Impacts of Humic Acid and Potassium Fulvate on Cadmium and Lead Accumulation and Translocation in Maize (Zea mays L.) Grown in Co-Contaminated Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.5. Data and Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Bioconcentration Factor (BCF)
2.5.2. Translocation Factor (TF)
3. Results
3.1. Effects of HA and PF on Soil Cd and Pb Concentrations
3.2. Effects of HA and PF on Maize Growth, Yield, and Correlation with Soil Heavy Metals
3.3. Effects of HA and PF on Cd and Pb Concentrations in Maize Tissues
3.4. Effects of HA and PF on Cd and Pb Bioconcentration in Maize
3.5. Effects of HA and PF on Cd and Pb Translocation in Maize
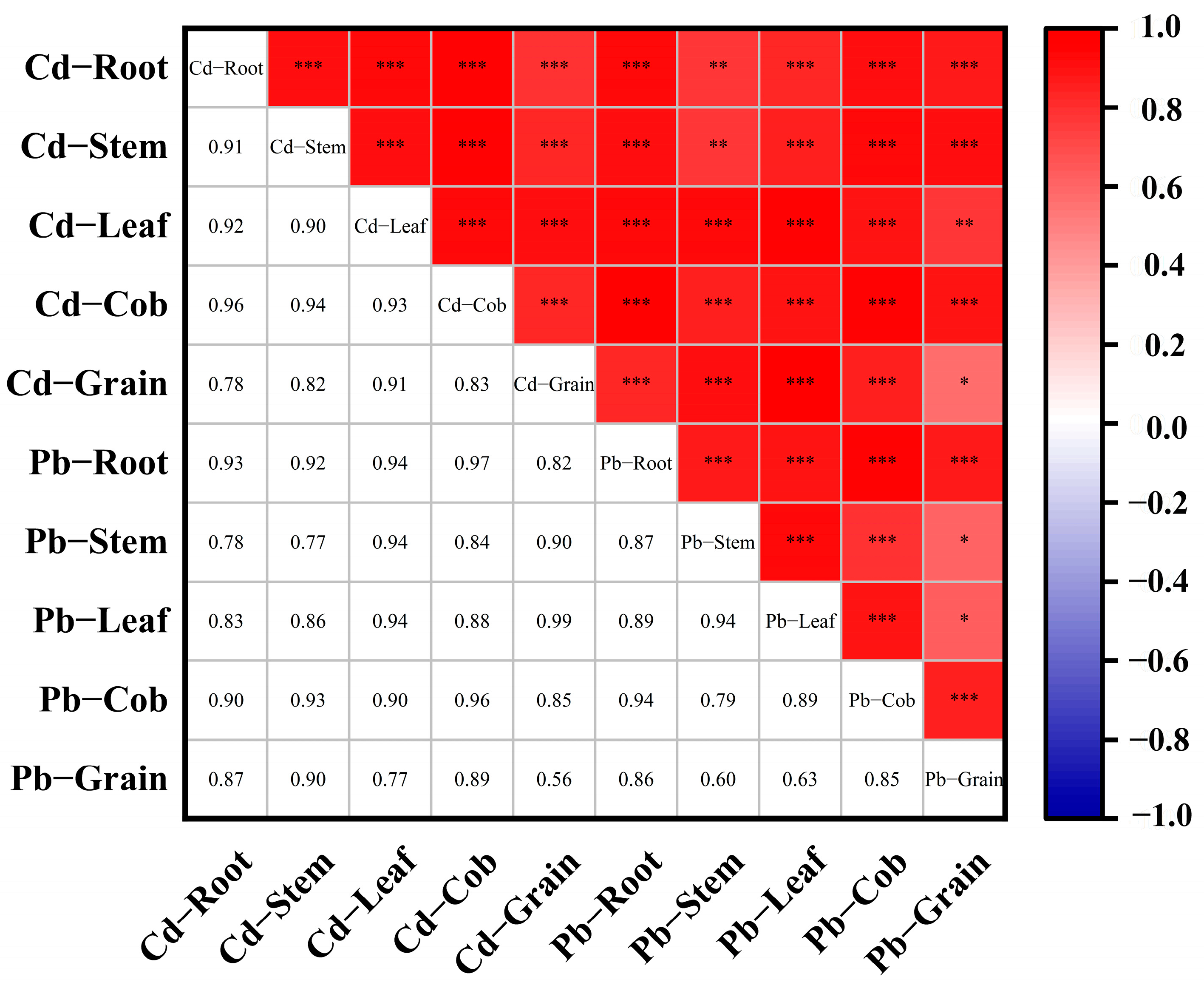
3.6. Synergistic Accumulation and Translocation of Cd and Pb in Maize
4. Discussion
4.1. Immobilization Mechanisms and Efficacy Differences in HA and PF
4.2. Accumulation and Translocation Mechanisms of Heavy Metals in Maize
4.3. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Soils for Nutrition: State of the Art; FAO: Quebec, QC, Canada, 2022; ISBN 978-92-5-136610-3. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, S. Identification of the Sources and Influencing Factors of Potentially Toxic Elements Accumulation in the Soil from a Typical Karst Region in Guangxi, Southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Jia, X.; Wang, L.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.-J.; Bank, M.S.; O’Connor, D.; Nriagu, J. Global Soil Pollution by Toxic Metals Threatens Agriculture and Human Health. Science 2025, 388, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-429-19203-6. [Google Scholar]
- Azhar, U.; Ahmad, H.; Shafqat, H.; Babar, M.; Shahzad Munir, H.M.; Sagir, M.; Arif, M.; Hassan, A.; Rachmadona, N.; Rajendran, S.; et al. Remediation Techniques for Elimination of Heavy Metal Pollutants from Soil: A Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Nepovimova, E.; Zhang, X.; Kuca, K. Revolutionizing Soil Heavy Metal Remediation: Cutting-Edge Innovations in Plant Disposal Technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoi, B.; Acharjee, S.A.; Bharali, P.; Sorhie, V.; Walling, B.; Alemtoshi. A Critical Review on the Ecotoxicity of Heavy Metal on Multispecies in Global Context: A Bibliometric Analysis. Environ. Res. 2024, 248, 118280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Zhou, H.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Lu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Bao, L. Effect of Biochar-Based Organic Fertilizer on the Growth of Maize in Cadmium-Contaminated Soil. Agriculture 2025, 15, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Kumar, P.S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Saravanan, R. A Review on Bioremediation Approach for Heavy Metal Detoxification and Accumulation in Plants. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 119035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuo, R. Removal of Heavy-Metal Pollutants by White Rot Fungi: Mechanisms, Achievements, and Perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 354, 131681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L. Environmental Soil Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; ISBN 978-0-12-656446-4. [Google Scholar]
