Abstract
Organic agriculture is widely regarded as an important approach to reducing biodiversity loss and promoting sustainable agricultural development compared to conventional agriculture. Notably, organic farming practices have substantially boosted the diversity of soil microbial communities. However, empirical studies on the functional structure of soil microbial communities in organic agroecosystems and the mechanisms influencing them remain relatively scarce. Using high-throughput sequencing technology, we analyzed soil microbial communities associated with organic (orange lands) and conventional (coffee and maize lands) farming practices in the Gaoligong Mountains (GLGM) region, with the aim of revealing differences in soil properties, microbial community structure, and functional composition across different agricultural management practices. The results revealed that organic farming boosted soil organic carbon and fertility, driving changes in the microbial community composition. Organic farming notably increased the abundance of bacterial functional groups involved in the carbon and nitrogen cycles but decreased the abundance of symbiotic fungi. Furthermore, no significant differences were observed in the abundance of saprotrophic and pathogenic fungi between the organic and conventional farming systems. The present study demonstrates that organic farming enhances the functional roles of oil microorganisms in nutrient cycling and overall ecosystem processes by enhancing soil’s organic carbon content and soil fertility, thereby modifying the soil’s microbial community structure and functions. Overall, organic farming contributes to improvements in soil health and supports the sustainable development of agriculture in the GLGM region.
1. Introduction
Since the Green Revolution, conventional agricultural practices have significantly boosted food production to meet rising population demands [1]. However, it has become increasingly dependent on chemical inputs for fertilization, crop protection, and irrigation, causing adverse environmental problems, such as water contamination, greenhouse gas emissions, and loss of biodiversity in both terrestrial and subterranean ecosystems [2,3,4,5]. In recent years, organic and conservation agricultural practices (e.g., no-tillage, crop rotation) have been increasingly adopted to mitigate the negative impacts of conventional farming and enhance the sustainability of agricultural systems [6,7]. Organic agroecosystems are low-input farming systems that enhance plant productivity and ecosystem functioning by relying on natural nutrient cycling, the use of green manures, and biological control of pathogens [8]. They provide an important approach to improving soil properties (e.g., organic carbon content, soil nutrients), reducing biodiversity loss, promoting sustainable food production, and enhancing human health and wellbeing [9,10].
As a key component of terrestrial ecosystems, soil plays a fundamental role in regulating energy flow and nutrient cycling [11,12]. Soil microbial communities are crucial to soil ecosystems, driving various biogeochemical cycles and acting as a primary source of soil biomass [13,14,15]. Meanwhile, environmental changes strongly influence soil microbial communities, which are often used as indicators of soil and environmental health [16,17,18]. Several studies have demonstrated that organic agroecological practices can improve soil physicochemical properties [7,19,20]. Organic agricultural practices increase soil organic carbon [21] and total nitrogen content [7] and lead to a microbial community structure that contrasts notably with that under conventional agricultural management. However, studies examining the impact of organic farming on soil microbial community structure have yielded inconsistent results. Some studies show that organic farming increases soil microbial abundance or diversity [20,22,23,24,25,26], while others suggest no change or a reduction in microbial diversity [27]. Therefore, systematic studies on the effects of organic agricultural practices on soil fertility and microbial communities are crucial to promoting sustainable agriculture [28].
Soil microorganisms play crucial ecological roles in maintaining soil structure, promoting organic matter decomposition, degrading pollutants, suppressing diseases, and enhancing soil fertility [29,30,31]. Modifications in agricultural practices not only alter the structure of microbial communities in soil but also profoundly affect their ecological functions. For example, different cropping practices can significantly alter the functional gene profiles of soil bacterial communities, particularly those involved in the carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycles. This variation arises because cropping practices are major contributors to environmental change, which in turn shapes soil function [11]. Intercropping increased the relative abundance of bacterial functional groups involved in C- and N-cycling compared to mono-cropping [32]. Also, organic agroecosystems enhance the diversity of N-cycling functional groups compared to conventional farming [28,33]. Previous studies have classified fungal community trophic guilds into three categories: saprotrophic fungi (which obtain nutrients by decomposing dead host cells), pathogenic fungi (which acquire nutrients by injuring host cells), and symbiotic fungi (which form mutually beneficial relationships with host cells) [34,35], and the interactions among these three can help create a relatively favorable growing environment for the plants and prevent serious harm to their growth and development [36]. Intercropping reduces the relative abundance of the pathogen guild compared to mono-cropping [37], as mono-cropping leads to the absence of key microbial taxa, putting them at a disadvantage in competing for limited secretion resources and diminishing their ability to protect plants from pathogen invasion [38]. However, key questions regarding how organic farming affects the structure and functional structure of soil microbial communities, particularly its impact on the function of the fungal community, remain inadequately addressed.
Stretching across the southeastern lowlands and marking the eastern frontier of the Himalayas, the Gaurigaon Mountains (GLGM) serve as a vital ecological bridge connecting three biodiversity hotspots, namely, the Himalayas, the Indo-Myanmar range, and the mountains of southwest China. This makes the region exceptionally rich in biodiversity and of considerable scientific interest [39,40,41]. With its exceptionally rich tree, bird, and mammal resources, the region offers an ideal natural laboratory for studying the diversity and functional structure of soil microbial communities. As the population continues to increase, the conflict between people and land is intensifying. Since the 1990s, while agricultural production has increased, there has been growing emphasis on ecological environmental protection and sustainable agricultural development. In the GLGM region, farmers have not only engaged in large-scale cultivation of traditional food crops such as maize, but also extensively cultivated coffee and oranges. Maize and coffee are cultivated under conventional agricultural practices, whereas oranges are grown using organic methods. In addition, studies have shown that different crop types release distinct root exudates that influence rhizosphere microorganisms [42], and microbial community compositions differ substantially between inter-root and non-inter-root soils [43]. For example, bacterial communities in the maize rhizosphere can help enhance the dissipation of phthalic acid esters in agricultural soils. To avoid the influence of crop-specific root exudates on soil microorganisms, we collected non-rhizosphere soils from both organic and conventional agricultural fields. However, key questions regarding how different agricultural practices in the region affect the structure and functions of soil microbial communities remain unanswered. Addressing these questions is crucial to understanding the current state of soil microbiology in the GLGM region and tackling issues such as soil degradation and biodiversity loss.
In the present study, we examined the effects of different agricultural management practices (conventional vs. organic farming) on the composition and functional structure of soil microbial communities in the GLGM region using high-throughput sequencing. We tested the hypothesis that organic agriculture (orange lands) exhibits the following advantages over conventional agriculture (maize and coffee lands): (1) improved soil properties with higher SOC, TN, TC, and TP content; (2) increased soil microbial diversity or abundance, along with changes in microbial community composition; and (3) increased abundance of bacterial functional groups involved in C and N-cycling, coupled with a reduction in potentially pathogenic fungi.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
The Gaoligong Mountains (23°50′–28°30′ N, 97°31′–99°05′ E) are situated across the entire Nujiang Lisu Autonomous Prefecture and the western portion of Baoshan City, Yunnan Province, and are recognized as one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots. Influenced by the southwest monsoon and shaped by its topography, the region has a distinctive subtropical plateau monsoon climate. The average annual temperature is 21.3 °C, with an annual rainfall of 1225 mm. Precipitation is unevenly distributed, with the western slopes receiving more rainfall than the eastern slopes. As the westernmost mountain range of the Hengduan Mountains, its upper regions are a national nature reserve, home to a wide variety of native plants and abundant biological resources. This study was conducted in Baihualing Village, which is located at the southern foot of Gaoligong Mountain and the edge of the Gaoligong Mountain Nature Reserve. In Baihualing Village, the main cash crops include maize, coffee, oranges, and walnuts. Among these, maize and coffee are grown using conventional farming methods, and oranges are cultivated organically (Figure 1).
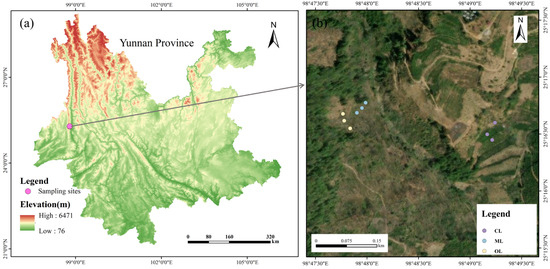
Figure 1.
Distribution of study areas (a) and sampling sites (b).
