Abstract
Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a vital food crop for majority of the world’s population. However, its yield potential is significantly threatened by insect pests, which adversely affect production, quality, and overall food security. The diverse array of insect pests throughout wheat’s growth stages necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their interactions with wheat cultivation. This review critically assesses the diversity, biology, ecology, and management strategies of major insect pests in North India, including aphids, termites, pink stem borer, gram pod borer, armyworm, and brown wheat mite. These pests infest wheat at various growth stages, posing significant challenges to sustainable production. Moreover, existing pest control strategies are challenged by evolving agronomic practices in the region and climate change globally. As agricultural systems worldwide aim for sustainability and resilience in the face of climate change, this review advocates for the adoption of an integrated pest management (IPM) approach combining innovative and traditional pest control strategies to enhance ecosystem services and fortify the resilience of agricultural systems. By interlinking these pivotal elements, this review presents a valuable perspective on the important pests affecting wheat and the currently used IPM practices, emphasizing the need for adaptive management in the context of evolving climate challenges.
1. Introduction
Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), an esteemed member of the grass family Poaceae, is a vital staple food crop for majority of the world’s population [1]. Globally, 798.98 million tons of wheat were harvested in 2023 from approximately 220.4 million hectares (Mha) of land, making wheat the top-ranked grain crop by cultivated area during 2023 [2]. This cereal crop contributes about 20% of the total dietary calories and proteins worldwide [3,4]. Wheat is cultivated across a wide range of latitudes, with China, India, U.S.A., Russia, France, Canada, Australia, Germany, Pakistan, and Ukraine being the top ten wheat-producing countries [2]. However, wheat productivity is primarily constrained by a plethora of biotic and abiotic stressors [5]. Among biotic stressors, insect pests and diseases are the main limiting factors for wheat production, causing significant quantitative and qualitative losses [6]. Of the 10,000 documented insect species that damage crops used by humans for food [7], about 100 are harmful to wheat [8].
In India, wheat is the second most important cereal crop after rice and serves as a staple food, particularly in Northern India [9]. The country is the second-largest consumer of wheat globally, after China. Wheat is produced in many regions of India, including Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, West Bengal, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Jammu and Kashmir. However, the northern states like Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan, together account for about 65% of the country’s total wheat production. Uttar Pradesh ranks first in wheat production, contributing approximately 35.34 million metric tons in 2024, followed by Punjab with 17.74 million metric tons and Haryana with 11.19 million metric tons [10].
In India, insect pests cause an annual loss of USD 49.85 million in wheat, with global losses estimated at 5–9% [11]. Before the Green Revolution, wheat was considered largely free from serious insect pests, with only the Gujhia weevil (Tanymecus indicus Faust) and grasshopper (Chrotogonus spp.) regarded as significant threats. However, the introduction of high-yielding semi-dwarf varieties, the increased use of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides, and advancements in production technologies have disrupted natural predator–prey balances, leading to pest outbreaks [12]. The shift to a monoculture rice–wheat cropping system further intensified pest pressures, as most wheat pests are either oligophagous or polyphagous, and this system provides a continuous food source that favors their buildup. As a result, new pests such as termites, aphids, armyworms, gram pod borers, and brown wheat mites have emerged as major threats [13,14,15]. Consequently, insect-induced yield losses in wheat have risen from an average of 3% in the pre-Green Revolution era to 5% in the post-Green Revolution era in India [16,17,18]. Furthermore, the continuous rice–wheat cropping system in the Indo-Gangetic Plains (area comprising Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal) has exacerbated pest pressures [19,20]. Mode of damage, and factors associated with increased incidence of major insect pests affecting wheat in North India are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
The main herbivorous insect pests affecting wheat crop in the North India.
Additionally, recent changes in climate, such as elevated temperatures and erratic rainfall patterns, are likely to amplify spatiotemporal variations in both abiotic and biotic stresses for wheat producers, leading to significant spatial changes in yield and grain quality [28]. This includes anticipated alterations in pest physiology and survival rates during heat waves or frosts, population growth dynamics and geographical range for insects, host-range expansion and shortened crop cycles [29,30,31]. For instance, warmer winters may increase the number of aphid generations within a single wheat growing season [32]. As temperatures rise, pests and pathogens are expected to spread beyond their traditional habitats; for instance, the English grain aphid, Sitobion avenae (Fabricius) has already expanded its range to cover nearly the entire Northern Hemisphere [33].
In recent years, to mitigate the adverse effects of residue burning on the environment, there has been a shift from conventional to conservation agriculture in North India. The adoption of residue management practices, such as using the Happy Seeder for sowing wheat in standing paddy stubbles, has inadvertently increased the prevalence of sporadic pests in wheat fields in North India. Such pests like pink stem borer (Sesamia inferens Walker), armyworm (Mythimna separata Walker), and root aphid (Rhopalosiphum rufiabdominalis Sasaki) have emerged as significant threats [14,17]. According to Singh et al. [34], 43% of farmers have reported moderate to severe pest issues in wheat crops grown with residue retention. This change in pest dynamics has also increased the cost of insecticide application by USD 8.6 per hectare (ha) in residue-retained wheat crops compared to those without residue [35].
The rapidly growing world population and urbanization has led to a significant surge in the demand for improving wheat production, which must rise at an annual rate of 2% despite limited land resources [36,37]. However, wheat yields are only increasing at a rate of 0.9% annually, falling short of the 2.4% needed to double global production by 2050 [38]. Kumar et al. [39] projected a reduction of 6–23% and 15–25% in wheat yield in India during the 2050s and 2080s, respectively, under projected climate change scenarios. Although disease-resistant varieties have been effective against wheat diseases like rust, chemical control remains the primary and most effective tool under high insect pest-pressure scenarios in wheat. To meet food security demands, substantial amounts of chemical fertilizers and pesticides are applied, elevating environmental issues, and contributing to pest resurgence due to economically misguided chemical control practices [40]. Indiscriminate pesticide use is costly, ecologically unsustainable, and leads to insect resistance development [41]. Therefore, it is crucial to explore alternative and more sustainable pest management practices that minimize these drawbacks while ensuring crop protection. Given the imperative to increase wheat productivity without expanding agricultural land area or intensifying water and fertilizer use, climate-smart innovative pest management techniques integrating interdisciplinary methodologies need to be developed. These approaches, aimed at reducing crop losses caused by various insect pests, should also enhance ecosystem services, and bolster the resilience of agricultural systems in response to climate change challenges. Implementing an integrated pest management (IPM) framework is essential in creating effective and resilient production systems. Like with other agricultural crops, IPM modules for wheat integrate diverse strategies including cultural, mechanical, biological, and refined chemical approaches, tailored to meet growers’ needs and address pest issues [20,42]. This review discusses the bio-ecology and current management practices of key wheat pests in North India, highlighting future challenges related to wheat IPM in this region.
2. Major Wheat Pests: Bio-Ecology and Their Management Strategies
In North India, wheat is sown during October–November and harvested in April. The primary insect pests currently causing economic damage at different growth stages of wheat (Figure 1 and Figure 2) include foliar aphids: corn leaf aphid (Rhopalosiphum maidis), bird cherry-oat aphid (Rhopalosiphum padi), English grain aphid (S. avenae), and Indian grain aphid (Sitobion miscanthi); termites (Microtermes obesi and Odontotermes obesus); oriental armyworm (M. separata); pink stem borer (S. inferens); gram pod borer (Helicoverpa armigera); brown wheat mite (Petrobia latens); and root aphid (R. rufiabdominalis). Among these, foliar aphids and termites are the most common and significant pests in this region. However, the pink stem borer and root aphids, traditionally pests of rice (Oryza sativa L.), are emerging as significant threats to wheat as well [17,43,44].
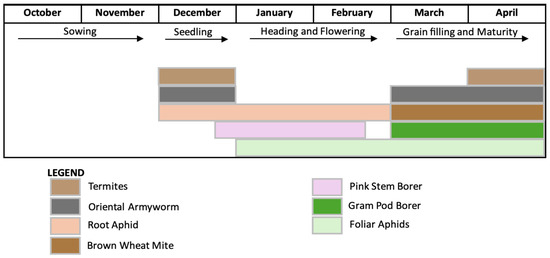
Figure 1.
Periods of activity of the major insect pests affecting wheat crop throughout the growing season in North India.
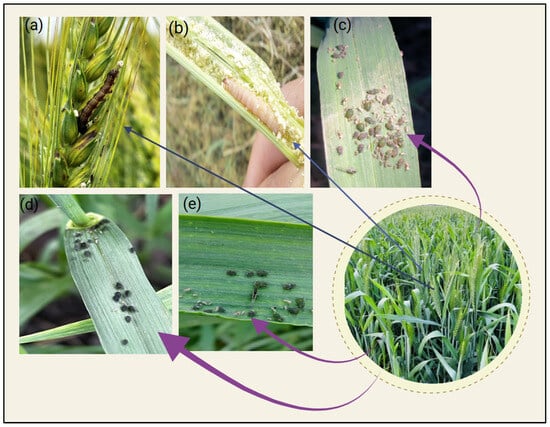
Figure 2.
Different species of foliar insect pests in wheat production in North India: (a) gram pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera, (b) pink stem borer, Sesamia inferens, (c) bird cherry-oat aphid nymphs, Rhopalosiphum padi, (d) black morph bird cherry-oat aphid adults in wingless form, and (e) olive green morph bird cherry-oat aphid adults in winged and wingless forms. Picture by Gurveer Singh.
2.1. Aphids
2.1.1. Pest Description
Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) are one of the major pests affecting agricultural crops including wheat globally, with more than 250 species known to infest both row and horticultural crops [45]. Globally, 64 aphid species are reported to colonize the bread wheat; however, the wheat crop is attacked predominantly by four aphid species viz. R. maidis (Corn leaf aphid), R. padi (Bird cherry-oat aphid), S. avenae (English grain aphid), and S. miscanthi (Indian grain aphid) in India. These aphid species are known to cause yield loss by directly (3–21%) sucking the plant sap and/or indirectly (20–80%) by transmitting fungal and viral diseases [46]. The cultivation of high-yielding Mexican varieties, coupled with increased use of fertilizers and irrigation, has contributed to the heightened prevalence of aphids [47]. Additionally, R. rufiabdominalis has been documented infesting wheat roots [48]. Recently, the potato aphid, Macrosiphum euphorbiae Thomas, initially a pest of solanaceous crops, has been reported in association with wheat crops in North India [49]. Interestingly, aphid species exhibit distinct feeding preferences on wheat. R. padi infests all above-ground plant parts, with a higher prevalence on leaves and stems. R. maidis is confined solely to leaf whorls. S. miscanthi infests leaves and earheads and is the dominant aphid species on earheads [50].