- Alloway, B.J. (Ed.) Heavy Metals in Soils; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; ISBN 978-94-010-4586-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.-H. Heavy Metals in Food Crops: Health Risks, Fate, Mechanisms, and Management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuo, R. Recent Advances in Phyto-Combined Remediation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soil. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 72, 108337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffia, A.; Oliva, M.; Marra, F.; Mallamaci, C.; Nardi, S.; Muscolo, A. Humic Substances: Bridging Ecology and Agriculture for a Greener Future. Agronomy 2025, 15, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition, Reactions, Second Edition. J. Chem. Educ. 1995, 72, A93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senesi, N.; Sposito, G.; Holtzclaw, K.M.; Bradford, G.R. Chemical Properties of Metal-Humic Acid Fractions of a Sewage Sludge-Amended Aridisol. J. Environ. Qual. 1989, 18, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębska, B.; Banach-Szott, M. Humic Acids Properties of Luvisol of 40-Year Fertilizer Experiment. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A. The Supramolecular Structure of Humic Substances: A Novel Understanding of Humus Chemistry and Implications in Soil Science. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 75, pp. 57–134. ISBN 978-0-12-000793-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Chang, J.; Li, C.; Lu, G. Potassium Fulvate Alleviates Salt–Alkali Stress and Promotes Comprehensive Growth of Oats in Saline–Alkali Soils of the Qaidam Basin. Plants 2025, 14, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, X.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y.; Bao, K.; Quan, Z.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Lu, G.; Zhang, H. Potassium Fulvate Alleviates Salinity and Boosts Oat Productivity by Modifying Soil Properties and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in the Saline–Alkali Soils of the Qaidam Basin. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi Aghbolaghi, M.; Sedghi, M.; Sharifi, R.S.; Dedicova, B. Germination and the Biochemical Response of Pumpkin Seeds to Different Concentrations of Humic Acid under Cadmium Stress. Agriculture 2022, 12, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelesz, J.É.; Csajbók, J.; Molnár, P.I.; Virág, I.C.; Kutasy, E.T. Mitigating the Accumulation of Mercury (Hg) and Lead (Pb) through Humic Acid Application under Aquaponic Conditions Using Watercress (Nasturtium Officinale R. Br.) as a Model Plant. Plants 2024, 13, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.-T.; Chen, X.-F.; Huang, W.-L.; Shen, Q.; Lu, F.; Lai, N.-W.; Guo, J.; Yang, L.-T.; Ye, X.; Chen, L.-S. Humic Acid Enhances Antioxidant and Glyoxalase Systems to Combat Copper Toxicity in Citrus. Agronomy 2025, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Bao, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, N. Accumulation and Transport of Cd, Pb, As, and Cr in Different Maize Varieties in Southwest China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- HJ 962-2018; Soil—Determination of pH—Potentiometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- NY/T 1121.6-2006; Soil Testing Part 6: Method for Determination of Soil Organic Matter. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- LY/T 1228-2015; Nitrogen Determination Methods of Forest Soils. National Forestry and Grassland Administration: Beijing, China, 2015.
