Intelligent Fruit Localization and Grasping Method Based on YOLO VX Model and 3D Vision
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The above studies provide some methods for fruit picking, but there are still deficiencies in fruit maturity matching, random location capture, and picking methods. In terms of application scenarios, this study is limited to greenhouse or strongly light-controlled environments, because the picking path of the robot is about 40 klux~80 klux, and the indoor light intensity is less than this value, so direct sunlight should be avoided as much as possible. To this end, this method focuses on using the latest YOLO VX deep learning model under the indoor constant-temperature condition, and synchronously calculates the spatial appearance and appearance characteristics sending the position information to the robotic arm in real time through visual calibration and servo control and then relying on the three-finger flexible claw to complete the picking. The principal contributions of this study are summarized as follows:
- (2)
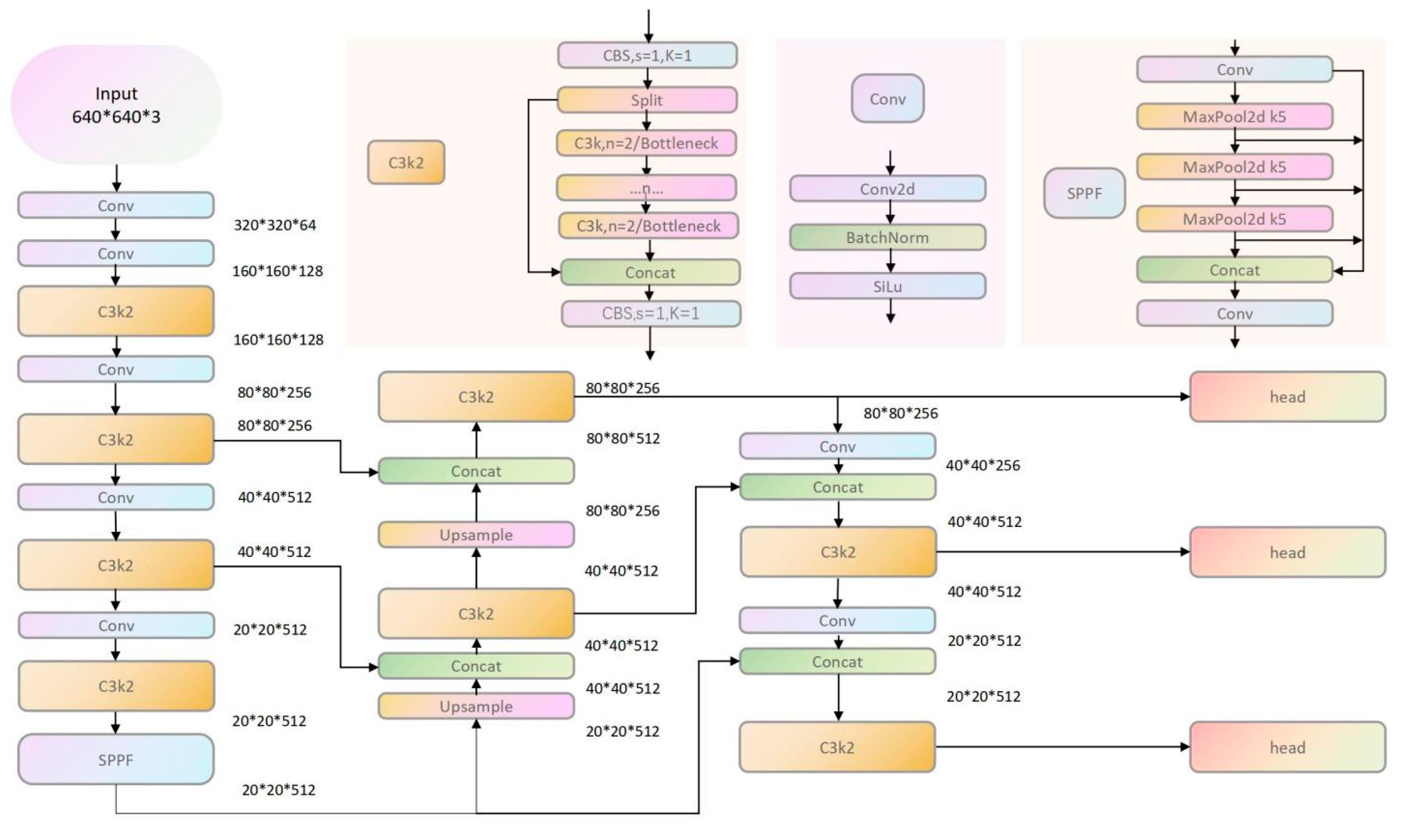
- We developed a hybrid multimodal autonomous fruit ripeness recognition algorithm based on C3K2 and SPPF, reducing real-time control latency to 30.9 ms; this is more efficient than earlier models. By implementing cascaded pooling to cover larger image regions, the system achieves enhanced robustness in detecting large-scale targets. Compared to conventional SPP methods, the serial design preserves richer edge information, resulting in finer feature extraction through small-kernel pooling.