Both adult and nymph aphids damage wheat plants by sucking cell sap, reducing the vitality of the plants. Infested plants exhibit pale and silky leaves and eventually wilt. Aphids also excrete honeydew, leading to the development of black sooty mold on leaves, which reduces the photosynthetic activity [51]. Infestation often starts from the field’s periphery, particularly where trees are planted [52]. Key feeding areas for aphids on wheat plants include the flag leaf sheath, main stem, and immature kernels during the flowering stage, resulting in the death of spikes, and shriveled or empty grains. Aphid saliva causes yellow or whitish streaks on leaves [51]. Heavy infestations can lead to stunted growth, reduced leaf size, bleached spikes, purplish streaks on tillers, loss of dry weight, and reduced chlorophyll content due to disruptions in the electron transport chain in leaves [53,54,55]. Late-sown wheat experiences higher aphid populations during the vegetative phase, while wheat sown in a timely manner has more aphids on earheads during the reproductive stage [56]. The economic threshold level for aphid infestation is set at five aphids per earhead, determined by observing ten randomly chosen earheads from each of the four sections in a one-acre field [21]. Furthermore, foliar aphids transmit barley yellow dwarf virus (BYDV), which causes severe damage to the crop [57]. BYDV is transmitted by three aphid species, i.e., R. maidis, R. padi, and S. avenae [24].
2.1.2. Bio-Ecology and Management
Adult aphids are soft-bodied and range in color from green to black, typically living in small colonies on leaves and spikes. They exhibit various stages, including winged (alates) and wingless (apterous) sexual and asexual forms [58]. Aphid infestations typically start from January until crop maturity, with the most severe damage observed during February-March when ears are ripening [58]. Their rapid spread is facilitated by asexual reproduction, where viviparous females directly give birth to nymphs rather than laying eggs. Rhopalosiphum padi reproduces parthenogenetically for several generations before switching to sexual reproduction [27]. Sitobion miscanthi reproduces year-round through viviparous parthenogenesis, while S. avenae can reproduce both sexually and parthenogenetically [58,59]. During autumn, alates fly to primary hosts such as Cynodon dactylon in the case of S. avenae to mate and lay eggs, without producing any visible feeding symptoms [27,58]. Aphids go through four nymphal instars, each lasting around 2–3 days, completing their development cycle in 7–8 days depending on temperature conditions. They can produce over 10–15 generations per season. Wingless forms produce more offsprings than winged forms but have a shorter lifespan. In the field conditions, viviparous wingless forms are common and present in large numbers [58]. While alate forms aid in long-distance movement and develop in response to food and space shortages, apterous forms physically damage the plant by sucking sap from young leaves, which leads to leaf distortion [27,52]. The rate of development, number of offspring, and adult lifespan are influenced by the type of host species, its age, and temperature conditions. Cold and dry weather conditions favor rapid reproduction, resulting in population explosions [27,60]. Temperature and the plant’s growth stage play crucial roles in aphid population dynamics. The minimum threshold temperature for nymphal development is 1.57 °C, while the highest intrinsic growth rate occurs during the wheat jointing stage at 18–21 °C. However, excessively high temperatures can reduce aphid survival and spread [27].
To control aphids, cultural, physical, mechanical, biological, chemical, and host plant resistance methods can be used. Singh and Singh [23] reported that the early sowing of wheat helps escape peak aphid attacks, while timely and late sowing wheat coincides with peak populations. Installing sticky traps at a rate of 12 to 15 per hectare for monitoring aphid incidence is recommended. Yellow sticky traps are more effective than blue traps [61,62]. Additionally, the zero-tillage system for sowing wheat can help reduce aphids. Compared to conventional tillage, zero-tillage often leads to sparser crop growth, which is less attractive to foliar aphids. The surface residues left in the field can also act like reflective mulch, making it harder for aphids to settle on the crop [22]. Reduced tillage has also been shown to limit root aphid damage. Increased soil compaction and lower porosity under this system restrict aphid movement, resulting in reduced infestation levels [19]. Chaudary et al. [63] evaluated a push and pull strategy for managing aphids in wheat and found that peas as a trap crop proved beneficial in reducing foliar aphid population from main crop without aid of pesticides. This effect is likely due to the pea crop attracting a higher abundance of natural enemies, such as lady beetles and parasitic wasps, which help regulate foliar aphid populations more effectively than in wheat monocultures. Additionally, intercropping may disrupt aphid host-finding ability, as volatiles from non-host plants (i.e., pea) can mask or overlap with wheat odors, reducing colonization [64]. Resistance to R. padi and S. avenae has also been identified in T. monococcum wheat genotypes MDR045 and MDR049 under field conditions, thus this resistance can be incorporated into commercial wheat varieties [65]. Singh and Singh [66] screened advanced breeding lines of wheat and observed moderate resistance to foliar aphids in lines HI 8823(d), DBW 317, MACS 6774, PBW 873, DBW 378, HD 3386, and UAS 310. Similarly, R. padi number, weight, survival, and reproduction potential was significantly lower on resistant lines viz., W064 and W068 [67]. Additionally, Sharma and Singh [68] reported that R. padi resistance in Aegilops tauschii accessions, i.e., PAU 14232 and PAU 14576 involves combination of antixenosis and antibiosis resistance mechanisms.
Under favorable weather conditions, aphids may reach devastating levels through asexual reproduction, such that chemical control often becomes necessary [44]. As the aphid incidence starts from periphery spraying border rows to control their spread into the interiors of wheat field is recommended. Spraying of thiamethoxam 25 WG (50 g/ha) or 5% neem seed kernel powder when aphid infestation exceeds economic threshold level is suggested [21,61]. Similarly, a study by Pathania et al. [69] found that the reduction in aphids using an aqueous neem extract (5 L/ha) and neem seed kernel extract (10%) was comparable to the reduction achieved with thiamethoxam; thus, neem (Azadirachta indica L.) can be a good eco-friendly alternative to synthetic pesticides. Moreover, Katare et al. [70] found that foliar application of sulfoxaflor 12 SC (24, 27 and 30 g active ingredient (a.i.)/ha) resulted in 94.54, 95.27 and 96.03% reduction in aphid populations, respectively, with 30 g a.i./ha being the most economical. A variety of natural enemies including different lady beetle species, hoverflies, parasitic wasps, and green lacewings attack aphids in wheat fields (Figure 3). Among these, the seven-spotted lady beetle (Coccinella septempunctata) is the most commonly observed predator of aphids in wheat. Important parasitoid wasp species include Lysiphlebus testaceipes, Diaeretiella rapae, and Aphelinus varipes. The larvae of green lacewings (Chrysoperla carnea) also feed primarily on aphids, although they are less frequently encountered in wheat ecosystems. These beneficial insects collectively help suppress aphid populations and prevent them from reaching economically damaging levels [27].
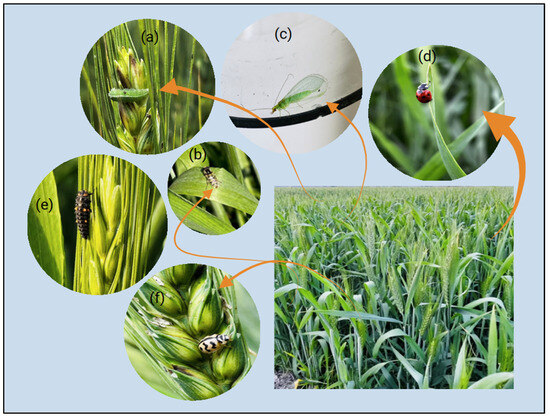

Figure 3.
Predatory insect species commonly found in wheat-growing regions of North India: (a) hoverfly larva; (b) hoverfly adult, Episyrphus balteatus; (c) green lacewing adult, Chrysoperla carnea; (d) seven spotted lady beetle adult, Coccinella septempunctata; (e) lady beetle larva; and (f) transverse lady beetle adult, Coccinella transversalis. Picture by: Gurveer Singh.
2.2. Termites
2.2.1. Pest Description
Termites are polyphagous social insects that belong to the order Blattodea and infra-order Isoptera, believed to have evolved around 220 million years ago from primitive wood-dwelling cockroaches [71,72]. They are classified into 12 families based on morphology and symbiotic relationships, with about 75% belonging to the largest family, Termitidae [73]. They live in highly organized colonies known as termitaria, with different castes such as workers, soldiers, and reproductive individuals [52]. Among the 300 termite species considered pests worldwide [74], about 35 species cause significant damage to both agricultural crops and infrastructure in India [75], leading to annual losses estimated at USD 35.12 million [76].
Ecologically, termites play a crucial role as major recyclers of lignocellulosic biomass from both live and dead plant material [73]. Termites are capable of degrading wheat straw lignin and polysaccharides with the help of their gut microbial symbionts [77]. Termites depend on enzymes secreted by intestinal protists like Mixotricha sp., and Trichonympha which are in turn associated with prokaryotes such as Bacillus sp., Enterobacter sp., Ochrobacterium sp., and Treponema sp. [73,78]; for the biodegradation of wheat straw [77]. Additionally, Termitomyces sp. fungus is cultivated within termite nests of higher termites, providing a protein-rich food source for the queen, king, and young termites [52,73].
Wheat is particularly susceptible to termite attacks throughout its growth stages with higher damage in rainfed and sandy soils than irrigated regions in India [21,75]. In particular, Odontotermes obesus and Microtermes obesi are the most destructive termite species of wheat in India, resulting in 43 to 80% yield losses [79,80,81]. Other termite species attacking wheat in North India include Odontotermes gurdaspurensis Holmgren and Holmgren and Microtermes mycophagus (Desneux) [82]. Overall, the damage due to termites can vary between 29 and 100% [83,84]. Termites feed on the roots and underground stem portions of plants at the seedling stage, typically 3–5 weeks after emergence [34,52]. Affected plants wither entirely and can be pulled and uprooted effortlessly, creating patchy gaps due to seedling death [52]. When termites attack plants during later growth stages, it leads to the development of white ears containing no grains.
2.2.2. Bio-Ecology and Management
Termites undergo the process of incomplete metamorphosis and complete their life cycle in three stages, i.e., egg, nymph, and adult [73]. Each termite colony is established and dominated by one queen and king. The queen can be up to 70 mm long while the king can be 10–20 mm long [52]. The queen lays thousands of eggs after mating in a nuptial chamber [85]. The eggs are generally dull, kidney-shaped, laid singly, and hatch in about 30–90 days. The nymph resembles the adult but are smaller in size and molts eight to nine times within 6–12 months to develop into a cream-colored adult with a dark-colored head [26,52]. The nymphs can either molt into workers or soldiers. A worker’s life span varies between 1 and 2 years with a mature colony comprising 200,000–2,000,000 workers [85]. Periodically, nymphs produce alate forms that swarm out for nuptial flights, typically during the monsoon season when the soil is wet from rain and therefore more easily penetrated by termites [26,52]. After mating, alates shed their wings and nest is established, and the abdomen of queen becomes substantially larger with thousands of eggs which upon oviposition hatch into young termites [52,86].
