Synergistic Effects of Sediment Size and Concentration on Performance Degradation in Centrifugal Irrigation Pumps: A Southern Xinjiang Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
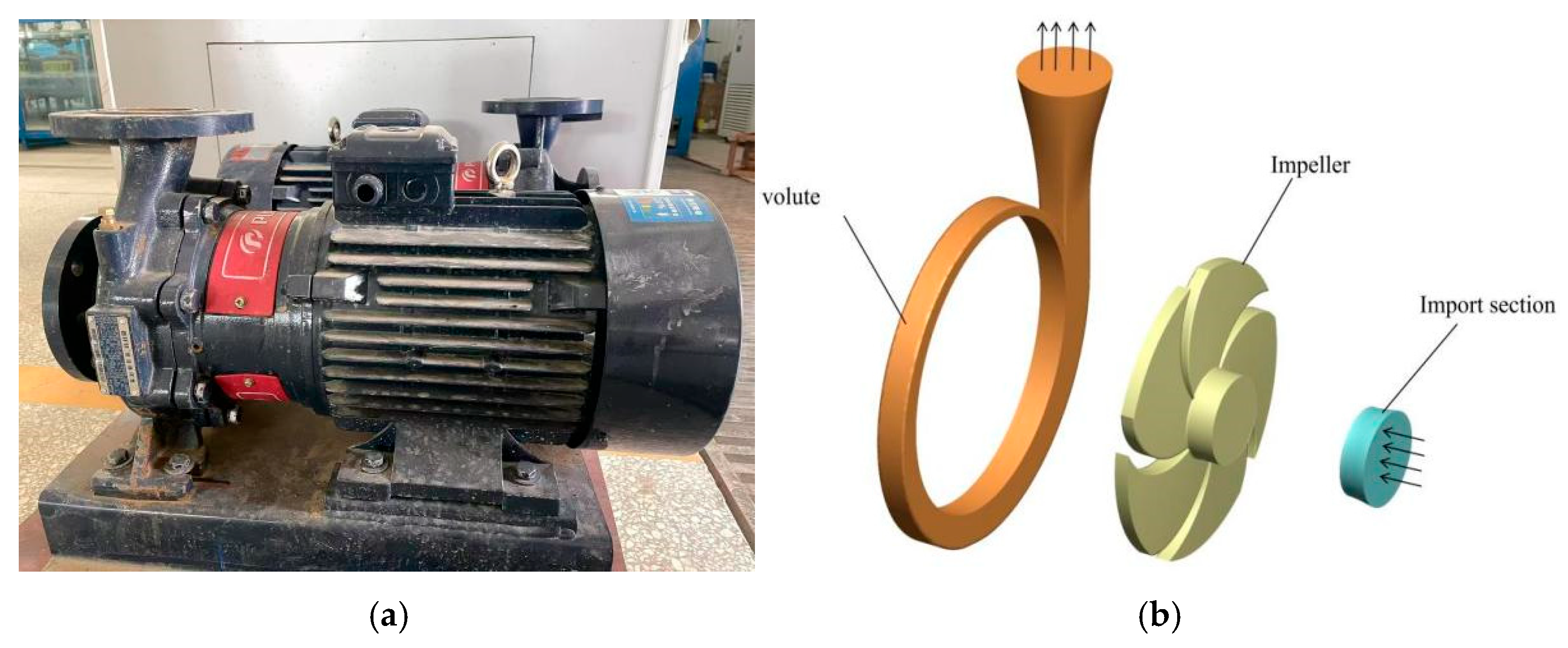
2.1. Modeling and Grid Generation
2.1.1. Model
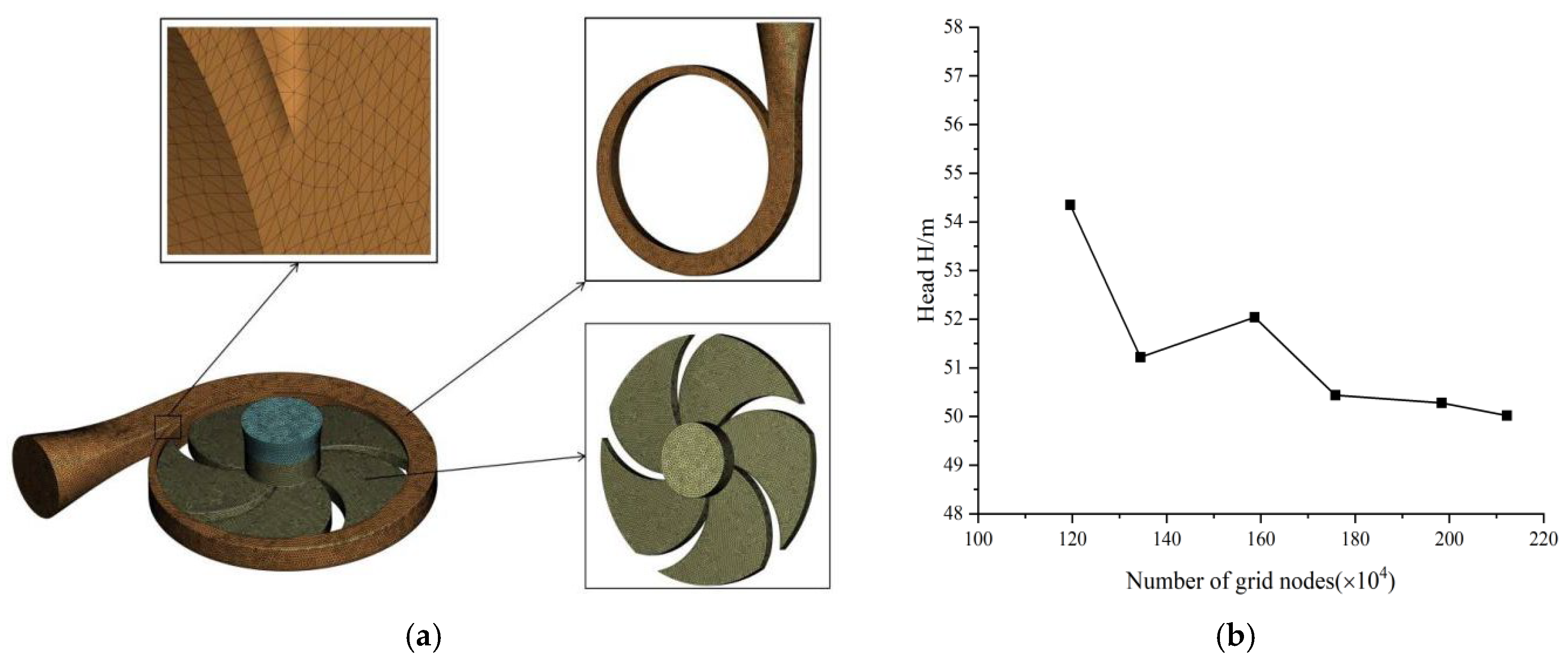
2.1.2. Grid Generation and Verification
2.2. Numerical Computation Methods
2.2.1. Turbulence Model Selection