In January 2024, we conducted soil sample collection in the study area. Plots with similar elevations and slopes were selected to study coffee lands (CL), maize lands (ML), and orange lands (OL) soils, with sampling elevations ranging from 1500 to 1800 m. Maize has been cultivated in the area for a long time, and maize land represents a traditional land use. From the 1990s to the early 2000s, traditional food crop cultivation (maize and rice) gradually shifted toward cash crops (coffee and orange) to promote income generation. In the present study, three 3 m × 3 m subplots were selected within each sample plot, and topsoil samples (0–10 cm) were collected from five randomly selected points along an “S”-shaped transect. Before sampling, we used a small shovel to remove surface litter. We wore new gloves to carefully remove root residues and decayed organic matter from the soil. Soil samples collected from each subplot were thoroughly mixed to form a composite sample, which was then transported back to the laboratory under refrigerated conditions. Each sample was divided into two subsamples using the quartering method: one was stored at −80 °C for high-throughput sequencing, and the other was air-dried and stored at 4 °C for the analysis of the soil’s physicochemical properties.
2.2. Determination of Soil Properties
First, the collected soil samples were dried and ground. Then, individual soil chemical properties were determined after passing through a 2 mm sieve. Soil pH was determined using a pH meter (PHS-3E, INESA, Shanghai, China) in a 1:25 soil/water solution. Soil organic carbon (SOC) and soluble organic carbon (DOC) were then determined using an electronic analytical balance. Soil total nitrogen (TN) and soil total carbon (TC) were determined by Kjeldahl solubilization and combustion-infrared absorption spectrometry using a fully automated Kjeldahl nitrogen tester (Haineng K9840, Shandong Haineng Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Dezhou, Shandong, China) and a high-frequency infrared carbon and sulfur meter (HCS-800, Shanghai Dekai Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), respectively, whereas the determination of soil total phosphorus (TP), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N), and ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) were carried out by UV-visible spectrophotometry.
2.3. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
Total genomic DNA was extracted from thawed soil samples using the FastDNA SPIN Soil Kit for soil (MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA) according to the protocol provided, with three replicate treatments per sample. The integrity of the extracted DNA was detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. Further, genomic DNA concentration and purity was measured by spectrophotometry, the instruments being Nanodrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, NC, USA) and Qubit 3.0 spectrophotometers (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, NC, USA) (Concentration ≥ 20 ng/μL, total ≥ 500 ng, OD260/280 = 1.8–2.0). The highly variable region V4–V5 of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified with the primers 515F (5′-GTGCGCMGCCGG-3′) and 907R (5′-CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGTTT-3′). The primers ITS1 (5′-CTTGTCATTTAGAGAAGTAA-3′) and ITS2 (5′-GTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′) were used to amplify the ITS1 gene with the ITS1. The PCR reaction was carried out under the PCR reaction conditions reported by Yang et al. [44] and three replicate experiments were set up. The amplified products were verified by 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis. Primers containing index sequences are used in high-fidelity PCR to add specific tag sequences to the end of the library, enabling the mixing of multiple samples during downstream up-sequencing and subsequent bioinformatic processing to distinguish between samples with different tag sequences. Nucleic acid purification magnetic beads were used to purify the amplified products, yielding a raw library for each sample. Based on preliminary quantification using agarose gel electrophoresis, libraries with their respective index tags were appropriately diluted. Accurate quantification was then performed using Qubit, and the samples were mixed according to the corresponding ratios of the sequencing throughput requirements of different samples. After pooling the samples, the size of the sequencing library inserts was assessed using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to confirm the absence of non-specific amplification between 120–200 bp, and the sequencing library concentration was accurately quantified. High-throughput sequencing was performed on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) platform. Initial bacterial and fungal sequencing data were processed using QIME 2.0 (University of California San Diego, San Diego, CA, USA) according to the method of Bolyen et al. [45] in the following steps: first, adapter and primer sequences were trimmed using the cutadapt plugin. Then, the DADA2 plugin was used for quality control and the identification of amplicon sequence variants (ASV) [46]. Finally, the classification of bacterial ASV representative sequences and fungal ASV representative sequences was performed on SILVA (version 138.1) and UNITE (version 9.0), respectively.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
All data were preprocessed using Excel 2016 and SPSS 27.0 software (IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and LSD (p < 0.05) multiple comparisons of differences in soil properties and the relative abundance and diversity of soil microbial communities were performed using SPSS software (IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0). We performed a quantification of shared and unique amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) using Venn diagrams, thus comparatively analyzing differences in microbial communities between conventional and organic farming. The α-diversity of soil microorganisms (Observed, Shannon, Chao1, and ACE indices) was calculated from the sequenced ASVs in R software (version 4.3.2) using the “mothur” package. Differences and similarities in soil microbial community composition were evaluated using principal coordinate analysis (PCA) based on Bray–Curtis distance using R software (version 4.3.2). Redundancy analysis (RDA) was used to study the environmental factors affecting changes in the composition of soil microbial communities. The relative abundance of soil microbial communities at the phylum and genus levels and functional groups were analyzed based on Spearman’s correlation analysis for correlation with soil physicochemical properties and visualized with correlation heat maps. Functional prediction of bacteria and fungi was performed using the FAPROTAX and FUNGuild tools [11,47]. All data were visualized after analysis by R software (version 4.3.2).
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Organic Farming on Soil Properties
There were significant differences in soil chemistry between organic (OL) and conventional (CL and ML) farming (Figure 2), with all three agricultural types exhibiting alkaline soils (7.6–8.3). Soil SOC, DOC, TC, TN, and TP were significantly higher (p < 0.05) under organic farming (OL) compared to conventional farming (CL and ML). Among the conventional farming systems, soil SOC, DOC, TC, TN, NO3−-N and NO4+-N were significantly higher in CL than in ML soils, while soil pH and TP were significantly lower (p < 0.05). Overall, soil fertility was significantly higher under organic farming compared to conventional farming, while CL soils exhibited significantly higher fertility (p < 0.05) than ML soils.
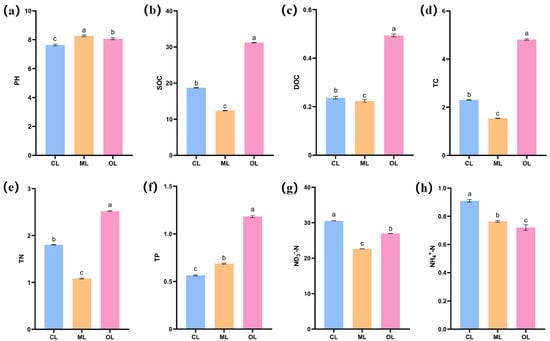
Figure 2.
Effect of organic farming on soil properties. (a) pH; (b) SOC, soil organic carbon; (c) DOC, dissolved organic carbon; (d) TC, total carbon; (e) TN, total nitrogen; (f) TP, total phosphorus; (g) NO3−-N, nitrate nitrogen; (h) NH4+-N, ammonium nitrogen. Different letters represent significant differences in soil properties across different cropping practices (p < 0.05).
3.2. Effects of Organic Farming on the Structure of Soil Microbial Communities
3.2.1. Effects of Organic Farming on Soil Microbial Abundance and Diversity
The number of unique bacterial ASVs was determined to be 2977, 3680, and 3619 for CL, ML, and OL, and the number of shared bacterial ASVs was 655, with the number of bacterial ASVs OL > ML > CL. Overall, bacterial ASV richness followed the order of OL > ML > CL. For fungi, the number of unique ASVs were 1008, 1032, and 937, respectively, with 239 shared ASVs among all groups. Fungal ASV richness followed the order of CL > ML > OL. These findings showed distinct differences in soil bacterial and fungal ASVs composition between organic (OL) and conventional (CL and ML) farming soils (Figure 3). From the results, the Shannon index of the soil bacterial community in OL was significantly higher than that in CL, but none of the other soil microbial community diversity indices were significantly different (p < 0.05; Figure 4). Overall, organic farming had a limited impact on soil microbial diversity, particularly for fungi. In contrast, soil bacterial diversity appeared more responsive to organic farming than fungal diversity.
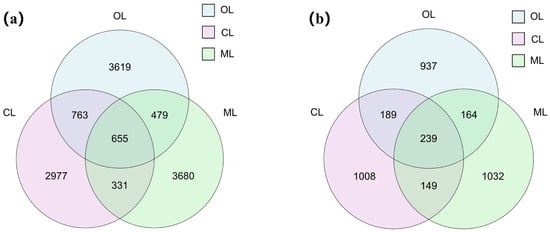
Figure 3.