Insecticides remain the primary strategy for termite management in wheat crops worldwide [87]. Cultural methods to prevent termite infestation include destroying or burning crop residues, deep summer plowing to expose termite mounds and tunnels to sunlight and predators, flood irrigation, and application of fully decomposed farmyard manure [88]. The high-density sowing of wheat is also suggested, with appropriate thinning of plants that survive termite damage [27]. Termite damage is significantly higher in the early-sown crop compared to the timely-sown and late-sown crops, hence avoid early sowing of wheat in areas where termite infestation is a problem [23].
Amongst the chemical methods, seed treatment is quite efficacious against termites. Particularly, seed treatment with 4 mL of chlorpyriphos 20 EC or 1 g thiamethoxam 70 WS per kilogram (kg) of wheat seed is recommended before sowing wheat. Additionally, broadcasting 50 kg soil per hectare treated with 3 L chlorpyriphos 20 EC or 17.5 kg fipronil 0.3 G, followed by light irrigation can be practiced under severe infestations [21]. A study performed under semi-arid irrigated conditions in southwestern Punjab observed that seed treatment with thiamethoxam at 1 g/kg seed and broadcasting fipronil 0.3 G at 20 kg/ha significantly reduced damaged tillers per meter row compared to other treatments resulting in higher grain yields and relatively fewer harmful effects on natural enemy populations [89]. Additionally, Singh and Bala [90] reported that a pre-mixed combination of imidacloprid 18.5% + hexaconazole 1.5% at 2 mL/kg of wheat seed did not adversely affect germination, effectively reduced termite infestation, increased seed yield, and eliminated the need for separate treatments for termites and smuts. Mukhopadhyay et al. [91,92] evaluated a Steinernema abbasi-nematode enriched bioinsecticidal powder under field conditions and found a significant reduction in termite damage in wheat fields compared to the synthetic insecticide (chlorpyriphos 20% EC). In treated plants, agronomic traits such as plant height, spike weight, and number of spikelets per spike were also positively influenced, validating its potential as an effective biopesticide for organic farming and integrated pest management.
2.3. Oriental Armyworm
2.3.1. Pest Description
The oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata Walker (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), is a defoliator pest that widely affects wheat crops in the Indo-Gangetic plains, including regions like Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh [21,93]. It is a typical long-distance migratory insect that became a regular pest of late-sown wheat during the late 20th century and has caused huge economic losses since then [94,95,96]. Caterpillars are the only destructive stage in its life cycle [97] as they are capable of feeding on more than 300 plant species belonging to 100 families, i.e., rice, maize, sorghum, barley, sugarcane, and a variety of grasses [52,98,99]. The pest is called “Armyworm” due to its tendency to spread in a line across fields, consuming foliage as it moves, thus resembling a slow march. The larvae, after devastating one field, migrate to another field such that the field looks as though it has been subjected to cattle grazing [60]. Newly hatched larvae consume tender leaves while mature larvae feed on leaves, flag leaves, and ears, including awns and immature grains, and can cause up to 40% yield reductions [52,100]. Moreover, under severe infestations larvae may climb up to cut the stem just below the earhead [58]. Therefore, its outbreak may lead to complete crop loss depending upon the stage of crop [95]. Armyworm larvae hide during the day in stubbles or tillers, feeding at night or early morning. In moist conditions, they might feed during the daytime also [58]. However, pest attacks can be detected by spotting larvae and dark green fecal pellets near the plant’s stem. Armyworm infestations are more prominent in rice–wheat cropping systems [14,52]. This pest typically attacks wheat crops during March–April, but recent damage has also been reported in December in Happy Seeder + Mulcher-sown wheat or fields with large paddy straw loads [21,34].
2.3.2. Bio-Ecology and Management
Adults of armyworm are robust and tan colored with dark specks [15]. They are smaller than other cutworm-armyworm moths, measuring around 12 mm in length with a wingspan of 25–40 mm [52]. Forewings are grayish-yellow with circular and reniform spots having indistinct margins. The outer wing margin is obliquely blackened from the top rearward, featuring a dark streak and a row of dark spots. Hind wings are gray, with dark outer margin. Antennae are thread-like. Female moths lay about 500 eggs [58]. The eggs are round, shiny with fine reticulations and are deposited on the leaf surface in groups [52,101]. The hatching period ranges between 4 and 11 days in summer and 19 days in winter [26]. Upon hatching, the neonate larvae are very active and start feeding on the seedling leaves, thus its color changes from pale to light green. The larval stage is 13–14 days long during spring, but ranges between 88 and 100 days during winter and includes 6 instars [26,52]. Mature larvae are 30–40 mm long, green to pink with longitudinal light gray to black stripes and have a brown to orange head marked with an A-shaped pattern [102]. Pupation typically occurs in the soil at a depth of 0.5–5 cm, though it can also take place beneath dry leaves and lasts for about 9–13 days in May and 36–48 days in the winter. Thus, the life cycle is completed in 30–35 days and is repeated many times in a year [26]. The pest is capable of surviving on summer season crops like rice and continues to survive in the stubbles [58]. Extended drought periods followed by heavy rainfall increase its population [95].
To control armyworm, the foliar application of 1 L of quinalphos or 100 mL of chlorantraniliprole 18.5 SC in 200–250 L of water per hectare is effective in wheat crops. These insecticides will also control aphids. To enhance insecticide efficacy, applications should be carried out in the evening when armyworm larvae are most active. Alternatively, 17.5 kg of fipronil 0.3 G or 2.5 L of chlorpyriphos 20 EC mixed with 50 kg of moist sand can be spread across one hectare before first irrigation [21]. Singh and Sarao [103] observed that foliar application of chlorantraniliprole and soil application of fipronil are effective for managing armyworms in the early stages of wheat. However, commercial Bt formulations showed relatively less reduction in damage, with a 47–51% reduction observed over 14 days. Biocontrol agents are also efficacious for controlling this pest. For instance, the stink bug Andrallus spinidens (F.), found in the Kumaon region of Uttarakhand, preys on armyworm in wheat so can be exploited for biocontrol interventions [104]. Entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae causes significant mortality in second and fourth instar larvae under laboratory conditions, achieving 100% mortality in larval stages and 75% in pupal stages [105]. Similarly, in a laboratory study, the third and fourth larval instars of M. separata were highly susceptible to Heterorhabditis bacteriophora strain S15 EPN infection, with the highest mortality rates of 96% and 98%, respectively [106]. Ji et al. [107] exploited the use of RNAi to target and suppress the clock gene Msper, reporting a significant reduction in M. separata flight and reproductive activities. Thus, gene silencing can be developed as a novel pest control method against M. separata thereby decreasing its population and impact.
2.4. Pink Stem Borer
2.4.1. Pest Description
The pink stem borer (PSB), Sesamia inferens Walker (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) is a polyphagous pest that is prevalent in South and Southeast Asian countries [60]. Some important hosts of this pest are rice, wheat, sugarcane, oats, maize, sorghum, and pearl millet [52]. The PSB feeds on rice from July to October in North India and then migrates to wheat crops. Infestation rates of 5.7–11.10% have been observed in wheat [108]. The incidence of PSB is increasing due to adoption of zero tillage system for sowing wheat [109,110]. Early sown wheat shows heavier PSB incidence than late sown crop [21,27]. Furthermore, the continuous rice–wheat cropping rotation in the northwestern plains of India, coupled with mild winters and a reduced fallow period between rice harvest and wheat sowing, has heightened the incidence of this pest in the region [111]. It attacks the wheat crop at seedling stage and can cause up to 50–60% damage [52,111]. The larva bores into the stem of the young plant and kills the central shoot thereby causing ‘dead heart’ symptoms. Upon destroying one young wheat tiller, the larva subsequently starts feeding onto adjacent tillers. Nonetheless, damage is confined to a few areas in a wheat field and does not follow any random distribution. However, if the larvae attack the wheat plant at heading stage, ‘white ears’ are produced [13,110].
2.4.2. Bio-Ecology and Management
The adult moth is small, stout, and straw-colored with a wingspan of about 28 mm [112]. While the hind wings have 3–4 veins and are white in color, the forewings have a reddish-brown suffusion along the median nervure with 2–5 veins [113]. The pest exhibits sexual dimorphism as in males the antennae are hairy/ciliated while females have simple antennae [113,114]. The adult female lays creamish-white eggs arranged in several rows under the leaf sheath. Occasionally, eggs can also be found positioned at the crown of wheat plants, on the soil or in the leftover stubbles of rice plants [112]. The larva hatch within 7–10 days and immediately bores into the stem to feed on internal tissues. The larval stage lasts up to 20–30 days and comprises 8 larval instars. Fully grown caterpillars have brown heads and pinkish 30–40 mm long cylindrical bodies with pink and buff markings [26,52,113]. They pupate in the stem of the wheat plant for 8–10 days [26]. Male pupa is about 10.5–12 mm long and 2.5–3 mm wide possessing two pads guarding the 9th sternite. In contrast, the female pupa can be 15.5–17.5 mm long and 3–4.5 mm wide, with a bursa copulatrix located on the 8th sternite [114]. The life cycle of this pest typically spans 40–70 days with 4–6 generations in a year influenced by the prevailing climatic conditions [26]. The larva remains dormant in winter and hibernates in rice stubbles [115].
