Mechanism Analysis of Soil Disturbance in Sodic Saline–Alkali Soil Tillage Based on Mathematical Modeling and Discrete Element Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Structural Parameters of Subsoiler
2.2. Development of the Mathematical Model
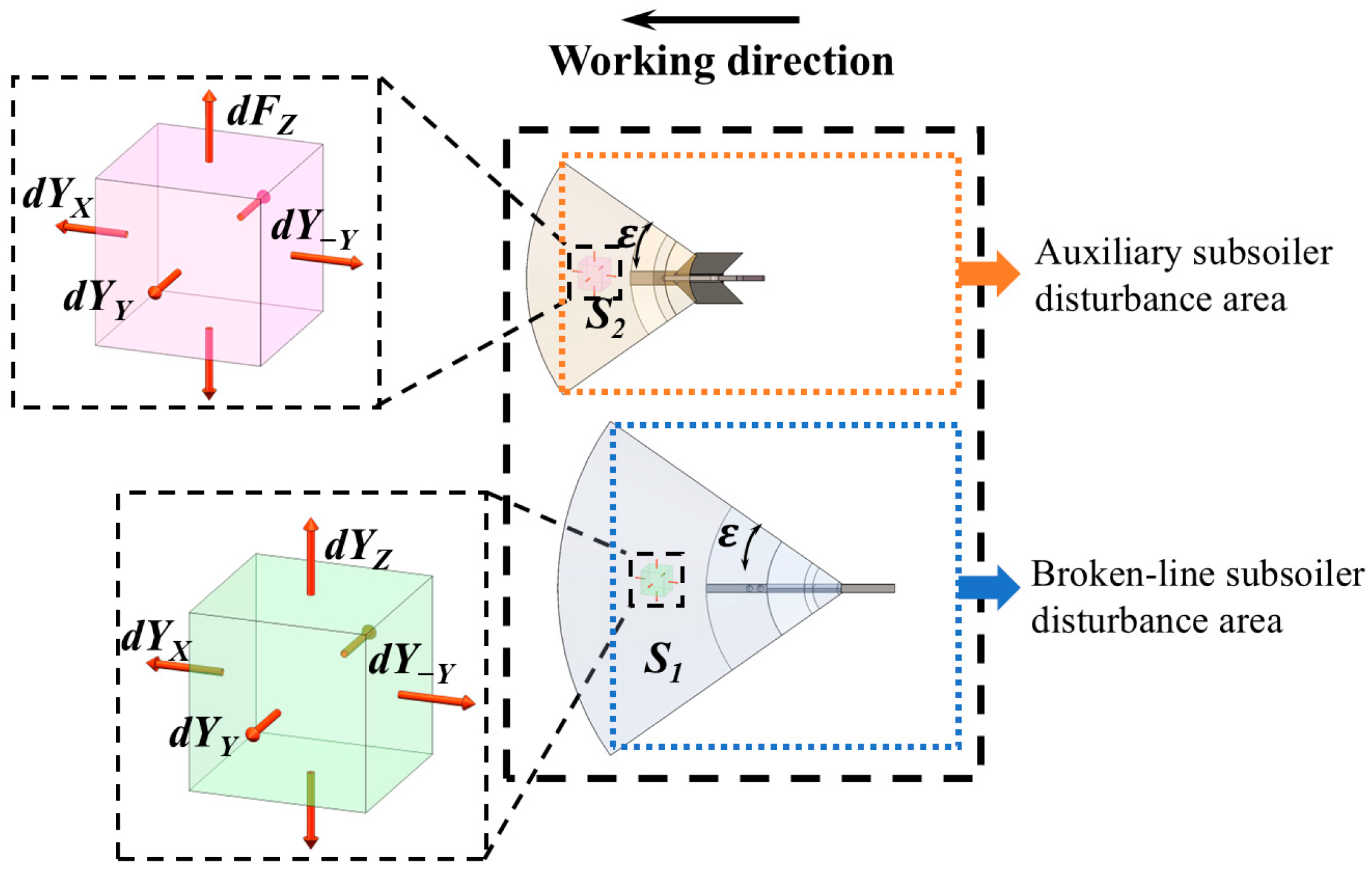
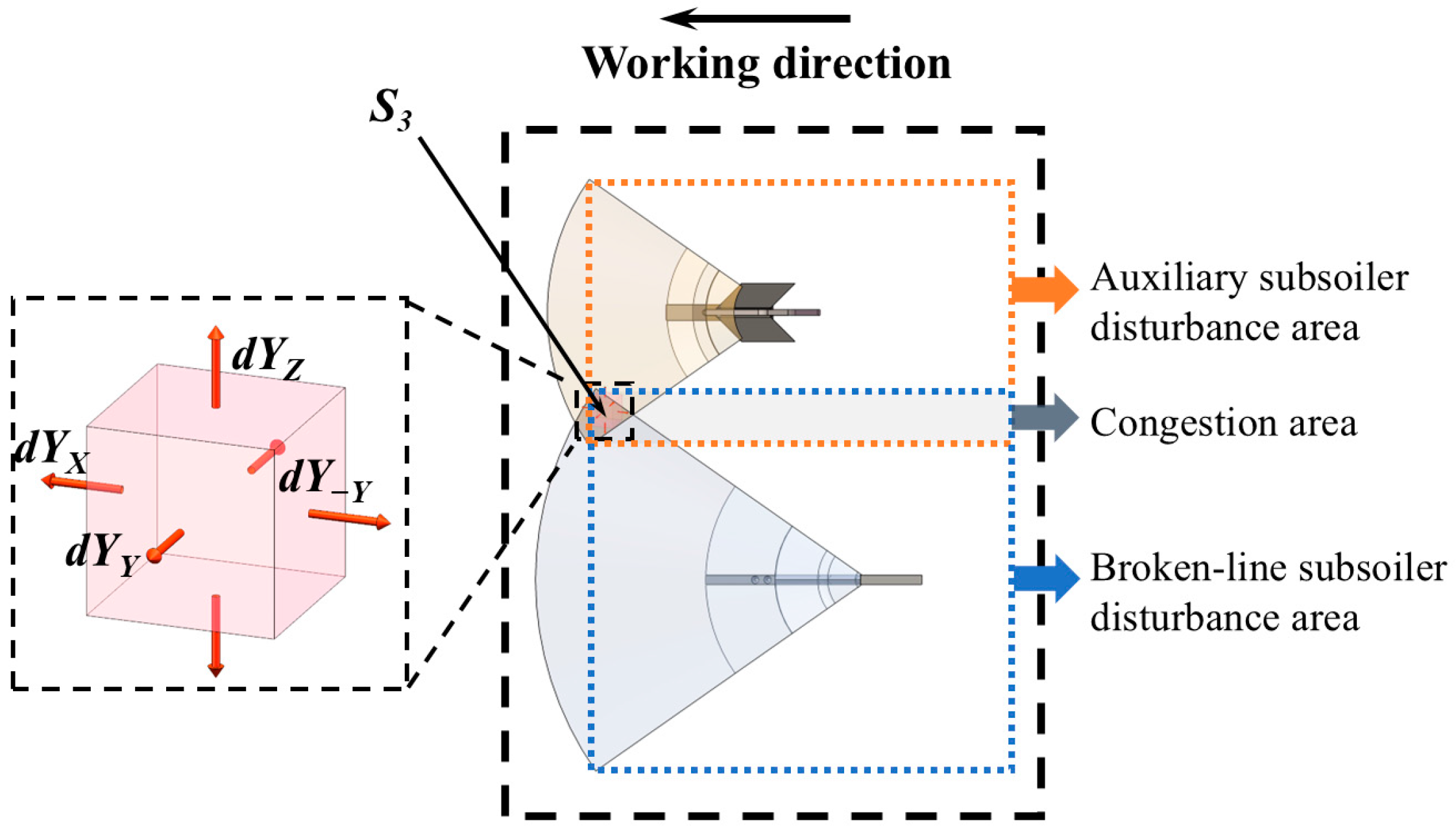
2.2.1. Construction of Soil Micro-Element Kinetic Equation
Without Interaction
Congestion Effect
Repetitive Perturbation Effect
2.2.2. Establishment of Prediction Model of Subsoiler Arrangement–Tillage Performance
Establishment of Draft Force Prediction Model
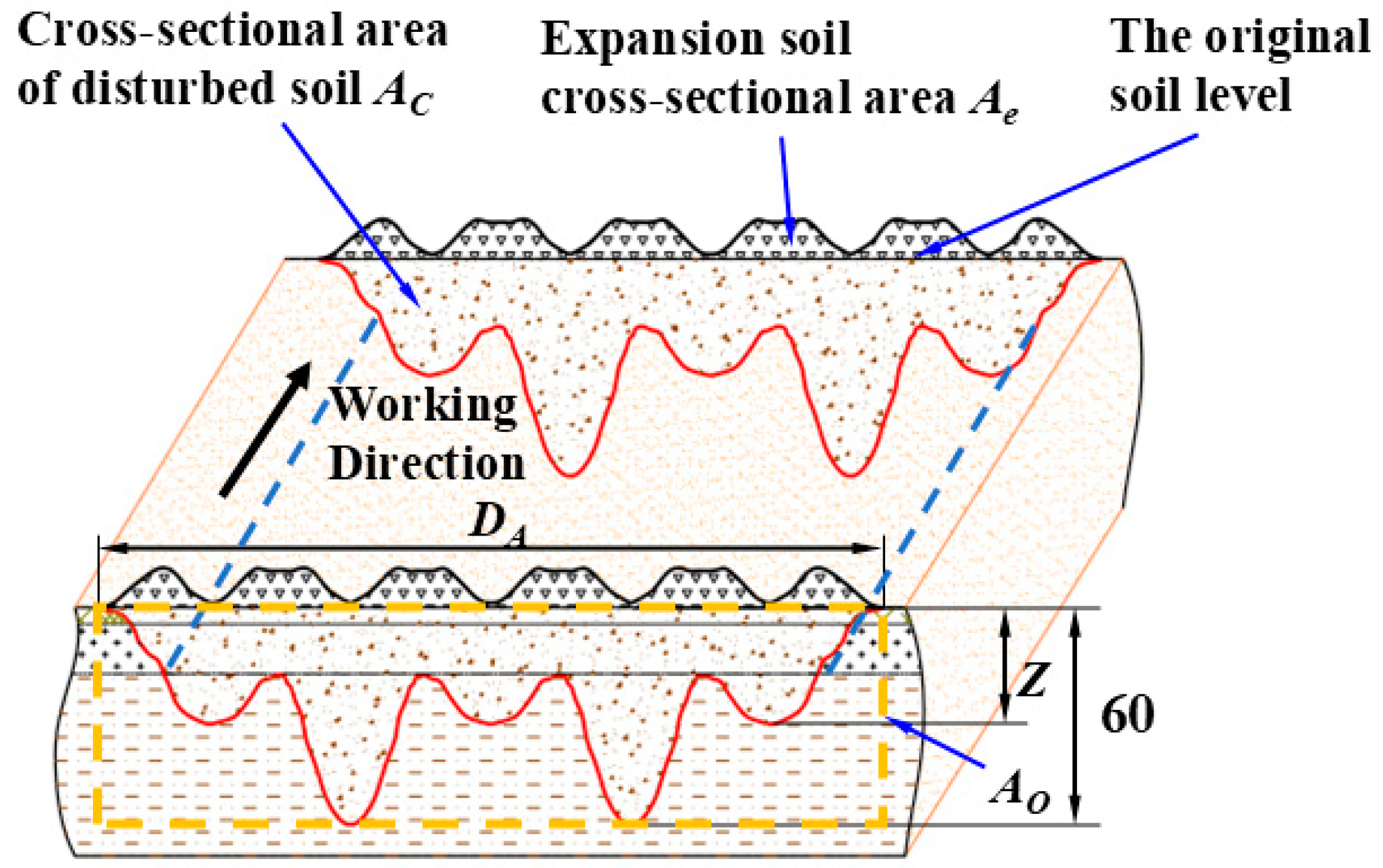
Establishment of Soil Disturbance Area Prediction Model
Establishment of Soil Bulkiness Prediction Model
2.3. Establishment of the Discrete Element Simulation Model
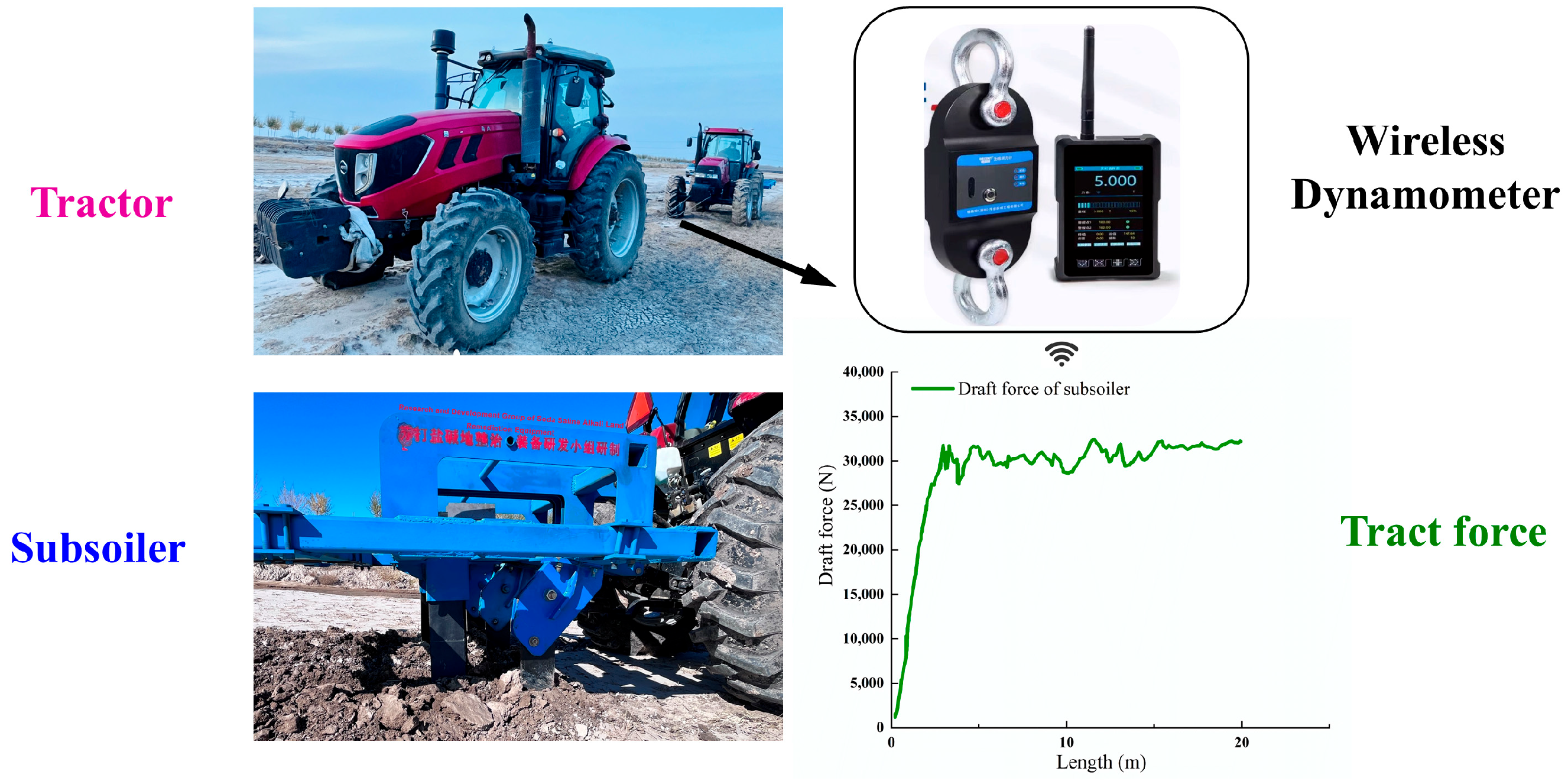
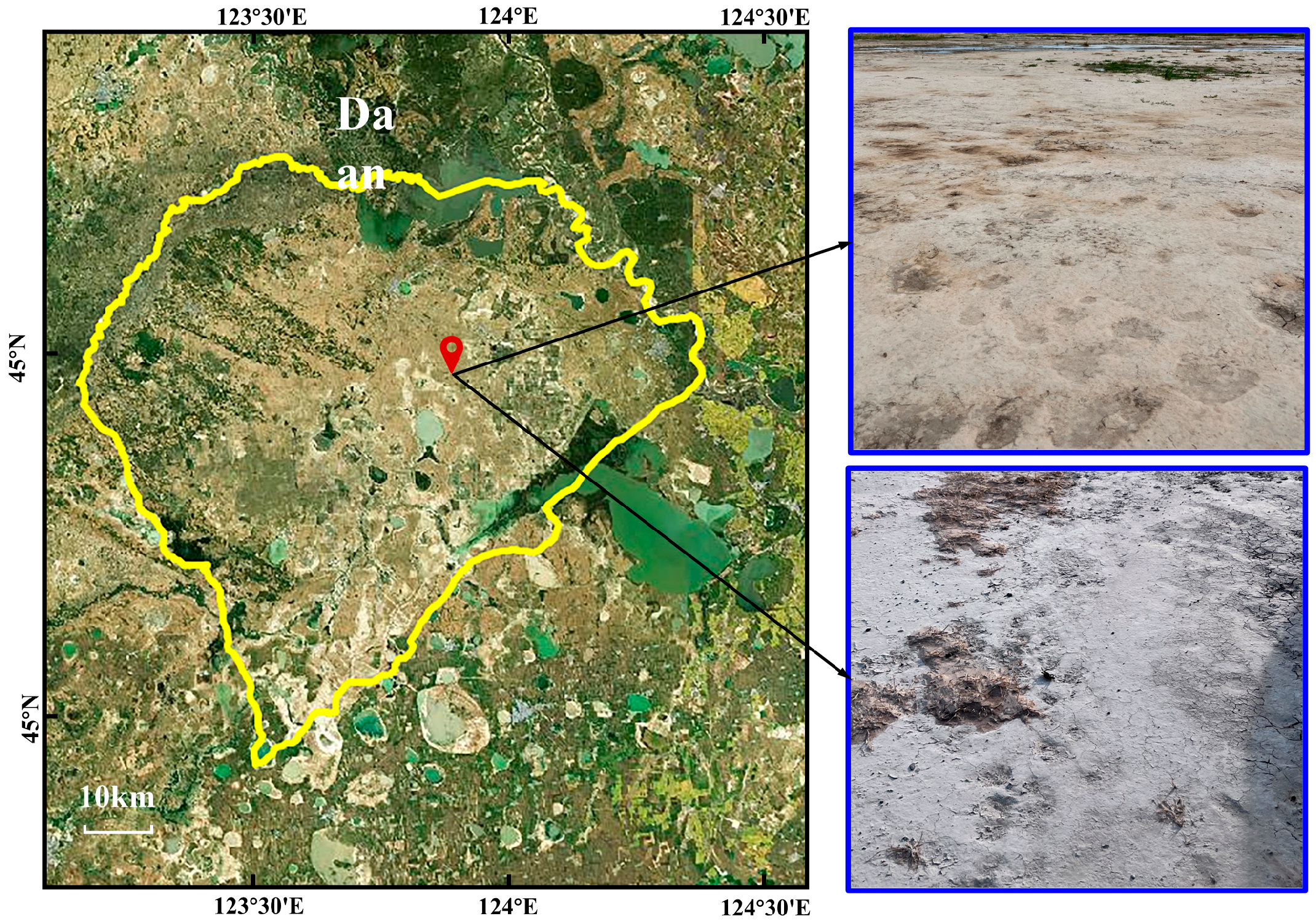
2.4. Field Test
3. Results
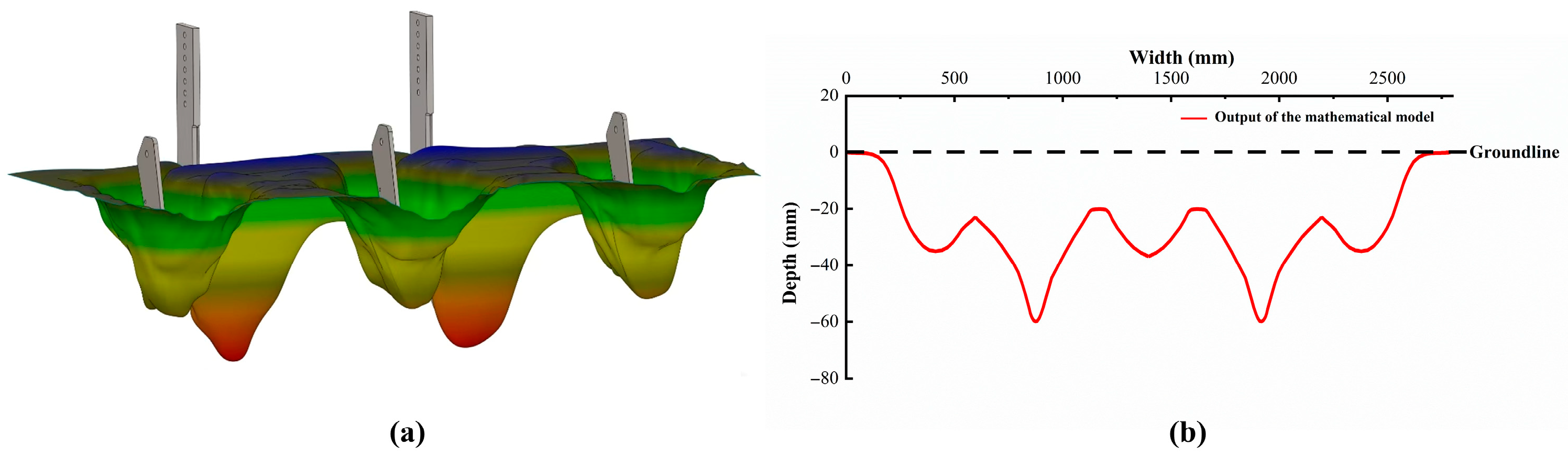
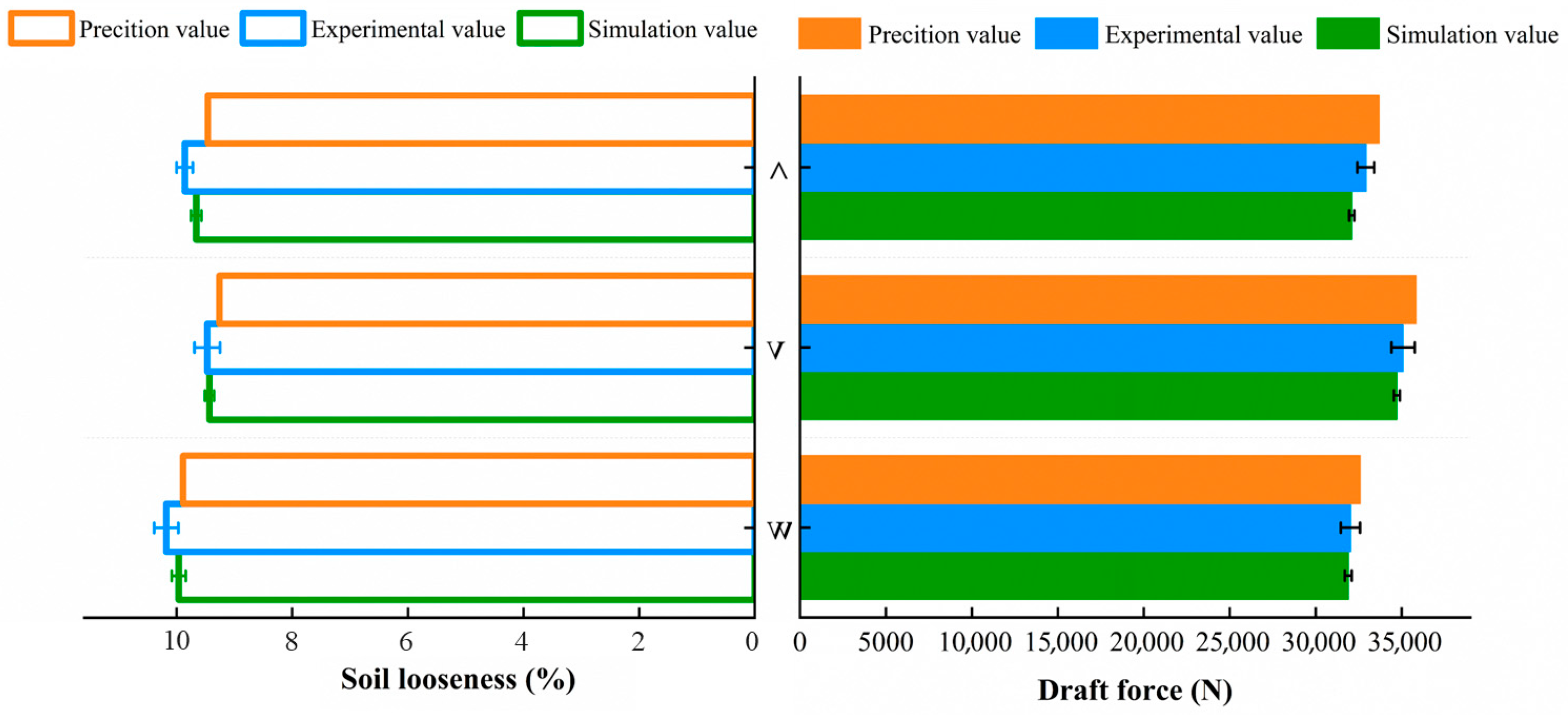
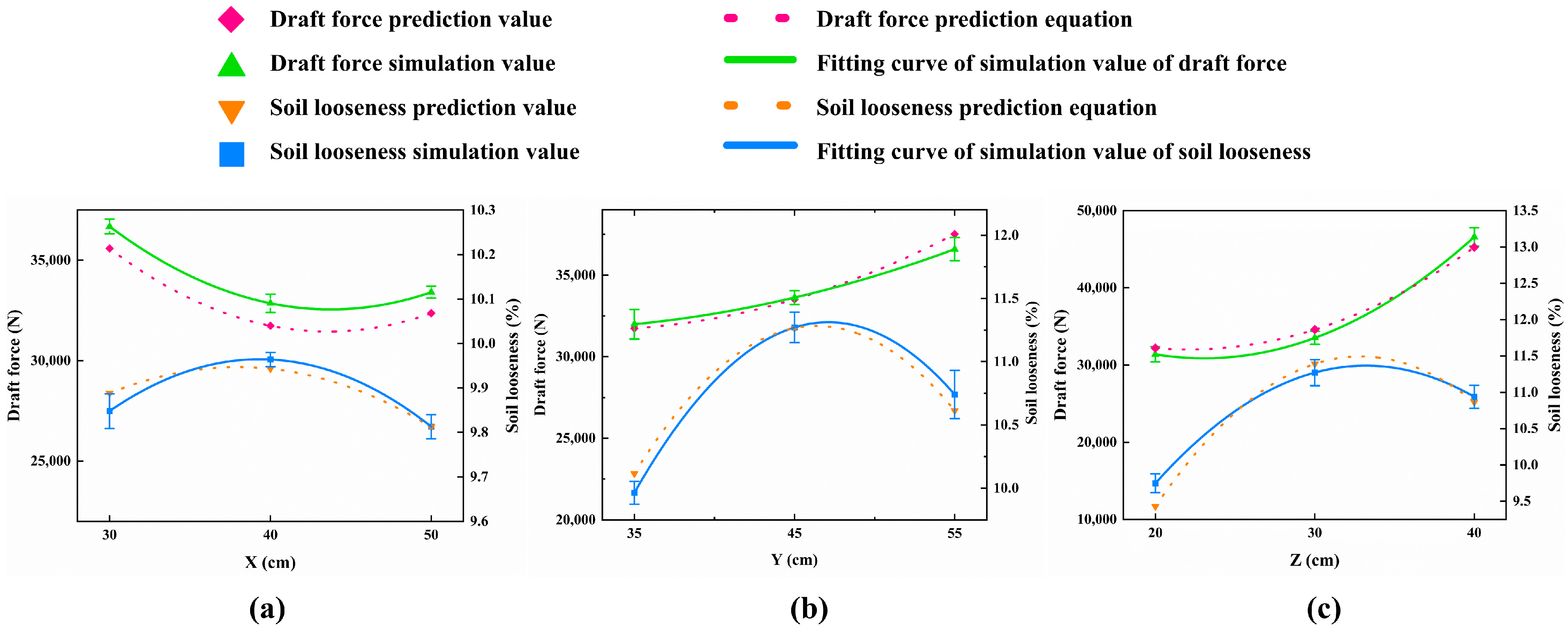
3.1. Comparison of Test, Simulation, and Prediction Results
3.2. The Effect of Arrangement on Tillage Performance
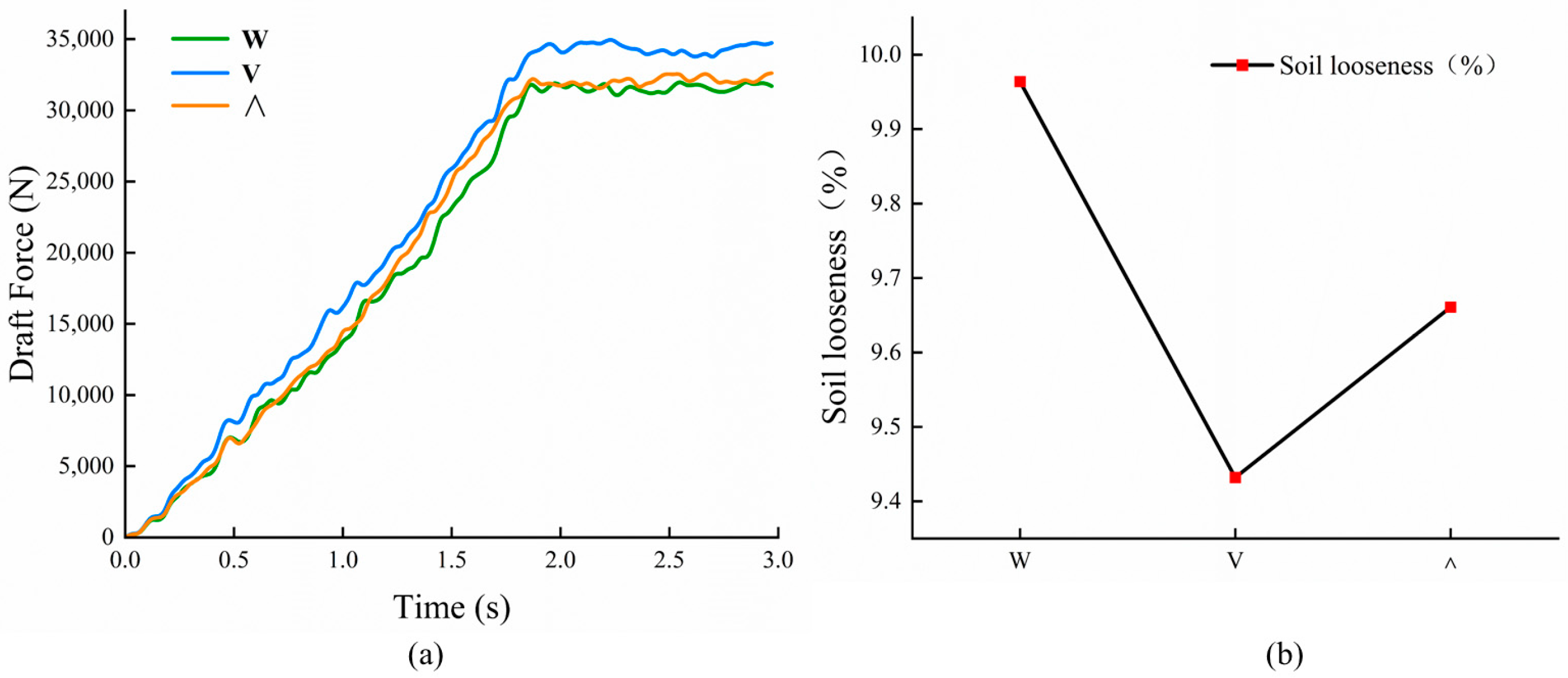
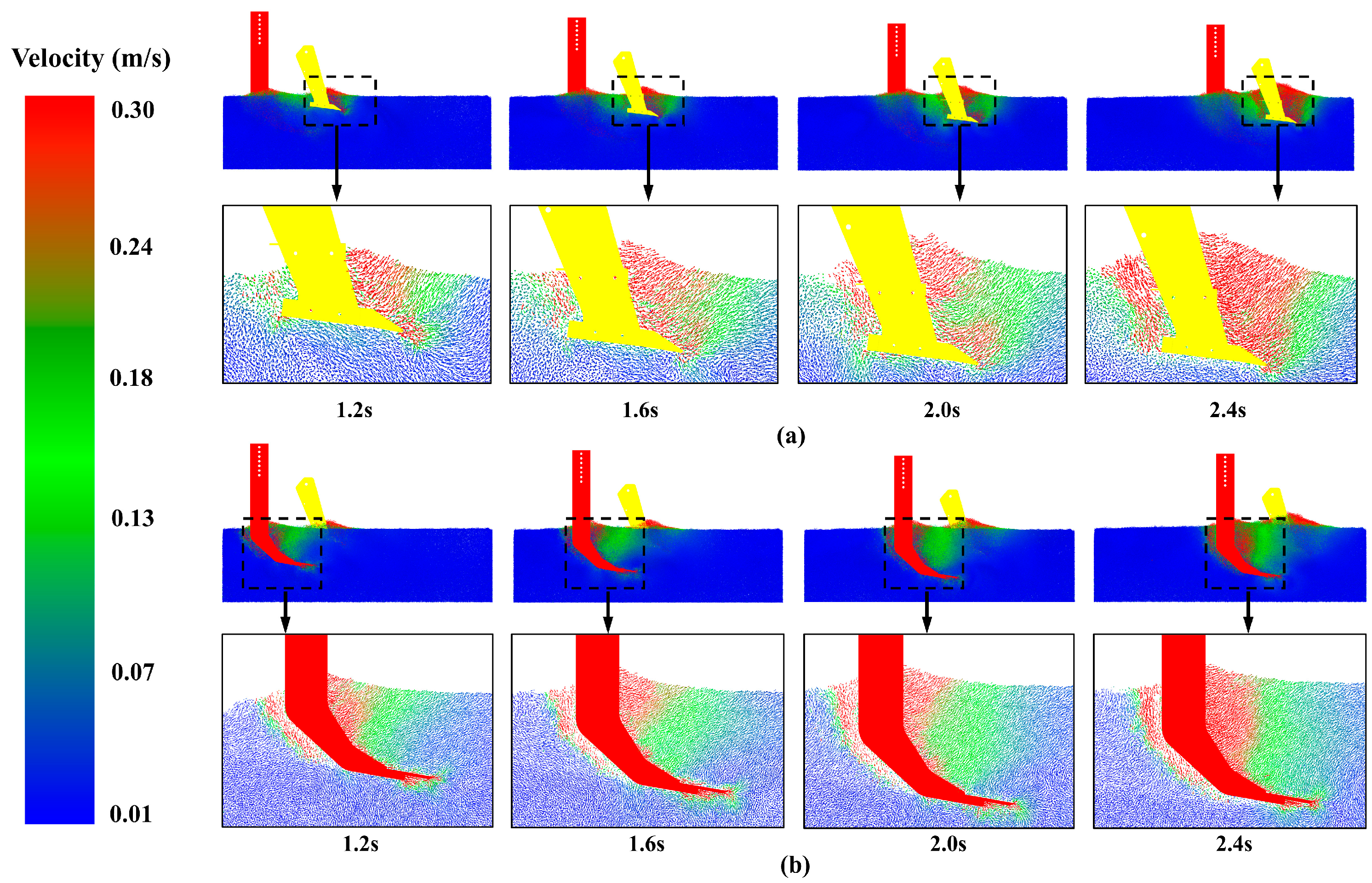
3.2.1. The Change in Draft Force and Looseness with the Arrangement Mode
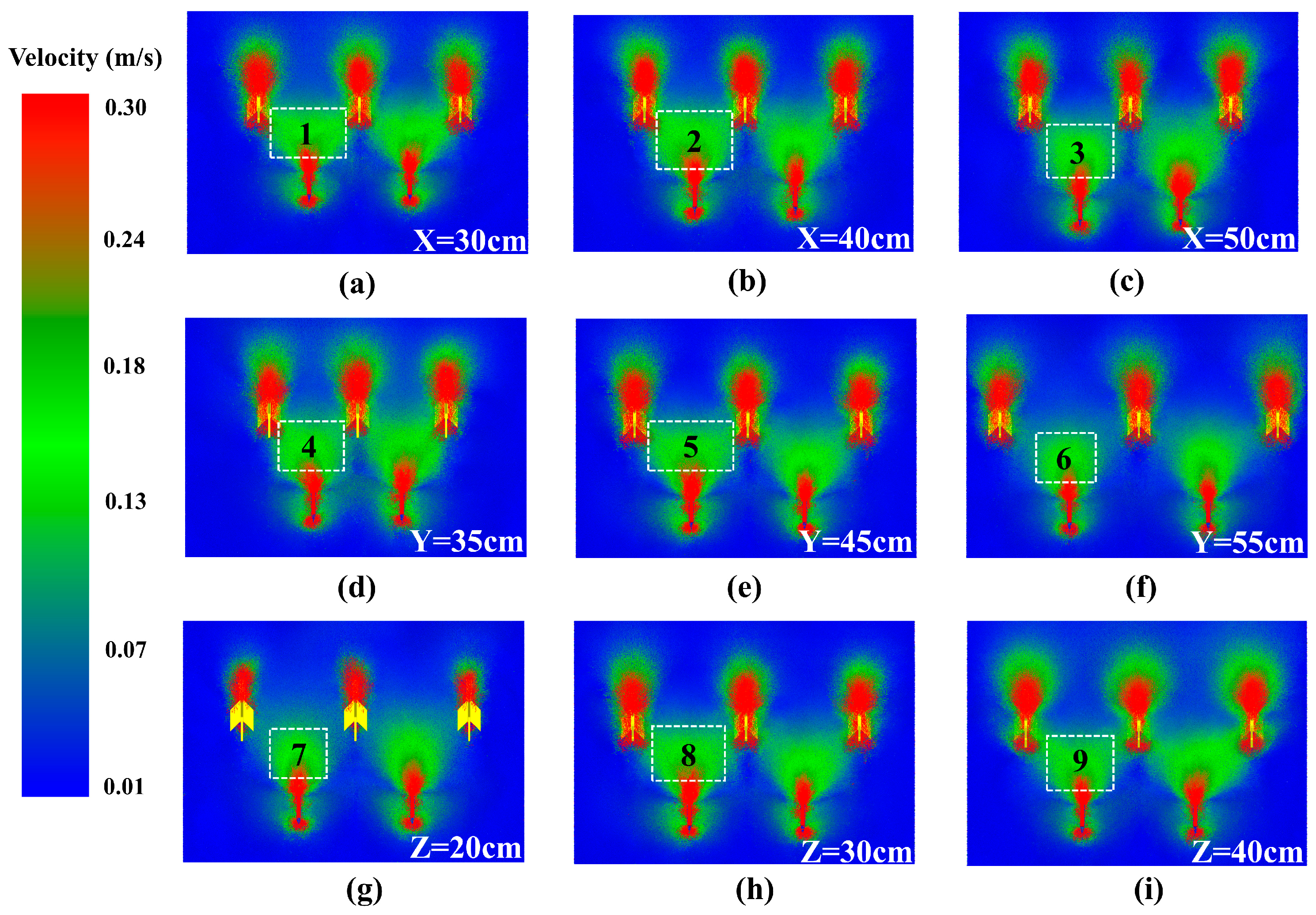
3.2.2. Change of Soil Disturbance Area