- (3)
- We implemented a spatial coordination framework that integrates 3D-vision-derived centroid coordinates and dimensional parameters into a collaborative robotic control system, enforcing synchronized locomotion between the mobile chassis and manipulator via triaxial coordinate system alignment.
- (4)
- A hybrid communication architecture combining TX/RX serial protocol and Ethernet connection is designed to establish a unified address scheme for 3D spatial data and Arduino-based motion control, which optimizes the path planning of autonomous mobile robot (AMR) operation compared with traditional methods.
- (5)
- Experimental validation demonstrated that the proposed machine vision–Arduino integrated framework achieves 91.14% target recognition accuracy with ±1.5 mm positioning precision in agricultural harvesting scenarios.
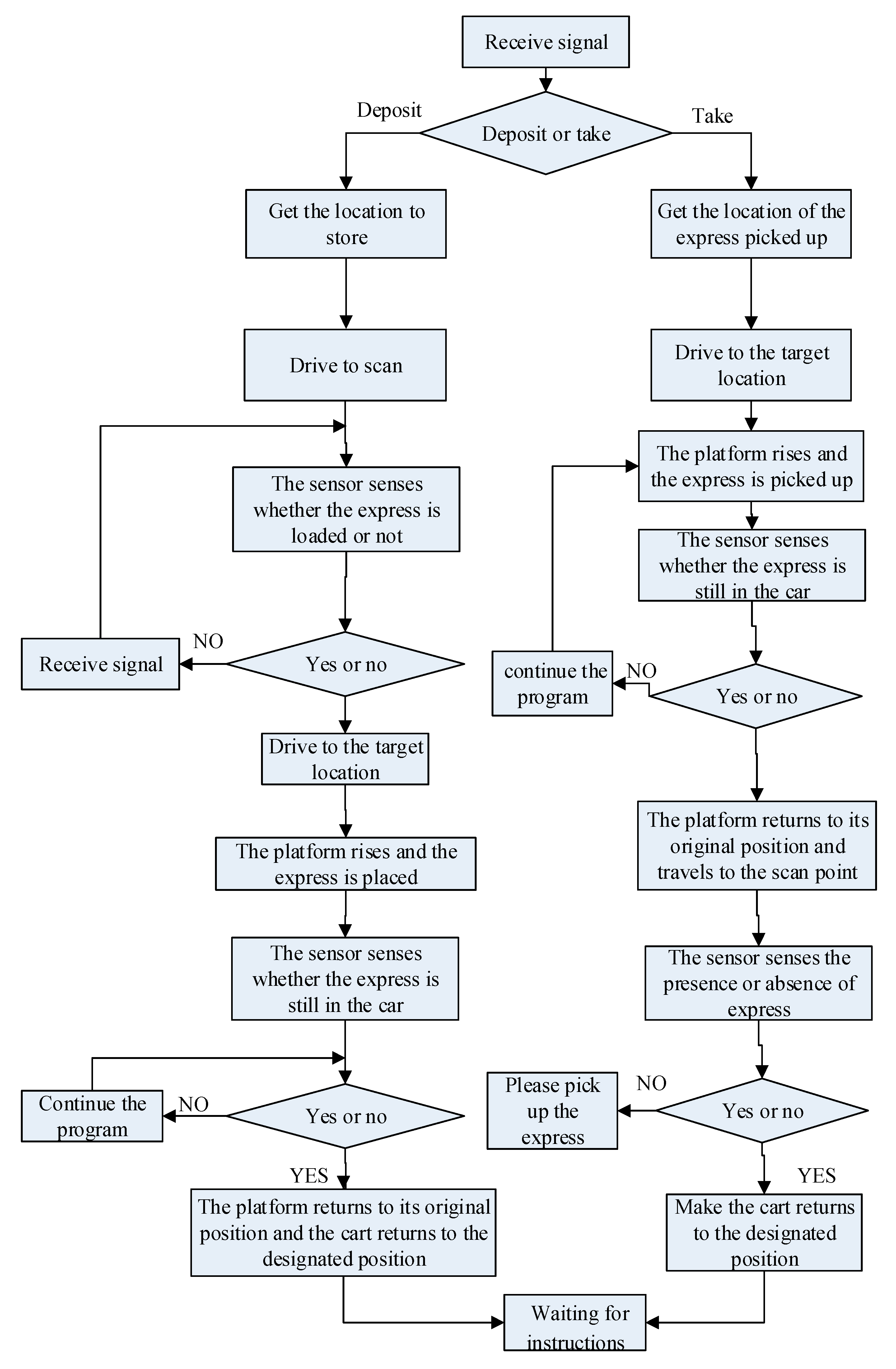
2. System Scheme Design
3. Establishing a YOLO X Network Model for Fruit Target Recognition
4. Visual Recognition System Design
4.1. Collaborative Robotic Arm and Binocular Camera Calibration
4.2. Obtaining Fruit Features
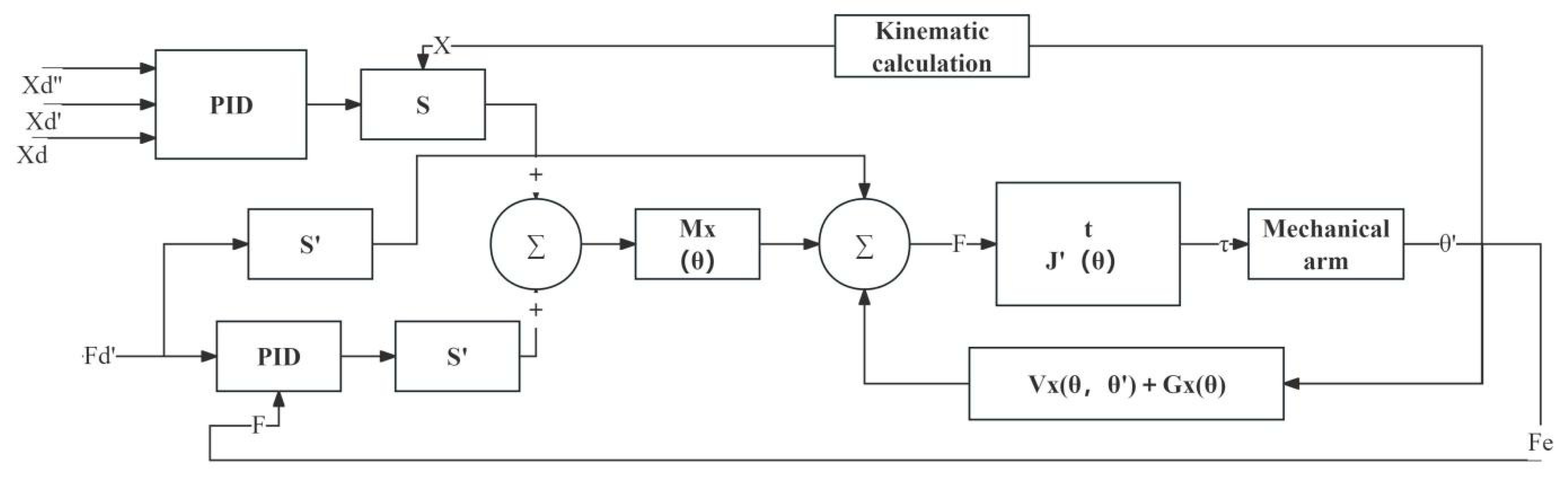
4.3. Fruit Grasping Position and Force Mixing Control
4.4. Motion Control System Design
5. Test
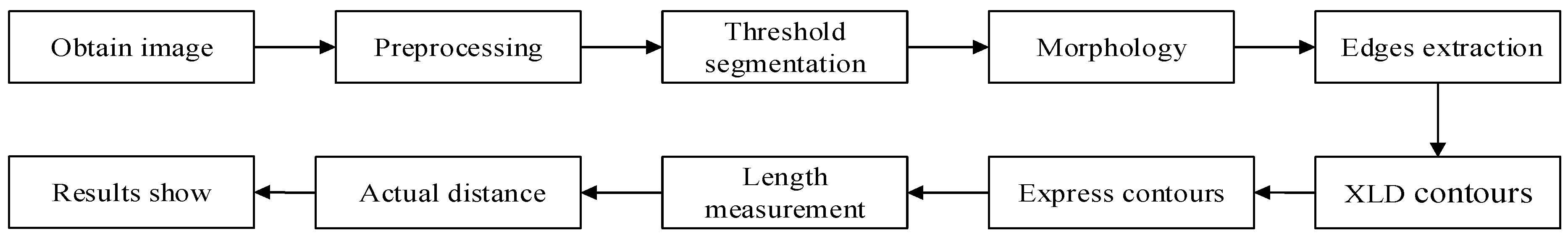
5.1. Dimensions and Location
5.2. Outline Dimension Test
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, C.; Jiang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Sun, X.; He, L.; Mao, W.; Majeed, Y.; Li, R.; et al. Improved binocular localization of kiwifruit in orchard based on fruit and calyx detection using YOLOv5x for robotic picking. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Luo, L.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wei, H.; Wang, J. Dynamic visual servo control methods for continuous operation of a fruit harvesting robot working throughout an orchard. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 219, 108774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pan, W.; Zou, T.; Li, C.; Han, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Zou, X. A Review of Perception Technologies for Berry Fruit-Picking Robots: Advantages, Disadvantages, Challenges, and Prospects. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Rong, J. Research on fruit spatial coordinate positioning by combining improved YOLOv8s and adaptive multi-resolution model. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Sun, B. Recent advances in molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) for visual recognition and inhibition of α-dicarbonyl compound-mediated Maillard reaction products. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Qu, H.; Li, N.; Wu, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Qiu, J. Improved Apple Fruit Target Recognition Method Based on YOLOv7 Model. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. Automatic Robot Hand-Eye Calibration Enabled by Learning-Based 3D Vision. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2024, 110, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Ye, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, S.; Song, Z. High-efficiency automated triaxial robot grasping system for motor rotors using 3D structured light sensor. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2024, 35, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Yin, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H. Research on Multi-Hole Localization Tracking Based on a Combination of Machine Vision and Deep Learning. Sensors 2024, 24, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Meng, H.; Gao, Y.; Gao, D. A real-time object detection method for underwater complex environments based on FasterNet-YOLOv7. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2024, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, S.; Martinez, J.C.; Montes, A.M.; Marín, C.; Bolaños, R.; Álvarez, D. Machine Vision-Assisted Design of End Effector Pose in Robotic Mixed Depalletizing of Heterogeneous Cargo. Sensors 2025, 25, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choutri, K.; Lagha, M.; Meshoul, S.; Batouche, M.; Bouzidi, F.; Charef, W. Fire detection and geo-localization using uav’s aerial images and YOLO-based models. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Wang, K.; Lian, S.; Zhao, K. Vision-based robotic grasping from object localization, object pose estimation to grasp estimation for parallel grippers: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 1677–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Wu, L.; Xu, H. 9dtact: A compact vision-based tactile sensor for accurate 3d shape reconstruction and generalizable 6d force estimation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 9, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wu, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, Y. Object Recognition and Grasping for Collaborative Robots Based on Vision. Sensors 2024, 24, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, Y. Flexible Hand Claw Picking Method for Citrus-Picking Robot Based on Target Fruit Recognition. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S. Target Localization and Grasping of Parallel Robots with Multi-Vision Based on Improved RANSAC Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Dai, S.L.; Liang, J. Adaptive constrained formation-tracking control for a tractor-trailer mobile robot team with multiple constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 68, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, D.; Gong, S. Uncalibrated visual positioning using adaptive Kalman Filter with dual rate structure for wafer chip in LED packaging. Measurement 2022, 191, 110829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Duan, J.; Ai, P.