2.2.2. Control Equation
2.2.3. Boundary Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
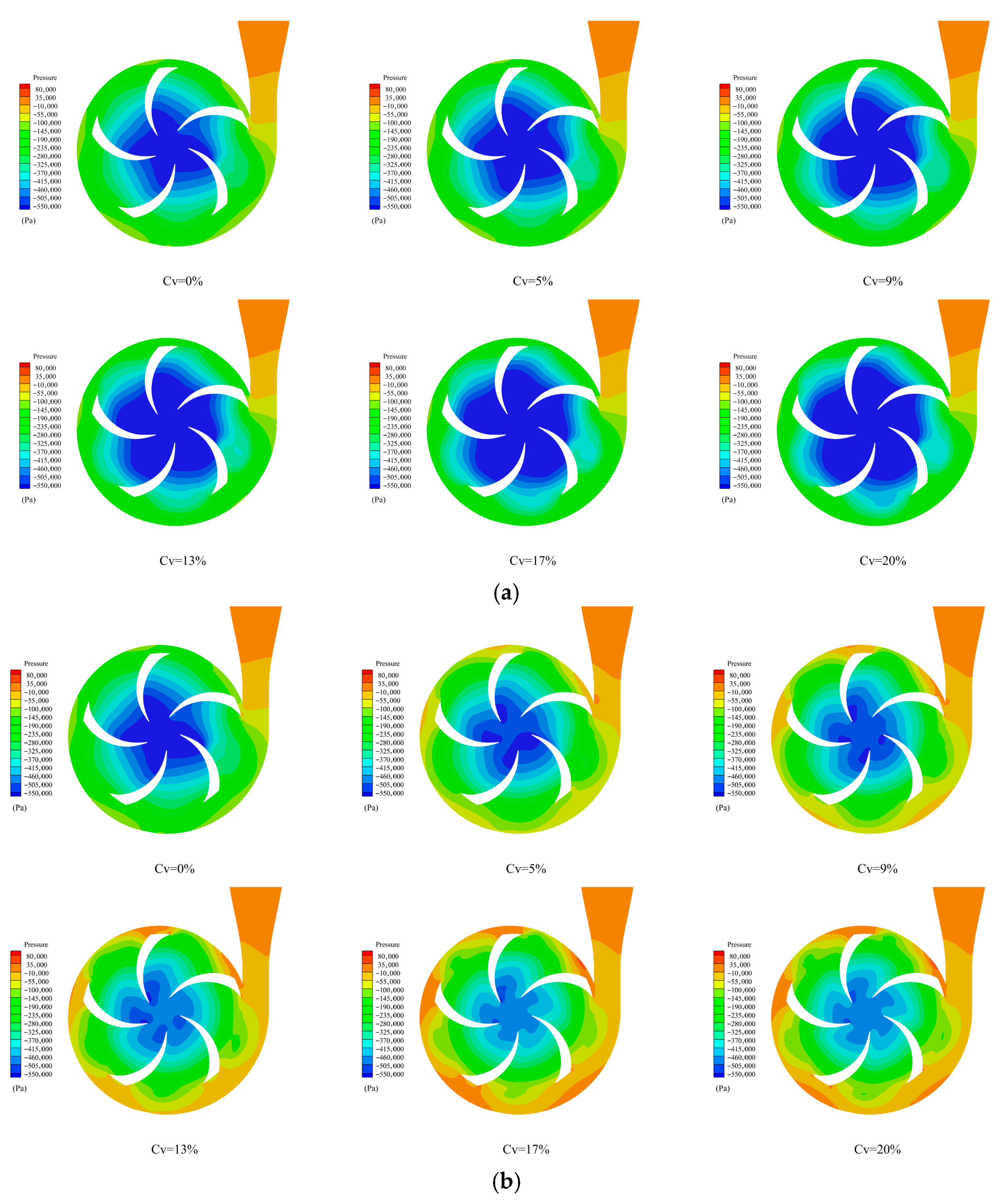
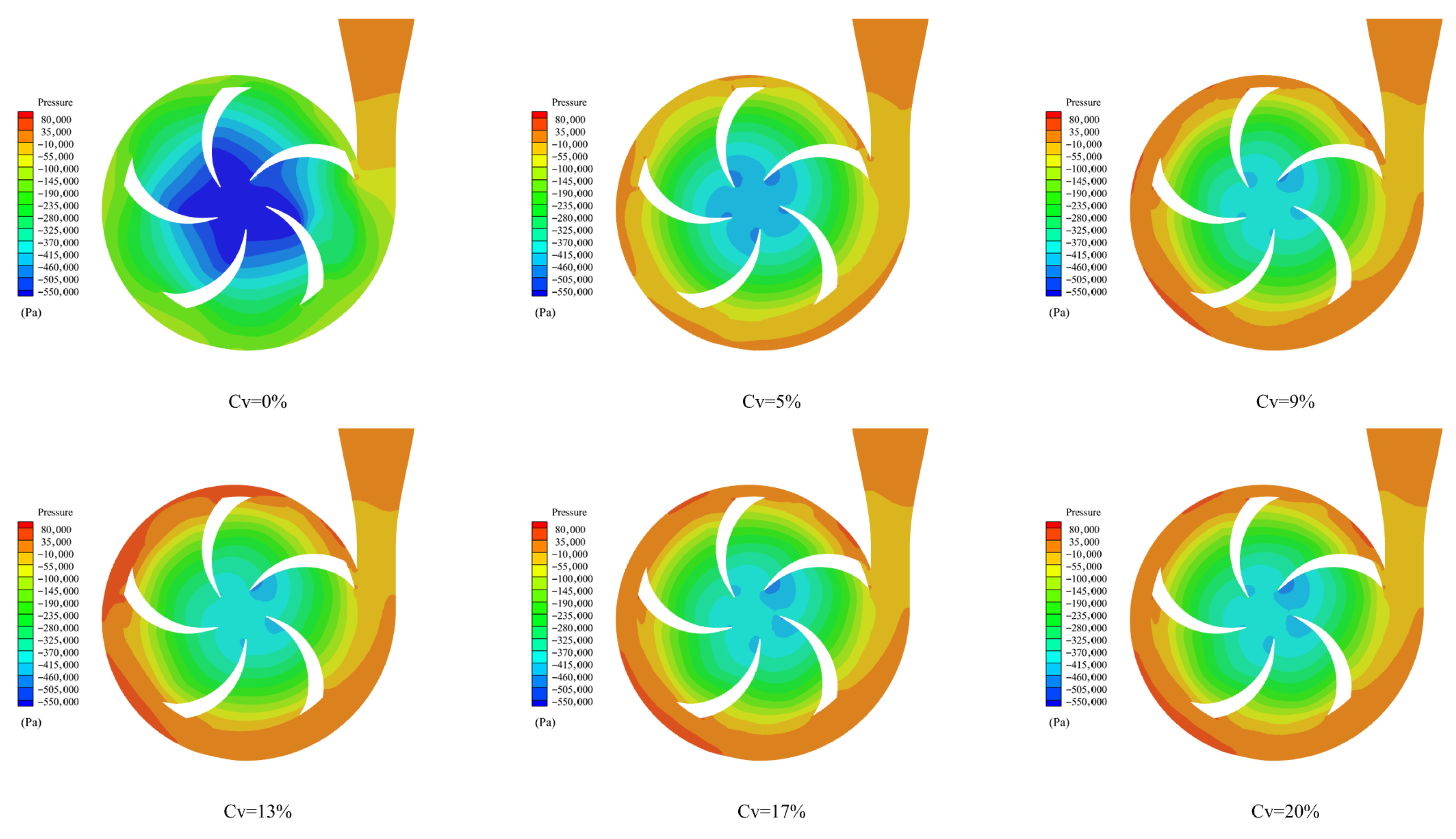
3.1. Pressure Characteristics Analysis
3.1.1. Different Sediment Particle Size
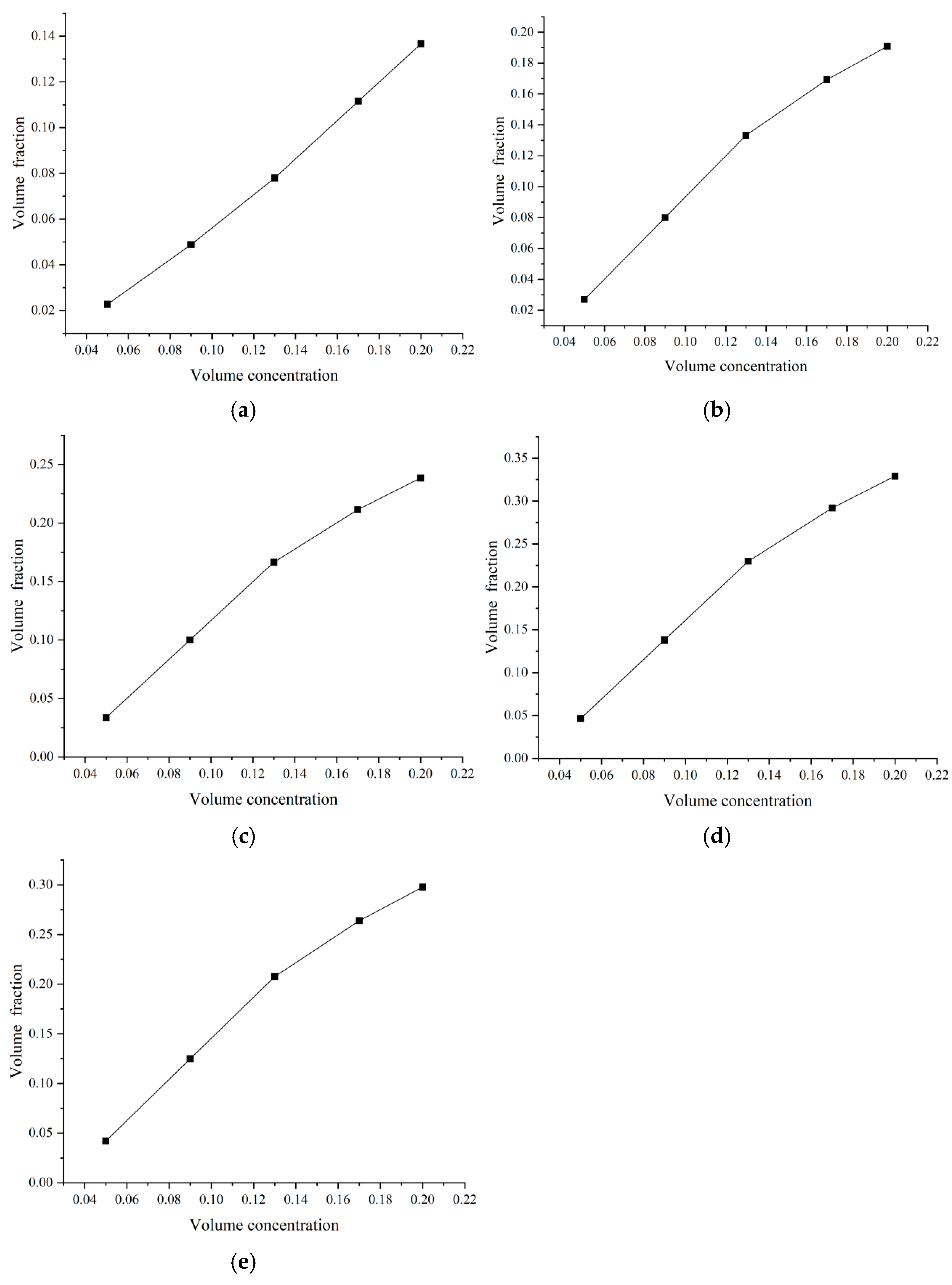
3.1.2. Variation Characteristics of Volume Concentration
3.1.3. Discussion
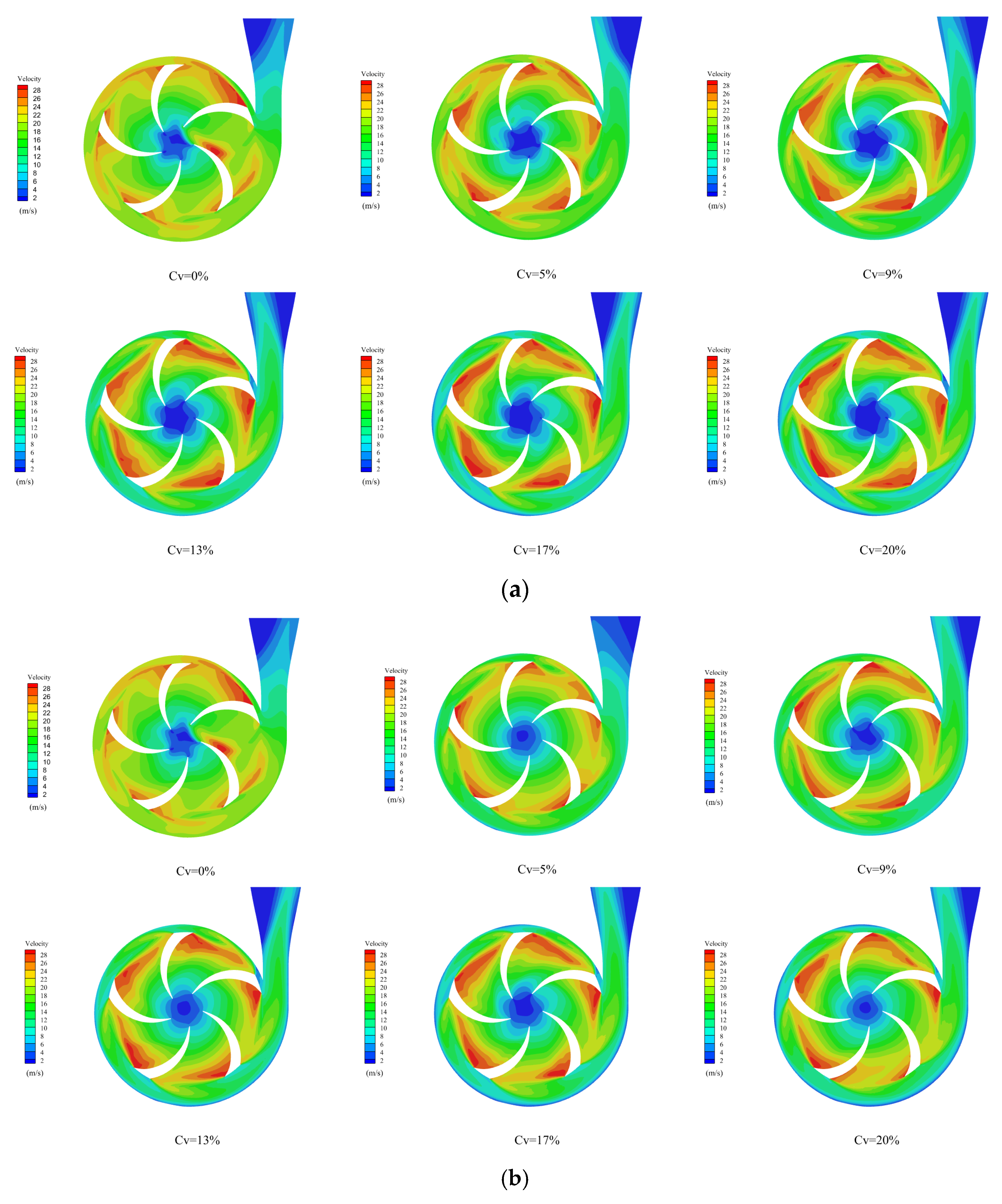
