resource Utilization Behaviors of Swine Farmers" Agriculture 15, no. 20: 2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202131
APA StyleLi, J., Liu, H., Zheng, X., Liu, W., & Wang, H. (2025). The Impact of Environmental Regulation and Cognition of Manure Treatment on the Resource Utilization Behaviors of Swine Farmers. Agriculture, 15(20), 2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202131