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zou, X. Rachis detection and three-dimensional localization of cut off point for vision-based banana robot. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, T.S.; Cheng, K.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, R.; Zhu, W.D.; Zhu, F.D.; Jiang, X.F.; Dong, X.T. Evaluation of a custom-designed human–robot collaboration control system for dental implant robot. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2022, 18, e2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, S.; Kothari, A.; Gupta, V. YOLO based human action recognition and localization. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 133, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, Z.; He, T. Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Optimization Method Based on Object Detection in Dynamic Scene. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guo, L.; Gao, H.; You, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z. YOLO-SLAM: A semantic SLAM system towards dynamic environment with geometric constraint. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 6011–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, B.; Wu, D.; Zhao, K.; Chen, S.; Lu, M.; Cong, J. A YOLO-GGCNN based grasping framework for mobile robots in unknown environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 225, 119993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, B.; Cao, M.; Ma, L. Research on visual slam based on improved YOLOv5s in dynamic scenes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2902, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharath, G.S.; Hiremath, N.; Manjunatha, G. Design and analysis of gantry robot for pick and place mechanism with Arduino Mega 2560 microcontroller and processed using pythons. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Fan, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Deng, B. An indoor delivery robot based on YOLOv8 and ROS. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2787, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rodriguez, F.M.; Cuesta, F. An android and arduino-based low-cost educational robot with applied intelligent control and machine learning. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.L.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.M. On safety improvement through process establishment for SOTIF application of autonomous driving logistics robot. Int. J. Internet Broadcast. Commun. 