The Effects of Different Straw-Returning Methods on Soil Organic Carbon Transformation in Rice–Rape Rotation Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Characterization
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Soil Sample Collection
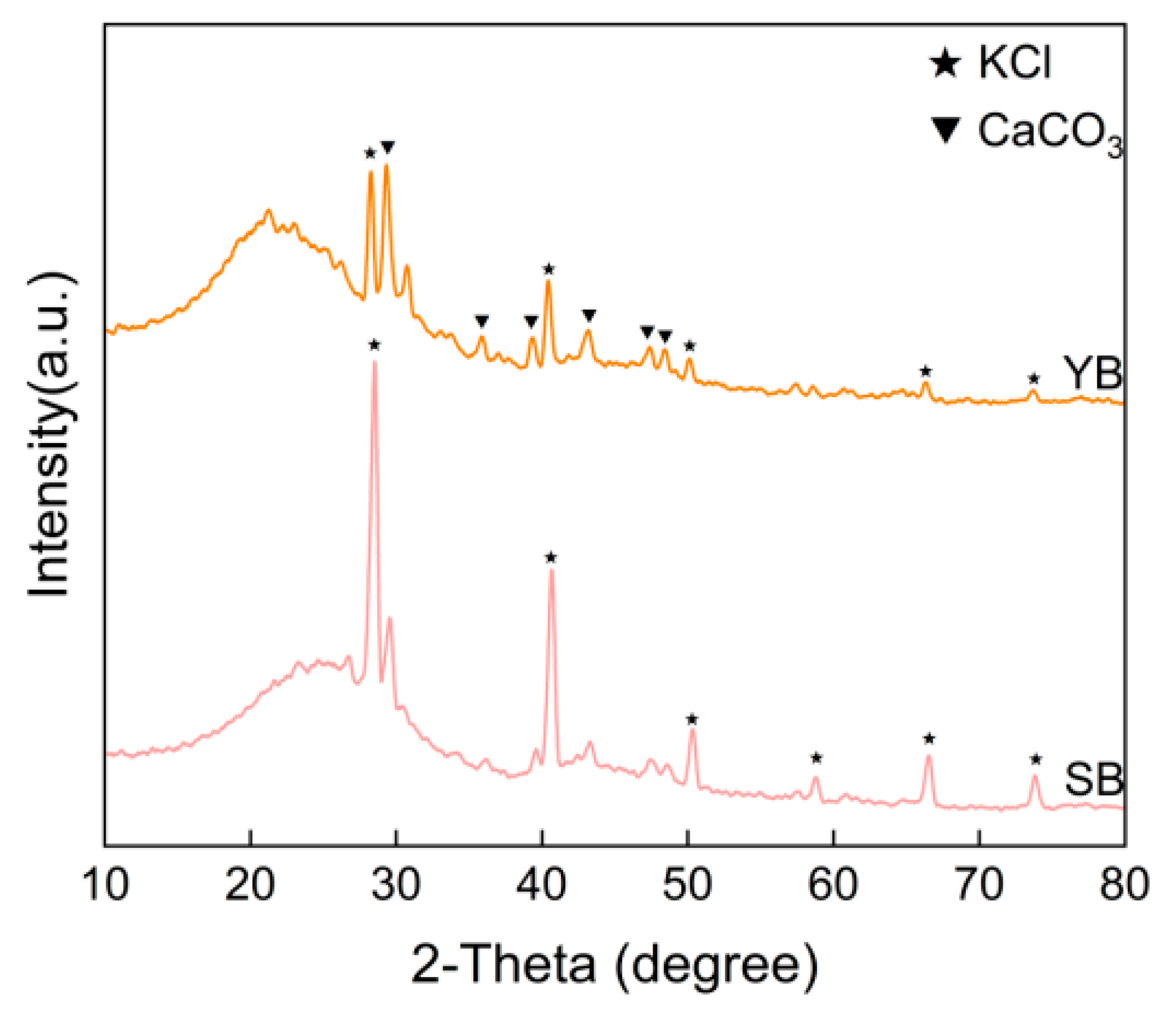
2.2.3. Basic Properties and Characterization of Returned Materials
2.2.4. Determination Methods
2.2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
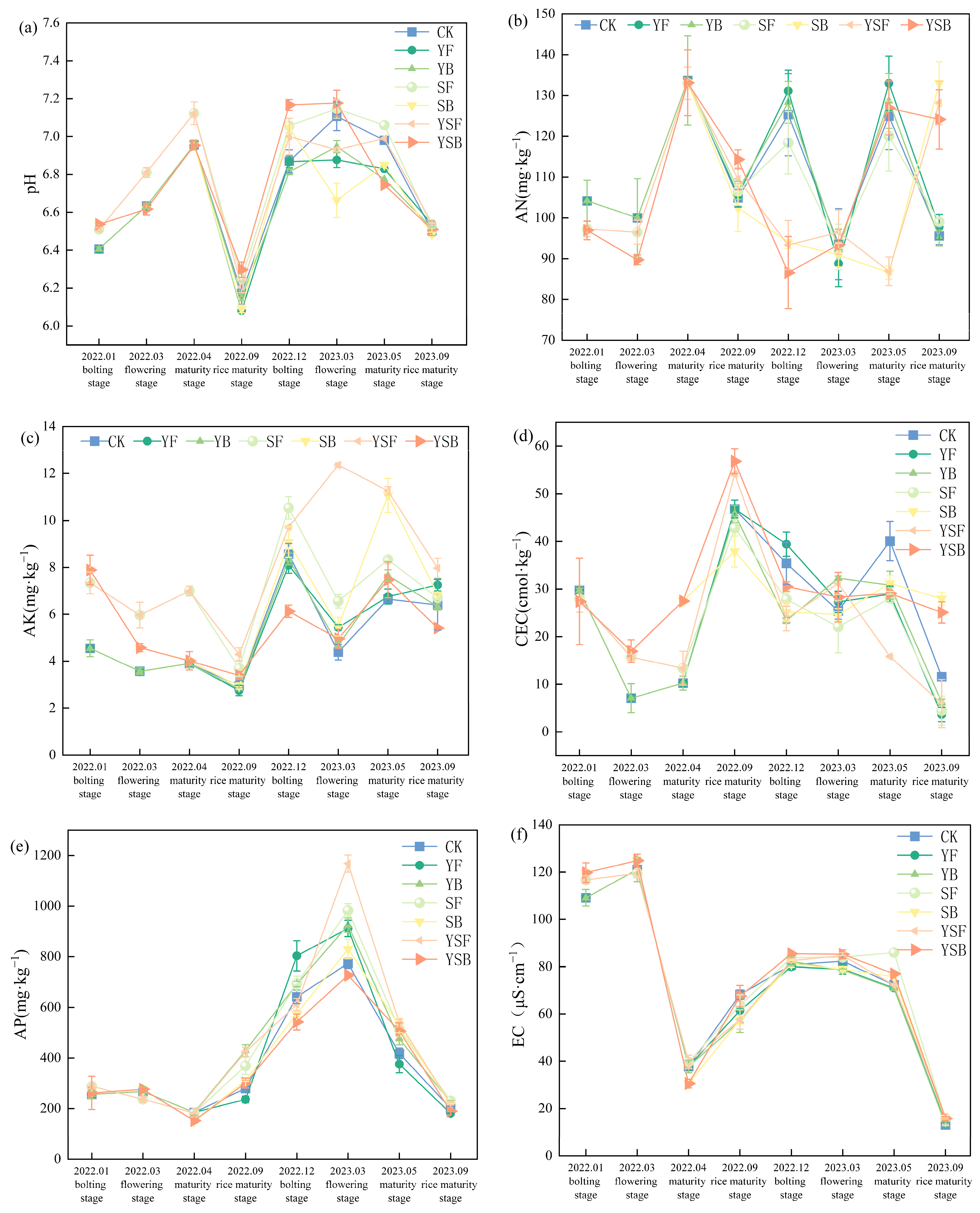
3.1. Effects of Different Treatments of Straw and Biochar on Basic Soil Properties
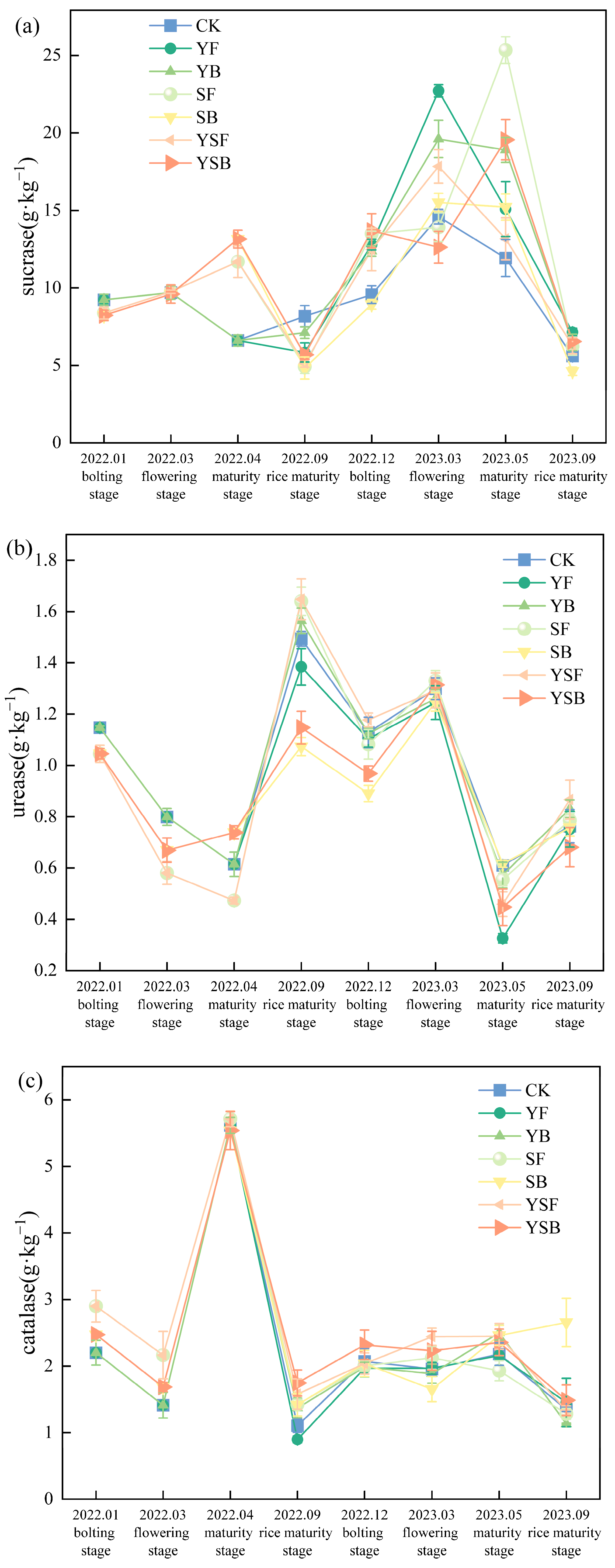
3.2. Changes in Soil Enzyme Activities with Different Straw and Biochar Return Treatments
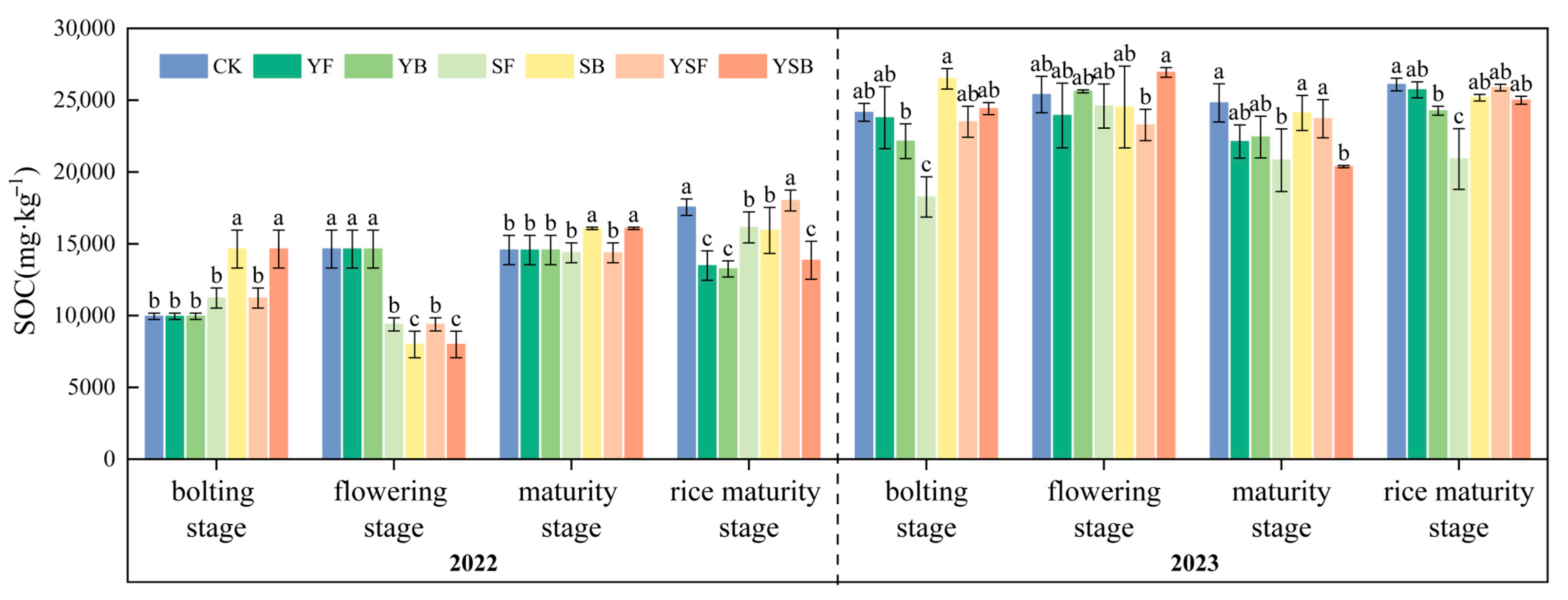
3.3. Changes in Soil Organic Carbon with Different Straw and Biochar Return Treatments
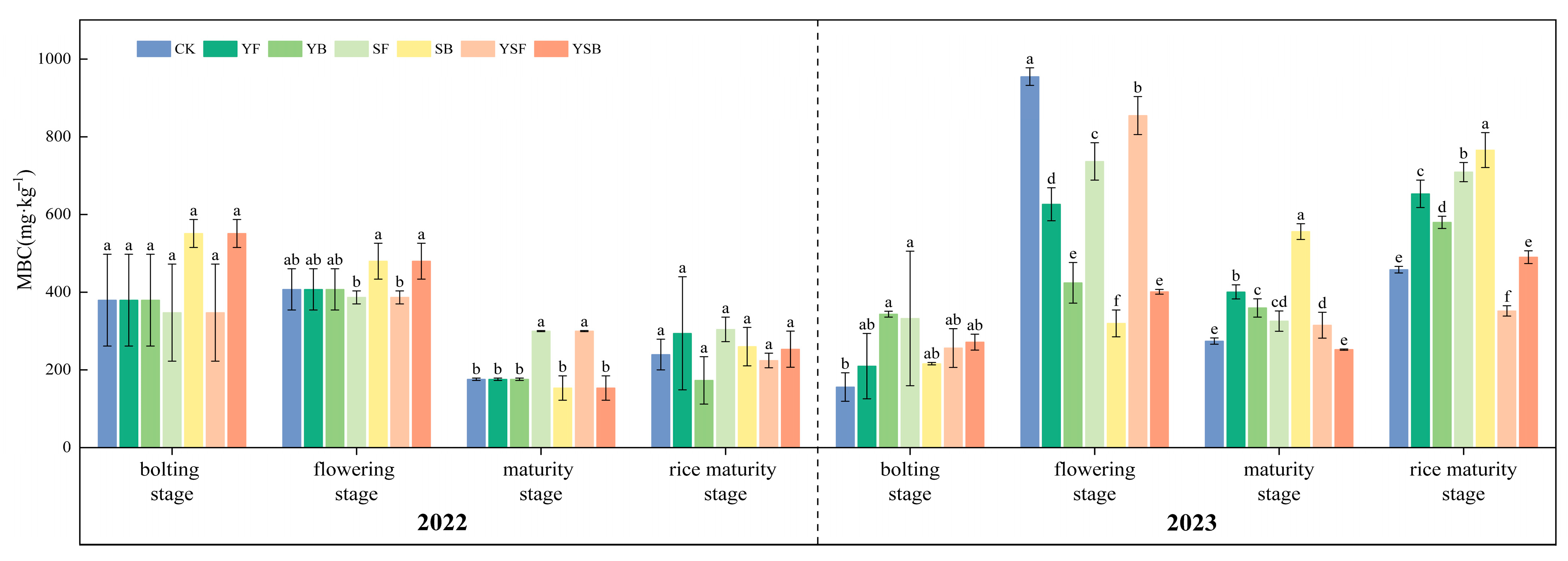
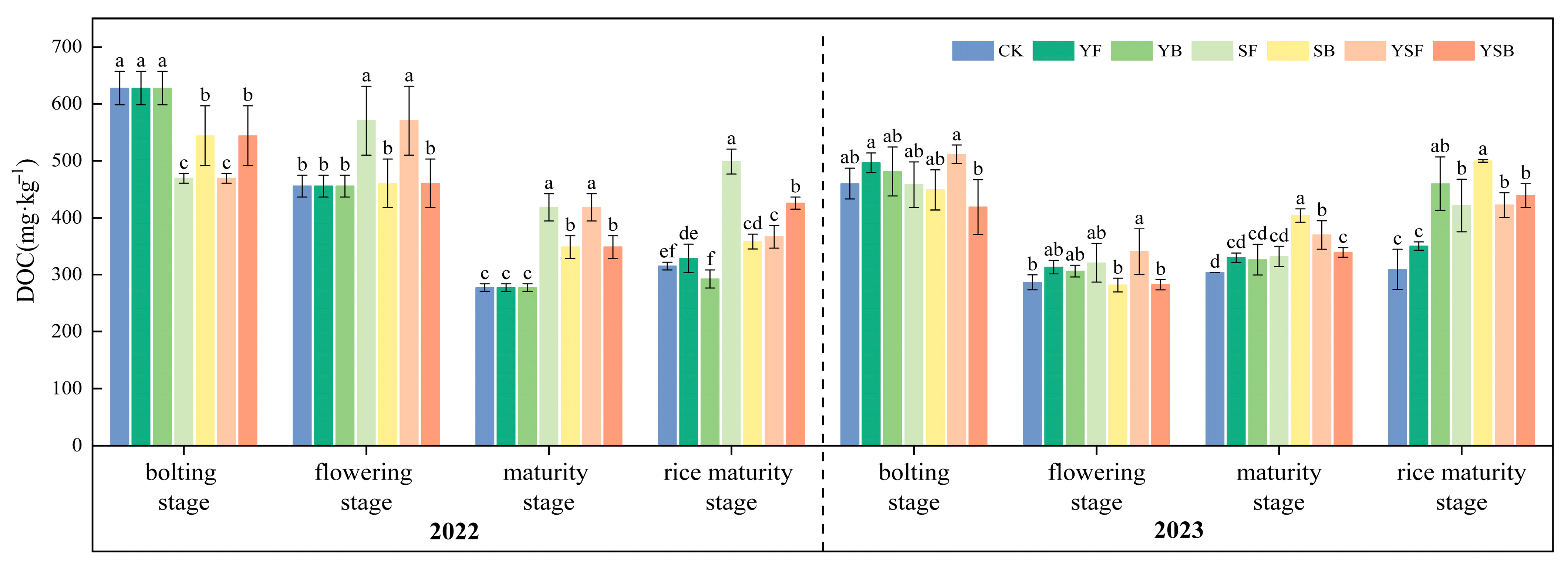
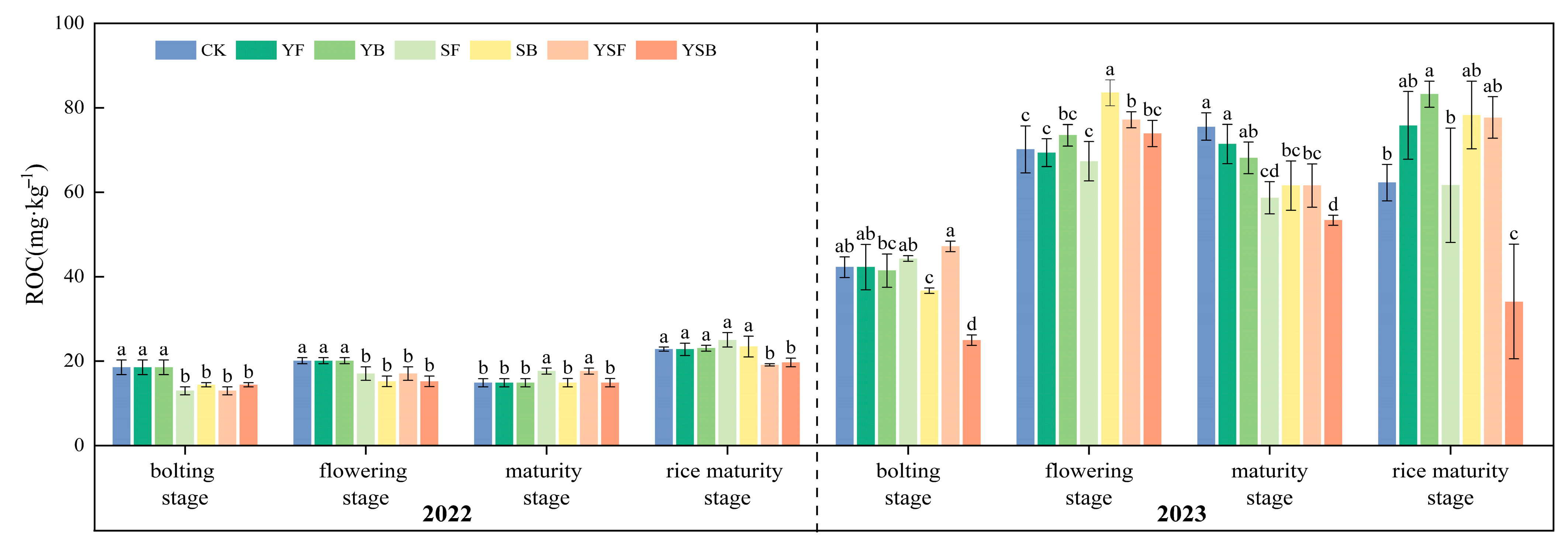
3.4. Changes in Soil Active Carbon Fractions by Different Treatments of Straw and Biochar Returned to the Field
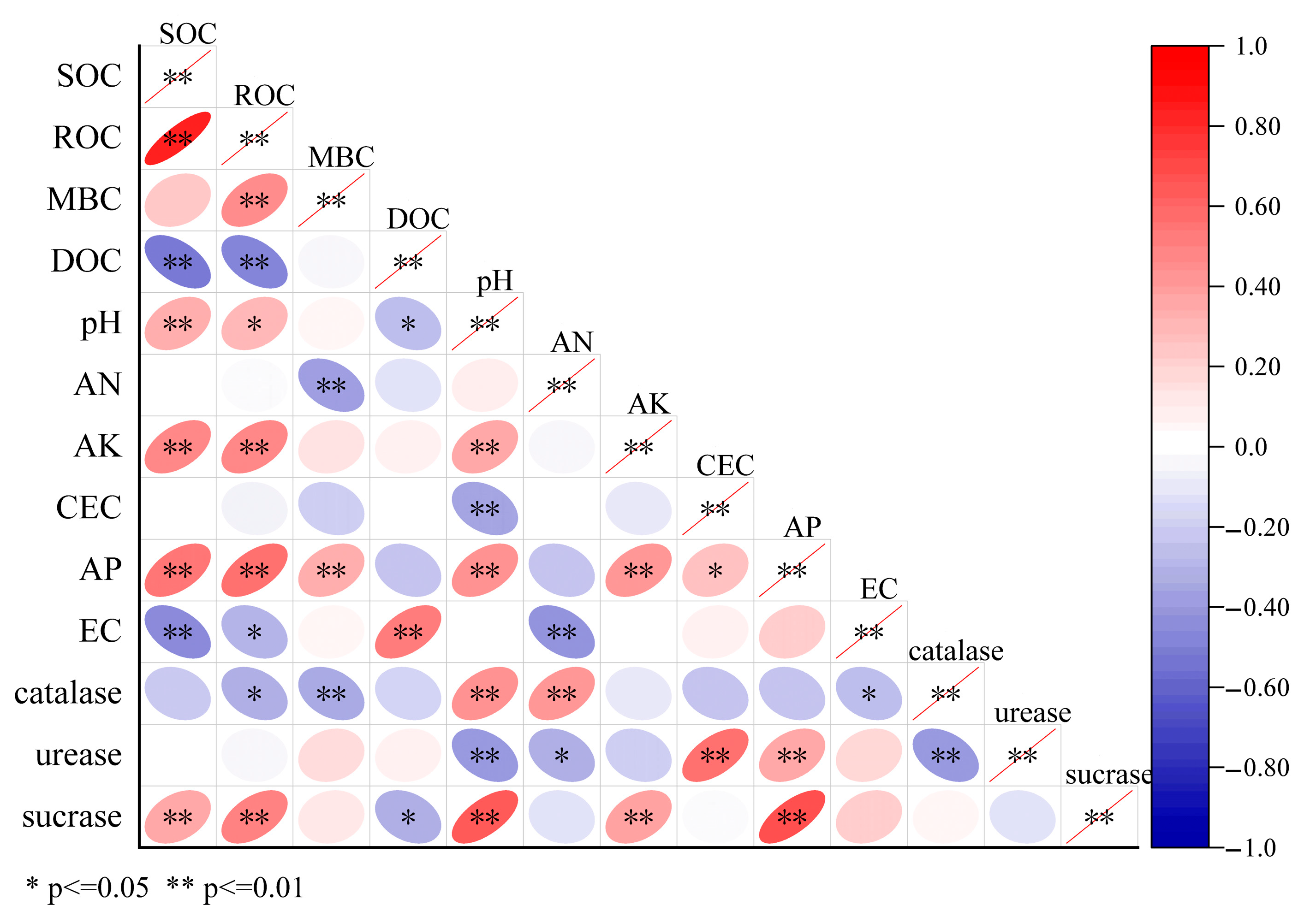
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Soil Carbon Components and Physicochemical/Enzymatic Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Returning Treatments on Basic Properties of Rice–Rapeseed Rotation Farmland
4.2. Effects of Different Returning Treatments on Soil Enzyme Activities in Rice–Rape Rotation Farmland
4.3. Effects of Different Return Treatments on SOC Transformation in Rice–Rape Rotation Farmland
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Shao, M. Soil Organic Carbon and Influencing Factors in Different Landscapes in an Arid Region of Northwestern China. Catena 2014, 116, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Jia, R.; Mganga, K.Z.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Peixoto, L.; Zang, H.; Zeng, Z. Legume-Based Crop Diversification Reinforces Soil Health and Carbon Storage Driven by Microbial Biomass and Aggregates. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 234, 105848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ge, T.; Wang, W.; Yuan, H.; Wegner, C.-E.; Zhu, Z.; Whiteley, A.S.; Wu, J. Cropping Systems Modulate the Rate and Magnitude of Soil Microbial Autotrophic CO2 Fixation in Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liang, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Shi, C.; Wang, S.; Zhou, W.; Lu, Q.; Islam, F.; Xu, W.; et al. Safety of Oilseed Rape Straw Mulch of Different Lengths to Rice and Its Suppressive Effects on Weeds. Agronomy 2020, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Gupta, R.; Kaur Sraw, P.; Singh Kang, J.; Kaur, J.; Kalia, A.; Sharma, V.; Singh Manhas, S.; Al-Ansari, N.; Alataway, A.; Dewidar, A.Z.; et al. Influence of 11 Years of Crop Residue Management on Rice Productivity Under Varied Nitrogen Levels in the Rice-Wheat Cropping System. Plant Soil Environ. 