Effects of Adding Lactobacillus Inoculants on the Nutritional Value of Sesbania cannabina and Whole Corn Mixed Silage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
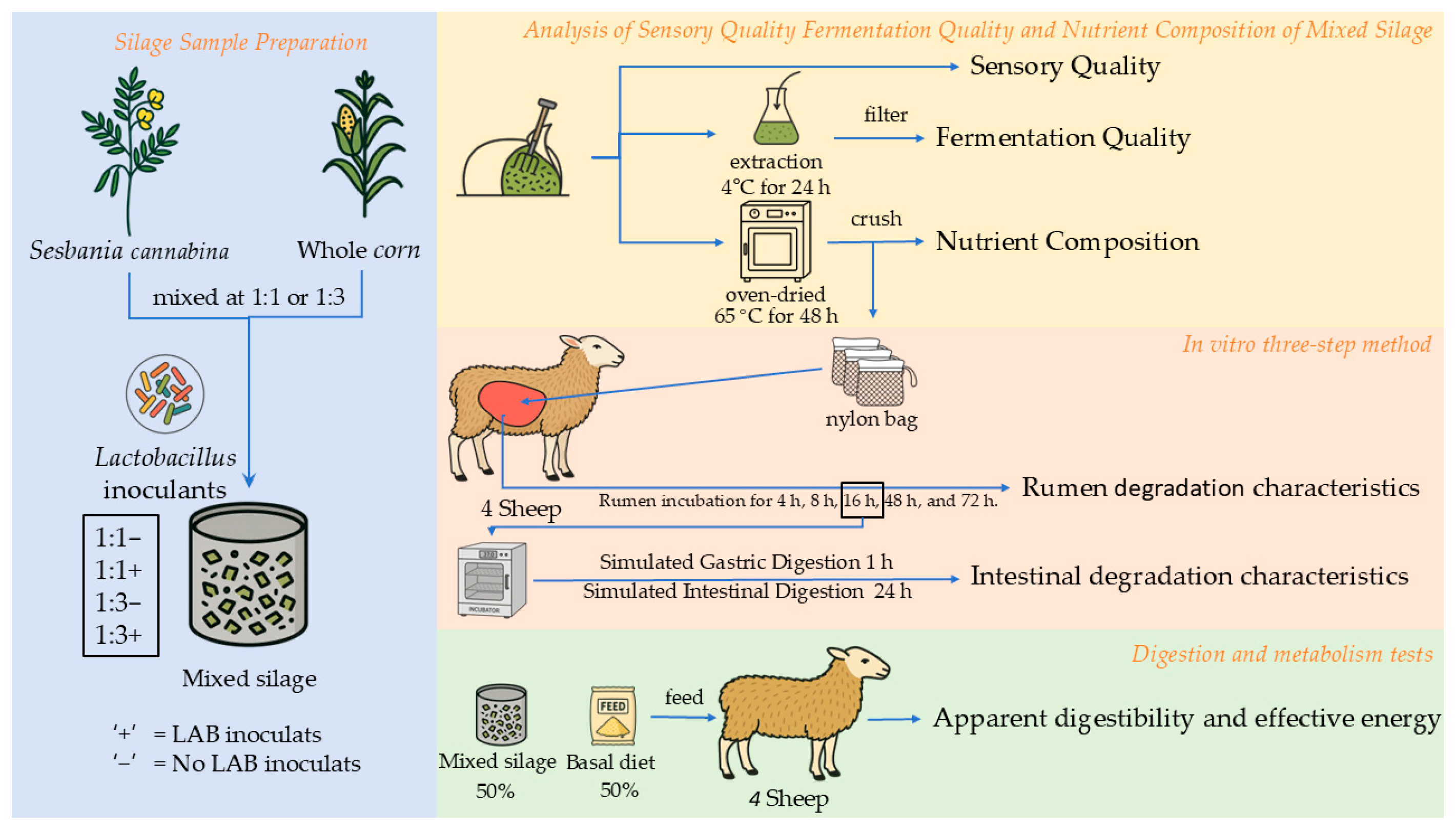
2.1. Silage Sample Preparation
2.2. Sensory Evaluation
2.3. Analysis of Fermentation Quality and Nutrient Composition of Mixed Silage
2.4. In Vitro Ruminal Degradability and Gastro-Intestinal Digestibility Analysis
- Step 1. Ruminal degradation
- Step 2. Gastric digestion of mixed silage residue after rumen incubation
- Step 3. Intestinal digestion of mixed silage residue after rumen and gastric incubation
2.5. In Vitro Ruminal Degradability and Gastro-Intestinal Digestibility Calculation
- ▪
- XD is the rumen degradation rate of X;
- ▪
- ICPD is the intestinal degradation rate of crude protein;
- ▪
- IDCP is the intestinal digestible protein, CP is the crude protein content of silage, RUP is rumen nondegradable protein, RDP is rumen degradable protein, 0.9 is the efficiency of conversion of rumen-degraded protein to microbial protein, 0.7 is the digestibility of microbial protein in the small intestine.