2022, 14, 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Kalpana, M.; Geethika, L.S.; Afzal, S.; Singh, R.; Nookaraju, A.; Kiran, T.T.S.; Praneeth, P.S. Design and Implementation of Versatile Delivery Robot. Eng. Proc. 2024, 66, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Tony, W.; Ansari, A.; Hoang, K.B. A Untethered Magnetic Micro-Robot for Local Therapeutic Delivery for Neurosurgical Oncology. Neurosurgery 2024, 70, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryan, A.; Modi, M.; Saha, I.; Majumdar, R.; Mohalik, S. Optimal Integrated Task and Path Planning and Its Application to Multi-Robot Pickup and Delivery. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.01277. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, M.; Lin, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, K.; He, Y.; Li, L. Vision-based three-dimensional reconstruction and monitoring of large-scale steel tubular structures. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1236021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, A.T.; Dosoftei, C.C.; Budaciu, C. Kinematics calibration and validation approach using indoor positioning system for an omnidirectional mobile robot. Sensors 2022, 22, 8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, J. Research on robot path perception and optimization technology based on whale optimization algorithm. J. Comput. Cogn. Eng. 2022, 1, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhao, J.S.; Misyurin, S.Y.; Martins, D. Precision-driven multi-target path planning and fine position error estimation on a dual-movement-mode mobile robot using a three-parameter error model. Sensors 2023, 23, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Wu, Z. Adaptive neural network control for image-based visual servoing of robot manipulators. IET Control Theory Appl. 2022, 16, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y. Visual servoing pushing control of the soft robot with active pushing force regulation. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.Q.; Aljazaery, I.A.; Al-zubidi, A.F.; ALRikabi, H.T.S. Design and implementation control system for a self-balancing robot based on internet of things by using Arduino microcontroller. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. (PEN) 2021, 9, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siregar, I.M.; Siagian, N.F.; Siregar, V.M.M. A design of an electric light control device using arduino uno microcontroller-based short message service. IOTA J. 2022, 2, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Top, A.; Gökbulut, M. Android application design with mit app inventor for bluetooth based mobile robot control. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 126, 1403–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Wu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chang, Q.; Liu, W.; Huang, X. A YOLO11-Based Method for Segmenting Secondary Phases in Cu-Fe Alloy Microstructures. Information 2025, 16, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhou, J. Nondestructive Detection and Quality Grading System of Walnut Using X-Ray Imaging and Lightweight WKNet. Foods 2025, 14, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, X.; Mao, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, G. Individual Recognition of a Group Beef Cattle Based on Improved YOLO v5. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Kwak, D.; Choi, S. YOLOv8 with Post-Processing for Small Object Detection Enhancement. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Vega, J.A.; Silva-López, J.O.; Salas Lopez, R.; Medina-Medina, A.J.; Tuesta-Trauco, K.M.; Rivera-Fernandez, A.S.; Silva-Melendez, T.B.; Oliva-Cruz, M.; Barboza, E.; da Silva Junior, C.A.; et al. Automatic Detection of Ceroxylon Palms by Deep Learning in a Protected Area in Amazonas (NW Peru). Forests 2025, 16, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özakar, R.; Gedikli, E. Hand Washing Gesture Recognition Using Synthetic Dataset. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.; Li, C.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z. MSUD-YOLO: A Novel Multiscale Small Object Detection Model for UAV Aerial Images. Drones 2025, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Peng, X.; Zhou, X.; Cao, H.; Shan, C.; Li, S.; Qiao, S.; Shi, F. Enhanced Defect Detection in Additive Manufacturing via Virtual Polarization Filtering and Deep Learning Optimization. Photonics 2025, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Wu, A.; Yang, Y.; Fu, Q. Efficient Brain Tumor Segmentation for MRI Images Using YOLO-BT. Sensors 2025, 25, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, H.; Qi, B.; Shan, G. BBW YOLO: Intelligent Detection Algorithms for Aluminium Profile Material Surface Defects. Coatings 2025, 15, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, V.; Ravikumar, D.; Manibha, M.P.; Kesavan, R.; Kusala Kumar, G.R.; Sasikumar, S. Development of Autonomous Unmanned Aerial Vehicle for Environmental Protection Using YOLO V3. Eng. Proc. 2025, 87, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Piratinskii, E.; Rabaev, I. COSMICA: A Novel Dataset for Astronomical Object Detection with Evaluation Across Diverse Detection Architectures. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Gong, H.; Luo, L.; Ni, L.; Li, Z.; Fan, J.; Hu, T.; Mu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gong, H. For Precision Animal Husbandry: Precise Detection of Specific Body Parts of Sika Deer Based on Improved YOLO11. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.L.E.; Cruz, J.C.D. Anomalous Weapon Detection for Armed Robbery Using Yolo V8. Eng. Proc. 2025, 92, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, N.; Gao, D.; Zhu, Z. YOLOv8n-SMMP: A Lightweight YOLO Forest Fire Detection Model. Fire 2025, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Hong, M. YOLO Object Detection for Real-Time Fabric Defect Inspection in the Textile