Sowing wheat in October can be discouraged in fields with severe PSB infestation in the preceding rice crop. Additionally, the removal and destruction of the rice stubbles at the time of first plowing after the harvest of rice crops also reduces the pest being carried over to the wheat. Fields can be irrigated, preferably during daytime, as this enhances insect predation by birds [21,58]. Moreover, Singh and Singh [23] investigated the effect of sowing dates on PSB, finding that PSB incidence was significantly higher in early-sown wheat (7.35%) compared to timely-sown (5.97%) and late-sown (3.01%) crops. Additionally, Muhammad et al. [116] demonstrated that the appropriate management of rice stubbles, particularly using a rotavator as a tillage tool before sowing wheat, significantly reduces the incidence of PSB in the wheat crop. In case of severe infestation, the soil application of 17.5 kg of fipronil 0.3 G or 2.5 L of chlorpyriphos 20 EC mixed with 50 kg of moist sand per hectare can be performed before first irrigation. Alternatively, the foliar application of 125 mL of chlorantraniliprole 18.5 SC in 200–250 L of water per hectare is also effective [21]. Similarly, fipronil 0.3% GR applied at 20 kg/hectare resulted in the maximum reduction in tiller damage and higher grain yield of wheat in the districts of Amritsar and Gurdaspur, located in the northwestern part of Punjab [117]. Timbadiya and Sisodiya [118] reported that chlorantraniliprole 18.5 SC at 0.006% resulted in the highest grain and straw yields and was similarly effective to Spinosad 45 SC in reducing dead heart percentage due to PSB in durum wheat. They also observed that seed treatment with chlorpyriphos 20 EC provided the highest incremental cost–benefit ratio, followed by chlorantraniliprole 18.5 SC and spinosad 45 SC. Soil application of diatomaceous earth (silicon source) at 300 kg/ha is more superior in reducing PSB population than conventional insecticides and improves wheat yield by enhancing total sugars, total phenols, antioxidant, and defensive enzyme activities [119]. Pawar et al. [120] investigated the effectiveness of octadecane, a plant herbivore induced volatile in combination with egg parasitoid Trichogramma chilonis releases, finding that it dramatically minimizes the damage caused by PSB by increasing the biocontrol potential of T. chilonis.
2.5. Gram Pod Borer
2.5.1. Pest Description
Helicoverpa armigera Hubner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), commonly known as the cotton bollworm, gram pod borer, corn earworm, or Old World (African) bollworm, is a highly polyphagous and sporadic pest of wheat and other crops. It affects over 181 plant species across 68 diverse families, including important crops such as cotton, sunflower, rice, maize, sorghum, tomato, chickpea, and other legumes [121,122,123,124,125]. This pest is distributed throughout Asia, Europe, Australia, and Africa [122,126] and is considered one of the most damaging insect pest species globally, with an estimated global loss exceeding USD 3 billion annually [125]. In India, this pest affects around 96 different crops and causing annual monetary losses of up to USD 2 billion [127]. It has been reported as a regular pest on wheat in Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Jammu and Kashmir [128].
Helicoverpa armigera’s notoriety stems from its polyphagy and the strong migratory abilities of its adults, capable of traveling up to 2000 km [129,130,131,132]. It is highly fecund, with rapid reproduction rates, completing 4–6 generations per year in most cropping regions, and up to 10–11 generations in some tropical climates [133,134,135]. Larvae are aggressive feeders, preferring reproductive structures but also consuming vegetative parts when necessary [136]. The pupae can enter facultative diapause during unfavorable conditions [135]. In wheat, a single caterpillar per tiller can cause a yield loss of 13.98% [137]. Young larvae consume leaves, while mature larvae feed directly on grains within heads, hollowing out internal tissues [26,52,138]. Additionally, its adults feed on wheat pollens, and first-generation larvae feed on wheat, while corn and cotton serve as hosts for subsequent generations [139]. The infestation rate on heads is up to 15%, but the grain damage on infested heads is about 3.90% [138].
2.5.2. Bio-Ecology and Management
Helicoverpa armigera is a holometabolous insect, which means that it has four major stages, the egg, larva, pupa, and adult [140]. The female moth lays 600–800 yellow ribbed eggs individually on the tender parts and buds of plants during the early evening hours [26,52,141]. The eggs are pomegranate shaped and 0.4–0.6 mm in diameter [140]. After 24 h of egg laying, a dark red or brown ring is developed on top of the eggs, which fully darken prior to hatching [52]. The eggs hatch in 2–4 days, and the caterpillars are initially brown and later turn green with dark broken lateral and dorsal stripes [26,141]. The larval stage comprises 4–6 instars and is completed in 28–35 days [52]. Fully mature larvae stop feeding and migrate to the soil for pupation. The pupa is dark brown in color and measures around 19 mm in length. The pupal stage lasts for 12–16 days [27,52]. Adult moths are strongly built and are 14–19 mm long with a wingspan ranging between 35 and 40 mm. Forewings are black or dark brown with kidney-shaped markings at the center. Hindwings display a gray band along the outer edges and are cream-white. Adults exhibit sexual dimorphism as male moths are yellowish-brown, while female moths are orange-brown in color [27]. The adults have a lifespan of 12–16 days [52]. Helicoverpa armigera is more prevalent in fields following a cotton–wheat rotation, typically infesting wheat near maturity, i.e., during March–April [21,27]. Staggered sowing and frequent irrigation can lead to heavy pest incidence [26]. However, wheat does not suffer significant harm from this pest and can act as a bridge host for H. armigera, facilitating its carry-over [26].
Protecting crops from H. armigera infestations is a significant challenge due to its polyphagous feeding behavior, extensive host range, ecological plasticity across diverse agro-climatic regions, and its demonstrated capacity to evolve resistance to multiple classes of chemical insecticides [142]. Despite various control measures, chemical control using synthetic and semi-synthetic insecticides remain the most widely used method. Approximately 50% of the total insecticide applications in India and China target H. armigera [143]. Nevertheless, regular pest population monitoring using light traps, pheromone traps, and in situ assessments at various levels is essential for its effective management [144]. Cultural practices like crop rotation with non-host crops and growing intercrops or barrier crops can minimize pest incidence [27,58]. The foliar spray of quinalphos at 2 L in 250 L of water per hectare is recommended for pest control in wheat crops [21]. Additionally, emamectin benzoate shows significant systemic toxicity on H. armigera larvae, making it a promising tool for IPM [145].
Furthermore, plant-derived products and biorational insecticides are being researched for their eco-safety and effectiveness in reducing pod borer growth and reproduction [146]. For instance, β-sitosterol a compound present in the stem extracts of Thevetia neriifolia has shown potential in inhibiting H. armigera growth by causing systemic toxicity and reducing midgut enzyme activities [147]. da Costa Inacio et al. [148] reported the use of tagitin and C-enriched leaf extract of Tithonia diversifolia provided high insect mortality, and antifeedant activity against H. armigera larvae. Furthermore, synergistic effects have been observed with a 1:1 combination of β-sitosterol and triflumuron, a chitin biosynthesis inhibitor, significantly inhibiting H. armigera larval growth and adult emergence [149]. These compounds can be promising alternatives to synthetic insecticides.
Various natural predators and parasitoids also play a crucial role in regulating Helicoverpa populations. These natural enemies can maintain pest levels below economic thresholds without insecticides [140]. Common natural enemies include hemipterans, coleopterans, chrysopids, ants, spiders, flies, and parasitoids wasps like Microplitis, Trichogramma, Telenomus, and others [150]. Moreover, the stink bug A. spinidens, found in the Kumaon region of Uttarakhand, preys on lepidopteran larvae, including H. armigera in wheat [104].
2.6. Brown Wheat Mite
2.6.1. Pest Description
The brown wheat mite (BWM), Petrobia latens, Muller 1776 (Acari: Tetranychidae), is a serious pest of dryland agriculture [151]. It is prevalent in the warmer regions of central India, extending somewhat into the northern plains. In Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, Delhi, Rajasthan, Punjab, and western Uttar Pradesh, it poses a significant threat to unirrigated wheat fields [152,153]. Damage is always associated with drought stress [154]. It was first documented on cumin in Rajasthan [155]. It can feed on onion, garlic, wild oat, melon, cucumber, coriander, carrot, strawberry, gladiolus, cotton, barley, lettuce, apple, lucerne, rice, and sorghum in addition to wheat [52]. It is mainly found on the upper surface of leaves [154]. Both adults and nymphs suck plant sap by inserting their needle-like stylets into the leaf blades, sheaths, green stem, and spikes [152]. Affected plants display a pale yellow/bronze appearance with stippling on leaves. Severe damage is inflicted on the lower leaves of wheat and barley, leading to iron deficiency and desiccation [156]. Mites start feeding from leaf tips, causing leaves to dry and die from the tip downwards. Infested fields look scorched and withered under heavy pest pressure. As a result of feeding, plants become chlorotic, resulting in unhealthy grain formation, but BWMs do not spin webs on the leaves [26]. The affected grains shrink and appear shriveled, thus losing their cosmetic and market value [52]. BWMs also transmit barley yellow streak mosaic virus on recrops of barley under dry conditions [154].
2.6.2. Bio-Ecology and Management
Mites are microscopic, measuring approximately 0.5 mm in length, with a metallic brown to black body and pale-yellow legs. Their front legs are noticeably longer than the remaining three pairs [61,157,158]. Eggs are typically laid under clods or in crevices, singly or in batches, in active (non-diapause) or dormant (diapause) states. Active eggs are invisible to the naked eye and are red in color, while dormant eggs are white and visible beneath clods. A female can lay 6–10 winter eggs and 1–3 summer eggs daily, resulting in 23–90 winter eggs (red in color) and 8–27 summer eggs (white in color) during her lifetime [158,159]. In cold and wet conditions, active eggs hatch in 9–11 days. Dormant eggs can persist in the soil for extended periods and hatch if wetted, usually in the following spring [26,154]. The nymphs are yellow in color and nymphal stage lasts 8–11 days. Adult females live for 10–20 days and reproduce through parthenogenesis. This parthenogenetic mite can raise three annual generations [159]. Consequently, mite populations often escalate to pest levels in dry conditions. The entire life cycle lasts 25.5 days, encompassing about eight developmental stages [26]. This mite thrives during long-term droughts lasting several years, as well as during extended dry spells within a cropping season [154].
BWM population levels are the highest in March–April in rainfed wheat [61]. Rainfall exceeding 6.35 mm often helps reduce mite populations and alleviate plant stress [27]. However, eggs laid in the soil can still lead to new generations [15]. Mites are active during the day and rest in the soil at night. While the economic threshold is not well defined, more damage occurs if plants are stressed or poorly tillered [52]. Research findings propose an economically justified treatment threshold of 25–50 BWMs per leaf in wheat plants that are 15.24 cm to 22.86 cm tall [27].
Rainfall or irrigation can significantly reduce mite numbers in wheat fields. For the proper management of the BWM, weekly monitoring should focus on field edges and corners where infestations are likely to begin. Managing volunteer wheat is crucial for preventing BWM [154]. Rotating wheat or barley with a non-host crop and deep plowing to eliminate diapausing mite eggs can also be effective. Adjusting planting dates to coincide with unfavorable weather conditions for mites can further help in their control [52]. Numerous natural predators have been reported to be effective against BWM under field environments. Recently, predatory mite viz., Tencateia villosa was reported in association with BWM from Rajasthan, while Anystis baccarum was reported from Punjab, and Himachal Pradesh, especially in dryland areas practicing rainfed farming [160]. Neoseiulus imbricatus is another predatory mite also associated with BWM and widely distributed throughout Punjab [161]. For chemical interventions, thiamethoxam 25 WG @ 50 g/ha or 5% neem seed kernel powder, typically used for aphid control, also helps manage BWM. However, a blanket application of thiamethoxam at the flag leaf stage can reduce coccinellid predators, ultimately increasing BWM populations [61]. Additionally foliar application of propargite at 0.15% have shown strong efficacy [27]. Certain wheat genotypes, such as NW 3069, MACS 6221, VI 924, PDW 315, PDW 317, DBW 46, HPW 308, HPW 309, HI 8692, and WH 1076, have demonstrated moderate resistance to mite infestations [162]. Singh and Singh [66] found that wheat germplasm VL 907, HI 1628, PBW 872, VL 3030, and UAS 310 exhibited the lowest BWM infestations, making them valuable sources for breeding programs focused on BWM resistance.