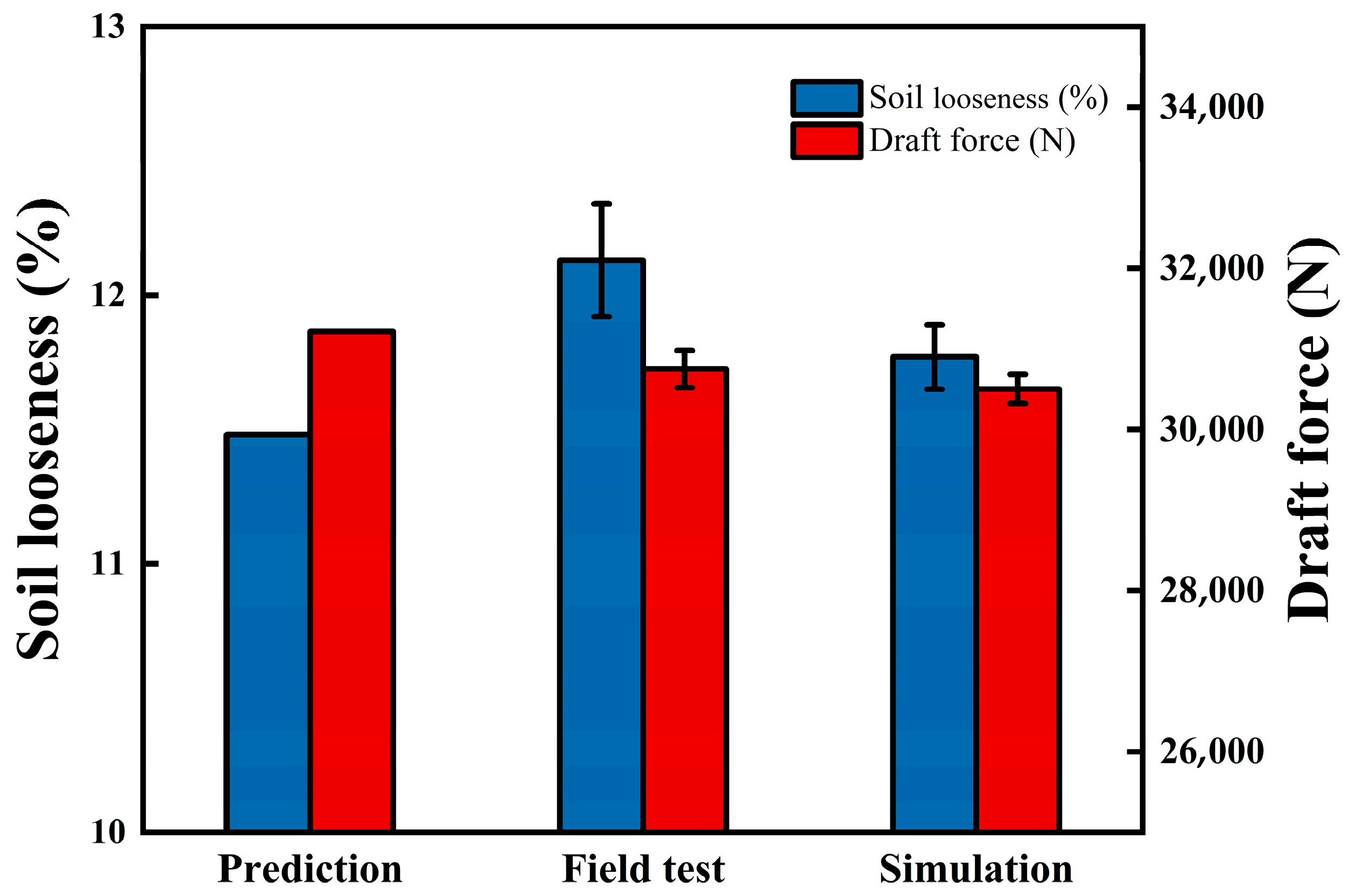
3.3. Verification Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, H.Y. Design and Experimental Study of a Self-Lubricating Drag-Reducing Deep Loosening Shovel for Soda Saline-Alkali Soils with Leaf Vein-like Internal Channels, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China, 2025.
- Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Wang, X.P.; Xie, W.P.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, R.J. Research on Salt-affected Soils in China: History, Status Quo and Prospect. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 10–27. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L.L.; Nie, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, R.Z.; Zhang, T.Y.; Miao, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Characteristics of Clay Dispersion and Its Influencing Factors in Saline-Sodic Soils of Songnen Plain, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 303, 109033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y. Effect of Different Improvement Measures on Soilaggregate Formation and Soybean Yield in Sodasaline, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqing, China, 2025.
- Shao, J. Enhancing the Coupling Coordination of Soil–Crop Systems by Optimising Soil Properties and Crop Production via Subsoiling. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Don, A.; Hennings, I.; Schmittmann, O.; Seidel, S.J. The Effect of Deep Tillage on Crop Yield—What Do We Really Know? Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 174, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Takano, T.; Liu, S. Screening and Evaluation of Saline–Alkaline Tolerant Germplasm of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Soda Saline–Alkali Soil. Agronomy 2018, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J.B.; Yang, H.J.; Li, F.; Hu, H.Y. Research status of modeling analysis of soil-tillage tool interaction. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2024, 45, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinian, S.H.; Hemmat, A.; Esehaghbeygi, A.; Shahgoli, G.; Baghbanan, A. Development of a Dual Sideway-Share Subsurface Tillage Implement: Part 1. Modeling Tool Interaction with Soil Using DEM. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhasselt, A.; Cool, S.; D’Hose, T.; Cornelis, W. How Tine Characteristics of Subsoilers Affect Fuel Consumption, Penetration Resistance and Potato Yield of a Sandy Loam Soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 228, 105631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gu, F.; Ding, Q. Simulation and Experimental Study of the Tillage Mechanism for the Optimal Design of Wheat Rotary Strip–Tiller Blades. Agriculture 2023, 13, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinian, S.H.; Hemmat, A.; Esehaghbeygi, A.; Shahgoli, G.; Baghbanan, A. Development of a Dual Sideway-Share Subsurface Tillage Implement: Part 2. Effect of Tool Geometry on Tillage Forces and Soil Disturbance Characteristics. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, X.R. Simulation and Experiment on the Influence of Subsoiler on Iateritic Soil Disturbance Behavior. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2024, 46, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakov, V.; Nadykto, V.; Orynycz, O.; Pascuzzi, S. Reduction in Energy Consumption by Mitigation of Cultivation Resistance Due to the New Fallow Harrow Concept. Energies 2022, 15, 8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein El-Din, A.; Youssef Taha, R.; Abdel Hamied, R. Mathematical Models for Predicating Draft Forces of Tillage Tools: A Review. J. Adv. Agric. Res. 2021, 26, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Guo, Y.; Guo, X.; Sang, H. A Mathematical Model for Predicting the Draft Force of Shank-Type Tillage Tine in a Compacted Sandy Loam. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 228, 105642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Khan, Z.; Attom, M.; Fattah, K.; Ali, T.; Mortula, M. Continuous Evaluation of Shear Wave Velocity from Bender Elements during Monotonic Triaxial Loading. Materials 2023, 16, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makange, N.R.; Ji, C.; Nyalala, I.; Sunusi, I.I.; Opiyo, S. Prediction of Precise Subsoiling Based on Analytical Method, Discrete Element Simulation and Experimental Data from Soil Bin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fechete-Tutunaru, L.V.; Gaspar, F.; Gyorgy, Z. Soil-Tool Interaction of a Simple Tillage Tool in Sand. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 85, 8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Pei, L.; Liu, H. Finite element simulation and experiment of impact damage of water chestnuts. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2025, 41, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.A.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.; Chandio, F.A.; Tunio, M.H.; Liang, Z.; Solangi, K.A. Discrete Element Method (DEM) Simulation of Single Grouser Shoe-Soil Interaction at Varied Moisture Contents. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 191, 106538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jiang, X.; Li, L.; Ren, L.; Tong, J. Increasing the Width of Disturbance of Plough Pan with Bionic Inspired Subsoilers. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucgul, M.; Fielke, J.M.; Saunders, C. 3D DEM Tillage Simulation: Validation of a Hysteretic Spring (Plastic) Contact Model for a Sweep Tool Operating in a Cohesionless Soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 144, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Chen, Y.; Sadek, M. Simulations of Soil Flow Properties Using the Discrete Element Method (DEM). Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikins, K.A.; Ucgul, M.; Barr, J.B.; Jensen, T.A.; Antille, D.L.; Desbiolles, J.M.A. Determination of Discrete Element Model Parameters for a Cohesive Soil and Validation through Narrow Point Opener Performance Analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Shi, Q.; Lv, P.; Guo, Y.; Fu, D.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, W. Development of a Mathematical Model and Structural Optimization of the Specific Resistance of a Broken Line Subsoiler. Agriculture 2025, 15, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Tong, J.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J. Development and Verification of a Mathematical Model for the Specific Resistance of a Curved Subsoiler. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 190, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


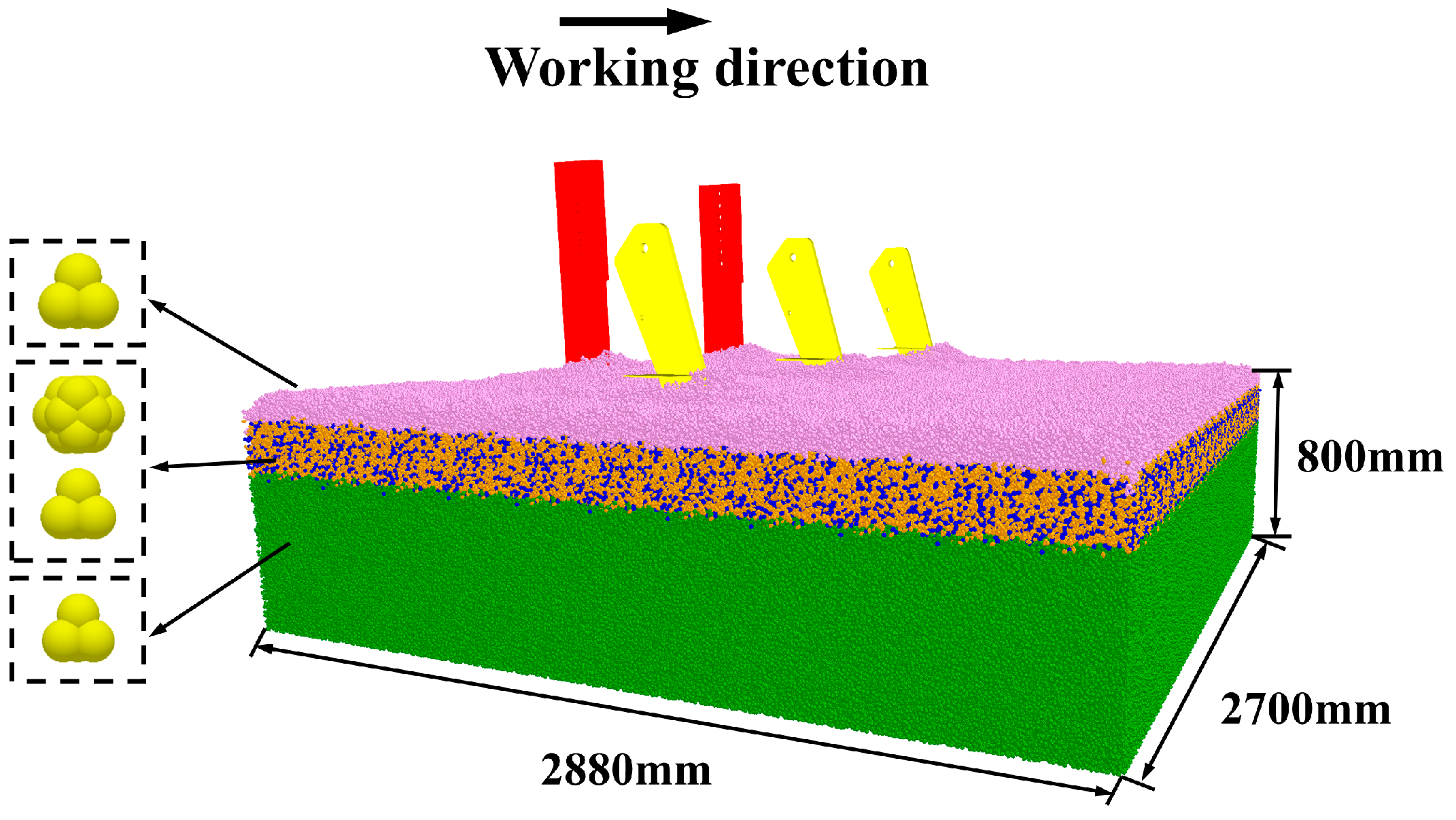


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Broken-line subsoiler penetration angle, θB (°) | 11 |
| Broken-line subsoiler fillet radius, R (cm) | 41 |
| Broken-line subsoiler straight section length, hB (cm) | 30 |
| Broken-line subsoiler thickness, WB (cm) | 3 |
| Broken-line subsoiler shank width, tB (cm) | 18.5 |