Industry: A Review of YOLOv1 to YOLOv11. Sensors 2025, 25, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, R.; Hu, J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, W. Crop-Free-Ridge Navigation Line Recognition Based on the Lightweight Structure Improvement of YOLOv8. Agriculture 2025, 15, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cui, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Shi, F.; Zhao, L. Intelligent Detection of Tomato Ripening in Natural Environments Using YOLO-DGS. Sensors 2025, 25, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Han, T.; Ye, Y. USD-YOLO: An Enhanced YOLO Algorithm for Small Object Detection in Unmanned Systems Perception. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Shi, J.; Gao, F.; Guo, J.; Wang, R. Paint Loss Detection and Segmentation Based on YOLO: An Improved Model for Ancient Murals and Color Paintings. Heritage 2025, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yoshida, S. Object Detection for Yellow Maturing Citrus Fruits from Constrained or Biased UAV Images: Performance Comparison of Various Versions of YOLO Models. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 4308–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shia, W.-C.; Ku, T.-H. Enhancing Microcalcification Detection in Mammography with YOLO-v8 Performance and Clinical Implications. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, J.G.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, D.; Kong, J.-W.; Kang, G.H.; Jang, Y.S.; Kim, W.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; et al. Detection of Aortic Dissection and Intramural Hematoma in Non-Contrast Chest Computed Tomography Using a You Only Look Once-Based Deep Learning Model. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
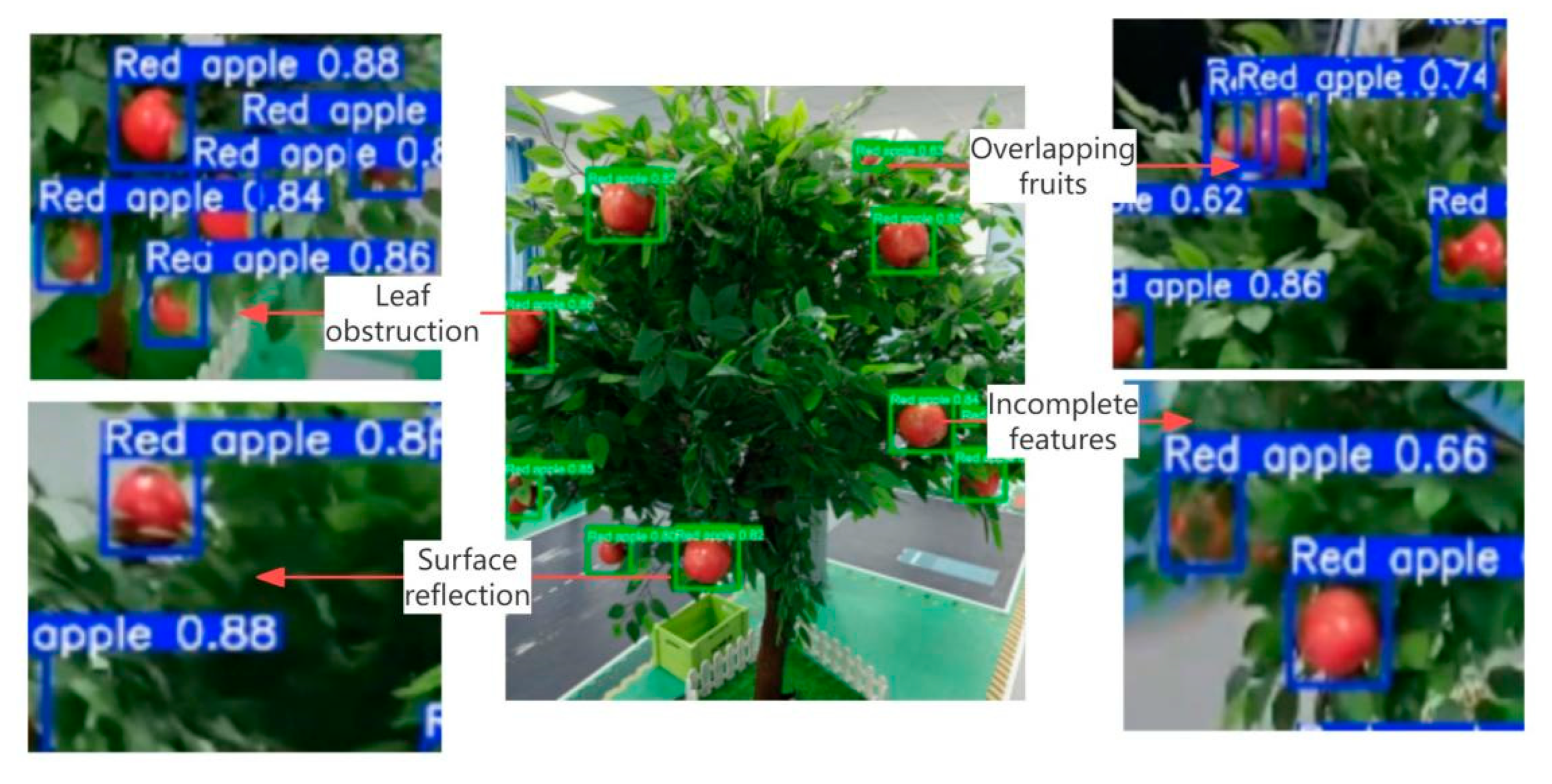









| I/O Parameter | Measurement Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Real-time image and video resolution | Live format (RGB/MP4) | Camera center position and distortion coefficient | Camera initialization parameters |
| Output | Image and video resolution | Image video format | Depth information after image/video matching | The distance of the target object from the camera |
| Camera Internal Parameter | Calibration Value | Camera Internal Parameter | Calibration Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focal length f/m | 0.0120 | Single pixel height/m | 4.400 × 10−6 |
| −397.275 | Center point X coordinate/pixel | 813.183 | |
| Single pixel width/m | 4.399 × 10−6 | Center point Y coordinate/pixel | 618.186 |
| Camera External Parameter | Calibration Value | Camera External Parameter | Calibration Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Translation matrix T | Rotation matrix R | ||
| Δx/m | −0.0301154 | α/(°) | 1.19178 |
| Δy/m | −0.0267293 | θ/(°) | 359.161 |