3. Challenges and Opportunities in Wheat Pest Management Under Changing Agroecological Conditions
Sustaining wheat production amidst changing climate and agricultural practices is crucial for food security. Continuous and large-scale rice–wheat cropping system in North India has intensified insect pest pressure on wheat [22]. The adoption of long-duration wheat varieties to increase the yield potential has reduced the fallow period between rice harvest and wheat sowing, facilitating the migration of pests like PSB and root aphid from rice to wheat crop [17,19,43,44]. Rice and wheat are typically harvested using combine harvesters, which leave stubbles of approximately 30–40 cm. While wheat straw is often salvaged for fodder, rice straw has limited fodder value due to its nutritional composition [163]. Consequently, rice residue has traditionally been disposed of through open-field burning [164]. However, environmental concerns over residue burning have prompted the adoption of conservation tillage, inadvertently increasing the threat posed by pests such as PSB and armyworm in subsequent wheat crops [19,164]. The integration of super straw management systems on combines results in loose straw spread evenly across fields [165,166], which, together with undisturbed stubble in reduced or zero tillage conditions, creates favorable conditions for pest survival. Under conventional tillage, the life cycles of pests are often disrupted through plowing because surviving insect stages are exposed to natural enemies as well as adverse environmental conditions. PSB, once regarded primarily as a rice pest, has now emerged as a cross-crop threat by surviving in rice stubble. In wheat crops sown under zero tillage, more than 70% of PSB larvae persist within underground rice stubble [167]. These surviving populations subsequently shift to wheat during favorable conditions, attacking wheat plants as early as the seedling stage, as illustrated in Figure 4 [19,22]. As a result, PSB incidence is lowest in conventionally sown wheat without residue (0.05%) but higher in residue-retained wheat (0.25%), showing that residue and zero-tillage help the pest survive and infest wheat earlier [110,168].
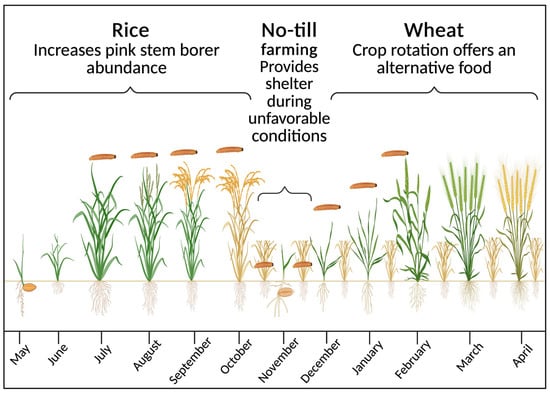
Figure 4.
Incidence and seasonal dynamics of pink stem borer (Sesamia inferens) in rice–wheat crop rotation under no-tillage agricultural practices in North India (months shown in parentheses). First, rice crops concentrate pink stem borers, and their larvae feed on rice during the summer months (July–October). Second, after harvesting, pink stem borer larvae hide under rice stubble in wheat crop fields sown under no-tillage conditions (October–November) and later begin feeding on wheat plants (December until mid-February).
Similarly, armyworm damage, historically reported during March–April, is now frequently observed as early as December in wheat crops sown under zero tillage conditions, likely due to rice straw residue that shelters the infesting larvae [21,103]. Farmers increasingly report challenges in pest management in residue-retained fields, compounded by shifts in pest occurrence and peak damage periods. Moreover, the timing of insecticide applications has shifted due to changes in the pest bioecology and earlier infestations. Consequently, farmers now need to target PSB in wheat at the seedling stage, while armyworm infestations require treatment as early as December [21,164]. Rice residue not only supports pest survival but also shields larvae beneath the straw, protecting them from both chemical sprays and natural enemies. As a result, insecticides often fail to reach target pests, prompting farmers to increase application rates and frequency to compensate for reduced efficacy, which further disrupts natural biological control. Tillage intensity also influences natural enemy dynamics. Reduced tillage practices benefit resident predators like rove beetles and spiders as these survive well under less disturbed habitats but disadvantage non-resident natural enemies such as wasps and coccinellids which are more attracted to vigorous and green crop plants produced in tilled fields. Thus, tillage practices and residue management strategies directly shape pest dynamics and determine the effectiveness of different biological control strategies [22,169,170,171]. This underscores the need for systematic studies to reevaluate how different residue management systems affect pest biology, seasonal population dynamics and their management.
Climate variations are also impacting insect pest biology and behavior, altering their distribution and severity [172]. Research indicates that pests and pathogens are moving towards the poles due to global warming, expanding their range by 2.7 km per year since 1960 [33]. For instance, drought stress can flare up armyworm infestation in wheat [173]. Similarly, climate change can also influence the efficacy of biocontrol agents. Moreover, due to the changing climate many insect species are shifting to unconventional host plants for survival. Examples of significant pests include the potato aphid, M. euphorbiae, notorious for infesting solanaceous crops, now shifting its host range to wheat fields in New Delhi [49]. Similarly, the heavy incidence of the sugarcane leafhopper, Pyrilla perpusilla Walker, a major pest of sugarcane, has been reported in wheat fields in Chhattisgarh, located in central India [174].
Therefore, when developing IPM strategies, the interaction between the insect pest complex, climate change, and tillage practices must be considered. Robust pest monitoring systems are essential for estimating economic thresholds and detecting secondary and invasive pests to minimize yield losses. Adapting planting systems with increased crop diversity can mitigate climate change effects. Developing pest-resistant cultivars that balance resistance traits with climate resilience is essential for IPM practices. The timely release of stress-tolerant biocontrol agents synchronized with crop phenology, considering climate change-induced stress on their biology, is crucial for effective pest management [175].
Future climate scenarios are likely to exacerbate the wheat insect pest management, potentially reducing the efficacy of current management strategies. To address these challenges, research should focus on developing accurate monitoring systems to predict the impact of climate change on wheat insect pests. Understanding the biology and ecology of these pests in relation to their interactions with crops will provide valuable insights for effective management. Multidisciplinary research on climate change impacts and mitigation strategies is crucial to sustaining global wheat productivity. Proactive strategies, such as frequent pest scouting for early detection and eradication, preventive control measures, and using predictive modeling to forecast potential outbreaks or new introductions, could significantly enhance future of wheat insect pest management.
In addition to climate change, the shift in wheat pest dynamics due to continuous rice–wheat cropping and conservation tillage highlights the urgent need for adaptive pest management strategies. Implementing IPM framework that combines key components like crop diversification, pest-resistant cultivars, and optimizing the use of biocontrol agents is essential. Exploring novel methods such as genetic engineering for development of pest resilient varieties, RNA interference to target vital pest genes, synergistic combinations of biorational pesticides, precision agriculture, and optimizing plant herbivore-induced volatiles for improved biological control are promising avenues for the advancement of wheat insect pest management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S. and N.K.J.; methodology, G.S. and N.K.J.; software, G.S. and N.K.J.; validation, G.S.; investigation, G.S.; resources, N.K.J.; data curation, G.S.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S.; writing—review and editing, N.K.J.; visualization, G.S. and N.K.J.; supervision, N.K.J.; project administration, N.K.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful for support from the Open Access Publishing Fund administered through the University of Arkansas Libraries. N.K.J. acknowledges support from the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture. Mention of commercial products or companies is for informational purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the authors or their affiliated institutions. The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of their institutions. Illustrations were created with BioRender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Erenstein, O.; Jaleta, M.; Mottaleb, K.A.; Sonder, K.; Donovan, J.; Braun, H.-J. Global trends in wheat production, consumption and trade. In Wheat Improvement: Food Security in a Changing Climate; Reynolds, M.P., Braun, H.-J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSTAT: Crops and Livestock Products; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2025; Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/visualize (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Shiferaw, B.; Smale, M.; Braun, H.-J.; Duveiller, E.; Reynolds, M.; Muricho, G. Crops that feed the world 10. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by wheat in global food security. Food Secur. 2013, 5, 291–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kaur, J.; Ram, H.; Singh, J.; Kaur, S. Agronomic bio-fortification of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to alleviate zinc deficiency in human being. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 22, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langridge, P.; Alaux, M.; Almeida, N.F.; Ammar, K.; Baum, M.; Bekkaoui, F.; Bentley, A.R.; Beres, B.L.; Berger, B.; Braun, H.-J.; et al. Meeting the Challenges Facing Wheat Production: The Strategic Research Agenda of the Global Wheat Initiative. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zia-Khan, S.; Owusu-Adu, S.; Miedaner, T.; Müller, J. Early detection of Zymoseptoria tritici in winter wheat by infrared thermography. Agriculture 2019, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, D. Predictions of climate change impacts on agricultural insect pests vis-à-vis food crop productivity: A critical review. Ethiop. J. Sci. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 7, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, M.A.; Saeed, S.; Naeem-Ullah, U.; Matloob, A.; Wajid, M.; Siddique, A.B.; Shahid, R.; Zia, H.U.U.R.; Bilal, H.; Ramzan, M. Insect pest complex of wheat crop. In Current Trends in Wheat Research; Ansari, M.-u.-R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadas, S.; Kumar, T.K.; Singh, G.P. Wheat production in India: Trends and prospects. In Recent Advances in Grain Crops Research; Iqbal, A., Shah, F., Khan, Z., Turan, M., Olgun, M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Production Volume of Wheat Across India in Financial Year 2024, by Leading State (in 1,000 Metric Tons). 2025. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1365756/india-wheat-production-by-leading-state/ (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Narang, D.; Singh, B.; Grewal, S.K.; Kaur, S.; Chhuneja, P. Comparative biochemical and transcriptomic analyses reveal the bases of Rhopalosiphum padi L. resistance in Aegilops tauschii Coss. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2025, 186, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, D.A.; Babu, G.R. Lessons from the aftermaths of Green Revolution on food system and health. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 644559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deol, G.S. Latest trends for insect-pest management in wheat. In Proceedings of the Specialized Workshop on Identification and Management of Weeds, Insect-Pests and Diseases in Wheat, CETWPT, PAU, Ludhiana, India, 20 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B. Changing scenario of insect pests of wheat and their management. In Theory and Practice of Integrated Pest Management; Arora, R., Singh, B., Dhawan, A.K., Eds.; Scientific Publishers: Rajasthan, India, 2017; ISBN 93-86347-82-2. [Google Scholar]