| Auxiliary subsoiler penetration angle, θA (°) | 30 |
| Auxiliary subsoiler thickness, WA (cm) | 1.8 |
| Auxiliary subsoiler shank width, tA (cm) | 16 |
| Auxiliary subsoiler tip length, LA (cm) | 5 |
| Auxiliary subsoiler tip width, JA (cm) | 6 |
| Auxiliary subsoiler wing width, IA (cm) | 12 |
| Parameters | Value (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–50 | 50–200 | 50–200 | 200–800 | |
| Density of soil particles (kg/m3) | 2.05 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.3 |
| Poisson’s ratio of soil | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| Shear modulus of soil (Pa) | 100 | 300 | 300 | 400 |
| Particle radius (mm) | 10 | 10 | 12 | 10 |
| Coefficient of restitution, soil–soil | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Coefficient of static friction, soil–soil | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.55 |
| Coefficient of rolling friction, soil–soil | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Coefficient of restitution, soil–steel | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Coefficient of static friction, soil–steel | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.55 |
| Coefficient of rolling friction, soil–steel | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| JKR surface energy | 1.2 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 5.9 |
| Density of steel (kg/m3) | 7865 | |||
| Poisson’s ratio of steel | 0.3 | |||
| Shear modulus of steel (1010) | 7.9 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Sun, J.; Huang, D.; Qiao, D.; Xiang, M.; Feng, W.; Fu, D.; Wang, J. Mechanism Analysis of Soil Disturbance in Sodic Saline–Alkali Soil Tillage Based on Mathematical Modeling and Discrete Element Simulation. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171885
Liu M, Sun J, Huang D, Qiao D, Xiang M, Feng W, Fu D, Wang J. Mechanism Analysis of Soil Disturbance in Sodic Saline–Alkali Soil Tillage Based on Mathematical Modeling and Discrete Element Simulation. Agriculture. 2025; 15(17):1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171885
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Min, Jinchun Sun, Dongyan Huang, Da Qiao, Meiqi Xiang, Weizhi Feng, Daping Fu, and Jingli Wang. 2025. "Mechanism Analysis of Soil Disturbance in Sodic Saline–Alkali Soil Tillage Based on Mathematical Modeling and Discrete Element Simulation" Agriculture 15, no. 17: 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171885
APA StyleLiu, M., Sun, J., Huang, D., Qiao, D., Xiang, M., Feng, W., Fu, D., & Wang, J. (2025). Mechanism Analysis of Soil Disturbance in Sodic Saline–Alkali Soil Tillage Based on Mathematical Modeling and Discrete Element Simulation. Agriculture, 15(17), 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171885