| Δz/m | 0.599653 | γ/(°) | 0.231355 |
| Dataset | Training Set | Validation Set | Test Set | Total Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
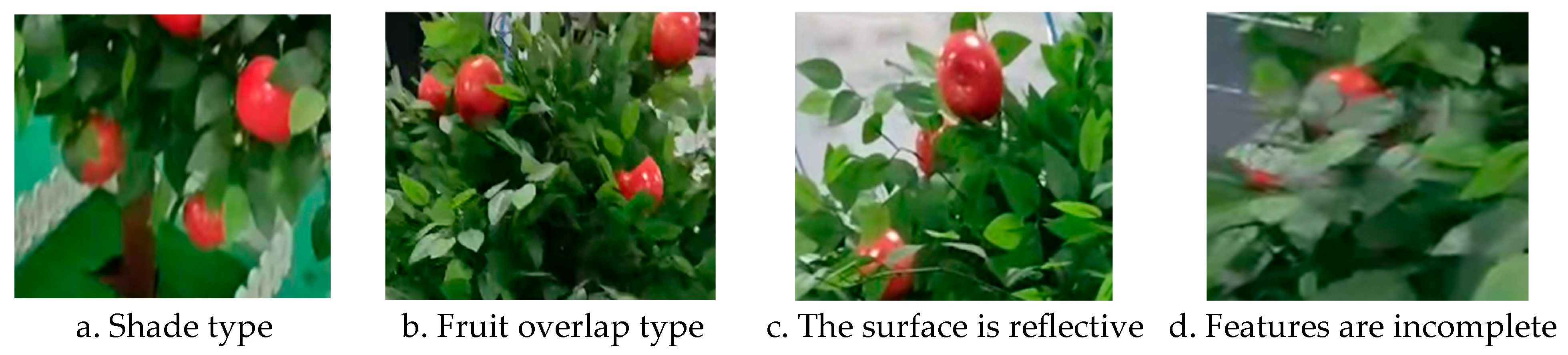
| Blade shielding type | 652 | 205 | 106 | 963 |
| Fruit overlapping type | 643 | 211 | 105 | 959 |
| Surface glare | 608 | 226 | 105 | 939 |
| Missing characteristics | 602 | 208 | 107 | 917 |
| Total quantity | 2505 | 850 | 523 | 3778 |
| Training Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input image size/pixel | 640 × 640 × 3 |
| Init learning rate | 0.01 |
| Batch_size | 16 |
| Epoch | 300 |
| Size Type | Measured Value/pix | Actual Value/pix | Differential Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length value of the identification box | 487.889 | 488.600 | 0.15 |
| Wide value of the identification box | 238.109 | 240.100 | 0.83 |
| Calculated length/mm | 8.990 | 9.770 | 8 |
| Calculated width/mm | 7.315 | 7.710 | 5 |
| Model Category | Accuracy | Recall | F1 Score | Mean Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO v8n | 90.66 | 84.57 | 87.36 | 93.32 |
| YOLO v10n | 90.98 | 84.05 | 87.38 | 90.06 |
| YOLO v12n | 91.14 | 84.32 | 87.60 | 91.76 |
| HALCON | 66.67 | 41.67 | / | 58.54 |
| Detection Link | HALCON | YOLO v8n | YOLO v10n | YOLO v12n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image preprocessing | 4.2 | 3.1 ms | 2.8 ms | 2.9 ms |
| image segmentation | 372.9 | / | / | / |
| Morphological processing | 708.3 | / | / | / |
| Feature extraction | 270.2 | / | / | / |
| Target screening/prediction | 280.1 | 29.8 | 30.2 | 29.1 |
| Result output | 40.2 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 1.8 |
| Total time/ms | 1675.9 | 31.6 | 32.1 | 30.9 |
| SPPF | C2PSA | Upsample | mAP50seg/% | mAP50 95seg/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| / | / | / | 97.5 | 74.2 |
| √ | / | / | 98.6 | 76.5 |
| √ | √ | / | 98.7 | 77.1 |
| √ | √ | √ | 98.7 | 78.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, R.; Wang, S. Intelligent Fruit Localization and Grasping Method Based on YOLO VX Model and 3D Vision. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141508
Mei Z, Li Y, Zhu R, Wang S. Intelligent Fruit Localization and Grasping Method Based on YOLO VX Model and 3D Vision. Agriculture. 2025; 15(14):1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141508
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Zhimin, Yifan Li, Rongbo Zhu, and Shucai Wang. 2025. "Intelligent Fruit Localization and Grasping Method Based on YOLO VX Model and 3D Vision" Agriculture 15, no. 14: 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141508
APA StyleMei, Z., Li, Y., Zhu, R., & Wang, S. (2025). Intelligent Fruit Localization and Grasping Method Based on YOLO VX Model and 3D Vision. Agriculture, 15(14), 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141508