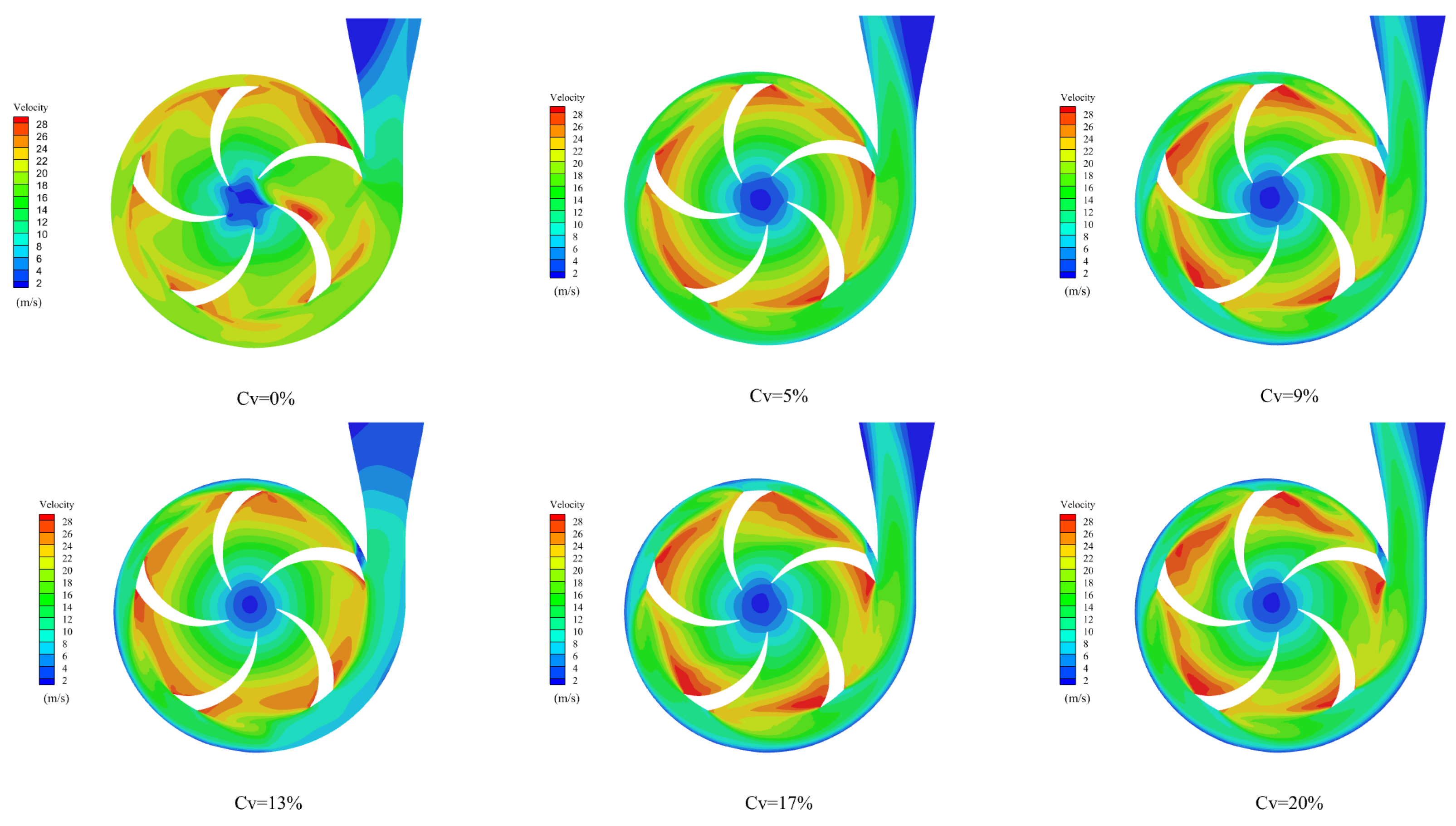
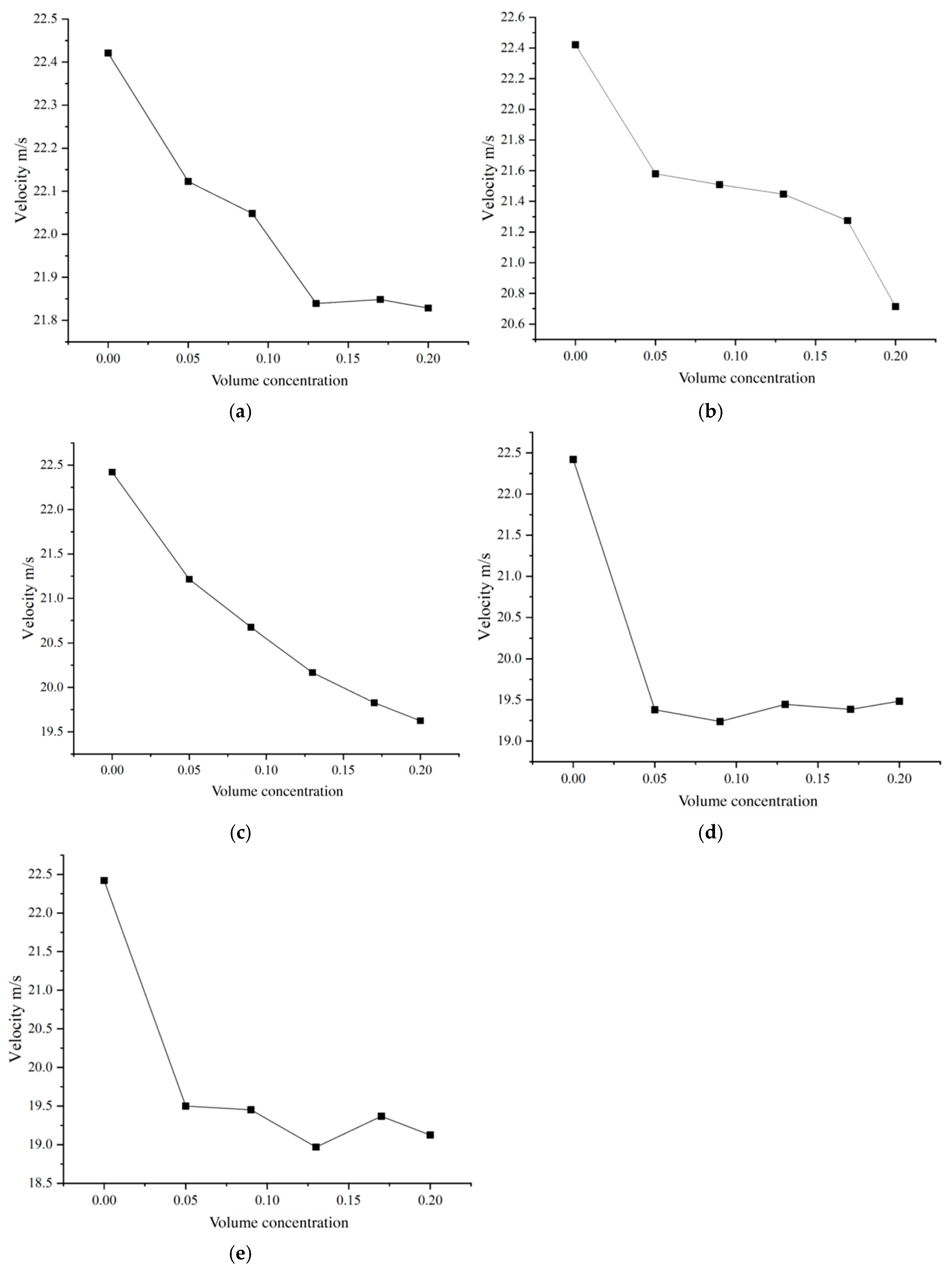
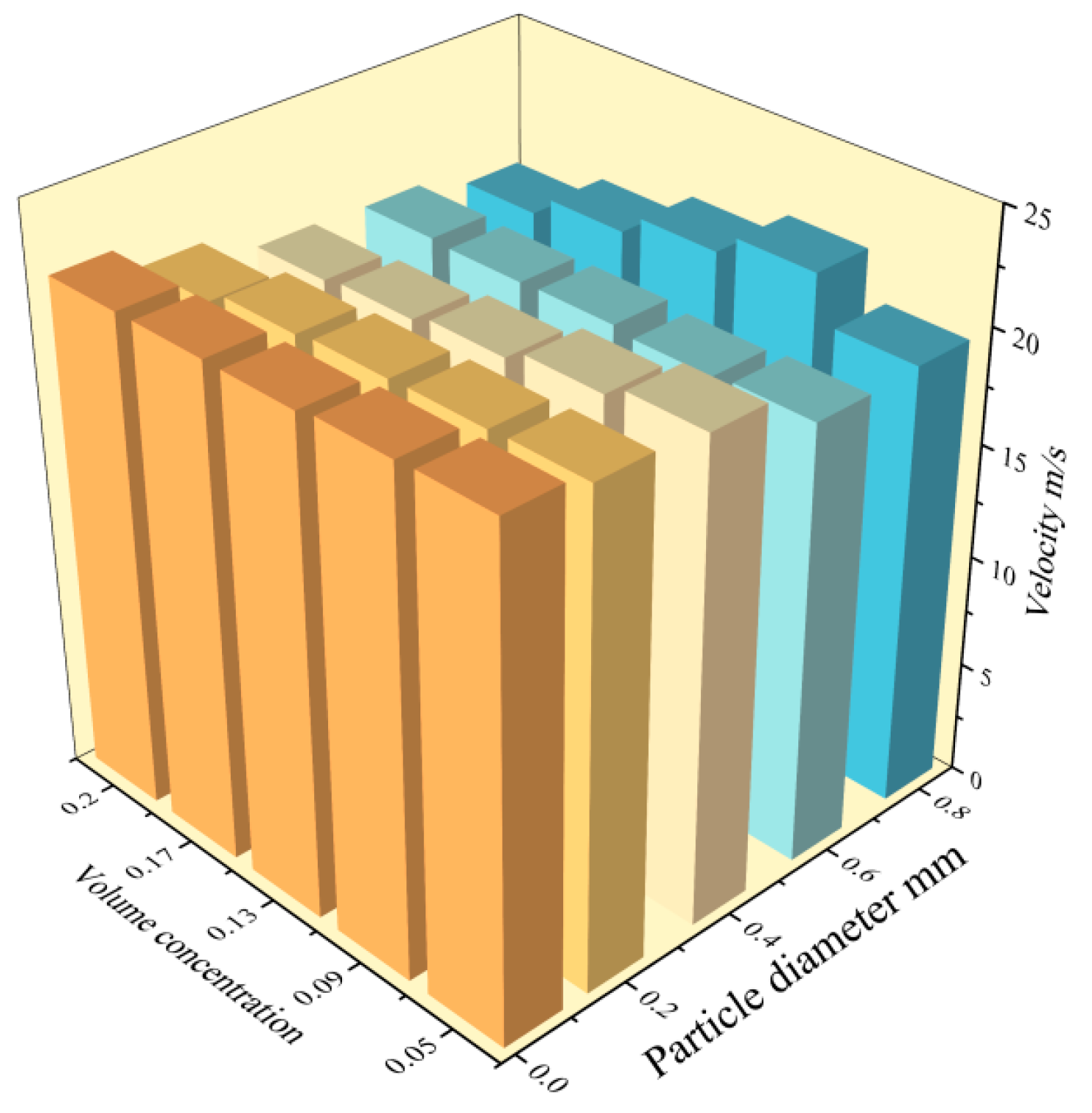
3.2. Velocity Characteristics Analysis
3.2.1. Different Sediment Particle Size
3.2.2. Velocity Variation Characteristics
3.2.3. Discussion
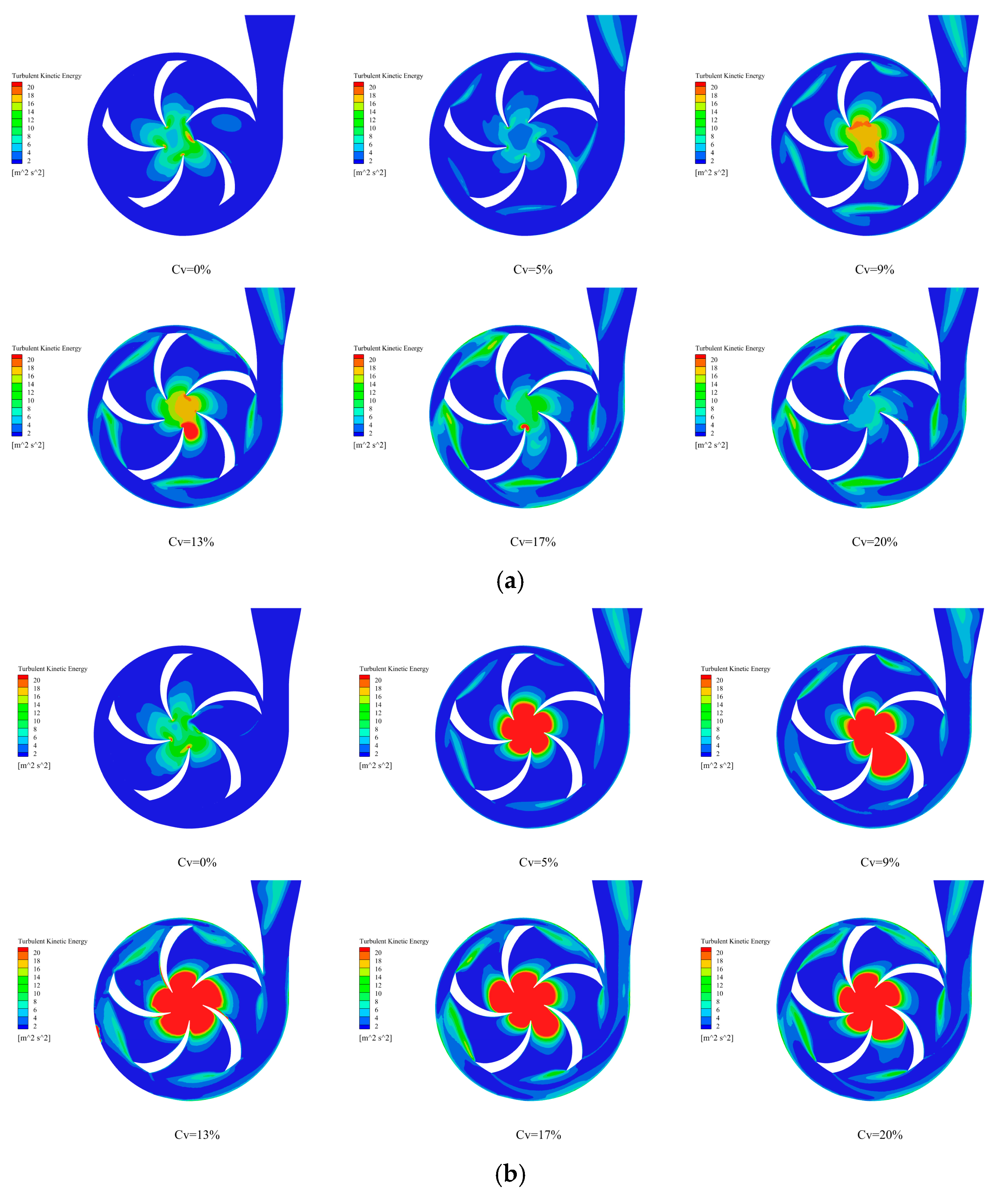
3.3. TKE
3.3.1. Different Sediment Particle Size
3.3.2. Discussion
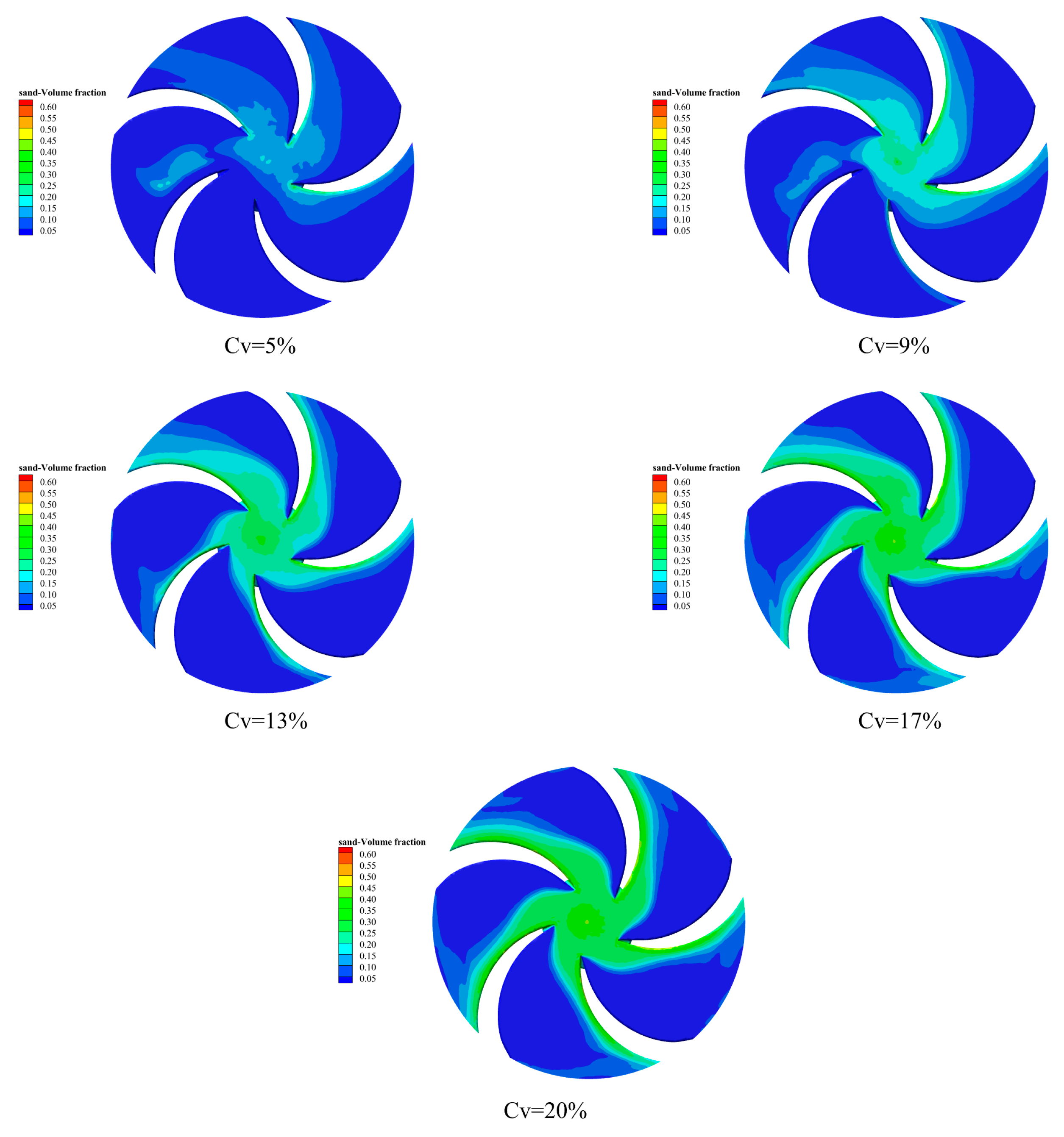