2023, 69, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Chaudhary, A.; Ahlawat, O.P.; Naorem, A.; Upadhyay, G.; Chhokar, R.S.; Gill, S.C.; Khippal, A.; Tripathi, S.C.; Singh, G.P. Crop Residue Management Challenges, Opportunities and Way Forward for Sustainable Food-Energy Security in India: A Review. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 228, 105641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Yadav, R.B.; Nath, A.; Patel, J.N.; Alam, M.S.; Kumar, A. In-Situ Rice Residue Management Practices and Its Impact on Climate, Soil Fertility and Crop Productivity: A Review. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2023, 35, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Powlson, D.S.; Liang, Y.; Chadwick, D.R.; Long, S.; Liu, D.; Chen, X. Significant Soil Degradation Is Associated with Intensive Vegetable Cropping in a Subtropical Area: A Case Study in Southwestern China. Soil 2021, 7, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, I.; Wang, P.; Mei, Q.; Huang, Y. Effects of Different Straw Biochars on Soil Organic Carbon, Nitrogen, Available Phosphorus, and Enzyme Activity in Paddy Soil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhou, X.; He, Y.; Liu, R.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, G.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Fu, Y.; Bai, S.H. Co-Application of Biochar and Organic Amendments on Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 166171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, N.; An, N. Effects of Biochar and Straw Application on the Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Paddy Soils in Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, M.; Osman, A.I.; Umetsu, K.; Rooney, D.W. Integration of Biogas Systems into a Carbon Zero and Hydrogen Economy: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2853–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Huang, S.; Cai, Z.; Gao, H.; Ma, J.; Cui, X.; Xu, M. Three-Decade Long Fertilization-Induced Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration Depends on Edaphic Characteristics in Six Typical Croplands. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.L.R.; Leal Júnior, A.L.B.; Barreto, A.C.; Carvalho, F.J.; De Assis, R.L.; Loss, A.; Lemes, E.M.; Da Silva Vieira, D.M. Mechanical and Biological Soil Decompaction for No-Tillage Maize Production. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Qiu, C.; Han, X.; Kwaw-Mensah, D.; Chen, X.; Yan, J.; Lu, X.; Zou, W. Effects of 10 Years of the Return of Corn Straw on Soil Aggregates and the Distribution of Organic Carbon in a Mollisol. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liao, B.; Fang, C.; Sheteiwy, M.S.; Yi, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Ma, G.; Tu, N. Effects of Applying Different Organic Materials on Grain Yield and Soil Fertility in a Double-Season Rice Cropping System. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Effects of Different Straw Biochar Combined with Microbial Inoculants on Soil Environment in Pot Experiment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tao, J.; Yan, X.; Zhou, B.; Mwangi, J.K. Short-Term Effects of Straw Application on Carbon Recycle in a Rice-Rapeseed Rotation System. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 3358–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xu, G.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; You, X.; Ren, H. Effects of Annual Straw Incorporation Combined with Application of Nitrogen Fertilizer in Rice Season on Dry Matter and Nutrient Accumulation Characteristics of Subsequent Rapeseed. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.V. Standard Methods for Soil, Water and Plant Analysis, 1st ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2024; ISBN 978-1-003-53430-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhao, T. Coal Mining Subsidence on Soil Nutrients and Enzymes of Artificial Forest in Northern China. Cienc. Rural 2024, 55, e20230348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Feng, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yao, Q. Cooperation of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Bacteria to Facilitate the Host Plant Growth Dependent on Soil pH. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1116943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Gao, G.; Yang, W.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Liang, X. High-Efficiency Remediation of Hg and Cd Co-Contaminated Paddy Soils by Fe–Mn Oxide Modified Biochar and Its Microbial Community Responses. Biochar 2024, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Hussain, Q.; Akmal, M.; Riaz, M.; Hu, H.; Ijaz, S.S.; Iqbal, M.; Abro, S.; Mehmood, S.; Ahmad, M. Sugarcane Bagasse-Derived Biochar Reduces the Cadmium and Chromium Bioavailability to Mash Bean and Enhances the Microbial Activity in Contaminated Soil. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, K.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, L. Changes in Soil Properties and CO2 Emissions after Biochar Addition: Role of Pyrolysis Temperature and Aging. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Yu, C.; Feng, Y. Organic Amendments Perform Better than Inorganic Amendments in Reducing the Absorption and Accumulation of Cadmium in Lettuce. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 117277–117287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Piao, S.; Chen, A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Peng, S.; Sardans, J.; Sun, Y.; Peñuelas, J.; Zeng, H. Afforestation Neutralizes Soil pH. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Qin, S.; Yang, G.; Fang, K.; Zhu, B.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y. Regulation of Priming Effect by Soil Organic Matter Stability over a Broad Geographic Scale. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C. Soil pH Is the Primary Factor Driving the Distribution and Function of Microorganisms in Farmland Soils in Northeastern China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y. Rhizosphere Enzyme Activities and Microorganisms Drive the Transformation of Organic and Inorganic Carbon in Saline–Alkali Soil Region. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1314. [Google Scholar]