Effect of organic farming on the number of ASVs in the soil microbial communities. (a) soil bacterial community; (b) soil fungal community.
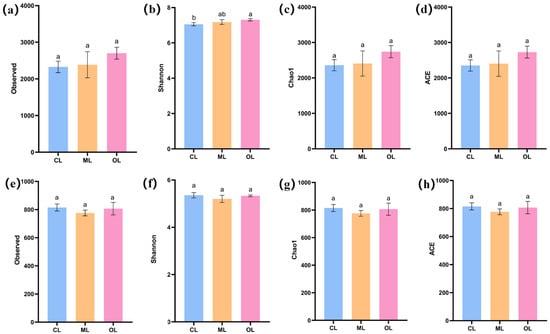
Figure 4.
Effects of organic farming on soil microbial diversity. (a–d) soil bacterial diversity indices; (e–h) soil fungal diversity indices. Different letters represent significant differences in the diversity indices across different cropping practices (p < 0.05).
3.2.2. Effects of Organic Farming on the Composition of Soil Microbial Communities
A total of 39 and 16 phyla of bacteria and fungi were detected in this study, including 557 genera of bacteria and 632 genera of fungi. The dominant bacterial phyla were consistent across CL, ML, and OL soils, although their relative abundance varied (Figure 5). The dominant bacterial phyla included Acidobacteriota (19.03–23.95%), Proteobacteria (16.49–21.17%), Chloroflexi (11.97–14.10%), Actinobacteria (9.44–13.88%), Bacteroidota (7.19–9.60%), Planctomycetota (5.92–10.01%), Gemmatimonadota (5.04–5.42%), Myxococcota (2.95–3.60%), and Methylomirabilota (1.27–2.88%). Acidobacteriota was the most abundant phylum in CL and OL soils, with relative abundances in the order of CL > OL > ML. Proteobacteria dominated in ML soils compared to CL and ML soils. Chloroflexi abundance was significantly lower in CL and OL soils compared to ML soils. In contrast, Actinobacteriota and Planctomycetota showed significantly higher abundance in OL soils than in CL and ML soils. Chloroflexi abudance was significantly lower in CL and OL soils compared to ML soils, while Actinobacteriota and Planctomycetota were significantly more abundant in OL soils than in CL and ML soils. Bacteroidota showed significantly lower relative abundance in OL soils than in CL and ML soils. No significant differences were observed in the abundance of Gemmatimonadota. However, Myxococcota and Methylomirabilota were significantly more abundant in OL soils than in ML and CL soils. The relative abundances of Myxococcota and Methylomirabilota were significantly higher in CL than in ML and OL (p < 0.05). The dominant fungal phyla included Ascomycota (66.88–68.35%), Basidiomycota (6.53–14.48%), Mortierellomycota (5.61–7.60%), Rozellomycota (2.21–5.55%), and Chytridiomycota (2.23–6.09%). Ascomycota was the most abundant fungal phylum, with no significant difference in its abundance or that of Mortierellomycota among CL, ML, and OL soils. However, Basidiomycota was significantly more abundant in CL and ML soils than in OL soils, while Rozellomycota and Chytridiomycota were significantly more abundant in OL soils than in CL and ML soils (p < 0.05).
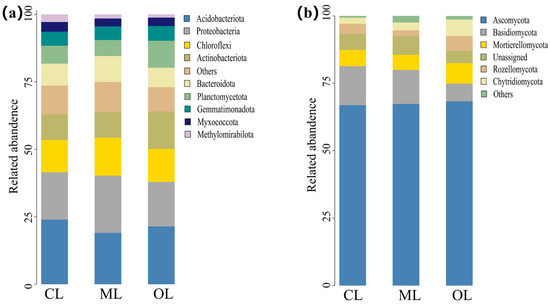
Figure 5.
Dominant microbial phyla with relative abundance > 1%. (a) Soil bacterial communities; (b) soil fungal communities.
From the test results, the top 10 dominant genera of soil bacteria in conventional and organic farming mainly included uncultured (10.08–11.22%), uncultured genus (5.88–7.76%), Vicinamibacteraceae genus (5.32–5.99%), RB41 (2.85–6.59%), UTCFX1 (1.68–2.69%), Rokubacteriales genus (1.19–2.80%), MND1 (1.17–2.32%), WD2101 soil group genus (0.87–2.57%), Latescibacterota genus (0.70–2.29%), and Nitrospira (0.82–1.89%). The top 10 dominant fungal genera were Trichomeriaceae gen Incertae sedis (2.26–19.32%), Fusarium (4.55–10.72%), Mortierella (3.65–5.04%), Rozellomycota gen Incertae sedis (0.96–5.41%), Neocosmospora (1.12–3.84%), Cladosporium (1.50–3.00%), Linnemannia (0.09–1.27%), Solicoccozyma (0.16–1.15%), Stagonosporopsis (0.07–0.80%), and Saitozyma (0.01–0.75%). The dominant genera were consistent across CL, ML, and OL soils, although their relative abundance varied significantly (p < 0.05; Figure 6).
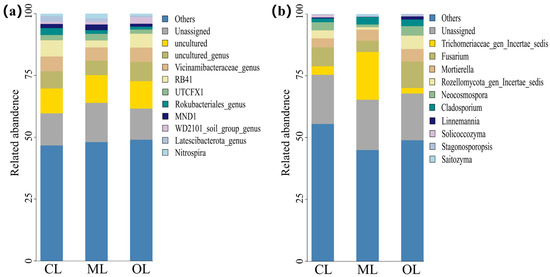
Figure 6.
Dominant microbial genera (top ten by relative abundance). (a) Soil bacterial communities; (b) soil fungal communities.
The results of principal component analysis (PCA) based on Bray–Curtis distance showed significant differences in soil microbial composition among CL, ML, and OL soils (Figure 7). For bacterial communities, the first (PC1) and the second (PC2) principal components explained 45.067% and 31.379% of the total variance, respectively. For fungal communities, PC1 and PC2 accounted for 49.047% and 25.607% of the variance, respectively. These results suggest that soil microbial composition differed significantly between organic (OL) and conventional (CL and ML) agricultural systems.
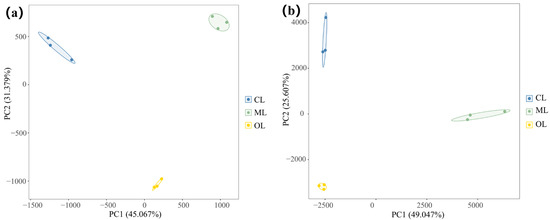
Figure 7.
Effects of organic farming on soil microbial composition. (a) Soil bacterial communities; (b) soil fungal communities.
3.2.3. Factors Regulating Changes in the Structure of Soil Microbial Communities Under Organic Farming
We relied on redundancy analysis (RDA) when studying the dependence of changes in soil microbial composition on soil environmental factors. Results indicated that soil chemical properties explained 86.17% of the variation in bacterial communities and 57.79% in fungal communities. Specifically, RDA1 accounted for 53.13% of the variance in bacterial composition and 37.58% in fungal composition, while RDA2 explained 33.04% and 20.21% of the variance in bacterial and fungal composition, respectively (Figure 8a,b).
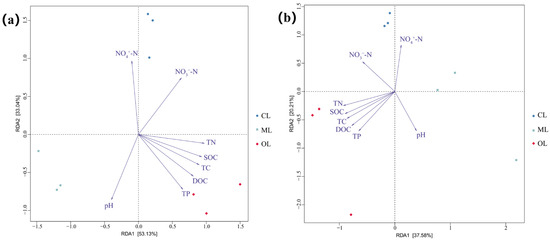
Figure 8.
Effects of organic farming on the composition of soil microbial communities. (a) Soil bacterial communities; (b)soil fungal communities.
Correlation analysis results showed that different dominant phyla exhibited different relationships with environmental factors (Figure 9a,c). For example, Proteobacteria showed significant negative relationships with TC, TN, SOC, and DOC, but no significant correlations with other environmental factors. Acidobacteriota displayed significant negative relationships with pH and significant positive relationships with NO3−-N, with no significant correlations to other environmental factors. Basidiomycpta had significant negative correlations with TP and DOC. Ascomycota showed no significant correlations with any of the soil chemical properties. In addition, correlations were observed between dominant genera and environmental factors (Figure 9b,d). Fusarium demonstrated a strong positive relationship with TC, TN, SOC, and DOC while showing no notable correlation with other environmental factors. Mortierella was positively correlated with TP and negatively correlated with NO4+-N.