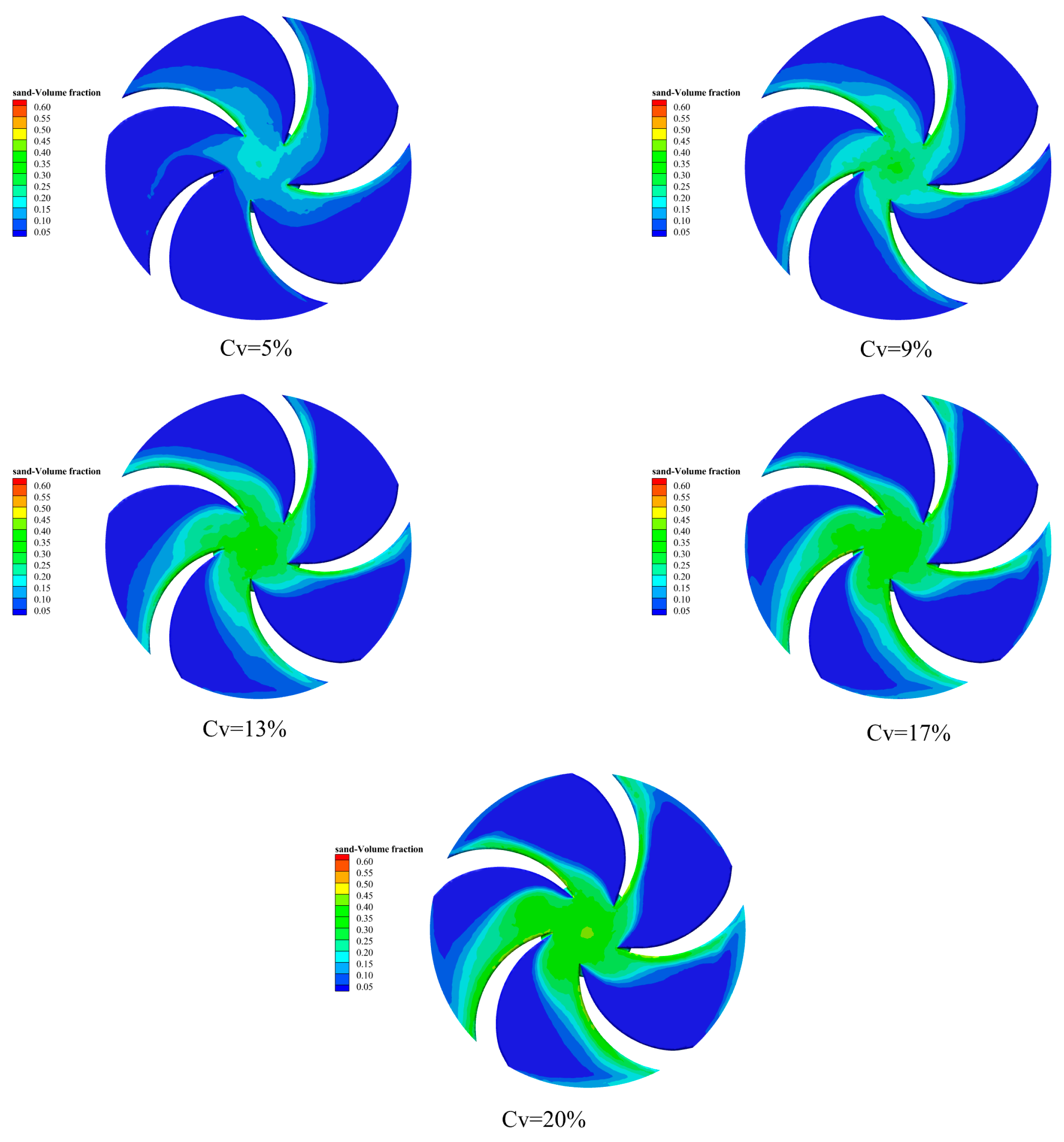
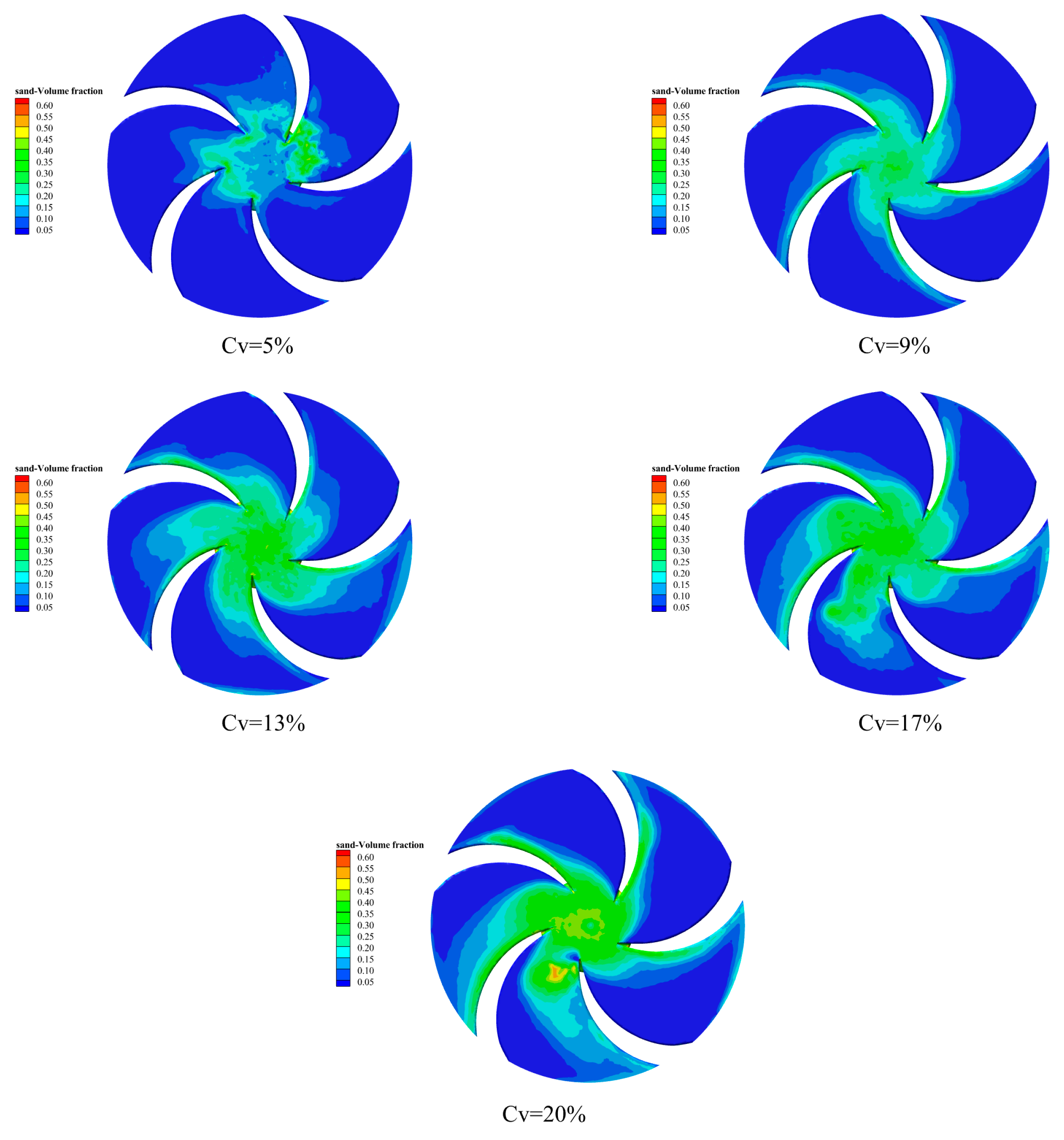
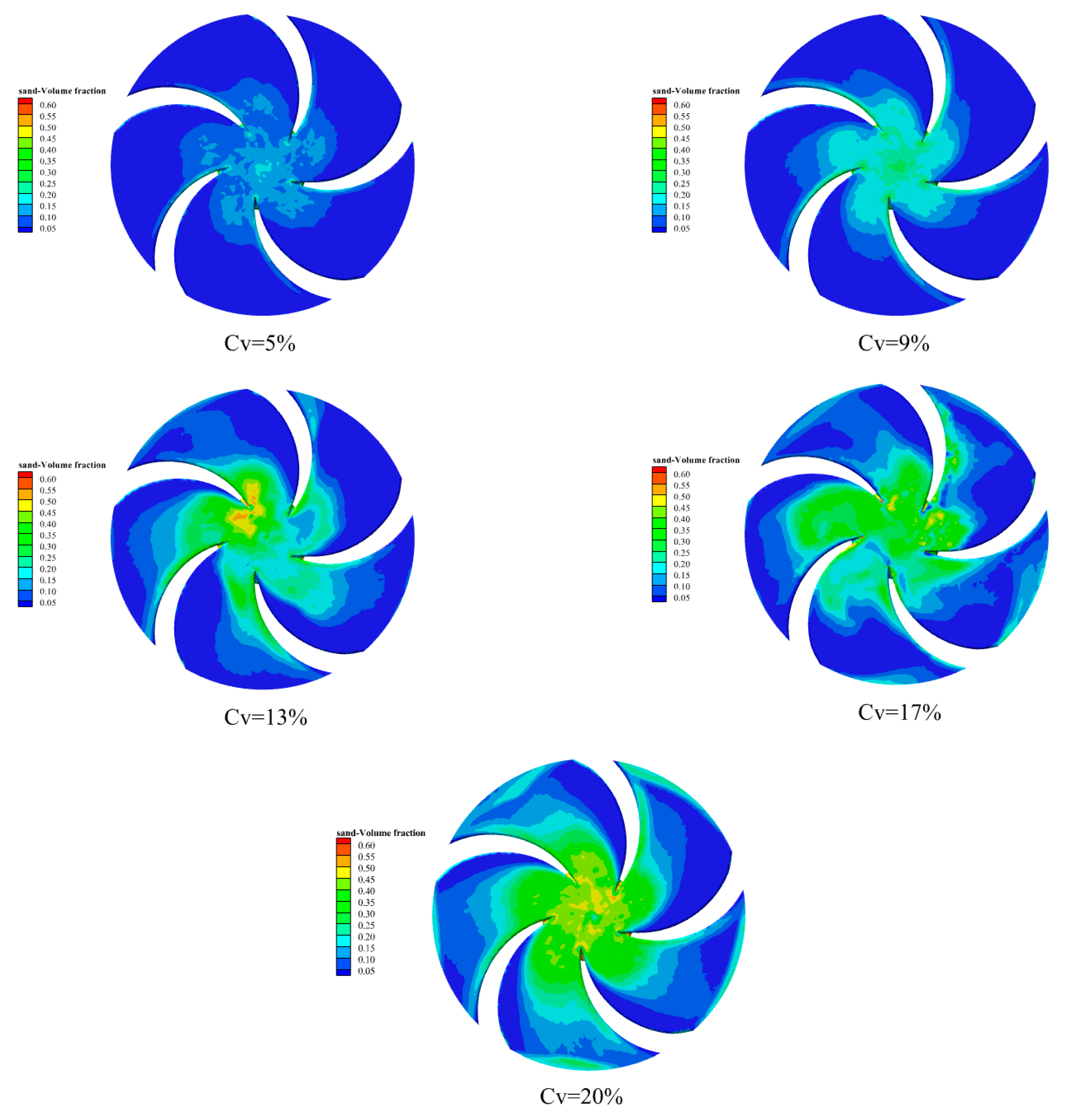
3.4. Sediment Volume Distribution
3.4.1. Sediment Particle Size: 0.05 mm
3.4.2. Sediment Particle Size: 0.2 mm
3.4.3. Sediment Particle Size: 0.4 mm
3.4.4. Sediment Particle Size: 0.6 mm
3.4.5. Sediment Particle Size: 0.8 mm
3.4.6. Particle Volume Distribution
3.4.7. Discussion
4. Experimental Verification
4.1. Experimental System
4.2. Experimental Process
- (1)
- Install the experimental pump on the experimental system, conduct a no-load experiment to check the motor, and verify whether the experimental system operates normally. The wear experiment can only be carried out after ensuring the entire system is functioning properly.
- (2)
- Disassemble the impeller and volute, wipe the inlet of the centrifugal pump and the impeller clean, respectively, apply a water-based paint of the same thickness, and reassemble the centrifugal pump after the coating is completely dry.
- (3)
- Add clean water and experimental sand into the water tank (added at a concentration of 5%), install the centrifugal pump on the experimental system, and check the correctness of the connections of pipes, valves, and other components.