2.6. Calculations of Degradation Kinetics Parameters
2.7. Determination of Nutrient Digestion Metabolism
2.8. Calculation of Apparent Digestibility and Effective Energy Value
- ▪
- XADdiet is apparent digestibility rate of X in the diet;
- ▪
- XADsilage is apparent digestibility rate of X in the silage;
- ▪
- DCPsilage is digestible crude protein in the silage;
- ▪
- Silage XE is X energy in the silage.
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sensory Quality
3.2. Fermentation Quality
3.3. Nutrient Composition
3.4. Effects of Adding LAB Inoculant S. cannabina and Whole Corn Mixed Silage on Rumen Effective Degradation Rate of Nutrients
3.5. Intestinal Digestible Protein
3.6. Effective Energy and Apparent Digestibility
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Adding LAB and Increasing the Proportion of Whole Corn on the Fermentation Quality of the Mixed Silage
4.2. Effect of Adding LAB and Increasing the Proportion of Whole Corn on the Nutrient Composition of the Mixed Silage
4.3. Effect of Adding LAB and Increasing the Proportion of Whole Corn on the Effective Rumen Degradation Rate of the Mixed Silage
4.4. Effect of Adding LAB and Increasing the Proportion of Whole Corn on the Degradation Characteristics of the Small Intestine of the Mixed Silage
4.5. Effect of Adding LAB and Increasing the Proportion of Whole Corn on the Nutrient Apparent Digestibility and Effective Energy of the Mixed Silage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NDF | Neutral Detergent Fiber |
| ADF | Acid Detergent Fiber |
| DM | Dry Matter |
| CP | Crude Protein |
| NH3-N | Ammonia Nitrogen |
| EE | Ether Extract |
| ED | Effective Degradability |
| IDG | Intestinal Digestibility |
| IDCP | Intestinal Digestible Crude Protein |
| RDP | Rumen Degradable Protein |
| RUP | Rumen Nondegradable Protein |
| LA | Lactic Acid |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| WSC | Water-Soluble Carbohydrates |
References
- Taelman, S.E.; De Meester, S.; Van Dijk, W.; Da Silva, V.; Dewulf, J. Environmental sustainability analysis of a protein-rich livestock feed ingredient in the netherlands: Microalgae production versus soybean import. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 101, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pexas, G.; Doherty, B.; Kyriazakis, I. The future of protein sources in livestock feeds: Implications for sustainability and food safety. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1188467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henchion, M.; Hayes, M.; Mullen, A.M.; Fenelon, M.; Tiwari, B. Future protein supply and demand: Strategies and factors influencing a sustainable equilibrium. Foods 2017, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Meng, R.; Feng, W.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X.; Chen, T.; Xue, Z.; Wang, X. Soil-improving effect of sesbania–sorghum rotation in a heavily saline–alkaline coastal region. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Jia, P.; Zou, J.; Ren, H.; Xi, M.; Jiang, Z. Improving soil properties and sesbania growth through combined organic amendment strategies in a coastal saline-alkali soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 374, 124041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, X.; You, C.; Wu, X.; Pan, D.; Lv, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, D.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Telomere-to-telomere genome of the allotetraploid legume sesbania cannabina reveals transposon-driven subgenome divergence and mechanisms of alkaline stress tolerance. Sci. China Life Sci. 2024, 67, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Becker, K. In vitro rumen degradability of crude protein in seeds from four Sesbania spp. and the effects of treatments designed to reduce the levels of antinutrients in the seeds. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2002, 95, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreyowhans, S.; Zegeye, T. Effect of dried sesbania sesban leaves supplementation on milk yield, feed intake, and digestibility of holstein friesian x zebu (arado) crossbred dairy cows. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, M.M.; Youssef, I.M.I.; Radwan, M.A.; Hamdon, H.A. Effect of feeding Sesbania sesban and reed grass on growth performance, blood parameters, and meat quality of growing lambs. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, P.; Singaravadivelan, A.; Senthilkumar, D.; Vasanthakumar, T.; Ramachandran, M. Effect of Sesbania grandiflora (agati) supplementation on weight gain of crossbred jersey heifer calves. Int. J. Econ. Plants 2021, 8, 162–164. [Google Scholar]