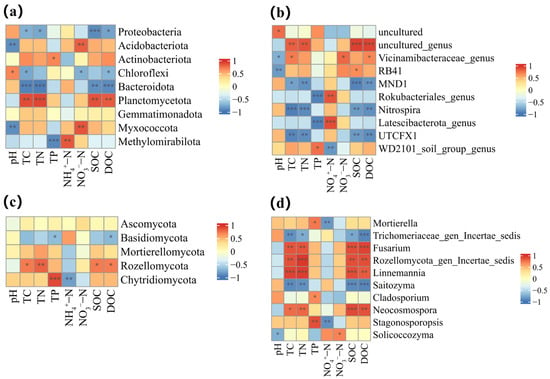
Figure 9.
Correlation of dominant bacterial and fungal phyla and genera with environmental factors. (a,b) Soil bacteria; (c,d) soil fungi. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
3.3. Effects of Organic Farming on Soil Microbial Functional Groups
The results showed that the first 30 functional communities among the identified 53 functional communities were mainly soil microorganisms involved in C- and N-cycling (Figure 10a). C-cycling functional groups mainly include aerobic chemoheterotrophy, predatory or exoparasitic, phototrophy, photoautotrophy, photosynthetic cyanobacteria, oxygenic photoautotrophy, aromatic compound degradation, fermentation, animal parasites or symbionts, intracellular parasites, methylotrophy, photoheterotrophy, methanol oxidation, and anoxygenic photoautotrophy. N-cycling functional groups mainly include chemoheterotrophy, nitrate reduction, chitinolysis, ureolysis, nitrogen fixation, nitrate respiration, nitrogen respiration, nitrite respiration, nitrate denitrification, nitrite denitrification, nitrous oxide denitrification, and denitrification. The relative abundances of C-cycling functional groups were 11.44%, 11.21%, and 15.65% in CL, ML, and OL, respectively, and the relative abundances of N-cycling functional groups were 9.59%, 8.98%, and 11.59% respectively. The relative abundances of C- and N-cycling functional groups in OL were higher than that in CL and ML. Therefore, OL increased the relative abundance of C- and N-cycling functional groups. Increased abundances of C-cycle functional groups were significantly and positively correlated with soil SOC, DOC, TC, TN, and TP, and although increased abundance of N-cycle functional groups was not significantly correlated with these environmental factors, they were all positively correlated (Table 1). Among them, chemoheterotrophy (6.21–9.98%) and aerobic chemoheterotrophy (5.48–9.48%) had the highest relative abundance, and both had their greatest relative abundances in OL soils. Correlation analyses showed that C- and N-cycling functional groups were associated with soil chemical properties (Figure 10b). For example, chemoheterotrophy and aerobic chemoheterotrophy were both significantly and positively correlated with TC, TN, SOC, DOC, nitrite respiration, nitrate denitrification, nitrite denitrification, nitrous oxide denitrification, denitrification, anoxygenic photoautotroph, and intracellular parasites. Several functional groups showed significant positive correlations with pH.
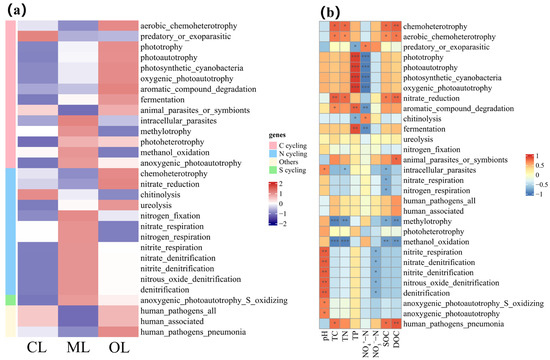
Figure 10.
Effects of organic farming on the C- and N-cycling functional groups. (a) Comparison of relative abundance of soil bacterial functional groups; (b) correlation of soil bacterial functional groups with environmental factors. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.

Table 1.
Relationship between C- and N-cycling functional groups and environmental factors.
Predictions using FUNGuild indicated that the main functional modes (relative abundance > 1%) of the soil fungal community were Saprotroph, Symbiotroph, Pathotroph-Saprotroph, Saprotroph-Symbiotroph, Pathotroph-Saprotroph-Symbiotroph, Pathotroph, and Pathotroph-Symbiotroph (Figure 11a). The relative abundances of Saprotroph were 17.79%, 14.86%, and 14.92% for CL, ML, and OL, respectively. The relative abundances for Symbiotroph were 4.06%, 20.19%, and 3.26%, respectively, and for Pathotroph they were 0.60%, 2.22%, and 1.23%, respectively. The functional mode with the highest relative abundances of CL and OL was Saprotroph, while the highest relative abundance of ML was Symbiotroph. Detailed species function prediction results for functional guilds with an average abundance greater than 0.5% in soil samples showed that relative abundances greater than 0.5% had Undefined Saprotroph, Epiphyte, Endophyte-Litter Saprotroph-Soil Saprotroph-Undefined Saprotroph, Wood Saprotroph, Animal Pathogen-Undefined Saprotroph, Animal Pathogen-Fungal Parasite-Undefined Saprotroph, Plant Pathogen-Wood Saprotroph, Plant Pathogen-Undefined Saprotroph, Endophyte-Lichen Parasite-Plant Pathogen-Undefined Saprotroph, Endophyte-Plant Pathogen, Plant Pathogen, and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal (Figure 11b). For CL and OL, the Undefined Saprotroph guild exhibited the highest relative abundance, while the Epiphyte guild was most abundant in ML. Correlation analyses showed that fungal functional modes were correlated with soil chemical properties (Figure 11c). For example, Symbiotroph showed a significant positive correlation with pH and a significant negative correlation with TC, SOC, and DOC. Pathotroph showed a significant positive correlation with pH and a significant negative correlation with NO3−-N. Similarly, the fungal functional guilds were correlated with environmental factors (Figure 11d). For example, Arbuscular Mycorrhizal was significantly positively correlated with TP and significantly negatively correlated with NO4+-N and NO3−-N.
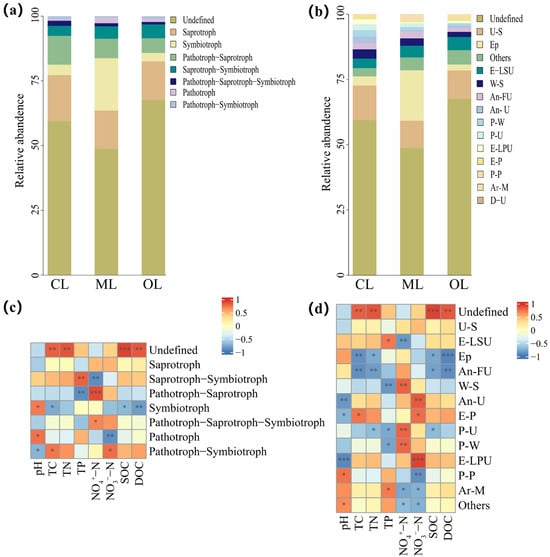
Figure 11.
Effect of organic farming on soil fungal functional mode and guilds. (a) relative abundance of fungal trophic mode; (b) relative abundance of fungal trophic guilds; (c) correlation of fungal trophic mode with environmental factors; (d) correlation of fungal trophic guilds with environmental factors. U-S, Undefined Saprotroph; Ep, Epiphyte; E-LUS, Endophyte-Litter Saprotroph-Soil Saprotroph-Undefined Saprotroph; W-S, Wood Saprotroph; An-U, Animal Pathogen-Undefined Saprotroph; An-FU, Animal Pathogen-Fungal Parasite-Undefined Saprotroph; P-W, Plant Pathogen-Wood Saprotroph; P-U, Plant Pathogen-Undefined Saprotroph; E-LPU, Endophyte-Lichen Parasite-Plant Pathogen-Undefined Saprotroph; P-P, Plant Pathogen; Ar-M, Arbuscular Mycorrhizal. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
Although organic agriculture is widely acknowledged for its role in promoting sustainable agricultural development, knowledge of the structures and functions of soil microbial communities in organic systems and the factors shaping them remains limited. In this study, we examined the structure and functions of soil microbial communities and their relationships with soil chemical properties in one long-term organic farming soil and two long-term conventional farming soils, with the goal of advancing our understanding of the effects of organic farming practices on the structure and functions of soil microbial communities.