- Sahrawat, K.L. Redox Potential and pH as Major Drivers of Fertility in Submerged Rice Soils: A Conceptual Framework for Management. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Xuan, J.; Chen, A.; You, C. Short-Term Phosphorus Addition Augments the Effects of Nitrogen Addition on Soil Respiration in a Typical Steppe. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Yang, N.; Lu, C.; Qin, X.; Siddique, K.H.M. Soil Organic Carbon, Total Nitrogen, Available Nutrients, and Yield Under Different Straw Returning Methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 214, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiao, X.; Li, H.; Hu, T.; Jiang, H.; Mahmoud, A. Effects of Biochar on Water Quality and Rice Productivity Under Straw Returning Condition in a Rice-Wheat Rotation Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, S.; Pan, R.; Bu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ding, A. Effects of Rice Husk Biochar on Nitrogen Leaching from Vegetable Soils by 15N Tracing Approach. Water 2022, 14, 3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Jeyakumar, P.; Yin, C.; Sun, H. Effects of Biochar in Combination with Varied N Inputs on Grain Yield, N Uptake, NH3 Volatilization, and N2O Emission in Paddy Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1174805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Zhi, M.; Zhao, W.; Pang, J.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, Y. Straw Retention Combined with Phosphorus Fertilizer Promotes Soil Phosphorus Availability by Enhancing Soil P-Related Enzymes and the Abundance of phoC and phoD Genes. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Gray, E.M.; Boyd, S.E.; Yang, H.; Zhang, D. Roles of Biochar in Improving Phosphorus Availability in Soils: A Phosphate Adsorbent and a Source of Available Phosphorus. Geoderma 2016, 276, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Gao, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Su, Z.; Hu, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X. Potentials of Straw Return and Potassium Supply on Maize (Zea mays L.) Photosynthesis, Dry Matter Accumulation and Yield. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, S.; Yao, B.; Peng, Y.; Gao, C.; Qin, T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C.; Quan, W. Effects of Straw Return and Straw Biochar on Soil Properties and Crop Growth: A Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 986763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Huang, R.; Zhou, L.; Qin, R.; He, X.; Deng, H.; Li, K. Effects of Magnesium-Modified Biochar on Soil Organic Carbon Mineralization in Citrus Orchard. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1109272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrameche, O.; Tul, S.; Manolikaki, I.; Digalaki, N.; Kaltsa, I.; Psarras, G.; Koubouris, G. Optimizing Agroecological Measures for Climate-Resilient Olive Farming in the Mediterranean. Plants 2024, 13, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintala, R.; Mollinedo, J.; Schumacher, T.E.; Malo, D.D.; Julson, J.L. Effect of Biochar on Chemical Properties of Acidic Soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, P.; Gozdowski, D.; Wójcik-Gront, E. Soil Electrical Conductivity and Satellite-Derived Vegetation Indices for Evaluation of Phosphorus, Potassium and Magnesium Content, pH, and Delineation of Within-Field Management Zones. Agriculture 2022, 12, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Park, J.H. Monitoring of Soil EC for the Prediction of Soil Nutrient Regime Under Different Soil Water and Organic Matter Contents. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yuan, G.; Wang, H.; Lu, D.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J. Effects of Full Straw Incorporation on Soil Fertility and Crop Yield in Rice-Wheat Rotation for Silty Clay Loamy Cropland. Agronomy 2019, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Cheng, R.; Xiao, W.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, N.; Zeng, L.; Lei, L.; Wang, X. Author Correction: Labile Organic Carbon Pools and Enzyme Activities of Pinus massoniana Plantation Soil as Affected by Understory Vegetation Removal and Thinning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikanová, O.; Šimon, T.; Kopecký, J.; Ságová-Marečková, M. Soil Biological Characteristics and Microbial Community Structure in a Field Experiment. Open Life Sci. 2015, 10, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, G.; Li, Y.; Qu, W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Qian, C.; Yang, G.; et al. Phenotype, Biomass, Carbon and Nitrogen Assimilation, and Antioxidant Response of Rapeseed Under Salt Stress. Plants 2024, 13, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, T.; Wu, S.; Wu, L.; Lai, X.; Xu, H.; Hu, H.; Ma, Y. Effects of Straw Returning and New Fertilizer Substitution on Rice Growth, Yield, and Soil Properties in the Chaohu Lake Region of China. Plants 2024, 13, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hassan Javed, H.; Peng, X.; Chen, H.; Tang, W.; Lai, Y.; Wu, Y. Controlled-Release Nitrogen Mixed with Common Nitrogen Fertilizer Can Maintain High Yield of Rapeseed and Improve Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency. Plants 2023, 12, 4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Peng, C.; Yuan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; Xu, D.; Wu, J. Changes in Soil Microbial Community Composition and Organic Carbon Fractions in an Integrated Rice–Crayfish Farming System in Subtropical China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miśkowiec, P.; Olech, Z. Searching for the Correlation Between the Activity of Urease and the Content of Nickel in the Soil Samples: The Role of Metal Speciation. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 1904–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.Â.; Afonso, S.; Tipewa, N.; Almeida, A.; Arrobas, M. Quantification of Loss in Oilseed Rape Yield Caused by Delayed Sowing Date in a Mediterranean Environment. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1630–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janušauskaitė, D.; Arlauskienė, A.; Maikštėnienė, S. Soil Mineral Nitrogen and Microbial Parameters as Influenced by Catch Crops and Straw Management. Zemdirbyste-Agriculture 2013, 100, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, R.; Wang, D.; Nan, W. Effects of Defoliation and Nitrogen on Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions and Microbial Communities in Soils of Cherry Tree Orchards. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A. Study on the Properties of Rice Straw Biochar Caused by the Soil Nitrogen Application Rate Difference. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 423, 01006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, S. Enhancing Sustainable Agriculture in China: A Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Straw and Manure on Crop Yield and Soil Fertility. Agriculture 2024, 14, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, Y.; Hui, D.; Jing, X.; Feng, W. Soil Properties Rather than Climate and Ecosystem Type Control the Vertical Variations of Soil Organic Carbon, Microbial Carbon, and Microbial Quotient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Gao, W.; Huang, S.; Tang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Masiliūnas, D. Organic Amendment Increases Soil Respiration in a Greenhouse Vegetable Production System through Decreasing Soil Organic Carbon Recalcitrance and Increasing Carbon-Degrading Microbial Activity. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2877–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot, R.S.; Bajpai, R.K.; Shrivastava, L.K.; Kumar, U.; Tedia, K.; Mishra, V.N. Evaluation of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Under Rice-Based Cropping System in Alfisols of Northern Hill Region of Chhattisgarh. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2021, 10, 2748–2761. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.W.I.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A.C.; et al. Persistence of Soil Organic Matter as an Ecosystem Property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsabimana, D.; Haynes, R.J.; Wallis, F.M. Size, Activity and Catabolic Diversity of the Soil Microbial Biomass as Affected by Land Use. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 26, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar Effects on Soil Biota—A Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahnila, M.; Koskela, A.; Sulasalmi, P.; Fabritius, T. A Review of Pyrolysis Technologies and the Effect of Process Parameters on Biocarbon Properties. Energies 2023, 16, 6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odugbenro, G.O.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y. Soil Aggregate Size Distribution and Total Organic Carbon in Intra-Aggregate Fractions as Affected by Addition of Biochar and Organic Amendments. Pol. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 53, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Shen, C.; Zou, Z.; Fan, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C.; Fu, J.; Han, W.; et al. Increased Soil Fertility in Tea Gardens Leads to Declines in Fungal Diversity and Complexity in Subsoils. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, K. Investigating Biochar-Derived Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) Components Extracted Using a Sequential Extraction Protocol. Materials 2022, 15, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lü, L.; Creamer, C.A.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Liu, H.; Feng, X.; Yu, G.; Han, X.; Jiang, Y. Alteration of Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Pools and Enzyme Activities as Affected by Increased Soil Coarseness. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2155–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Li, X.; Song, R.; Xie, H.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Du, Y.; Xu, M.; Ren, C.; et al. Mechanisms of Litter Input Changes on Soil Organic Carbon Dynamics: A Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency-Based Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Tian, D.; Liu, J.; Lv, S.; He, X.; Gao, M. Responses of Soil Carbon Pool and Soil Aggregates Associated Organic Carbon to Straw and Straw-Derived Biochar Addition in a Dryland Cropping Mesocosm System. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.; Ming, A.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Min, H.; Ma, J.; Yang, K.; Li, Z.; Zeng, J.; Wei, J.; et al. Effects of Close-to-Nature Transformation on Soil Enzyme Activities and Organic Carbon Fractions in Cuninghamia Lanceolata and Pinus massoniana Plantations. Forests 2022, 13, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zeng, Q.; An, S.; Dong, Y.; Darboux, F. Soil Carbon Fractions and Enzyme Activities Under Different Vegetation Types on the Loess Plateau of China. Solid Earth Discuss. 2016; preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, N.; Wu, L.; Lu, T.; Hu, Z. Impacts of Biochar Amendment and Straw Incorporation on Soil Heterotrophic Respiration and Desorption of Soil Organic Carbon. Geosci. Lett. 2023, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.R.; Gao, B.; Ahn, M.-Y. Positive and Negative Carbon Mineralization Priming Effects Among a Variety of Biochar-Amended Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Li, L. Appropriate Dense Planting with N Fertilisation Increased Maize Grain Yield and Soil Organic Carbon. Zemdirbyste-Agriculture 2023, 110, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Ecological Function and Impact on Soil Aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, F.; Gebrande, C.; Bichler, R.M.; Vogel, R.F. Insights into the pH-Dependent, Extracellular Sucrose Utilization and Concomitant Levan Formation by Gluconobacter Albidus TMW 2.1191. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.