- Farook, U.B.; Khan, Z.H.; Ahad, I.; Maqbool, S.; Yaqoob, M.; Rafieq, I.; Rehman, S.A.; Sultan, N. A review on insect pest complex of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2019, 7, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, G.S.; Dhawan, A.K.; Singh, R. Biodiversity and ecological agriculture: Issues and perspectives. Indian J. Ecol. 2007, 34, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, G.S.; Jindal, V.; Dhawan, A.K. Insect pest problems and crop losses: Changing trends. Indian J. Ecol. 2010, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Rutkoski, J.E.; Velu, G.; Singh, P.K.; Crespo-Herrera, L.A.; Guzmán, C.; Bhavani, S.; Lan, C.; He, X.; Singh, R.P. Harnessing diversity in wheat to enhance grain yield, climate resilience, disease and insect pest resistance and nutrition through conventional and modern breeding approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kular, J.S.; Ram, H.; Mahal, M.S. Relative abundance and damage of some insect pests of wheat under different tillage practices in rice–wheat cropping in India. Crop Prot. 2014, 61, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katare, S.; Reza, M.W.; Jasrotia, P.; Saharan, M.S.; Sharma, I. Efficacy of botanicals and biopesticides against foliage feeding aphids in wheat. Indian J. Entomol. 2018, 80, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PAU. Package of Practices for Crops of Punjab. Rabi 2024–25; Punjab Agricultural University: Ludhiana, India, 2024; pp. 1–22. Available online: https://www.pau.edu/content/ccil/pf/pp_rabi.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Jasrotia, P.; Bhardwaj, A.K.; Katare, S.; Yadav, J.; Kashyap, P.L.; Kumar, S.; Singh, G.P. Tillage intensity influences insect-pest and predator dynamics of wheat crop grown under different conservation agriculture practices in rice-wheat cropping system of Indo-Gangetic Plain. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, P. Influence of sowing date and weather parameters on the relative abundance and damage of major insect-pests of wheat in north-western plains of India. Agric. Res. J. 2021, 58, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaich, B.B.; Vashisth, K.S. Barley yellow dwarf: A new viral disease for India. Indian Phytopathol. 1963, 16, 318–319. [Google Scholar]
- Nogia, V.K.; Sharma, A. Biology of the brown wheat mite Petrobia latens. Indian J. Entomol. 2003, 65, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Navik, O.S.; Varshney, R. Field pests of wheat and their management. In Wheat a Premier Food Crop; Kumar, A., Kumar, A., Prasad, B., Eds.; Kalyani Publishers: Kolkata, India, 2017; pp. 322–347. [Google Scholar]
- Jasrotia, P.; Singh, B.; Nagpal, M. Biology and management strategies of major insect-pests of wheat. In New Horizons in Wheat and Barley Research: Crop Protection and Resource Management; Kashyap, P.L., Gupta, V., Prakash Gupta, O., Sendhil, R., Gopalareddy, K., Jasrotia, P., Singh, G.P., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradgley, N.S.; Bacon, J.; Bentley, A.R.; Costa-Neto, G.; Cottrell, A.; Crossa, J.; Cuevas, J.; Kerton, M.; Pope, E.; Swarbreck, S.M.; et al. Prediction of near-term climate change impacts on UK wheat quality and the potential for adaptation through plant breeding. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 1296–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, N.J.; Urwin, P.E. The interaction of plant biotic and abiotic stresses: From genes to the field. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3523–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrode, S.D.; Macfadyen, S. The impact of climate change on wheat insect pests: Current knowledge and future trends. In Achieving Sustainable Cultivation of Wheat Volume 1: Breeding, Quality Traits, Pests and Diseases; Langridge, P., Ed.; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 545–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, P.; Ammunét, T.; Barton, M.; Battisti, A.; Eigenbrode, S.D.; Jepsen, J.U.; Kalinkat, G.; Neuvonen, S.; Niemelä, P.; Terblanche, J.S.; et al. Complex responses of global insect pests to climate warming. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 18, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, H.R.; Macfadyen, S.; Kriticos, D.J. The geographical distribution of Yellow dwarf viruses and their aphid vectors in Australian grasslands and wheat. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2012, 41, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebber, D.P.; Ramotowski, M.A.T.; Gurr, S.J. Crop pests and pathogens move polewards in a warming world. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Suri, K.S.; Chhuneja, P.K. Insect pest infestation in wheat sown in paddy-straw managed fields. Progress. Farming 2019, 55, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, G.S. Comparative evaluation of happy seeder technology versus normal sowing in wheat (Triticum aestivum) in adopted village Killi Nihal Singh of Bathinda district of Punjab. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2016, 8, 2278–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, F.M.; Bentley, A.R.; Charmet, G.; Ortiz, R.; Crossa, J. Breeding schemes for the implementation of genomic selection in wheat (Triticum spp.). Plant Sci. 2016, 242, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Fiyaz, R.; Ajay, B.C.; Ramya, K.T.; Kumar, J.A.; Sundaram, R.M.; Subba Rao, L.V. Speed breeding: Methods and applications. In Accelerated Plant Breeding, Volume 1: Cereal Crops; Gosal, S.S., Wani, S.H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.K.; Mueller, N.D.; West, P.C.; Foley, J.A. Yield trends are insufficient to double global crop production by 2050. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.S.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Swaroopa Rani, D.N.; Saxena, R.; Chauhan, N.; Jain, S. Vulnerability of wheat production to climate change in India. Clim. Res. 2014, 59, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.P.; Paul, V.L.; Slater, R.; Warren, A.; Denholm, I.; Field, L.M.; Williamson, M.S. A mutation (L1014F) in the voltage-gated sodium channel of the grain aphid, Sitobion avenae, is associated with resistance to pyrethroid insecticides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, N.; Bansal, L.; Furlong, M.; Kumar, S. Introduction. In Plant Resistance to Insects in Major Field Crops; Kumar, S., Furlong, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeb, L.; Jenner, E.; Cock, M.J. Climate-smart pest management: Building resilience of farms and landscapes to changing pest threats. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 951–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaipal, S.; Malik, R.K.; Yadav, A.; Gupta, R. IPM issues in zero-tillage system in rice–wheat cropping sequence. Tech. Bull. 2005, 8, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Jasrotia, P.; Katare, S. Compatibility of insecticides with propiconazole against foliar aphid Rhopalosiphum maidis (Fitch) and yellow rust in wheat. Indian J. Entomol. 2018, 80, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.D. Economically important aphids and their management. In IPM System in Agriculture; Upadhyay, R.K., Mukerji, K.G., Dubey, O.P., Eds.; Aditya Books Private Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2000; Volume 7, pp. 143–168. [Google Scholar]
- Keerthana, A.; Keerthana, M.; Shireesh Kumar, M.P.; Bahuguna, R.N.; Singh, S.K.; Rai, D.; Reddy, M.S.S. Characterizing and assessing the wheat–aphid complex under varying temperature and humidity. Cereal Res. Commun. 2023, 29, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, J.P.; Ramzan, M.; Atwal, A.S. Preliminary studies on biology of wheat aphid. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 1968, 39, 672–675. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, S. Infestation of root and foliage/ear head aphids on wheat in relation to predators. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 1998, 68, 754–755. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, Y.N.; Rajna, S.; Suroshe, S.S.; Joshi, S.; Chander, S. Wheat as a new host for potato aphid Macrosiphum euphorbiae (Thomas) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and construction of its age-stage two-sex life tables. Cereal Res. Commun. 2024, 52, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, S.M.V.; Singh, V.S. Incidence and species composition of aphids infesting wheat. Indian J. Entomol. 1999, 61, 291–295. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi, M.H.; Talebi-Chaichi, P.; Shakiba, M.R.; Mashhadi-Jafarloo, M. Biological responses of Russian wheat aphid, Diuraphis noxia (Mordvilko) (Homoptera: Aphididae) to different wheat varieties. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2001, 3, 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, S.K.; Verma, R.K.; Singh, B. Integrated pest management in wheat. In Wheat: Recent Trends on Production Strategies of Wheat in India; Shukla, R., Mishra, P., Chatrath, R., Gupta, R., Tomar, S., Sharma, I., Eds.; Jawaharlal Nehru Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya (JNKVV) and ICAR–Indian Institute of Wheat and Barley Research: Jabalpur, India, 2014; pp. 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, I.M. A Catalogue of the Aphids (Homoptera: Aphidoidea) of Sub-Saharan Africa; Handbook No. 4; Biosystematics Division, Plant Protection Research Institute, Agricultural Research Council: Pretoria, South Africa, 1994; ISBN 978-1868490127. [Google Scholar]