4.1. Organic Farming Leads to Improvements in Soil Properties
Consistent with the results of many other studies [20,48,49,50], our results showed that the properties of soils under organic farming management differed significantly from those under conventional farming management (p < 0.05; Figure 2). Soil carbon content is a key indicator for assessing the environmental benefits of and impacts on soil health of changes in agricultural management practices [51]. Although farmland soils generally exhibit low organic carbon levels, organic farming practices, such as manure application and crop rotation, can significantly promote soil organic carbon accumulation [48]. This study reached similar conclusions, suggesting that organic farming fosters the accumulation of soil organic carbon and improves soil’s carbon storage capacity. In general, soils with higher organic carbon content exhibit more stable structures, making them less susceptible to nutrient loss, erosion, or surface capping, while also improving permeability, water retention, and porosity [52,53,54,55]. Additionally, organic farming significantly increased soil fertility indicators, including soil TC, TN, and TP (p < 0.05), likely due to the application of farmyard manure [56]. Overall, organic farming agroecosystems showed increased levels of soil organic carbon and dissolved organic carbon as well as enhanced soil properties, thereby supporting our first hypothesis.
4.2. Organic Farming Alters Soil Microbial Communities Structure
Changes in agricultural management practices also modify the soil environment, affecting factors such as aggregate stability, soil water content, organic carbon, effective carbon, nutrient availability, moisture, and temperature [57,58,59], which in turn affect soil microbial communities [60,61,62]. In our study, organic farming practices increased the Shannon index of soil bacteria. This finding is supported by several studies suggesting that organic farming can promote soil bacterial diversity to some extent [20,26]. However, most diversity indices of soil microbial communities under organic and conventional agricultural management in our study did not differ significantly (p < 0.05; Figure 4), particularly for the fungal communities. This could be attributed to the higher environmental sensitivity of bacteria compared to fungi [63]. Overall, there was no notable effect of organic farming on soil microbial diversity, which does not align with our second hypothesis.
Soil microbial community composition and functions are key indicators for assessing soil quality [64]. Because of functional redundancy, community composition is considered more influential than diversity in determining soil ecological functions [28]. Therefore, the assessment of microbial diversity should be complemented by analyses of community composition [65]. In our study, principal component analysis revealed significant differences in soil microbial community composition between organic and conventional farming systems (Figure 7), consistent with previous findings [47,66]. Although the dominant phyla were similar across systems, their relative abundance varied (Figure 5). Acidobacteriota was the dominant bacterial phylum in both OL and CL soils. However, its relative abundance was significantly lower in OL compared to CL soils. This may be attributed to the oligotrophic nature of Acidobacteriota, which are adapted to low-nutrient environments and capable of metabolizing recalcitrant C substrates [67]. A lower pH environment favors the enrichment of Acidobacteriota [68]. Consequently, Acidobacteriota were significantly less abundant in ML soils than in OL soils, and their abundance was negatively correlated with pH. Unlike CL and OL, Proteobacteria was the most dominant bacterium in ML soils, and was among the most abundant and widely distributed bacteria groups [69]. In addition, OL soils significantly enhanced the relative abundance of Actinobacteriota and Planctomycetota, both of which play key roles in organic matter decomposition, carbon cycling processes, and overall soil functionality [70]. Bacteria from these phyla respond rapidly to root exudates, supplying plants with readily available nutrients and contributing to the suppression of root pathogens [71]. Moreover, they contribute to the degradation of recalcitrant organic matter [72,73], thereby supplying more nutrients to plants. Overall, the soil microbial community composition under organic farming differs from that under conventional farming, supporting our second hypothesis.
Ascomycota, one of the most diverse fungal lineages, was the most abundant phylum in both farming systems. It facilitates carbon cycling through the decomposition of organic matter [74] and significantly influences the structure of fungal communities [75]. In addition, organic farming practice significantly increased the relative abundance of Rozellomycota and Chytridiomycota, which may contribute to the improvement of soil fertility. Our results showed that organic farming practice significantly increased the relative abundance of Mortierella, Fusarium, Linnemannia, Neocosmospora, and Stagonosporopsis. Studies have shown that Mortierella and Linnemannia are beneficial fungi. Mortierella is widely distributed in soil, closely associated with soil health, and considered valuable in agriculture for its role in soil carbon cycling, exogenous biodegradation, and the promotion of plant growth [76,77,78,79]. However, Fusarium, Neocosmospora, and Stagonosporopsis are potential plant pathogens. For example, Fusarium is a major causal agent of several important crop diseases worldwide [80], including soybean root rot [81] and tomato wilt [79]. The increased relative abundance of both beneficial and potentially pathogenic fungi was closely associated with higher soil organic carbon and improved soil fertility (Figure 9). For example, Fusarium, Linnemannia, and Neocosmospora were all significantly and positively correlated with TC, TN, SOC, and DOC. However, while organic farming promotes beneficial fungi, it may also increase the risk of crop diseases by enriching potential pathogens. Future research should further explore soil beneficial bacteria, potential pathogens, and the development of effective biological control strategies in organic agroecosystems.
It is well known that both soil microbial community structure and key microbial species affect crop growth, phenological stages, and yields. For example, Fang et al. reported that changes in microbial community structure could stimulate the production of crop growth hormones, cytokinins, and gibberellins, which regulate root development, shoot growth, and nutrient transport [82], ultimately affecting crop yield. In addition, specific key microorganisms play key roles in shaping crop growth, development, and yield. For example, nitrogen-fixing bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi can significantly enhance nutrient uptake in crops, thereby directly influencing their growth and yield [83,84]. In the present study, the latter seems to be better supported, as organic cultivation affected certain key soil microorganisms which in turn affected the growth of subsequently planted crops, despite the overall microbial community structure being not similar between organic and conventional practices but similar in terms of diversity.
Redundancy analysis showed that the selected soil chemical factors explained much of the variation in microbial community composition, especially among bacterial communities (Figure 8). Among these properties, soil pH is a key factor shaping bacterial community composition, consistent with findings from several previous studies [85,86,87]. In fact, high or low pH levels can significantly affect the growth and physiological activities of soil bacterial communities [88], and even small pH changes may alter bacterial community composition and trigger sensitive responses from core bacterial taxa [89]. In contrast, fungal communities tend to tolerate a broader pH range [90], with SOC, DOC, TN, TC, and TP being the major factors influencing their community composition.
4.3. Organic Farming Enhances the Abundance of Soil Microbial Groups Related to C- and N-Cycling
C, N, and S cycling and their roles in terrestrial ecosystems are key research areas in soil carbon and nutrient cycling [91]. FAPROTAX, a tool for annotating the ecological and metabolic functions of bacterial communities based on 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing [92], has been widely applied to study potential functional groups of soil bacteria across various terrestrial ecosystems [68,93]. Our results show that, compared to conventional farming, organic farming management significantly increased the relative abundance of bacterial groups involved in soil C-cycling (e.g., aerobic chemoheterotrophy, phototrophy, photoautotrophy, photosynthetic cyanobacteria, oxygenic photoautotrophy, aromatic compound degradation, fermentation, and animal parasites or symbionts) and N-cycling (e.g., chemoheterotrophy, nitrate reduction, and ureolysis). These findings are consistent with previous studies [11,33]. We also observed that the increase in the relative abundance of C- and N-cycling bacteria under organic farming exhibited a high degree of consistency, which may be attributed to organic farming practices enhancing soil microbial community composition and thereby promoting soil nutrient cycling. In addition, C-cycling functional groups were significantly correlated with soil SOC, DOC, TC, TN, and TP. Although there was no significant correlation between N-cycling functional groups and these soil properties, an overall positive trend was observed. This suggests that the increase in C- and N-cycling bacteria may be closely related to the improvement of soil properties [11,68]. Furthermore, dominated by chemoheterotrophy and aerobic chemoheterotrophy, OL soils contained the highest levels of these functions compared to other microbial processes involved in carbon and nitrogen cycling. These bacterial groups play a crucial role in the uptake and utilization of apoplastic carbon [94]. Thus, organic farming markedly increased the abundance of bacteria associated with soil carbon and nitrogen cycling, supporting our third hypothesis.