- HJ 704-2014; Soil Quality—Determination of Available Phosphorus—Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate Solution-Mo-Sb Anti spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- NY/T 889-2004; Determination of Exchangeable Potassium Andnon-Exchangeable Potassium Content in Soil. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- DZ/T 0279.5-2016; Analysis Methods for Regional Geochemical Sample-Part 5: Determination of Cadmium Contents by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- DZ/T 0279.3-2016; Analysis Methods for Regional Geochemical Sample-Part 3: Determination of 15 Elements Including Barium, Beryllium, Bismuth etc. by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- HJ 804-2016; Soil—Determination of Bioavailable Form of Eight Elements—Extraction with Buffered DTPA Solution/Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.15-2023; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Cadmium in Foodstuffs. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- GB 5009.12-2023; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Lead in Foodstuffs. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- GB 13078-2017; Hygienical Standard for Feeds. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard Limits for Contaminants in Foodstuffs. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Mackiewicz-Walec, E.; Olszewska, M. Biostimulants in the Production of Forage Grasses and Turfgrasses. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ortiz, R.; Naranjo, M.Á.; Atares, S.; Vicente, O. Antioxidant Responses of Water-Stressed Cherry Tomato Plants to Natural Biostimulants. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsudays, I.M.; Alshammary, F.H.; Alabdallah, N.M.; Alatawi, A.; Alotaibi, M.M.; Alwutayd, K.M.; Alharbi, M.M.; Alghanem, S.M.S.; Alzuaibr, F.M.; Gharib, H.S.; et al. Applications of Humic and Fulvic Acid under Saline Soil Conditions to Improve Growth and Yield in Barley. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Ren, J.; Tao, L.; Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lv, M. Potential of Attapulgite/Humic Acid Composites for Remediation of Cd-Contaminated Soil. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Xiao, R.; Cheng, S.; Luo, H.; Wen, X.; Wu, L.; Zhong, Q. Removal of Cu and Pb from Contaminated Agricultural Soil Using Mixed Chelators of Fulvic Acid Potassium and Citric Acid. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Cai, D.; Xu, H. Multi-Source Fulvic-like Acids from Different Organic Wastes and Comparison of Their Structures, Compositions and Agricultural Effects. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 522, 167576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid and Potassium Humate on Microbial Biodiversity in Bulk Soil and Rhizosphere Soil of Panax Ginseng. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 254, 126914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Aneefi, A.G.; Sisuvanh, H.; Singkham, S.; Pius, M.V.; Akter, F.; Kwon, E.-H.; Kang, S.-M.; Woo, Y.-J.; Yun, B.-W.; et al. Dynamics of Humic Acid, Silicon, and Biochar under Heavy Metal, Drought, and Salinity with Special Reference to Phytohormones, Antioxidants, and Melatonin Synthesis in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabi, F.; Sarfaraz, A.; Kama, R.; Kanwal, R.; Li, H. Structure-Based Function of Humic Acid in Abiotic Stress Alleviation in Plants: A Review. Plants 2025, 14, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W. Melatonin: A Key Player in Alleviating Heavy Metal Stress in Plants—Current Insights and Future Directions. Hortic. Plant J. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.; He, R.; Zhen, Q.; She, D. Synergistic Effects of Aged Lignin-Based Biochar and Selenium Fertilization on Heavy Metal Remediation in Agricultural Soils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 225, 120464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Proshad, R.; Lu, Y.; Tan, R.; Ding, Z.; Cheng, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z. Goethite-Humic Acid Composites for Multi-Metal Soil Remediation: Mechanisms and Environmental Transformation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Song, G.; Zheng, Z.; Song, Z.; Mi, X. Phytoremediation of Molybdenum (Mo)-Contaminated Soil Using Plant and Humic Substance. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 117011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldo, D.A.; Garland, T.R.; Wildung, R.E. Cadmium Distribution and Chemical Fate in Soybean Plants. Plant Physiol. 1981, 68, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochian, L.V. Cellular Mechanisms of Aluminum Toxicity and Resistance in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1995, 46, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, J.J.; Welch, R.M.; Norvell, W.A.; Sullivan, L.A.; Kochian, L.V. Characterization of Cadmium Binding, Uptake, and Translocation in Intact Seedlings of Bread and Durum Wheat Cultivars. Plant Physiol. 1998, 116, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antu, U.B.; Roy, T.K.; Kulsum, T.I.; Mitu, P.R.; Ismail, Z.; Arifin, M.; Datta, M.; Hossain, S.A.; Islam, M.S.; Mahiddin, N.A.; et al. Role of Humic Acid for Climate Change Adaptation Measures to Boost up Sustainable Agriculture and Soil Health: A Potential Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 313, 144043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, S.; Gong, P.; Li, P.; Liu, H. Effect of Fulvic Acid on Aggregate Characteristics and Humus Composition in Saline-Alkali Soil. Plant Soil, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Sun, T.