- Burd, J.D.; Elliott, N.C. Changes in chlorophyll a fluorescence induction kinetics in cereals infested with Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1996, 89, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, F.J.; Higley, L.G.; Ni, X.; Quisenberry, S.S. Physiological and growth tolerance in wheat to Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) injury. Environ. Entomol. 1999, 28, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, S.; Husain, M.; Pal, V.; Pathak, H.; Singh, S.D.; Harit, R.; Kumar, V. Effect of sowing date and cultivars on aphid infestation in wheat with climate change adaptation perspective. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India B Biol. Sci. 2016, 86, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedell, W.E.; Kieckhefer, R.W.; Haley, S.D.; Langham, M.A.C.; Evenson, P.D. Winter wheat responses to bird cherry-oat aphids and barley yellow dwarf virus infection. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyagopal, K.; Sushil, S.N.; Jeyakumar, P.; Shankar, G.; Sharma, O.P.; Sain, S.K.; Boina, D.R.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Rao, N.S.; Sunanda, B.S.; et al. AESA Based IPM Package for Wheat; National Institute of Plant Health Management: Hyderabad, India, 2014. Available online: https://niphm.gov.in/IPMPackages/Wheat.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Srivastava, A.; Singh, R. Systematics, nymphal characteristics and food plants of Sitobion (Sitobion) miscanthi (Takahashi) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Int. J. Res. Stud. Biosci. 2014, 2, 17–41. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, N.; Mogalapu, S. Pests of wheat. In Pests and Their Management; Omkar, Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Jasrotia, P. Impact of integrated pest management (IPM) module on major insect-pests of wheat and their natural enemies in north-western plains of India. J. Cereal Res. 2020, 12, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasrotia, P.; Yadav, J.; Singh, B.; Patil, S.D.; Kumar, S.; Singh, G.P. Efficiency of sticky traps for monitoring aphids in wheat under north-western plains and peninsular zones of India. J. Environ. Biol. 2022, 43, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudary, F.K.; Khan, B.; Khan, P.; Hafeez, A.; Liaqat, F.; Shams, S.; Din, A.S.U. Assessment of peas as a trap crop in wheat ecosystem. Pak.-Eur. J. Med. Life Sci. 2024, 7, 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Haicui, X.; Chen, J.; Cheng, D.; Zhou, H.; Sun, J.; Yong, L.; Francis, F. The function of ecological regulation to aphids in the wheat intercropping field. Plant Protect. 2012, 38, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, A.L.; Caulfield, J.C.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E. Identifying aphid resistance in the ancestral wheat Triticum monococcum under field conditions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, H. Relative susceptibility of advanced breeding lines against major insect pests of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Cereal Res. 2023, 15, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Simon, A.; Halsey, K.; Kurup, S.; Clark, S.; Aradottir, G.I. Characterisation of bird cherry-oat aphid (Rhopalosiphum padi L.) behaviour and aphid host preference in relation to partially resistant and susceptible wheat landraces. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2020, 177, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Singh, B. Unravelling the category of host plant resistance in Aegilops tauschii Coss. against the bird cherry-oat aphid, Rhopalosiphum padi L. Euphytica 2022, 218, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, M.; Kaur, J.; Singh, B. Efficacy of neem-based formulations against wheat aphids under semi-arid irrigated conditions in south-west Punjab. Indian J. Entomol. 2023, 85, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katare, S.; Jasrotia, P.; Yadav, J.; Saharan, M.S. Efficacy of sulfoxaflor 12% SC against aphids complex and Coccinella septempunctata L. in wheat. Indian J. Entomol. 2022, 84, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, N.M. Termites. In Key Environments: Malaysia; Cranbrook, E., Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, B.L.; Carpenter, J.M. Phylogeny of the Dictyoptera. Syst. Entomol. 1992, 17, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappan, M.; Ranjith, M.T. Termites. In Polyphagous Pests of Crops; Omkar, Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 51–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Patil, K.; Sharma, S. Farmer friendly ways to control termites. Pop. Kheti 2013, 1, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, M.; Sharma, S.; Prasad, R. Biological alternatives for termite control: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.K.; Singh, N.P.; Singh, N.N.; Gerpacio, R.V.; Pingali, P.L. Maize in India: Production Systems, Constraints, and Research Priorities; CIMMYT: Texcoco, Mexico, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Borji, M.; Rahimi, S.; Ghorbani, G.R.; Vandyousefi, J.; Fazaeli, H. Isolation and identification of some bacteria from termites’ gut capable in degrading straw lignin and polysaccharides. J. Vet. Res. 2003, 58, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Rouland-Lefevre, C. Termites as pests of agriculture. In Biology of Termites: A Modern Synthesis; Bignell, D., Roisin, Y., Lo, N., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 499–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhillar, B.S.; Saini, R.K.; Roshanlal, K. Emerging Trends in Economic Entomology; Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University Press: Hissar, India, 2006; pp. 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- Roonwal, M.L. Termite Life and Termite Control in Tropical South Asia; Scientific Publishers: Jodhpur, India, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Sattar, A.; Salihah, Z. Detection and control of subterranean termites. In Technologies for Sustainable Agriculture, Proceedings of the National Workshop, Faisalabad, Pakistan, 24–26 September 2001; National Institute for Agricultural and Biology: Faisalabad, Pakistan, 2001; pp. 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, B.; Khan, M.A.; Paul, S.; Shankarganesh, K.; Chakravorty, S. Termites and Indian agriculture. In Termites and Sustainable Management, Volume 2; Khan, M.A., Ahmad, W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 51–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parween, T.; Bhandari, P.; Raza, S.K. Survey and identification of termite in some selected parts of India. Res. J. Life Sci. Bioinform. Pharm. Chem. Sci. 2016, 2, 122–135. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, V.; Singh, H.; Yadav, A. Effect of organic amendments on termite population and yield of wheat in arid eco-system of Rajasthan. J. Pharm. Phytochem. 2018, SP1, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, K.P. A Textbook of Applied Entomology; Kalyani Publishers: New Delhi, India, 1993; pp. 256–265. [Google Scholar]
- Parihar, D.R. Termite Pest of Vegetation in Rajasthan and Their Management; CAZRI Monograph No. 16; Central Arid Zone Research Institute: Jodhpur, India, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, A.; Chandel, R.S.; Verma, K.S.; Joshi, M.J. Termites in important crops and their management. Indian J. Entomol. 2021, 83, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpeyi, M.M.; Kumar, A.; Aman, A.S.; Kushwaha, D. Integrated management of soil dwelling pests of wheat crop. Biot. Res. Today 2023, 5, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, J.; Pathania, M. Bioefficacy of insecticides for the management of termites in wheat under semi-arid irrigated conditions of South-Western Punjab. Pestic. Res. J. 2021, 33, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Bala, R. Effect of imidacloprid-hexaconazole seed treatment mixture on germination, seedling growth and termite damage in wheat. Pestic. Res. J. 2020, 32, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Chaudhary, S.; Antil, J.; Somvanshi, V.S.; Nebapure, S.M.; Patanjali, N.; Dutta, A.; Babu, S.; Bharadwaj, C.; Sudhishri, S.; et al. Novel moisture retaining dustable powder containing Steinernema abbasi effectively controls damage of subterranean termite in wheat and chickpea. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2023, 58, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Chaudhary, S.; Somvanshi, V.S.; Nebapure, S.M.; Babu, S.; Singh, A. Field efficacy of Steinernema abbasi-nematodes enriched bio-insecticidal powder to control termite in wheat and chickpea. Allelopathy J. 2024, 62, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, S.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Kalra, N.; Swaruparani, D.N. Changes in pest profiles in rice-wheat cropping system in Indo-Gangetic plains. Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 2003, 11, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Deol, G.S. Outbreak of armyworm on wheat in India. Trop. Pest Manag. 1982, 28, 175. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.C.; Sullivan, D.J.; Bhatnagar, V.S. Population dynamics and natural mortality factors of the Oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), in South Central India. Crop Prot. 2002, 21, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Zeng, J.; Liu, J. Population dynamics of the armyworm in China: A review of the past 60 years’ research. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2014, 51, 890–898. [Google Scholar]
- Hamblyn, C.J. Army caterpillar damage on East Coast hill country. N. Z. J. Agric. 1959, 98, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.-J.; Fang, Y.; Li, L.-Y.; Zhang, L.-Z.; Gao, S.-J.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.-D. The insecticidal effect of the botanical insecticide chlorogenic acid on Mythimna separata (Walker) is related to changes in MsCYP450 gene expression. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1015095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-N.; Song, H.-S.; Li, C.-S.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Lei, C.-L. Effect of several factors on the phototactic response of the oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deol, G.S.; Singh, D. Biology and behavior of armyworm Mythimna separata (Walker) (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera) on wheat. J. Res. PAU 1991, 28, 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- David, B.V. General and Applied Entomology, 2nd ed.; Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited: New Delhi, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tanwar, R.K.; Prakash, A.; Panda, S.K.; Swain, N.C.; Garg, D.K.; Singh, S.P.; Kumar, S.S.; Bambawale, O.M. Rice Swarming Caterpillar (Spodoptera mauritia) and Its Management Strategies; Technical Bulletin 24; NCIPM: New Delhi, India, 2010; Available online: http://nriipm.res.in/NCIPMPDFs/Publication/Swarming_caterpillar_.pdf (accessed on 18 July 2025).