Soil fungi are essential for regulating plant productivity, facilitating carbon mineralization and sequestration, and maintaining critical ecosystem functions [95,96,97]. Most Saprotrophic fungi belong to the phylum Ascomycota and acquire C by decomposing organic matter [98]. In contrast, this study found no significant differences in the abundance of saprotrophic fungi between soils managed organically and conventionally, indicating that the enhancement of microorganisms involved in soil carbon cycling under organic farming is mainly attributable to bacteria. In addition, the absence of significant changes in saprotrophic fungi abundance suggests that improvements in soil nutrient levels do not necessarily translate into shifts in saprotrophic fungal communities [97]. Although the application of organic fertilizers improves soil nutrient levels and supports plant growth, it may lessen plant communities’ reliance on symbiotic fungi [99], leading to a reduced relative abundance of symbiotrophic fungi. Our results suggest that soil fertility in ML soils is lower than those of CL and OL soils. Therefore, the significant increase in symbiotrophic fungi in ML soils, along with the significant negative correlations between their abundance and soil nutrient indexes (e.g., TC, SOC, and DOC) (p < 0.05) further supports this conclusion. Previous studies have shown that the application of organic fertilizers decreases the relative abundance of pathotrophic fungi [100]. Despite differences in management practices, the abundance of pathotrophic fungi remained statistically similar between organic and conventional farming in the present study. Overall, among the three trophic fungal types, organic farming reduced the dependence on symbiotrophic fungi due to improved soil fertility, while no significant differences were observed in saprotrophic and sathotrophic fungi compared to conventional farming, which is inconsistent with our third hypothesis. Nonetheless, our results suggest that organic farming modifies the composition and structure of soil fungal functional guilds, which may, in turn, influence their contributions to nutrient cycling and overall ecosystem processes.
5. Conclusions
Organic farming promoted soil organic carbon and improved overall soil fertility. While microbial diversity showed no significant differences between organic (orange) and conventional (coffee and maize) farming soils, organic practices significantly influenced community composition and enhanced the abundance of plant-beneficial microorganisms. In addition, organic farming significantly increased the abundance of bacteria involved in carbon and nitrogen cycling, thereby improving soil nutrient cycling. Simultaneously, organic farming altered the reliance on symbiotrophic fungi, potentially reshaping the role of fungi in nutrient cycling and overall ecosystem functioning. Shifts in the taxonomic and functional profiles of soil microbial communities were closely correlated with variations in soil chemical characteristics, notably soil pH and organic carbon levels. Overall, organic orange farming in the GLGM region represents a relatively sustainable practice, improving soil fertility, enhancing carbon sequestration, and supporting microbial communities involved in carbon and nitrogen cycling. This study deepens our understanding of nutrient and energy cycling processes within the agroecosystems of the GLGM region and provides valuable insights for the sustainable development and management of local agroecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.H. and W.L.; methodology, R.H., M.N. and B.H.; software, R.H., M.N. and B.H.; validation, R.H.; formal analysis, R.H.; investigation, R.H.; resources, R.H. and W.L.; data curation, R.H., M.N. and B.H.; writing—original draft preparation, R.H., W.L., M.N. and B.H.; writing—review and editing, R.H. and W.L.; visualization, R.H., M.N. and B.H.; supervision, W.L.; project administration, W.L.; funding acquisition, W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the First-Class Discipline Program of Soil and Water Conservation and Desertification Prevention, Yunnan Province (SBK20240042).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions, which helped to improve the quality of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abdo, A.I.; Sun, D.; Shi, Z.; Abdel-Fattah, M.K.; Zhang, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Conventional Agriculture Increases Global Warming While Decreasing System Sustainability. Nat. Clim. Change 2025, 15, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, P.A.; Parton, W.J.; Power, A.G.; Swift, M.J. Agricultural Intensification and Ecosystem Properties. Science 1997, 277, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Naylor, R.; Crews, T.; David, M.B.; Drinkwater, L.E.; Holland, E.; Johnes, P.J.; Katzenberger, J.; Martinelli, L.A.; Matson, P.A.; et al. Nutrient Imbalances in Agricultural Development. Science 2009, 324, 1519–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommarco, R.; Kleijn, D.; Potts, S.G. Ecological Intensification: Harnessing Ecosystem Services for Food Security. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiafouli, M.A.; Thébault, E.; Sgardelis, S.P.; De Ruiter, P.C.; Van Der Putten, W.H.; Birkhofer, K.; Hemerik, L.; De Vries, F.T.; Bardgett, R.D.; Brady, M.V.; et al. Intensive Agriculture Reduces Soil Biodiversity across Europe. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boselli, R.; Fiorini, A.; Santelli, S.; Ardenti, F.; Capra, F.; Maris, S.C.; Tabaglio, V. Cover Crops during Transition to No-till Maintain Yield and Enhance Soil Fertility in Intensive Agro-Ecosystems. Field Crops Res. 2020, 255, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbolat, O.; Sánchez-Navarro, V.; Zornoza, R.; Egea-Cortines, M.; Cuartero, J.; Ros, M.; Pascual, J.A.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Almagro, M.; De Vente, J.; et al. Long-Term Adoption of Reduced Tillage and Green Manure Improves Soil Physicochemical Properties and Increases the Abundance of Beneficial Bacteria in a Mediterranean Rainfed Almond Orchard. Geoderma 2023, 429, 116218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammerts Van Bueren, E.T.; Struik, P.C.; Jacobsen, E. Ecological Concepts in Organic Farming and Their Consequences for an Organic Crop Ideotype. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2002, 50, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonthier, D.J.; Ennis, K.K.; Farinas, S.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Iverson, A.L.; Batáry, P.; Rudolphi, J.; Tscharntke, T.; Cardinale, B.J.; Perfecto, I. Biodiversity Conservation in Agriculture Requires a Multi-Scale Approach. Proc. R. Soc. B 2014, 281, 20141358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján Soto, R.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Cuéllar Padilla, M.; De Vente, J. Restoring Soil Quality of Woody Agroecosystems in Mediterranean Drylands through Regenerative Agriculture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 306, 107191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Qi, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Y. Changes of Soil Bacterial Community, Network Structure, and Carbon, Nitrogen and Sulfur Functional Genes under Different Land Use Types. Catena 2023, 231, 107385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medriano, C.A.; Chan, A.; De Sotto, R.; Bae, S. Different Types of Land Use Influence Soil Physiochemical Properties, the Abundance of Nitrifying Bacteria, and Microbial Interactions in Tropical Urban Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miltner, A.; Bombach, P.; Schmidt-Brücken, B.; Kästner, M. SOM Genesis: Microbial Biomass as a Significant Source. Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Thornton, P.E.; Post, W.M. A Global Analysis of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Terrestrial Ecosystems: Global Soil Microbial Biomass C, N and P. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Dsouza, M.; Lou, J.; He, Y.; Dai, Z.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.; Gilbert, J.A. Geographic Patterns of Co-Occurrence Network Topological Features for Soil Microbiota at Continental Scale in Eastern China. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, D.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; He, N.; Niu, S. Microbes Drive Global Soil Nitrogen Mineralization and Availability. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Reich, P.B.; Banerjee, S.; Van Der Heijden, M.G.A.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Ishii, S.; Jia, X.; Shao, M.; et al. Erosion Reduces Soil Microbial Diversity, Network Complexity and Multifunctionality. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2474–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Maron, P.A.; Chemidlin-Prevost Boure, N.; Bernard, N.; Gilbert, D.; Ranjard, L. Microbial Diversity and Ecological Networks as Indicators of Environmental Quality. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, D.; Liang, S.; Dang, P.; Qin, X.; Liao, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effect of No-Tillage on Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Diversity: A Meta-Analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyal, D.C.; Soni, R.; Singh, D.K.; Goel, R. Microbiome Change of Agricultural Soil under Organic Farming Practices. Biologia 2021, 76, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, M.; Wiesmeier, M.; Don, A.; Cuperus, F.; Gattinger, A.; Gruber, S.; Haagsma, W.K.; Peigné, J.; Palazzoli, M.C.; Schulz, F.; et al. Reduced Tillage in Organic Farming Affects Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Temperate Europe. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 216, 105262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lori, M.; Symnaczik, S.; Mäder, P.; De Deyn, G.; Gattinger, A. Organic Farming Enhances Soil Microbial Abundance and Activity—A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupatini, M.; Korthals, G.W.; De Hollander, M.; Janssens, T.K.S.; Kuramae, E.E. Soil Microbiome Is More Heterogeneous in Organic Than in Conventional Farming System. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihelič, R.; Pintarič, S.; Eler, K.; Suhadolc, M. Effects of Transitioning from Conventional to Organic Farming on Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Community: A Comparison of Long-Term Non-Inversion Minimum Tillage and Conventional Tillage. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2024, 60, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, R.R.; Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Al Hamdi, A.; Rehman, A. Organic Management and Intercropping of Fruit Perennials Increase Soil Microbial Diversity and Activity in Arid Zone Orchard Cropping Systems. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundel, D.; Bodenhausen, N.; Jørgensen, H.B.; Truu, J.; Birkhofer, K.; Hedlund, K.; Mäder, P.; Fliessbach, A. Effects of Simulated Drought on Biological Soil Quality, Microbial Diversity and Yields under Long-Term Conventional and Organic Agriculture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanja, E.N.; Fliessbach, A.; Adamtey, N.; Kambura, A.K.; Musyoka, M.; Fiaboe, K.; Mwirichia, R. Diversity and Structure of Prokaryotic Communities within Organic and Conventional Farming Systems in Central Highlands of Kenya. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, P.; Cui, J.; Sui, P.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Organic Management Increases Beneficial Microorganisms and Promotes the Stability of Microecological Networks in Tea Plantation Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1237842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. The importance of soil microorganisms in aggregate stability. In Proceedings of the North Central Extension Industry Soil Fertility Conference Proceedings, Monticello, IL, USA, 19 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, N.; Zhu, C.; Xue, C.; Chen, H.; Duan, Y.; Peng, C.; Guo, S.; Shen, Q. Insight into How Organic Amendments Can Shape the Soil Microbiome in Long-Term Field Experiments as Revealed by Network Analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzemann, F.R.; Plieger, U.; Probst, M.; Spiegel, H.; Sandén, T.; Ros, M.; Insam, H. Long-Term Fertilization Affects Soil Microbiota, Improves Yield and Benefits Soil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, H. The Effect of Torreya Grandis Inter-Cropping with Polygonatum Sibiricum on Soil Microbial Community. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1487619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuartero, J.; Özbolat, O.; Sánchez-Navarro, V.; Weiss, J.; Zornoza, R.; Pascual, J.A.; Vivo, J.-M.; Ros, M. Long-Term Compost Amendment Changes Interactions and Specialization in the Soil Bacterial Community, Increasing the Presence of Beneficial N-Cycling Genes in the Soil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Song, Z.; Bates, S.T.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Schilling, J.S.; Kennedy, P.G. FUNGuild: An Open Annotation Tool for Parsing Fungal Community Datasets by Ecological Guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ren, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, N.; Zhao, X.; Wei, G.; Shu, D. Land Abandonment Transforms Soil Microbiome Stability and Functional Profiles in Apple Orchards of the Chinese Losses Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, C.; Torino, V.; Minotti, P.; Pietrantonio, L.; Del Grosso, C.; Palmieri, D.; Palumbo, G.; Crawford, T.W.; Carfagna, S. Mycorrhized Wheat Plants and Nitrogen Assimilation in Coexistence and Antagonism with Spontaneous Colonization of Pathogenic and Saprophytic Fungi in a Soil of Low Fertility. Plants 2022, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablimit, R.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Gao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, M.; Meng, X.; An, L.; Chen, Y. Altering Microbial Community for Improving Soil Properties and Agricultural Sustainability during a 10-Year Maize-Green Manure Intercropping in Northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Dai, C.; Zhang, T.; Carrión, V.J.; Wei, Z.; Cao, F.; et al. Crop Rotation and Native Microbiome Inoculation Restore Soil Capacity to Suppress a Root Disease. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbacher, J.P.; Miller, J.; Flannery, M.E.; Xiaojun, Y. Avifauna of the Gaoligong Shan Mountains of Western China: A Hotspot of Avian Species Diversity. Ornithol. Monogr. 2011, 70, 30–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jin, M.; Cai, C.; Ma, C.; Chen, Z.; Gao, L. Soil Microbial Community Structure and Physicochemical Properties in Amomum Tsaoko-Based Agroforestry Systems in the Gaoligong Mountains, Southwest China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Lin, S.; Wu, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.; Li, J.; Long, C. Study on Medicinal Food Plants in the Gaoligongshan Biosphere Reserve, the Richest Biocultural Diversity Center in China. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2024, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.L.; Vetukuri, R.R.; Kelbessa, B.G.; Gepts, P.; Heslop-Harrison, P.; Araujo, A.S.F.; Sharma, S.; Ortiz, R. Exploitation of Rhizosphere Microbiome Biodiversity in Plant Breeding. Trends Plant Sci. 2025, 30, S1360138525001037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.-J.; Wu, X.; Zhu, C.-L.; Lü, H.; Zhao, H.-M.; Xiang, L.; Li, H.; Mo, C.-H.; Li, Y.-W.; et al. Adaptation of Bacterial Community in Maize Rhizosphere for Enhancing Dissipation of Phthalic Acid Esters in Agricultural Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 444, 130292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Li, T.; Hou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhang, S.; Yu, A.; et al. Soil Microbial Subcommunity Assembly Mechanisms Are Highly Variable and Intimately Linked to Their Ecological and Functional Traits. Mol. Ecol. 2024, 33, e17302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fließbach, A.; Oberholzer, H.-R.; Gunst, L.; Mäder, P. Soil Organic Matter and Biological Soil Quality Indicators after 21 Years of Organic and Conventional Farming. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijssel, S.Q.; Veen, G.F.; Koorneef, G.J.; Bakx-Schotman, J.M.T.; Ten Hooven, F.C.; Geisen, S.; Van Der Putten, W.H. Soil Microbial Diversity and Community Composition during Conversion from Conventional to Organic Agriculture. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 4017–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P. Effects of Conventional and Organic Agriculture on Soil Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Community in Low-Quality Farmland. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 914627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.M.; Wittwer, R.; Hartmann, M.; Keller, T.; Buchmann, N.; Van Der Heijden, M.G.A. Effects of Conventional, Organic and Conservation Agriculture on Soil Physical Properties, Root Growth and Microbial Habitats in a Long-Term Field Experiment. Geoderma 2024, 447, 116927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G.; Anderson, D.W.; Doran, J.W.; Janzen, H.H.; Pierce, F.J. Concepts of soil quality and their significance. In Soil Quality for Crop Product; Gregorich, E.G., Carter, M.R., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, V.A.; Vazquez, M.A. Structure. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Hillell, D., Hatfield, J.L., Powlson, D.S., Rozenweig, C., Scow, K.M., Singer, M.J., Sparks, D.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; Volume 4, pp. 54–68. [Google Scholar]
- Abiven, S.; Menasseri, S.; Chenu, C. The Effects of Organic Inputs over Time on Soil Aggregate Stability—A Literature Analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogal, A.; Nicholson, F.A.; Chambers, B.J. Organic Carbon Additions: Effects on Soil Bio-physical and Physico-chemical Properties. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 60, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.E.; Poulton, P.R.; Coleman, K. Chapter 1 Soil Organic Matter. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 101, pp. 1–57. ISBN 978-0-12-374817-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Ma, Q.; Marsden, K.A.; Chadwick, D.R.; Luo, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wu, L.; Jones, D.L. Microbial Community Succession in Soil Is Mainly Driven by Carbon and Nitrogen Contents Rather than Phosphorus and Sulphur Contents. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 180, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Hedlund, K.; Jackson, L.E.; Kätterer, T.; Lugato, E.; Thomsen, I.K.; Jørgensen, H.B.; Isberg, P.-E. How Does Tillage Intensity Affect Soil Organic Carbon? A Systematic Review. Environ. Evid. 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Caspari, T.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Batjes, N.H.; Mäder, P.; Bünemann, E.K.; De Goede, R.; Brussaard, L.; Xu, M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; et al. Effects of Agricultural Management Practices on Soil Quality: A Review of Long-Term Experiments for Europe and China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabian, S.; Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Denton, M.D. Do Tillage Systems Influence Nitrogen Fixation in Legumes? A Review. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 185, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.M.; Ritz, K. Tillage, Habitat Space and Function of Soil Microbes. Soil Tillage Res. 2000, 53, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntz, M.; Berner, A.; Gattinger, A.; Scholberg, J.M.; Mäder, P.; Pfiffner, L. Influence of Reduced Tillage on Earthworm and Microbial Communities under Organic Arable Farming. Pedobiologia 2013, 56, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dai, Z.; Veach, A.M.