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Sun, Y. In–situ Immobilization Remediation, Soil Aggregate Distribution, and Microbial Community Composition in Weakly Alkaline Cd–contaminated Soils: A Field Study. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Huang, X.; Lu, L. Mitigating Cadmium Contamination in Rice: Insights from a Large-Scale Meta-Analysis of Amendment Effects. Plant Soil 2024, 505, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
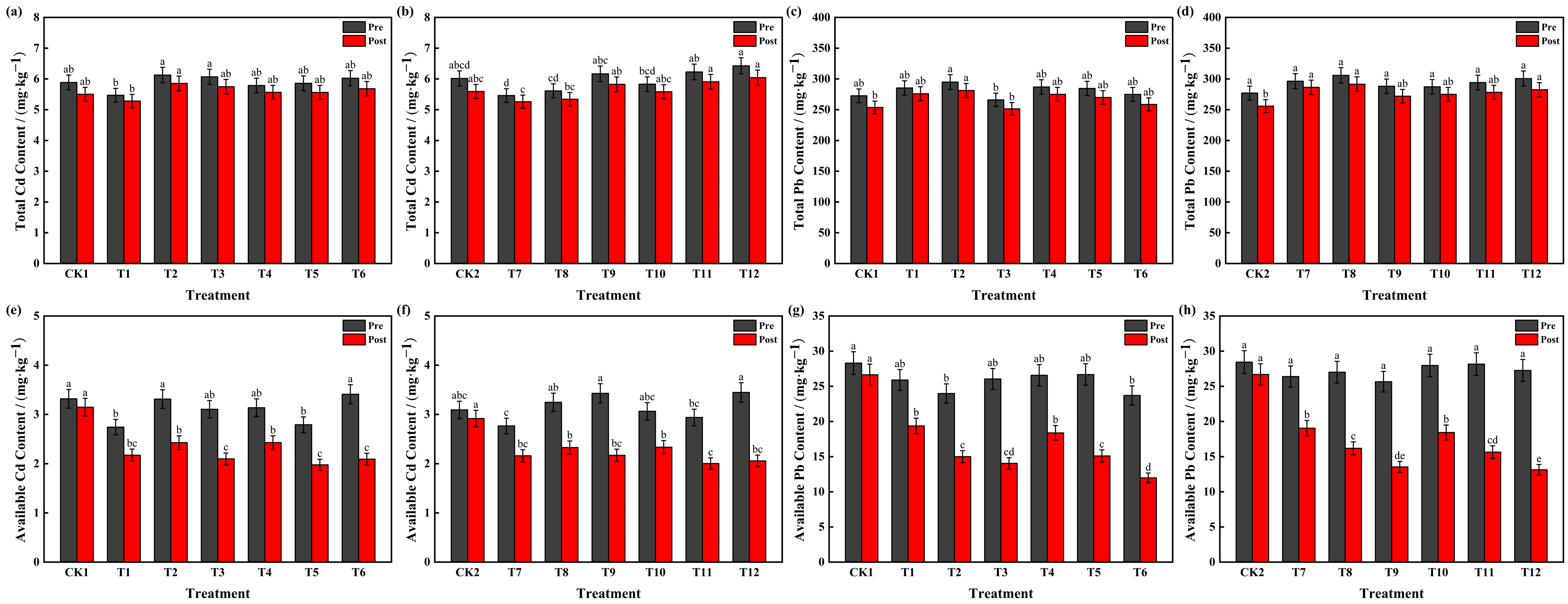
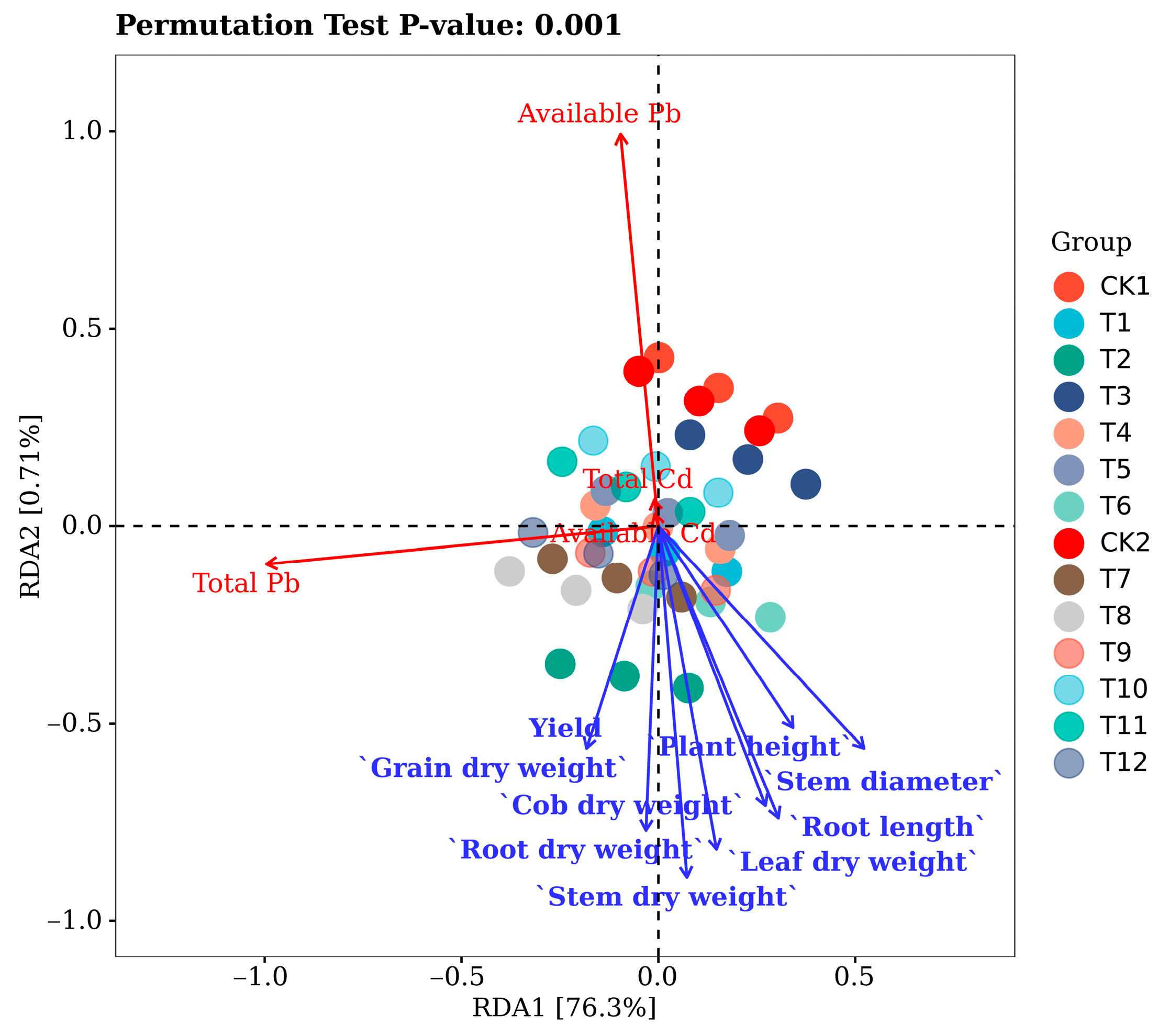
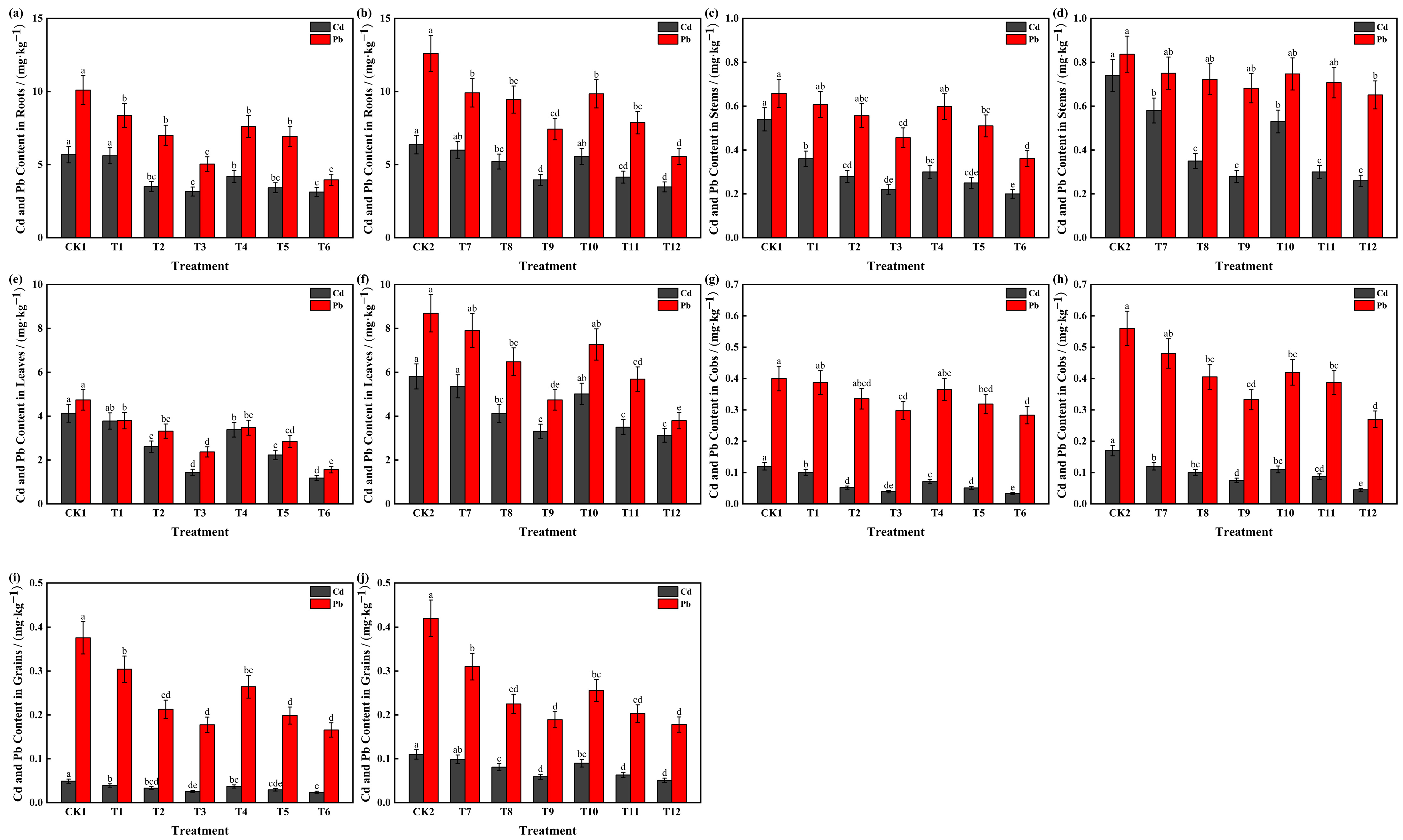

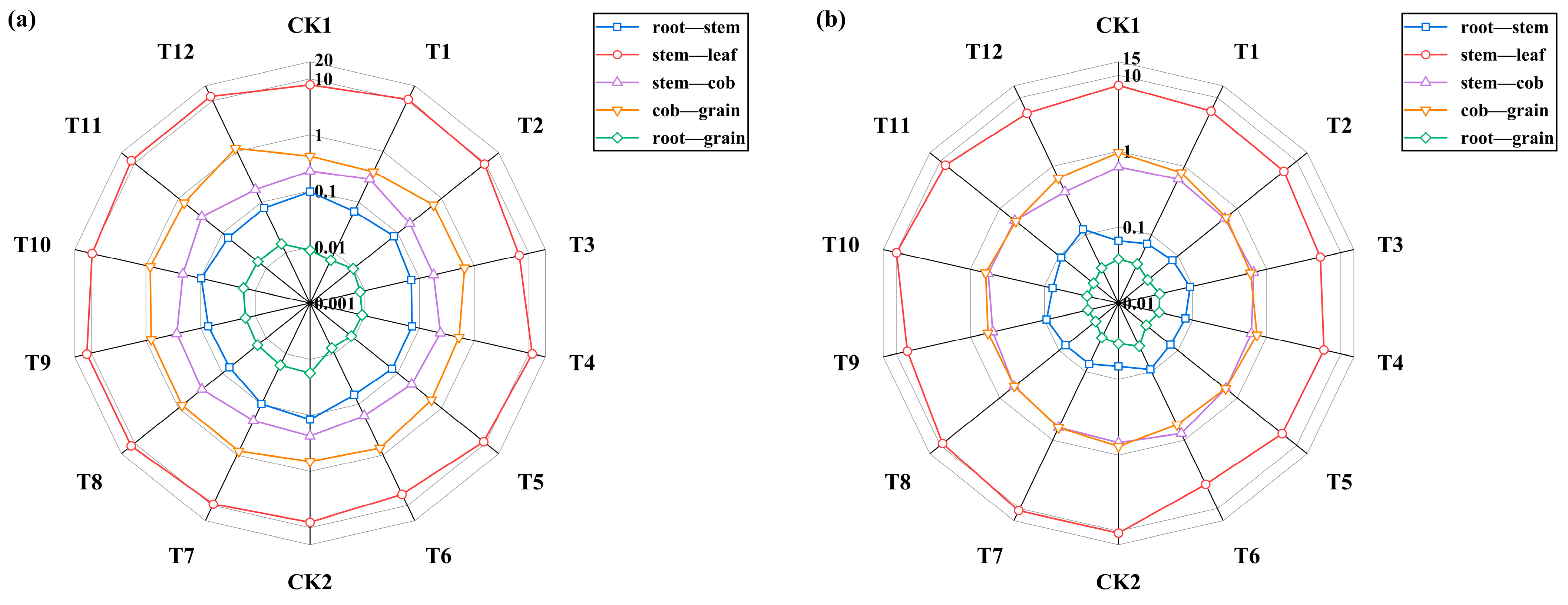
| pH | Organic Matter /(g·kg−1) | Available N /(mg·kg−1) | Available P /(mg·kg−1) | Available K (mg·kg−1) | Total Cd /(mg·kg−1) | Available Cd /(mg·kg−1) | Total Pb /(mg·kg−1) | Available Pb /(mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.14 ± 0.17 | 24.7 ± 3.3 | 200.4 ± 33.5 | 18.9 ± 1.7 | 402.7 ± 13.0 | 5.62 ± 0.23 | 1.64 ± 0.15 | 271.9 ± 12.2 | 18.3 ± 3.2 |
| Treatment | Amendment | Application Rate /(kg·ha−1) | Maize Cultivar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | CK | / | / | LD12 |
| T1 | HA1 | HA | 1500 | |
| T2 | HA2 | 3000 | ||
| T3 | HA3 | 4500 | ||
| T4 | PF1 | PF | 1500 | |
| T5 | PF2 | 3000 | ||
| T6 | PF3 | 4500 | ||
| CK2 | CK | / | / | SY607 |
| T7 | HA1 | HA | 1500 | |
| T8 | HA2 | 3000 | ||
| T9 | HA3 | 4500 | ||
| T10 | PF1 | PF | 1500 | |
| T11 | PF2 | 3000 | ||
| T12 | PF3 | 4500 | ||
| Treatment | Root Dry Weight (g·plant−1) | Stem Dry Weight (g·plant−1) | Leaf Dry Weight (g·plant−1) | Cob Dry Weight (g·plant−1) | Grain Dry Weight (g·plant−1) | Yield (kg·ha−1) | Plant Height (cm) | Stem Diameter (mm) | Root Length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 17.6 ± 1.7 b | 53.8 ± 5.3 e | 63.5 ± 6.2 c | 52.3 ± 5.1 b | 169.3 ± 8.3 b | 6840 ± 333 b | 250.0 ± 5.7 b | 19.1 ± 2.5 b | 22.3 ± 1.2 b |