- Singh, B.; Sarao, P.S. Efficacy of biopesticides and insecticides against army worm Mythimna separata (Walker). Indian J. Entomol. 2020, 82, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.; Maurya, R.; Brijwal, L.; Patwal, H.; Suyal, P. Host range and distribution of predatory stink bug Andrallus spinidens (F.) in Uttarakhand. Indian J. Entomol. 2021, 83, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.; Vijayakumar, R.; Linga, V.; Sivakumar, G. Susceptibility of Oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae and pupae to native entomopathogenic nematodes. J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 144, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, P.; Thakur, N.; Yadav, A.N. Indigenous entomopathogenic nematode as biocontrol agents for insect pest management in hilly regions. Plant Sci. Today 2022, 8, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Stanley, D.; Jiang, X. The clock gene, period, influences migratory flight and reproduction of the oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker). Insect Sci. 2023, 30, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.S. Management of insect and mite pests. In Twenty Years of Coordinated Wheat Research 1961–1986; Tandon, J.P., Sethi, A.P., Eds.; Wheat Project Directorate, All India Coordinated Wheat Improvement Project; ICAR: New Delhi, India, 1986; pp. 158–188. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaq, A. Control of insect pests on rice crop using tillage practices. Agric. Mech. Asia Pac. Lat. Am. 1997, 28, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B. Incidence of the pink noctuid stem borer, Sesamia inferens (Walker), on wheat under two tillage conditions and three sowing dates in north-western plains of India. J. Entomol. 2012, 9, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kular, J.S. Influence of abiotic factors on population dynamics of pink stem borer (Sesamia inferens Walker) in rice-wheat cropping system of India. J. Wheat Res. 2015, 7, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Kular, J.S. Notes on the bionomics of the pink stem borer Sesamia inferens Walker (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): An upcoming pest of wheat in India. Acta Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 2015, 50, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, G.F. The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma: Moths; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1892; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, R.K.; Verma, R. Sex dimorphism in pink stem borer, Sesamia inferens Walk (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Sci. Cult. 1980, 46, 195–196. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, D.K. Host range and overwintering of rice pink stem borer (PSB) in a hilly region of India. Int. Rice Res. Notes 1988, 13, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, W.; Hussain, S.; Zubair, M.; Shehzad, M.W. Control strategy for rice stem borer in wheat crop by the management of rice straw. Plant Prot. 2022, 6, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Bal, R. Bio-efficacy of Mortel (Fipronil 0.3 G) against pink stem borer, Sesamia inferens in wheat. J. Krishi Vigyan 2022, 11, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timbadiya, B.G.; Sisodiya, D.B. Evaluation of insecticides against pink stem borer Sesamia inferens (Walker) infesting durum wheat. Indian J. Entomol. 2021, 83, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeer, M.; Yele, Y.; Sharma, K.C.; Prakash, N.B. Exogenous application of different silicon sources and potassium reduces pink stem borer damage and improves photosynthesis, yield and related parameters in wheat. Silicon 2021, 13, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.; Baskaran, R.K.M.; Sharma, K.C.; Marathe, A. Enhancing biocontrol potential of Trichogramma chilonis against borer pests of wheat and chickpea. iScience 2023, 26, 106512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, J.P.; Zalucki, M.P. Understanding heliothine (Lepidoptera: Heliothinae) pests: What is a host plant? J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, A.; Maqsood, A.; Ahmed, M.; Tariq, M.; Ali, M.; Qureshi, R. Toxicity, antifeedant and sub-lethal effects of Citrullus colocynthis extracts on cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pak. J. Zool. 2017, 49, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, P.C.; Del Socorro, A.P.; Le Mottee, K.; Tann, C.R.; Fitt, G.P.; Zalucki, M.P. Host plants and habitats of Helicoverpa punctigera and H. armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in inland Australia. Austral Entomol. 2019, 58, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, A.G.; Giri, A.P.; Harsulkar, A.M.; Sainani, M.N.; Deshpande, V.V.; Ranjekar, P.K.; Gupta, V.S. Complexity in specificities and expression of Helicoverpa armigera gut proteinases explains polyphagous nature of the insect pest. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 31, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haile, F.; Tim, N.; Nicolas, S. Overview of pest status, potential risk, and management considerations of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) for U.S. soybean production. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2021, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, W.T.; Soria, M.F.; Walsh, T.; Thomazoni, D.; Silvie, P.; Behere, G.T.; Anderson, C.; Downes, S. A brave new world for an old world pest: Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, S.; Srivastava, C.P.; Keval, R. Interbreeding status of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) populations across India. J. Exp. Zool. India 2019, 22, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Doval, S.L.; Bohra, O.P.; Sharma, S.K. New records of Heliothis armigera Hubn. as a pest of wheat in India and efficacy of some insecticides against its larvae. Indian J. Entomol. 1972, 34, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.Q.; Wu, X.F.; Wu, B.; Wu, K.M. Seasonal migration of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) over the Bohai Sea. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behere, G.T.; Tay, W.T.; Russell, D.A.; Kranthi, K.R.; Batterham, P. Population genetic structure of the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in India as inferred from EPIC-PCR DNA markers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.M.; Papanicolaou, A.; Mironidis, G.K.; Vontas, J.; Yang, Y.; Lim, K.S.; Oakeshott, J.G.; Bass, C.; Chapman, J.W. Genomewide transcriptional signatures of migratory flight activity in a globally invasive insect pest. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 4901–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibouche, S.; Buès, R.; Toubon, J.-F.; Poitout, S. Allozyme polymorphism in the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Comparison of African and European populations. Heredity 1998, 80, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.M.; Mastrangelo, T.; Rodrigues, J.C.V.; Paulo, D.F.; Omoto, C.; Corrêa, A.S.; de Azeredo-Espin, A.M.L. Invasion origin, rapid population expansion, and the lack of genetic structure of cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera) in the Americas. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 7378–7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coaker, T.H. Investigations on Heliothis armigera in Uganda. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1959, 50, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitt, G.P.; Zalucki, M.P.; Twine, P. Temporal and spatial patterns in pheromone-trap catches of Helicoverpa spp. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in cotton-growing areas of Australia. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1989, 79, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingotti Dias, P.E.; de Souza Loureiro, L.G.A.; Pessoa, F.M.A.; de Oliveira Neto, R.A.; de Souza Tosta, A.; Teodoro, P.E. Interactions between fungal-infected Helicoverpa armigera and the predator Chrysoperla externa. Insects 2019, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Rashid, A. Helicoverpa armigera infestation on various wheat varieties. Ann. Wheat Newsl. 2000, 46, 101–102. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.S.; Chhillar, B.S.; Dahiya, K.K. Incidence of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) in wheat in Haryana. Ann. Biol. 2003, 19, 219–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.M.; Guo, Y.Y. The evolution of cotton pest management practices in China. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2005, 50, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, G.; Omkar. Gram Pod Borer (Helicoverpa armigera). In Polyphagous Pests of Crops; Omkar, Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 311–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.B.S. Heliothis/Helicoverpa (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In Insect Pests of Cotton; Matthews, G.A., Tunstall, J.P., Eds.; University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; pp. 39–106. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, S.; Johnson, J.B.; Ahmad, M.; Fitt, G.P.; Naiker, M. A review on biological interactions and management of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2021, 145, 467–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, J.W.; MacLeod, A. Report of a Pest Risk Analysis: Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner, 1808). Plant Protection Service (NL) and Central Science Laboratory (UK) Joint Pest Risk Analysis for Helicoverpa armigera (European Union), 2007. Available online: https://planthealthportal.defra.gov.uk/pests-and-diseases/uk-plant-health-risk-register/downloadExternalPra.cfm?id=3879 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- TNAU Agritech Portal. Crop Protection: Pests of Cotton. 2025. Available online: http://www.agritech.tnau.ac.in/crop_protection/crop_prot_crop_insectpest%20_cottonmain.html (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Dagar, V.S.; Mishra, M.; Kumar, S. Effect of dietary stress of emamectin benzoate on the fitness cost of American bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner, 1808). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2020, 40, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Gupta, K.K.; Kumar, S. Growth regulatory and growth inhibitory effects of Thevetia neriifolia stem extracts on Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2018, 51, 895–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Sharma, A.; Dagar, V.S.; Kumar, S. Effects of β-sitosterol on growth, development and midgut enzymes of Helicoverpa armigera Hübner. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2020, 72, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Inácio, G.; Alves, J.V.B.; Santos, M.F.C.; Vacari, A.M.; Figueiredo, G.P.; Bernardes, W.A.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Ambrósio, S.R. Feeding deterrence towards Helicoverpa armigera by Tithonia diversifolia tagitinin C-enriched extract. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5292–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Sharma, A.; Dagar, V.S.; Warikoo, R.; Kumar, S. Synergistic efficacy of β-sitosterol on the growth inhibitory impacts of triflumuron on an Indian strain of cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2024, 44, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CABI. Invasive Species Compendium: Detailed Coverage of Invasive Species Threatening Livelihoods and the Environment Worldwide. Helicoverpa armigera (Cotton bollworm), 2021. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/26757 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Bhullar, M.B.; Kaur, P.; Singh, B.; Brar, P.K.; Thakur, J. Forecasting model for brown wheat mite, Petrobia latens (Müller) on rainfed wheat and distribution in North-West India. Indian J. Ecol. 2024, 51, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K. Handbook of Plant Mites in India; Zoological Survey of India: Calcutta, India, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A. Mites. In Polyphagous Pests of Crops; Omkar, Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 409–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhooria, M.S. Mite pests of field crops. In Fundamentals of Applied Acarology; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.M. Occurrence of brown wheat mite, Petrobia latens (Müller) on cumin in Rajasthan. Indian Cocoa Arecanut Spices J. 1990, 13, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagat, K.C. Occurrence of brown wheat mite, Petrobia latens (Müller) (Acari: Tetranychidae: Bryobiinae) in Jammu. Insect Environ. 2003, 9, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.Q.; Han, R.J.; Shi, J.H. The occurrence of brown wheat mite on wheat in an arid area and methods of control. Appl. At. Energy Agric. (Yuanzineng Nongye Yingyong) 1985, 1, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.M.; Doval, S.L.; Joshi, H.C. Biology of brown wheat mite, Petrobia latens (Müller). Indian J. Entomol. 1969, 31, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, M. Mite (Acari: Acarina) vectors involved in transmission of plant viruses. In Applied Plant Virology; Awasthi, L.P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Bhullar, M.B.; Kaur, P. Five new records and distribution of predatory mite fauna (Arachnida: Acari) associated with crop ecosystems of northern India. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2023, 43, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Bhullar, M.B.; Karmakar, K.; Kaur, P. Seven new records and distribution of phytoseiid (Acari: Mesostigmata) mite fauna associated with agri-horticultural crops in Northern India. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2022, 42, 2425–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICAR-Indian Institute of Wheat and Barley Research. Annual Report 2014–15; ICAR-IIWBR: Karnal, Haryana, India, 2015; p. 9. Available online: https://iiwbr.org.in/annual-reports/ (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, D.K.; Singh, D.R.; Biswas, H.; Praveen, K.V.; Sharma, V. Estimating loss of ecosystem services due to paddy straw burning in North-West India. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2019, 17, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Kaur, S.; Deol, J.S.; Sharma, R.; Kaur, T.; Brar, A.S.; Choudhary, O.P. Soil Properties and Weed Dynamics in Wheat as Affected by Rice Residue Management in the Rice–Wheat Cropping System in South Asia: A Review. Plants 2021, 10, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillion, B.S.; Kataria, P.; Dhillion, P.K. National food security vis-à-vis sustainability of agriculture in high crop productivity regions. Curr. Sci. 2010, 98, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.; Gangaiah, B.; Aipe, K.C. Effect of crop residue management in a rice-wheat cropping system on growth and yield of crop and on soil fertility. Exp. Agric. 1999, 35, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Biswas, R.; Garg, D.K.; Gyawali, B.K.; Haque, N.M.M.; Ijaj, P.; Jaipal, S.; Kamal, N.Q.; Kumar, P.; Pathak, M.; et al. Management of Stem Borers of Rice and Wheat in Rice-Wheat Systems of Pakistan, Nepal, India and Bangladesh; Rice-Wheat Consortium Paper Series 17; Rice-Wheat Consortium: New Delhi, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, B.S.; Dhaliwal, N.S.; Sandhu, G.S. Production potential and economics of wheat, Triticum aestivum as influenced by different planting methods in Punjab, India. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2016, 8, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A. Long-term experiments with reduced tillage in spring cereals. II. Effects on pests and beneficial insects. Crop Prot. 2003, 22, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, G.; De Simone, S.; Sigura, M.; Boscutti, F.; Marini, L. Conservation tillage mitigates the negative effect of landscape simplification on biological control. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.E.; Wilde, G.E. Aphid predators associated with conventional- and conservation-tillage winter wheat. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1991, 64, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa, A.A.; Farooq, M.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Nawaz, A.; Jabran, K.; Siddique, K.H.M. Impact of climate change on biology and management of wheat pests. Crop Prot. 2020, 137, 105304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutbrodt, B.; Mody, K.; Dorn, S. Drought changes plant chemistry and causes contrasting responses in lepidopteran herbivores. Oikos 2011, 120, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeer, M.; Yele, Y.; Jain, S.K. Heavy infestation of sugarcane leafhopper Pyrilla perpusilla on wheat and oats in Chhattisgarh. Indian J. Entomol. 2019, 81, 516–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-X.; Hof, A.R.; Ma, C.-S. Impacts of climate change on crop production, pests, and pathogens of wheat and rice. Front. Agr. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).