-S.; Hausinger, R.P. Diethylpyrocarbonate Reactivity ofKlebsiella Aerogenes Urease: Effect ofpH and Active Site Ligands on the Rate of Inactivation. J. Protein Chem. 1993, 12, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsell, V.; Saartama, V.; Turja, R.; Haimi, J.; Selonen, S. Reproduction, Growth and Oxidative Stress in Earthworm Eisenia andrei Exposed to Conventional and Biodegradable Mulching Film Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Xu, P.; Li, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Zou, J. Microbial Diversity and the Abundance of Keystone Species Drive the Response of Soil Multifunctionality to Organic Substitution and Biochar Amendment in a Tea Plantation. GCB Bioenergy 2022, 14, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, T.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Muhammad, I.; Chi, Y.X.; Zhou, X.B. Straw Incorporation and Nitrogen Fertilization Regulate Soil Quality, Enzyme Activities and Maize Crop Productivity in Dual Maize Cropping System. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| pH | Cation Exchange Capacity CEC (g·kg−1) | Electrical Conductivity EC (μm·cm−1) | Acid Phosphatase AP (mg·kg−1) | Available Potassium AK (mg·kg−1) | Alkali-Hydrolysable Nitrogen AN (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.32 ± 0.04 | 5.02 ± 0.30 | 85.53 ± 1.04 | 128.57 ± 1.46 | 5.67 ± 0.19 | 157.19 ± 6.21 |
| Treatment | Rape Season Planting Period | Rice Season Planting Period |
|---|---|---|
| CK | - | - |
| YF | - | Rape straw |
| YB | - | Rape straw biochar |
| SF | Rice straw | - |
| YSF | Rice straw | Rape straw |
| SB | Rice straw biochar | - |
| YSB | Rice straw biochar | Rape straw biochar |
| pH | Agricultural Productivity (%) | C (%) | H (%) | O (%) | N (%) | C/N | C/H | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF | - | - | 43.12 | 6.00 | - | 1.36 | 31.71 | 7.19 |
| YF | - | - | 40.09 | 6.59 | - | 0.44 | 91.11 | 6.08 |
| SB | 10.15 | 30.64 | 60.44 | 3.75 | 34.39 | 1.42 | 42.55 | 16.11 |
| YB | 10.03 | 27.42 | 68.31 | 3.76 | 27.6 | 0.33 | 206.08 | 18.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, L.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Li, A.; Deng, H.; He, T. The Effects of Different Straw-Returning Methods on Soil Organic Carbon Transformation in Rice–Rape Rotation Systems. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141468
Hu L, Ge Y, Zhou L, Li Z, Li A, Deng H, He T. The Effects of Different Straw-Returning Methods on Soil Organic Carbon Transformation in Rice–Rape Rotation Systems. Agriculture. 2025; 15(14):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141468
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Lening, Yujiao Ge, Liming Zhou, Zhongyi Li, Anyu Li, Hua Deng, and Tieguang He. 2025. "The Effects of Different Straw-Returning Methods on Soil Organic Carbon Transformation in Rice–Rape Rotation Systems" Agriculture 15, no. 14: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141468
APA StyleHu, L., Ge, Y., Zhou, L., Li, Z., Li, A., Deng, H., & He, T. (2025). The Effects of Different Straw-Returning Methods on Soil Organic Carbon Transformation in Rice–Rape Rotation Systems. Agriculture, 15(14), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141468






