Evaluation of the Effect of Tenebrio molitor Frass on the Growth Parameters of Canasta Lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. capitata) as a Model Plant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Frass Producing
2.2. Frass Characterisation
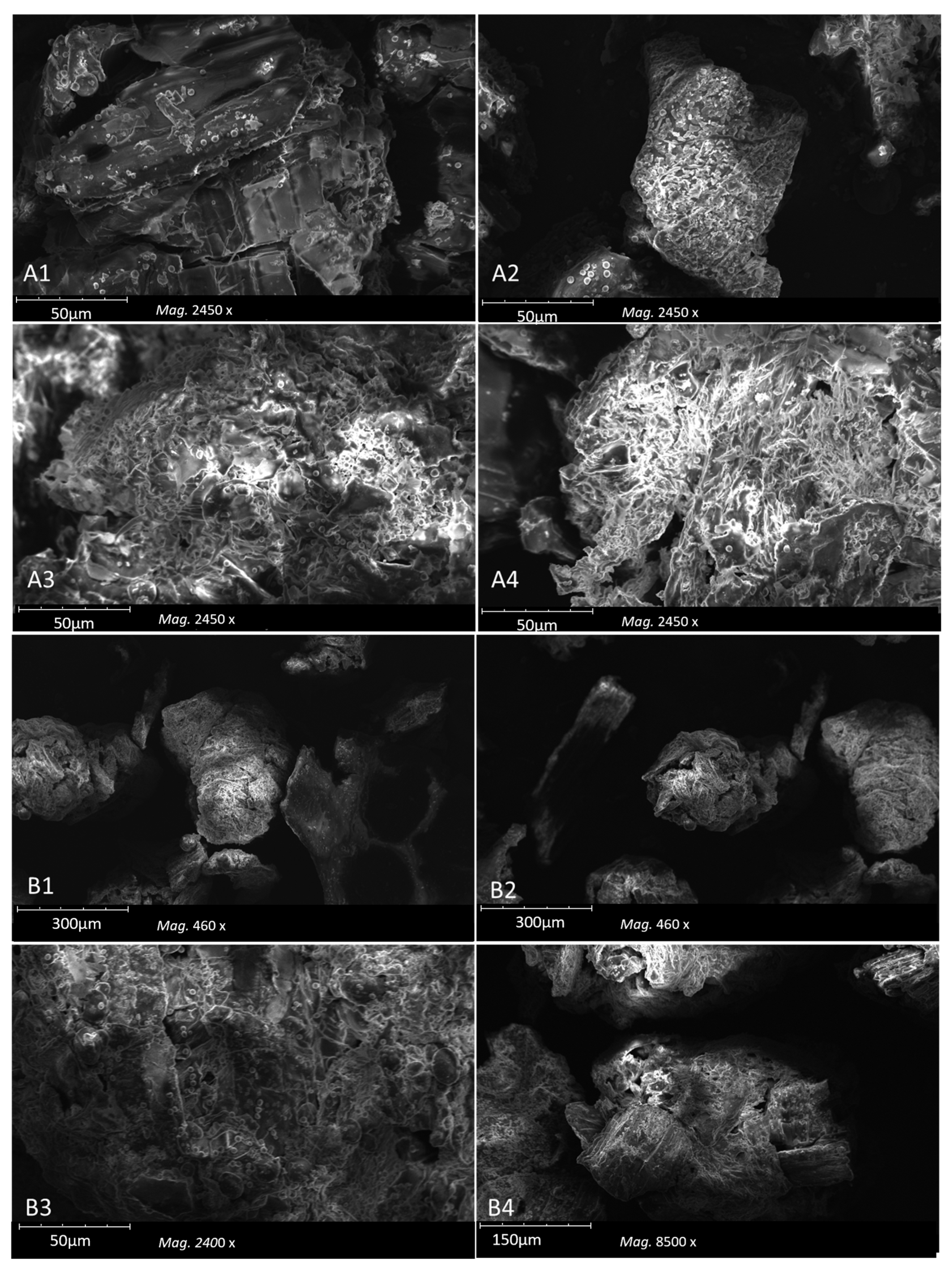
2.2.1. SEM Analysis
2.2.2. Frass and Substrate pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC)
2.3. Canasta Trials
2.3.1. Preparation of Soil with Frass Pots
2.3.2. Trials on Canasta with Different Percentages of UT-TMF and TT-TMF
- -
- Plant height (PH): distance from the stem cutting point to the apex;
- -
- Number of edible leaves (LN);
- -
- Stem diameter (SD): measured at the base of the plant;
- -
- Fresh weight (FW): weight of all edible leaves, determined using an analytical balance (Gibertini Elettronica, Novate Milanese, Italy, mod. E42S-B; precision ± 0.1 mg).