- Makau, D.N.; VanLeeuwen, J.A.; Gitau, G.K.; McKenna, S.L.; Walton, C.; Muraya, J.; Wichtel, J.J. Effects of Calliandra and sesbania supplementation on weight gain in dairy calves on smallholder farms in kenya. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 172, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatta, R.; Saravanan, M.; Baruah, L.; Sampath, K.T. Nutrient content, in vitro ruminal fermentation characteristics and methane reduction potential of tropical tannin-containing leaves. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2929–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Geng, X.; Shi, W.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C. Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome reveals the different metabolite biosynthesis profiles related to palatability in winter and spring shoot in moso bamboo. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 202, 107973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeparusi, E.O. Effect of processing on the nutrients and anti-nutrients of lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) Flour. Die Nahr. 2001, 45, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Li, D.X.; Wang, X.K.; Lin, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Yang, F.Y. Fermentation dynamics and diversity of bacterial community in four typical woody forages. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Xia, T.; Deng, X.; Cao, X.; Zhong, J. Compound lactic acid bacteria enhance the aerobic stability of sesbania cannabina and corn mixed silage. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Sun, J.; Xia, T.; Huang, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Teng, K.; Zhong, J. Dynamic changes in fermentation quality and structure and function of the microbiome during mixed silage of sesbania cannabina and sweet sorghum grown on saline-alkaline land. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e248322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, S.T.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Ensiling characteristics, structural and nonstructural carbohydrate composition and enzymatic digestibility of napier grass ensiled with additives. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur Thomas, T. An automated procedure for the determination of soluble carbohydrates in herbage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1977, 28, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrez, A.Z.; Ørskov, E.R.; McDonald, I. Rates of rumen fermentation in relation to ammonia concentration. Br. J. Nutr. 1977, 38, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, L.; Mo, F.; Zhang, W. In situ degradation kinetics of 25 feedstuffs and the selection of time points in mathematical statistics. Animals 2023, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo, S.; Calsamiglia, S.; Ferret, A. Technical note: A modified three-step in vitro procedure to determine intestinal digestion of proteins. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 2163–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørskov, E.R.; McDonald, I. The estimation of protein degradability in the rumen from incubation measurements weighted according to rate of passage. J. Agric. Sci. 1979, 92, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9831:1998; Animal Feeding Stuffs, Animal Products, and Faeces or Urine—Determination of Gross Calorific Value—Bomb Calorimeter Method. International Standardization Organization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- Lewis, A.J.; Southern, L.L. Swine Nutrition; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 906–907. [Google Scholar]