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J.; Schadt, C.W. Global Meta-Analyses Show That Conservation Tillage Practices Promote Soil Fungal and Bacterial Biomass. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 293, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-X.; Lyu, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Xiong, M.-M.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Sun, H.; Xu, J.-L. Differential Spatial Responses and Assembly Mechanisms of Soil Microbial Communities across Region-Scale Taiga Ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, A.; Vivanco, J.M.; Jayanty, S.S.; Manter, D.K. Pyrosequencing Assessment of Soil Microbial Communities in Organic and Conventional Potato Farms. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; De Filippis, F.; Cesarano, G.; La Storia, A.; Ercolini, D.; Scala, F. Organic Farming Induces Changes in Soil Microbiota That Affect Agro-Ecosystem Functions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, K.; Van Der Heijden, M.G.A.; Wittwer, R.A.; Banerjee, S.; Walser, J.-C.; Schlaeppi, K. Cropping Practices Manipulate Abundance Patterns of Root and Soil Microbiome Members Paving the Way to Smart Farming. Microbiome 2018, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an Ecological Classification of Soil Bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, F.; Cao, W.; Yue, H.; Peng, S. Soil Nutrients Drive Changes in the Structure and Functions of Soil Bacterial Communities in a Restored Forest Soil Chronosequence. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 195, 105247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, A.; Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Długosz, J.; Frąc, M. The Microbiome Structure and Shifts in Surface and Subsurface Soil Horizon of Haplic Luvisol under Different Crops Cultivation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjani, A.; Dhanasekaran, D.; Gopinath, P.M. An Introduction to Actinobacteria. In Actinobacteria-Basics and Biotechnological Applications; Dhanasekaran, D., Jiang, Y., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2248-7. [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts, B.; Mezzalama, M.; Sayre, K.D.; Crossa, J.; Lichter, K.; Troch, V.; Vanherck, K.; De Corte, P.; Deckers, J. Long-Term Consequences of Tillage, Residue Management, and Crop Rotation on Selected Soil Micro-Flora Groups in the Subtropical Highlands. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 38, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagova-Mareckova, M.; Zadorova, T.; Penizek, V.; Omelka, M.; Tejnecky, V.; Pruchova, P.; Chuman, T.; Drabek, O.; Buresova, A.; Vanek, A.; et al. The Structure of Bacterial Communities along Two Vertical Profiles of a Deep Colluvial Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 101, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suominen, S.; Van Vliet, D.M.; Sánchez-Andrea, I.; Van Der Meer, M.T.J.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Villanueva, L. Organic Matter Type Defines the Composition of Active Microbial Communities Originating From Anoxic Baltic Sea Sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 628301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, T.; Lei, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, L.; Zou, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, X.; Fang, W. Leguminous Green Manure Intercropping Changes the Soil Microbial Community and Increases Soil Nutrients and Key Quality Components of Tea Leaves. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Ren, C.J.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Wang, J. Changes in Soil Microbial Community Are Linked to Soil Carbon Fractions after Afforestation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, L.; Redmile-Gordon, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Ning, Q.; Li, W. Mortierella Elongata ’s Roles in Organic Agriculture and Crop Growth Promotion in a Mineral Soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozimek, E.; Hanaka, A. Mortierella Species as the Plant Growth-Promoting Fungi Present in the Agricultural Soils. Agriculture 2020, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, H.; Niehs, S.P.; Vandelannoote, K.; Cseresnyés, Z.; Dose, B.; Richter, I.; Gerst, R.; Figge, M.T.; Stinear, T.P.; Pidot, S.J.; et al. Bacterial Endosymbionts Protect Beneficial Soil Fungus from Nematode Attack. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2110669118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, A.Y.; Kang, S. Trichoderma Application Methods Differentially Affect the Tomato Growth, Rhizomicrobiome, and Rhizosphere Soil Suppressiveness against Fusarium Oxysporum. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1366690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perincherry, L.; Lalak-Kańczugowska, J.; Stępień, Ł. Fusarium-Produced Mycotoxins in Plant-Pathogen Interactions. Toxins 2019, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Dai, H.; Wang, D.; Zhou, H.; He, W.; Fu, Y.; Ibrahim, F.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, G.; Shang, J.; et al. Identification of Fusarium Species Associated with Soybean Root Rot in Sichuan Province, China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 151, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-Based Assessment of Soil pH as a Predictor of Soil Bacterial Community Structure at the Continental Scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Tian, W.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.; Cao, A.; Wang, Q. Linkages between Soil Nutrient Turnover and Above-ground Crop Nutrient Metabolism: The Role of Soil Microbes. iMetaOmics 2025, 2, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, J.A.; Görres, J.H. Potential for Mycorrhizae-Assisted Phytoremediation of Phosphorus for Improved Water Quality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Xu, L.; González-Hernández, A.I.; Camañes, G.; Vicedo, B.; Scalschi, L.; Llorens, E. Harnessing Green Helpers: Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria and Other Beneficial Microorganisms in Plant–Microbe Interactions for Sustainable Agriculture. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Purahong, W.; Yang, L. Contrasting Altitudinal Patterns and Co-Occurrence Networks of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities along Soil Depths in the Cold-Temperate Montane Forests of China. Catena 2022, 209, 105844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; He, X.; Zhang, W.; Hu, P.; Sun, M.; Wang, K. Comparison of Bacterial and Fungal Diversity and Network Connectivity in Karst and Non-Karst Forests in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, J.; Qu, C.; Chen, W.; Chen, C.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q. Diverse Regulations on the Accumulation of Fungal and Bacterial Necromass in Cropland Soils. Geoderma 2022, 410, 115675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Calviño, D.; Bååth, E. Growth Response of the Bacterial Community to pH in Soils Differing in pH: Growth Response of the Bacterial Community to pH. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 73, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities across a pH Gradient in an Arable Soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.R.; Viger, M.; Arnold, E.C.; Harris, Z.M.; Ventura, M.; Miglietta, F.; Girardin, C.; Edwards, R.J.; Rumpel, C.; Fornasier, F.; et al. Biochar Alters the Soil Microbiome and Soil Function: Results of Next-generation Amplicon Sequencing across Europe. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling Function and Taxonomy in the Global Ocean Microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansupa, C.; Wahdan, S.F.M.; Hossen, S.; Disayathanoowat, T.; Wubet, T.; Purahong, W. Can We Use Functional Annotation of Prokaryotic Taxa (FAPROTAX) to Assign the Ecological Functions of Soil Bacteria? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; An, S.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, B.; Bai, X.; Huang, Q. Decay Stages and Meteorological Factors Affect Microbial Community during Leaf Litter in Situ Decomposition. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2023, 5, 220160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peay, K.G.; Kennedy, P.G.; Talbot, J.M. Dimensions of Biodiversity in the Earth Mycobiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semchenko, M.; Leff, J.W.; Lozano, Y.M.; Saar, S.; Davison, J.; Wilkinson, A.; Jackson, B.G.; Pritchard, W.J.; De Long, J.R.; Oakley, S.; et al. Fungal Diversity Regulates Plant-Soil Feedbacks in Temperate Grassland. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekberg, Y.; Arnillas, C.A.; Borer, E.T.; Bullington, L.S.; Fierer, N.; Kennedy, P.G.; Leff, J.W.; Luis, A.D.; Seabloom, E.W.; Henning, J.A. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilization Consistently Favor Pathogenic over Mutualistic Fungi in Grassland Soils. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Rhodes, G.; Huang, Q.; Shen, Q. Plant Growth Stages and Fertilization Regimes Drive Soil Fungal Community Compositions in a Wheat-Rice Rotation System. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, B.K.; Rúa, M.A.; Mitchell, C.E. Viral Pathogen Production in a Wild Grass Host Driven by Host Growth and Soil Nitrogen. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yu, Y.; Tang, C.; Zong, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, L.; Li, Y. Organic Fertilizers Increase the Proportion of Saprotrophs Favoring Soil Nitrification under Medicinal Plants Fritillaria Thunbergii. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 219, 119129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).