2.3.3. Trials on Canasta with Minor Percentages of TT-TMF
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Frass Characterisation
3.1.1. SEM Analysis
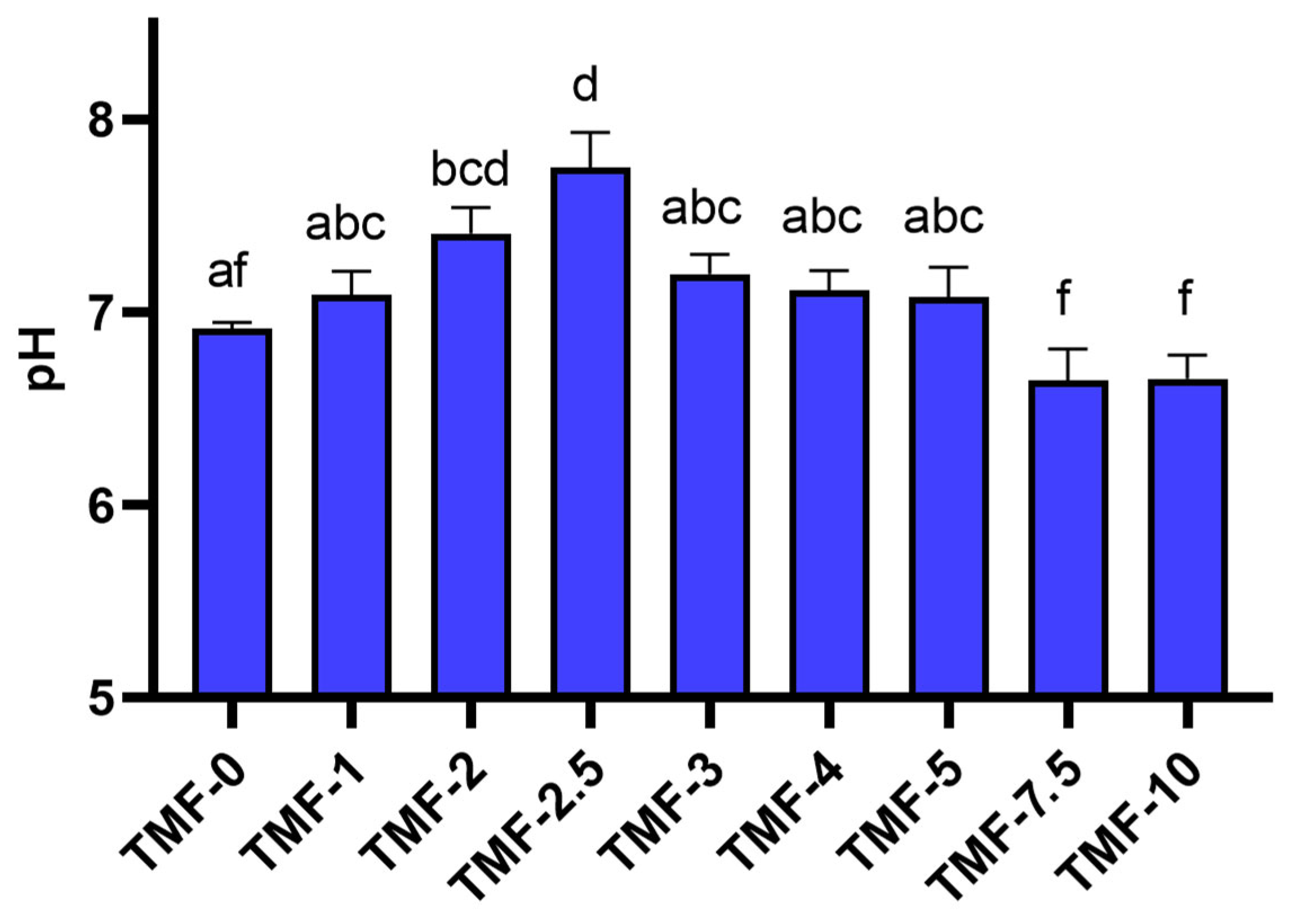
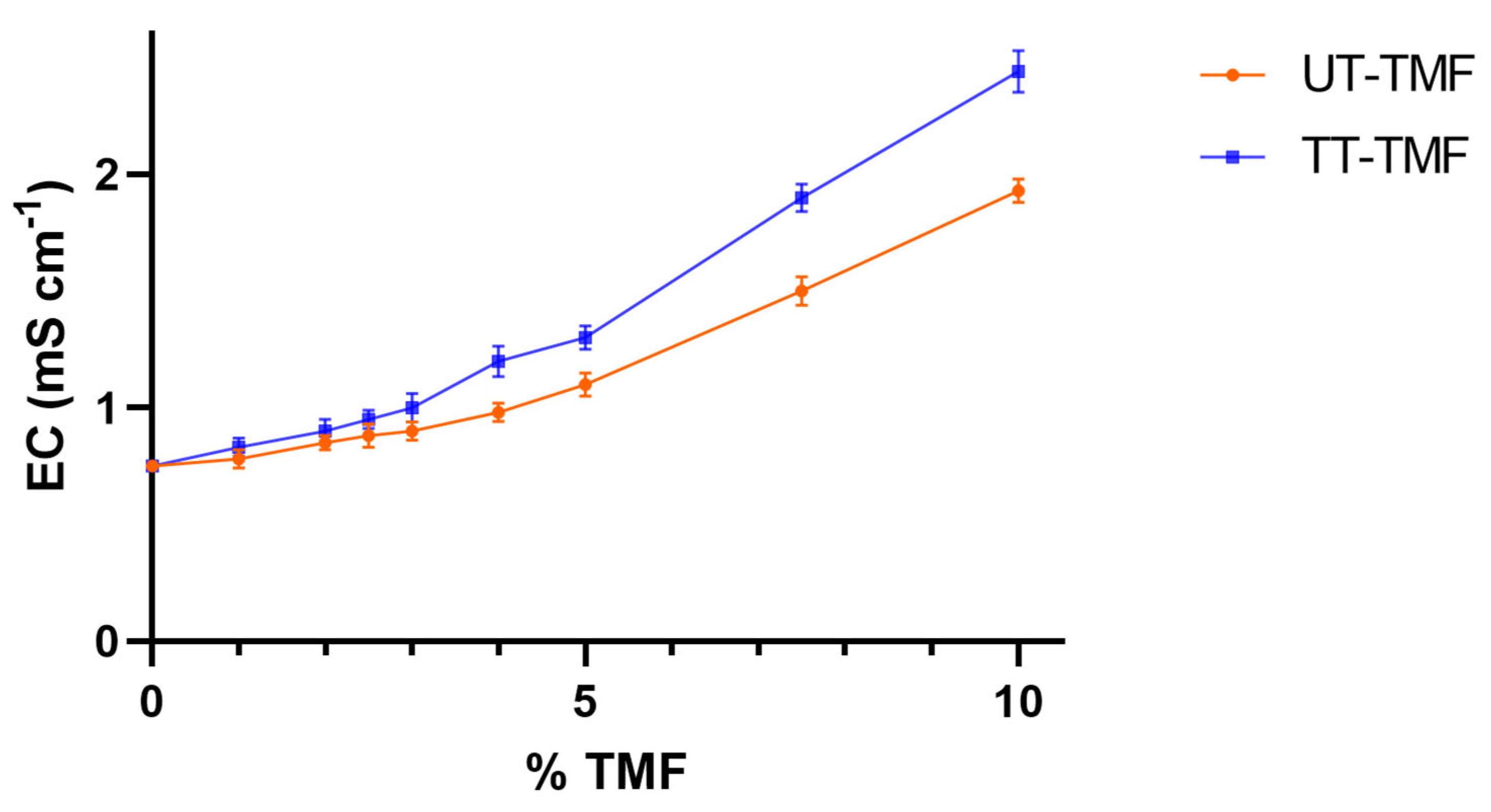
3.1.2. Frass and Substrate pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC)
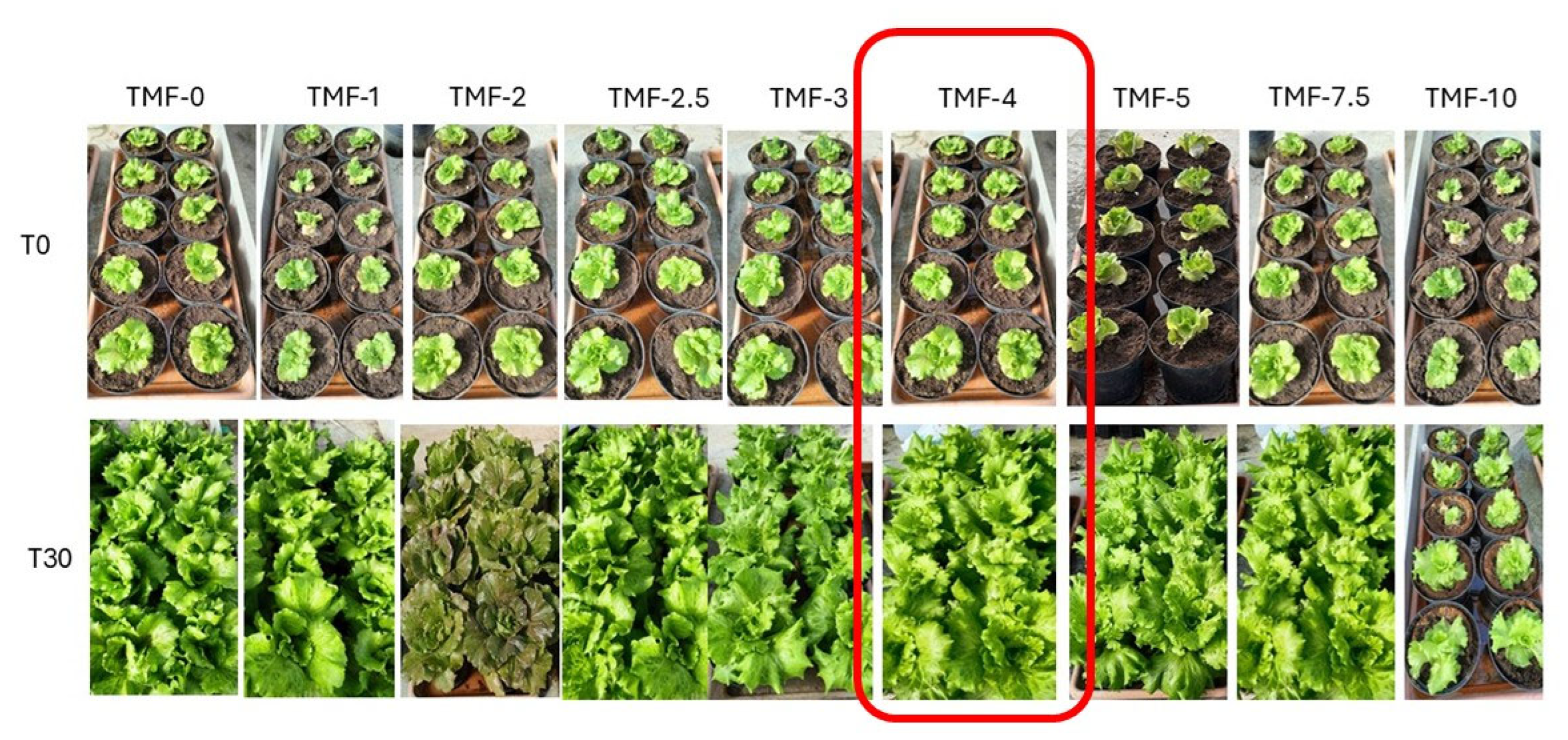
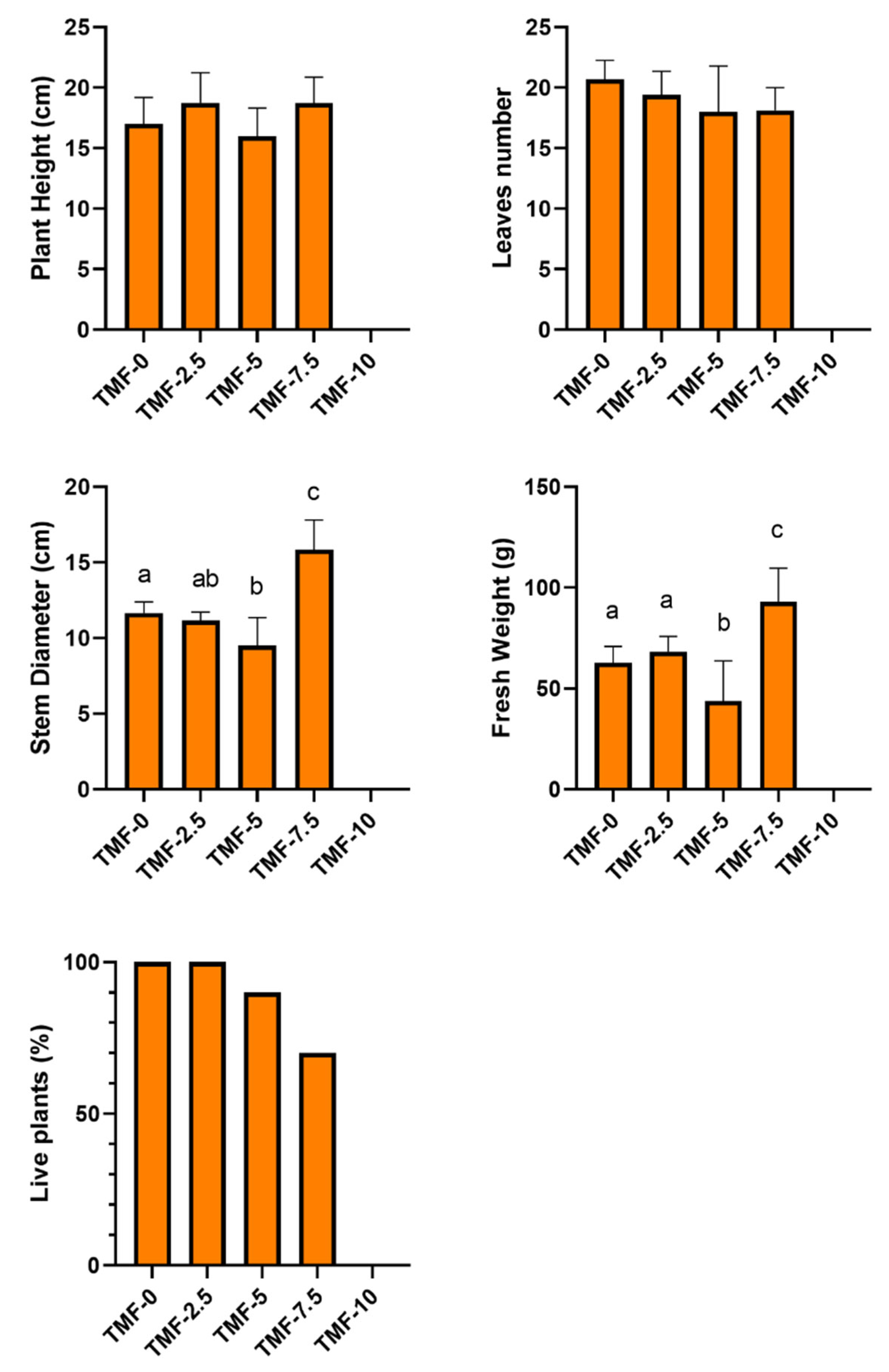
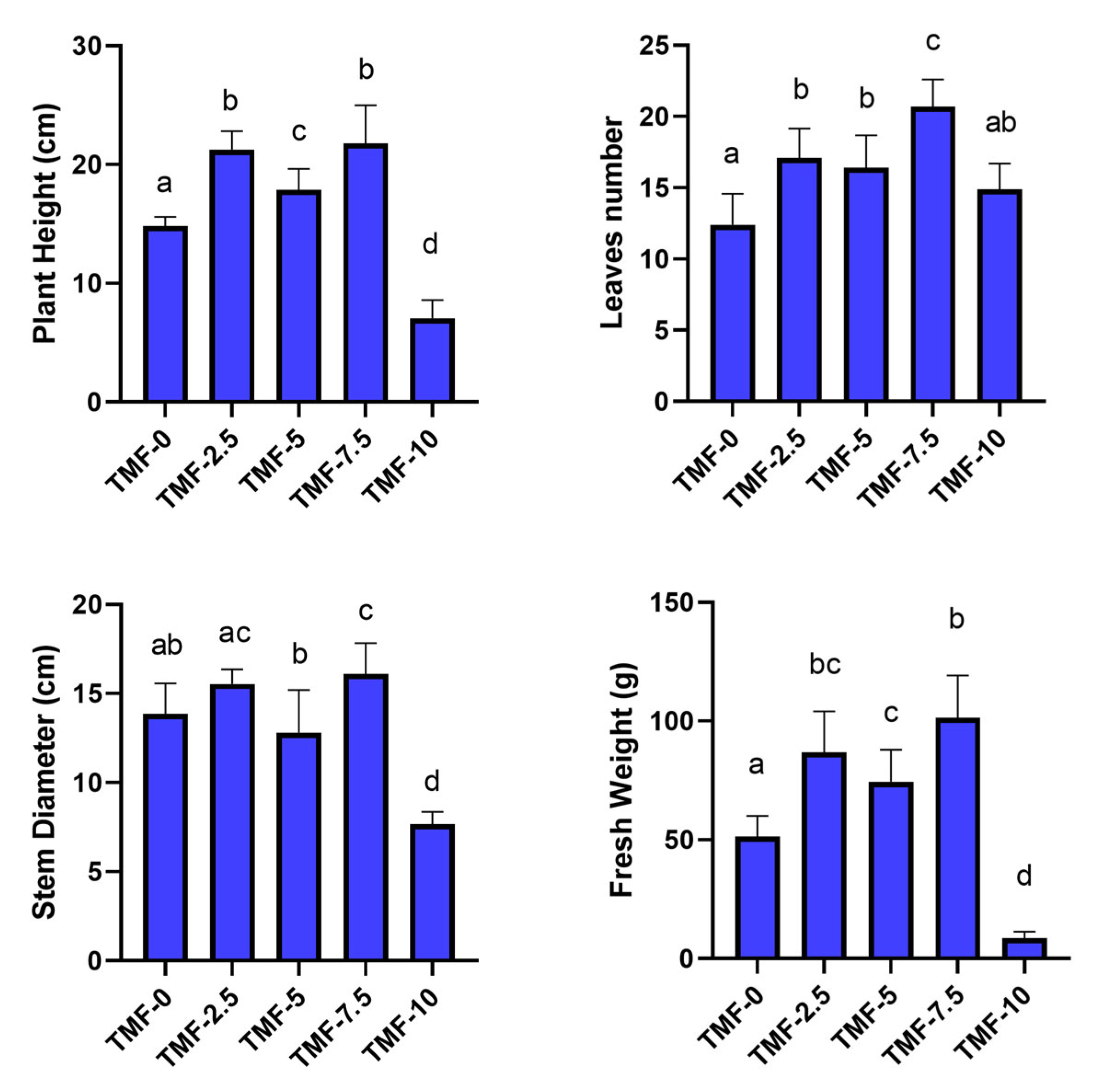
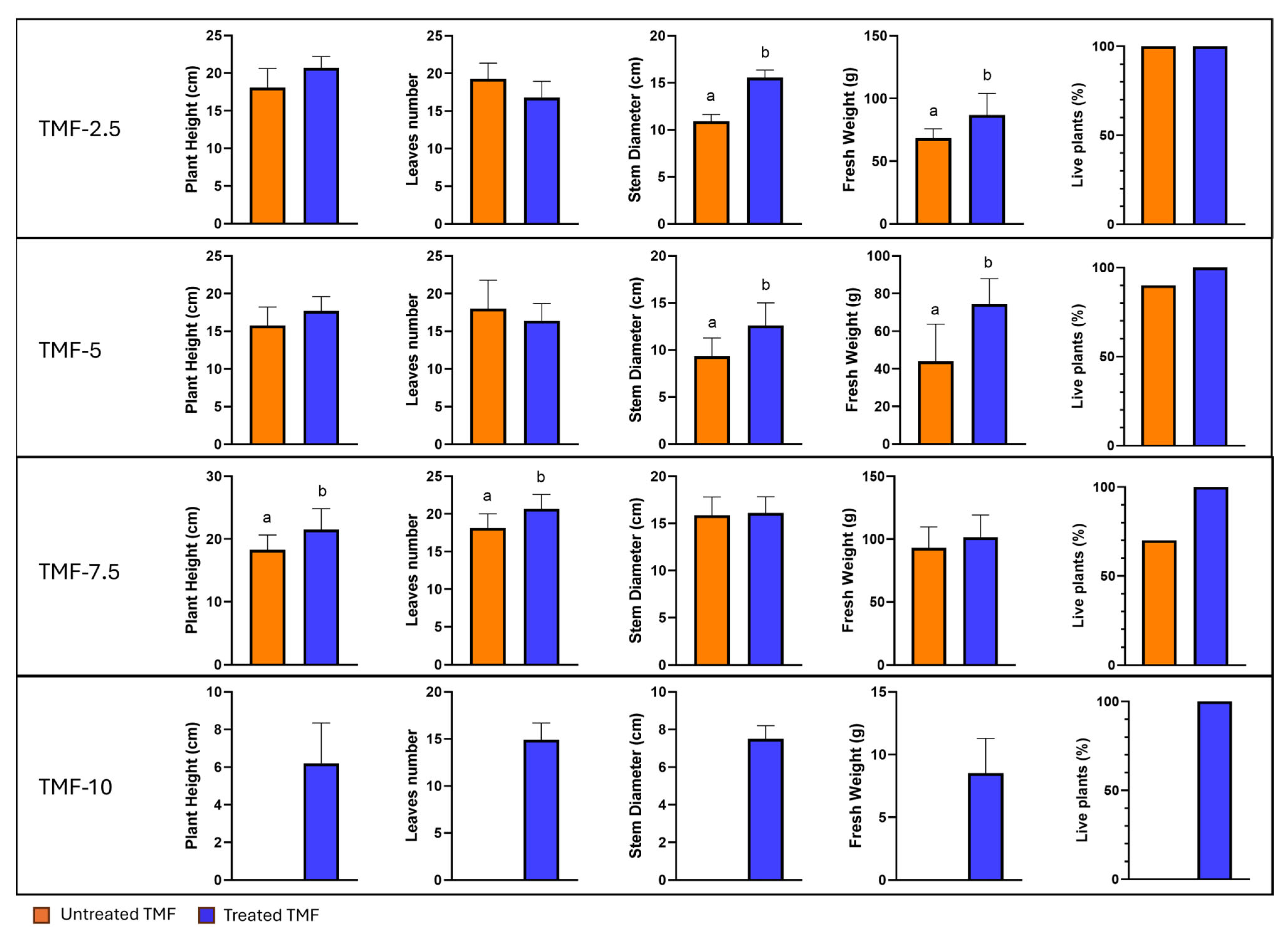
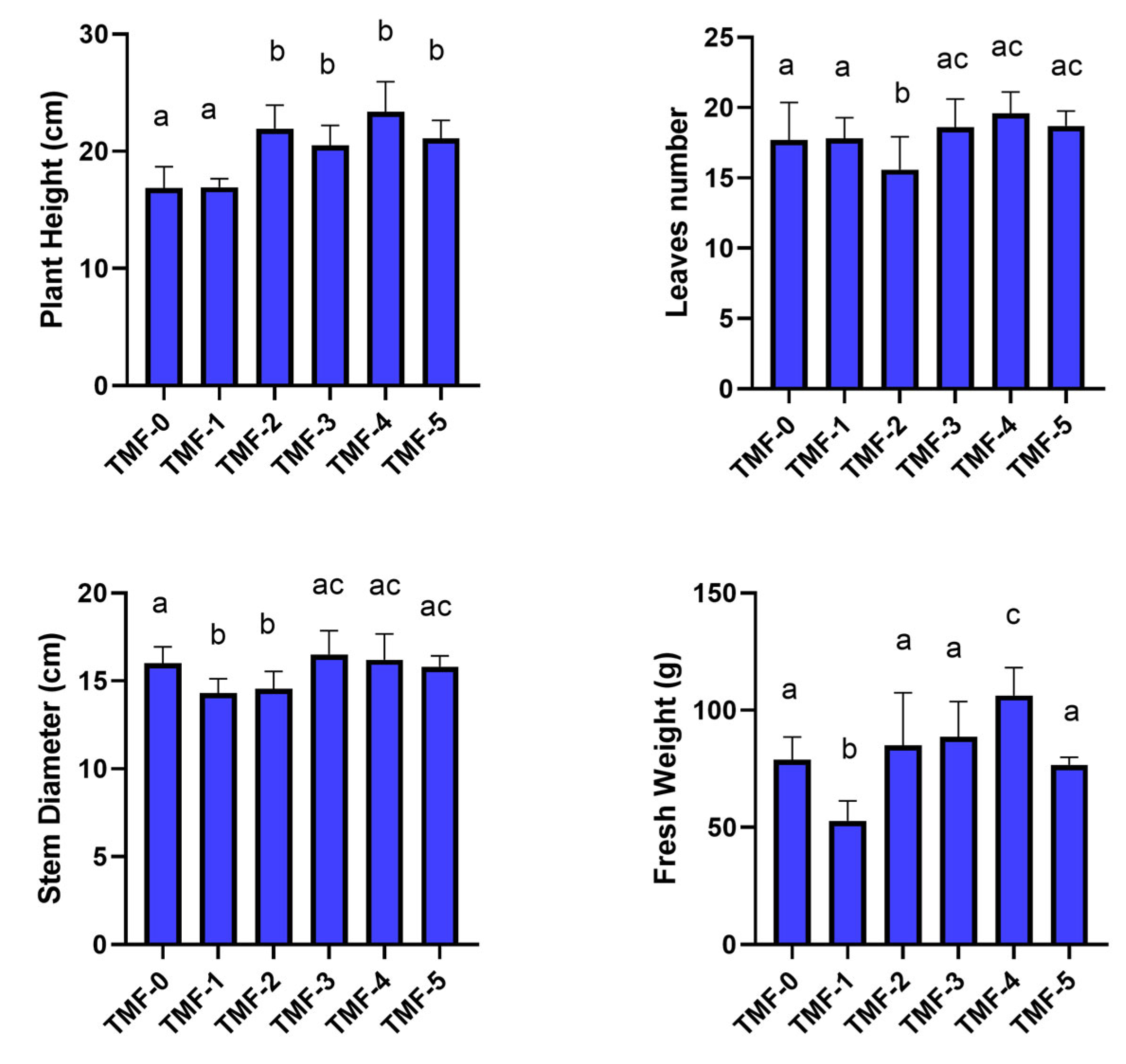
3.2. Canasta Trials
Trials on Canasta with Different Percentages of UT-TMF and TT-TMF
4. Discussion
- -
- ammonium ions (NH4+), which can release NH3 (a basic compound);
- -
- carbonates and bicarbonates formed during larval metabolism;
- -
- basic components such as chitin, chitosan, and peptidoglycans.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TM | Tenebrio molitor |
| TMF | Tenebrio molitor Frass |
| TML | Tenebrio molitor Larvae |
| BSF | Black Soldier Fly |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| PH | Plant height |
| LN | Number of edible leaves |
| SD | Stem diameter at the base of the plant |
| FW | Fresh weight |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
References
- Worldometers. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/ (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- United Nations. World Population Prospects 2024: Summary of Results; UNDESA/POP/2024/TR/NO 9; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World; FAO Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, A.D.; Mishra, R.; Maurya, K.K.; Singh, R.B.; Wilson, D.W. Estimates for World Population and Global Food Availability for Global Health. In The Role of Functional Food Security in Global Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Calicioglu, O.; Flammini, A.; Bracco, S.; Bellù, L.; Sims, R. The Future Challenges of Food and Agriculture: An Integrated Analysis of Trends and Solutions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabi-Floody, M.; Medina, J.; Rumpel, C.; Condron, L.M.; Hernandez, M.; Dumont, M.; de la Luz Mora, M. Smart Fertilizers as a Strategy for Sustainable Agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2018, 147, 119–157. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, D.; Chopra, A.K. An Overview of Pesticides in the Development of Agriculture Crops. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2020, 12, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, A.L. Chemical Fertilizers and Pesticides: Role in Groundwater Contamination. In Agrochemicals Detection, Treatment and Remediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, A.; Tyagi, M.; Sharma, N. Impact of Chemical Pesticides vs. Biopesticides on Human Health and Environment. Int. J. All Res. Writ. 2019, 2, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten, W.H.; Bardgett, R.D.; Bever, J.D.; Bezemer, T.M.; Casper, B.B.; Fukami, T.; Kardol, P.; Klironomos, J.N.; Kulmatiski, A.; Schweitzer, J.A.; et al. Plant–Soil Feedbacks: The Past, the Present and Future Challenges. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakachew, K.; Yigermal, H.; Assefa, F.; Gelaye, Y.; Ali, S. Review on Enhancing the Efficiency of Fertilizer Utilization: Strategies for Optimal Nutrient Management. Open Agric. 2024, 9, 20220356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, M.; Yao, H.; Lv, L.; Shen, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; et al. Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer by Organic Fertilizer Benefits Grain Yield, Water Use Efficiency, and Economic Return of Summer Maize. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 217, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Huis, A.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B. The Environmental Sustainability of Insects as Food and Feed: A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C.; Megharaj, M. Insect Farming: A Bioeconomy-Based Opportunity to Revalorize Plastic Wastes. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2025, 23, 100521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, S.; You, L.; Song, J. Application of Edible Insects to Food Products: A Review on the Functionality, Bioactivity and Digestibility of Insect Proteins under High-Pressure/Ultrasound Processing. Food Chem. 2024, 468, 142469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verardi, A.; Sangiorgio, P.; Della Mura, B.; Moliterni, S.; Spagnoletta, A.; Dimatteo, S.; Bassi, D.; Cortimiglia, C.; Rebuzzi, R.; Palazzo, S.; et al. Tenebrio molitor Frass: A Cutting-Edge Biofertilizer for Sustainable Agriculture and Advanced Adsorbent Precursor for Environmental Remediation. Agronomy 2025, 15, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/882 of 1 June 2021 authorising the placing on the market of dried Tenebrio molitor larva as a novel food under Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament of the council amending Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/2470. Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, 194, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke, N.; Baur, A.; Böschen, V.; Demtröder, S.; Benning, R.; Delgado, A. Automation of Insect Mass Rearing and Processing Technologies of Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor). In African Edible Insects As Alternative Source of Food, Oil, Protein and Bioactive Components; Mariod, A.A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.-Q.; Li, M.-X.; Ding, J.; Bai, S.-W.; Wu, Q.-L.; Zhao, L.; Cao, G.-L.; Ren, N.-Q.; et al. Sustainable Strategy for Lignocellulosic Crop Wastes Reduction by Tenebrio molitor Linnaeus (Mealworm) and Potential Use of Mealworm Frass as a Fertilizer. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deruytter, D.; Coudron, C.L. The Effects of Density on the Growth, Survival and Feed Conversion of Tenebrio molitor Larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakstad, J.I.; Strimbeck, R.; Poveda, J.; Bones, A.M.; Kissen, R. Frass from Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) as Plant Fertilizer and Defense Priming Agent. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 53, 102862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesigamukama, D.; Subramanian, S.; Tanga, C.M. Nutrient Quality and Maturity Status of Frass Fertilizer from Nine Edible Insects. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes-Mendizábal, T.; Salcedo, I.; Huérfano, X.; Riga, P.; Estavillo, J.M.; Ávila Blanco, D.; Duñabeitia, M.K. Mealworm Frass as a Potential Organic Fertilizer in Synergy with PGP-Based Biostimulant for Lettuce Plants. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, H.C.S.; Ashworth, A.J.; Arsi, K.; Rojas, M.G.; Morales-Ramos, J.A.; Donoghue, A.; Robinson, K. Insect Frass Composition and Potential Use as an Organic Fertilizer in Circular Economies. J. Econ. Ento-mol. 2024, 117, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, A.J.; Amorim, H.C.S.; Drescher, G.L.; Moore, P.A.; Rojas, M.G.; Morales-Ramos, J.; Donoghue, A.M. Insect Frass Fertilizer as Soil Amendment for Improved Forage and Soil Health in Circular Systems. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénault-Ethier, L.; Reid, B.; Hotte, N.; Paris, N.; Quinche, M.; Lachance, C.; Fortin, A.; Normandin, É.; Laderriere, V.; Vandenberg, G. Growth Trials on Vegetables, Herbs, and Flowers Using Mealworm Frass, Chicken Manure, and Municipal Compost. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunzunegui, I.; Martín-García, J.; Santamaría, Ó.; Poveda, J. Analysis of Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) Frass as a Resource for a Sustainable Agriculture. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 460, 142608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouche, J.; Campbell, B.; Hénault-Éthier, L.; Banks, I.J.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Preyer, C.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Vandenberg, G.W. The Edible Insect Sector in Canada and the United States. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarelli, S. The Food Safety Law in China: Regulatory Framework and Implications for International Trade. Master’s Thesis, Ca’ Foscari University, Venice, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- EU Regulation 2021/1925. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2021/1925/oj/eng (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Pinarelli Fazion, J.; Marzoli, F.; Pezzuto, A.; Bertola, M.; Antonelli, P.; Dolzan, B.; Barco, L.; Belluco, S. A Systematic Review of Experimental Studies on Salmonella Persistence in Insects. npj Sci. Food 2023, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.; Seinige, D.; Grabowski, N.T.; Ahlfeld, B.; Yue, M.; Kehrenberg, C. Characterization of Escherichia coli from Edible Insect Species: Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing Isolate. Foods. 2021, 10, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praeg, N.; Klammsteiner, T. Primary Study on Frass Fertilizers from Mass-Reared Insects: Species Variation, Heat Treatment Effects, and Implications for Soil Application at Laboratory Scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J. Insect Frass in the Development of Sustainable Agriculture. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; Jiménez-Gómez, A.; Saati-Santamaría, Z.; Usategui-Martín, R.; Rivas, R.; García-Fraile, P. Mealworm Frass as a Potential Biofertilizer and Abiotic Stress Tolerance-Inductor in Plants. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klammsteiner, T.; Walter, A.; Bogataj, T.; Heussler, C.D.; Stres, B.; Steiner, F.M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Arthofer, W.; Insam, H. The Core Gut Microbiome of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Raised on Low-Bioburden Diets. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Garofalo, C.; Clementi, F.; Pasquini, M.; Riolo, P.; Ruschioni, S.; Isidoro, N.; Loreto, N.; et al. The Bacterial Biota of Laboratory-Reared Edible Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor L.): From Feed to Frass. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 272, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, G.; Delisle-Houde, M.; Tweddell, R.J.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Dorais, M.; Lebeuf, Y.; Derome, N.; Vandenberg, G. Diet composition influences growth performance, bioconversion of black soldier fly larvae: Agronomic value and in vitro biofungicidal activity of derived frass. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, G.; Delisle-Houde, M.; Vandenberg, G.W.; Derome, N.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Dorais, M.; Vincent, A.T.; Tweddell, R.J. Assessment of antifungal/anti-oomycete activity of frass derived from black soldier fly larvae to control plant pathogens in horticulture: Involvement of Bacillus velezensis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, G.; Delisle-Houde, M.; Vandenberg, G.W.; Deschamps, M.H.; Dorais, M.; Derome, N.; Tweddell, R.J. Suppressive Effect of Black Soldier Fly Larvae Frass on Fusarium Wilt Disease in Tomato Plants. Insects 2024, 15, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPIFF Contribution Paper on the Inclusion of Insect Frass as Part of the EU Fertilisers’ Regulation, 2 December 2022. Available online: https://ipiff.org/position-papers/ (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Mattioli, S.; Paci, G.; Fratini, F.; Dal Bosco, A.; Tuccinardi, T.; Mancini, S. Former Foodstuff in Mealworm Farming: Effects on Fatty Acids Profile, Lipid Metabolism and Antioxidant Molecules. LWT 2021, 147, 111644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuoli, R.; Finco, A.; Chiesa, M.; Gerosa, G. A dose-response relationship for marketable yield reduction of two lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) cultivars exposed to tropospheric ozone in Southern Europe. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26249–26258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar-Gutiérrez, A.J.; Burns, I.G.; Lee, A.; Edmondson, R.N. Screening Lettuce Cultivars for Low Nitrate Content. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2002, 77, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, D.; Daoulas, G.; Faucon, M.-P.; Dulaurent, A.-M. Potential Use of Mealworm Frass as a Fertilizer: Impact on Crop Growth and Soil Properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foscari, A.; Dalla Costa, L.; Tulli, F.; Uboni, C.; Fellet, G. Frass from Tenebrio molitor as Alternative to NPK-Mineral Fertilization. Ital. J. Agron. 2024, 19, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, H.; El-Fadel, M.A.; El-Badawy, M.; Phillip, Y.; Hussein, A.; Khayyal, A.; Elmenniawy, M.; El-Sanafawy, H.A.; Radwan, M.A.; Rodríguez, G.B.; et al. Dietary Inclusion of Tenebrio molitor Frass Affects Nutrient Digestibility and Milk Performance in Goats. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 19, 101727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemi, H.; Kianmehr, M.H.; Borghaee, A.M. Effect of Pellet Processing of Fertilizer on Slow-Release Nitrogen in Soil. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2010, 9, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.K.; Rubel, R.I.; Gupta, S.; Wu, Y.; Wei, L.; Brözel, V.S. Impacts of Biochar-Based Controlled-Release Nitrogen Fertilizers on Soil Prokaryotic and Fungal Communities. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.I.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Al-Farraj, A.S.F.; Ahmad, M.; Aouak, T.; Al-Swadi, H.A.; Mousa, M.A. Incorporation of biochar and semi-interpenetrating biopolymer to synthesize new slow release fertilizers and their impact on soil moisture and nutrients availability. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, C.G.; Rumbos, C.I. Frass and Furious: Unfolding the Potential of Insect Frass as Soil Fertilizer. Agrochemicals 2025, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, V.; Molla, A.; Grammenou, A.; Apostolidis, V.; Athanassiou, C.G.; Rumbos, C.I.; Levizou, E. Insect Frass as a Novel Organic Soil Fertilizer for Spinach. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5935–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zim, J.; Aitikkou, A.; El Omari, M.H.; Malahi, S.E.L.; Azim, K.; Hirich, A.; Nilahyane, A.; Oumouloud, A. A New Organic Amendment Based on Insect Frass for Zucchini. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Bea, S.-M.; Park, J.-H.; Jang, D.-H.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, Y.-H.; Seo, D.-C. Effects of Tenebrio molitor (Mealworm) Frass on the Growth of Ginseng Sprout (Panax ginseng) in Commercial Potting Soil. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fert. 2023, 56, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Errico, S.; Sangiorgio, P.; Dimatteo, S.; Moliterni, S.; Rebuzzi, R.; Coppola, G.; Lopresto, C.G.; Verardi, A. Evaluation of the Effect of Tenebrio molitor Frass on the Growth Parameters of Canasta Lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. capitata) as a Model Plant. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161731
Errico S, Sangiorgio P, Dimatteo S, Moliterni S, Rebuzzi R, Coppola G, Lopresto CG, Verardi A. Evaluation of the Effect of Tenebrio molitor Frass on the Growth Parameters of Canasta Lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. capitata) as a Model Plant. Agriculture. 2025; 15(16):1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161731
Chicago/Turabian StyleErrico, Simona, Paola Sangiorgio, Salvatore Dimatteo, Stefania Moliterni, Raffaella Rebuzzi, Gerardo Coppola, Catia Giovanna Lopresto, and Alessandra Verardi. 2025. "Evaluation of the Effect of Tenebrio molitor Frass on the Growth Parameters of Canasta Lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. capitata) as a Model Plant" Agriculture 15, no. 16: 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161731
APA StyleErrico, S., Sangiorgio, P., Dimatteo, S., Moliterni, S., Rebuzzi, R., Coppola, G., Lopresto, C. G., & Verardi, A. (2025). Evaluation of the Effect of Tenebrio molitor Frass on the Growth Parameters of Canasta Lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. capitata) as a Model Plant. Agriculture, 15(16), 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161731