- Barzegar, S.; Wu, S.; Noblet, J.; Swick, R.A. Metabolizable energy of corn, soybean meal and wheat for laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5876–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htet, M.N.S.; Soomro, R.N.; Bo, H. Effects of different planting pattern of maize (Zea mays L.) and soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) intercropping in resource consumption on fodder yield, and silage quality. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, M.L.; Niu, D.Z.; Jiang, D.; Zuo, S.S.; Xu, C.C. Dynamics of microbial community during ensiling direct-cut alfalfa with and without lab inoculant and sugar. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 1456–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Li, H.; Gan, L.; Chen, S.; Yan, Y.; Jia, Z.; Liu, W.; Wei, X.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Q. The effects of native lactic acid bacteria on the microbiome, fermentation profile, and nutritive value of napier grass silage prepared with different legume ratios. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1112058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, L. Exploring the differences between sole silages of gramineous forages and mixed silages with forage legumes using 16s/its full-length sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1120027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Q.; Degen, A.A.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; et al. Effects of different additives on fermentation quality, microbial communities, and rumen degradation of alfalfa silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Hu, J.; Ma, R.; Liu, H.; Shao, T. Improving total mixed ration silage: Effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculants and antimicrobial additives on fermentation quality and aerobic stability. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussian, H.M.; Saeed, A.A. Effect of adding fermented juice of epiphytic lactic acid bacteria prepared with different sources and levels of soluble carbohydrates on chemical composition, fermentation and quality characteristics of wheat straw silages. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1262, 72063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøseth, M.; Karlsson, L.; Steinshamn, H.; Johansen, M.; Kidane, A.; Prestløkken, E. Effects of dry matter concentration in grass silage on milk production of dairy cows fed concentrates high or low in metabolizable protein concentration. Livest. Sci. 2025, 291, 105611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, W.; Xing, Y.; Pian, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Improving the quality of rice straw silage with moringa oleifera leaves and propionic acid: Fermentation, nutrition, aerobic stability and microbial communities. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Ren, T.; Cao, X.; Wu, T.; Hu, Z.; Ai, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Du, L.; et al. Emerging and innovative utilisation of herbal medicine residues in anaerobic fermentation of corn straw: Cellulose degradation, fermentation characteristics, and microbial community structure and co-occurrence network. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 227, 120802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucetti, P.; Valadares Filho, S.D.C.; Silva, J.T.D.; Oliveira, K.R.D.; Souza, G.A.P.D.; Cidrini, F.A.; Hollerbach, L.G.; Silva, B.D.C.; Renno, L.N.; Sampaio, C.B.; et al. Effects of different concentrate levels in agri-002e sorghum silage-based diets on nutrient intake and digestibility, ruminal ph and ammonia concentration, ruminal degradability, and microbial efficiency in beef cattle. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2024, 315, 116026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y. Cellulase interacts with lactic acid bacteria to affect fermentation quality, microbial community, and ruminal degradability in mixed silage of soybean residue and corn stover. Animals 2021, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Lv, L.; Zheng, Z.; Lu, H.; Ren, Y. Comparative study of the nutritional value and degradation characteristics of amaranth hay in the rumen of goats at different growth stages. Animals 2022, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirkovic Velickovic, T.D.; Stanic-Vucinic, D.J. The role of dietary phenolic compounds in protein digestion and processing technologies to improve their antinutritive properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 82–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Lin, Y.