| T1 | 21.6 ± 2.1 ab | 77.3 ± 7.6 d | 115.7 ± 11.3 ab | 61.8 ± 6.1 ab | 173.0 ± 10.0 b | 6990 ± 404 b | 254.0 ± 9.0 b | 22.5 ± 4.2 ab | 23.0 ± 2.3 b |
| T2 | 22.5 ± 2.2 ab | 88.2 ± 8.6 cd | 123.3 ± 12.1 ab | 66.1 ± 6.5 ab | 197.0 ± 8.0 a | 7960 ± 324 a | 271.3 ± 13.1 ab | 23.8 ± 2.0 ab | 28.7 ± 0.9 a |
| T3 | 23.9 ± 2.3 a | 107.3 ± 10.5 bc | 132.1 ± 12.9 ab | 72.2 ± 7.1 a | 213.8 ± 10.9 a | 8638 ± 441 a | 275.3 ± 10.2 ab | 24.6 ± 1.6 ab | 29.3 ± 3.4 a |
| T4 | 24.6 ± 2.4 a | 84.5 ± 8.9 d | 113.1 ± 11.1 b | 62.3 ± 6.1 ab | 196.2 ± 10.3 a | 7927 ± 418 a | 261.0 ± 6.7 b | 23.8 ± 2.0 ab | 28.3 ± 1.2 a |
| T5 | 25.3 ± 2.5 a | 112.3 ± 11.0 ab | 118.0 ± 11.6 ab | 65.3 ± 6.4 ab | 205.7 ± 8.7 a | 8310 ± 352 a | 275.0 ± 18.8 ab | 24.3 ± 3.3 ab | 28.7 ± 0.9 a |
| T6 | 25.9 ± 2.5 a | 128.6 ± 12.6 a | 141.4 ± 13.9 a | 66.2 ± 6.5 ab | 208.3 ± 11.9 a | 8415 ± 480 a | 294.3 ± 18.5 a | 26.8 ± 1.8 a | 29.7 ± 1.2 a |
| Average | 23.1 | 93.1 | 115.3 | 63.8 | 194.8 | 7869 | 268.7 | 23.5 | 27.1 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 11.3% | 24.8% | 20.0% | 8.8% | 8.2% | 8.2% | 5.2% | 9.3% | 10.6% |
| CK2 | 18.4 ± 1.8 c | 55.2 ± 5.4 d | 77.8 ± 7.6 d | 62.3 ± 6.1 b | 198.3 ± 11.1 c | 8011 ± 450 c | 251.0 ± 10.7 b | 22.2 ± 4.4 a | 24.0 ± 2.4 c |
| T7 | 19.0 ± 1.9 c | 65.0 ± 6.4 cd | 87.1 ± 8.5 cd | 63.5 ± 6.2 ab | 224.9 ± 9.7 b | 9086 ± 393 b | 253.0 ± 48.1 b | 22.8 ± 2.1 a | 25.3 ± 2.9 c |
| T8 | 27.8 ± 2.7 b | 83.9 ± 8.2 bc | 109.0 ± 10.7 bc | 72.6 ± 7.1 ab | 228.9 ± 1.7 b | 9249 ± 70 b | 276.3 ± 22.7 ab | 24.3 ± 3.3 a | 26.0 ± 0.8 c |
| T9 | 28.0 ± 2.7 b | 93.9 ± 9.2 b | 159.8 ± 15.7 a | 76.9 ± 7.5 ab | 263.6 ± 8.0 a | 10,650 ± 322 a | 305.0 ± 15.6 ab | 25.5 ± 0.3 a | 30.3 ± 0.9 ab |
| T10 | 28.9 ± 2.8 b | 118.9 ± 11.7 a | 119.9 ± 11.7 b | 70.5 ± 6.9 ab | 226.0 ± 7.6 b | 9130 ± 307 b | 261.0 ± 6.7 b | 23.8 ± 1.9 a | 25.7 ± 2.5 c |