- (4)
- Turn on the power switch on the main console, control the flow rate at the rated flow rate (25 m3/h), record the experimental data, and turn off the power switch to stop the experiment after the experimental pump has been running for 10 h.
- (5)
- Disassemble the impeller and volute of the experimental pump, observe the wear status of the water-based coating in the inlet and impeller flow channels, and take photos to retain the results.
- (6)
- After the experiment, tidy up the experimental site and organize all materials in a unified manner.
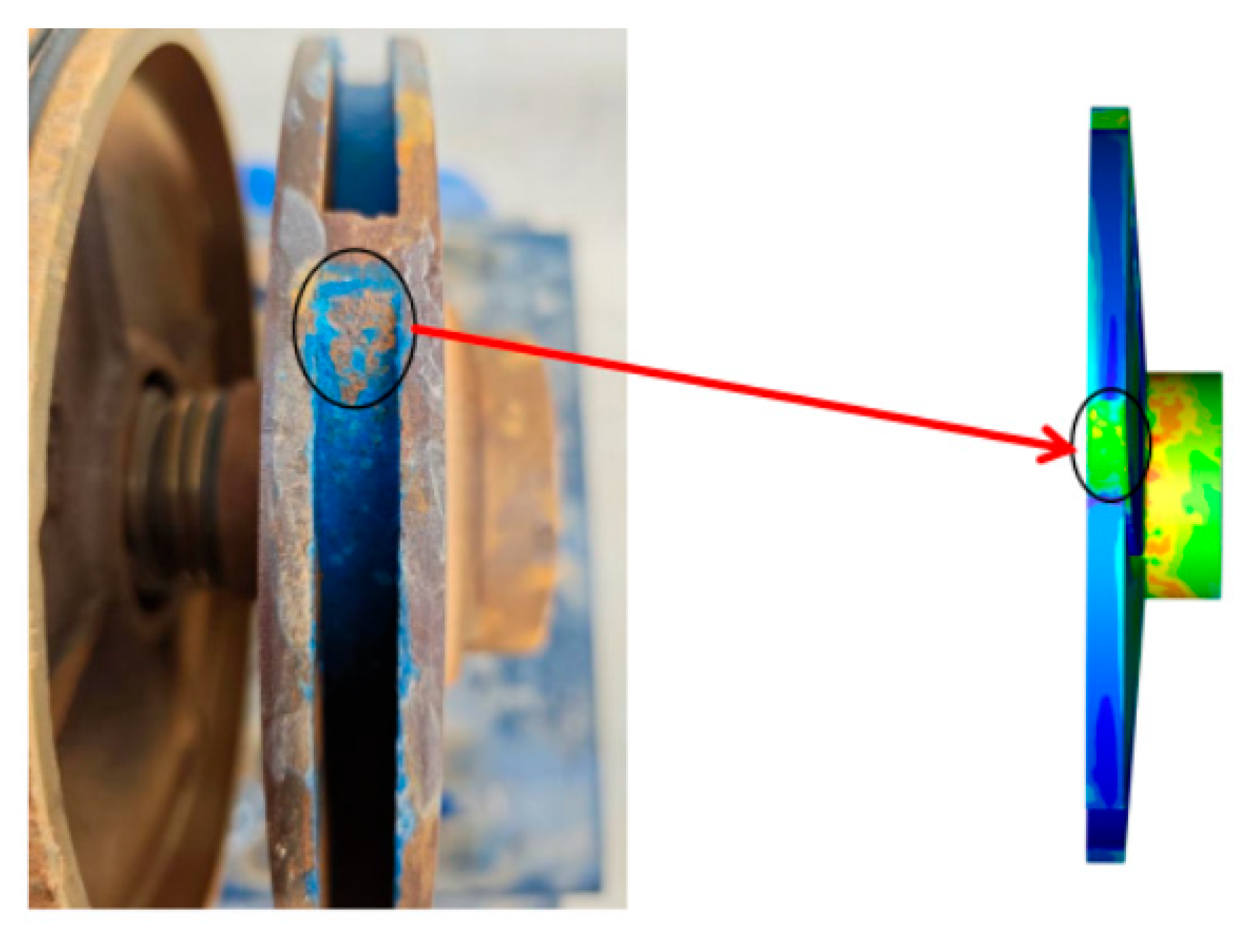
4.3. Comparison and Analysis of Results
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Synergistic Thresholds Dominate Performance Degradation: Critical particle size (≥0.4 mm) triggers a phase transition from localized disturbance to global flow disorder, expanding low-pressure zones by 37% at equivalent concentrations. Concurrently, exceeding the 13% concentration threshold accelerates nonlinear pressure decay through collective particle interactions, shifting energy dissipation from discrete-phase dominance to systematic continuous-phase weakening.
- (2)
- Size-Specific Deterioration Pathways: Fine sediments (≤0.2 mm) induce gradual “fast-then-slow” velocity attenuation via micro-scale drag accumulation, with inflection at Cv = 10%. In contrast, coarse sediments (≥0.6 mm) cause “cliff-like” degradation (e.g., 22.4 to 19.4 m/s at Cv = 5% through inertial impact-blockade chains, evolving into fluctuating velocity oscillations under high-concentration “blockage–fragmentation–reblockage” cycles.
- (3)
- Engineering Validation and Design Implications: Experimental wear tests’ accuracy of numerical models in predicting erosion hotspots at impeller inlets (large-angle particle collisions) and outlets (high-kinetic-energy erosion) meets the requirements. For Southern Xinjiang’s silt-dominated canals (Cv = 0.05~0.2 mm), maintaining Cv < 13% and optimizing blade curvature to suppress particle aggregation are proposed as critical anti-wear protocols.
- (4)
- This study establishes universal thresholds for sediment-induced degradation. These mechanisms transcend specific pump geometries, providing broad-spectrum anti-wear protocols: optimizing blade curvature to suppress particle aggregation in similar high-sediment conditions, directly transferable to centrifugal pumps across irrigation systems. The limitation of the study lies in the simplification of certain structures of the centrifugal pump during three-dimensional modeling. Future research will focus on the effects of shape-size-concentration coupling on the wear of key flow-passing components in centrifugal pumps.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, C.; Cao, Q.; Teng, S.; Liu, H.X.; Ding, K.J. Wear characteristics of a centrifugal pump transporting solid-liquid mixture: An experimental and numerical study. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.J.; Chen, Q.; Bai, L.; Hu, Z.Q.; Zhou, L.; Huang, X. Wear mechanism investigation in a centrifugal slurry pump impeller by numerical simulation and experiments. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 128, 105637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Mohapatra, S.K.; Kumar, S. Performance analysis of pump materials employed in bottom ash slurry erosion conditions. J. Tribol. 2021, 30, 73–89. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Li, R.; Han, W.; Quan, H.; Guo, R. Erosion wear on impeller of double-suction centrifugal pump due to sediment flow. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2020, 13, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.J.; Chu, W.L.; Li, X.J.; Dong, W. Sediment erosion in the impeller of a double-suction centrifugal pump—A case study of the Jingtai Yellow River Irrigation Project, China. Wear 2019, 422, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandi, S.; Banka, J.; Kumar, A.; Rai, A.K. Effects of sediment properties on abrasive erosion of a centrifugal pump. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 277, 118873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, J.; Li, G.X.; Liu, H.L.; Xiong, W. Numerical simulation of the influence of mixed sand on erosion characteristics of centrifugal pump. Eng. Comput. 2022, 39, 2053–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarodiya, R.; Gandhi, B.K. Effect of particle size distribution on performance and particle kinetics in a centrifugal slurry pump handling multi-size particulate slurry. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 4751–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, Z.C. Analysis of particle motion and wear characteristics for mixed particle sizes in centrifugal pumps. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 4705–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yang, Y.C.; Liu, P.Z.; Kim, Y.J. Prediction of abrasive and impact wear due to multi-shaped particles in a centrifugal pump via CFD-DEM coupling method. Energies 2021, 14, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kumar, S.; Mohapatra, S.K. Study on role of particle shape in erosion wear of austenitic steel using image processing analysis technique. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2019, 233, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarodiya, R.; Gandhi, B.K. Numerical investigation of erosive wear of a centrifugal slurry pump due to solid–liquid flow. J. Tribol. 2021, 143, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarodiya, R.; Gandhi, B.K. Numerical simulation of a centrifugal slurry pump handling solid-liquid mixture: Effect of solids on flow field and performance. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2225–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Tan, Z.; Kuang, S.B.; Yu, A.B. Numerical modeling and analysis of particle-fluid flow and wall erosion in centrifugal slurry pumps under different solid concentrations. Powder Technol. 2022, 410, 117861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, G.X.; Zhou, H. Solid-liquid two-phase flow and wear analysis in a large-scale centrifugal slurry pump. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 114, 104602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Hu, L.H.; Tao, J.Y.; Zhu, X.J.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, Y. Analysis of high-concentration solid-liquid flow and erosion characteristics of centrifugal pump based on CFD-DEM. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 317, 122106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.D.; Tan, L. Solid-liquid multiphase flow and erosion in the energy storage pump using modified drag model and erosion model. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 108859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Bai, Y.M.; Wu, Y.C. Influence of blade thickness on solid–liquid two-phase flow and impeller wear in a ceramic centrifugal slurry pump. Processes 2021, 9, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Shi, G.T.; Xiao, Y.X.; Ye, X.Y. A study of the relationship between sand movement and flow field distribution and wear causes in a multiphase pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Huang, F.Y.; Mohammad, F.; Kuang, S.B.; Yu, A.B. CFD-DEM investigation of centrifugal slurry pump with polydisperse particle feeds. Powder Technol. 2024, 447, 120204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.C.; Pan, J.P.; Wu, L.J.; Zhang, X.K.; Qiu, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.D. A prediction method of wear for volute casing of a centrifugal slurry pump. Geofluids 2020, 2020, 8847087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirouzpanah, S.; Patil, A.; Chen, Y.M.; Morrison, G. Predictive erosion model for mixed flow centrifugal pump. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2019, 141, 092001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarodiya, R.; Gandhi, B.K. Experimental investigation of centrifugal slurry pump casing wear handling solid-liquid mixtures. Wear 2019, 434, 202972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Tan, Z.; Kuang, S.B.; Yu, A.B. Systematic investigation of centrifugal slurry pump under different operating condition by DDPM method. Powder Technol. 2023, 430, 119024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Tan, Z.T.; Kuang, S.B.; Yu, A.B. DDPM investigation on centrifugal slurry pump with inlet and sideline configuration retrofit. Powder Technol. 2025, 449, 120386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, S.C.; He, F.; Fan, X.G.; Li, P.X. Effect of variable conditions on transient flow in a solid–liquid two-phase centrifugal pump. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 073340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Tao, R.L.; Han, C.F.; Li, W.Q.; He, T.L.; Zhu, Z.C. Numerical study on flow and wear characteristics of dense fine particle solid–liquid two-phase flow in centrifugal pump. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 045109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Yang, S.; Wu, D.Z.A.; Mou, J.G. Effect of particle mass concentration on erosion characteristics of self-priming pump. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2021, 235, 6782–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Kang, C.; Li, M.H.; Qiao, Y.J.; Ding, K.J. Blockage of the deep-sea mining pump transporting large particles with different sphericity. China Ocean Eng. 2023, 37, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhu, Z.C.; Su, X.H.; Tang, Z.J. Coarse Particle Motion Characteristics in a Double-Stage Slurry Pump Considering Leakage Flow. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 5904446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.H.; Tang, Z.J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.C.; Mianowicz, K.; Balaz, P. Research of particle motion in a two-stage slurry transport pump for deep-ocean mining by the CFD-DEM method. Energies 2020, 13, 6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Peng, G.J.; Chang, H.; Yu, D.H.; Ji, G.C.; Ma, L.; Wang, Z.Q. Numerical study of erosion characteristics in U-shaped elbow and slurry pump. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 073343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.W.; Ding, W.J.; Xu, C.J.; Xie, F.W.; Tian, Z.Z. Numerical investigation of inlet section structure effect on wear characteristic of particle condition in centrifugal slurry pump by CFD-DEM coupling. Part. Sci. Technol. 2023, 41, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.J.; Yao, R.; Shen, Y.B.; Bi, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.P.; Wang, Z.W. Numerical prediction of erosion based on the solid-liquid two-phase flow in a double-suction centrifugal pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Q.; Zeng, X.D.; Li, Y. Study on the relationship between wear and flow characteristics of a centrifugal pump at different mass concentrations. Processes 2021, 9, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, J.X.; Guo, J.W.; Mo, Y.S. Study on wear properties of the flow parts in a centrifugal pump based on EDEM-fluent coupling. Processes 2019, 7, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.J.; Kong, F.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, J.L.; Yang, W.G.; Wu, J.B. Erosion Analysis of Static Components in Slurry Pumps Based on Reverse Modeling. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. 2025, 21, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.D.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.A. Study on wear characteristics of a guide vane centrifugal pump based on CFD-DEM. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; He, T.L.; Ding, Q.M.; Gao, P.L.; Tao, R.L.; Zhu, Z.C. Analysis of internal flow and wear characteristics of binary mixture particles in centrifugal pump based on CFD-DEM. Processes 2022, 10, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Jiang, Z.Q. Study of the two-phase flow and wear of a pump with mixed-size particles. Processes 2022, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Li, W.Q.; He, T.L.; Liu, H.; Han, C.F.; Zhu, Z.C. Experimental study on the influence of particle diameter, mass concentration, and impeller material on the wear performance of solid-liquid two-phase centrifugal pump blade. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 893385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Han, C.F.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Z.; Ma, J.F.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, W. Wear Characteristics of Dense Fine Particles Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Fluid Centrifugal Pump with Open Impellers. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 6635630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.B.; Gu, Y.Q.; Xia, K.; Mou, C.Q.; Mou, J.G.; Wu, D.H.; Yan, M.H. Influence of bionic circular groove blade surface on wear performance. Lubricants 2022, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.Q.; Liu, N.J.; Mou, J.G.; Zhou, P.J.; Qian, H.; Dai, D.S. Study on solid–liquid two-phase flow characteristics of centrifugal pump impeller with non-smooth surface. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814019848269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.S.; Jiang, J.R.; Islam, M.A. Applications of elastomers in slurry transport. Wear 2021, 477, 203773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, P.K.P.; Selvarajan, L.; Mathan, K.P.; Shriguppikar, S. Enhancing mechanical and morphological properties of glass fiber reinforced epoxy polymer composites through rutile nanoparticle incorporation. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2025, 10, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.C.; Zhou, K.L.; Pan, J.P.; Zhang, X.K.; Ying, R.M.; Wu, L.J.; Zhang, Y.D. PIV test of the flow field of a centrifugal pump with four types of impeller blades. J. Mech. 2021, 37, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.W.; Wang, W.R.; Shi, W.D.; Yang, Y.; Bao, L.L.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, T.; Li, H. A study on the internal vortex structure within a single-blade pump via numerical methods and particle image velocimetry experiments. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 115130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Ji, L.L.; Li, W.; Yang, Q.Y.; Liu, Z.B.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.M.; Huang, W.; Agarwal, R. Experimental study on the unsteady evolution mechanism of centrifugal pump impeller wake under solid–liquid two-phase conditions: Impact of particle concentration. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 113327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.L.; Mao, Y.H.; Liu, H.L. Numerical investigation on the internal flow and wear characteristics of solid–liquid two-phase flow in a centrifugal pump under different stall levels. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 113367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, G.X.; Liu, H.L.; Xiong, W. An experimental insight into dynamic characteristics and wear of centrifugal pump handling multi-size particulate slurry. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 138, 106303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.Q.; Lin, Z.; Chen, D.S.; Li, Y. A review on the hydraulic performance and erosion wear characteristic of the centrifugal slurry pump. Particuology 2024, 95, 370–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.D.; Tang, L. Role of particle motion on pressure fluctuation and erosion for a centrifugal pump in energy storage pump station. J. Energy Storage 2024, 99, 113252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zheng, S.H.; Zhao, Y.J. Numerical investigation of flow characteristics in the front and rear chambers of centrifugal pump and pump as turbine. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Rated speed | r/min | 2900 |
| Rated flow rate | m3/h | 25 |
| Head | m | 50 |
| Power | kW | 7.5 |
| Efficiency | % | 52.9% |
| Inlet Diameter | mm | 60 |
| Impeller Diameter | mm | 200 |
| Blade outlet width | mm | 10 |
| Number of blades | individual | 5 |
| Outlet blade angle | ° | 23.6 |
| Blade wrap angle | ° | 100 |
| Base circle diameter of the volute | mm | 210 |
| Scheme | Number of Grids | Head (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,195,283 | 54.35 |
| 2 | 1,344,419 | 51.22 |
| 3 | 1,586,656 | 52.04 |
| 4 | 1,758,117 | 50.44 |
| 5 | 1,983,627 | 50.28 |
| 6 | 2,122,051 | 50.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, R.; Hong, S.; Yang, Z.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Han, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, X. Synergistic Effects of Sediment Size and Concentration on Performance Degradation in Centrifugal Irrigation Pumps: A Southern Xinjiang Case Study. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171843
Xu R, Hong S, Yang Z, Hu X, Jiang Y, Han Y, Gao C, Wang X. Synergistic Effects of Sediment Size and Concentration on Performance Degradation in Centrifugal Irrigation Pumps: A Southern Xinjiang Case Study. Agriculture. 2025; 15(17):1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171843
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Rui, Shunjun Hong, Zihai Yang, Xiaozhou Hu, Yang Jiang, Yuqi Han, Chungong Gao, and Xingpeng Wang. 2025. "Synergistic Effects of Sediment Size and Concentration on Performance Degradation in Centrifugal Irrigation Pumps: A Southern Xinjiang Case Study" Agriculture 15, no. 17: 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171843
APA StyleXu, R., Hong, S., Yang, Z., Hu, X., Jiang, Y., Han, Y., Gao, C., & Wang, X. (2025). Synergistic Effects of Sediment Size and Concentration on Performance Degradation in Centrifugal Irrigation Pumps: A Southern Xinjiang Case Study. Agriculture, 15(17), 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171843