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on fermentation quality and anti-nutritional factors of paper mulberry silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.J.; Taylor, C.C.; Lynch, M.P.; Neylon, J.M. The effect of treating alfalfa with Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and nutritive value for lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, A.N.; Harper, M.T.; Roth, G.; Canale, C.; Huhtanen, P.; Richard, T.L.; DiMarco, K. Effects of ensiling time on corn silage neutral detergent fiber degradability and relationship between laboratory fiber analyses and in vivo digestibility. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2333–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Fan, X.; Wu, T.; Zhou, J.; Huang, H.; Qiu, T.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, F.; Gan, S. Lactic acid bacteria and cellulase improve the fermentation characteristics, aerobic stability and rumen degradation of mixed silage prepared with amaranth and rice straw. Fermentation 2023, 9, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, C.A.; Cabrera, D.L.; Zou, M.; Boland, M.J.; Moughan, P.J. The rate at which digested protein enters the small intestine modulates the rate of amino acid digestibility throughout the small intestine of growing pigs. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Chen, D.; Huang, P.; Gao, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. Effects of tannin-tolerant lactic acid bacteria in combination with tannic acid on the fermentation quality, protease activity and bacterial community of stylo silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 2540–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, B.; Lv, B.; Liu, C.; Chen, D. Ruminal degradability and intestinal digestibility of individual amino acids in mixed diets with different crude protein levels measured by the modified in vitro three-step and mobile nylon bag technique. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Sun, B.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Qian, Z.; Zhuang, X. Fermentation characteristics and microbiota during the ensiling of myriophyllum aquaticum inoculated with lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sesbania cannabina | Whole Corn | |
|---|---|---|
| DM (%) | 30.47 | 28.20 |
| CP (%) | 20.74 | 8.27 |
| NDF (%) | 46.43 | 49.63 |
| ADF (%) | 36.32 | 29.75 |
| WSC (%) | 6.13 | 18.00 |
| Starch (%) | 2.18 | 5.37 |
| Ingredients | Content |
|---|---|
| Concentrate feed 1 (%) | 28.57 |
| Compound grass particles 2 (%) | 71.43 |
| Total (%) | 100 |
| Nutrient composition (%) | |
| DM (%) | 94.02 |
| CP (%) | 10.03 |
| EE (%) | 2.13 |
| NDF (%) | 48.71 |
| ADF (%) | 32.46 |
| Ca (%) | 1.41 |
| P (%) | 0.86 |
| Ca/P (%) | 1.64 |
| Sensory Quality | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | 1:1− | 1:1+ | 1:3− | 1:3+ |
| Smell | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| Texture | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Color | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Score | 19 | 19 | 20 | 20 |
| Rank | excellent | excellent | excellent | excellent |
| Fermentation Quality | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | LAB | 1:1 | 1:3 | T (LAB) | M (Ratio) | T × M |
| pH | − | 3.77 ± 0.04 | 3.69 ± 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.22 |
| + | 3.69 ± 0.01 b | 3.69 ± 0.09 b | ||||
| NH3-N (mg/kg DM) | − | 4.57 ± 0.55 Aa | 3.73 ± 0.31 b | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.17 |
| + | 3.73 ± 0.32 Bb | 3.51 ± 0.13 b | ||||
| LA (mg/kg DM) | − | 55.88 ± 9.96 Bb | 61.27 ± 7.20 Ba | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.83 |
| + | 62.31 ± 27.55 Ab | 75.86 ± 10.81 Aa | ||||
| AA (mg/kg DM) | − | 10.07 ± 0.01 Aa | 9.87 ± 0.01 Ab | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| + | 9.65 ± 0.01 Ba | 8.80 ± 0.01 Bb | ||||
| PA (mg/kg DM) | − | 10.01 ± 0.05 | 9.99 ± 0.09 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| + | 10.13 ± 0.08 a | 8.91 ± 0.01 b | ||||
| Nutrient Composition | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | LAB | 1:1 | 1:3 | T (LAB) | M (Ratio) | T × M |
| DM | − | 34.33 ± 1.86 | 33.52 ± 1.06 | 0.06 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| + | 33.05 ± 1.13 b | 37.59 ± 0.59 a | ||||
| CP (%DM) | − | 12.10 ± 0.71 a | 10.87 ± 0.29 b | 0.07 | <0.05 | 0.73 |
| + | 11.71 ± 0.19 a | 10.31 ± 0.18 b | ||||