| T11 | 34.0 ± 3.3 ab | 132.2 ± 13.0 a | 122.6 ± 12.0 b | 75.1 ± 7.4 ab | 244.7 ± 11.0 ab | 9887 ± 446 ab | 276.3 ± 22.7 ab | 24.5 ± 4.3 a | 27.5 ± 0.4 bc |
| T12 | 39.0 ± 3.8 a | 138.4 ± 13.6 a | 124.8 ± 12.2 b | 80.0 ± 7.8 a | 250.1 ± 9.0 a | 10,104 ± 363 a | 323.0 ± 9.2 a | 27.1 ± 4.2 a | 31.7 ± 1.2 a |
| Average | 27.9 | 98.2 | 114.4 | 71.6 | 233.8 | 9445 | 278.0 | 24.3 | 27.2 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 24.7% | 30.7% | 21.9% | 8.6% | 8.4% | 8.4% | 9.0% | 6.3% | 9.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Bao, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, N. Impacts of Humic Acid and Potassium Fulvate on Cadmium and Lead Accumulation and Translocation in Maize (Zea mays L.) Grown in Co-Contaminated Soil. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192064
Liu Q, Sun X, Wang S, Zhao R, Li L, Zhou J, Bao L, Zhou W, Zhang N. Impacts of Humic Acid and Potassium Fulvate on Cadmium and Lead Accumulation and Translocation in Maize (Zea mays L.) Grown in Co-Contaminated Soil. Agriculture. 2025; 15(19):2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192064
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qi, Xuchao Sun, Sheng Wang, Rongteng Zhao, Lanfeng Li, Jijiang Zhou, Li Bao, Wenbing Zhou, and Naiming Zhang. 2025. "Impacts of Humic Acid and Potassium Fulvate on Cadmium and Lead Accumulation and Translocation in Maize (Zea mays L.) Grown in Co-Contaminated Soil" Agriculture 15, no. 19: 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192064
APA StyleLiu, Q., Sun, X., Wang, S., Zhao, R., Li, L., Zhou, J., Bao, L., Zhou, W., & Zhang, N. (2025). Impacts of Humic Acid and Potassium Fulvate on Cadmium and Lead Accumulation and Translocation in Maize (Zea mays L.) Grown in Co-Contaminated Soil. Agriculture, 15(19), 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192064