| NDF (%DM) | − | 57.18 ± 3.98 a | 46.91 ± 3.37 Ab | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| + | 51.56 ± 1.61 a | 43.83 ± 9.64 Bb | ||||
| ADF (%DM) | − | 45.58 ± 1.11 a | 41.27 ± 5.26 b | 0.83 | <0.05 | 0.95 |
| + | 45.00 ± 2.78 | 44.32 ± 3.00 | ||||
| EE (%DM) | − | 2.18 ± 0.14 | 2.16 ± 0.08 | 0.69 | 0.9979 | 0.86 |
| + | 2.13 ± 0.06 a | 2.15 ± 0.02 a | ||||
| Ash | − | 5.79 ± 0.23 a | 4.63 ± 0.24 b | 0.57 | <0.05 | 0.76 |
| + | 5.89 ± 0.56 b | 4.56 ± 0.36 c | ||||
| Ruminal Effective Degradability | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | LAB | 1:1 | 1:3 | T (LAB) | M (Ratio) | T × M |
| DMED (%) | − | 55.66 ± 3.30 Bb | 62.01 ± 0.04 a | 0.12 | 0.74 | 0.61 |
| + | 63.33 ± 2.50 A | 63.15 ± 1.47 | ||||
| CPED (%) | − | 76.05 ± 1.47 B | 74.62 ± 1.22 B | <0.05 | 0.10 | 0.08 |
| + | 80.00 ± 0.64 A | 80.21 ± 0.93 A | ||||
| NDFED (%) | − | 50.58 ± 2.04 a | 42.96 ± 4.97 b | 0.13 | <0.05 | 0.81 |
| + | 47.72 ± 0.80 a | 40.56 ± 1.38 b | ||||
| ADFED (%) | − | 25.43 ± 3.40 a | 17.45 ± 0.68 Bb | 0.71 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| + | 22.60 ± 4.60 | 20.25 ± 2.72 A | ||||
| Intestinal Digestible Protein | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | LAB | 1:1 | 1:3 | T (LAB) | M (Ratio) | T × M |
| RDP (g/kg) | − | 92.02 ± 4.79 a | 81.11 ± 2.47 b | 0.40 | <0.05 | 0.98 |
| + | 93.68 ± 2.61 a | 82.70 ± 1.63 b | ||||
| RUP (g/kg) | − | 28.98 ± 1.51 A | 27.59 ± 0.84 A | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.18 |
| + | 23.42 ± 0.65 Ba | 20.40 ± 0.40 Bb | ||||
| ICPD (%) | − | 72.75 ± 7.88 A | 70.13 ± 2.98 A | <0.05 | 0.5095 | 0.79 |
| + | 59.73 ± 6.14 B | 59.47 ± 5.23 B | ||||
| IDCP (g/kg) | − | 79.06 ± 4.12 | 70.45 ± 2.15 A | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.95 |
| + | 73.01 ± 2.03 a | 64.23 ± 1.27 Bb | ||||
| Effective Energy and Apparent Digestibility | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | LAB | 1:1 | 1:3 | T (LAB) | M (Ratio) | T × M |
| GE (MJ/kg) | − | 16.47 ± 0.20 | 16.73 ± 0.06 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.45 |
| + | 16.65 ± 0.23 | 17.13 ± 0.14 | ||||
| DE (MJ/kg) | − | 13.96 ± 1.18 | 12.50 ± 0.98 | 0.52 | 0.11 | 0.30 |
| + | 13.07 ± 1.00 | 13.19 ± 0.76 | ||||
| ME (MJ/kg) | − | 11.78 ± 0.55 | 10.29 ± 1.98 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.20 |
| + | 10.87 ± 0.42 | 10.99 ± 0.27 | ||||
| DMAD | − | 68.25 ± 11.58 B | 71.22 ± 6.72 B | <0.05 | 0.82 | 0.51 |
| + | 78.48 ± 3.02 A | 76.17 ± 6.45 A | ||||
| CPAD | − | 80.66 ± 11.68 | 82.76 ± 8.02 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.45 |
| + | 87.29 ± 7.26 | 86.41 ± 7.27 | ||||
| NDFAD | − | 61.96 ± 9.44 | 65.28 ± 10.45 | 0.47 | 0.94 | 0.58 |
| + | 68.73 ± 6.60 | 66.18 ± 12.05 | ||||
| ADFAD | − | 62.12 ± 3.00 | 68.98 ± 8.12 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.98 |
| + | 68.38 ± 6.19 | 71.99 ± 12.08 | ||||
| DCP (g/kg) | − | 97.60 ± 14.13 | 82.76 ± 8.02 | 0.58 | <0.05 | 0.95 |
| + | 102.22 ± 8.50 | 86.41 ± 7.27 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, T.; Song, S.; Song, X.; Pan, D.; Zhao, Q.; He, L.; Tang, D.; Jia, Y.; Cao, X.; Deng, X.; et al. Effects of Adding Lactobacillus Inoculants on the Nutritional Value of Sesbania cannabina and Whole Corn Mixed Silage. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15181913
Yin T, Song S, Song X, Pan D, Zhao Q, He L, Tang D, Jia Y, Cao X, Deng X, et al. Effects of Adding Lactobacillus Inoculants on the Nutritional Value of Sesbania cannabina and Whole Corn Mixed Silage. Agriculture. 2025; 15(18):1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15181913
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Tianzhu, Shuai Song, Xianwei Song, Duofeng Pan, Qinghua Zhao, Liwen He, Ding Tang, Yajun Jia, Xiaofeng Cao, Xian Deng, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Adding Lactobacillus Inoculants on the Nutritional Value of Sesbania cannabina and Whole Corn Mixed Silage" Agriculture 15, no. 18: 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15181913
APA StyleYin, T., Song, S., Song, X., Pan, D., Zhao, Q., He, L., Tang, D., Jia, Y., Cao, X., Deng, X., & Zhang, W. (2025). Effects of Adding Lactobacillus Inoculants on the Nutritional Value of Sesbania cannabina and Whole Corn Mixed Silage. Agriculture, 15(18), 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15181913





